Deck 22: Carbohydrates
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/104
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 22: Carbohydrates
1
Which is a ketohexose?
A) D-Glucose
B) D-Fructose
C) D-Mannose
D) D-Ribose
E) (+)-Sucrose
A) D-Glucose
B) D-Fructose
C) D-Mannose
D) D-Ribose
E) (+)-Sucrose
D-Fructose
2
Which of these is a component of the mixture formed when D-galactose is placed in aqueous base (de Bruyn - van Ekenstein transformation)? 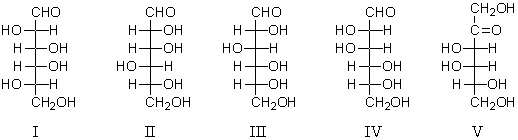
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V

A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V
V
3
Which of the following is a D-aldotetrose? 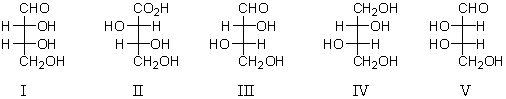
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V

A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V
I
4
A glycoside is a compound which contains the structural features of these classes of organic compounds:
A) Aldehydes and alcohols
B) Acetals and alcohols
C) Hemiacetals and alcohols
D) Ketones and alcohols
E) Alcohols and carboxylic acids
A) Aldehydes and alcohols
B) Acetals and alcohols
C) Hemiacetals and alcohols
D) Ketones and alcohols
E) Alcohols and carboxylic acids

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following is an L-aldotetrose? 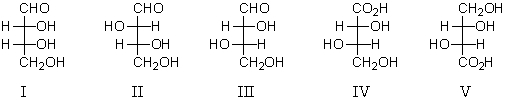
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V

A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which reagent would cause the following conversion to take place? 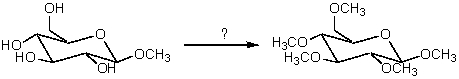
A) Excess CH3OH and KOH
B) Excess CH3OH and HCl
C) Excess (CH3)2SO4 and OH-
D) Excess CH3I and H3O+
E) Excess (CH3CO)2O
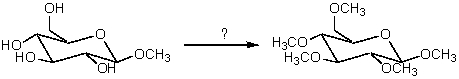
A) Excess CH3OH and KOH
B) Excess CH3OH and HCl
C) Excess (CH3)2SO4 and OH-
D) Excess CH3I and H3O+
E) Excess (CH3CO)2O

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Refer to the following structures.Which aldohexose when subjected to Fischer's end-group interchange would be converted to a compound identical with itself? 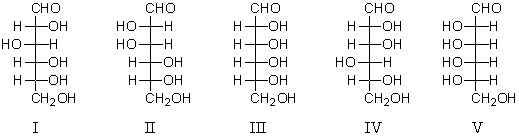
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V

A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which are the anomers? 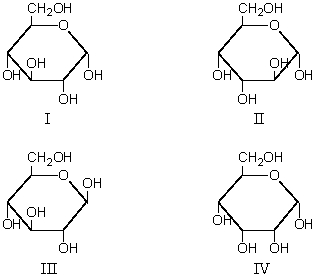
A) I and II
B) I and III
C) II and III
D) II and IV
E) III and IV

A) I and II
B) I and III
C) II and III
D) II and IV
E) III and IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of these is α-D-glucopyranose? 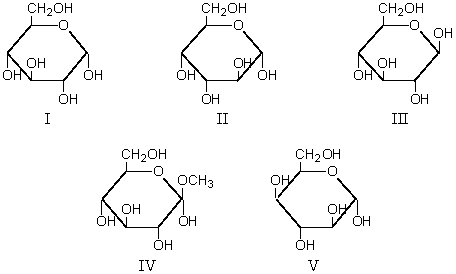
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V

A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
How many stereoisomers of the L series would exist for the following pentose? O=CHCHOHCHOHCHOHCH2OH
A) 2
B) 3
C) 4
D) 5
E) 8
A) 2
B) 3
C) 4
D) 5
E) 8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of these is a glycoside? 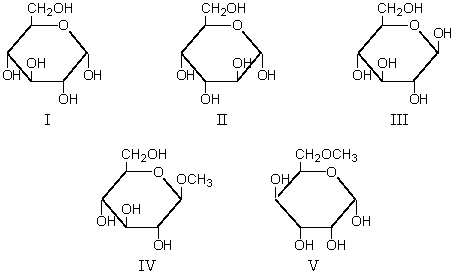
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V

