Deck 24: Amino Acids and Proteins
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/94
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 24: Amino Acids and Proteins
1
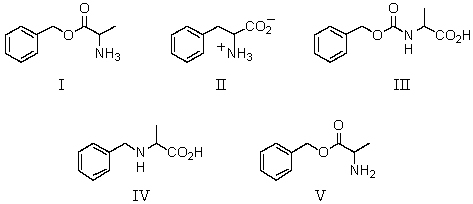
Which amino acid would have its isoelectric point near pH 10? 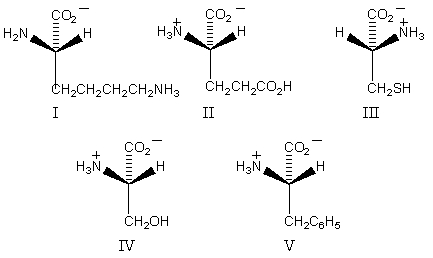
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V

A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V
I
2
What is the pI of the following amino acid? 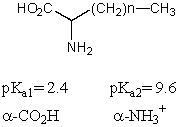
A) 12
B) 3.6
C) 4.8
D) 6.0
E) 7.2

A) 12
B) 3.6
C) 4.8
D) 6.0
E) 7.2
6.0
3
What might be concluded upon determining that an unknown amino acid has its isoelectric point near pH 10?
A) It must have a hydrophobic side chain
B) It must have a hydrophilic side chain
C) Its side chain must contain more basic groups then acidic functions
D) Its side chain must contain an acidic group
E) None of the above is a valid conclusion
A) It must have a hydrophobic side chain
B) It must have a hydrophilic side chain
C) Its side chain must contain more basic groups then acidic functions
D) Its side chain must contain an acidic group
E) None of the above is a valid conclusion
Its side chain must contain more basic groups then acidic functions
4
Which amino acid is achiral? 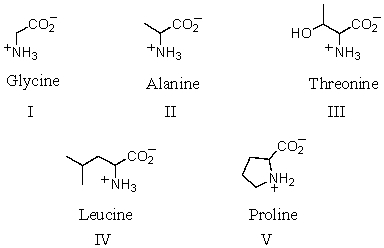
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V

A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Disulfide bonds in proteins:
A) result from an oxidation of thiols.
B) help to maintain the shape of proteins.
C) can be broken by reduction.
D) can link two cysteine amino acid residues.
E) All of the above
A) result from an oxidation of thiols.
B) help to maintain the shape of proteins.
C) can be broken by reduction.
D) can link two cysteine amino acid residues.
E) All of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which amino acid would have its isoelectric point near pH 10?
A) Glycine
B) Tryptophan
C) Serine
D) Proline
E) Lysine
A) Glycine
B) Tryptophan
C) Serine
D) Proline
E) Lysine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which amino acid is unlikely to be found in a natural protein? 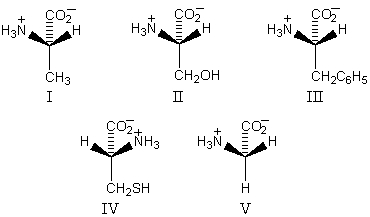
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V

A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which amino acid would not have its isoelectric point in the pH range 5-7?
A) Leucine
B) Threonine
C) Methionine
D) Arginine
E) Cysteine
A) Leucine
B) Threonine
C) Methionine
D) Arginine
E) Cysteine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of these amino acids cannot be described as an L amino acid? 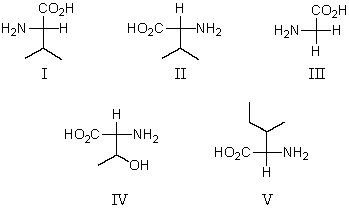
A) I
B) II,IV and V
C) I and III
D) II and IV
E) III and V

A) I
B) II,IV and V
C) I and III
D) II and IV
E) III and V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
What is the pI of the following amino acid? 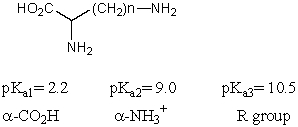
A) 1.5
B) 6.3
C) 5.6
D) 9.8
E) 6.8
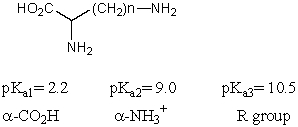
A) 1.5
B) 6.3
C) 5.6
D) 9.8
E) 6.8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which amino acid would have its isoelectric point near pH 3? 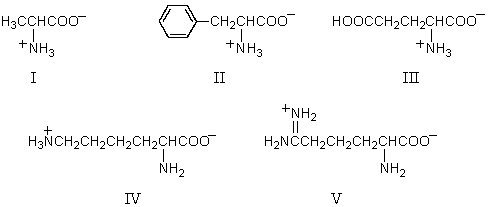
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V

