Deck 12: Monetary Policy and the Phillips Curve
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/132
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 12: Monetary Policy and the Phillips Curve
1
According to the Fisher equation, the nominal interest rate is equal to the:
A) rate of inflation
B) real interest rate minus the rate of inflation
C) real interest rate plus the rate of inflation
D) rate of unemployment
E) real interest rate plus short-run economic fluctuations
A) rate of inflation
B) real interest rate minus the rate of inflation
C) real interest rate plus the rate of inflation
D) rate of unemployment
E) real interest rate plus short-run economic fluctuations
C
2
According to the Fisher equation, the real interest rate is given by:
A) zero
B) the nominal interest rate plus the rate of inflation
C) the nominal interest rate minus the rate of unemployment
D) the rate of economic growth
E) the nominal interest rate minus the rate of inflation
A) zero
B) the nominal interest rate plus the rate of inflation
C) the nominal interest rate minus the rate of unemployment
D) the rate of economic growth
E) the nominal interest rate minus the rate of inflation
E
3
Which of the following is the mission of the Federal Reserve Bank?
I) Preserve price stability
Ii) Foster economic growth and employment
Iii) Promote a stable financial system
A) i only
B) ii only
C) iii only
D) i, ii, and iii
E) i and ii
I) Preserve price stability
Ii) Foster economic growth and employment
Iii) Promote a stable financial system
A) i only
B) ii only
C) iii only
D) i, ii, and iii
E) i and ii
D
4
What is the main policy tool available to the Federal Reserve?
A) the reserve rate
B) the discount rate
C) the federal funds rate
D) printing money
E) the mortgage rate
A) the reserve rate
B) the discount rate
C) the federal funds rate
D) printing money
E) the mortgage rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Refer to the following figure when answering
Figure 12.2: IS-MP Curve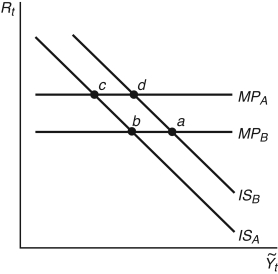
-Consider Figure 12.2. If the Fed raises interest rates and there are no aggregate demand shocks, the economy moves from:
A) point b to d
B) point b to a
C) point b to c
D) point c to d
E) Not enough information is given.
Figure 12.2: IS-MP Curve

-Consider Figure 12.2. If the Fed raises interest rates and there are no aggregate demand shocks, the economy moves from:
A) point b to d
B) point b to a
C) point b to c
D) point c to d
E) Not enough information is given.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
An implication of sticky inflation is that, through monetary policy changes, the Federal Reserve:
A) has no impact on inflation
B) can alter the real interest rate in the long run
C) can alter the real interest rate in the short run
D) has no impact on the real interest rate
E) has no impact on the unemployment rate
A) has no impact on inflation
B) can alter the real interest rate in the long run
C) can alter the real interest rate in the short run
D) has no impact on the real interest rate
E) has no impact on the unemployment rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A key assumption of the short-run model is:
A) zero inflation
B) perfect price flexibility
C) that unemployment always equals its natural rate
D) that the economy never deviates from its long-run equilibrium
E) sticky inflation
A) zero inflation
B) perfect price flexibility
C) that unemployment always equals its natural rate
D) that the economy never deviates from its long-run equilibrium
E) sticky inflation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following is the mission of the Federal Reserve Bank?
I) Preserve price stability
Ii) Foster stable fiscal policy
Iii) Ensure taxes are fair
A) ii only
B) i only
C) iii only
D) i and ii
E) i and iii
I) Preserve price stability
Ii) Foster stable fiscal policy
Iii) Ensure taxes are fair
A) ii only
B) i only
C) iii only
D) i and ii
E) i and iii

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Figure 12.1: MP Curve 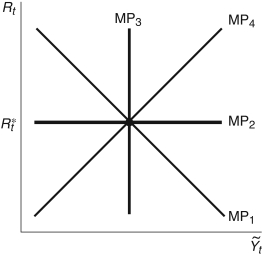
-In Figure 12.1, if the Federal Reserve sets the real interest rate at , which line represents the MP curve?
A)
B)
C)
D)
E) Not enough information is given.

-In Figure 12.1, if the Federal Reserve sets the real interest rate at , which line represents the MP curve?
A)
B)
C)
D)
E) Not enough information is given.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The MP curve stands for ________ and describes ________.
A) monopoly pricing; how firms set prices
B) monetary policy; how the Federal Reserve sets the inflation rate
C) monetary policy; how the federal government sets short-run output fluctuations
D) money prices; how the Federal Reserve sets the inflation rate
E) monetary policy; how the Federal Reserve sets the nominal interest rate
A) monopoly pricing; how firms set prices
B) monetary policy; how the Federal Reserve sets the inflation rate
C) monetary policy; how the federal government sets short-run output fluctuations
D) money prices; how the Federal Reserve sets the inflation rate
E) monetary policy; how the Federal Reserve sets the nominal interest rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The link between real and nominal interest rates is summarized in:
A) the MP curve
B) the Phillips curve
C) Okun's law
D) the Fisher equation
E) Jones's equality
A) the MP curve
B) the Phillips curve
C) Okun's law
D) the Fisher equation
E) Jones's equality

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following is the Fisher equation?
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Refer to the following figure when answering
Figure 12.2: IS-MP Curve
-Consider Figure 12.2. If the Fed lowers interest rates and there are no aggregate demand shocks, the economy moves from:
A) point e to b
B) point d to c
C) point d to a
D) point e to d
E) Not enough information is given.
Figure 12.2: IS-MP Curve

