Deck 20: International Trade
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/151
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 20: International Trade
1
Which country is the United States' largest trading partner in terms of volume of trade?
A) Mexico
B) Japan
C) China
D) Canada
A) Mexico
B) Japan
C) China
D) Canada
Canada
2
In the United States, exports of goods and services accounted for about what percentage of GDP (total output) in 2011?
A) 6 percent
B) 14 percent
C) 24 percent
D) 42 percent
A) 6 percent
B) 14 percent
C) 24 percent
D) 42 percent
14 percent
3
The slopes of the production possibilities curves for two nations reflect the:
A) Relative prices of the resources in the two nations
B) Amounts of imports and exports of the two nations
C) Average income levels in the two nations
D) Opportunity costs of production in the two nations
A) Relative prices of the resources in the two nations
B) Amounts of imports and exports of the two nations
C) Average income levels in the two nations
D) Opportunity costs of production in the two nations
Opportunity costs of production in the two nations
4
Adam Smith recognized the benefits from trade based on ____, and David Ricardo recognized the benefits from trade based on ____:
A) Comparative advantage; resource endowments
B) Absolute advantage; comparative advantage
C) Absolute advantage; resource endowments
D) Comparative advantage; absolute advantage
A) Comparative advantage; resource endowments
B) Absolute advantage; comparative advantage
C) Absolute advantage; resource endowments
D) Comparative advantage; absolute advantage

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
What other economic process needs to accompany international trade, for nations to benefit from such trade?
A) Specialization in production
B) Nationalization of industries
C) Regulation of production and trade
D) Spreading out of resources in more industries
A) Specialization in production
B) Nationalization of industries
C) Regulation of production and trade
D) Spreading out of resources in more industries

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A natural-resource abundant nation would be expected to export a land-intensive commodity such as:
A) Tractors
B) DVD players
C) Meat
D) Chemicals
A) Tractors
B) DVD players
C) Meat
D) Chemicals

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A basic assumption in comparing the production possibilities curves of two nations is that those possibilities curves reflect differences in:
A) Consumer tastes and preferences
B) Resource availability and technological capabilities
C) The nations' incomes and income distribution
D) Unemployment and inflation rates
A) Consumer tastes and preferences
B) Resource availability and technological capabilities
C) The nations' incomes and income distribution
D) Unemployment and inflation rates

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Benefits from international trade are based on the following differences, except:
A) In resource endowments
B) In technological capabilities
C) In product quality and other attributes
D) In income levels
A) In resource endowments
B) In technological capabilities
C) In product quality and other attributes
D) In income levels

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
In which of the following countries did exports account for the biggest percent of GDP in 2011?
A) Japan
B) United States
C) Netherlands
D) Germany
A) Japan
B) United States
C) Netherlands
D) Germany

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which nation had the largest share of world exports in 2011?
A) Japan
B) Germany
C) China
D) United States
A) Japan
B) Germany
C) China
D) United States

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Specialization and trade between individuals or between nations leads to:
A) Greater self-sufficiency
B) Higher product prices
C) Higher utilization of resources
D) Higher total output
A) Greater self-sufficiency
B) Higher product prices
C) Higher utilization of resources
D) Higher total output

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A nation with abundant capital resources tends to be an exporter of:
A) Labor-intensive products
B) Capital-intensive products
C) Natural resource-based products
D) Consumer products
A) Labor-intensive products
B) Capital-intensive products
C) Natural resource-based products
D) Consumer products

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
In a two-nation two-good world, if both nations have identical production possibilities curves with constant costs, then one nation would have:
A) No comparative advantage over the other nation
B) A comparative advantage in one good and a comparative disadvantage in the other good
C) No absolute advantage over the other nation
D) An absolute advantage in one good and an absolute disadvantage in the other good
A) No comparative advantage over the other nation
B) A comparative advantage in one good and a comparative disadvantage in the other good
C) No absolute advantage over the other nation
D) An absolute advantage in one good and an absolute disadvantage in the other good

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
If Nation A requires more resources to produce each bale of cloth than Nation B does, then we say that:
A) Nation A has the absolute advantage over Nation B in producing cloth
B) Nation B has the absolute advantage over Nation A in producing cloth
C) Nation A has the comparative advantage over Nation B in producing cloth
D) Nation B has the comparative advantage over Nation A in producing cloth
A) Nation A has the absolute advantage over Nation B in producing cloth
B) Nation B has the absolute advantage over Nation A in producing cloth
C) Nation A has the comparative advantage over Nation B in producing cloth
D) Nation B has the comparative advantage over Nation A in producing cloth

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following product-groups is a leading export of the United States?
A) Home appliances
B) Metals
C) Agricultural products
D) Computers
A) Home appliances
B) Metals
C) Agricultural products
D) Computers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The ratio at which nations will exchange one product for another is known as the:
A) Exchange rate
B) Discount rate
C) Terms of trade
D) Balance of trade
A) Exchange rate
B) Discount rate
C) Terms of trade
D) Balance of trade

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
A trade deficit refers to a situation where:
A) Government spending (including transfer payments) exceeds tax revenues
B) A nation's purchases from other nations are less than its sales to other nations
C) Assets are less than liabilities
D) Exports are less than imports
A) Government spending (including transfer payments) exceeds tax revenues
B) A nation's purchases from other nations are less than its sales to other nations
C) Assets are less than liabilities
D) Exports are less than imports