A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
What might be concluded upon determining that an unknown amino acid has its isoelectric point near pH 3?
A) It must have a hydrophobic side chain
B) It must have a hydrophilic side chain
C) Its side chain must contain a basic group
D) Its side chain must contain more acidic groups then basic groups
E) None of the above is a valid conclusion
A) It must have a hydrophobic side chain
B) It must have a hydrophilic side chain
C) Its side chain must contain a basic group
D) Its side chain must contain more acidic groups then basic groups
E) None of the above is a valid conclusion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which amino acid would not have its isoelectric point in the pH range 5-7?
A) Glycine
B) Proline
C) Cysteine
D) Glutamine
E) All of these amino acids have isoelectric point in the pH range 5-7
A) Glycine
B) Proline
C) Cysteine
D) Glutamine
E) All of these amino acids have isoelectric point in the pH range 5-7

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The pH at which the concentration of the dipolar ion (zwitterion)form of an amino acid is at a maximum and the cationic and anionic forms are at equal concentrations is termed the
A) end point.
B) equivalence point.
C) neutral point.
D) isoelectric point.
E) dipolar point.
A) end point.
B) equivalence point.
C) neutral point.
D) isoelectric point.
E) dipolar point.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of these amino acids is an R amino acid? 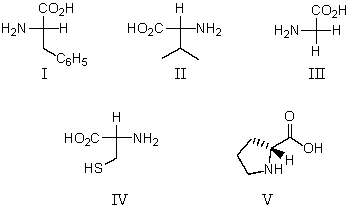
A) II and IV
B) IV and V
C) I and III
D) V
E) All of these are R amino acids

A) II and IV
B) IV and V
C) I and III
D) V
E) All of these are R amino acids

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following amino acids is theoretically capable of existing in diastereomeric forms? 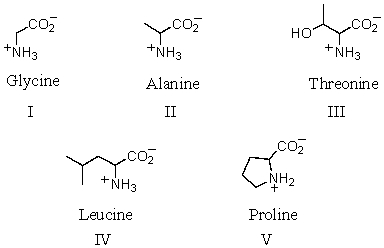
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V

A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of these amino acids has the R configuration at the stereogenic center but,nonetheless,is an L amino acid? 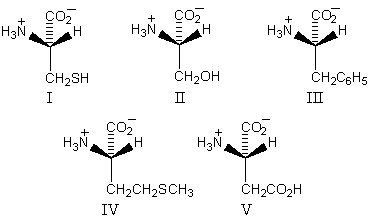
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V

A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which amino acid would have its isoelectric point near pH 10? 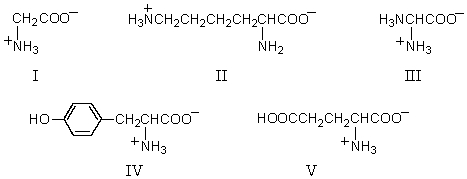
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V

A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
What is the pI of the following amino acid? 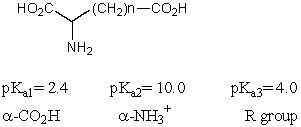
A) 1.6
B) 3.2
C) 5.5
D) 6.2
E) 7.0
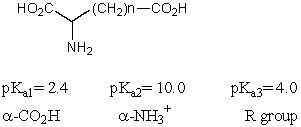
A) 1.6
B) 3.2
C) 5.5
D) 6.2
E) 7.0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of these amino acids is a D amino acid? 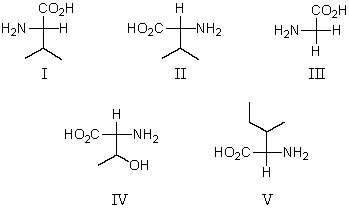
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V

A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of these amino acids is described as an "essential" amino acid?
A) Methionine
B) Phenylalanine
C) Isoleucine
D) Tryptophan
E) All of these are "essential" amino acids
A) Methionine
B) Phenylalanine
C) Isoleucine
D) Tryptophan
E) All of these are "essential" amino acids

