Deck 18: International Economics
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/261
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 18: International Economics
1
When a country allows trade and becomes an importer of goods, producers gain more than consumers lose.
False
2
A nation can gain from international trade when the relative domestic prices of the nation differs from that in other countries, and it imports goods for which it is a high opportunity cost producer.
True
3
When a country allows trade and becomes an exporter of goods, producers gain more than consumers lose.
True
4
The intended gains from U.S.tariffs and other trade restrictions can backfire if foreign governments retaliate by imposing additional trade restrictions on U.S.goods sold in their countries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
If England uses one week's time to produce ten yards of cloth or two barrels of wine and Portugal uses one week's time to produce twelve yards of cloth or six barrels of wine, England has the comparative advantage in both goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
When a country allows trade and becomes an exporter of goods everyone benefits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Generally, restrictions limiting imports will also help domestic producers who are exporters.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A tariff on a good increases the domestic price of the good, increases domestic production of the good, reduces the amount of the good sold, and decreases imports of the good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A country that is half as productive at producing some goods as another country, but is one quarter as productive at producing others, will not be able to gain from trade.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A country has an absolute advantage over another if it can produce a good with fewer resources.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Trade occurs when a country has an absolute advantage and not just a comparative advantage over another country.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
If it can be shown that a tariff on steel imports will increase employment in the steel industry, we can be sure that the effect of the tariff on U.S.employment will also be positive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Tariffs contribute to higher prices of textile products imported into the United States, but import quotas on textiles brought into the United States do not.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A U.S.tariff on French wine will likely benefit U.S.wine producers and the U.S.government (by increasing tax revenue), but harm U.S.wine drinkers and French wine producers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The quantity supplied by domestic producers in an importing country must be less than the quantity demanded by its population.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
When a country allows trade and becomes an exporter of goods consumers gain more than producers lose.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
When a country allows trade and becomes an importer of goods everyone benefits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The inevitable cost of protecting domestic industries from foreign competition will be higher prices for domestic consumers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Import tariffs in the United States are likely to reduce U.S.exports, both because of the resulting decrease in foreign earnings of dollars from exports to the United States and because of the likelihood of increases in other countries' import restrictions against U.S.goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
If two countries produce both wheat and sugar and one country has the comparative advantage in producing wheat than the other country must have the absolute advantage producing sugar.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Import quotas generate more government revenue than a tariff that is designed to allow the same level of imports.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
With flexible exchange rates, the imbalance between debits and credits arising from shifts in currency demand and/or supply is accommodated through special financial borrowings or reserve movements.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The balance on goods and services is the same as the balance on the current account.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Stock in a German corporation can be purchased directly with currency from any other country.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
In 2009 the U.S.current account balance was zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The exchange rate of a currency will increase if the quantity demanded exceeds quantity supplied at the current exchange rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
All exports of U.S.goods are considered credit items in the U.S.balance of payments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The dollar appreciates when U.S.demands for foreign currencies decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Import quotas contribute to higher prices of products imported into the U.S., but tariffs do not.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
If interest rates rise in the United States relative to those in the rest of the world, the exchange value of the dollar will tend to appreciate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
In recent years the United States has run persistent deficits in its balance on the current account.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
If as a result of NAFTA the demand for American exports rises, it would tend to increase the exchange value of the U.S.dollar as a result.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Deflation in the United States would tend to make the exchange value of the dollar depreciate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The current exchange rate system is effectively a dirty float system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Differences among nations in real economic growth rates, real interest rates, and inflation rates will each affect the exchange rates among their currencies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
If incomes decrease in the United States, Americans will buy more goods, including foreign goods.This increase in demand for foreign goods will cause an increase in the demand for Euros.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Prior to 1973, the world operated on a system of fixed exchange rates called the Bretton Woods system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The exchange rate is the price of one currency in terms of a second currency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
It is possible for some individuals within countries to lose from reducing international trade barriers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Major U.S.exporters would be likely to oppose the sort of protectionist policies favored by domestic producers that compete with imports.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
What is producer surplus? How is it different from consumer surplus?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
"Tariffs are necessary for reasons of national security." Discuss the validity of this statement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
What factors will shift the supply and demand for currency?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
How do subsidies distort trade patterns and lead to inefficiencies?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Fixed exchange rates give countries too much freedom over their monetary policies, thereby threatening higher rates of inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Trade restrictions will stop foreign imports, which will increase American employment and protect American jobs.Most economists realize this argument is wrong.Can you explain why?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Classify each of the following as debits or credits in the U.S.balance of payments. 