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
In 2012, U.S. exports of services ______ U.S. imports of services by about _____.
A) exceeded; $19B
B) fell short of; $19B
C) exceeded; $196 B
D) fell short of; $196B
A) exceeded; $19B
B) fell short of; $19B
C) exceeded; $196 B
D) fell short of; $196B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following countries had the smallest share of exports as a percentage of GDP in 2011?
A) Canada
B) France
C) United Kingdom
D) United States
A) Canada
B) France
C) United Kingdom
D) United States

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following products is a leading import of the United States?
A) Grains
B) Aircraft
C) Petroleum
D) Generating equipment
A) Grains
B) Aircraft
C) Petroleum
D) Generating equipment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The principle of comparative advantage indicates that mutually beneficial international trade can take place only when:
A) Tariffs are eliminated
B) Transportation costs are almost zero
C) Relative costs of production differ between nations
D) A country can produce more of some product than other nations can
A) Tariffs are eliminated
B) Transportation costs are almost zero
C) Relative costs of production differ between nations
D) A country can produce more of some product than other nations can

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The benefits to trading nations based on comparative advantage accrue from:
A) Specialization only
B) Specialization and trading
C) Trading only
D) Protection of domestic industries
A) Specialization only
B) Specialization and trading
C) Trading only
D) Protection of domestic industries

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
In Germany, one worker can produce either one cuckoo clock or one beer mug. In Taiwan, one worker can produce either two cuckoo clocks or three beer mugs. Who has the comparative advantage in each good?
A) Taiwan in both goods
B) Taiwan in clocks and Germany in mugs
C) Germany in clocks and Taiwan in mugs
D) Germany in both goods
A) Taiwan in both goods
B) Taiwan in clocks and Germany in mugs
C) Germany in clocks and Taiwan in mugs
D) Germany in both goods

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The table below shows labor-productivity figures in two countries facing constant costs:  Refer to the table above. Based on the data provided, it can be deduced that:
Refer to the table above. Based on the data provided, it can be deduced that:
A) Country A can produce more meat and houses than country B
B) Country A has a comparative advantage in producing houses
C) Country B has the absolute advantage in producing houses
D) Country B has a comparative advantage in producing houses
 Refer to the table above. Based on the data provided, it can be deduced that:
Refer to the table above. Based on the data provided, it can be deduced that:A) Country A can produce more meat and houses than country B
B) Country A has a comparative advantage in producing houses
C) Country B has the absolute advantage in producing houses
D) Country B has a comparative advantage in producing houses

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The principal concept behind comparative advantage is that a nation should:
A) Maximize its volume of trade with other nations
B) Use tariffs and quotas to protect the production of vital products for the nation
C) Concentrate production on those products for which it has the lowest domestic opportunity cost
D) Strive to be self-sufficient in the production of essential goods and services
A) Maximize its volume of trade with other nations
B) Use tariffs and quotas to protect the production of vital products for the nation
C) Concentrate production on those products for which it has the lowest domestic opportunity cost
D) Strive to be self-sufficient in the production of essential goods and services

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
In a two-nation, two-good world, if country A has the comparative advantage in producing good X over country B, then country A:
A) Should not trade with country B
B) Could have the comparative advantage in producing the other good Y as well
C) Must have the comparative disadvantage in producing the other good Y
D) Can produce good X with fewer resources than country B
A) Should not trade with country B
B) Could have the comparative advantage in producing the other good Y as well
C) Must have the comparative disadvantage in producing the other good Y
D) Can produce good X with fewer resources than country B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Specialization and trade based on comparative advantage allow nations to attain the following results, except:
A) Higher combined output
B) Higher consumption and standard of living
C) Rising total employment
D) Consuming combinations of products that are outside their PPCs
A) Higher combined output
B) Higher consumption and standard of living
C) Rising total employment
D) Consuming combinations of products that are outside their PPCs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The domestic opportunity cost of producing 100 barrels of chemicals in Germany is one ton of steel. In France, the domestic opportunity cost of producing 100 barrels of chemicals is two tons of steel. In this case:
A) France has a comparative advantage in the production of chemicals
B) Germany has a comparative advantage in the production of chemicals
C) France has an absolute advantage in the production of chemicals
D) Germany has an absolute advantage in the production of chemicals
A) France has a comparative advantage in the production of chemicals
B) Germany has a comparative advantage in the production of chemicals
C) France has an absolute advantage in the production of chemicals
D) Germany has an absolute advantage in the production of chemicals

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The table below shows the output (either machines or wine) that each unit of input in France and Germany can produce:  Refer to the table above. Based on the given information, we see that:
Refer to the table above. Based on the given information, we see that:
A) France has a comparative advantage in producing wine
B) Germany has a comparative advantage in producing wine
C) Neither country has a comparative advantage in producing wine
D) Germany can produce machines at a lower opportunity cost than France
 Refer to the table above. Based on the given information, we see that:
Refer to the table above. Based on the given information, we see that:A) France has a comparative advantage in producing wine
B) Germany has a comparative advantage in producing wine
C) Neither country has a comparative advantage in producing wine
D) Germany can produce machines at a lower opportunity cost than France