A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Sugars that undergo mutarotation in neutral aqueous solution are: 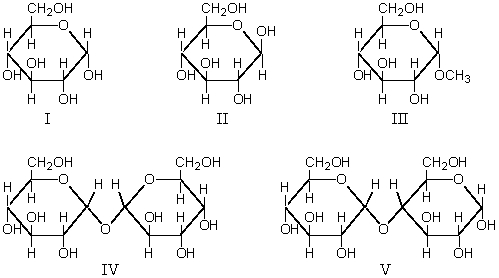
A) I and III
B) III and IV
C) II,III,and IV
D) I and IV
E) I,II,and V

A) I and III
B) III and IV
C) II,III,and IV
D) I and IV
E) I,II,and V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which would undergo mutarotation in neutral aqueous solution? 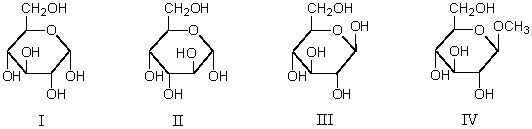
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) I,II and III

A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) I,II and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of these reacts with dilute HCl to produce methanol? 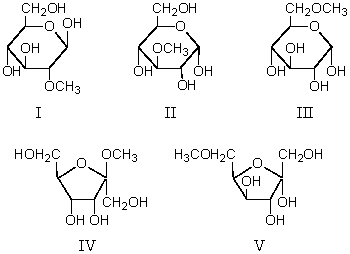
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V

A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following structures represent enantiomers? 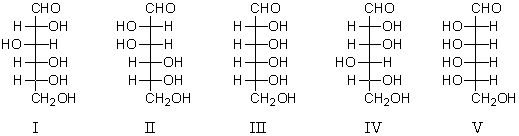
A) I and II
B) II and III
C) III and IV
D) III and V
E) IV and V

A) I and II
B) II and III
C) III and IV
D) III and V
E) IV and V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Consider the structures shown below.Which structure represents -D-glucopyranose? 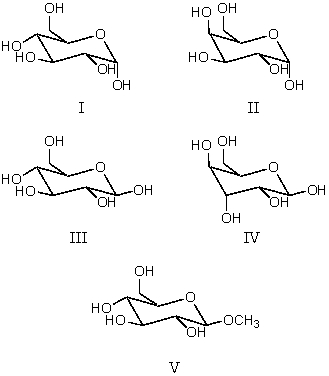
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V

A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Refer to the structures below.Which are L-sugars? 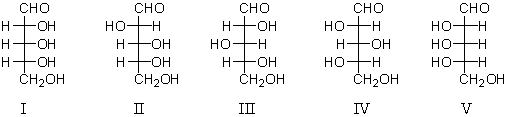
A) II and IV
B) I,II,and III
C) I and V
D) III,IV,and V
E) IV and V

A) II and IV
B) I,II,and III
C) I and V
D) III,IV,and V
E) IV and V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which reagent would be used for the following transformation? 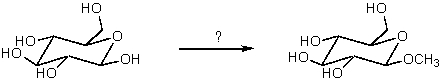
A) CH3I,KOH
B)
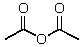
C) (CH3)2SO4,NaOH
D) CH3OH,HCl
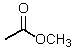
E)

A) CH3I,KOH
B)

C) (CH3)2SO4,NaOH
D) CH3OH,HCl
E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
What can be said,correctly,about a monosaccharide,the name of which is preceded only by (+)?
A) The compound is the α-anomer.
B) The compound exists in the pyranose form.
C) The compound is dextrorotatory.
D) The compound has the same stereochemistry at the penultimate carbon as D-(+)-glucose.
E) The compound exists only in open-chain form.
A) The compound is the α-anomer.
B) The compound exists in the pyranose form.
C) The compound is dextrorotatory.
D) The compound has the same stereochemistry at the penultimate carbon as D-(+)-glucose.
E) The compound exists only in open-chain form.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
What compounds (other than methanol)would be formed in the solution if glycoside presented below was treated with dilute aqueous hydrochloric acid and the solution allowed to stand? 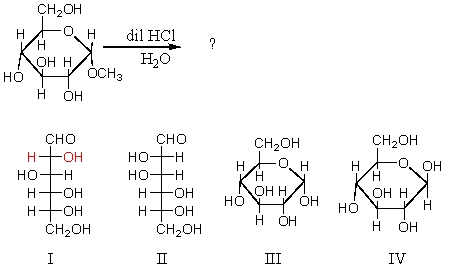
A) I and II
B) I and III
C) II and III
D) I,III,and IV
E) II,III,and IV

