Deck 19: Current Issues in Macro Theory and Policy
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/134
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 19: Current Issues in Macro Theory and Policy
1
The equation of exchange suggests that if the velocity of money and the quantity of goods and services are held constant, a(n):
A) Decrease in the money supply will increase the price level
B) Increase in the money supply will decrease the price level
C) Increase in the money supply will increase the price level
D) Decrease in the money supply will have no effect on the price level
A) Decrease in the money supply will increase the price level
B) Increase in the money supply will decrease the price level
C) Increase in the money supply will increase the price level
D) Decrease in the money supply will have no effect on the price level
Increase in the money supply will increase the price level
2
In the mainstream view, the economic instability brought about by "oil shocks" works through changes in:
A) Aggregate demand
B) Wage and price inflexibility
C) Money supply
D) Aggregate supply
A) Aggregate demand
B) Wage and price inflexibility
C) Money supply
D) Aggregate supply
Aggregate supply
3
According to mainstream economists the basic determinant of real output, employment, and the price level is:
A) Information and people's expectations
B) The level of aggregate expenditures
C) The incentive to work, save, and invest
D) The supply of money
A) Information and people's expectations
B) The level of aggregate expenditures
C) The incentive to work, save, and invest
D) The supply of money
The level of aggregate expenditures
4
The equation of exchange indicates that:
A) MQ equals VP
B) The velocity of money and the supply of money vary proportionately with one another
C) Other things being equal, an increase in V will increase P and/or Q
D) Other things being equal, M and P are inversely related
A) MQ equals VP
B) The velocity of money and the supply of money vary proportionately with one another
C) Other things being equal, an increase in V will increase P and/or Q
D) Other things being equal, M and P are inversely related

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
From the mainstream perspective, instability in the economy is due to:
A) Price flexibility, and shocks to either aggregate demand or aggregate supply
B) Price stickiness, and shocks to either aggregate demand or aggregate supply
C) Price flexibility, and government policies and regulation
D) Price stickiness, and government policies and regulation
A) Price flexibility, and shocks to either aggregate demand or aggregate supply
B) Price stickiness, and shocks to either aggregate demand or aggregate supply
C) Price flexibility, and government policies and regulation
D) Price stickiness, and government policies and regulation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
From a monetarist perspective, instability in the macro economy arises from:
A) Secular trends in the economy
B) The instability of velocity as a policy tool
C) Discretionary changes in monetary policy
D) The use of a monetary rule for monetary policy
A) Secular trends in the economy
B) The instability of velocity as a policy tool
C) Discretionary changes in monetary policy
D) The use of a monetary rule for monetary policy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
In the monetarist view:
A) Changes in investment spending are a major source of macroeconomic instability
B) Inappropriate monetary policy is a major source of macroeconomic stability
C) Adverse aggregate supply shocks are a major source of macroeconomic instability
D) The fact that prices and wages are flexible is a major source of macroeconomic instability
A) Changes in investment spending are a major source of macroeconomic instability
B) Inappropriate monetary policy is a major source of macroeconomic stability
C) Adverse aggregate supply shocks are a major source of macroeconomic instability
D) The fact that prices and wages are flexible is a major source of macroeconomic instability

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
In the mainstream view, one major source of instability in the macro economy is the volatility of:
A) Product prices
B) Investment spending
C) Consumer spending
D) Labor wages
A) Product prices
B) Investment spending
C) Consumer spending
D) Labor wages

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following is the basic equation underlying aggregate expenditures?
A) MV = PQ
B) AS = AD
C) Saving = Income - Consumption
D) Ca + Ig + Xn + G = GDP
A) MV = PQ
B) AS = AD
C) Saving = Income - Consumption
D) Ca + Ig + Xn + G = GDP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Mainstream economics views monetary policy as a:
A) Source of instability, similar to the view of monetarism
B) Stabilizing factor, similar to the view of monetarism
C) Source of instability, while monetarism views it as a stabilizing factor
D) Stabilizing factor, while monetarism views it as a source of instability
A) Source of instability, similar to the view of monetarism
B) Stabilizing factor, similar to the view of monetarism
C) Source of instability, while monetarism views it as a stabilizing factor
D) Stabilizing factor, while monetarism views it as a source of instability