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Why is the demand for foreign currencies known as a derived demand?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
What are the effects of a tariff, and who benefits and who loses when tariffs are imposed? What are the effects of a quota, and who benefits and who loses when quotas are imposed?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
What is the law of comparative advantage, and why is it important in international trade?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
What benefits are to be gained from countries producing according to the law of comparative advantage? What if a country is absolutely more productive in all goods?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Steve and Lee have been shipwrecked on a deserted island in the Hawaiian chain.Their economic activity consists of either gathering pineapples or fishing.We know Steve can catch four fish in one hour or harvest two baskets of pineapples.In the same time Lee can reel in two fish or harvest two baskets of pineapples.If they each spend four hours a day fishing and four hours a day harvesting pineapples, how many of each will Steve produce? How many will Lee produce? What will their total production be? If Steve and Lee don't trade with each other, who is better off? Why?
Assume Lee and Steve both operate on straight-line production possibilities curves.What is Steve's opportunity cost of producing a basket of pineapples? Of a producing a fish? What is Lee's opportunity cost of producing a basket of pineapples? Of a producing a fish? If Steve and Lee traded, who has the comparative advantage in fish? Pineapples?
If Lee and Steve specialize in and trade the good in which they have a comparative advantage, how much of each good will be produced in an eight hour day? What are the gains from trade?
Assume Lee and Steve both operate on straight-line production possibilities curves.What is Steve's opportunity cost of producing a basket of pineapples? Of a producing a fish? What is Lee's opportunity cost of producing a basket of pineapples? Of a producing a fish? If Steve and Lee traded, who has the comparative advantage in fish? Pineapples?
If Lee and Steve specialize in and trade the good in which they have a comparative advantage, how much of each good will be produced in an eight hour day? What are the gains from trade?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Explain how an increase in the American demand for German goods leads to a change in the Euro relative to the U.S.dollar.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
What will happen to the supply of dollars, the demand for dollars, and the equilibrium exchange rate of the dollar in each of the following cases?
a.Americans buy more European goods.
b.Europeans invest in U.S. stock market.
c.European tourists flock to United States.
d.Europeans buy U.S. government bonds.
e.American tourists flock to Europe.
a.Americans buy more European goods.
b.Europeans invest in U.S. stock market.
c.European tourists flock to United States.
d.Europeans buy U.S. government bonds.
e.American tourists flock to Europe.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The U.S.has committed itself to creating a free trade zone between the U.S., Canada and Mexico.Why might this be important? Relative to imports and exports to other nations, what is the size of these two North American trading partners trade relationship with the U.S.?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Explain how each of the following will affect the relative values of the dollar and the French franc:
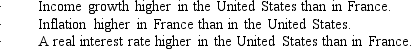
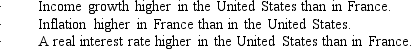

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Suppose that in the absence of trade, the U.S.price for bicycles was higher than the world price for bicycles.Would allowing international trade, mean that the U.S.would import or export bicycles? Who in the U.S.would benefit and who would lose with a free trade policy, and would the gains be greater than the losses?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
What are the commonly used arguments for the use of tariffs?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Ceteris paribus, if the dollar appreciated in relation to a foreign currency, would the U.S.sell more goods or fewer goods to consumers in that foreign country? Why?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Since the advent of flexible exchange rates, world trade has not only continued but also expanded.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
What are the main arguments presented against flexible exchange rates?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Iceland can produce 32 units of food per person per year or 16 units of clothing per person per year, but Lavaland can produce 24 units of food per year or 12 units of clothing.Which of the following is true?
A)Iceland has both a comparative and absolute advantage in producing food.
B)Iceland has a comparative advantage, but not an absolute advantage in producing food.
C)Lavaland has both a comparative and absolute advantage in producing clothing.
D)Lavaland has a comparative advantage, but not an absolute advantage in producing clothing.
E)None of the above are true.
A)Iceland has both a comparative and absolute advantage in producing food.
B)Iceland has a comparative advantage, but not an absolute advantage in producing food.
C)Lavaland has both a comparative and absolute advantage in producing clothing.
D)Lavaland has a comparative advantage, but not an absolute advantage in producing clothing.
E)None of the above are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
If the United States could produce 4 tons of potatoes or 2 tons of wheat per worker per year, while Ireland could produce 2 tons of potatoes or 3 tons of wheat per worker per year, the country with the comparative advantage in producing potatoes is ____ and the country with the absolute advantage in producing potatoes is ____.
A)the United States; the United States
B)the United States; Ireland
C)Ireland; the United States
D)Ireland; Ireland
A)the United States; the United States
B)the United States; Ireland
C)Ireland; the United States
D)Ireland; Ireland