A) I and II
B) I and III
C) II and III
D) I,III,and IV
E) II,III,and IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the following substances will afford an optically inactive product upon reaction with nitric acid? 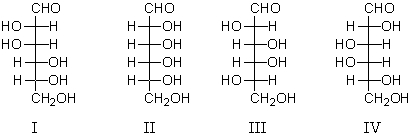
A) I
B) II
C) III and IV
D) II,III and IV
E) All of the above

A) I
B) II
C) III and IV
D) II,III and IV
E) All of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which aldohexose would yield an optically active aldaric acid when treated with nitric acid? 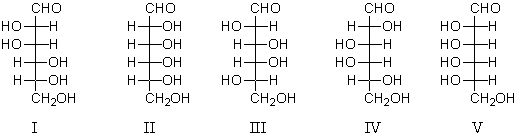
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V

A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
What is the ratio of products formed by the reaction of periodic acid with the following compound? 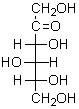 H2C=O HCO2H
H2C=O HCO2H
CO2
I
5
1
0
II
3
3
0
III
1
5
0
IV
2
3
1
V
0
4
2
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V
 H2C=O HCO2H
H2C=O HCO2HCO2
I
5
1
0
II
3
3
0
III
1
5
0
IV
2
3
1
V
0
4
2
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
An aldonic acid is represented by: 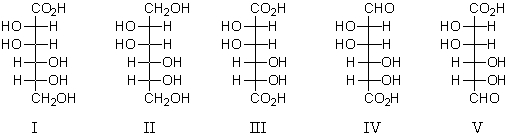
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V

A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Reaction of the following substance with bromine water would yield: 
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V

A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following would give a positive test with Benedict's solution? 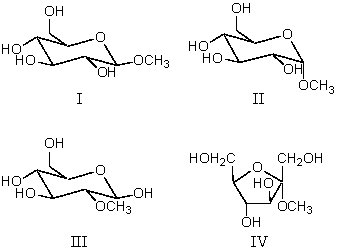
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) All of these

A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) All of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The pyranose form of an aldohexose which can react 1:2 with acetone in the presence of acid is which of these? 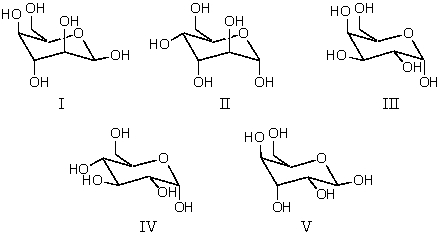
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V

A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Consider the structures below.Which monosaccharides would yield an optically active aldonic acid when oxidized with bromine water? 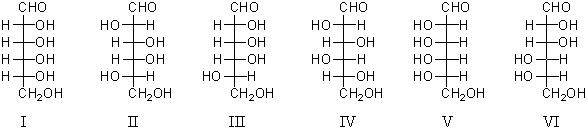
A) I,II,and III
B) I,II,and V
C) III,IV,and VI
D) II,III,and IV
E) All of these

A) I,II,and III
B) I,II,and V
C) III,IV,and VI
D) II,III,and IV
E) All of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following substances will afford a meso- product upon reaction with Br2/H2O ? 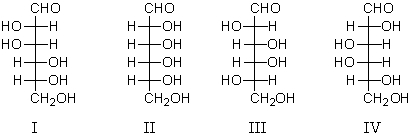
A) I
B) II
C) III and IV
D) II,III and IV
E) None of the above

A) I
B) II
C) III and IV
D) II,III and IV
E) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
A compound X reacts with 3 mol of HIO4 to yield 2 mol of HCO2H and 2 mol of HCHO.What is the structure of X? 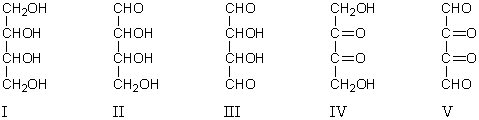
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V