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Given the equation of exchange, if V is stable, an increase in M will necessarily increase:
A) The demand for money
B) The price level
C) Nominal GDP
D) Real GDP
A) The demand for money
B) The price level
C) Nominal GDP
D) Real GDP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The equation of exchange is:
A) AS = AD
B) Saving = Income - Spending
C) MV = PQ
D) AD = C + Ig + G + Xn
A) AS = AD
B) Saving = Income - Spending
C) MV = PQ
D) AD = C + Ig + G + Xn

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Monetarists argue that the amount of money the public will want to hold depends primarily on the level of:
A) Nominal GDP
B) Investment
C) Consumption
D) Prices
A) Nominal GDP
B) Investment
C) Consumption
D) Prices

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
In the monetarist equation of exchange, MV is the monetarist counterpart of:
A) Money supply
B) Aggregate expenditures
C) Total saving
D) Government spending
A) Money supply
B) Aggregate expenditures
C) Total saving
D) Government spending

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The average number of times per year that a dollar bill is used to pay for final goods and services is the:
A) Monetary rule
B) Velocity of money
C) Asset demand for money
D) Transactions demand for money
A) Monetary rule
B) Velocity of money
C) Asset demand for money
D) Transactions demand for money

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Dividing nominal gross domestic product (GDP) by the money supply (M) is a way to obtain the:
A) Velocity of money
B) Monetary multiplier
C) Equation of exchange
D) Monetary rule
A) Velocity of money
B) Monetary multiplier
C) Equation of exchange
D) Monetary rule

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The view that changes in the money supply is the primary cause of change in real output and the price level is most closely associated with:
A) Rational expectations theory
B) Real business cycle theory
C) Mainstream economics
D) Monetarism
A) Rational expectations theory
B) Real business cycle theory
C) Mainstream economics
D) Monetarism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Monetarists argue that the relationship between:
A) The quantity of money the public wants to hold and the level of GDP is not stable
B) The quantity of money the public wants to hold and the level of GDP is stable
C) The quantity of money the public wants to hold and the level of saving is stable
D) Velocity and the interest rate varies directly
A) The quantity of money the public wants to hold and the level of GDP is not stable
B) The quantity of money the public wants to hold and the level of GDP is stable
C) The quantity of money the public wants to hold and the level of saving is stable
D) Velocity and the interest rate varies directly

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
In the strict monetarist view, a large increase in the money supply will have:
A) A large impact on the velocity of money and a large impact on nominal output
B) A large impact on the velocity of money and a small impact on nominal output
C) No effect on the velocity of money and a large impact on nominal output
D) No effect on the velocity of money and a small impact on the nominal output
A) A large impact on the velocity of money and a large impact on nominal output
B) A large impact on the velocity of money and a small impact on nominal output
C) No effect on the velocity of money and a large impact on nominal output
D) No effect on the velocity of money and a small impact on the nominal output

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
If the velocity of money remains unchanged and the economy is at full employment, then the equation of exchange predicts that a rise in the money supply will:
A) Increase prices
B) Increase interest rates
C) Increase real output
D) Decrease nominal GDP
A) Increase prices
B) Increase interest rates
C) Increase real output
D) Decrease nominal GDP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Within the aggregate demand-aggregate supply framework, monetarists argue that a change in aggregate:
A) Demand will have a large effect on the price level, but a temporary effect on output
B) Demand will have a small effect on the price level, but a permanent effect on output
C) Demand will have a large effect on the price level and a large effect on output
D) Supply will have a large effect on the price level, but a temporary effect on output
A) Demand will have a large effect on the price level, but a temporary effect on output
B) Demand will have a small effect on the price level, but a permanent effect on output
C) Demand will have a large effect on the price level and a large effect on output
D) Supply will have a large effect on the price level, but a temporary effect on output

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Real-business-cycle theory focuses on factors affecting:
A) Aggregate demand
B) Aggregate supply
C) The velocity of money
D) Consumer spending
A) Aggregate demand
B) Aggregate supply
C) The velocity of money
D) Consumer spending

