Deck 7: Firms in Competitive Markets
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/200
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 7: Firms in Competitive Markets
1
Firms should shut down in the short run whenever price is less than the average total cost.
False
2
The behavior of an individual perfectly competitive firm has a perceptible influence on the market price.
False
3
The market demand curve in a perfectly competitive industry is horizontal, while the demand curve faced by an individual perfectly competitive firm is downward sloping.
False
4
In long-run equilibrium, a perfectly competitive firm produces the output level that minimizes average total cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The demand curve faced by a perfectly competitive firm is vertical.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The market demand curve in a perfectly competitive industry is downward sloping, while the demand curve faced by an individual perfectly competitive firm is horizontal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Economic profits in a perfectly competitive industry will encourage entry of new firms, which will shift the market supply curve to the right.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A perfectly competitive firm faces a perfectly elastic demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Perfectly competition is characterized by a large number of buyers and sellers with identical products and no significant barriers to entry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
In short-run equilibrium in a perfectly competitive market, firms always make zero economic profit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
It is relatively easy for firms to enter and exit a perfectly competitive market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
In a perfectly competitive market, marginal revenue is the same as the market price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Perfectly competitive firms earn zero economic profit in the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
In the long run, a perfectly competitive firm is expected to generate either an economic profit or an economic loss.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
In order to maximize profits, a firm should produce the level of output at which total revenue is maximized.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A firm that is earning zero economic profits has a strong incentive to exit the industry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
If price is less than the average variable cost, firms that seek to maximize profit should shut down.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
As an industry's output increases, the industry's demand for the inputs that it uses will also increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Whenever marginal revenue is greater than marginal cost, a profit-maximizing firm should reduce its output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
In a constant cost industry, the cost curves of individual firms will shift upward as the industry output expands.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Perfectly competitive markets are characterized by:
A)rivalry in product design.
B)competition in terms of product quality.
C)attempts by sellers to outdo one another with good service.
D)all of the above.
E)none of the above.
A)rivalry in product design.
B)competition in terms of product quality.
C)attempts by sellers to outdo one another with good service.
D)all of the above.
E)none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following is true about perfect competition?
A)Since a perfectly competitive seller can sell all he wants at the market price, her demand curve is horizontal at the market price over the entire range of output that she could possibly produce.
B)Because perfectly competitive markets have many buyers and sellers, each firm is so small in relation to the industry that its production decisions have no impact on the market.
C)Because consumers believe that all firms in a perfectly competitive market sell identical (homogeneous) products, the products of all the firms are perfect substitutes.
D)Perfectly competitive markets have easy entry and exit.
E)All of the above are true about perfect competition.
A)Since a perfectly competitive seller can sell all he wants at the market price, her demand curve is horizontal at the market price over the entire range of output that she could possibly produce.
B)Because perfectly competitive markets have many buyers and sellers, each firm is so small in relation to the industry that its production decisions have no impact on the market.
C)Because consumers believe that all firms in a perfectly competitive market sell identical (homogeneous) products, the products of all the firms are perfect substitutes.
D)Perfectly competitive markets have easy entry and exit.
E)All of the above are true about perfect competition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The perfectly competitive model assumes that:
A)individual sellers can influence the market price.
B)sellers can increase their total revenue by raising prices.
C)firms can enter and exit the industry with relative ease.
D)firms compete by varying a product's quality rather than a product's price.
A)individual sellers can influence the market price.
B)sellers can increase their total revenue by raising prices.
C)firms can enter and exit the industry with relative ease.
D)firms compete by varying a product's quality rather than a product's price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Perfect competition is the term used to describe:
A)an industry in which a few price-taking firms produce identical products.
B)an industry in which numerous price-taking firms produce identical products.
C)an industry in which firms are price takers and compete for market share by varying the qualitative characteristics of products.
D)an industry in which numerous firms are price makers and produce identical products.
A)an industry in which a few price-taking firms produce identical products.
B)an industry in which numerous price-taking firms produce identical products.
C)an industry in which firms are price takers and compete for market share by varying the qualitative characteristics of products.
D)an industry in which numerous firms are price makers and produce identical products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of the following is a characteristic of perfect competition?
