Deck 26: Accounting for Manufacturing Activities
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/89
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 26: Accounting for Manufacturing Activities
1
The raw materials inventory, the work in process inventory, and the finished goods inventory are all shown in the Current Assets section of the balance sheet.
True
2
Cleaning materials and lubricants used in factory operations and maintenance are considered manufacturing overhead.
True
3
Immediately before it is closed, the balance of the Manufacturing Summary account represents the cost of goods manufactured.
True
4
Amounts paid to factory repair and maintenance employees are considered direct labor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
If there are no errors, the amount needed to balance the Cost of Goods Manufactured columns of a worksheet will also be the amount required to balance the Balance Sheet columns.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Six adjusting entries are made for inventory accounts in a manufacturing operation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The amounts of the raw materials used, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead for a fiscal period are reported on the statement of cost of goods manufactured.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
If the ending finished goods inventory is greater than the beginning finished goods inventory, the cost of goods sold will be higher than the cost of goods manufactured.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The Cost of Goods Sold section of the income statement for a manufacturing business shows the work in process inventory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
In a manufacturing company, it is not necessary to take a physical inventory of the finished goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The beginning and ending balances of the finished goods inventory are not used in the computation of cost of goods manufactured.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A statement of cost goods manufactured supports the income statement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Gross profit for a manufacturing business is computed by deducting cost of goods manufactured from net sales.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Reversing entries help save time and prevent errors in the period being closed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Information about depreciation, insurance, and property taxes for the factory building of a manufacturing business would be shown in the Operating Expenses section of the income statement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The beginning inventory of raw materials is shown in the Income Statement Credit column and the Balance Sheet Debit column of a worksheet for a manufacturing business.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Products that are only partially completed are called work in process.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The balance of the Manufacturing Summary account is closed into the Income Summary account.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The adjusting entry to close out the beginning work in process inventory includes a debit to Income Summary and a credit to Work in Process Inventory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Raw Materials Used is not an element of manufacturing overhead.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
As part of the adjusting entries, the beginning inventory of work in process is closed into the ____________________ Summary account.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The entry to close the Manufacturing Summary account includes a(n) ____________________ to Manufacturing Summary.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
For a manufacturing business, net sales minus cost of goods ____________________ equals gross profit on sales.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The end-of-period adjusting entries are
A) recorded and posted in the ledger.
B) recorded in the journal and posted in the ledger.
C) recorded in the ledger and posted in the journal.
D) recorded and posted in the journal.
A) recorded and posted in the ledger.
B) recorded in the journal and posted in the ledger.
C) recorded in the ledger and posted in the journal.
D) recorded and posted in the journal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The cost of indirect materials and supplies used in manufacturing operations would be included in the computation of total manufacturing costs as ________________________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Closing entries for a manufacturing firm include all of the following except
A) transferring all manufacturing cost accounts to Manufacturing Summary.
B) transferring all Revenue and Expense account balances to Income Summary.
C) closing Manufacturing Summary to Income Summary.
D) closing Income Summary to Net Income.
A) transferring all manufacturing cost accounts to Manufacturing Summary.
B) transferring all Revenue and Expense account balances to Income Summary.
C) closing Manufacturing Summary to Income Summary.
D) closing Income Summary to Net Income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The beginning and ending ____________________ inventories appear in the Cost of Goods Sold section of the income statement of a manufacturing business.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The Balance Sheet of a manufacturing firm will include which account that will not be included in the Balance Sheet of a service firm?
A) Purchases
B) Accounts Payable
C) Prepaid Wages
D) Work in Process Inventory
A) Purchases
B) Accounts Payable
C) Prepaid Wages
D) Work in Process Inventory

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The raw materials inventory is shown in the ____________________ section of the balance sheet of a manufacturing business.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
All of the items that are purchased for manufacturing operations, that go into a product and become part of it, are called ____________________ materials.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The salary paid to a factory supervisor would be classified as ____________________ labor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Under the perpetual inventory method, additions and deletions are recorded as they occur to which of the following?