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Nation Alpha can produce employing all its available resources either 800 units of chemicals or 1,600 units of clothing. Nation Beta can produce either 200 units of chemicals or 800 units of clothing:
A) Nation Alpha has a comparative advantage in producing clothing
B) Nation Beta has a comparative advantage in producing chemicals
C) Nation Alpha has a comparative advantage in producing chemicals
D) Nation Beta is the high-cost producer of clothing
A) Nation Alpha has a comparative advantage in producing clothing
B) Nation Beta has a comparative advantage in producing chemicals
C) Nation Alpha has a comparative advantage in producing chemicals
D) Nation Beta is the high-cost producer of clothing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The table below shows labor-productivity figures in two countries facing constant costs:  Refer to the table above. Based on the data provided, it can be deduced that:
Refer to the table above. Based on the data provided, it can be deduced that:
A) Country A has the absolute advantage in producing both meat and houses
B) Country B has the absolute advantage in producing both meat and houses
C) Country A has a comparative advantage in producing both meat and houses
D) Country B has a comparative advantage in producing both meat and houses
 Refer to the table above. Based on the data provided, it can be deduced that:
Refer to the table above. Based on the data provided, it can be deduced that:A) Country A has the absolute advantage in producing both meat and houses
B) Country B has the absolute advantage in producing both meat and houses
C) Country A has a comparative advantage in producing both meat and houses
D) Country B has a comparative advantage in producing both meat and houses

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The productivity table given below shows how many bushels of either wheat or rice can be produced in India and Canada with 1 unit of input. To achieve gains from specialization and trade: 
A) India should export rice to Canada and import Canadian wheat
B) India should export wheat to Canada and import Canadian rice
C) Canada should produce both wheat and rice and not trade with India
D) India cannot offer any benefits to Canada from trading with her

A) India should export rice to Canada and import Canadian wheat
B) India should export wheat to Canada and import Canadian rice
C) Canada should produce both wheat and rice and not trade with India
D) India cannot offer any benefits to Canada from trading with her

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The domestic opportunity cost of producing a television in the United States is 20 bushels of wheat. In Korea, the domestic opportunity cost of producing a television is 10 bushels of wheat. In this case:
A) Korea has a comparative advantage in the production of wheat
B) The United States has a comparative advantage in the production of televisions
C) Mutual gains from trade can be obtained if the United States imports televisions from Korea and Korea imports wheat from the United States
D) Mutual gains from trade can be obtained if the United States imports wheat from Korea and Korea imports televisions from the United States
A) Korea has a comparative advantage in the production of wheat
B) The United States has a comparative advantage in the production of televisions
C) Mutual gains from trade can be obtained if the United States imports televisions from Korea and Korea imports wheat from the United States
D) Mutual gains from trade can be obtained if the United States imports wheat from Korea and Korea imports televisions from the United States

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
In a two-nation world, comparative advantage in the production of a particular product means that one nation can produce:
A) The product with fewer inputs than the other nation
B) The product at lower average cost than the other nation
C) The product at a lower domestic opportunity cost than the other nation
D) More of the product than the other nation
A) The product with fewer inputs than the other nation
B) The product at lower average cost than the other nation
C) The product at a lower domestic opportunity cost than the other nation
D) More of the product than the other nation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
If Countries A and B produce only either rubber bands or paper clips, their maximum outputs are shown in the production possibilities schedules below:  In country A the opportunity cost of 1 paper clip is:
In country A the opportunity cost of 1 paper clip is:
A) 2 rubber bands
B) 1 rubber band
C) 1/2 rubber band
D) 1/4 rubber band
 In country A the opportunity cost of 1 paper clip is:
In country A the opportunity cost of 1 paper clip is:A) 2 rubber bands
B) 1 rubber band
C) 1/2 rubber band
D) 1/4 rubber band

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The table below shows the output (either machines or wine) that each unit of input in France and Germany can produce:  Refer to the table above. Based on the given information, we see that:
Refer to the table above. Based on the given information, we see that:
A) France has an absolute advantage over Germany in producing either output
B) Germany has an absolute disadvantage in producing wine
C) Germany has no absolute advantage over France in producing either output
D) France will see no economic basis for trading with Germany
 Refer to the table above. Based on the given information, we see that:
Refer to the table above. Based on the given information, we see that:A) France has an absolute advantage over Germany in producing either output
B) Germany has an absolute disadvantage in producing wine
C) Germany has no absolute advantage over France in producing either output
D) France will see no economic basis for trading with Germany

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
In a two-nation, two-good world, which of the following statements is true?
A) One nation cannot possibly have an absolute advantage over the other nation in both products
B) If one nation as the comparative advantage in one product, then the other nation would have the comparative advantage in the other product
C) One nation will always have the comparative advantage over the other nation in one of the products
D) If one nation has the absolute advantage in one product, then the other nation would have the absolute advantage in the other product
A) One nation cannot possibly have an absolute advantage over the other nation in both products
B) If one nation as the comparative advantage in one product, then the other nation would have the comparative advantage in the other product
C) One nation will always have the comparative advantage over the other nation in one of the products
D) If one nation has the absolute advantage in one product, then the other nation would have the absolute advantage in the other product

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Given the following maximum-output alternatives for Brazil and Poland, it can be seen that if the two nations open up trade with each other, then: 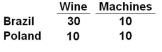
A) Brazil will specialize in producing machines, and import wine
B) Poland will specialize in producing machines, and import wine
C) Poland will export wine
D) Brazil will not gain from specializing and trading, but Poland will gain

A) Brazil will specialize in producing machines, and import wine
B) Poland will specialize in producing machines, and import wine
C) Poland will export wine
D) Brazil will not gain from specializing and trading, but Poland will gain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The production possibilities for country X are either 6,000 bushels of soybeans or 10,000 bushels of wheat. The production possibilities for country Y are either 2,000 bushels of soybeans or 4,000 bushels of wheat. Which of the following is true?
A) Country Y should specialize in the growing of soybeans according to the principle of comparative advantage
B) Country X is the least cost producer of wheat
C) The domestic opportunity cost of wheat production is lower in country Y
D) The high cost producer of soybeans is country X
A) Country Y should specialize in the growing of soybeans according to the principle of comparative advantage
B) Country X is the least cost producer of wheat
C) The domestic opportunity cost of wheat production is lower in country Y
D) The high cost producer of soybeans is country X