-Consider Figure 12.2. If the Fed lowers interest rates and there are no aggregate demand shocks, the economy moves from:
A) point e to b
B) point d to c
C) point d to a
D) point e to d
E) Not enough information is given.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
When economists say "sticky inflation," they mean:
A) inflation does not immediately react to changes in monetary policy
B) inflation adjusts quickly
C) inflation does not react directly to changes in fiscal policy
D) taxes do not react to changes in prices
E) inflation never responds to monetary policy
A) inflation does not immediately react to changes in monetary policy
B) inflation adjusts quickly
C) inflation does not react directly to changes in fiscal policy
D) taxes do not react to changes in prices
E) inflation never responds to monetary policy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The equation is called the ________ and
Is the ________.
A) risk premium; discount rate
B) ex ante real interest rate; ex post real interest rate
C) bond yield; real interest rate
D) ex ante nominal interest rate; nominal interest rate
E) nominal interest rate; real interest rate
Is the ________.
A) risk premium; discount rate
B) ex ante real interest rate; ex post real interest rate
C) bond yield; real interest rate
D) ex ante nominal interest rate; nominal interest rate
E) nominal interest rate; real interest rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
What is the main policy tool available to the Federal Reserve?
A) the discount rate
B) the federal funds rate
C) government expenditures
D) printing money
E) taxes
A) the discount rate
B) the federal funds rate
C) government expenditures
D) printing money
E) taxes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The structure of the short-run model is best described as which of the following?
A) Nominal interest rate Real interest rate Short-run output Change in inflation
B) Nominal interest rate Real interest rate Change in inflation
C) Nominal interest rate Short-run output Change in inflation
D) Real interest rate Short-run output Change in inflation Nominal interest rate
E) Short-run output Change in inflation Real interest rate Nominal interest rate
A) Nominal interest rate Real interest rate Short-run output Change in inflation
B) Nominal interest rate Real interest rate Change in inflation
C) Nominal interest rate Short-run output Change in inflation
D) Real interest rate Short-run output Change in inflation Nominal interest rate
E) Short-run output Change in inflation Real interest rate Nominal interest rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The federal funds rate is:
A) equal to the rate of inflation
B) the interest rate at which banks borrow from the Federal Reserve
C) the interest rate at which banks borrow from and loan to each other overnight
D) an interest rate that is some fixed amount above the prime lending rate
E) the return to stock markets over the long term
A) equal to the rate of inflation
B) the interest rate at which banks borrow from the Federal Reserve
C) the interest rate at which banks borrow from and loan to each other overnight
D) an interest rate that is some fixed amount above the prime lending rate
E) the return to stock markets over the long term

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
If we replace the actual rate of inflation with the expected inflation rate in the Fisher equation we get the:
A) risk premium
B) rational expectations level of inflation
C) discount rate
D) ex ante real interest rate
E) ex post nominal interest rate
A) risk premium
B) rational expectations level of inflation
C) discount rate
D) ex ante real interest rate
E) ex post nominal interest rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following is the mission of the Federal Reserve Bank?
i. Preserve price stability
ii. Foster economic growth and employment
iii. Ensure taxes are fair
A) i only
B) ii only
C) iii only
D) i and ii
E) i and iii
i. Preserve price stability
ii. Foster economic growth and employment
iii. Ensure taxes are fair
A) i only
B) ii only
C) iii only
D) i and ii
E) i and iii

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Refer to the following figure when answering
Figure 12.3: Yield Curves December 4, 2006 and 2012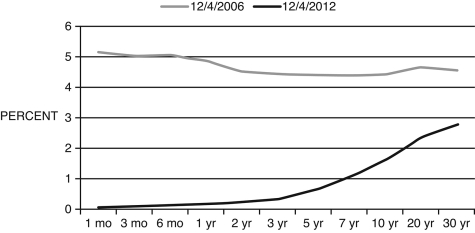 (Source: U.S. Treasury)
(Source: U.S. Treasury)
-Consider the yield curves in Figure 12.3. The curve for 12/4/2012 is unusual because:
A) it has no relationship to the real economy
B) its short-term interest rates are lower than long-term interest rates
C) It is not unusual.
D) it is lower than the yield curve for 2006
E) it is generally very low
Figure 12.3: Yield Curves December 4, 2006 and 2012
 (Source: U.S. Treasury)
(Source: U.S. Treasury)-Consider the yield curves in Figure 12.3. The curve for 12/4/2012 is unusual because:
A) it has no relationship to the real economy
B) its short-term interest rates are lower than long-term interest rates
C) It is not unusual.
D) it is lower than the yield curve for 2006
E) it is generally very low

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The Phillips curve assumes that inflation expectations are:
A) rational
B) adaptive
C) always wrong
D) equal to zero
E) None of these answers are correct.
A) rational
B) adaptive
C) always wrong
D) equal to zero
E) None of these answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Economists who study monetary policy believe that it takes anywhere from ________ for monetary policy to have a substantial effect on economic activity.
A) 3 to 6 weeks
B) 6 to 18 days
C) 6 to 18 months
D) 3 to 6 months
E) 6 to 18 weeks
A) 3 to 6 weeks
B) 6 to 18 days
C) 6 to 18 months
D) 3 to 6 months
E) 6 to 18 weeks

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Refer to the following figure when answering
Figure 12.2: IS-MP Curve
-Consider the economy presented in Figure 12.2. If housing prices drop sharply, there is a loss in consumer and investor confidence and the economy moves from ________. To prevent a ________, the Fed ________, and the economy moves from ________.
A) point a to d; recession; lowers interest rates; point d to b
B) point a to d; recession; lowers interest rates; point d to c
C) point c to b; bubble; raises interest rates; point b to c
D) point d to c; recession; lowers interest rates; point c to b
E) Not enough information is given.
Figure 12.2: IS-MP Curve

-Consider the economy presented in Figure 12.2. If housing prices drop sharply, there is a loss in consumer and investor confidence and the economy moves from ________. To prevent a ________, the Fed ________, and the economy moves from ________.
A) point a to d; recession; lowers interest rates; point d to b
B) point a to d; recession; lowers interest rates; point d to c
C) point c to b; bubble; raises interest rates; point b to c
D) point d to c; recession; lowers interest rates; point c to b
E) Not enough information is given.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Normally yields on short-term Treasury bonds are ________ long-term Treasury bond yields.
A) equal to the fed funds rate minus
B) equal to inflation plus
C) the same as
D) higher than
E) lower than
A) equal to the fed funds rate minus
B) equal to inflation plus
C) the same as
D) higher than
E) lower than

