Deck 13: Stabilization Policy and the Asad Framework
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/109
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 13: Stabilization Policy and the Asad Framework
1
Using the simple monetary rule, if the inflation rate is 2 percent below the target inflation rate and the marginal product of capital is 1 percent, the Federal Reserve will:
A) lower the target rate by 2 percent
B) raise the interest rate by 1 percent
C) lower the interest rate by 1 percent
D) lower the discount rate by 1 percent
E) Not enough information is given.
A) lower the target rate by 2 percent
B) raise the interest rate by 1 percent
C) lower the interest rate by 1 percent
D) lower the discount rate by 1 percent
E) Not enough information is given.
E
2
The simple monetary policy rule discussed in the chapter "dictates" the:
A) optimal rate of inflation
B) choice of federal funds rate
C) marginal product of capital
D) natural rate of unemployment
E) None of these answers are correct.
A) optimal rate of inflation
B) choice of federal funds rate
C) marginal product of capital
D) natural rate of unemployment
E) None of these answers are correct.
B
3
If is close to zero, monetary policy is relatively:
A) aggressive and the AD curve is relatively flat
B) permissive and the AD curve is relatively steep
C) aggressive and the AD curve is relatively steep
D) permissive and the AD curve is relatively flat
E) permissive and the AD curve is vertical
A) aggressive and the AD curve is relatively flat
B) permissive and the AD curve is relatively steep
C) aggressive and the AD curve is relatively steep
D) permissive and the AD curve is relatively flat
E) permissive and the AD curve is vertical
permissive and the AD curve is relatively steep
4
The simple monetary policy rule may contain which of the following?
A) short-term output
B) the inflation rate
C) the unemployment rate
D) All of these answers are correct.
E) None of these answers are correct.
A) short-term output
B) the inflation rate
C) the unemployment rate
D) All of these answers are correct.
E) None of these answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
If is close to zero, the AD curve is:
A) vertical
B) relatively flat
C) horizontal
D) relatively steep
E) Not enough information is given.
A) vertical
B) relatively flat
C) horizontal
D) relatively steep
E) Not enough information is given.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
If equals zero, the AD curve is:
A) horizontal
B) relatively steep
C) relatively flat
D) vertical
E) Not enough information is given.
A) horizontal
B) relatively steep
C) relatively flat
D) vertical
E) Not enough information is given.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The simple monetary policy rule discussed at length in the text is:
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Refer to the following figure when answering
Figure 13.1: AD Curve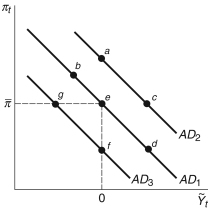
-Consider Figure 13.1, beginning at point e. If there is a change in the inflation rate:
A) there is movement along the AD curve to point b
B) the AD curve shifts right to point a
C) the AD curve shifts left to point g
D) there is movement along the AD curve to point d
E) Not enough information is given.
Figure 13.1: AD Curve

-Consider Figure 13.1, beginning at point e. If there is a change in the inflation rate:
A) there is movement along the AD curve to point b
B) the AD curve shifts right to point a
C) the AD curve shifts left to point g
D) there is movement along the AD curve to point d
E) Not enough information is given.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
If in the simple monetary rule and the inflation rate is 2 percent below the target inflation rate, the Federal Reserve will:
A) lower the target rate by 2 percent
B) raise the interest rate by 1 percent
C) lower the interest rate by 1 percent
D) lower the marginal product of capital by 1 percent
E) Not enough information is given.
A) lower the target rate by 2 percent
B) raise the interest rate by 1 percent
C) lower the interest rate by 1 percent
D) lower the marginal product of capital by 1 percent
E) Not enough information is given.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following best describes movement along the AD curve?
A) A change in the inflation rate causes the central bank to change interest rates, thereby causing a corresponding proportional change in investment.
B) A sudden increase in the tax rate.
C) A change in monetary policy.
D) A change in the inflation rate causes the federal government to reduce discretionary spending.
E) A change in unemployment causes the federal government to reduce discretionary spending.
A) A change in the inflation rate causes the central bank to change interest rates, thereby causing a corresponding proportional change in investment.
B) A sudden increase in the tax rate.
C) A change in monetary policy.
D) A change in the inflation rate causes the federal government to reduce discretionary spending.
E) A change in unemployment causes the federal government to reduce discretionary spending.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
In the simple monetary policy rule ,
Measures:
A) the marginal product of capital
B) the deviation of the inflation rate from the target rate
C) how sensitive monetary policy is to changes in inflation
D) the target rate of inflation
E) the debt to GDP ratio
Measures:
A) the marginal product of capital
B) the deviation of the inflation rate from the target rate
C) how sensitive monetary policy is to changes in inflation
D) the target rate of inflation
E) the debt to GDP ratio