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Nation Alpha has a comparative advantage in product X and nation Beta has a comparative advantage in product Y. Trade in the two products will only benefit the two nations if:
A) The exchange ratio of X for Y is fixed
B) The terms of trade increase in both nations
C) There is excess capacity in both economies
D) The prices charged for X and Y reflect their domestic opportunity costs
A) The exchange ratio of X for Y is fixed
B) The terms of trade increase in both nations
C) There is excess capacity in both economies
D) The prices charged for X and Y reflect their domestic opportunity costs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Autos and chemicals are in million of units in the following production possibilities tables: 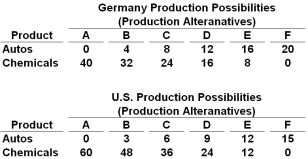 Refer to the tables above. If Germany and the United States engage in trade, the mutually-beneficial terms of trade will be between:
Refer to the tables above. If Germany and the United States engage in trade, the mutually-beneficial terms of trade will be between:
A) 3 and 4 units of autos for 1 unit of chemicals
B) 2 and 4 units of autos for 1 unit of chemicals
C) 2 and 4 units of chemicals for 1 unit of autos
D) 0.33 and 0.5 units of autos for 1 unit of chemicals
 Refer to the tables above. If Germany and the United States engage in trade, the mutually-beneficial terms of trade will be between:
Refer to the tables above. If Germany and the United States engage in trade, the mutually-beneficial terms of trade will be between:A) 3 and 4 units of autos for 1 unit of chemicals
B) 2 and 4 units of autos for 1 unit of chemicals
C) 2 and 4 units of chemicals for 1 unit of autos
D) 0.33 and 0.5 units of autos for 1 unit of chemicals

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Use the following table to answer the question below for Country Y. Column 1 is the price of a product. Column 2 is the quantity demanded domestically (Qdd) and Column 3 is the quantity supplied domestically (Qsd). 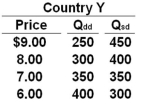 Refer to the table above. If the world price of the product is $6, then Country Y will:
Refer to the table above. If the world price of the product is $6, then Country Y will:
A) Export 100 units of the product
B) Import 100 units of the product
C) Exports of 300 units of the product
D) Imports of 400 units of the product
 Refer to the table above. If the world price of the product is $6, then Country Y will:
Refer to the table above. If the world price of the product is $6, then Country Y will:A) Export 100 units of the product
B) Import 100 units of the product
C) Exports of 300 units of the product
D) Imports of 400 units of the product

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Use the following table for Country X to answer the question below. Column 1 of the table is the price of a product. Column 2 is the quantity demanded domestically (Qdd) and Column 3 is the quantity supplied domestically (Qsd). 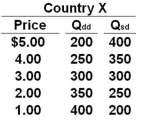 Refer to the table above. If the world price is $5.00, there will be:
Refer to the table above. If the world price is $5.00, there will be:
A) A domestic surplus of 100 units that will be exported
B) A domestic shortage of 100 units that will be imported
C) A domestic surplus of 200 units that will be exported
D) Neither a domestic surplus nor a shortage
 Refer to the table above. If the world price is $5.00, there will be:
Refer to the table above. If the world price is $5.00, there will be:A) A domestic surplus of 100 units that will be exported
B) A domestic shortage of 100 units that will be imported
C) A domestic surplus of 200 units that will be exported
D) Neither a domestic surplus nor a shortage

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
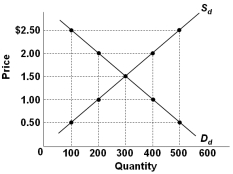 Refer to the graph above showing the domestic demand and supply curves for a specific product in a hypothetical nation called Econland. If the world price for this product is $2.00, then Econland will:
Refer to the graph above showing the domestic demand and supply curves for a specific product in a hypothetical nation called Econland. If the world price for this product is $2.00, then Econland will:A) Export 200 units
B) Export 400 units
C) Import 200 units
D) Import 400 units

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Autos and chemicals are in million of units in the following production possibilities tables: 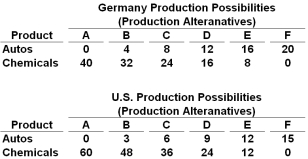 Refer to the tables above. Suppose that each nation specialized in producing the product for which it has a comparative advantage, and the terms of trade were set at 3 units of chemicals for 1 unit of autos. In this case, Germany could obtain and consume a maximum combination of 8 million units of autos and:
Refer to the tables above. Suppose that each nation specialized in producing the product for which it has a comparative advantage, and the terms of trade were set at 3 units of chemicals for 1 unit of autos. In this case, Germany could obtain and consume a maximum combination of 8 million units of autos and:
A) 12 million units of chemicals
B) 24 million units of chemicals
C) 36 million units of chemicals
D) 48 million units of chemicals
 Refer to the tables above. Suppose that each nation specialized in producing the product for which it has a comparative advantage, and the terms of trade were set at 3 units of chemicals for 1 unit of autos. In this case, Germany could obtain and consume a maximum combination of 8 million units of autos and:
Refer to the tables above. Suppose that each nation specialized in producing the product for which it has a comparative advantage, and the terms of trade were set at 3 units of chemicals for 1 unit of autos. In this case, Germany could obtain and consume a maximum combination of 8 million units of autos and:A) 12 million units of chemicals
B) 24 million units of chemicals
C) 36 million units of chemicals
D) 48 million units of chemicals