A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which is an L-monosaccharide that would yield an optically active aldaric acid on oxidation by nitric acid? 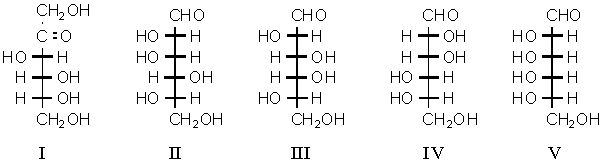
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) II and IV
E) V

A) I
B) II
C) III
D) II and IV
E) V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of these compounds,I,II,III,IV,is a reducing disaccharide? 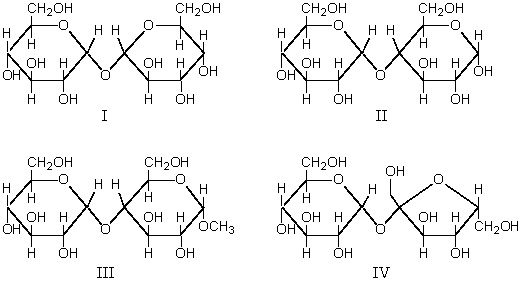
A) I alone
B) II alone
C) III alone
D) IV alone
E) I,II,III,and IV

A) I alone
B) II alone
C) III alone
D) IV alone
E) I,II,III,and IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Consider the structures shown below.Which compound is not a reducing sugar? 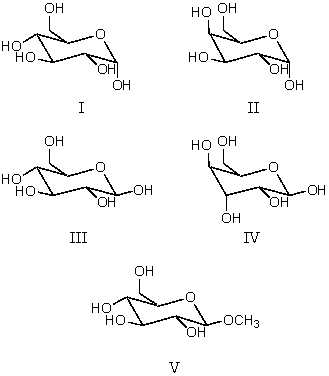
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V

A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
An aldaric acid is represented by: 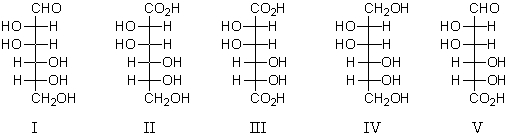
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V

A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which reagent would be used for the following transformation? 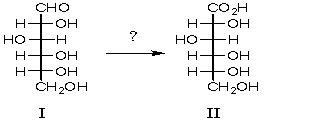
A) Ag(NH3)2+
B) HNO3
C) Br2/H2O
D) HCl
E) A and C

A) Ag(NH3)2+
B) HNO3
C) Br2/H2O
D) HCl
E) A and C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Refer to the structures below.Which sugar(s)would yield an optically active aldaric acid on oxidation with nitric acid? 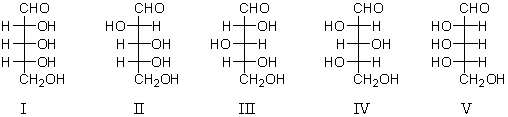
A) I and III
B) I,II,III,and V
C) II
D) III and IV
E) I and V

A) I and III
B) I,II,III,and V
C) II
D) III and IV
E) I and V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of these is a non-reducing monosaccharide? 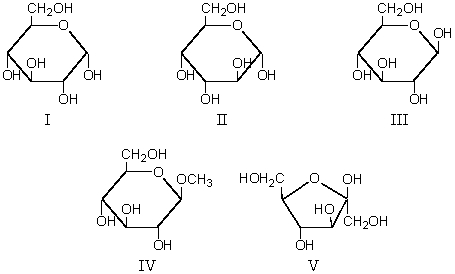
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V

A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which compound will not reduce Ag(NH3)2+ ? 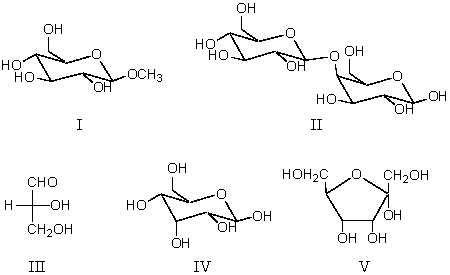
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V