A) Finished Goods
B) Work in Process
C) Materials
D) All of the above
A) Finished Goods
B) Work in Process
C) Materials
D) All of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The Manufacturing Summary account is closed into the ____________________ account.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Finished goods inventory is used in the computation of cost of goods ___________________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
As part of the adjusting entries, the beginning inventory of finished goods is closed into the ____________________ Summary account.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The ending inventory of raw materials is shown on the worksheet of a manufacturing business in the Cost of Goods Manufactured ____________________ column.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
All manufacturing costs except those for direct labor and direct materials are included in manufacturing ___________________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
To compute the cost of goods ___________________, it is necessary to subtract the ending work in process inventory from the sum of the beginning work in process inventory and the total manufacturing cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
On a worksheet for a manufacturing business, the beginning inventory of finished goods is extended to the ____________________ Debit column.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Organizations that utilize the perpetual inventory method record additions and deletions
A) daily.
B) monthly.
C) quarterly.
D) yearly.
A) daily.
B) monthly.
C) quarterly.
D) yearly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The Indirect Labor account is closed by crediting it and debiting
A) Wages Payable.
B) Income Summary.
C) Manufacturing Summary.
D) Wages Expense.
A) Wages Payable.
B) Income Summary.
C) Manufacturing Summary.
D) Wages Expense.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The balance of the Manufacturing Summary account is closed into
A) Income Summary.
B) Cost of Goods Manufactured.
C) Retained Earnings.
D) Manufacturing Overhead.
A) Income Summary.
B) Cost of Goods Manufactured.
C) Retained Earnings.
D) Manufacturing Overhead.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The balance sheet of a manufacturing business shows
A) the finished goods inventory and the cost of goods manufactured.
B) the cost of goods manufactured rather than inventory figures.
C) a single inventory figure-the amount of the finished goods inventory.
D) the raw materials inventory, the work in process inventory, and the finished goods inventory.
A) the finished goods inventory and the cost of goods manufactured.
B) the cost of goods manufactured rather than inventory figures.
C) a single inventory figure-the amount of the finished goods inventory.
D) the raw materials inventory, the work in process inventory, and the finished goods inventory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The ending balance of the work in process inventory is recorded by debiting Work in Process Inventory and crediting
A) Income Summary.
B) Cost of Goods Sold.
C) Manufacturing Summary.
D) Merchandise Inventory.
A) Income Summary.
B) Cost of Goods Sold.
C) Manufacturing Summary.
D) Merchandise Inventory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Reversing entries for a manufacturing business are
A) made prior to preparing the postclosing trial balance.
B) made for the inventory accounts only.
C) closed into the Manufacturing Summary account.
D) made for accrual adjustments.
A) made prior to preparing the postclosing trial balance.
B) made for the inventory accounts only.
C) closed into the Manufacturing Summary account.
D) made for accrual adjustments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Once the financial statements have been prepared, the steps in the accounting cycle are complete. Which of the following is NOT one of the steps in the accounting cycle?
A) Adjusting entries
B) Closing Trial Balance
C) Post Closing Trial Balance
D) Closing entries
A) Adjusting entries
B) Closing Trial Balance
C) Post Closing Trial Balance
D) Closing entries

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
All manufacturing costs that are NOT classified as direct materials or direct labor are
A) indirect materials.
B) indirect labor.
C) manufacturing overhead.
D) semidirect costs.
A) indirect materials.
B) indirect labor.
C) manufacturing overhead.
D) semidirect costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Wages paid to the factory maintenance and repair personnel of a manufacturing business are shown
A) in the Operating Expenses section of the income statement.
B) as Direct Labor on the statement of cost goods manufactured.
C) as part of Manufacturing Overhead on the statement cost of goods manufactured.
D) as a part of the Cost of Goods Sold section of the income statement.
A) in the Operating Expenses section of the income statement.
