Deck 2: Nucleus
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/14
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 2: Nucleus
1
During meiosis some chromosomes do not separate from each other. This is called
A) diplotene
B) nondisjunction
C) diakinesis
D) zygotene
E) leptotene
A) diplotene
B) nondisjunction
C) diakinesis
D) zygotene
E) leptotene
B
2
A patient with cancer possesses cells that are undergoing mitosis at a very rapid rate. The contractile rings that are formed during cytokinesis are composed of
A) thin filaments
B) intermediate filaments
C) thick filaments
D) microtubules
E) neurofilaments
A) thin filaments
B) intermediate filaments
C) thick filaments
D) microtubules
E) neurofilaments
A
3
A patient with a chromosomal complement of XXX has
A) a male phenotype
B) a female phenotype
C) a very short life span
D) a higher IQ than his/her siblings
E) trisomy of autosomes
A) a male phenotype
B) a female phenotype
C) a very short life span
D) a higher IQ than his/her siblings
E) trisomy of autosomes
B
4
A 2-month old infant is brought to the physician's office to be examined, and the physician notices that he has flaccid muscles, a smaller head than usual, a large tongue, and a short nose and broad face. The parents say that the baby is very quiet and hardly ever cries. The pediatrician suspects aneuploidy. The baby probably has which of the following chromosomal configurations?
A) monosomy
B) trisomy
C) normal diploid complement
D) haploid complement
E) tetraploid complement
A) monosomy
B) trisomy
C) normal diploid complement
D) haploid complement
E) tetraploid complement

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which RNA synthesis is catalyzed by RNA polymerase II?
A) tRNA
B) rRNA that codes for the large ribosomal subunit
C) rRNA that codes for the small ribosomal subunit
D) mRNA
E) tRNA that carries the start codon
A) tRNA
B) rRNA that codes for the large ribosomal subunit
C) rRNA that codes for the small ribosomal subunit
D) mRNA
E) tRNA that carries the start codon

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
In Fig. Img_010, the cell at the tip of the pointer is in which of the following phases of mitosis? 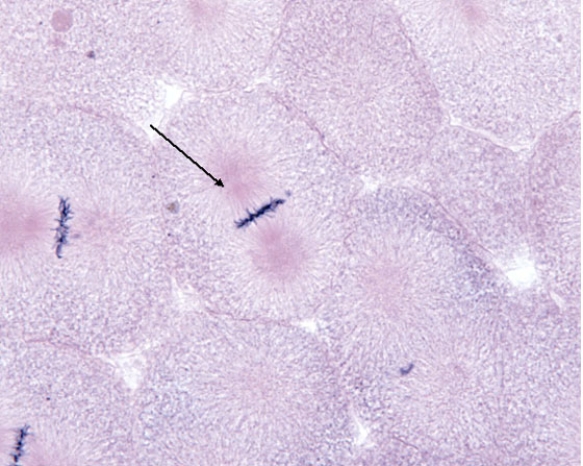
A) prophase
B) prometaphase
C) metaphase
D) anaphase
E) telophase

A) prophase
B) prometaphase
C) metaphase
D) anaphase
E) telophase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A patient with a chromosomal complement of XO has
A) trisomy of the sex chromosomes
B) Turner's syndrome
C) monosomy of the autosomes
D) Klinefelter syndrome
E) a male phenotype
A) trisomy of the sex chromosomes
B) Turner's syndrome
C) monosomy of the autosomes
D) Klinefelter syndrome
E) a male phenotype

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Chiasmata formation
A) occurs during metaphase II
B) results in the exchange of genetic material between nonhomologous chromosomes
C) occurs during the pachytene phase
D) results in nondisjunction
E) results in the formation of the synaptonemal complex
A) occurs during metaphase II
B) results in the exchange of genetic material between nonhomologous chromosomes
C) occurs during the pachytene phase
D) results in nondisjunction
E) results in the formation of the synaptonemal complex

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
During a routine examination of a 3-year-old child, the pediatrician notes that the color of the pupil is white and that the child is cross-eyed. She asks the child's father if there are any cases of retinoblastoma in the family, and when the answer is in the affirmative she calls in a pediatric ophthalmologist. The ophthalmologist knows that retinoblastoma is due to the mutation of the Rb gene (retinoblastoma gene) and that it is a recessive trait. Not all cases of retinoblastoma have a familial component. In the sporadic form of retinoblastoma, the child's normal genetic complement does not predispose the child to have retinoblastoma. If this child had the sporadic form of retinoblastoma, then
A) one copy of the Rb gene mutated
B) both copies of the Rb gene mutated
C) the patient's future children will most probably will have one mutated Rb gene
D) the patient's future children will most probably have two mutated Rb genes
E) the mutated Rb gene is known as a protooncogene
A) one copy of the Rb gene mutated
B) both copies of the Rb gene mutated
C) the patient's future children will most probably will have one mutated Rb gene
D) the patient's future children will most probably have two mutated Rb genes
E) the mutated Rb gene is known as a protooncogene

