Deck 12: Fiscal Policy
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/169
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 12: Fiscal Policy
1
Fiscal policy focuses on manipulating
A)aggregate demand to smooth out business fluctuations
B)aggregate supply to smooth out business fluctuations
C)both aggregate supply and aggregate demand to smooth out business fluctuations
D)aggregate demand to stimulate the economy and aggregate supply to contract it
E)short-run aggregate supply to stimulate the economy and aggregate demand to contract it
A)aggregate demand to smooth out business fluctuations
B)aggregate supply to smooth out business fluctuations
C)both aggregate supply and aggregate demand to smooth out business fluctuations
D)aggregate demand to stimulate the economy and aggregate supply to contract it
E)short-run aggregate supply to stimulate the economy and aggregate demand to contract it
A
2
The distinction between discretionary fiscal policy and the use of automatic stabilizers is that
A)only discretionary fiscal policy can stimulate the economy
B)only automatic stabilizers can stimulate the economy
C)discretionary fiscal policy,once adopted,is built into the structure of the economy
D)automatic stabilizers,once adopted,are built into the structure of the economy
E)only discretionary fiscal policy can be used by the federal government
A)only discretionary fiscal policy can stimulate the economy
B)only automatic stabilizers can stimulate the economy
C)discretionary fiscal policy,once adopted,is built into the structure of the economy
D)automatic stabilizers,once adopted,are built into the structure of the economy
E)only discretionary fiscal policy can be used by the federal government
D
3
Most government purchases are made at the federal,not the state,level of government.
False
4
A contractionary gap exists when aggregate demand is insufficient to sustain real output at the economy's potential output level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following best illustrates the use of discretionary fiscal policy?
A)Congress provides $1 billion in relief aid for hurricane victims.
B)Congress appropriates $500 million to help the needy,and the appropriation is financed by a tax on wealth.
C)Income tax receipts are smaller because of a decline in real GDP during a recession.
D)The Federal Reserve tightens credit when it receives news of accelerating inflation.
E)Congress passes a bill authorizing $2 billion in additional spending when it receives news of a deepening recession.
A)Congress provides $1 billion in relief aid for hurricane victims.
B)Congress appropriates $500 million to help the needy,and the appropriation is financed by a tax on wealth.
C)Income tax receipts are smaller because of a decline in real GDP during a recession.
D)The Federal Reserve tightens credit when it receives news of accelerating inflation.
E)Congress passes a bill authorizing $2 billion in additional spending when it receives news of a deepening recession.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following are used in fiscal policy?
A)transfer payments only
B)taxes and government purchases
C)government purchases only
D)government purchases,transfer payments,and taxes
E)taxes and transfer payments
A)transfer payments only
B)taxes and government purchases
C)government purchases only
D)government purchases,transfer payments,and taxes
E)taxes and transfer payments

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The only way in which government can affect aggregate demand is through changes in its own purchases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Discretionary fiscal policy is policy that
A)is developed in secret
B)applies to some states but not others
C)applies to some industries but not others
D)works automatically without public announcement or plan
E)is an intentional change in taxation or government spending
A)is developed in secret
B)applies to some states but not others
C)applies to some industries but not others
D)works automatically without public announcement or plan
E)is an intentional change in taxation or government spending

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Fiscal policy
A)uses the federal government's powers of spending and taxation to affect employment,the price level,and GDP
B)uses the federal government's powers over the money supply and interest rates to affect employment,the price level,and GDP
C)can affect employment and prices,but not the level of GDP
D)can affect employment and the level of GDP,but not the price level
E)is most effective when employed by state governments rather than by the federal government
A)uses the federal government's powers of spending and taxation to affect employment,the price level,and GDP
B)uses the federal government's powers over the money supply and interest rates to affect employment,the price level,and GDP
C)can affect employment and prices,but not the level of GDP
D)can affect employment and the level of GDP,but not the price level
E)is most effective when employed by state governments rather than by the federal government

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Discretionary fiscal policy works by shifting the aggregate demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
All of the following are tools of fiscal policy except one.Which is the exception?
A)taxes
B)transfer payments
C)interest rates
D)government purchases of goods
E)government purchases of services
A)taxes
B)transfer payments
C)interest rates
D)government purchases of goods
E)government purchases of services