B) as Direct Labor on the statement of cost goods manufactured.
C) as part of Manufacturing Overhead on the statement cost of goods manufactured.
D) as a part of the Cost of Goods Sold section of the income statement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The statement of cost of goods manufactured
A) supports the income statement.
B) replaces the income statement.
C) is not related to the income statement.
D) supports the balance sheet.
A) supports the income statement.
B) replaces the income statement.
C) is not related to the income statement.
D) supports the balance sheet.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
On a worksheet for a manufacturing firm, the beginning balance of the Finished Goods Inventory account should
A) be extended to the Cost of Goods Manufactured Debit column.
B) be extended to the Income Statement Debit column.
C) be extended to the Balance Sheet Debit column.
D) not be listed.
A) be extended to the Cost of Goods Manufactured Debit column.
B) be extended to the Income Statement Debit column.
C) be extended to the Balance Sheet Debit column.
D) not be listed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The manufacturing costs incurred during the year are
A) shown by the expense accounts such as Wages Expense and Utilities Expense that are listed in the Operating Expenses section of the income statement.
B) shown as Direct Labor, Raw Materials, and Manufacturing Overhead in the Operating Expenses section of the income statement.
C) used in the computation of cost of goods manufactured.
D) shown in the Cost of Goods Sold section of the income statement.
A) shown by the expense accounts such as Wages Expense and Utilities Expense that are listed in the Operating Expenses section of the income statement.
B) shown as Direct Labor, Raw Materials, and Manufacturing Overhead in the Operating Expenses section of the income statement.
C) used in the computation of cost of goods manufactured.
D) shown in the Cost of Goods Sold section of the income statement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Reversing entries are required by
A) the Internal Revenue Service.
B) Generally Accepted Accounting Principles.
C) the International Accounting Standards Board.
D) none of the above.
A) the Internal Revenue Service.
B) Generally Accepted Accounting Principles.
C) the International Accounting Standards Board.
D) none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which of the following is NOT an adjusting entry?
A) Administrative Expense
Allowance for Doubtful Accounts
B) Supplies on Hand
Supplies Expense
C) Insurance-Factory
Administrative Expense
D) Income Tax Expense
Income Tax Payable
A) Administrative Expense
Allowance for Doubtful Accounts
B) Supplies on Hand
Supplies Expense
C) Insurance-Factory
Administrative Expense
D) Income Tax Expense
Income Tax Payable

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
In adjusting entries for a manufacturing business, the beginning balance of the work in process inventory is eliminated by crediting Work in Process Inventory and debiting
A) Finished Goods Inventory.
B) Manufacturing Summary.
C) Income Summary.
D) Merchandise Inventory.
A) Finished Goods Inventory.
B) Manufacturing Summary.
C) Income Summary.
D) Merchandise Inventory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The cost of goods manufactured for a fiscal period is reported on
A) both the statement of cost of goods manufactured and the income statement.
B) both the statement of the cost of goods manufactured and the balance sheet.
C) both the income statement and the balance sheet.
D) the statement of cost of goods manufactured only.
A) both the statement of cost of goods manufactured and the income statement.
B) both the statement of the cost of goods manufactured and the balance sheet.
C) both the income statement and the balance sheet.
D) the statement of cost of goods manufactured only.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Indirect labor for a manufacturing business includes the wages of
A) factory repair and maintenance employees.
B) employees who assemble the product.
C) employees who sell the product.
D) office employees.
A) factory repair and maintenance employees.
B) employees who assemble the product.
C) employees who sell the product.
D) office employees.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The three components of total manufacturing cost are
A) cost of goods manufactured, cost of goods sold, and work in process.
B) raw materials used, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead.
C) selling expenses, administrative expenses, and manufacturing overhead.
D) raw materials used, direct labor, and cost of goods sold.
A) cost of goods manufactured, cost of goods sold, and work in process.
B) raw materials used, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead.
C) selling expenses, administrative expenses, and manufacturing overhead.