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of these natural amino acids contains a heterocyclic ring?
A) Asparagine
B) Proline
C) Arginine
D) Histidine
E) B and D
A) Asparagine
B) Proline
C) Arginine
D) Histidine
E) B and D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of these natural amino acids contains an -OH group?
A) Serine
B) Threonine
C) Tyrosine
D) Two of these
E) All of these
A) Serine
B) Threonine
C) Tyrosine
D) Two of these
E) All of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Pipecolic acid logically would be substituted for which natural amino acid in the synthesis of peptide analogs? 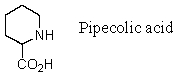
A) Histidine
B) Proline
C) Tryptophan
D) Phenylalanine
E) Tyrosine

A) Histidine
B) Proline
C) Tryptophan
D) Phenylalanine
E) Tyrosine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of these natural amino acids contains two carboxylic acid groups?
A) Cystine
B) Cysteine
C) Glutamic acid
D) A and B
E) A and C
A) Cystine
B) Cysteine
C) Glutamic acid
D) A and B
E) A and C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which is an isolable intermediate in the Strecker synthesis of an amino acid? 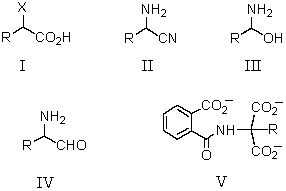
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V

A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of these natural amino acids,when present in a polypeptide,is likely to exhibit significant hydrogen bonding through its side chain?
A) Serine
B) Threonine
C) Tyrosine
D) Two of these
E) All of these
A) Serine
B) Threonine
C) Tyrosine
D) Two of these
E) All of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of these amino acids is formed from a precursor amino acid only after the latter has been incorporated into a polypeptide chain?
A) Serine
B) Arginine
C) Isoleucine
D) Tryptophan
E) Hydroxyproline
A) Serine
B) Arginine
C) Isoleucine
D) Tryptophan
E) Hydroxyproline

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
What would be the predominant form of lysine in water at pH 14? 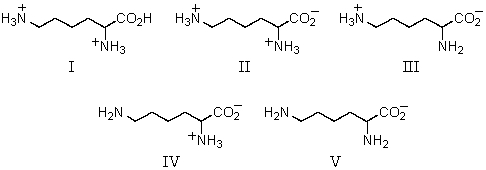
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V

A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of these natural amino acids contains an indole ring?
A) Phenylalanine
B) Tyrosine
C) Tryptophan
D) 4-Hydroxyproline
E) Asparigine
A) Phenylalanine
B) Tyrosine
C) Tryptophan
D) 4-Hydroxyproline
E) Asparigine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of these natural amino acids contains an amide function?
A) Asparagine
B) Methionine
C) Cysteine
D) Glutamine
E) Two of these
A) Asparagine
B) Methionine
C) Cysteine
D) Glutamine
E) Two of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of these natural amino acids,when present in a polypeptide,is not likely to exhibit significant hydrogen bonding through its side chain?
A) Leucine
B) Threonine
C) Tyrosine
D) Serine
E) All of these are likely to exhibit significant hydrogen bonding through the side chain
A) Leucine
B) Threonine
C) Tyrosine
D) Serine
E) All of these are likely to exhibit significant hydrogen bonding through the side chain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of these natural amino acids contains an imidazole ring?
A) Histidine
B) Lysine
C) Tryptophan
D) 4-Hydroxyproline
E) Two of the above
A) Histidine
B) Lysine
C) Tryptophan
D) 4-Hydroxyproline
E) Two of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which of these natural amino acids contains a pyrrolidine ring?
A) Phenylalanine
B) Tyrosine
C) Tryptophan
D) 4-Hydroxyproline
E) Serine
A) Phenylalanine
B) Tyrosine
C) Tryptophan
D) 4-Hydroxyproline
E) Serine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of these amino acids is described as an "essential" amino acid?
A) Threonine
B) Glycine
C) Tyrosine
D) Serine
E) All of these are "essential" amino acids
A) Threonine
B) Glycine
C) Tyrosine
D) Serine
E) All of these are "essential" amino acids

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of these amino acids contains a hydrophobic side chain?
A) Lysine
B) Serine
C) Methionine
D) Arginine
E) Cysteine
A) Lysine
B) Serine
C) Methionine
D) Arginine
E) Cysteine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
For the accompanying fully-protonated amino acid,what is the arrangement of pKa values in order of increasing magnitude? 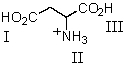
A) I < II < III
B) II < I < III
C) III < I < II
D) III < II < I
E) II < III < I