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The simple monetary policy rule implies that:
A) if the Federal Reserve should lower the interest rate
B) if the Federal Reserve should lower the interest rate
C) if the Federal Reserve should raise the interest rate
D) if the interest rate is zero
E) All of these answers are correct.
A) if the Federal Reserve should lower the interest rate
B) if the Federal Reserve should lower the interest rate
C) if the Federal Reserve should raise the interest rate
D) if the interest rate is zero
E) All of these answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Combining the IS and monetary policy rule curves gives us:
A) Okun's law
B) the Phillips curve
C) the aggregate demand curve
D) the MP curve
E) current output
A) Okun's law
B) the Phillips curve
C) the aggregate demand curve
D) the MP curve
E) current output

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Consider the monetary rule . If the inflation rate is 4 percent, the marginal product of capital is 2 percent, and the target rate of inflation is 3 percent, then the real interest rate should be:
A) 3.50 percent
B) 3.25 percent
C) 2.25 percent
D) 1.75 percent
E) 2.50 percent
A) 3.50 percent
B) 3.25 percent
C) 2.25 percent
D) 1.75 percent
E) 2.50 percent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
If is relatively high, monetary policy is relatively:
A) permissive and the AD curve is relatively flat
B) aggressive and the AD curve is relatively steep
C) aggressive and the AD curve is relatively flat
D) permissive and the AD curve is relatively steep
E) permissive and the AD curve is vertical
A) permissive and the AD curve is relatively flat
B) aggressive and the AD curve is relatively steep
C) aggressive and the AD curve is relatively flat
D) permissive and the AD curve is relatively steep
E) permissive and the AD curve is vertical

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
When we raise the federal funds rate by 2 percent for every 1 percent increase in the inflation rate, this is an example of:
A) a fiscal policy rule
B) a monetary policy rule
C) discretionary monetary policy
D) discretionary fiscal policy
E) None of these answers are correct.
A) a fiscal policy rule
B) a monetary policy rule
C) discretionary monetary policy
D) discretionary fiscal policy
E) None of these answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
A policy rule that dictates what interest rates monetary policy should follow is:
A) written down
B) at the discretion of the president
C) at the discretion of the chairman of the Federal Reserve
D) independent of the state of the economy
E) a function of the state of the economy
A) written down
B) at the discretion of the president
C) at the discretion of the chairman of the Federal Reserve
D) independent of the state of the economy
E) a function of the state of the economy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The aggregate demand curve is given by:
A)
B)
C)
D) .
E)
A)
B)
C)
D) .
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The simple monetary policy rule may contain which of the following?
A) price shocks
B) long-term output
C) the unemployment rate
D) stock indices
E) All of these answers are correct.
A) price shocks
B) long-term output
C) the unemployment rate
D) stock indices
E) All of these answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
In the simple monetary policy rule ,
Represents:
A) the marginal product of capital
B) how sensitive monetary policy is to changes in inflation
C) the deviation of the inflation rate from the target rate
D) the target rate of inflation
E) the risk premium
Represents:
A) the marginal product of capital
B) how sensitive monetary policy is to changes in inflation
C) the deviation of the inflation rate from the target rate
D) the target rate of inflation
E) the risk premium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Refer to the following figure when answering
Figure 13.1: AD Curve
-Consider Figure 13.1. Holding inflation constant, if the interest rate increases, the economy would move from point e to point:
A) b
B) c
C) d
D) a
E) None of these answers are correct.
Figure 13.1: AD Curve

-Consider Figure 13.1. Holding inflation constant, if the interest rate increases, the economy would move from point e to point:
A) b
B) c
C) d
D) a
E) None of these answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
A change in which of the following parameters shifts the AD curve ?
A)
B)
C)
D)
E) None of these answers are correct.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E) None of these answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Refer to the following figure when answering
Figure 13.1: AD Curve
-Consider Figure 13.1. If Europe goes into a recession and inflation remains constant, the economy would move from point e to point:
A) g
B) a
C) c
D) b
E) c.
Figure 13.1: AD Curve