D) raw materials used, direct labor, and cost of goods sold.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Gross profit for a manufacturing business is computed by
A) deducting cost of goods sold from net sales.
B) deducting cost of goods manufactured from net sales.
C) deducting the ending finished goods inventory from the total goods available for sale.
D) deducting operating expenses from the costs of goods sold.
A) deducting cost of goods sold from net sales.
B) deducting cost of goods manufactured from net sales.
C) deducting the ending finished goods inventory from the total goods available for sale.
D) deducting operating expenses from the costs of goods sold.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
On the completed worksheet of a manufacturing business, the accounts related to materials purchases, direct labor, and factory overhead
A) appear in the Income Statement section.
B) do not appear.
C) appear in the Balance Sheet section.
D) appear in the Cost of Goods Manufactured section.
A) appear in the Income Statement section.
B) do not appear.
C) appear in the Balance Sheet section.
D) appear in the Cost of Goods Manufactured section.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The cost of goods manufactured is computed by
A) adding raw materials used and direct labor to manufacturing overhead.
B) deducting the ending work in process inventory from the sum of the total manufacturing cost and the beginning work in process inventory.
C) deducting the ending finished goods inventory from the beginning finished goods inventory.
D) adding operating expenses to direct labor costs.
A) adding raw materials used and direct labor to manufacturing overhead.
B) deducting the ending work in process inventory from the sum of the total manufacturing cost and the beginning work in process inventory.
C) deducting the ending finished goods inventory from the beginning finished goods inventory.
D) adding operating expenses to direct labor costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
What are the three inventory accounts for a manufacturing firm? List the three inventory accounts and indicate for each the name(s) of the statement(s) in which it appears.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Selected account balances for Reed Manufacturing Company on December 31, 2013, the end of the fiscal year, are given below. Data about the beginning and ending inventories are also given. Use this information to prepare a statement of cost of goods manufactured and an income statement for 2013. 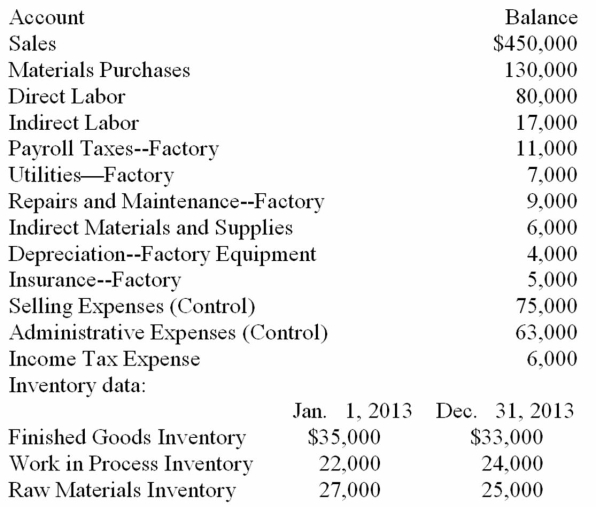


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The following information appears on the income statement of the Davis Company at the end of the year. Ending finished goods inventory was:
A) $140,000.
B) $160,000.
C) $200,000.
D) $220,000. Cost of Goods Sold = 500,000 - 160,000 = 340,000.
Ending finished goods inventory = 120,000 + 360,000 - 340,000 = 140,000.
A) $140,000.
B) $160,000.
C) $200,000.
D) $220,000. Cost of Goods Sold = 500,000 - 160,000 = 340,000.
Ending finished goods inventory = 120,000 + 360,000 - 340,000 = 140,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The following information appears on the income statement of the Richer Company at the end of the year. Gross Profit on Sales was:
A) $140,000.
B) $160,000.
C) $200,000.
D) $220,000. Cost of Goods Sold = 200,000 + 120,000 - 180,000 = 140,000.
Gross Profit = 360,000 - 140,000 = 220,000.
A) $140,000.
B) $160,000.
C) $200,000.