A) I < II < III
B) II < I < III
C) III < I < II
D) III < II < I
E) II < III < I

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which of these natural amino acids contains a phenolic group?
A) Phenylalanine
B) Tyrosine
C) Tryptophan
D) 4-Hydroxyproline
E) Serine
A) Phenylalanine
B) Tyrosine
C) Tryptophan
D) 4-Hydroxyproline
E) Serine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of these natural amino acids contains an amide function?
A) Asparagine
B) Proline
C) Arginine
D) Histidine
E) None of these
A) Asparagine
B) Proline
C) Arginine
D) Histidine
E) None of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The predominant form of aspartic acid in water at pH 1 would be: 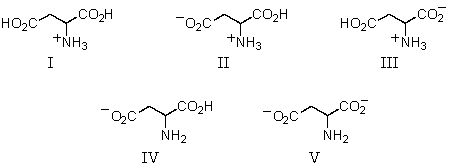
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V

A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
What product(s)would you expect from the following reaction? 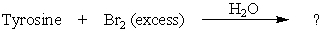
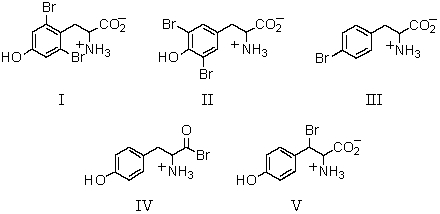
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V
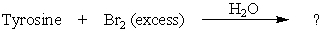

A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The Edman degradation uses this reagent to identify the N-terminal amino acid of a peptide or protein.
A) C6H5NHNH2
B) C6H5NH2
C) C6H5N=C=S
D) C6H5N=C=O
E) Aminopeptidase
A) C6H5NHNH2
B) C6H5NH2
C) C6H5N=C=S
D) C6H5N=C=O
E) Aminopeptidase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
How many different tripeptides can exist,each containing one residue of glycine,one of L-threonine,and one of L-arginine?
A) 2
B) 3
C) 6
D) 8
E) 9
A) 2
B) 3
C) 6
D) 8
E) 9

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The purple color of the anion formed in the ninhydrin test for α-amino acids is due to:
A) the attraction of the anion to a metal in a pi-complex.
B) intermolecular hydrogen bonding.
C) molecular vibrations.
D) the highly conjugated nature of the anion.
E) the color of the ninhydrin.
A) the attraction of the anion to a metal in a pi-complex.
B) intermolecular hydrogen bonding.
C) molecular vibrations.
D) the highly conjugated nature of the anion.
E) the color of the ninhydrin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Which amino acid of a polypeptide would become labeled when the polypeptide is treated with 2,4-dinitrofluorobenzene in base,even though the amino acid is not a terminal amino acid?
A) Lysine
B) Glycine
C) Alanine
D) Phenylalanine
E) Leucine
A) Lysine
B) Glycine
C) Alanine
D) Phenylalanine
E) Leucine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Why is this sequence,CH2=CHCH2OH + HBr,then CrO3/H2SO4/H2O,finally xs NH3,not a good method for the preparation of L-alanine?
A) NH3 is not sufficiently nucleophilic to perform the final step.
B) HBr does not add to substituted alkenes.
C) 1° alcohols are not oxidized by CrO3 in acidic solution.
D) Initial HBr addition produces a racemic intermediate which leads to racemic product.
E) Steric hindrance precludes nucleophilic substitution at a 2° carbon atom.
A) NH3 is not sufficiently nucleophilic to perform the final step.
B) HBr does not add to substituted alkenes.
C) 1° alcohols are not oxidized by CrO3 in acidic solution.
D) Initial HBr addition produces a racemic intermediate which leads to racemic product.
E) Steric hindrance precludes nucleophilic substitution at a 2° carbon atom.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
When the pentapeptide below is heated first with 2,4-dinitrofluorobenzene (and base)and then subjected to acidic hydrolysis,which amino acid will bear the dinitrophenyl group? Leu·Val·Gly·Phe·Ile
A) Leucine
B) Valine
C) Glycine
D) Phenylalanine
E) Isoleucine
A) Leucine
B) Valine
C) Glycine
D) Phenylalanine
E) Isoleucine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
A pentapeptide has the molecular formula: Asp,Glu,His,Phe,Val.Partial hydrolysis of the pentapeptide gives: Val·Asp,Glu·His,Phe·Val,and Asp·Glu.What is the amino acid sequence of the pentapeptide?
A) Phe·Val·Asp·Glu·His
B) His·Glu·Asp·Val·Phe
C) Asp·Glu·His·Phe·Val
D) Phe·Val·Glu·His·Asp
E) Glu·His·Phe·Val·Asp
A) Phe·Val·Asp·Glu·His
B) His·Glu·Asp·Val·Phe
C) Asp·Glu·His·Phe·Val
D) Phe·Val·Glu·His·Asp
E) Glu·His·Phe·Val·Asp