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Adaptive expectations imply that firms:
A) adapt their prices to what the Fed does
B) constantly update their inflation expectations
C) slowly adjust their inflation expectations
D) base prices on the rate of unemployment
E) always know what the rate of inflation is
A) adapt their prices to what the Fed does
B) constantly update their inflation expectations
C) slowly adjust their inflation expectations
D) base prices on the rate of unemployment
E) always know what the rate of inflation is

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
According to the Phillips curve, if current output is above potential output:
A) inflation falls
B) inflation rises
C) unemployment falls
D) inflation is constant
E) tax rates rise
A) inflation falls
B) inflation rises
C) unemployment falls
D) inflation is constant
E) tax rates rise

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
If prices are sticky and there are no aggregate demand shocks, and if the Fed raises the interest rate, ________ and ________.
A) unemployment falls; potential output falls
B) the real interest rate falls; short-run output falls
C) the unemployment rate rises; short-run output rises
D) the real interest rate rises; short-run output falls
E) the real interest rate falls; current output falls
A) unemployment falls; potential output falls
B) the real interest rate falls; short-run output falls
C) the unemployment rate rises; short-run output rises
D) the real interest rate rises; short-run output falls
E) the real interest rate falls; current output falls

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Expected inflation is:
A) equal to zero
B) equal to the real interest rate
C) equal to future periods' inflation rates
D) the rate of inflation that firms believe will prevail in macroeconomy
E) about 2 percent
A) equal to zero
B) equal to the real interest rate
C) equal to future periods' inflation rates
D) the rate of inflation that firms believe will prevail in macroeconomy
E) about 2 percent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Refer to the following figure when answering
Figure 12.2: IS-MP Curve
-Consider the economy presented in Figure 12.2. If there is a sharp increase in consumer confidence, the economy moves from ________. To prevent a ________, the Fed ________, and the economy moves from ________.
A) point a to d; recession; lowers interest rates; point d to b
B) point a to d; recession; lowers interest rates; point d to c
C) point c to b; bubble; raises interest rates; point b to c
D) point d to c; recession; lowers interest rates; point c to b
E) point b to a; bubble; raises interest rates; point a to d
Figure 12.2: IS-MP Curve

-Consider the economy presented in Figure 12.2. If there is a sharp increase in consumer confidence, the economy moves from ________. To prevent a ________, the Fed ________, and the economy moves from ________.
A) point a to d; recession; lowers interest rates; point d to b
B) point a to d; recession; lowers interest rates; point d to c
C) point c to b; bubble; raises interest rates; point b to c
D) point d to c; recession; lowers interest rates; point c to b
E) point b to a; bubble; raises interest rates; point a to d

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
In the text inflation is given by the equation ________, where is the current price level and
is the future price level.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
is the future price level.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The economywide rate of inflation is given by:
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Refer to the following figure when answering
Figure 12.2: IS-MP Curve
-Consider the economy presented in Figure 12.2. If the stock market drops sharply, there is a loss in consumer and investor confidence and the economy moves from ________. To prevent a ________, the Fed ________, and the economy moves from ________.
A) point a to d; recession; lowers interest rates; point d to b
B) point d to c; recession; lowers interest rates; point c to b
C) point c to b; bubble; raises interest rates; point b to c
D) point a to d; recession; lowers interest rates; point d to c
E) Not enough information is given.
Figure 12.2: IS-MP Curve

-Consider the economy presented in Figure 12.2. If the stock market drops sharply, there is a loss in consumer and investor confidence and the economy moves from ________. To prevent a ________, the Fed ________, and the economy moves from ________.
A) point a to d; recession; lowers interest rates; point d to b
B) point d to c; recession; lowers interest rates; point c to b
C) point c to b; bubble; raises interest rates; point b to c
D) point a to d; recession; lowers interest rates; point d to c
E) Not enough information is given.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
According to the Phillips curve, if current output equals potential output:
A) unemployment is zero
B) inflation fluctuates a lot
C) inflation is steady
D) unemployment is negative
E) the economy is booming
A) unemployment is zero
B) inflation fluctuates a lot
C) inflation is steady
D) unemployment is negative
E) the economy is booming

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Refer to the following figure when answering
Figure 12.3: Yield Curves December 4, 2006 and 2012 (Source: U.S. Treasury)
(Source: U.S. Treasury)
-Consider the yield curves in Figure 12.3. The curve for 12/4/2006 is unusual because:
A) it has no relationship to the real economy
B) its short-term interest rates are higher than long-term interest rates
C) it is inverted
D) it is higher than the yield curve for 2012
E) It is not unusual.
Figure 12.3: Yield Curves December 4, 2006 and 2012
 (Source: U.S. Treasury)
(Source: U.S. Treasury)-Consider the yield curves in Figure 12.3. The curve for 12/4/2006 is unusual because:
A) it has no relationship to the real economy
B) its short-term interest rates are higher than long-term interest rates
C) it is inverted
D) it is higher than the yield curve for 2012
E) It is not unusual.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Firms alter their prices based on:
A) expected inflation
B) expected inflation and supply conditions
C) expected inflation and demand conditions
D) demand conditions
E) the previous period's aggregate supply
A) expected inflation
B) expected inflation and supply conditions
C) expected inflation and demand conditions
D) demand conditions
E) the previous period's aggregate supply