A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Reaction of the following substance with nitric acid would yield: 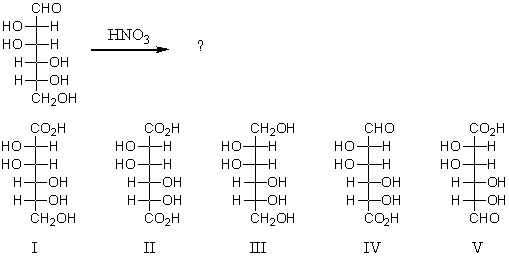
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V

A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
What is the ratio of products formed by the reaction of periodic acid with the following compound? 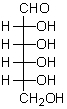 H2C=O HCO2H
H2C=O HCO2H
CO2
I
5
1
0
II
3
3
0
III
1
5
0
IV
1
4
1
V
0
4
2
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V
 H2C=O HCO2H
H2C=O HCO2HCO2
I
5
1
0
II
3
3
0
III
1
5
0
IV
1
4
1
V
0
4
2
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Consider the structures above.Which monosaccharides would yield the same phenylosazone when treated with excess phenylhydrazine? 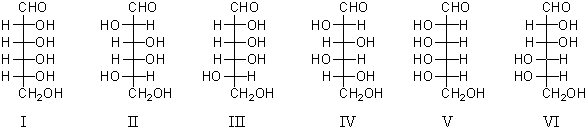
A) I and V
B) I and III
C) II and III
D) III and VI
E) IV and V

A) I and V
B) I and III
C) II and III
D) III and VI
E) IV and V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Sucrose reacts with which of these reagents?
A) C6H5NHNH2
B) Cu2+
C) Br2/H2O
D) H3O+
E) Ag(NH3)2+
A) C6H5NHNH2
B) Cu2+
C) Br2/H2O
D) H3O+
E) Ag(NH3)2+

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which reagent would be used for the following transformation? 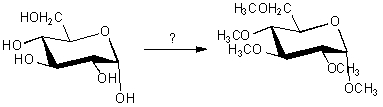
A) CH3OH/HCl
B) AgNO3/C2H5OH
C) Br2/CCl4
D) KMnO4
E) HIO4

A) CH3OH/HCl
B) AgNO3/C2H5OH
C) Br2/CCl4
D) KMnO4
E) HIO4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Reaction of the following substance with sodium borohydride (NaBH4)would yield: 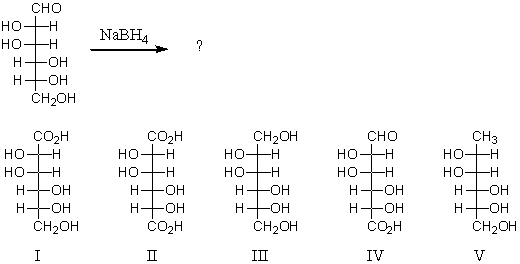
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V

A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Epimers are represented by: 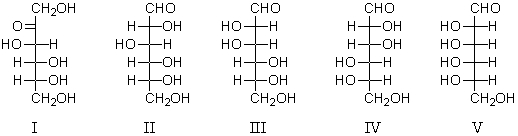
A) I and II
B) II and III
C) I,II,and III
D) III and IV
E) I,II,and V

A) I and II
B) II and III
C) I,II,and III
D) III and IV
E) I,II,and V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Refer to the following structures.Which D-aldohexose would react with NaBH4 to yield an optically inactive alditol? 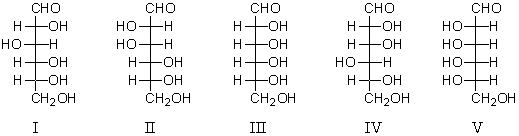
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V

A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
If the methyl glycoside of an aldohexose is treated with HIO4,one molar equivalent of HCHO is formed but no HCOOH.What size ring is present in the glycoside?
A) Three-membered
B) Four-membered
C) Five-membered
D) Six-membered
E) Seven-membered
A) Three-membered
B) Four-membered
C) Five-membered
D) Six-membered
E) Seven-membered