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
All of the following are variables that can be manipulated to affect fiscal policy except one.Which is the exception?
A)personal income taxes
B)government expenditures on goods and services
C)government expenditures on unemployment benefits
D)the interest rate
E)corporate income taxes
A)personal income taxes
B)government expenditures on goods and services
C)government expenditures on unemployment benefits
D)the interest rate
E)corporate income taxes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
An increase in government purchases must always be accompanied by an increase in autonomous net taxes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Exhibit 11-1 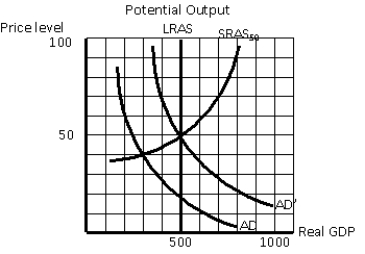
In an economy characterized by the aggregate demand curve AD and the short-run aggregate supply curve SRAS50 in Exhibit 11-1,what would be the short-run equilibrium level of real GDP and the price level?
A)$300 and 20
B)$500 and 20
C)$300 and 40
D)$500 and 50
E)$300 and 50

In an economy characterized by the aggregate demand curve AD and the short-run aggregate supply curve SRAS50 in Exhibit 11-1,what would be the short-run equilibrium level of real GDP and the price level?
A)$300 and 20
B)$500 and 20
C)$300 and 40
D)$500 and 50
E)$300 and 50

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Discretionary fiscal policy works by shifting the short-run aggregate supply curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
By how much would government purchases have to change if the government wanted to increase income by $1,000 and the MPC were 0.9?
A)$100
B)$900
C)$1,000
D)$10,000/9
E)$10,000
A)$100
B)$900
C)$1,000
D)$10,000/9
E)$10,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following is not a tool of fiscal policy?
A)money supply
B)government purchases
C)taxes
D)Social Security program
E)unemployment benefits
A)money supply
B)government purchases
C)taxes
D)Social Security program
E)unemployment benefits

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
If the short-run aggregate supply curve has a positive slope,effective fiscal policy to correct for an expansionary gap will
A)only reduce the price level
B)only reduce real GDP
C)only increase the price level
D)only increase real GDP
E)reduce both the price level and real GDP
A)only reduce the price level
B)only reduce real GDP
C)only increase the price level
D)only increase real GDP
E)reduce both the price level and real GDP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Fiscal policy is concerned with
A)government spending and taxation only
B)government spending and money only
C)money and taxation only
D)government spending,taxation,and money
E)money only
A)government spending and taxation only
B)government spending and money only
C)money and taxation only
D)government spending,taxation,and money
E)money only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following is not a goal of fiscal policy?
A)full employment
B)price stability
C)economic growth
D)job creation
E)balanced budget
A)full employment
B)price stability
C)economic growth
D)job creation
E)balanced budget

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
In an economy characterized by the aggregate demand curve AD and the short-run aggregate supply curve SRAS50 in Exhibit 11-1,the government could decrease government spending to shift the aggregate demand curve to AD' in order to eliminate the recessionary gap.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Exhibit 11-2 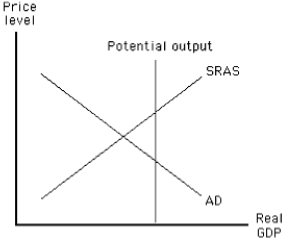
What happens in the economy illustrated in Exhibit 11-2 if government purchases increase by the amount necessary to achieve full employment?
A)The AD curve shifts to the right,the SRAS curve shifts to the left,and long-run equilibrium is achieved.
B)The AD curve shifts to the right,the price level increases,and long-run equilibrium is achieved.
C)The AD curve shifts to the right,the price level increases,and the expansionary gap worsens.
D)The AD curve shifts to the left,the price level increases,and the contractionary gap worsens.
E)The SRAS curve shifts to the left,the price level decreases,and long-run equilibrium is achieved.