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
In a weakening economy, you might expect producers to:
A) lower wages to increase quantity demand for their output
B) lower prices to increase quantity demand for their output
C) increase prices to increase quantity demand for their output
D) lower prices to reduce quantity demand for their output
E) raise wages to hire more productive workers
A) lower wages to increase quantity demand for their output
B) lower prices to increase quantity demand for their output
C) increase prices to increase quantity demand for their output
D) lower prices to reduce quantity demand for their output
E) raise wages to hire more productive workers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The term structure of interest rates shows the relationship between:
A) corporate bonds and the federal funds rate
B) high and low quality corporate bonds
C) U.S. Treasury bills with different maturities
D) U.S. Treasury rates and municipal bond yields
E) mortgage rates and LIBOR
A) corporate bonds and the federal funds rate
B) high and low quality corporate bonds
C) U.S. Treasury bills with different maturities
D) U.S. Treasury rates and municipal bond yields
E) mortgage rates and LIBOR

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Refer to the following figure when answering
Figure 12.2: IS-MP Curve
-Consider Figure 12.2. If the Fed lowers interest rates and there are no aggregate demand shocks, the economy moves from:
A) point d to a
B) point c to a
C) point a to b
D) point d to c
E) None of these answers are correct.
Figure 12.2: IS-MP Curve

-Consider Figure 12.2. If the Fed lowers interest rates and there are no aggregate demand shocks, the economy moves from:
A) point d to a
B) point c to a
C) point a to b
D) point d to c
E) None of these answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Refer to the following figure when answering
Figure 12.4: Phillips Curve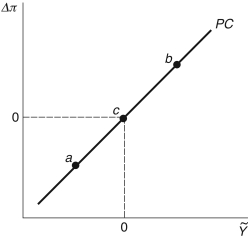
-Consider the Phillips curve in Figure 12.4. At point a, the economy is ________; at point c, the economy is ________.
A) in recession; booming
B) in recession; in recession
C) in recession; in its long-run equilibrium
D) booming; in recession
E) in its long-run equilibrium; in recession
Figure 12.4: Phillips Curve

-Consider the Phillips curve in Figure 12.4. At point a, the economy is ________; at point c, the economy is ________.
A) in recession; booming
B) in recession; in recession
C) in recession; in its long-run equilibrium
D) booming; in recession
E) in its long-run equilibrium; in recession

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
According to reasoning by Milton Friedman and Edmund Phelps:
A) economic stimulus programs were destined to fail in the long run
B) economic stimulus programs were destined to fail in the short and long runs
C) unemployment does not react to fluctuations in output
D) there is a theoretical maximum level of potential output that can be produced
E) firms do not react to real interest rate changes
A) economic stimulus programs were destined to fail in the long run
B) economic stimulus programs were destined to fail in the short and long runs
C) unemployment does not react to fluctuations in output
D) there is a theoretical maximum level of potential output that can be produced
E) firms do not react to real interest rate changes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Figure 12.6: IS-MP Curve 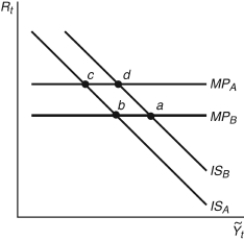
Start from any equilibrium in Figure 12.6 to answer the following question. In 1980, U.S. inflation hit about 14 percent; Federal Reserve chairman ________ engineered a decline in inflation by ________, shown in the figure as movement from ________.
A) Volcker; raising inflation rates; point b to c
B) Bernanke; raising interest rates; point b to d
C) Volcker; lowering interest rates; point c to b
D) Volcker; raising interest rates; point b to c
E) Greenspan; lowering interest rates; point a to b

Start from any equilibrium in Figure 12.6 to answer the following question. In 1980, U.S. inflation hit about 14 percent; Federal Reserve chairman ________ engineered a decline in inflation by ________, shown in the figure as movement from ________.
A) Volcker; raising inflation rates; point b to c
B) Bernanke; raising interest rates; point b to d
C) Volcker; lowering interest rates; point c to b
D) Volcker; raising interest rates; point b to c
E) Greenspan; lowering interest rates; point a to b

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Refer to the following figure when answering
Figure 12.5: Phillips Curve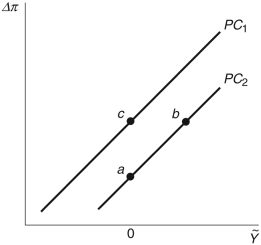
-Starting from any point in the Phillips curve in Figure 12.5, an unexpected decrease in oil prices will move the economy from:
A) point c to b
B) point c to a
C) point a to b
D) point b to c
E) Not enough information is given.
Figure 12.5: Phillips Curve

-Starting from any point in the Phillips curve in Figure 12.5, an unexpected decrease in oil prices will move the economy from:
A) point c to b
B) point c to a
C) point a to b
D) point b to c
E) Not enough information is given.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Refer to the following figure when answering
Figure 12.4: Phillips Curve
-Consider the Phillips curve in Figure 12.4. At point b, the economy is ________, and at point a, the economy is ________.
A) in recession; booming
B) in recession; in its long-run equilibrium
C) in recession; in recession
D) booming; in recession
E) in its long-run equilibrium; in recession
Figure 12.4: Phillips Curve

-Consider the Phillips curve in Figure 12.4. At point b, the economy is ________, and at point a, the economy is ________.
A) in recession; booming
B) in recession; in its long-run equilibrium
C) in recession; in recession
D) booming; in recession
E) in its long-run equilibrium; in recession

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Refer to the following figure when answering
Figure 12.5: Phillips Curve
-Starting from any point in the Phillips curve in Figure 12.5, an unexpected increase in oil prices will move the economy from:
A) point a to b
B) point c to b
C) point a to c
D) point b to c
E) Not enough information is given.
Figure 12.5: Phillips Curve