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which of the following statements is true?
A) Comparative advantage means that total world output will be greatest when each good is produced by the nation that has the highest domestic opportunity cost of producing it
B) Comparative advantage means that a nation can gain from trade only if it has a lower labor productivity than its trading partner
C) Specialization will be complete among nations when opportunity costs increase as the nations produce more of a particular product
D) Specialization will be less than complete among nations when opportunity costs increase as the nations produce more of a particular product
A) Comparative advantage means that total world output will be greatest when each good is produced by the nation that has the highest domestic opportunity cost of producing it
B) Comparative advantage means that a nation can gain from trade only if it has a lower labor productivity than its trading partner
C) Specialization will be complete among nations when opportunity costs increase as the nations produce more of a particular product
D) Specialization will be less than complete among nations when opportunity costs increase as the nations produce more of a particular product

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Suppose the world economy is composed of just two countries: Italy and Greece. Each can produce steel or chemicals, but at different levels of economic efficiency. The production possibilities curves for the two countries are shown in the graphs below. 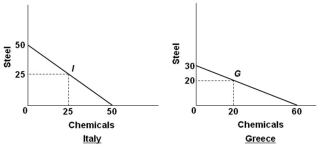 Refer to the graphs and information above. It can be deduced that:
Refer to the graphs and information above. It can be deduced that:
A) Greece has a comparative advantage in chemicals
B) Greece has the absolute advantage in both products
C) Italy has a comparative advantage in chemicals
D) It is more costly in terms of resources to produce steel in Italy
 Refer to the graphs and information above. It can be deduced that:
Refer to the graphs and information above. It can be deduced that:A) Greece has a comparative advantage in chemicals
B) Greece has the absolute advantage in both products
C) Italy has a comparative advantage in chemicals
D) It is more costly in terms of resources to produce steel in Italy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Answer the following question based on the data provided in the tables below for two hypothetical nations, Wat and Xat. The nations have the production possibilities for rice and corn given in the following table: 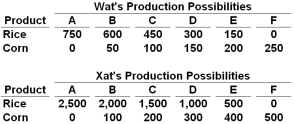 Refer to the data above. The mutually-beneficial terms of trade will be:
Refer to the data above. The mutually-beneficial terms of trade will be:
A) Less than 2 units of rice for 1 unit of corn
B) Greater than 4 units of rice for 1 unit of corn
C) Between 3 and 5 units of corn for 1 unit of rice
D) Between 3 and 5 units of rice for 1 unit of corn
 Refer to the data above. The mutually-beneficial terms of trade will be:
Refer to the data above. The mutually-beneficial terms of trade will be:A) Less than 2 units of rice for 1 unit of corn
B) Greater than 4 units of rice for 1 unit of corn
C) Between 3 and 5 units of corn for 1 unit of rice
D) Between 3 and 5 units of rice for 1 unit of corn

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Suppose the world economy is composed of just two countries: Italy and Greece. Each can produce steel or chemicals, but at different levels of economic efficiency. The production possibilities curves for the two countries are shown in the graphs below. 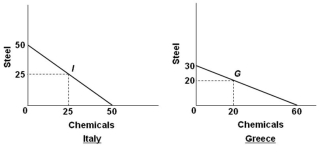 Refer to the graphs and information above. Assume that prior to specialization and trade, Italy and Greece preferred points I and G on their respective production possibilities curves. As a result of complete specialization according to comparative advantage, the resulting gains in total output will be:
Refer to the graphs and information above. Assume that prior to specialization and trade, Italy and Greece preferred points I and G on their respective production possibilities curves. As a result of complete specialization according to comparative advantage, the resulting gains in total output will be:
A) 5 steel and 15 chemicals
B) 10 chemicals
C) 15 steel and 5 chemicals
D) 25 steel
 Refer to the graphs and information above. Assume that prior to specialization and trade, Italy and Greece preferred points I and G on their respective production possibilities curves. As a result of complete specialization according to comparative advantage, the resulting gains in total output will be:
Refer to the graphs and information above. Assume that prior to specialization and trade, Italy and Greece preferred points I and G on their respective production possibilities curves. As a result of complete specialization according to comparative advantage, the resulting gains in total output will be:A) 5 steel and 15 chemicals
B) 10 chemicals
C) 15 steel and 5 chemicals
D) 25 steel

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Use the following table to answer the question below for Country Y. Column 1 is the price of a product. Column 2 is the quantity demanded domestically (Qdd) and Column 3 is the quantity supplied domestically (Qsd). 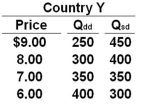 Refer to the table above. At what price will Country Y export 100 units of the product?
Refer to the table above. At what price will Country Y export 100 units of the product?
A) $9.00
B) $8.00
C) $7.00
D) $6.00
 Refer to the table above. At what price will Country Y export 100 units of the product?
Refer to the table above. At what price will Country Y export 100 units of the product?A) $9.00
B) $8.00
C) $7.00
D) $6.00

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
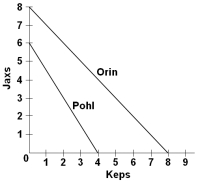 The graph above shows the production possibilities curves for two hypothetical nations, Orin and Pohl, which each make two hypothetical products, jaxs and keps. Which of the following statements is correct?
The graph above shows the production possibilities curves for two hypothetical nations, Orin and Pohl, which each make two hypothetical products, jaxs and keps. Which of the following statements is correct?A) Orin has a comparative advantage in both jaxs and keps
B) Pohl has a comparative advantage in jaxs
C) The opportunity cost of making jaxs is lower in Orin than in Pohl
D) Orin is more efficient than Pohl