-Consider Figure 13.1. If Europe goes into a recession and inflation remains constant, the economy would move from point e to point:
A) g
B) a
C) c
D) b
E) c.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Refer to the following figure when answering
Figure 13.3: Aggregate Supply Curve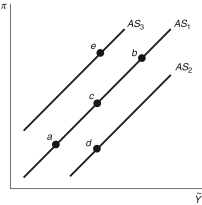
-Consider Figure 13.3. If there is a positive inflation shock, ceteris paribus, the economy would move from point ________ to point ________.
A) c; d
B) c; b
C) c; e
D) b; e
E) Not enough information is given.
Figure 13.3: Aggregate Supply Curve

-Consider Figure 13.3. If there is a positive inflation shock, ceteris paribus, the economy would move from point ________ to point ________.
A) c; d
B) c; b
C) c; e
D) b; e
E) Not enough information is given.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Refer to the following figure when answering
Figure 13.1: AD Curve
-Consider Figure 13.1. Holding inflation constant, if there is a negative aggregate demand shock, the economy would move from point e to point:
A) g
B) c
C) d
D) b
E) a
Figure 13.1: AD Curve

-Consider Figure 13.1. Holding inflation constant, if there is a negative aggregate demand shock, the economy would move from point e to point:
A) g
B) c
C) d
D) b
E) a

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The aggregate supply curve is derived from:
A) Okun's law
B) the Phillips curve
C) the Fisher equation
D) the monetary policy rule
E) the interaction of the IS and MP curves
A) Okun's law
B) the Phillips curve
C) the Fisher equation
D) the monetary policy rule
E) the interaction of the IS and MP curves

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A change in which of the following parameters would cause a movement along the AD curve ?
A)
B)
C)
D)
E) None of these answers are correct.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E) None of these answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Refer to the following figure when answering
Figure 13.2: AD Curve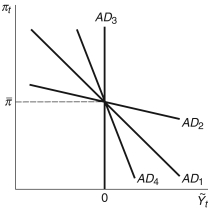
-Consider Figure 13.2. The aggregate demand curve ________ displays a relatively aggressive monetary policy, while the curve ________ displays a monetary policy completely unresponsive to changes in inflation.
A)
B)
C)
D) All of these answers are correct.
E) None of these answers are correct.
Figure 13.2: AD Curve

-Consider Figure 13.2. The aggregate demand curve ________ displays a relatively aggressive monetary policy, while the curve ________ displays a monetary policy completely unresponsive to changes in inflation.
A)
B)
C)
D) All of these answers are correct.
E) None of these answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Refer to the following figure when answering
Figure 13.2: AD Curve
-Consider Figure 13.2. Each of the aggregate demand curves pictured represents a different economy. In which economy is the central bank most concerned with inflation?
A) Economy 4
B) Economy 1
C) Economy 3
D) Economy 2
E) Not enough information is given.
Figure 13.2: AD Curve

-Consider Figure 13.2. Each of the aggregate demand curves pictured represents a different economy. In which economy is the central bank most concerned with inflation?
A) Economy 4
B) Economy 1
C) Economy 3
D) Economy 2
E) Not enough information is given.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
On the aggregate supply curve, when short-run output deviations are equal to zero, the y-intercept is equal to:
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
On the aggregate supply curve, an increase in inflation causes ________, while a price shock causes ________.
A) upward movement along the curve; the curve to shift
B) downward movement along the curve; the curve to shift
C) the curve to shift; movement along the curve
D) downward movement along the curve; upward movement along the curve
E) Not enough information is given.
A) upward movement along the curve; the curve to shift
B) downward movement along the curve; the curve to shift
C) the curve to shift; movement along the curve
D) downward movement along the curve; upward movement along the curve
E) Not enough information is given.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following shifts the aggregate supply curve?
A) a change in
B) an increase in the price of oil
C) the current inflation rate
D) raising the federal funds rate
E) All of these answers are correct.
A) a change in
B) an increase in the price of oil
C) the current inflation rate
D) raising the federal funds rate
E) All of these answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Refer to the following figure when answering
Figure 13.1: AD Curve
-Consider Figure 13.1. Holding inflation constant, if the interest rate increases, the economy would move from point e to point:
A) b
B) c
C) d
D) a
E) g
Figure 13.1: AD Curve

-Consider Figure 13.1. Holding inflation constant, if the interest rate increases, the economy would move from point e to point:
A) b
B) c
C) d
D) a
E) g