A)substantial barriers to entry
B)differentiated products
C)few sellers
D)each firm has significant control over the market
E)none of the above
A)substantial barriers to entry
B)differentiated products
C)few sellers
D)each firm has significant control over the market
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following is a characteristic of perfect competition?
A)zero barriers to entry
B)homogeneous products
C)many sellers
D)many buyers
E)all of the above
A)zero barriers to entry
B)homogeneous products
C)many sellers
D)many buyers
E)all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A firm that is a price taker:
A)competes with other producers who produce differentiated products.
B)must be a relatively large producer compared to other firms in the market.
C)can exert a major influence on the overall market.
D)will lose all sales if it prices its product in excess of the market equilibrium price.
A)competes with other producers who produce differentiated products.
B)must be a relatively large producer compared to other firms in the market.
C)can exert a major influence on the overall market.
D)will lose all sales if it prices its product in excess of the market equilibrium price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the following is true of perfectly competitive firms?
A)It is difficult for entrepreneurs to become suppliers of a product in a perfectly competitive market structure.
B)A perfectly competitive firm has a perfectly elastic supply curve.
C)In a perfectly competitive market, an individual seller can change his price and it will not alter the output he sells.
D)All of the above are true.
E)None of the above are true.
A)It is difficult for entrepreneurs to become suppliers of a product in a perfectly competitive market structure.
B)A perfectly competitive firm has a perfectly elastic supply curve.
C)In a perfectly competitive market, an individual seller can change his price and it will not alter the output he sells.
D)All of the above are true.
E)None of the above are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Why can't a firm in a perfectly competitive industry charge a price above the market-clearing price?
A)Government-imposed price ceilings prevent prices from being raised.
B)Firms in a perfectly competitive industry face significant barriers to entry.
C)Perfectly competitive firms are price searchers.
D)Numerous competitors produce the same product and charge the market price.
A)Government-imposed price ceilings prevent prices from being raised.
B)Firms in a perfectly competitive industry face significant barriers to entry.
C)Perfectly competitive firms are price searchers.
D)Numerous competitors produce the same product and charge the market price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following is a characteristic of perfect competition?
A)substantial barriers to entry
B)homogeneous products
C)few sellers
D)each firm has significant control over the market
E)none of the above
A)substantial barriers to entry
B)homogeneous products
C)few sellers
D)each firm has significant control over the market
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
In the perfectly competitive model, all firms are assumed to be producing:
A)products that are heavily advertised.
B)differentiated products.
C)identical products.
D)complementary products.
A)products that are heavily advertised.
B)differentiated products.
C)identical products.
D)complementary products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which market structure is characterized by many sellers, easy entry, and homogeneous products?
A)perfect competition
B)monopolistic competition
C)oligopoly
D)monopoly
E)none of the above
A)perfect competition
B)monopolistic competition
C)oligopoly
D)monopoly
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of the following is characteristic of a perfectly competitive market?
A)There is free entry into and exit from the market.
B)Individual firms can exert a perceptible influence on the market price.
C)Firms in the market produce a differentiated product.
D)All of the above are true.
A)There is free entry into and exit from the market.
B)Individual firms can exert a perceptible influence on the market price.
C)Firms in the market produce a differentiated product.
D)All of the above are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which one of the following is not a characteristic of a perfectly competitive market?
A)Firms advertise in order to distinguish their products and increase market share.
B)Firms earn zero economic profit in the long run.
C)Competing products are virtually identical.
D)Firms are price takers.
E)There are a large number of buyers and sellers interacting in the market.
A)Firms advertise in order to distinguish their products and increase market share.
B)Firms earn zero economic profit in the long run.
C)Competing products are virtually identical.
D)Firms are price takers.
E)There are a large number of buyers and sellers interacting in the market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The demand curve facing a perfectly competitive firm is:
A)perfectly inelastic.
B)perfectly elastic.
C)unit elastic.
D)downward sloping.
E)upward sloping.
A)perfectly inelastic.
B)perfectly elastic.
C)unit elastic.
D)downward sloping.
E)upward sloping.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following most closely resembles a perfectly competitive market?