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which is not an intermediate monosaccharide in the Kiliani-Fischer synthesis of D-mannose from D-glyceraldehyde?
A) D-Ribose
B) D-Threose
C) D-Arabinose
D) D-Erythrose
E) More than one of these A and B
A) D-Ribose
B) D-Threose
C) D-Arabinose
D) D-Erythrose
E) More than one of these A and B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
A D-aldohexose,Z,is subjected to a Ruff degradation.The degradation product is treated with nitric acid to yield an optically active aldaric acid.A possible structure for Z is: 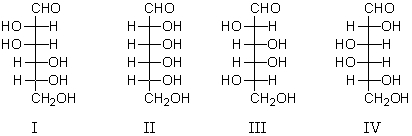
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) I,III,IV

A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) I,III,IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which of the following structures represent epimers? 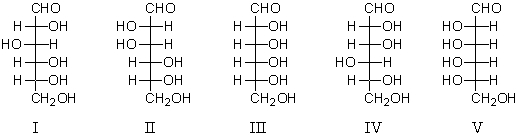
A) I and II
B) II and III
C) III and IV
D) III and V
E) A and C

A) I and II
B) II and III
C) III and IV
D) III and V
E) A and C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The Ruff degradation is the reaction of an aldose with:
A) Br2/H2O;then HCN;then H3O+;then Na-Hg,H2O
B) HCN;then Ba(OH)2;then H3O+;then Na-Hg,H2O
C) HCN;then H3O+;then Ba(OH)2;then Na-Hg,H2O
D) Br2/H2O;then H2O2,Fe2(SO4)3
E) Br2/H2O
A) Br2/H2O;then HCN;then H3O+;then Na-Hg,H2O
B) HCN;then Ba(OH)2;then H3O+;then Na-Hg,H2O
C) HCN;then H3O+;then Ba(OH)2;then Na-Hg,H2O
D) Br2/H2O;then H2O2,Fe2(SO4)3
E) Br2/H2O

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Sugars that would yield the same phenylosazone are: 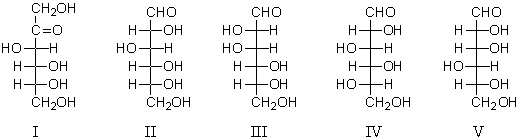
A) I and II
B) II and III
C) I,II,and III
D) III and IV
E) I,II,and V

A) I and II
B) II and III
C) I,II,and III
D) III and IV
E) I,II,and V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which compound is D-galactose? 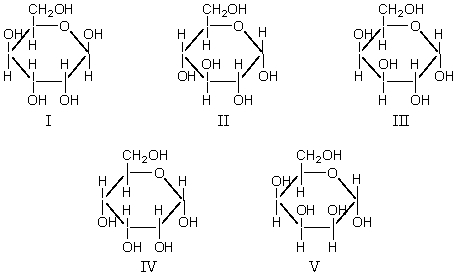
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V

A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Consider the structures below: what term(s)describe(s)the relationship between them? 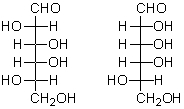
A) Enantiomers
B) Epimers
C) Diastereomers
D) Anomers
E) More than one of the above

A) Enantiomers
B) Epimers
C) Diastereomers
D) Anomers
E) More than one of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The Kiliani-Fisher Synthesis is the reaction of an aldose with:
A) Br2/H2O;then HCN;then H3O+;then Na-Hg,H2O
B) HCN;then Ba(OH)2;then H3O+;then Na-Hg,H2O
C) HCN;then H3O+;then Ba(OH)2;then Na-Hg,H2O
D) Br2/H2O;then H2O2,Fe2(SO4)3
E) Br2/H2O
A) Br2/H2O;then HCN;then H3O+;then Na-Hg,H2O
B) HCN;then Ba(OH)2;then H3O+;then Na-Hg,H2O
C) HCN;then H3O+;then Ba(OH)2;then Na-Hg,H2O
D) Br2/H2O;then H2O2,Fe2(SO4)3
E) Br2/H2O

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which compound or compounds would be formed when D-glucose is dissolved in methanol and then treated with anhydrous acid? 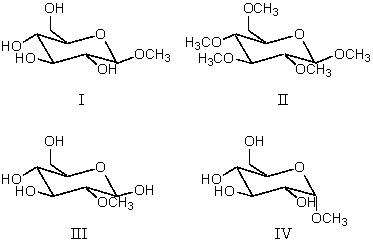
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) I and IV