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
If the United States could produce 4 tons of potatoes or 2 tons of wheat per worker per year, while Ireland could produce 3 tons of potatoes or 2 tons of wheat per worker per year, the country with the comparative advantage in producing potatoes is ____ and the country with the absolute advantage in producing potatoes is ____.
A)the United States; the United States
B)the United States; Ireland
C)Ireland; the United States
D)Ireland; Ireland
A)the United States; the United States
B)the United States; Ireland
C)Ireland; the United States
D)Ireland; Ireland

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
If the United States could produce 1/2 ton of potatoes or 1 ton of wheat per worker per year, while Ireland could produce 3 tons of potatoes or 2 tons of wheat per worker per year, the country with the comparative advantage in producing wheat is ____ and the country with the absolute advantage in producing potatoes is ____.
A)the United States; the United States
B)the United States; Ireland
C)Ireland; the United States
D)Ireland; Ireland
A)the United States; the United States
B)the United States; Ireland
C)Ireland; the United States
D)Ireland; Ireland

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Columbia produces coffee with less labor and land than any other country; it therefore necessarily has
A)an absolute advantage in coffee production.
B)a comparative advantage in coffee production.
C)both a comparative and absolute advantage in coffee production.
D)an absolute advantage and comparative disadvantage in coffee production.
A)an absolute advantage in coffee production.
B)a comparative advantage in coffee production.
C)both a comparative and absolute advantage in coffee production.
D)an absolute advantage and comparative disadvantage in coffee production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Comparative advantage occurs when a person or a country can produce a good or service at a lower ____ than others.
A)marginal cost
B)variable cost
C)opportunity cost
D)total cost
A)marginal cost
B)variable cost
C)opportunity cost
D)total cost

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
From which of the following countries does the U.S.import the largest dollar value of goods?
A)Canada
B)Mexico
C)Great Britain
D)Japan
A)Canada
B)Mexico
C)Great Britain
D)Japan