A)the airline industry
B)the soft drink industry
C)the wheat market
D)long-distance telephone service
A)the airline industry
B)the soft drink industry
C)the wheat market
D)long-distance telephone service

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the following is most likely to be a price taker?
A)a respected heart surgeon
B)an ice cream shop owner located in Atlanta, Georgia
C)a beachside tourist resort
D)a Kansas wheat farmer
A)a respected heart surgeon
B)an ice cream shop owner located in Atlanta, Georgia
C)a beachside tourist resort
D)a Kansas wheat farmer

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A perfectly competitive firm is a:
A)price giver.
B)price taker.
C)price maker.
D)price leader.
A)price giver.
B)price taker.
C)price maker.
D)price leader.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
A perfectly competitive firm faces a demand curve that is:
A)horizontal and perfectly inelastic.
B)horizontal and perfectly elastic.
C)vertical and perfectly inelastic.
D)vertical and perfectly elastic.
A)horizontal and perfectly inelastic.
B)horizontal and perfectly elastic.
C)vertical and perfectly inelastic.
D)vertical and perfectly elastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following best resembles a perfectly competitive market?
A)a stock market
B)the book publishing industry
C)the steel industry
D)the used car industry
A)a stock market
B)the book publishing industry
C)the steel industry
D)the used car industry

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
If a price-taking firm selling in a competitive market raises the price of its product above the market-clearing price, it will:
A)increase its profits.
B)maintain its profit base since the demand for the product is inelastic.
C)be able to increase its sales.
D)not be able to sell any output.
A)increase its profits.
B)maintain its profit base since the demand for the product is inelastic.
C)be able to increase its sales.
D)not be able to sell any output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Marginal revenue is:
A)the additional cost incurred from producing one more unit of output.
B)the addition to total profit from selling one more unit of output.
C)the addition to total revenue from selling one more unit of output.
D)the addition to total output from hiring one more unit of labor.
A)the additional cost incurred from producing one more unit of output.
B)the addition to total profit from selling one more unit of output.
C)the addition to total revenue from selling one more unit of output.
D)the addition to total output from hiring one more unit of labor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
In a perfectly competitive industry, influence over price is exerted by:
A)individual sellers.
B)individual buyers.
C)the largest firms.
D)the forces of supply and demand.
A)individual sellers.
B)individual buyers.
C)the largest firms.
D)the forces of supply and demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
If a competitive firm is operating in short run equilibrium and then its fixed costs fall by 40 percent, it should:
A)use more labor and less capital in current production.
B)not change its output.
C)increase its output.
D)decrease its output.
E)stop producing.
A)use more labor and less capital in current production.
B)not change its output.
C)increase its output.
D)decrease its output.
E)stop producing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Which of the following is true?
A)The objective of the firm is to maximize profits, by producing the amount that equates total revenue and total cost.
B)The objective of the firm is to maximize profits, by producing the amount that equates average revenue and average total cost.
C)The objective of the firm is to maximize profits, by producing the amount that equates average revenue and average variable cost.
D)The objective of the firm is to maximize profits, by producing the amount that equates marginal revenue and marginal cost.
E)None of the above is true.
A)The objective of the firm is to maximize profits, by producing the amount that equates total revenue and total cost.
B)The objective of the firm is to maximize profits, by producing the amount that equates average revenue and average total cost.
C)The objective of the firm is to maximize profits, by producing the amount that equates average revenue and average variable cost.
D)The objective of the firm is to maximize profits, by producing the amount that equates marginal revenue and marginal cost.
E)None of the above is true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Assume you know the following short run information for a perfectly competitive firm:
Based on the information above, which of the following is true?
A)The marginal revenue for the 12th unit of output will be less than $10.
B)The firm would earn higher profits if it produced 10 units than if it produced 9 units.
C)The profit from producing 12 units of output will be the same as for producing 6 units of output.
D)Fixed costs for the firm are $30.
E)None of the above is true.
Based on the information above, which of the following is true?
A)The marginal revenue for the 12th unit of output will be less than $10.
B)The firm would earn higher profits if it produced 10 units than if it produced 9 units.
C)The profit from producing 12 units of output will be the same as for producing 6 units of output.
D)Fixed costs for the firm are $30.