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A change in which of the following parameters does NOT shift the AD curve ?
A)
B)
C)
D)
E) None of these answers are correct.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E) None of these answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of the following shifts the aggregate supply curve?
A) an increase in the price of oil
B) a change in the previous period's inflation rate
C) higher taxes on firms
D) All of these answers are correct.
E) None of these answers are correct.
A) an increase in the price of oil
B) a change in the previous period's inflation rate
C) higher taxes on firms
D) All of these answers are correct.
E) None of these answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Refer to the following figure when answering
Figure 13.2: AD Curve
-Consider Figure 13.2. Each of the aggregate demand curves pictured represents a different economy. Which of the four economies' central banks would be most concerned with unemployment rather than inflation?
A) Economy 2
B) Economy 4
C) Economy 3
D) Economy 1
E) Not enough information is given.
Figure 13.2: AD Curve

-Consider Figure 13.2. Each of the aggregate demand curves pictured represents a different economy. Which of the four economies' central banks would be most concerned with unemployment rather than inflation?
A) Economy 2
B) Economy 4
C) Economy 3
D) Economy 1
E) Not enough information is given.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Refer to the following figure when answering
Figure 13.2: AD Curve
-Consider Figure 13.2. Each of the aggregate demand curves pictured represents a different economy. In which economy would fighting inflation have the biggest impact on real output?
A) Economy 3
B) Economy 1
C) Economy 2
D) Economy 4
E) Not enough information is given.
Figure 13.2: AD Curve

-Consider Figure 13.2. Each of the aggregate demand curves pictured represents a different economy. In which economy would fighting inflation have the biggest impact on real output?
A) Economy 3
B) Economy 1
C) Economy 2
D) Economy 4
E) Not enough information is given.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Refer to the following figure when answering
Figure 13.1: AD Curve
-Consider Figure 13.1. Holding the inflation rate constant, beginning at point e, if there is an aggregate demand shock, the AD curve shifts:
A) right to point c
B) right to point a
C) left to point g
D) to point d
E) Not enough information is given.
Figure 13.1: AD Curve

-Consider Figure 13.1. Holding the inflation rate constant, beginning at point e, if there is an aggregate demand shock, the AD curve shifts:
A) right to point c
B) right to point a
C) left to point g
D) to point d
E) Not enough information is given.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of the following is the aggregate supply curve?
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Refer to the following figure when answering
Figure 13.1: AD Curve
-Consider Figure 13.1. If there is a positive aggregate demand shock and inflation remains constant, the economy would move from point e to point:
A) d
B) a
C) c
D) b
E) None of these answers are correct.
Figure 13.1: AD Curve

-Consider Figure 13.1. If there is a positive aggregate demand shock and inflation remains constant, the economy would move from point e to point:
A) d
B) a
C) c
D) b
E) None of these answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The adjustment process back to the steady state in the short-run model hinges on the:
A) rate of unemployment
B) immediate reaction to a change in the inflation rate
C) consumers' response to inflation shocks
D) government's response to inflation shocks
E) slow adjustment of inflation reflected in the aggregate supply curve
A) rate of unemployment
B) immediate reaction to a change in the inflation rate
C) consumers' response to inflation shocks
D) government's response to inflation shocks
E) slow adjustment of inflation reflected in the aggregate supply curve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Refer to the following figure when answering
Figure 13.3: Aggregate Supply Curve
-Consider Figure 13.3. Over the past few years the "Arab Spring" has caused radical political and economic changes, particularly Syria, Egypt, and Libya. These events can be characterized in the aggregate supply curve as a movement from point ________ to point ________.
A) d; a
B) c; a
C) a; d
D) e; b
E) c; b
Figure 13.3: Aggregate Supply Curve

-Consider Figure 13.3. Over the past few years the "Arab Spring" has caused radical political and economic changes, particularly Syria, Egypt, and Libya. These events can be characterized in the aggregate supply curve as a movement from point ________ to point ________.
A) d; a
B) c; a
C) a; d
D) e; b
E) c; b