A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) I and IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Consider the structures of D-allose below: 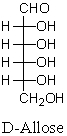 Which of the following structures represents L-allose?
Which of the following structures represents L-allose? 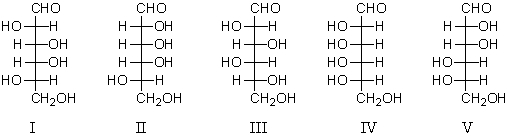
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V
 Which of the following structures represents L-allose?
Which of the following structures represents L-allose? 
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Refer to the structures below.Which sugars would react with phenylhydrazine to yield the same phenylosazone? 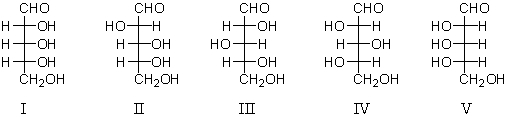
A) I and II
B) III and IV
C) I and V
D) II and III
E) III and V

A) I and II
B) III and IV
C) I and V
D) II and III
E) III and V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
A D-aldohexose X,is subjected to a Ruff degradation.The degradation product is treated with nitric acid to yield an optically inactive aldaric acid.A possible structure for X is: 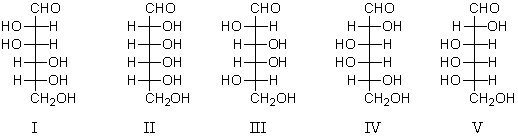
A) I
B) II
C) III and IV
D) IV
E) V and II

A) I
B) II
C) III and IV
D) IV
E) V and II

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Which reagent would be used for the following transformation? 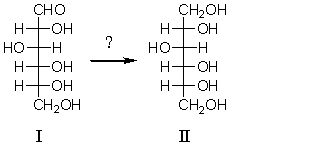
A) NaBH4
B) AgNO3/C2H5OH
C) Br2/CCl4
D) HCl
E) Hot KMnO4

A) NaBH4
B) AgNO3/C2H5OH
C) Br2/CCl4
D) HCl
E) Hot KMnO4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Which is a reducing sugar with an α-glycosidic linkage?
A) Sucrose
B) Maltose
C) Lactose
D) Cellobiose
E) None of these
A) Sucrose
B) Maltose
C) Lactose
D) Cellobiose
E) None of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Compound X is a reducing sugar which,on hydrolysis,affords two molar equivalents of D-glucose.This hydrolysis is catalyzed by an enzyme specific for glucosides of this type: 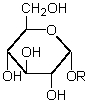 What is the identity of X?
What is the identity of X?
A) Sucrose
B) Lactose
C) Maltose
D) Cellobiose
E) None of these
 What is the identity of X?
What is the identity of X?A) Sucrose
B) Lactose
C) Maltose
D) Cellobiose
E) None of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Which of the following is the structure of D-galacturonic acid? 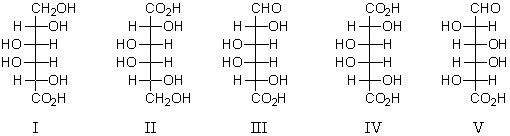
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V

A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Many carbohydrates exist in equilibrium with cyclic hemiacetals.Those carbohydrates that form a five-membered cyclic hemiacetal are called _____________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Which monosaccharide is recovered from the hydrolysis of glycogen?
A) D-Galactose
B) D-Glucose
C) D-Gulose
D) Cellobiose
E) Maltose
A) D-Galactose
B) D-Glucose
C) D-Gulose
D) Cellobiose
E) Maltose

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The simplest carbohydrates (those that cannot be hydrolyzed to simpler carbohydrates)are called ______________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Consider the structures below.An L-aldohexose,X,is treated with nitric acid to yield an optically inactive aldaric acid.The same L-aldohexose,X,is subjected to a Ruff degradation and the degradation product is oxidized with nitric acid to produce an optically inactive aldaric acid.Which is a possible structure for X? 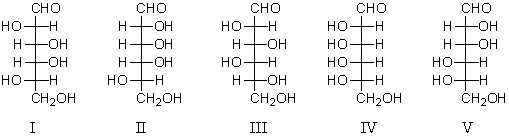
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V