What happens in the economy illustrated in Exhibit 11-2 if government purchases increase by the amount necessary to achieve full employment?
A)The AD curve shifts to the right,the SRAS curve shifts to the left,and long-run equilibrium is achieved.
B)The AD curve shifts to the right,the price level increases,and long-run equilibrium is achieved.
C)The AD curve shifts to the right,the price level increases,and the expansionary gap worsens.
D)The AD curve shifts to the left,the price level increases,and the contractionary gap worsens.
E)The SRAS curve shifts to the left,the price level decreases,and long-run equilibrium is achieved.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following might be considered the most expansionary set of fiscal policies?
A)increase in government purchases,increase in taxes,and decrease in transfer payments
B)decrease in government purchases,increase in taxes,and decrease in transfer payments
C)increase in government purchases,decrease in taxes,and increase in transfer payments
D)increase in government purchases,increase in taxes,and increase in transfer payments
E)decrease in government purchases,decrease in taxes,and decrease in transfer payments
A)increase in government purchases,increase in taxes,and decrease in transfer payments
B)decrease in government purchases,increase in taxes,and decrease in transfer payments
C)increase in government purchases,decrease in taxes,and increase in transfer payments
D)increase in government purchases,increase in taxes,and increase in transfer payments
E)decrease in government purchases,decrease in taxes,and decrease in transfer payments

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Exhibit 11-2 
If the government wants the economy illustrated in Exhibit 11-2 to be at full employment,it should
A)increase taxes
B)decrease transfer payments
C)decrease government purchases
D)wait for the SRAS curve to shift to the left
E)do none of the above

If the government wants the economy illustrated in Exhibit 11-2 to be at full employment,it should
A)increase taxes
B)decrease transfer payments
C)decrease government purchases
D)wait for the SRAS curve to shift to the left
E)do none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Exhibit 11-1 
The economy characterized by the aggregate demand curve AD and the short-run aggregate supply curve SRAS50 in Exhibit 11-1 is facing an expansionary gap.

The economy characterized by the aggregate demand curve AD and the short-run aggregate supply curve SRAS50 in Exhibit 11-1 is facing an expansionary gap.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
When net taxes increase and government purchases decrease,
A)the price level will rise
B)the money supply must rise
C)the aggregate demand curve shifts leftward
D)output and employment both rise
E)the aggregate supply curve shifts leftward
A)the price level will rise
B)the money supply must rise
C)the aggregate demand curve shifts leftward
D)output and employment both rise
E)the aggregate supply curve shifts leftward

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
If the government wants to increase equilibrium by $100 billion through a change in autonomous net taxes,it could __________ autonomous net taxes by __________.
A)increase; $100 billion
B)decrease; $100 billion
C)decrease; $100 billion MPC/(1 - MPC)
D)increase; $100 billion MPC/(1 - MPC)
E)decrease; $100 billion (1 - MPC)/MPC
A)increase; $100 billion
B)decrease; $100 billion
C)decrease; $100 billion MPC/(1 - MPC)
D)increase; $100 billion MPC/(1 - MPC)
E)decrease; $100 billion (1 - MPC)/MPC

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the following government policies would increase aggregate demand?
A)a deficit in the government budget
B)a stimulation of investment through an increase in taxes
C)a stimulation of consumption through an increase in taxes
D)a surplus in the government budget
E)a decrease in government spending
A)a deficit in the government budget
B)a stimulation of investment through an increase in taxes
C)a stimulation of consumption through an increase in taxes
D)a surplus in the government budget
E)a decrease in government spending

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
An increase in the federal budget deficit
A)only occurs when there is a deficit in the balance of trade
B)creates deflation
C)decreases aggregate demand
D)decreases aggregate quantity demanded along a stationary aggregate demand curve
E)raises the equilibrium level of output and employment
A)only occurs when there is a deficit in the balance of trade
B)creates deflation
C)decreases aggregate demand
D)decreases aggregate quantity demanded along a stationary aggregate demand curve
E)raises the equilibrium level of output and employment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
An increase in federal budget deficit
A)only occurs when there is a surplus in the balance of trade
B)may create inflation
C)decreases aggregate supply
D)decreases aggregate quantity demanded along a stationary curve
E)may reduce the equilibrium level of output and employment
A)only occurs when there is a surplus in the balance of trade
B)may create inflation
C)decreases aggregate supply
D)decreases aggregate quantity demanded along a stationary curve
E)may reduce the equilibrium level of output and employment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
If the government wants to cause equilibrium income to rise by $100 through a change in autonomous net taxes and the MPC is 0.8,it should decrease autonomous net taxes by
A)$100
B)$25
C)$20
D)$300
E)$400
A)$100
B)$25
C)$20
D)$300
E)$400