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Iceland can produce 32 units of food per person per year or 16 units of clothing per person per year, but Lavaland can produce 24 units of food per year or 12 units of clothing.Which of the following is true?
A)Iceland has both a comparative and absolute advantage in producing food.
B)Iceland has a comparative advantage, but not an absolute advantage in producing food.
C)Lavaland has both a comparative and absolute disadvantage in producing clothing.
D)Lavaland has an absolute disadvantage, but not a comparative disadvantage in producing clothing.
E)None of the above are true.
A)Iceland has both a comparative and absolute advantage in producing food.
B)Iceland has a comparative advantage, but not an absolute advantage in producing food.
C)Lavaland has both a comparative and absolute disadvantage in producing clothing.
D)Lavaland has an absolute disadvantage, but not a comparative disadvantage in producing clothing.
E)None of the above are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Economists sometimes say that the current exchange rate system is a dirty float system.What does this mean?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Why would a new limit on trade in goods with the United States by Canada be more important to the U.S.economy than the same type of policy in Italy?
A)Canadians speak English so U.S. citizens are more interested in what they do.
B)Canada ranks behind only the United Kingdom as our second most important trade partner.
C)Canada is the U.S.' largest trading partner.
D)Canada exports most of the hockey players who play for the National Hockey Leagues.
A)Canadians speak English so U.S. citizens are more interested in what they do.
B)Canada ranks behind only the United Kingdom as our second most important trade partner.
C)Canada is the U.S.' largest trading partner.
D)Canada exports most of the hockey players who play for the National Hockey Leagues.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Say that Iceland can produce 32 units of food per person per year or 16 units of clothing per person per year, but Lavaland can produce 24 units of food per year or 12 units of clothing.Which of the following is true?
A)Iceland has both a comparative and absolute advantage in producing food.
B)Iceland has a comparative advantage, but not an absolute advantage in producing food.
C)Lavaland has both a comparative and absolute advantage in producing clothing.
D)Lavaland has a comparative advantage, but not an absolute advantage in producing clothing.
E)None of the above are true.
A)Iceland has both a comparative and absolute advantage in producing food.
B)Iceland has a comparative advantage, but not an absolute advantage in producing food.
C)Lavaland has both a comparative and absolute advantage in producing clothing.
D)Lavaland has a comparative advantage, but not an absolute advantage in producing clothing.
E)None of the above are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
If the United States could produce 4 tons of potatoes or 2 tons of wheat per worker per year, while Ireland could produce 3 tons of potatoes or 2 tons of wheat per worker per year, the country with the comparative advantage in producing wheat is ____ and the country with the absolute advantage in producing potatoes is ____.
A)the United States; the United States
B)the United States; Ireland
C)Ireland; the United States
D)Ireland; Ireland
A)the United States; the United States
B)the United States; Ireland
C)Ireland; the United States
D)Ireland; Ireland

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Iceland can produce 32 units of food per person per year or 16 units of clothing per person per year, but Lavaland can produce 36 units of food per year or 18 units of clothing.Which of the following is true?
A)Iceland has both an absolute and a comparative advantage in producing food.
B)Iceland has an absolute but not a comparative advantage in producing food.
C)Lavaland has both an absolute and a comparative advantage in producing clothing.
D)Lavaland has an absolute but not a comparative advantage in producing clothing.
E)None of the above are true.
A)Iceland has both an absolute and a comparative advantage in producing food.
B)Iceland has an absolute but not a comparative advantage in producing food.
C)Lavaland has both an absolute and a comparative advantage in producing clothing.
D)Lavaland has an absolute but not a comparative advantage in producing clothing.
E)None of the above are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Iceland can produce 32 units of food per person per year or 16 units of clothing per person per year, but Lavaland can produce 36 units of food per year or 18 units of clothing.Which of the following is true?
A)Iceland has both a comparative and absolute advantage in producing food.
B)Iceland has a comparative advantage, but not an absolute advantage in producing food.
C)Lavaland has both a comparative and absolute advantage in producing clothing.
D)Lavaland has a comparative advantage, but not an absolute advantage in producing clothing.
E)None of the above are true.
A)Iceland has both a comparative and absolute advantage in producing food.
B)Iceland has a comparative advantage, but not an absolute advantage in producing food.
C)Lavaland has both a comparative and absolute advantage in producing clothing.
D)Lavaland has a comparative advantage, but not an absolute advantage in producing clothing.
E)None of the above are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Which of the following is correct?
A)U.S. International trade represents about 50 percent of U.S. GDP.
B)Less than 5 percent of world output is sold in a country different from the one in which it is produced.
C)Without tariff protection the number of jobs available to domestic workers would decline.
D)The volume of international trade has grown rapidly.
A)U.S. International trade represents about 50 percent of U.S. GDP.
B)Less than 5 percent of world output is sold in a country different from the one in which it is produced.
C)Without tariff protection the number of jobs available to domestic workers would decline.
D)The volume of international trade has grown rapidly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Which of the following is not a major trading partner of the U.S.?
A)Canada
B)Mexico
C)Russia
D)China
E)Japan
A)Canada
B)Mexico
C)Russia
D)China
E)Japan

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Under a system of fixed exchange rates, what will happen if the price of a currency is set above market equilibrium? How can this be remedied?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
What will happen to a country that fixes the price of foreign exchange below equilibrium?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
What matters most in determining the efficient distribution of production over the world is
A)absolute advantage.
B)efficiency.
C)the stock of resources.
D)comparative advantage.
A)absolute advantage.
B)efficiency.
C)the stock of resources.
D)comparative advantage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