-Starting from any point in the Phillips curve in Figure 12.5, an unexpected increase in oil prices will move the economy from:
A) point a to b
B) point c to b
C) point a to c
D) point b to c
E) Not enough information is given.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
With adaptive expectations, the Phillips curve can be written as:
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
According to the Phillips curve, if the:
A) inflation rate is falling, the economy is booming
B) inflation rate is rising, the economy is in recession
C) inflation rate is rising, the economy is booming
D) unemployment rate is falling, the economy is booming
E) None of these answers are correct.
A) inflation rate is falling, the economy is booming
B) inflation rate is rising, the economy is in recession
C) inflation rate is rising, the economy is booming
D) unemployment rate is falling, the economy is booming
E) None of these answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Recent energy legislation that dictates increased use of ethanol as automobile fuel might ________ overall inflation because corn prices ________, affecting all downstream industries that use corn ________.
A) decrease; will rise; as a final good
B) increase; will rise; as an input
C) not change; will stay constant; as a final good
D) increase; will rise; as a final good
E) Not enough information is given.
A) decrease; will rise; as a final good
B) increase; will rise; as an input
C) not change; will stay constant; as a final good
D) increase; will rise; as a final good
E) Not enough information is given.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
In the Phillips curve 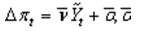 is a:
is a:
A) temporary demand shock
B) permanent price change
C) temporary cost shock
D) temporary unemployment shock
E) structural macroeconomic change
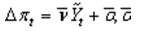 is a:
is a:A) temporary demand shock
B) permanent price change
C) temporary cost shock
D) temporary unemployment shock
E) structural macroeconomic change

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
In the Phillips curve, the term ________ reflects ________.
A) ; cost-push inflation
B) ; cost-push inflation
C) ; the "true" rate of inflation
D) ; demand-pull inflation
E) ; the responsiveness of inflation to cost shocks
A) ; cost-push inflation
B) ; cost-push inflation
C) ; the "true" rate of inflation
D) ; demand-pull inflation
E) ; the responsiveness of inflation to cost shocks

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
An increase in the interest rate by the Federal Reserve will affect only real interest rates because:
A) inflation is sticky in the short run
B) of the quantity theory of money
C) prices are flexible in the short and long runs
D) contracts apply only in the very short run
E) we are in the long run
A) inflation is sticky in the short run
B) of the quantity theory of money
C) prices are flexible in the short and long runs
D) contracts apply only in the very short run
E) we are in the long run

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
According to the quantity theory of money, an increase in GDP ________ inflation, and the Phillips curve demonstrates that inflation ________ with rising GDP. This is because the quantity theory is a ________ theory of price behavior.
A) reduces; increases; long-run
B) raises; decreases; short-run
C) has zero influence on; decreases; money-neutral
D) raises; increases; short-run
E) reduces; does not move; Keynesian
A) reduces; increases; long-run
B) raises; decreases; short-run
C) has zero influence on; decreases; money-neutral
D) raises; increases; short-run
E) reduces; does not move; Keynesian

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
In the Phillips curve measures:
A) a price shock
B) how sensitive inflation is to interest rates
C) how sensitive inflation is to aggregate demand conditions
D) how sensitive inflation is to aggregate supply conditions
E) how sensitive inflation is to price shocks
A) a price shock
B) how sensitive inflation is to interest rates
C) how sensitive inflation is to aggregate demand conditions
D) how sensitive inflation is to aggregate supply conditions
E) how sensitive inflation is to price shocks

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
In the Phillips curve 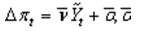 is:
is:
A) a demand shock
B) an inflation shock
C) a measure of the sensitivity of inflation to demand conditions
D) a permanent price trend
E) fiscal policy shock
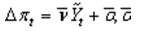 is:
is:A) a demand shock
B) an inflation shock
C) a measure of the sensitivity of inflation to demand conditions
D) a permanent price trend
E) fiscal policy shock

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
In the Phillips curve, the term ________ reflects ________.
A) demand-pull inflation
B) ; cost-push inflation
C) ; the "true" rate of inflation
D) ; demand-pull inflation
E) , the responsiveness of inflation to cost shocks
A) demand-pull inflation
B) ; cost-push inflation
C) ; the "true" rate of inflation
D) ; demand-pull inflation
E) , the responsiveness of inflation to cost shocks

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The most immediate and visible form of inflation shock is/are:
A) the real wage
B) the price of corn
C) the price of oil
D) growth in the stock market
E) bond prices
A) the real wage
B) the price of corn
C) the price of oil
D) growth in the stock market
E) bond prices

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which of the following contributed to high levels of inflation in the 1970s?
I) Oil price shocks
Ii) Lower taxes
Iii) A productivity slowdown
A) i only
B) ii only
C) iii only
D) i and iii
E) ii and iii
I) Oil price shocks
Ii) Lower taxes
Iii) A productivity slowdown
A) i only
B) ii only
C) iii only
D) i and iii
E) ii and iii

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Oil prices are closely watched because:
A) they hurt automobile owners
B) they affect inflation directly
C) of their impact on stock markets
D) of their immediate impact on subsidies and taxes
E) they affect inflation both directly and indirectly
A) they hurt automobile owners
B) they affect inflation directly
C) of their impact on stock markets
D) of their immediate impact on subsidies and taxes
E) they affect inflation both directly and indirectly