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Exhibit 11-1 
In an economy characterized by the aggregate demand curve AD and the short-run aggregate supply curve SRAS50 in Exhibit 11-1,what would be the size of the recessionary gap?
A)$500
B)$400
C)$300
D)$200
E)$100

In an economy characterized by the aggregate demand curve AD and the short-run aggregate supply curve SRAS50 in Exhibit 11-1,what would be the size of the recessionary gap?
A)$500
B)$400
C)$300
D)$200
E)$100

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
All of the following might be effective in eliminating a contractionary gap except one.Which is the exception?
A)reducing Social Security payments to beneficiaries
B)reducing personal income taxes
C)increasing expenditures for the interstate highway system
D)increasing farm subsidies
E)reducing corporate income taxes
A)reducing Social Security payments to beneficiaries
B)reducing personal income taxes
C)increasing expenditures for the interstate highway system
D)increasing farm subsidies
E)reducing corporate income taxes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
If government purchases increase and net taxes decrease,
A)the price level will fall
B)the money supply must rise
C)the aggregate demand curve shifts leftward
D)aggregate supply shifts rightward
E)output and employment will increase
A)the price level will fall
B)the money supply must rise
C)the aggregate demand curve shifts leftward
D)aggregate supply shifts rightward
E)output and employment will increase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
To close a contractionary gap using fiscal policy,the government can
A)increase taxes by the size of the gap
B)decrease taxes by the size of the gap
C)increase taxes by more than the size of the gap
D)decrease taxes by less than the size of the gap
E)decrease taxes by more than the size of the gap
A)increase taxes by the size of the gap
B)decrease taxes by the size of the gap
C)increase taxes by more than the size of the gap
D)decrease taxes by less than the size of the gap
E)decrease taxes by more than the size of the gap

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
A federal budget deficit occurs when
A)there is deflation
B)federal government purchases exceed net taxes
C)there is inflation
D)aggregate demand is greater than aggregate supply
E)aggregate supply is greater than aggregate demand
A)there is deflation
B)federal government purchases exceed net taxes
C)there is inflation
D)aggregate demand is greater than aggregate supply
E)aggregate supply is greater than aggregate demand

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
To close a contractionary gap using fiscal policy,the government can
A)increase government spending by the size of the gap
B)decrease government spending by the size of the gap
C)increase government spending by more than the size of the gap
D)increase government spending by less than the size of the gap
E)decrease government spending by more than the size of the gap
A)increase government spending by the size of the gap
B)decrease government spending by the size of the gap
C)increase government spending by more than the size of the gap
D)increase government spending by less than the size of the gap
E)decrease government spending by more than the size of the gap

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
When spending by the federal government exceeds net taxes,
A)the price level tends to fall
B)the money supply must fall
C)the aggregate demand curve shifts rightward
D)aggregate supply moves rightward
E)there is a federal budget surplus
A)the price level tends to fall
B)the money supply must fall
C)the aggregate demand curve shifts rightward
D)aggregate supply moves rightward
E)there is a federal budget surplus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Exhibit 11-2 
Which of the following sets of policies would unquestionably move the economy illustrated in Exhibit 11-2 to full employment?
A)increase in government purchases,increase in taxes,and decrease in transfer payments
B)decrease in government purchases,increase in taxes,and decrease in transfer payments
C)increase in government purchases,decrease in taxes,and increase in transfer payments
D)increase in government purchases,increase in taxes,and increase in transfer payments
E)decrease in government purchases,decrease in taxes,and decrease in transfer payments

Which of the following sets of policies would unquestionably move the economy illustrated in Exhibit 11-2 to full employment?
A)increase in government purchases,increase in taxes,and decrease in transfer payments
B)decrease in government purchases,increase in taxes,and decrease in transfer payments
C)increase in government purchases,decrease in taxes,and increase in transfer payments
D)increase in government purchases,increase in taxes,and increase in transfer payments
E)decrease in government purchases,decrease in taxes,and decrease in transfer payments