E)None of the above is true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
For a perfectly competitive firm, which of the following is always true?
A)P = MR only
B)ATC = MR only
C)AR = D only
D)P = MR = D
E)none of the above
A)P = MR only
B)ATC = MR only
C)AR = D only
D)P = MR = D
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Marginal revenue for a perfectly competitive firm equals:
A)the addition to total cost from producing one more unit of output.
B)average revenue at all levels of output.
C)marginal cost at all levels of output.
D)average total cost at all levels of output.
A)the addition to total cost from producing one more unit of output.
B)average revenue at all levels of output.
C)marginal cost at all levels of output.
D)average total cost at all levels of output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Farmer Brady sells wheat in a market where sellers are price takers.Which of the following is true in regard to Farmer Brady's production and pricing decisions?
A)Farmer Brady will be able to increase the total revenue from the sale of his wheat if he increases the price of the wheat.
B)Since the market dictates the price of his product, Farmer Brady will have no incentive to minimize per-unit production costs.
C)Since the market dictates the price of his product, Farmer Brady has no production decisions to make.
D)It would be senseless for Farmer Brady to try to increase sales by lowering the price of his product. His entire output can be sold at the market price.
A)Farmer Brady will be able to increase the total revenue from the sale of his wheat if he increases the price of the wheat.
B)Since the market dictates the price of his product, Farmer Brady will have no incentive to minimize per-unit production costs.
C)Since the market dictates the price of his product, Farmer Brady has no production decisions to make.
D)It would be senseless for Farmer Brady to try to increase sales by lowering the price of his product. His entire output can be sold at the market price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
A profit-maximizing firm in a perfectly competitive market will always produce a quantity of output that:
A)minimizes the per-unit cost of production.
B)is expected to maximize total revenue.
C)maximizes the amount by which total revenue exceeds total cost.
D)brings average total cost and price into equality.
A)minimizes the per-unit cost of production.
B)is expected to maximize total revenue.
C)maximizes the amount by which total revenue exceeds total cost.
D)brings average total cost and price into equality.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
A firm facing a horizontal demand curve:
A)cannot affect the price it receives for its output.
B)is unlikely to price its goods below market price.
C)faces a perfectly elastic demand curve for its product.
D)is characterized by all of the above.
A)cannot affect the price it receives for its output.
B)is unlikely to price its goods below market price.
C)faces a perfectly elastic demand curve for its product.
D)is characterized by all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which of the following is false of perfectly competitive firms?
A)A perfectly competitive market is approximated most closely in highly organized markets for securities and agricultural commodities.
B)The perfectly competitive model does not require any knowledge on the part of individual buyers and sellers about market demand and supply curves.
C)Because perfectly competitive firms are price takers, each firm's demand curve remains unchanged even when the market price changes.
D)In a perfectly competitive market, marginal revenue is constant and equal to the market price.
A)A perfectly competitive market is approximated most closely in highly organized markets for securities and agricultural commodities.
B)The perfectly competitive model does not require any knowledge on the part of individual buyers and sellers about market demand and supply curves.
C)Because perfectly competitive firms are price takers, each firm's demand curve remains unchanged even when the market price changes.
D)In a perfectly competitive market, marginal revenue is constant and equal to the market price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Assume you know the following short run information for a perfectly competitive firm:
Based on the information above, which of the following is false?
A)The firm's average total cost of production increases for outputs in excess of 8 units.
B)The firm's average total cost of producing 7 units is the same as for producing 6 units.
C)The profit maximizing level of output for the firm would be 10 units.
D)In the long run, the firm's price would be less than $10.
Based on the information above, which of the following is false?
A)The firm's average total cost of production increases for outputs in excess of 8 units.
B)The firm's average total cost of producing 7 units is the same as for producing 6 units.
C)The profit maximizing level of output for the firm would be 10 units.
D)In the long run, the firm's price would be less than $10.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Assuming a price was $2.00, how many units should this perfectly competitive firm produce and sell in order to maximize profits?
A)24
B)25
C)26
D)27
E)28
A)24
B)25
C)26
D)27
E)28

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The horizontal demand curve facing an individual firm in a perfectly competitive market:
A)violates the law of demand, which states that demand curves slope downward.