D) $220,000. Cost of Goods Sold = 200,000 + 120,000 - 180,000 = 140,000.
Gross Profit = 360,000 - 140,000 = 220,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Define the term manufacturing overhead and give three examples of manufacturing overhead for a bakery.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Stellar Manufacturing had a beginning raw materials inventory of $220,000. The firm had net purchases of $625,000 for the period and an ending raw materials inventory of $199,000. What was the cost of raw materials used?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The following information appears on the Statement of Cost of Goods Manufactured for the Coleman Company at the end of the year. The cost for Direct Labor was:
A) $40,000.
B) $60,000.
C) $110,000.
D) $120,000. Direct Labor = Total Manufacturing Costs - Raw Material Used - Manufacturing Overhead = 170,000 - 50,000 - 60,000 = 60,000.
A) $40,000.
B) $60,000.
C) $110,000.
D) $120,000. Direct Labor = Total Manufacturing Costs - Raw Material Used - Manufacturing Overhead = 170,000 - 50,000 - 60,000 = 60,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68

Calculate net income for the year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Using only the relevant items from the information given, determine the total product cost for Donnybrook Corporation, a manufacturer of children's furniture. All materials purchased were used in inventory during the current period. There was no beginning inventory. 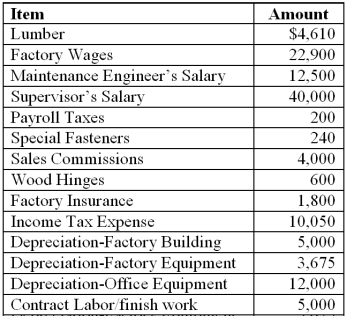


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The following information appears on the Statement of Cost of Goods Manufactured for the Coleman Company at the end of the year. The balance in Work in Process Inventory at year-end was:
A) $30,000.
B) $40,000.
C) $60,000.
D) $20,000. Ending Work in Process Inventory = 10,000 + 170,000 - 150,000 = 30,000.
A) $30,000.
B) $40,000.
C) $60,000.
D) $20,000. Ending Work in Process Inventory = 10,000 + 170,000 - 150,000 = 30,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71

Calculate the Cost of Goods Manufactured.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
The following information appears on the income statement of the Richer Company at the end of the year. Cost of Goods Manufactured was:
A) $246,000.
B) $280,000.
C) $264,000.
D) $240,000. Cost of Goods Sold = 400,000 - 120,000 = 280,000.
Cost of Goods Manufactured = 144,000 + 280,000 - 160,000 = 264,000.
A) $246,000.
B) $280,000.
C) $264,000.
D) $240,000. Cost of Goods Sold = 400,000 - 120,000 = 280,000.
Cost of Goods Manufactured = 144,000 + 280,000 - 160,000 = 264,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
From the information given, determine total direct and total indirect costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The following information appears on the Statement of Cost of Goods Manufactured for the Poster Company at the end of the year. Manufacturing Overhead for the year was:
A) $60,000.
B) $50,000.
C) $40,000.
D) $30,000. Manufacturing Cost = Ending Work in Process + Costs of Goods Manufacturing - Beginning Work in Process = 20,000 + 200,000 - 30,000 = 190,000.
Overhead = Total Manufacturing Costs - Raw Material Used - Direct Labor
= 190,000 - 70,000 - 90,000 = 30,000.
A) $60,000.
B) $50,000.
C) $40,000.
D) $30,000. Manufacturing Cost = Ending Work in Process + Costs of Goods Manufacturing - Beginning Work in Process = 20,000 + 200,000 - 30,000 = 190,000.
Overhead = Total Manufacturing Costs - Raw Material Used - Direct Labor
= 190,000 - 70,000 - 90,000 = 30,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75

The above listed items are used by Paige Manufacturing to make dollhouses. Categorize each as Direct Materials (DM), Direct Labor (DL), or Manufacturing Overhead (MOH).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Fill in the missing line items on the Statement of Cost of Goods Manufactured given. Include correct indentations, underlines, dates, and capitalization when needed. 