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
When spending by the federal government exceeds net taxes,
A)the price level tends to rise
B)the money supply must fall
C)the aggregate demand curve shifts leftward
D)aggregate supply moves leftward
E)there is a federal budget surplus
A)the price level tends to rise
B)the money supply must fall
C)the aggregate demand curve shifts leftward
D)aggregate supply moves leftward
E)there is a federal budget surplus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
When the government closes an expansionary gap with a change in government spending,the __________ in government spending leads to __________.
A)decrease; a decrease in both real GDP and the price level
B)decrease; a decrease in real GDP and an increase in the price level
C)decrease; an increase in both real GDP and the price level
D)decrease; an increase in real GDP and a decrease in the price level
E)increase; a decrease in both real GDP and the price level
A)decrease; a decrease in both real GDP and the price level
B)decrease; a decrease in real GDP and an increase in the price level
C)decrease; an increase in both real GDP and the price level
D)decrease; an increase in real GDP and a decrease in the price level
E)increase; a decrease in both real GDP and the price level

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
If net taxes increase and government purchases decrease,
A)the price level will rise
B)the money supply must increase
C)the aggregate demand will shift rightward
D)output and employment will fall
E)there will be a federal budget deficit
A)the price level will rise
B)the money supply must increase
C)the aggregate demand will shift rightward
D)output and employment will fall
E)there will be a federal budget deficit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The government can close an expansionary gap by increasing the price level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
To close an expansionary gap,the government can
A)increase government spending,which will increase aggregate demand
B)increase government spending,which will decrease aggregate demand
C)decrease government spending,which will increase aggregate demand
D)decrease government spending,which will decrease aggregate demand
E)increase government spending,which will increase aggregate supply
A)increase government spending,which will increase aggregate demand
B)increase government spending,which will decrease aggregate demand
C)decrease government spending,which will increase aggregate demand
D)decrease government spending,which will decrease aggregate demand
E)increase government spending,which will increase aggregate supply

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Suppose that instead of using discretionary fiscal policy to close an expansionary gap,policy makers left the economy alone.What would probably happen?
A)depression would result
B)the economy would be stuck in an expansionary gap
C)the aggregate demand curve would shift,eliminating the problem
D)the gap would close after a spurt of inflation
E)the short-run aggregate supply curve would shift to the right
A)depression would result
B)the economy would be stuck in an expansionary gap
C)the aggregate demand curve would shift,eliminating the problem
D)the gap would close after a spurt of inflation
E)the short-run aggregate supply curve would shift to the right

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
A decrease in government purchases can close an expansionary gap by shifting the aggregate demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
If net taxes exceed government purchases,
A)the price level will rise
B)the money supply must fall
C)the aggregate demand curve will shift rightward
D)the short-run aggregate supply curve will leftward
E)there will be a federal budget surplus
A)the price level will rise
B)the money supply must fall
C)the aggregate demand curve will shift rightward
D)the short-run aggregate supply curve will leftward
E)there will be a federal budget surplus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Reducing net taxes and reducing government purchases are both effective ways of eliminating an expansionary gap.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
If fiscal policy is used to close an expansionary gap,the
A)SRAS curve shifts leftward and the price level falls
B)SRAS curve shifts rightward and the price level increases
C)SRAS curve shifts rightward and the price level falls
D)AD curve shifts leftward and the price level decreases
E)AD curve shifts rightward and the price level decreases
A)SRAS curve shifts leftward and the price level falls
B)SRAS curve shifts rightward and the price level increases
C)SRAS curve shifts rightward and the price level falls
D)AD curve shifts leftward and the price level decreases
E)AD curve shifts rightward and the price level decreases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
What set of policies could the government use to close an expansionary gap?
A)decrease taxes,increase government purchases and transfer payments
B)increase taxes,government purchases,and transfer payments
C)increase taxes and transfer payments and decrease government purchases
D)increase taxes,decrease transfer payments and government purchases
E)decrease taxes,transfer payments,and government purchases
A)decrease taxes,increase government purchases and transfer payments
B)increase taxes,government purchases,and transfer payments
C)increase taxes and transfer payments and decrease government purchases
D)increase taxes,decrease transfer payments and government purchases
E)decrease taxes,transfer payments,and government purchases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
To close an expansionary gap using fiscal policy,the government can
A)increase government spending
B)increase government spending and decrease taxes at the same time
C)decrease taxes
D)decrease government spending or increase taxes
E)decrease government spending by the size of the gap
A)increase government spending
B)increase government spending and decrease taxes at the same time
C)decrease taxes
D)decrease government spending or increase taxes
E)decrease government spending by the size of the gap