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which of the following best describes why the aggregate demand curve slopes downward?
A) If the central bank observes a high rate of inflation, the monetary policy rule dictates an increase in the real interest rate. The high interest rate reduces output by reducing investment demand in the economy.
B) If the central bank observes a low rate of inflation, the monetary policy rule dictates an increase in the real interest rate. The high interest rate reduces output by reducing investment demand in the economy.
C) If the central bank observes a high rate of inflation, the monetary policy rule dictates a decrease in the real interest rate. The low interest rate increases output by reducing investment demand in the economy.
D) If the central bank observes a low rate of inflation, the monetary policy rule dictates a decrease in the real interest rate. The low interest rate reduces output by reducing investment demand in the economy.
E) None of these answers are correct.
A) If the central bank observes a high rate of inflation, the monetary policy rule dictates an increase in the real interest rate. The high interest rate reduces output by reducing investment demand in the economy.
B) If the central bank observes a low rate of inflation, the monetary policy rule dictates an increase in the real interest rate. The high interest rate reduces output by reducing investment demand in the economy.
C) If the central bank observes a high rate of inflation, the monetary policy rule dictates a decrease in the real interest rate. The low interest rate increases output by reducing investment demand in the economy.
D) If the central bank observes a low rate of inflation, the monetary policy rule dictates a decrease in the real interest rate. The low interest rate reduces output by reducing investment demand in the economy.
E) None of these answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
If the current rate of inflation is 1 percent, using the values suggested by Professor Taylor, , the Taylor rule predicts a federal funds rate of:
A) 0 percent
B) 1.5 percent
C) 1 percent
D) 0.5 percent
E) 3.5 percent
A) 0 percent
B) 1.5 percent
C) 1 percent
D) 0.5 percent
E) 3.5 percent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Which of the following best describes why the aggregate supply curve slopes upward?
A) When actual output exceeds potential, firms struggle to keep production in line with the high demand. Firms therefore raise their prices by more than the usual amount in an attempt to cover increased production costs.
B) When actual output exceeds potential, firms have an easy time keeping production in line with the high demand. Firms therefore lower their prices by more than the usual amount in an attempt to cover increased production costs.
C) When actual output exceeds potential, firms struggle to keep production in line with the high demand. Firms therefore lower their prices with decreased production costs.
D) When actual output falls below potential, firms easily keep production in line with the high demand. Firms therefore raise their prices by more than the usual amount in an attempt to cover increased production costs.
E) None of these answers are correct.
A) When actual output exceeds potential, firms struggle to keep production in line with the high demand. Firms therefore raise their prices by more than the usual amount in an attempt to cover increased production costs.
B) When actual output exceeds potential, firms have an easy time keeping production in line with the high demand. Firms therefore lower their prices by more than the usual amount in an attempt to cover increased production costs.
C) When actual output exceeds potential, firms struggle to keep production in line with the high demand. Firms therefore lower their prices with decreased production costs.
D) When actual output falls below potential, firms easily keep production in line with the high demand. Firms therefore raise their prices by more than the usual amount in an attempt to cover increased production costs.
E) None of these answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Refer to the following figure when answering
Figure 13.4: AS/AD Model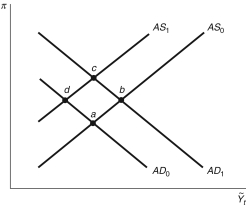
-Use the aggregate supply/aggregate demand model in Figure 13.4 to answer the following scenario. Nigerian rebels taking over privately owned oil wells would cause the economy to initially move from point________ to point ________.
A) c; b
B) b; c
C) c; a
D) b; a
E) Not enough information is given.
Figure 13.4: AS/AD Model

-Use the aggregate supply/aggregate demand model in Figure 13.4 to answer the following scenario. Nigerian rebels taking over privately owned oil wells would cause the economy to initially move from point________ to point ________.
A) c; b
B) b; c
C) c; a
D) b; a
E) Not enough information is given.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
In the short-run model, the steady state is characterized by:
A)
B)
C)
D) All of these answers are correct.
E) None of these answers are correct.
A)
B)
C)
D) All of these answers are correct.
E) None of these answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Professor John Taylor suggested using which set of values for the Taylor rule?
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Refer to the following figure when answering
Figure 13.4: AS/AD Model
-Use the aggregate supply/aggregate demand model in Figure 13.4 to answer the following scenario. Unrest in the Middle Eastern country of Syria would cause the economy to initially move from point ________ to point ________; eventually the economy would return to the steady state at point ________.
A) c; a; b
B) c; d; a
C) a; d; a
D) b; a; c
E) Not enough information is given.
Figure 13.4: AS/AD Model

-Use the aggregate supply/aggregate demand model in Figure 13.4 to answer the following scenario. Unrest in the Middle Eastern country of Syria would cause the economy to initially move from point ________ to point ________; eventually the economy would return to the steady state at point ________.
A) c; a; b
B) c; d; a
C) a; d; a
D) b; a; c
E) Not enough information is given.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which of the following equations, discussed in the text, can be used to predict the federal funds rate?
A)
B)
C)
D)
E) None of these answers are correct.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E) None of these answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
If the current rate of inflation is 4 percent, using the values suggested by Professor Taylor, the Taylor rule predicts a federal funds rate of:
A) 1 percent
B) 4.5 percent
C) 3 percent
D) 4 percent
E) 0.5 percent
A) 1 percent
B) 4.5 percent
C) 3 percent
D) 4 percent
E) 0.5 percent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Refer to the following figure when answering
Figure 13.4: AS/AD Model
-Use the aggregate supply/aggregate demand model in Figure 13.4 to answer the following scenario. The terrorist attacks on 9/11 caused the economy to initially move from point ________ to point ________.
A) c; a
B) c; b
C) b; a
D) a; b
E) Not enough information is given.
Figure 13.4: AS/AD Model