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Predict the direction of migration (toward anode or cathode)of alanine during electrophoresis at pH = 5.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Why is dicyclohexylcarbodiimide (DCC)used in peptide synthesis?
A) DCC "protects" the amino group of the intended N-terminal amino acid.
B) DCC activates the carboxyl group of one amino acid so that this amino acid reacts more readily with a second amino acid.
C) DCC cleaves the blocking groups from the final peptide.
D) DCC is the resin used in the automated synthesis of peptides.
E) DCC removes the peptide from the resin at the conclusion of the synthesis.
A) DCC "protects" the amino group of the intended N-terminal amino acid.
B) DCC activates the carboxyl group of one amino acid so that this amino acid reacts more readily with a second amino acid.
C) DCC cleaves the blocking groups from the final peptide.
D) DCC is the resin used in the automated synthesis of peptides.
E) DCC removes the peptide from the resin at the conclusion of the synthesis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The primary structure of a protein refers to its:
A) sequence of amino acid residues.
B) disulfide bonds.
C) helical structure.
D) hydrogen bonding.
E) All of these
A) sequence of amino acid residues.
B) disulfide bonds.
C) helical structure.
D) hydrogen bonding.
E) All of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which of these is used to convert a protein into smaller,more manageable fragments for subsequent structural studies?
A) Insulin
B) Aminopeptidase
C) Carboxypeptidase
D) Trypsin which is produced in the HYPERLINK "http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pancreas" \o "Pancreas" pancreas as the inactive HYPERLINK "http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Proenzyme" \o "Proenzyme" proenzyme HYPERLINK "http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Trypsinogen" \o "Trypsinogen" trypsinogen.
E) 2,4-Dinitrofluorobenzene
A) Insulin
B) Aminopeptidase
C) Carboxypeptidase
D) Trypsin which is produced in the HYPERLINK "http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pancreas" \o "Pancreas" pancreas as the inactive HYPERLINK "http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Proenzyme" \o "Proenzyme" proenzyme HYPERLINK "http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Trypsinogen" \o "Trypsinogen" trypsinogen.
E) 2,4-Dinitrofluorobenzene

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The occurrence of this amino acid in a polypeptide chain disrupts an α-helix:
A) Proline
B) Alanine
C) Methionine
D) Histidine
E) Tyrosine
A) Proline
B) Alanine
C) Methionine
D) Histidine
E) Tyrosine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
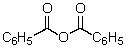
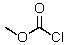
This reagent is used to "protect" the amino group of an amino acid which is to be joined to a second amino acid by a peptide bond.
A)
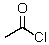
B)
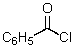
C)
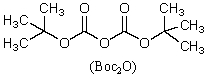
D)
E)
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
What product would be obtained upon treating alanine with the following reagent ? 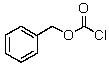
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V


A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The secondary structure of proteins is derived from:
A) peptide linkages.
B) disulfide linkages.
C) hydrogen bond formation.
D) hydrophobic interactions.
E) acid-base interactions.
A) peptide linkages.
B) disulfide linkages.
C) hydrogen bond formation.
D) hydrophobic interactions.
E) acid-base interactions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
A "conjugated protein" is one which:
A) possesses catalytic properties.
B) is a digestive enzyme.
C) exists largely as an α-helix.
D) contains unsaturated amino acids.
E) contains a nonprotein group as part of the molecule.
A) possesses catalytic properties.
B) is a digestive enzyme.
C) exists largely as an α-helix.
D) contains unsaturated amino acids.
E) contains a nonprotein group as part of the molecule.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which one of these amino acids does not give the usual purple color with ninhydrin?
A) Histidine
B) Proline
C) Tryptophan
D) Leucine
E) Aspartic acid
A) Histidine
B) Proline
C) Tryptophan
D) Leucine
E) Aspartic acid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
A heptapeptide Ala2,Glu,Phe,Pro,Tyr,Val gives labeled alanine when heated with DNFB followed by hydrolysis.On partial hydrolysis the unlabeled heptapeptide gives the following: Ala·Glu,Pro·Tyr,Ala·Val,Tyr·Ala,Val·Phe·Pro.
What is the amino acid sequence of the heptapeptide?
A) Ala·Phe·Pro·Tyr·Ala·Glu·Val
B) Ala·Val·Phe·Pro·Tyr·Ala·Glu
C) Ala·Val·Phe·Pro·Tyr·Glu·Ala
D) Ala·Val·Phe·Tyr·Pro·Ala·Glu
E) Val·Ala·Phe·Tyr·Pro·Ala·Glu
What is the amino acid sequence of the heptapeptide?
A) Ala·Phe·Pro·Tyr·Ala·Glu·Val
B) Ala·Val·Phe·Pro·Tyr·Ala·Glu
C) Ala·Val·Phe·Pro·Tyr·Glu·Ala
D) Ala·Val·Phe·Tyr·Pro·Ala·Glu
E) Val·Ala·Phe·Tyr·Pro·Ala·Glu