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Expansionary and contractionary gaps are automatically eliminated by shifts in aggregate demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
One disadvantage of discretionary fiscal policy is that it can return the economy to its potential level of output but at the cost of increasing the price level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Suppose the government reduces its budget deficit at the same time that energy prices rise sharply.Which of the following will happen?
A)The price level will rise,since higher energy prices increase the cost of production.
B)real GDP will fall,since both events will tend to cause an economic contraction.
C)The price level will fall,because the aggregate demand curve has shifted leftward.
D)real GDP will rise; with less government spending,there are more opportunities for the private sector.
E)Both the price level and real GDP will fall.
A)The price level will rise,since higher energy prices increase the cost of production.
B)real GDP will fall,since both events will tend to cause an economic contraction.
C)The price level will fall,because the aggregate demand curve has shifted leftward.
D)real GDP will rise; with less government spending,there are more opportunities for the private sector.
E)Both the price level and real GDP will fall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
A change in government spending can close an expansionary gap by shifting the short-run aggregate supply curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which of the following might be considered the most contractionary set of fiscal policies?
A)increase in government purchases,increase in taxes,and decrease in transfer payments
B)decrease in government purchases,increase in taxes,and decrease in transfer payments
C)increase in government purchases,decrease in taxes,and increase in transfer payments
D)increase in government purchases,increase in taxes,and increase in transfer payments
E)decrease in government purchases,decrease in taxes,and decrease in transfer payments
A)increase in government purchases,increase in taxes,and decrease in transfer payments
B)decrease in government purchases,increase in taxes,and decrease in transfer payments
C)increase in government purchases,decrease in taxes,and increase in transfer payments
D)increase in government purchases,increase in taxes,and increase in transfer payments
E)decrease in government purchases,decrease in taxes,and decrease in transfer payments

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which of the following is an appropriate fiscal policy to address the inflation that occurs when the economy is above potential GDP?
A)Decrease taxes to protect consumers from the effects of inflation.
B)Increase taxes to reduce aggregate demand.
C)Increase government spending to provide some of the goods consumers can no longer afford at the higher prices.
D)Decrease government spending so that the demand for money will fall.
E)Increase transfer payments to poor people,who are hurt the most by the inflation.
A)Decrease taxes to protect consumers from the effects of inflation.
B)Increase taxes to reduce aggregate demand.
C)Increase government spending to provide some of the goods consumers can no longer afford at the higher prices.
D)Decrease government spending so that the demand for money will fall.
E)Increase transfer payments to poor people,who are hurt the most by the inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Either an increase in autonomous net taxes or a decrease in government purchases can close an expansionary gap.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
A $100 billion increase in government purchases has a greater effect on real GDP than a $100 billion reduction in net taxes because
A)some of the income consumers gain from the tax reduction will be saved rather than spent
B)some of the income consumers gain from the tax reduction will be spent on services rather than products
C)some of the income consumers gain from the tax reduction will be spent on goods made in foreign countries
D)the consumers' MPC is higher than the government's
E)the consumers' MPC is 1
A)some of the income consumers gain from the tax reduction will be saved rather than spent
B)some of the income consumers gain from the tax reduction will be spent on services rather than products
C)some of the income consumers gain from the tax reduction will be spent on goods made in foreign countries
D)the consumers' MPC is higher than the government's
E)the consumers' MPC is 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
A federal budget surplus occurs when
A)there is deflation
B)federal government net taxes exceed purchases
C)there is inflation
D)aggregate demand is greater than aggregate supply
E)aggregate supply is greater than aggregate demand
A)there is deflation
B)federal government net taxes exceed purchases
C)there is inflation
D)aggregate demand is greater than aggregate supply
E)aggregate supply is greater than aggregate demand

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The classical economists believed that the economy automatically move toward equilibrium at full employment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Who argued that the economy should be left to itself to close a contractionary gap?
A)John F.Kennedy
B)John Maynard Keynes
C)the mercantilists
D)the classical economists
E)the socialists
A)John F.Kennedy
B)John Maynard Keynes
C)the mercantilists
D)the classical economists
E)the socialists