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
In the Phillips curve, , if Is large, then:
A) price-setting behavior is completely insensitive to short-run fluctuations
B) price-setting behavior is very insensitive to short-run fluctuations
C) inflation is not very sensitive to short-run fluctuations
D) price-setting behavior is very sensitive to short-run fluctuations
E) Not enough information is given.
A) price-setting behavior is completely insensitive to short-run fluctuations
B) price-setting behavior is very insensitive to short-run fluctuations
C) inflation is not very sensitive to short-run fluctuations
D) price-setting behavior is very sensitive to short-run fluctuations
E) Not enough information is given.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Based on the reasoning of the original version of the Phillips curve, conventional wisdom of the 1960s was that:
A) money is not neutral
B) there is a strong positive relationship between unemployment and inflation
C) there is no relationship between economic growth and the savings rate
D) there is a permanent trade-off between inflation and economic performance
E) the real interest rate is always equal to 2 percent
A) money is not neutral
B) there is a strong positive relationship between unemployment and inflation
C) there is no relationship between economic growth and the savings rate
D) there is a permanent trade-off between inflation and economic performance
E) the real interest rate is always equal to 2 percent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Which of the following statements is NOT true?
A) Many agents suffer from money illusion.
B) Small menu prices lead to price stickiness.
C) Under adaptive expectations, prices are perfectly flexible.
D) In the classical dichotomy, all prices are flexible.
E) Imperfect competition may lead to price inflexibility.
A) Many agents suffer from money illusion.
B) Small menu prices lead to price stickiness.
C) Under adaptive expectations, prices are perfectly flexible.
D) In the classical dichotomy, all prices are flexible.
E) Imperfect competition may lead to price inflexibility.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Figure 12.7: Output 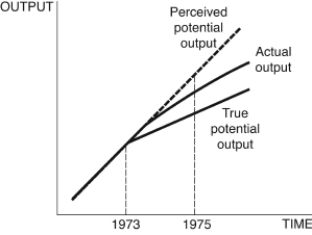
Consider Figure 12.7. You are chairman of the Federal Reserve in 1975. You believe potential output follows the dotted line after 1973, but in actuality, it follows the line denoted "True potential output." The current state of the economy is given by the curve "Actual output." Given the information in the figure, you ________, because you believe the economy is in a ________, but your advice instead ________.
A) lower interest rates; recession; accelerates inflation
B) raise interest rates; recession; accelerates inflation
C) keep interest rates the same; boom; accelerates inflation
D) lower interest rates; boom; increases unemployment
E) Not enough information is given.

Consider Figure 12.7. You are chairman of the Federal Reserve in 1975. You believe potential output follows the dotted line after 1973, but in actuality, it follows the line denoted "True potential output." The current state of the economy is given by the curve "Actual output." Given the information in the figure, you ________, because you believe the economy is in a ________, but your advice instead ________.
A) lower interest rates; recession; accelerates inflation
B) raise interest rates; recession; accelerates inflation
C) keep interest rates the same; boom; accelerates inflation
D) lower interest rates; boom; increases unemployment
E) Not enough information is given.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
If nominal interest rates are high, you:
A) hold only cash
B) hold less savings and more cash
C) hold all your money in a different currency
D) never have any cash in your checking account
E) hold less cash and more savings
A) hold only cash
B) hold less savings and more cash
C) hold all your money in a different currency
D) never have any cash in your checking account
E) hold less cash and more savings

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Refer to the following figure when answering the next two questions.
Figure 12.11: Change in Inflation by Month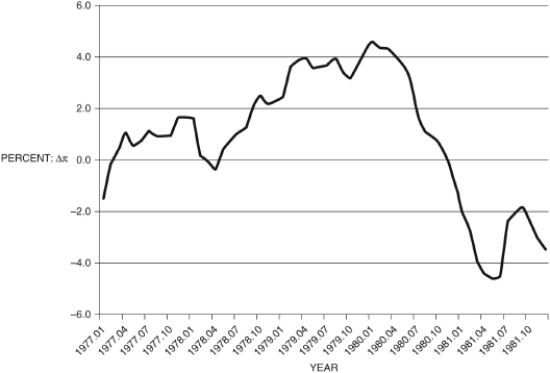 (Source: Federal Reserve Economic Data, St. Louis Federal Reserve)
(Source: Federal Reserve Economic Data, St. Louis Federal Reserve)
-Consider Figure 12.11, which shows the change in inflation from 1977 to 1981, by quarter. You are Federal Reserve chairman Volcker and today's date is mid-1977. You suggest the appropriate policy would be to ________. You reevaluate your policy in mid-1979 and conclude that you ________; using the Phillips curve, you see the country is now in ________.
A) lower taxes; failed to tame inflation; debt
B) lower interest rates; failed at taming inflation; a recession
C) raise interest rates; failed in taming inflation; expansion
D) raise interest rates; succeeded in taming inflation; a recession
E) raise taxes; succeeded in taming inflation; debt
Figure 12.11: Change in Inflation by Month
 (Source: Federal Reserve Economic Data, St. Louis Federal Reserve)
(Source: Federal Reserve Economic Data, St. Louis Federal Reserve)-Consider Figure 12.11, which shows the change in inflation from 1977 to 1981, by quarter. You are Federal Reserve chairman Volcker and today's date is mid-1977. You suggest the appropriate policy would be to ________. You reevaluate your policy in mid-1979 and conclude that you ________; using the Phillips curve, you see the country is now in ________.
A) lower taxes; failed to tame inflation; debt
B) lower interest rates; failed at taming inflation; a recession
C) raise interest rates; failed in taming inflation; expansion
D) raise interest rates; succeeded in taming inflation; a recession
E) raise taxes; succeeded in taming inflation; debt

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Which of the following scenarios best describes the short-run model?
A)
B)
C)
D)
E) None of these answers are correct.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E) None of these answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Which of the following scenarios best describes the short-run model?
A)
B)
C)
D)
E) None of these answers are correct.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E) None of these answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Which of the following contributed to high levels of inflation in the 1970s?
I) Soviet invasion of Afghanistan
Ii) Loose monetary policy
Iii) A productivity slowdown
A) i only
B) ii only
C) iii only
D) i and iii
E) ii and iii
I) Soviet invasion of Afghanistan
Ii) Loose monetary policy
Iii) A productivity slowdown
A) i only
B) ii only
C) iii only
D) i and iii
E) ii and iii