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Suppose the world economy is composed of just two countries: Italy and Greece. Each can produce steel or chemicals, but at different levels of economic efficiency. The production possibilities curves for the two countries are shown in the graphs below. 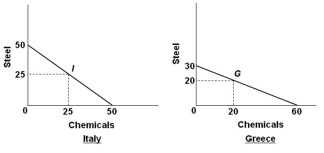 Refer to the graphs and information above. The assumption made about the domestic production opportunity costs in both countries is that they are:
Refer to the graphs and information above. The assumption made about the domestic production opportunity costs in both countries is that they are:
A) Constant
B) Variable
C) Increasing
D) Decreasing
 Refer to the graphs and information above. The assumption made about the domestic production opportunity costs in both countries is that they are:
Refer to the graphs and information above. The assumption made about the domestic production opportunity costs in both countries is that they are:A) Constant
B) Variable
C) Increasing
D) Decreasing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Autos and chemicals are in million of units in the following production possibilities tables: 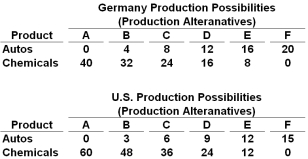 The data in the tables above suggest that production in:
The data in the tables above suggest that production in:
A) Germany is subject to increasing opportunity costs and the United States to constant opportunity costs
B) The United States is subject to increasing opportunity costs and Germany to constant opportunity costs
C) Both Germany and the United States are subject to constant opportunity costs
D) Both Germany and the United States are subject to increasing opportunity costs
 The data in the tables above suggest that production in:
The data in the tables above suggest that production in:A) Germany is subject to increasing opportunity costs and the United States to constant opportunity costs
B) The United States is subject to increasing opportunity costs and Germany to constant opportunity costs
C) Both Germany and the United States are subject to constant opportunity costs
D) Both Germany and the United States are subject to increasing opportunity costs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Use the following table for Country X to answer the question below. Column 1 of the table is the price of a product. Column 2 is the quantity demanded domestically (Qdd) and Column 3 is the quantity supplied domestically (Qsd). 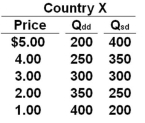 Refer to the table above. At what price will Country X import 100 units of the product?
Refer to the table above. At what price will Country X import 100 units of the product?
A) $4.00
B) $3.00
C) $2.00
D) $1.00
 Refer to the table above. At what price will Country X import 100 units of the product?
Refer to the table above. At what price will Country X import 100 units of the product?A) $4.00
B) $3.00
C) $2.00
D) $1.00

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Suppose the world economy is composed of just two countries: Italy and Greece. Each can produce steel or chemicals, but at different levels of economic efficiency. The production possibilities curves for the two countries are shown in the graphs below. 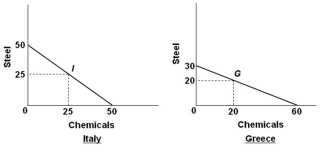 Refer to the graphs and information above. If Italy and Greece should open up trade with each other, which of the following terms of trade is mutually beneficial?
Refer to the graphs and information above. If Italy and Greece should open up trade with each other, which of the following terms of trade is mutually beneficial?
A) 1 ton of chemicals = 1 ton of steel
B) 2 tons of chemicals = 1 ton of steel
C) 5 tons of chemicals = 2 tons of steel
D) 9 tons of chemicals = 5 tons of steel
 Refer to the graphs and information above. If Italy and Greece should open up trade with each other, which of the following terms of trade is mutually beneficial?
Refer to the graphs and information above. If Italy and Greece should open up trade with each other, which of the following terms of trade is mutually beneficial?A) 1 ton of chemicals = 1 ton of steel
B) 2 tons of chemicals = 1 ton of steel
C) 5 tons of chemicals = 2 tons of steel
D) 9 tons of chemicals = 5 tons of steel

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Use the following table for Country X to answer the question below. Column 1 of the table is the price of a product. Column 2 is the quantity demanded domestically (Qdd) and Column 3 is the quantity supplied domestically (Qsd). 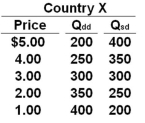 Refer to the table above. If Country X opens itself up to international trade, at what world price will it begin importing some units of the product?
Refer to the table above. If Country X opens itself up to international trade, at what world price will it begin importing some units of the product?
A) Any price below $5.00
B) Any price above $5.00
C) Any price below $3.00
D) Any price above $3.00
 Refer to the table above. If Country X opens itself up to international trade, at what world price will it begin importing some units of the product?
Refer to the table above. If Country X opens itself up to international trade, at what world price will it begin importing some units of the product?A) Any price below $5.00
B) Any price above $5.00
C) Any price below $3.00
D) Any price above $3.00

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Answer the following question based on the data provided in the tables below for two hypothetical nations, Wat and Xat. The nations have the production possibilities for rice and corn given in the following table: 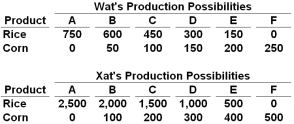 Refer to the data above. Which of the following statements about the two nations is correct based on the principle of comparative advantage?
Refer to the data above. Which of the following statements about the two nations is correct based on the principle of comparative advantage?
A) Xat should specialize in the production of corn
B) Wat should specialize in the production of rice
C) Xat has a comparative advantage in the production of rice
D) Xat has a comparative advantage in the production of corn
 Refer to the data above. Which of the following statements about the two nations is correct based on the principle of comparative advantage?
Refer to the data above. Which of the following statements about the two nations is correct based on the principle of comparative advantage?A) Xat should specialize in the production of corn
B) Wat should specialize in the production of rice
C) Xat has a comparative advantage in the production of rice
D) Xat has a comparative advantage in the production of corn