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The following information appears on the Statement of Cost of Goods Manufactured for the Ethridge Company at the end of the year. Cost of Goods Manufactured for the year was:
A) $200,000.
B) $210,000.
C) $220,000.
D) $240,000. Total Manufacturing Costs = Raw Material Used + Direct Labor + Manufacturing Overhead
= 70,000 + 90,000 + 60,000 = 220,000.
Cost of Goods Manufactured = 20,000 + 220,000 - 30,000 = 210,000.
A) $200,000.
B) $210,000.
C) $220,000.
D) $240,000. Total Manufacturing Costs = Raw Material Used + Direct Labor + Manufacturing Overhead
= 70,000 + 90,000 + 60,000 = 220,000.
Cost of Goods Manufactured = 20,000 + 220,000 - 30,000 = 210,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Selected account balances for Reed Manufacturing Company on December 31, 2013, the end of the fiscal year, are given below. Data about the beginning and ending inventories are also given. Record the adjusting entries for the inventory accounts on page 5 of a general journal. Skip a line and record the entry to close the manufacturing cost accounts. Omit descriptions. 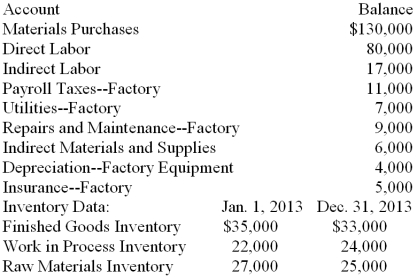


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
The accounts and the Adjusted Trial Balance section of Spencer Manufacturing's worksheet are given below. 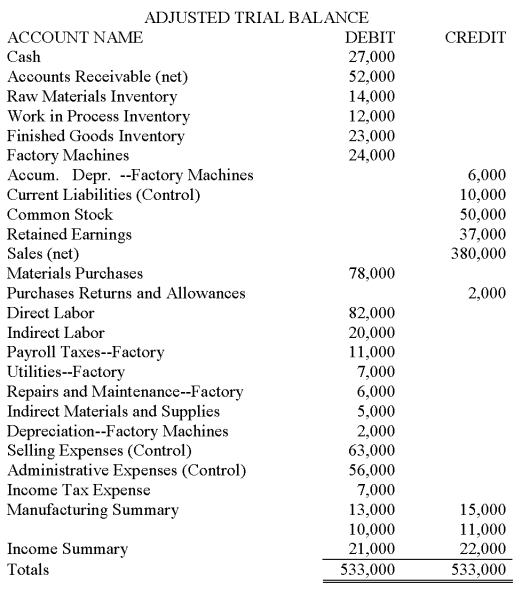 Instructions:
Instructions:
(1) Enter the account names in the Account Name column and the adjusted trial balance in the Adjusted Trial Balance columns of a 12-column manufacturing worksheet. Or use a 10-column worksheet and use the last four columns, changing the column headings as needed.
(2) Extend the balances to the appropriate columns and complete the worksheet for the year ended December 31, 2013.
(3) Record the closing entries for all revenue and expense accounts and the Manufacturing Summary account on page 9 of a general journal. Omit descriptions.
 Instructions:
Instructions:(1) Enter the account names in the Account Name column and the adjusted trial balance in the Adjusted Trial Balance columns of a 12-column manufacturing worksheet. Or use a 10-column worksheet and use the last four columns, changing the column headings as needed.
(2) Extend the balances to the appropriate columns and complete the worksheet for the year ended December 31, 2013.
(3) Record the closing entries for all revenue and expense accounts and the Manufacturing Summary account on page 9 of a general journal. Omit descriptions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Bolton Company's total manufacturing cost for the year was $1,785,000. The firm's manufacturing overhead was $315,000, and its cost of raw materials used was $842,000. What was the direct labor cost for the year?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