B)is a reflection of the firm's small size relative to the total market.
C)is maintained only with the help of high barriers to entry.
D)is a reflection of the inelastic demand for its product.
A)violates the law of demand, which states that demand curves slope downward.
B)is a reflection of the firm's small size relative to the total market.
C)is maintained only with the help of high barriers to entry.
D)is a reflection of the inelastic demand for its product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
A competitive firm facing a perfectly elastic demand curve can:
A)increase price without losing any sales.
B)sell all of its output at any price it chooses.
C)sell all of its output at the market price.
D)sell more output only by reducing its price.
A)increase price without losing any sales.
B)sell all of its output at any price it chooses.
C)sell all of its output at the market price.
D)sell more output only by reducing its price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
A firm sells grapefruit in a perfectly competitive market at a price of $1.50 per pound.The firm's marginal revenue:
A)equals $1.50.
B)is less than $1.50.
C)is greater than $1.50.
D)cannot be determined from the information provided.
A)equals $1.50.
B)is less than $1.50.
C)is greater than $1.50.
D)cannot be determined from the information provided.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
A perfectly competitive firm has no influence over price because:
A)its output is insignificant relative to the market as a whole.
B)antitrust laws constrain perfectly competitive firms.
C)consumers establish the prices of products.
D)it is unaware of the demand curve it faces.
A)its output is insignificant relative to the market as a whole.
B)antitrust laws constrain perfectly competitive firms.
C)consumers establish the prices of products.
D)it is unaware of the demand curve it faces.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
A perfectly competitive firm seeking to maximize its profits would want to maximize the difference between:
A)its marginal revenue and its marginal cost.
B)its total revenue and its total cost.
C)its accounting revenue and its accounting cost.
D)its price and its marginal cost.
A)its marginal revenue and its marginal cost.
B)its total revenue and its total cost.
C)its accounting revenue and its accounting cost.
D)its price and its marginal cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Which of the following is true?
A)The objective of the firm is to maximize profits, by producing the amount that maximizes the difference between its total revenues and total cost.
B)The objective of the firm is to maximize profits, by producing the amount that maximizes the difference between its average revenue and average total cost.
C)The objective of the firm is to maximize profits, by producing the amount that maximizes the difference between its average revenue and average variable cost.
D)The objective of the firm is to maximize profits, by producing the amount that maximizes the difference between its marginal revenue and marginal cost.
E)None of the above is true.
A)The objective of the firm is to maximize profits, by producing the amount that maximizes the difference between its total revenues and total cost.
B)The objective of the firm is to maximize profits, by producing the amount that maximizes the difference between its average revenue and average total cost.
C)The objective of the firm is to maximize profits, by producing the amount that maximizes the difference between its average revenue and average variable cost.
D)The objective of the firm is to maximize profits, by producing the amount that maximizes the difference between its marginal revenue and marginal cost.
E)None of the above is true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
William's Widget Works, sells in a perfectly competitive market, with an equilibrium price of $12.Its marginal revenue:
A)is greater than $12.
B)is $12.
C)is less than $12.
D)cannot be determined from the above information.
A)is greater than $12.
B)is $12.
C)is less than $12.
D)cannot be determined from the above information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Toys for Twerps, Inc., sells in a perfectly competitive market, with an equilibrium price of $5.Its marginal revenue:
A)is greater than $5.
B)is $5.
C)is less than $5.
D)is less than zero.
E)cannot be determined from the above information.
A)is greater than $5.
B)is $5.
C)is less than $5.
D)is less than zero.
E)cannot be determined from the above information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
At the level of output where marginal revenue equals marginal cost, price is less than average total cost but greater than average variable cost.In this instance, a profit-maximizing firm should:
A)cease production as it is incurring an economic loss.
B)continue operating at that output level in the short term, since total revenue will cover all of the firm's variable costs and some of its fixed costs.
C)continue operating at that output level in the short term, since total revenue will cover all of the firm's fixed costs and a portion of its variable costs.
D)decrease output to where marginal revenue exceeds marginal cost by the greatest dollar amount.
E)increase the production of output.
A)cease production as it is incurring an economic loss.