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The steeper the short-run aggregate supply curve,
A)the smaller the impact of a shift in aggregate demand on equilibrium output
B)the larger the value of the spending multiplier
C)the larger the impact of a shift in aggregate demand on equilibrium output
D)the smaller the change in government spending needed to achieve the desired change in equilibrium output
E)the flatter the aggregate demand curve
A)the smaller the impact of a shift in aggregate demand on equilibrium output
B)the larger the value of the spending multiplier
C)the larger the impact of a shift in aggregate demand on equilibrium output
D)the smaller the change in government spending needed to achieve the desired change in equilibrium output
E)the flatter the aggregate demand curve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
If the economy is already producing at its potential,
A)the spending multiplier equals 1/(1 - MPC)in the long run
B)the spending multiplier is less than 1/(1 - MPC)in the long run
C)the spending multiplier is more than 1/(1 - MPC)in the long run
D)the spending multiplier equals zero in the long run
E)the aggregate demand curve is horizontal
A)the spending multiplier equals 1/(1 - MPC)in the long run
B)the spending multiplier is less than 1/(1 - MPC)in the long run
C)the spending multiplier is more than 1/(1 - MPC)in the long run
D)the spending multiplier equals zero in the long run
E)the aggregate demand curve is horizontal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
If the economy is already at its potential output,then the spending multiplier is
A)zero in the long run
B)infinite in the long run
C)1 in the long run
D)zero in the short run
E)1 in the short run
A)zero in the long run
B)infinite in the long run
C)1 in the long run
D)zero in the short run
E)1 in the short run

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Suppose that the economy is experiencing an expansionary gap of $1,000 and the MPC equals 0.8.With an upward-sloping short-run aggregate supply curve,the government can close the gap if it decreases purchases by
A)$1,000
B)$800
C)$200
D)more than $200
E)less than $200
A)$1,000
B)$800
C)$200
D)more than $200
E)less than $200

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Suppose that the economy has an expansionary gap of $1,000 and the MPC equals 0.8.With an upward-sloping short-run aggregate supply curve,the government can close the gap if it increases autonomous net taxes by
A)$1,000
B)$800
C)$250
D)more than $250
E)less than $250
A)$1,000
B)$800
C)$250
D)more than $250
E)less than $250

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Keynes believed that the economy does not automatically move toward an equilibrium at full employment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Which of the following is not true about classical economists?
A)They criticized mercantilism as an economic system.
B)They advocated laissez-faire policies to promote economic growth.
C)They believed the economy would naturally tend toward full employment.
D)They believed prices and wages react slowly to market changes.
E)They discouraged government intervention in markets.
A)They criticized mercantilism as an economic system.
B)They advocated laissez-faire policies to promote economic growth.
C)They believed the economy would naturally tend toward full employment.
D)They believed prices and wages react slowly to market changes.
E)They discouraged government intervention in markets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
According to Keynesian theory,the natural forces in the economy may not quickly move the economy toward potential real GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Classical economists believed that if investment were greater than saving,the interest rate would __________,causing saving to __________ and investment to __________ until the two were equal.
A)rise; decrease; increase
B)fall; decrease; increase
C)fall; increase; decrease
D)rise; increase; decrease
E)fall; increase; increase
A)rise; decrease; increase
B)fall; decrease; increase
C)fall; increase; decrease
D)rise; increase; decrease
E)fall; increase; increase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Which of the following best describes the concept of laissez-faire?
A)Government should not intervene in the economy.
B)Government should actively intervene in the economy whenever it judges the action to be beneficial.
C)Government should intervene in the economy only to promote short-term economic stability.
D)Government should intervene in the economy only to maximize long-term growth rates.
E)Government should intervene in the economy only when the economy is not at full employment or there is substantial inflation.
A)Government should not intervene in the economy.
B)Government should actively intervene in the economy whenever it judges the action to be beneficial.
C)Government should intervene in the economy only to promote short-term economic stability.
D)Government should intervene in the economy only to maximize long-term growth rates.
E)Government should intervene in the economy only when the economy is not at full employment or there is substantial inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Under which of the following conditions will a change in government purchases have the greatest effect on the economy in the short run?
A)The aggregate demand curve is relatively flat.
B)The aggregate demand curve is relatively steep.
C)The short-run aggregate supply curve is relatively flat.
D)The aggregate demand curve is vertical.
E)The short-run aggregate supply curve is vertical.
A)The aggregate demand curve is relatively flat.
B)The aggregate demand curve is relatively steep.
C)The short-run aggregate supply curve is relatively flat.
D)The aggregate demand curve is vertical.
E)The short-run aggregate supply curve is vertical.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
According to classical economists,government intervention is
A)necessary to maintain a stable price level in the long run
B)necessary to maintain a stable price level in the short run
C)necessary to maintain full employment in the long run
D)necessary to maintain full employment in the short run
E)not necessary to maintain full employment
A)necessary to maintain a stable price level in the long run
B)necessary to maintain a stable price level in the short run
C)necessary to maintain full employment in the long run
D)necessary to maintain full employment in the short run
E)not necessary to maintain full employment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The steeper the short-run aggregate supply curve,
A)the steeper the aggregate demand curve
B)the larger the value of the spending multiplier
C)the smaller the value of the spending multiplier
D)the larger the impact of a shift in aggregate demand on the equilibrium price level
E)the larger the impact of a shift in aggregate demand on the equilibrium output level
A)the steeper the aggregate demand curve
B)the larger the value of the spending multiplier
C)the smaller the value of the spending multiplier
D)the larger the impact of a shift in aggregate demand on the equilibrium price level
E)the larger the impact of a shift in aggregate demand on the equilibrium output level