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Refer to the following figure when answering the next two questions.
Figure 12.11: Change in Inflation by Month (Source: Federal Reserve Economic Data, St. Louis Federal Reserve)
(Source: Federal Reserve Economic Data, St. Louis Federal Reserve)
-Consider Figure 12.11, which shows the change in inflation from 1977 to 1981, by quarter. You are Federal Reserve chairman Volcker and today's date is the first quarter of 1980 (1980.1). You suggest the appropriate policy would be to ________. In the second quarter of 1981, you consider your performance, and you conclude that you ________; using the Phillips curve, you see the country is now ________.
A) lower taxes; failed to tame inflation; in debt
B) lower interest rates; failed at taming inflation; in a recession
C) raise interest rates; succeeded in taming the recession; booming
D) raise interest rates; succeeded in taming inflation; in a recession
E) raise taxes; succeeded in taming inflation; in debt
Figure 12.11: Change in Inflation by Month
 (Source: Federal Reserve Economic Data, St. Louis Federal Reserve)
(Source: Federal Reserve Economic Data, St. Louis Federal Reserve)-Consider Figure 12.11, which shows the change in inflation from 1977 to 1981, by quarter. You are Federal Reserve chairman Volcker and today's date is the first quarter of 1980 (1980.1). You suggest the appropriate policy would be to ________. In the second quarter of 1981, you consider your performance, and you conclude that you ________; using the Phillips curve, you see the country is now ________.
A) lower taxes; failed to tame inflation; in debt
B) lower interest rates; failed at taming inflation; in a recession
C) raise interest rates; succeeded in taming the recession; booming
D) raise interest rates; succeeded in taming inflation; in a recession
E) raise taxes; succeeded in taming inflation; in debt

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The money demand curve:
A) slopes downward with respect to the discount rate
B) slopes downward with respect to the nominal interest rate
C) slopes upward with respect to the nominal interest rate
D) always is flat with respect to the nominal interest rate
E) is flat with respect to the inflation rate
A) slopes downward with respect to the discount rate
B) slopes downward with respect to the nominal interest rate
C) slopes upward with respect to the nominal interest rate
D) always is flat with respect to the nominal interest rate
E) is flat with respect to the inflation rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Refer to the following figure when answering
Figure 12.9: Change in Inflation by Quarter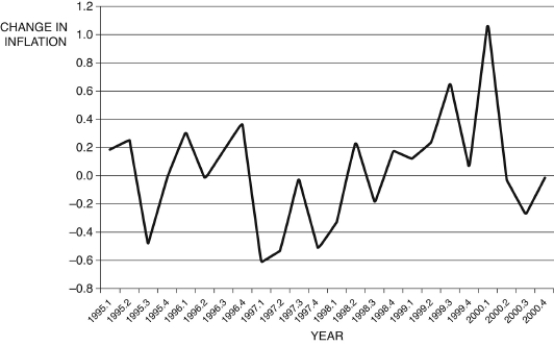 (Source: Federal Reserve Economic Data, St. Louis Federal Reserve)
(Source: Federal Reserve Economic Data, St. Louis Federal Reserve)
-Consider Figure 12.9, which shows the change in inflation from 1995 to 2000, by quarter. You are Federal Reserve chairman Greenspan and today's date is the first quarter of 1999 (1999.1). Given the information you have, using the Phillips curve, to stabilize the economy you would ________ interest rates, risking ________.
A) raise; inflation
B) raise; recession
C) lower; recession
D) lower; higher unemployment
E) Not enough information is given.
Figure 12.9: Change in Inflation by Quarter
 (Source: Federal Reserve Economic Data, St. Louis Federal Reserve)
(Source: Federal Reserve Economic Data, St. Louis Federal Reserve)-Consider Figure 12.9, which shows the change in inflation from 1995 to 2000, by quarter. You are Federal Reserve chairman Greenspan and today's date is the first quarter of 1999 (1999.1). Given the information you have, using the Phillips curve, to stabilize the economy you would ________ interest rates, risking ________.
A) raise; inflation
B) raise; recession
C) lower; recession
D) lower; higher unemployment
E) Not enough information is given.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The "jobless recovery" in the aftermath of the 2001 recession was an apparent violation of:
A) Okun's law
B) the Phillips curve
C) the quantity theory
D) the neoclassical model
E) moral hazard
A) Okun's law
B) the Phillips curve
C) the quantity theory
D) the neoclassical model
E) moral hazard

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Refer to the following figure when answering
Figure 12.9: Change in Inflation by Quarter (Source: Federal Reserve Economic Data, St. Louis Federal Reserve)
(Source: Federal Reserve Economic Data, St. Louis Federal Reserve)
-Consider Figure 12.9, which shows the change in inflation from 1995 to 2000, by quarter. You are Federal Reserve chairman Greenspan and today's date is the second quarter of 1997 (1997.2). Given the information you have, using the Phillips curve, to stabilize the economy you would ________ interest rates, risking ________.
A) raise; recession
B) raise; inflation
C) lower; inflation
D) lower; higher unemployment
E) Not enough information is given.
Figure 12.9: Change in Inflation by Quarter
 (Source: Federal Reserve Economic Data, St. Louis Federal Reserve)
(Source: Federal Reserve Economic Data, St. Louis Federal Reserve)-Consider Figure 12.9, which shows the change in inflation from 1995 to 2000, by quarter. You are Federal Reserve chairman Greenspan and today's date is the second quarter of 1997 (1997.2). Given the information you have, using the Phillips curve, to stabilize the economy you would ________ interest rates, risking ________.
A) raise; recession
B) raise; inflation
C) lower; inflation
D) lower; higher unemployment
E) Not enough information is given.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The nominal interest rate:
A) is set by Congress
B) is equal to the rate of inflation
C) always is equal to the 10-year bond rate of return
D) is the opportunity cost of holding money
E) is constant
A) is set by Congress
B) is equal to the rate of inflation
C) always is equal to the 10-year bond rate of return
D) is the opportunity cost of holding money
E) is constant