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Use the following table for Country X to answer the question below. Column 1 of the table is the price of a product. Column 2 is the quantity demanded domestically (Qdd) and Column 3 is the quantity supplied domestically (Qsd). 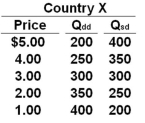 Refer to the table above. If Country X opens itself up to international trade and the world-market price of the product is $3, then Country X will:
Refer to the table above. If Country X opens itself up to international trade and the world-market price of the product is $3, then Country X will:
A) Neither export nor import the product
B) Export some units of the product
C) Import some units of the product
D) Not produce the product
 Refer to the table above. If Country X opens itself up to international trade and the world-market price of the product is $3, then Country X will:
Refer to the table above. If Country X opens itself up to international trade and the world-market price of the product is $3, then Country X will:A) Neither export nor import the product
B) Export some units of the product
C) Import some units of the product
D) Not produce the product

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
In a world with two products, wheat (W) and coffee (C), nation Alpha produces wheat and nation Beta produces coffee. Nation Alpha prefers an exchange rate of 1W = 2C and nation Beta prefers an exchange rate of 1W = 1C. The exchange rate preferred by nation:
A) Alpha will prevail if world demand for coffee is great relative to its supply
B) Alpha will prevail if world demand for wheat is weak relative to its supply
C) Beta will prevail if world demand for coffee is great relative to its supply
D) Beta will prevail if world demand for wheat is great relative to its supply
A) Alpha will prevail if world demand for coffee is great relative to its supply
B) Alpha will prevail if world demand for wheat is weak relative to its supply
C) Beta will prevail if world demand for coffee is great relative to its supply
D) Beta will prevail if world demand for wheat is great relative to its supply

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Use the following table for Country X to answer the question below. Column 1 of the table is the price of a product. Column 2 is the quantity demanded domestically (Qdd) and Column 3 is the quantity supplied domestically (Qsd). 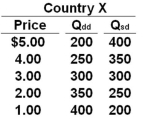 Refer to the table above. If Country X opens itself up to international trade, at what world price will it begin exporting some units of the product?
Refer to the table above. If Country X opens itself up to international trade, at what world price will it begin exporting some units of the product?
A) Any price below $1.00
B) Any price above $1.00
C) Any price below $3.00
D) Any price above $3.00
 Refer to the table above. If Country X opens itself up to international trade, at what world price will it begin exporting some units of the product?
Refer to the table above. If Country X opens itself up to international trade, at what world price will it begin exporting some units of the product?A) Any price below $1.00
B) Any price above $1.00
C) Any price below $3.00
D) Any price above $3.00

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
An example of a nontariff barrier would be:
A) A minimum limit on the quantity of imports
B) Excessive licensing requirements
C) A tax on an imported product
D) Voluntary export restraints
A) A minimum limit on the quantity of imports
B) Excessive licensing requirements
C) A tax on an imported product
D) Voluntary export restraints

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
An excise tax on imported items is known as a(n):
A) Quota
B) Tariff
C) Export restriction
D) Price ceiling
A) Quota
B) Tariff
C) Export restriction
D) Price ceiling

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
If the United States government were to impose a quota on wristwatches imported from Switzerland, then the:
A) Price of wristwatches in the United States would decrease and total quantity consumed (domestic and imported) will increase
B) Prices of wristwatches in Switzerland would rise and that's how Switzerland would be hurt by the quota
C) Price of wristwatches in the United States would remain the same, but the quantity will fall as imports fall
D) Total quantity of wristwatches (domestic and imported) purchased would decline as prices rise
A) Price of wristwatches in the United States would decrease and total quantity consumed (domestic and imported) will increase
B) Prices of wristwatches in Switzerland would rise and that's how Switzerland would be hurt by the quota
C) Price of wristwatches in the United States would remain the same, but the quantity will fall as imports fall
D) Total quantity of wristwatches (domestic and imported) purchased would decline as prices rise

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
A tariff is a:
A) Tax
B) Price ceiling
C) Quantity limit
D) Subsidy
A) Tax
B) Price ceiling
C) Quantity limit
D) Subsidy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
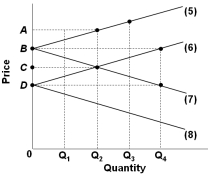 Refer to the graph above which shows the import demand and export supply curves for two nations that produce a certain product. Lines 6 and 8 apply to one nation and represent, respectively:
Refer to the graph above which shows the import demand and export supply curves for two nations that produce a certain product. Lines 6 and 8 apply to one nation and represent, respectively:A) Import demand and export supply
B) Export supply and import demand
C) Domestic supply and domestic demand
D) Domestic demand and domestic supply

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
If a nation agrees to set an upper limit on the total amount of a product that it exports to another nation, then this situation would be an example of:
A) An import quota
B) A revenue tariff
C) A protective tariff
D) A voluntary export restriction
A) An import quota
B) A revenue tariff
C) A protective tariff
D) A voluntary export restriction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Which of the following statements best describes a protective tariff?
A) An excise tax that is usually applied to products which are not produced domestically in order to raise revenues for government
B) An excise tax that is designed to put foreign producers at a competitive disadvantage in selling in domestic markets
C) A specification of the maximum amount of a product that may be imported in any period of time which is often used to protect domestic producers of a product
D) Such activities as restricting the issuance of licenses for imported products or setting unreasonable standards for quality or safety in order to restrict imports and protect domestic markets
A) An excise tax that is usually applied to products which are not produced domestically in order to raise revenues for government
B) An excise tax that is designed to put foreign producers at a competitive disadvantage in selling in domestic markets
C) A specification of the maximum amount of a product that may be imported in any period of time which is often used to protect domestic producers of a product
D) Such activities as restricting the issuance of licenses for imported products or setting unreasonable standards for quality or safety in order to restrict imports and protect domestic markets