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Which attractive force is responsible for maintaining the tertiary structure of a protein?
A) Disulfide linkages
B) Hydrogen bonds
C) van der Waals forces
D) Hydrophobic interactions
E) All of these
A) Disulfide linkages
B) Hydrogen bonds
C) van der Waals forces
D) Hydrophobic interactions
E) All of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Give the structure of the aldehyde which,upon treatment with HCN and ammonia,followed by heating with aqueous acid,would afford racemic tryptophan.What is this strategy for the synthesis of -amino acids called?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Peptide synthesis has four basic steps.These are:

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Beginning with a three-carbon alcohol,outline all necessary steps in the preparation of D,L-alanine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Complete the following equations: 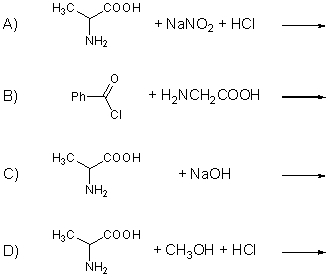


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Amino acids can be prepared from aldehydes by treatment with ammonia and HCN followed by hydrolysis.This method is known as the ___________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
What is the final product formed when potassium phthalimide is subjected to the following reaction sequence? Give structural details of all significant intermediates,including stereochemistry,as applicable. 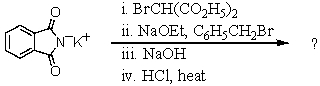
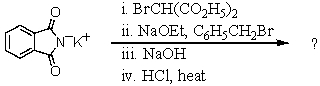

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Complete the reaction presented below: 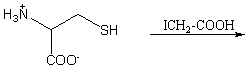


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The amino acid threonine, (2S,3R)-2-amino-3-hydroxybutanoic acid,has two chiral
centers.Draw a Fisher projection of threonine.
centers.Draw a Fisher projection of threonine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The pH at which the concentration of the zwitterionic form (dipolar form)of an amino acid is at its highest and the concentrations of the cationic and anionic forms are equal is called the _____________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Draw the structures of ValAla and AlaVal as zwitterions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Draw the structures of the predominant forms of glycine at pH = 2.0,6.0,and 10.Indicate the direction of migration (toward anode or cathode)for each structure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Draw the Fisher projection of a threonine diastereomer,and label the chiral centers as R
or S.
or S.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
A reagent that reacts with most amino acids to give an intense purple color is called ___________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Draw the structure of L-phenylalanine and L-valine in Fischer projection.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The 22 -amino acids can be subdivided into three different types on the basis of the structures of their side chains.These three types are: ____________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Show how a Strecker synthesis might be used to prepare phenylalanine starting from phenylacetldehyde.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Using the three-letter code names for amino acids,write the structures of all possible peptides containing these amino acids: Val,Ser,Leu

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
What is the final product formed via the following reaction sequence? Give structural details of all significant intermediates. 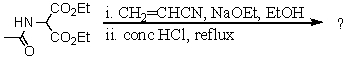


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
What are the name and the structure of the products A and B? 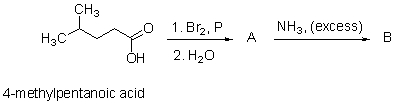
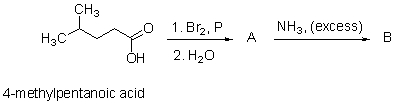

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
The Henderson-Hasselbach equation shows that the ________________ of an acid is the ________________ at which the acid is half-neutralized.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