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Refer to the following figure when answering
Figure 12.9: Change in Inflation by Quarter (Source: Federal Reserve Economic Data, St. Louis Federal Reserve)
(Source: Federal Reserve Economic Data, St. Louis Federal Reserve)
-Consider Figure 12.9, which shows the change in inflation from 1995 to 2000, by quarter. You are Federal Reserve chairman Greenspan and today's date is the fourth quarter of 1997 (1997.4). Given the information you have, using the Phillips curve, to stabilize the economy you would ________ interest rates, risking ________.
A) raise; inflation
B) lower; inflation
C) raise; recession
D) lower; higher unemployment
E) Not enough information is given.
Figure 12.9: Change in Inflation by Quarter
 (Source: Federal Reserve Economic Data, St. Louis Federal Reserve)
(Source: Federal Reserve Economic Data, St. Louis Federal Reserve)-Consider Figure 12.9, which shows the change in inflation from 1995 to 2000, by quarter. You are Federal Reserve chairman Greenspan and today's date is the fourth quarter of 1997 (1997.4). Given the information you have, using the Phillips curve, to stabilize the economy you would ________ interest rates, risking ________.
A) raise; inflation
B) lower; inflation
C) raise; recession
D) lower; higher unemployment
E) Not enough information is given.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Which of the following statements is NOT true?
A) Small menu prices lead to price stickiness.
B) In the classical dichotomy, some prices are sticky.
C) In the classical dichotomy, an increase in money supply growth leads to a corresponding increase in inflation.
D) Short-run contracts lead to price persistence.
E) Imperfect information may lead to price inflexibility.
A) Small menu prices lead to price stickiness.
B) In the classical dichotomy, some prices are sticky.
C) In the classical dichotomy, an increase in money supply growth leads to a corresponding increase in inflation.
D) Short-run contracts lead to price persistence.
E) Imperfect information may lead to price inflexibility.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
One of the remarkable things about the 2001 recession was the:
A) fact that unemployment fell
B) jobless recovery
C) rapid return to potential output
D) deflation
E) impact of Hurricane Katrina on it
A) fact that unemployment fell
B) jobless recovery
C) rapid return to potential output
D) deflation
E) impact of Hurricane Katrina on it

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Refer to the following figure when answering
Figure 12.10: Output Gap: 1990-2000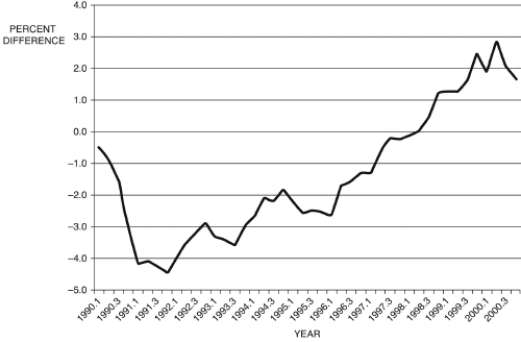
(Source: Federal Reserve Economic Data, St. Louis Federal Reserve)
-Consider Figure 12.10, which shows the output gap from 1990 to 2000, by quarter. If this is all the information you have, during the period 1997.1-1999.4, from the Phillips curve, you would conclude that:
A) inflation is accelerating,
B) inflation is decelerating,
C) unemployment is falling
D) unemployment is rising
E) Not enough information is given.
Figure 12.10: Output Gap: 1990-2000

(Source: Federal Reserve Economic Data, St. Louis Federal Reserve)
-Consider Figure 12.10, which shows the output gap from 1990 to 2000, by quarter. If this is all the information you have, during the period 1997.1-1999.4, from the Phillips curve, you would conclude that:
A) inflation is accelerating,
B) inflation is decelerating,
C) unemployment is falling
D) unemployment is rising
E) Not enough information is given.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Figure 12.8: Output 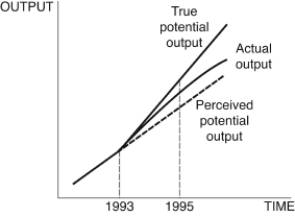
Consider Figure 12.8. You are chairman of the Federal Reserve in 1995. You believe potential output follows the dotted line after 1993, but in actuality, it follows the line denoted "True potential output." The current state of the economy is given by the curve "Actual output." Given the information in the figure, you ________, because you believe the economy is in a ________, but your advice instead ________.
A) lower interest rates; recession; accelerates inflation
B) raise interest rates; boom; accelerates a recession
C) keep interest rates the same; boom; accelerates inflation
D) lower interest rates; boom; increases unemployment
E) Not enough information is given.

Consider Figure 12.8. You are chairman of the Federal Reserve in 1995. You believe potential output follows the dotted line after 1993, but in actuality, it follows the line denoted "True potential output." The current state of the economy is given by the curve "Actual output." Given the information in the figure, you ________, because you believe the economy is in a ________, but your advice instead ________.
A) lower interest rates; recession; accelerates inflation
B) raise interest rates; boom; accelerates a recession
C) keep interest rates the same; boom; accelerates inflation
D) lower interest rates; boom; increases unemployment
E) Not enough information is given.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
As lender in the last resort, the Fed loans money to banks at:
A) the federal funds rate
B) the three month T-bill interest rate
C) the prime interest rate
D) LIBOR
E) the discount rate
A) the federal funds rate
B) the three month T-bill interest rate
C) the prime interest rate
D) LIBOR
E) the discount rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Refer to the following figure when answering
Figure 12.10: Output Gap: 1990-2000
(Source: Federal Reserve Economic Data, St. Louis Federal Reserve)
-Consider Figure 12.10, which shows the output gap from 1990 to 2000, by quarter. If this is all the information you have, during the period 1993.1-1993.4, from the Phillips curve, you would conclude that:
A) inflation is decelerating,
B) inflation is accelerating,
C) unemployment is falling
D) unemployment is rising
E) Not enough information is given.
Figure 12.10: Output Gap: 1990-2000

(Source: Federal Reserve Economic Data, St. Louis Federal Reserve)
-Consider Figure 12.10, which shows the output gap from 1990 to 2000, by quarter. If this is all the information you have, during the period 1993.1-1993.4, from the Phillips curve, you would conclude that:
A) inflation is decelerating,
B) inflation is accelerating,
C) unemployment is falling
D) unemployment is rising
E) Not enough information is given.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