B)continue operating at that output level in the short term, since total revenue will cover all of the firm's variable costs and some of its fixed costs.
C)continue operating at that output level in the short term, since total revenue will cover all of the firm's fixed costs and a portion of its variable costs.
D)decrease output to where marginal revenue exceeds marginal cost by the greatest dollar amount.
E)increase the production of output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Which of the following is true of perfectly competitive firms?
A)For a perfectly competitive firm, as long as the price derived from expanded output exceeds the marginal cost of that output, the expansion of output creates additional economic profits.
B)Producing at the profit-maximizing output level means that a firm is actually earning economic profits.
C)A competitive firm earning zero economic profit will be unable to continue in operation over time.
D)A perfectly competitive firm will operate in the short run only at price levels greater than or equal to average total costs.
E)As new firms enter an industry where sellers are earning economic profits, the result will include an increase in the equilibrium price.
A)For a perfectly competitive firm, as long as the price derived from expanded output exceeds the marginal cost of that output, the expansion of output creates additional economic profits.
B)Producing at the profit-maximizing output level means that a firm is actually earning economic profits.
C)A competitive firm earning zero economic profit will be unable to continue in operation over time.
D)A perfectly competitive firm will operate in the short run only at price levels greater than or equal to average total costs.
E)As new firms enter an industry where sellers are earning economic profits, the result will include an increase in the equilibrium price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Assume that the equilibrium price in a perfectly competitive industry is $4.25.If a firm in this industry produced and sold 10 units with an average total cost of $5.00, what would be the result would be:
A)a profit of $0.75
B)a profit of $7.50
C)a loss of $0.75
D)a loss of $7.50
E)a loss of $75.00
A)a profit of $0.75
B)a profit of $7.50
C)a loss of $0.75
D)a loss of $7.50
E)a loss of $75.00

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
In the short run, a perfectly competitive firm can earn:
A)positive economic profits.
B)zero economic profits.
C)negative economic profits.
D)any of the above.
A)positive economic profits.
B)zero economic profits.
C)negative economic profits.
D)any of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
If a profit-maximizing firm finds that price exceeds average variable cost and marginal cost is greater than marginal revenue, it should:
A)reduce output, but continue producing in the short run.
B)increase output.
C)shut down.
D)not alter its production level since it is earning a profit.
A)reduce output, but continue producing in the short run.
B)increase output.
C)shut down.
D)not alter its production level since it is earning a profit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Assume a perfectly competitive firm sells its output for $250 per unit.At its current 2,000 units of output, marginal cost is $180 and increasing, and average variable cost is $160.Assuming it wants to maximize its profits, it should:
A)increase output.
B)decrease output, but not shut down.
C)maintain its current output rate.
D)shut down.
E)There is not enough information to determine what the firm should do.
A)increase output.
B)decrease output, but not shut down.
C)maintain its current output rate.
D)shut down.
E)There is not enough information to determine what the firm should do.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Darlene runs a fruit and vegetable stand in a medium-sized community where there are many such stands.Her weekly total revenue equals $3,500.Her weekly total cost of running the stand equals $3,500, consisting of $2,500 of variable costs and $1,000 of fixed costs.An economist would likely advise Darlene to:
A)shut down as quickly as possible because the stand is generating losses.
B)keep the stand open because it is generating a normal profit.
C)keep the stand open for a while longer because she is covering all of her variable costs and some of her fixed costs.
D)keep the stand open for a while longer because she is covering all of her fixed costs and some of her variable costs.
E)shut down as quickly as possible because the stand is generating no economic profit.
A)shut down as quickly as possible because the stand is generating losses.
B)keep the stand open because it is generating a normal profit.
C)keep the stand open for a while longer because she is covering all of her variable costs and some of her fixed costs.
D)keep the stand open for a while longer because she is covering all of her fixed costs and some of her variable costs.
E)shut down as quickly as possible because the stand is generating no economic profit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
What is the maximum amount of profit the perfectly competitive firm depicted below could earn in the short run? 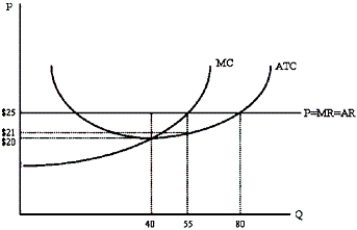
A)$40
B)$55
C)$200
D)$220
E)$320

A)$40
B)$55
C)$200
D)$220
E)$320

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
In perfect competition, at the firm's profit maximizing short run output, which of the following is true?