-Use the aggregate supply/aggregate demand model in Figure 13.4 to answer the following scenario. The terrorist attacks on 9/11 caused the economy to initially move from point ________ to point ________.
A) c; a
B) c; b
C) b; a
D) a; b
E) Not enough information is given.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Refer to the following figure when answering
Figure 13.4: AS/AD Model
-Use the aggregate supply/aggregate demand model in Figure 13.4 to answer the following scenario. The United Auto Workers were able to negotiate a contract for higher wages and better benefits. The economy initially moves from point ________ to point ________; eventually the economy returns to the steady state at point ________.
A) c; d; a
B) a; d; a
C) c; a; b
D) b; a; c
E) Not enough information is given.
Figure 13.4: AS/AD Model

-Use the aggregate supply/aggregate demand model in Figure 13.4 to answer the following scenario. The United Auto Workers were able to negotiate a contract for higher wages and better benefits. The economy initially moves from point ________ to point ________; eventually the economy returns to the steady state at point ________.
A) c; d; a
B) a; d; a
C) c; a; b
D) b; a; c
E) Not enough information is given.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Refer to the following figure when answering
Figure 13.4: AS/AD Model
-Use the aggregate supply/aggregate demand model in Figure 13.4 to answer the following scenario. The terrorist attacks on 9/11 caused the economy initially to move from point ________ to point ________; eventually the economy returned to the steady state at point ________.
A) c; a; b
B) c; b; a
C) c; d; c
D) a; b; c
E) Not enough information is given.
Figure 13.4: AS/AD Model

-Use the aggregate supply/aggregate demand model in Figure 13.4 to answer the following scenario. The terrorist attacks on 9/11 caused the economy initially to move from point ________ to point ________; eventually the economy returned to the steady state at point ________.
A) c; a; b
B) c; b; a
C) c; d; c
D) a; b; c
E) Not enough information is given.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which of the following equations, discussed in the text, can be used to predict the federal funds rate?
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The equation used to predict the federal funds rate is called the:
A) Phillips curve
B) monetary policy rule
C) Taylor rule
D) marginal product of capital
E) Slutsky equation
A) Phillips curve
B) monetary policy rule
C) Taylor rule
D) marginal product of capital
E) Slutsky equation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
If the simple Taylor rule models the "ideal" federal funds rate, the ________ displayed a monetary policy that was too loose.
A) 1960s
B) 1970s
C) 1980s
D) 1990s
E) 2000s
A) 1960s
B) 1970s
C) 1980s
D) 1990s
E) 2000s

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Refer to the following figure when answering
Figure 13.4: AS/AD Model
-Use the aggregate supply/aggregate demand model in Figure 13.4 to answer the following scenario. In the 1990s, Japan experienced a prolonged sluggish economy. If the Bank of Japan targeted inflation, it would have responded to this situation by ________, pushing the economy from point ________ to point ________; eventually the economy would have returned to the steady state at point ________.
A) raising the inflation target rate; a; b; c
B) lowering the inflation target rate; a; b; c
C) raising the inflation target rate; a; d; c
D) lowering the inflation target rate; c; d; a
E) Not enough information is given.
Figure 13.4: AS/AD Model

-Use the aggregate supply/aggregate demand model in Figure 13.4 to answer the following scenario. In the 1990s, Japan experienced a prolonged sluggish economy. If the Bank of Japan targeted inflation, it would have responded to this situation by ________, pushing the economy from point ________ to point ________; eventually the economy would have returned to the steady state at point ________.
A) raising the inflation target rate; a; b; c
B) lowering the inflation target rate; a; b; c
C) raising the inflation target rate; a; d; c
D) lowering the inflation target rate; c; d; a
E) Not enough information is given.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Refer to the following figure when answering
Figure 13.3: Aggregate Supply Curve
-Consider Figure 13.3. If rebels in Nigeria, a major oil producing country, temporarily hijack privately owned and operated oil wells, this would be characterized in the aggregate supply curve as a movement from point ________ to point ________.
A) c; b
B) c; e
C) c; d
D) b; e
E) Not enough information is given.
Figure 13.3: Aggregate Supply Curve