A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Cellulose lacks nutritive value for humans because:
A) the products of its digestion are excreted without utilization.
B) its conformation prevents attack by digestive enzymes.
C) we lack the enzymes which can catalyze the hydrolysis of the glycosidic linkages.
D) it passes through the digestive tract so rapidly.
E) the molecules possess such a high molecular weight.
A) the products of its digestion are excreted without utilization.
B) its conformation prevents attack by digestive enzymes.
C) we lack the enzymes which can catalyze the hydrolysis of the glycosidic linkages.
D) it passes through the digestive tract so rapidly.
E) the molecules possess such a high molecular weight.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
A monosaccharide containing six carbon atoms and an aldehyde functionality is called an _____________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Carbohydrates are synthesized in green plants by _____________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Which of these is an example of a glucan?
A) Maltose
B) Sucrose
C) Lactose
D) Cellobiose
E) Amylose
A) Maltose
B) Sucrose
C) Lactose
D) Cellobiose
E) Amylose

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
α-D-Glucose has [α]D = +112o,and β-D-glucose has [α]D = +19o.If either anomer is dissolved in water and allowed to reach equilibrium,the specific rotation of the solution is + 52o.What are the percentages of each anomer at equilibrium?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Cellulose differs from chitin in which way?
A) Cellulose has -glycosidic linkages;chitin has -glycosidic linkages.
B) Cellulose contains only D-glucose units;chitin contains only N-acetyl-D-glucosamine units.
C) Cellulose cannot be hydrolyzed;chitin can be hydrolyzed.
D) Cellulose has a linear structure;chitin has a helical structure.
E) Cellulose chains are branched;chitin chains are unbranched.
A) Cellulose has -glycosidic linkages;chitin has -glycosidic linkages.
B) Cellulose contains only D-glucose units;chitin contains only N-acetyl-D-glucosamine units.
C) Cellulose cannot be hydrolyzed;chitin can be hydrolyzed.
D) Cellulose has a linear structure;chitin has a helical structure.
E) Cellulose chains are branched;chitin chains are unbranched.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Carbohydrates that hydrolyze to give a large number of molecules of monosaccharides are called _____________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The D-glucose unit at the branching point of amylopectin has free hydroxyl groups at which positions?
A) C2,C3,and C6
B) C2 and C3
C) C3 and C4
D) C3,C4,and C6
E) C4 and C6
A) C2,C3,and C6
B) C2 and C3
C) C3 and C4
D) C3,C4,and C6
E) C4 and C6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
What is the correct description of this disaccharide? 
A) The α-anomer of two D-glucose units joined by an α(1 4)linkage
B) The α-anomer of two D-galactose units joined by an α(1 4)linkage
C) The -anomer of two D-galactose units joined by a (1 4)linkage
D) The -anomer of two D-glucose units joined by a (1 4)linkage
E) The α-anomer of two D-galactose units joined by a (1 4)linkage

A) The α-anomer of two D-glucose units joined by an α(1 4)linkage
B) The α-anomer of two D-galactose units joined by an α(1 4)linkage
C) The -anomer of two D-galactose units joined by a (1 4)linkage
D) The -anomer of two D-glucose units joined by a (1 4)linkage
E) The α-anomer of two D-galactose units joined by a (1 4)linkage

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
An aldopentose,X,is subjected to a Kiliani-Fischer synthesis to produce two aldohexoses,Y and Z.Both Y and Z,when oxidized with nitric acid,yield optically active aldaric acids.Which structure represents X? 
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V

A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Lactose exists in two forms α and β.Anomer α has [α]D = +92.6o,and anomer β has [α]D = +34o.What are the percentages of each anomer at equilibrium when the specific rotation of the water solution is + 52o?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Which of the following would yield D-glucose and D-mannose when subjected to a Kiliani-Fischer synthesis? 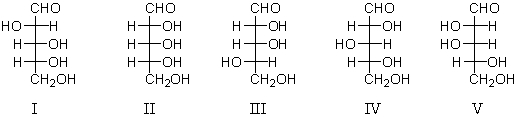
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V

A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Which monosaccharide is recovered from the hydrolysis of starch?
A) D-Galactose
B) D-Glucose
C) D-Gulose
D) Cellobiose
E) Maltose
A) D-Galactose
B) D-Glucose
C) D-Gulose
D) Cellobiose
E) Maltose

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