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
The flatter the short-run aggregate supply curve,
A)the flatter the aggregate demand curve
B)the larger the value of the spending multiplier
C)the smaller the value of the spending multiplier
D)the larger the impact of a shift in aggregate demand on the equilibrium price level
E)the larger the impact of a shift in aggregate demand on the equilibrium output level
A)the flatter the aggregate demand curve
B)the larger the value of the spending multiplier
C)the smaller the value of the spending multiplier
D)the larger the impact of a shift in aggregate demand on the equilibrium price level
E)the larger the impact of a shift in aggregate demand on the equilibrium output level

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The opposite of a laissez-faire economic policy is
A)active government intervention
B)a reliance on prices to adjust to changing market conditions
C)classical economics
D)neoclassical economics
E)quantity supplied creates its own quantity demanded
A)active government intervention
B)a reliance on prices to adjust to changing market conditions
C)classical economics
D)neoclassical economics
E)quantity supplied creates its own quantity demanded

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
John Maynard Keynes influenced the use of fiscal policy in the U.S.by arguing effectively that
A)balancing the national budget at all times was sound economic policy
B)natural economic forces were not necessarily adequate to move the economy toward its potential output level
C)the government did not need to stimulate output in order for the economy to achieve its potential output level
D)increases in taxes and increases in government purchases are equally effective in closing an expansionary gap
E)increases in taxes and increases in government purchases are equally effective in closing a contractionary gap
A)balancing the national budget at all times was sound economic policy
B)natural economic forces were not necessarily adequate to move the economy toward its potential output level
C)the government did not need to stimulate output in order for the economy to achieve its potential output level
D)increases in taxes and increases in government purchases are equally effective in closing an expansionary gap
E)increases in taxes and increases in government purchases are equally effective in closing a contractionary gap

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Classical economists believed that if saving were greater than investment,the interest rate would __________,causing saving to __________ and investment to __________ until the two were equal.
A)rise; decrease; increase
B)fall; decrease; increase
C)fall; increase; decrease
D)rise; increase; decrease
E)fall; increase; increase
A)rise; decrease; increase
B)fall; decrease; increase
C)fall; increase; decrease
D)rise; increase; decrease
E)fall; increase; increase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Which of the following is not true about classical economists?
A)They criticized mercantilism as an economic system.
B)They advocated laissez-faire policies to promote economic growth.
C)They believed the economy would naturally tend toward full employment.
D)They believed prices and wages were flexible.
E)They sought government intervention in markets to promote fairness.
A)They criticized mercantilism as an economic system.
B)They advocated laissez-faire policies to promote economic growth.
C)They believed the economy would naturally tend toward full employment.
D)They believed prices and wages were flexible.
E)They sought government intervention in markets to promote fairness.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