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
During a routine examination of a 3-year-old child, the pediatrician notes that the color of the pupil is white and that the child is cross-eyed. She asks the child's father if there are any cases of retinoblastoma in the family, and when the answer is in the affirmative she calls in a pediatric ophthalmologist. The ophthalmologist knows that retinoblastoma is due to the mutation of the Rb gene (retinoblastoma gene) and that it is a recessive trait. Retinoblastoma can metastasize to the brain via the
A) optic nerve
B) superior division of the oculomotor nerve
C) trochlear nerve
D) abducent nerve
E) inferior division of the oculomotor nerve
A) optic nerve
B) superior division of the oculomotor nerve
C) trochlear nerve
D) abducent nerve
E) inferior division of the oculomotor nerve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
In Fig. Img_009, the cell at the tip of the pointer is in which of the following phases of mitosis? 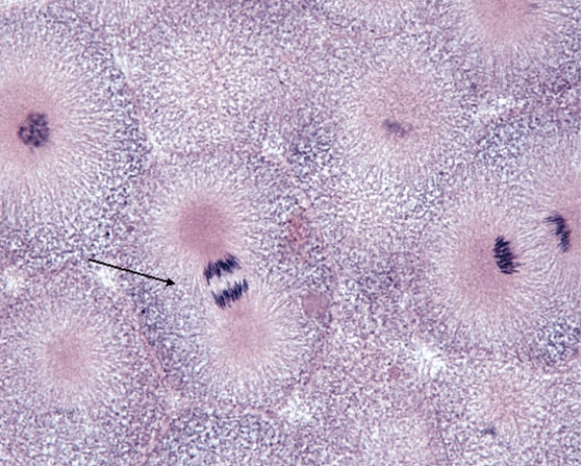
A) prophase
B) prometaphase
C) metaphase
D) anaphase
E) telophase

A) prophase
B) prometaphase
C) metaphase
D) anaphase
E) telophase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A patient with a chromosomal complement of XXY has
A) trisomy of the autosomes
B) Turner's syndrome
C) monosomy of the sex chromosomes
D) Klinefelter syndrome
E) a female phenotype
A) trisomy of the autosomes
B) Turner's syndrome
C) monosomy of the sex chromosomes
D) Klinefelter syndrome
E) a female phenotype

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
In the Fig. Nucleus, the cell depicted in this electron micrograph synthesize 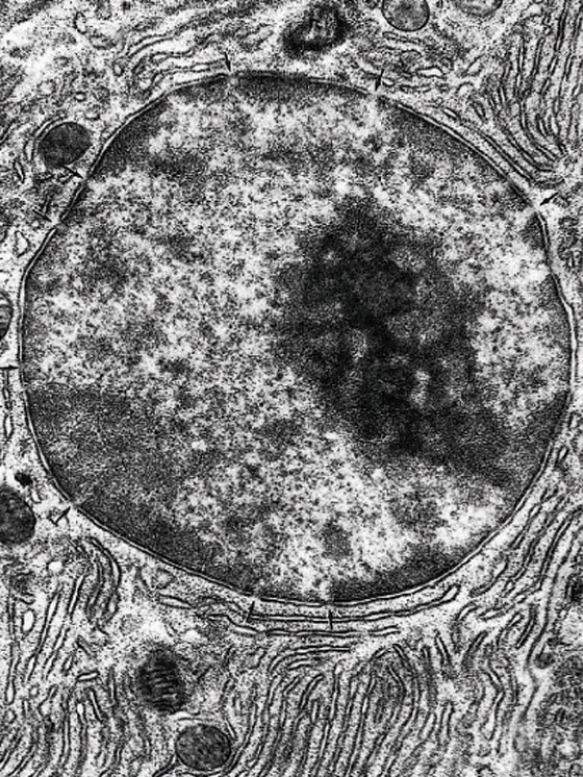
A) short-chain lipids
B) proteins destined for the cytosol
C) cholesterol
D) proteins destined to be packaged
E) long-chain lipids

A) short-chain lipids
B) proteins destined for the cytosol
C) cholesterol
D) proteins destined to be packaged
E) long-chain lipids

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The binding of cyclin B to CDK1 (cyclin-dependent kinase 1) permits the cell to progress from
A) S phase into G2 phase
B) G2 phase into M phase
C) G1 phase into G2 phase
D) G1 phase into S phase
E) prometaphase into metaphase
A) S phase into G2 phase
B) G2 phase into M phase
C) G1 phase into G2 phase
D) G1 phase into S phase
E) prometaphase into metaphase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