-Consider Figure 13.3. If rebels in Nigeria, a major oil producing country, temporarily hijack privately owned and operated oil wells, this would be characterized in the aggregate supply curve as a movement from point ________ to point ________.
A) c; b
B) c; e
C) c; d
D) b; e
E) Not enough information is given.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
In the short-run model, the steady state is characterized by:
A)
B)
C)
D) All of these answers are correct.
E) None of these answers are correct.
A)
B)
C)
D) All of these answers are correct.
E) None of these answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Economic forecasters use which of the following leading economic indicators:
I) term structure of interest rates
Ii) new claims for unemployment insurance
Iii) price of tea in China
A) i only
B) ii only
C) ii and iii
D) i and ii
E) i and iii
I) term structure of interest rates
Ii) new claims for unemployment insurance
Iii) price of tea in China
A) i only
B) ii only
C) ii and iii
D) i and ii
E) i and iii

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Assuming the simple Taylor rule for dictating the federal funds rate, when the actual federal funds rate deviates from the suggested rate, it can be explained by:
A) bad monetary policy
B) discretionary fiscal policy
C) a richer version of the Taylor Rule
D) poorly informed monetary policy
E) poorly informed fiscal policy
A) bad monetary policy
B) discretionary fiscal policy
C) a richer version of the Taylor Rule
D) poorly informed monetary policy
E) poorly informed fiscal policy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
A policy rule dictates that monetary policy is at the discretion of the president.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Most Fed watchers are convinced that the Fed is committed to:
A) high inflation
B) low and volatile inflation
C) low and stable inflation
D) a high unemployment rate
E) high and stable inflation
A) high inflation
B) low and volatile inflation
C) low and stable inflation
D) a high unemployment rate
E) high and stable inflation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Policy is conducted by discretion if policymakers:
A) size up the economy and choose whatever policy seems appropriate at the time
B) announce in advance how policy will respond to various situations and commit themselves to following through on this announcement
C) maintain a constant growth rate of the money supply without making their decision public
D) announce and achieve a balanced government budget
E) announce and maintain a constant interest rate
A) size up the economy and choose whatever policy seems appropriate at the time
B) announce in advance how policy will respond to various situations and commit themselves to following through on this announcement
C) maintain a constant growth rate of the money supply without making their decision public
D) announce and achieve a balanced government budget
E) announce and maintain a constant interest rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The advantage of an explicit inflation target is that it:
A) helps anchor inflation expectations
B) allows banks to set interest rates
C) stabilizes employment
D) raises the marginal product of capital
E) completely eradicates discretionary monetary policy
A) helps anchor inflation expectations
B) allows banks to set interest rates
C) stabilizes employment
D) raises the marginal product of capital
E) completely eradicates discretionary monetary policy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Refer to the following figure when answering
Figure 13.5: AS/AD Model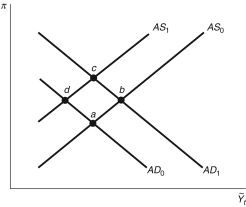
-Consider Figure 13.5. If the Fed sets a higher inflation target, under rational expectations, the economy moves from point ________ to point ________.
A) a; c slowly
B) a; c instantly
C) a; d instantly
D) b; d slowly
E) b; c instantly
Figure 13.5: AS/AD Model

-Consider Figure 13.5. If the Fed sets a higher inflation target, under rational expectations, the economy moves from point ________ to point ________.
A) a; c slowly
B) a; c instantly
C) a; d instantly
D) b; d slowly
E) b; c instantly

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
When the central bank pursues expansionary monetary policy and all other economic agents build this into their decision making, ________ with no economic benefit; this is called the ________ problem.
A) output rises; policy lag
B) unemployment rises; time inconsistency
C) expectations rise; adaptive expectations
D) inflation rises; time inconsistency
E) inflation rises; discretionary
A) output rises; policy lag
B) unemployment rises; time inconsistency
C) expectations rise; adaptive expectations
D) inflation rises; time inconsistency
E) inflation rises; discretionary