A)Marginal revenue equals marginal cost.
B)Price equals marginal cost.
C)Average revenue equals marginal revenue.
D)It could be earning either economic profits or losses.
E)All of the above are true.
A)Marginal revenue equals marginal cost.
B)Price equals marginal cost.
C)Average revenue equals marginal revenue.
D)It could be earning either economic profits or losses.
E)All of the above are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
If a perfectly competitive firm is operating in the short run and seeks to maximize profit, the firm should:
A)increase output whenever marginal cost is less than average total cost.
B)increase output whenever marginal revenue is less than marginal cost.
C)choose the output where per-unit profit is greatest.
D)increase output whenever price exceeds marginal cost.
A)increase output whenever marginal cost is less than average total cost.
B)increase output whenever marginal revenue is less than marginal cost.
C)choose the output where per-unit profit is greatest.
D)increase output whenever price exceeds marginal cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
A profit-maximizing firm that is operating in the short run will sell an additional unit of output as long as:
A)as doing so reduces the firm's per-unit costs.
B)doing so reduces the firm's marginal costs.
C)doing so adds more to revenue than it adds to cost.
D)there is additional plant capacity with which to produce.
A)as doing so reduces the firm's per-unit costs.
B)doing so reduces the firm's marginal costs.
C)doing so adds more to revenue than it adds to cost.
D)there is additional plant capacity with which to produce.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
If the market price was $9.50, how many units should the perfectly competitive firm depicted below produce in order to maximize profits?
A)10
B)11
C)12
D)13
E)14
A)10
B)11
C)12
D)13
E)14

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
If a profit-maximizing firm finds that price exceeds average variable cost and marginal revenue is greater than marginal cost, it should:
A)reduce output, but continue producing in the short run.
B)increase output.
C)shut down.
D)not alter its production level since it is earning a profit.
A)reduce output, but continue producing in the short run.
B)increase output.
C)shut down.
D)not alter its production level since it is earning a profit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
When price exceeds average variable cost for a firm, it is possible that:
A)it is earning an economic profit.
B)it is breaking even.
C)it is suffering an economic loss.
D)any of the above is true.
A)it is earning an economic profit.
B)it is breaking even.
C)it is suffering an economic loss.
D)any of the above is true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
What is the maximum amount of profit the perfectly competitive firm depicted below could earn in the short run? 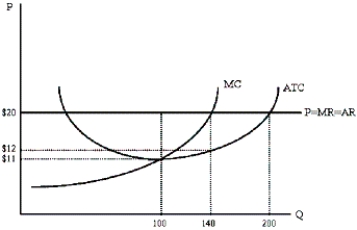
A)$900
B)$1,120
C)$1,260
D)$2,000
E)$2,800

A)$900
B)$1,120
C)$1,260
D)$2,000
E)$2,800

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
A firm receives $10 per unit at an equilibrium level of output of 80 units.The average total cost at 80 units of output is $8.The firm makes a total economic profit of:
A)$120.
B)$160.
C)$100
D)$80
A)$120.
B)$160.
C)$100
D)$80

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
A firm in a perfectly competitive industry will expand output as long as:
A)marginal revenue is less than average revenue.
B)marginal cost is less than marginal revenue.
C)marginal cost is less than average total cost.
D)marginal revenue is less than average total cost.
E)marginal revenue is less than marginal cost.
A)marginal revenue is less than average revenue.
B)marginal cost is less than marginal revenue.
C)marginal cost is less than average total cost.
D)marginal revenue is less than average total cost.
E)marginal revenue is less than marginal cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
In the short run, a perfectly competitive firm will maximize profit by producing where:
A)MC = MR.
B)MC = ATC.
C)ATC = MR.
D)AVC = MC.
A)MC = MR.
B)MC = ATC.
C)ATC = MR.
D)AVC = MC.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 200 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