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
An import-licensing requirement, or import restrictions pertaining to the product quality and safety, are examples of:
A) Protective tariffs
B) Nontariff barriers
C) Voluntary export restrictions
D) Quotas on imported products
A) Protective tariffs
B) Nontariff barriers
C) Voluntary export restrictions
D) Quotas on imported products

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
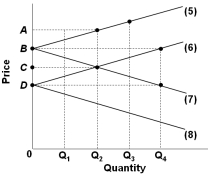 Refer to the graph above which shows the import demand and export supply curves for two nations that produce a certain product. In this two-nation model, the equilibrium world price and quantity will be:
Refer to the graph above which shows the import demand and export supply curves for two nations that produce a certain product. In this two-nation model, the equilibrium world price and quantity will be:A) A and Q2
B) B and Q4
C) C and Q2
D) D and Q4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
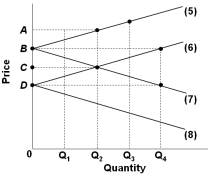 Refer to the graph above which shows the import demand and export supply curves for two nations that produce a certain product. The import demand curves for the two nations are represented by lines:
Refer to the graph above which shows the import demand and export supply curves for two nations that produce a certain product. The import demand curves for the two nations are represented by lines:A) 5 and 6
B) 5 and 7
C) 6 and 8
D) 7 and 8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
A maximum limit set on the amount of a specific good that may be imported into a country over a given period of time is called a:
A) Tariff
B) Quota
C) Nontariff barrier
D) Voluntary export restriction
A) Tariff
B) Quota
C) Nontariff barrier
D) Voluntary export restriction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
The "Buy American" policy is equivalent to a(n):
A) Tariff
B) Quota
C) Export subsidy
D) Voluntary export restriction
A) Tariff
B) Quota
C) Export subsidy
D) Voluntary export restriction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
If the world price of a product rises relative to the domestic price in a trading nation, then for that product:
A) Exports and imports will increase
B) Exports and imports will decrease
C) Exports will increase and imports will decrease
D) Imports will increase and exports will decrease
A) Exports and imports will increase
B) Exports and imports will decrease
C) Exports will increase and imports will decrease
D) Imports will increase and exports will decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The imposition of a tariff on a product is least likely to result in a(n):
A) Increase in the efficiency in the domestic industry producing the product
B) Increase in the price of the product
C) Decrease in the quantity of imports
D) Decrease in the real incomes of workers in other industries
A) Increase in the efficiency in the domestic industry producing the product
B) Increase in the price of the product
C) Decrease in the quantity of imports
D) Decrease in the real incomes of workers in other industries

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
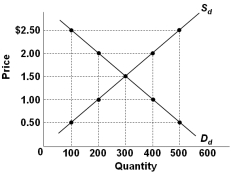 Refer to the graph above showing the domestic demand and supply curves for a specific product in a hypothetical nation called Econland. When the world price for this product is $0.50, Econland will:
Refer to the graph above showing the domestic demand and supply curves for a specific product in a hypothetical nation called Econland. When the world price for this product is $0.50, Econland will:A) Import 500 units
B) Import 100 units
C) Import 400 units
D) Export 100 units

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
An excise tax that is applied to an imported product which is not at all produced domestically is called a(n):
A) Protective tariff
B) Revenue tariff
C) Import quota
D) Nontariff barrier
A) Protective tariff
B) Revenue tariff
C) Import quota
D) Nontariff barrier

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
If a nation exports a product, then the price of that product in the nation:
A) Will rise above the domestic (no-trade) equilibrium price
B) Will fall below the domestic (no-trade) equilibrium price
C) Will remain the same as the domestic (no-trade) equilibrium price
D) May either rise or fall, depending on the product
A) Will rise above the domestic (no-trade) equilibrium price
B) Will fall below the domestic (no-trade) equilibrium price
C) Will remain the same as the domestic (no-trade) equilibrium price
D) May either rise or fall, depending on the product

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
When a nation starts opening up to international trade, it will see falling prices for:
A) Goods that it exports
B) Goods that it imports
C) Goods that it has a comparative advantage in
D) All goods traded
A) Goods that it exports
B) Goods that it imports
C) Goods that it has a comparative advantage in
D) All goods traded

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
A key difference between import quotas and voluntary export restraints (VERs) is that the:
A) Domestic government administers the former, whereas the foreign government administers the latter
B) Foreign government administers the former, whereas the domestic government administers the latter
C) One is a tax, whereas the other is a quantity limit
D) One raises the price of the imported product involved, whereas the other one does not
A) Domestic government administers the former, whereas the foreign government administers the latter
B) Foreign government administers the former, whereas the domestic government administers the latter
C) One is a tax, whereas the other is a quantity limit
D) One raises the price of the imported product involved, whereas the other one does not

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
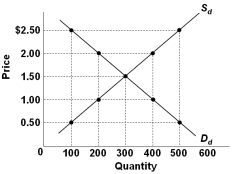 Refer to the graph above showing the domestic demand and supply curves for a specific product in a hypothetical nation called Econland. At what price will Econland be neither importing nor exporting the product?
Refer to the graph above showing the domestic demand and supply curves for a specific product in a hypothetical nation called Econland. At what price will Econland be neither importing nor exporting the product?A) $1.00
B) $1.50
C) $2.00
D) $2.50

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