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Under rational expectations, people use:
A) all the information at their disposal to make their best forecasts of the coming rate of inflation
B) all past rates of inflation to make their best forecasts of the coming rate of inflation
C) announcements by the Fed to make their best forecasts of the coming rate of inflation
D) only the Fed's inflation target to make their best forecasts of the coming rate of inflation
E) the unemployment rate to make their best forecasts of the coming rate of inflation
A) all the information at their disposal to make their best forecasts of the coming rate of inflation
B) all past rates of inflation to make their best forecasts of the coming rate of inflation
C) announcements by the Fed to make their best forecasts of the coming rate of inflation
D) only the Fed's inflation target to make their best forecasts of the coming rate of inflation
E) the unemployment rate to make their best forecasts of the coming rate of inflation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The reputations of ________, ________, and ________ have convinced observers that the Fed is committed to low and stable inflation.
A) John Taylor; Milton Friedman; Karl Marx
B) George H. W. Bush; Bill Clinton; George W. Bush
C) Ronald Reagan; Alan Greenspan; Ben Bernanke
D) Paul Volcker; Alan Greenspan; Ben Bernanke
E) David Ricardo; John Stuart Mill; Alfred Marshall
A) John Taylor; Milton Friedman; Karl Marx
B) George H. W. Bush; Bill Clinton; George W. Bush
C) Ronald Reagan; Alan Greenspan; Ben Bernanke
D) Paul Volcker; Alan Greenspan; Ben Bernanke
E) David Ricardo; John Stuart Mill; Alfred Marshall

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The simple monetary rule states that if the current rate of inflation is below the inflation target, interest rates should fall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
During the ________, the actual federal funds rate was substantially lower than the rate suggested by the simple Taylor rule.
A) early 1960s
B) late 1990s
C) early to mid-1980s
D) early 1990s
E) None of these answers are correct.
A) early 1960s
B) late 1990s
C) early to mid-1980s
D) early 1990s
E) None of these answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Refer to the following figure when answering
Figure 13.5: AS/AD Model
-Consider Figure 13.5. If the Fed sets a lower inflation target, under rational expectations, the economy moves from point ________ to point ________.
A) c; a instantly
B) a; c slowly
C) c; d instantly
D) c; b slowly
E) b; a instantly
Figure 13.5: AS/AD Model

-Consider Figure 13.5. If the Fed sets a lower inflation target, under rational expectations, the economy moves from point ________ to point ________.
A) c; a instantly
B) a; c slowly
C) c; d instantly
D) c; b slowly
E) b; a instantly

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Since the 1990s, the country with the lowest rate of inflation has been:
A) Russia
B) the United States
C) the United Kingdom
D) Japan
E) Italy
A) Russia
B) the United States
C) the United Kingdom
D) Japan
E) Italy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The fact that any model that utilizes adaptive expectations necessarily will be misspecified is called:
A) Okun's law
B) time inconsistency
C) the Lucas critique
D) the Slutsky paradox
E) monetarism
A) Okun's law
B) time inconsistency
C) the Lucas critique
D) the Slutsky paradox
E) monetarism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
In the presence of rational expectations, the central banks' willingness to battle inflation:
A) causes future inflation
B) becomes a determinant of past inflation
C) undermines the ability to fight inflation
D) becomes a determinant of expected inflation
E) weakens the central government
A) causes future inflation
B) becomes a determinant of past inflation
C) undermines the ability to fight inflation
D) becomes a determinant of expected inflation
E) weakens the central government

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Which of the following countries does not adopt an explicit inflation target?
A) Mexico
B) the United Kingdom
C) the United States
D) Brazil
E) None of these answers are correct.
A) Mexico
B) the United Kingdom
C) the United States
D) Brazil
E) None of these answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
The ultimate goal of macroeconomic policy is:
A) zero inflation
B) full employment; output at potential; and low, stable inflation
C) full employment; output above potential; and low, stable inflation
D) zero unemployment and inflation
E) low interest rates
A) zero inflation
B) full employment; output at potential; and low, stable inflation
C) full employment; output above potential; and low, stable inflation
D) zero unemployment and inflation
E) low interest rates

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
The central bank often deviates from simple policy rules because:
A) the rules are always wrong
B) they have new and more detailed information
C) they are ordered to by the president
D) they have no discretion
E) the federal government is more interested in unemployment
A) the rules are always wrong
B) they have new and more detailed information
C) they are ordered to by the president
D) they have no discretion
E) the federal government is more interested in unemployment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Policymakers will find it easier to achieve their goals by sticking to policy rules rather than discretion if they face the problem of:
A) very short policy lags
B) adaptive expectations
C) time inconsistency
D) discretionary fiscal policy
E) a weak central bank
A) very short policy lags
B) adaptive expectations
C) time inconsistency
D) discretionary fiscal policy
E) a weak central bank

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