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
If the amount of money in circulation is $8 billion and the value of total output is $40 billion in an economy, then the:
A) Velocity of money is 5
B) Money supply is $40 billion
C) Level of the price index is 320
D) Equilibrium level of GDP is $320 billion
A) Velocity of money is 5
B) Money supply is $40 billion
C) Level of the price index is 320
D) Equilibrium level of GDP is $320 billion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
If there is an unanticipated increase in aggregate demand, then according to new classical economics, the economy will self-correct with a(n):
A) Decrease in short-run aggregate supply, so output returns to its initial level, but the price level rises
B) Decrease in short-run aggregate supply, so output increases and the price level rises
C) Decrease in short-run aggregate supply, so output returns to its initial level and the price level falls
D) Increase in short-run aggregate supply, so output increases and the price level rises
A) Decrease in short-run aggregate supply, so output returns to its initial level, but the price level rises
B) Decrease in short-run aggregate supply, so output increases and the price level rises
C) Decrease in short-run aggregate supply, so output returns to its initial level and the price level falls
D) Increase in short-run aggregate supply, so output increases and the price level rises

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The idea that business fluctuations are primarily caused by factors affecting aggregate supply rather than aggregate demand is a central tenet of:
A) Efficiency wage theory
B) Real-business-cycle theory
C) Mainstream economics
D) Monetarism
A) Efficiency wage theory
B) Real-business-cycle theory
C) Mainstream economics
D) Monetarism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
If M is $800, P is $2, and Q is 1,200, then:
A) Aggregate expenditures will be $1,600
B) Aggregate expenditures will be $960,000
C) V must be 3
D) V must be 1.5
A) Aggregate expenditures will be $1,600
B) Aggregate expenditures will be $960,000
C) V must be 3
D) V must be 1.5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Assume that M is $200 billion and V is 6. If V increases by 15 percent, then, according to the monetarist equation, nominal GDP will have increased by:
A) $140 billion
B) $180 billion
C) $220 billion
D) $260 billion
A) $140 billion
B) $180 billion
C) $220 billion
D) $260 billion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
According to real-business-cycle theory, recessions are caused by:
A) Deviations of aggregate supply from long-term growth trends
B) Monetary factors affecting aggregate demand
C) People choosing leisure rather than work
D) A decline in the supply of money
A) Deviations of aggregate supply from long-term growth trends
B) Monetary factors affecting aggregate demand
C) People choosing leisure rather than work
D) A decline in the supply of money

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Real-business-cycle theory suggests that changes in:
A) Monetary policy is the single most important cause of macroeconomic instability
B) Investment spending will have a direct and significant effect on aggregate demand
C) Technology and resources affect productivity, and thus the long-run growth of aggregate supply
D) The velocity of money is gradual and predictable, and thus is able to accommodate the long-run changes in nominal GDP
A) Monetary policy is the single most important cause of macroeconomic instability
B) Investment spending will have a direct and significant effect on aggregate demand
C) Technology and resources affect productivity, and thus the long-run growth of aggregate supply
D) The velocity of money is gradual and predictable, and thus is able to accommodate the long-run changes in nominal GDP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
In real-business-cycle theory, changes in the:
A) Demand for money respond to changes in the supply of money
B) Supply of money respond to changes in the demand for money
C) Demand for money respond to changes in efficiency wages
D) Supply of money respond to changes in coordination failures
A) Demand for money respond to changes in the supply of money
B) Supply of money respond to changes in the demand for money
C) Demand for money respond to changes in efficiency wages
D) Supply of money respond to changes in coordination failures

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Assume monetary equilibrium exists; that is, the desired and actual supply of money are equal. Also assume that nominal GDP equals $960 billion and the money supply is $160 billion. From a strict monetarist view, an increase in the money supply by $12 billion will increase nominal GDP by:
A) $13 billion
B) $24 billion
C) $72 billion
D) $80 billion
A) $13 billion
B) $24 billion
C) $72 billion
D) $80 billion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
New classical economics suggests that in the long-run changes in aggregate demand will cause:
A) Only short-run changes in output and employment
B) Long-run changes in output and employment
C) Only short-run changes in the price level
D) No change in output and employment
A) Only short-run changes in output and employment
B) Long-run changes in output and employment
C) Only short-run changes in the price level
D) No change in output and employment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
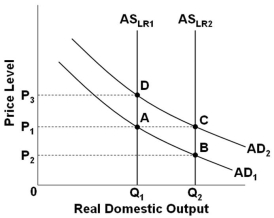 Refer to the graph above. Assume that the economy is in initial equilibrium where AD1 intersects ASLR1. If the economy experiences a change in technology that increases productivity and resources, then real-business-cycle theory would suggest that this macroeconomic instability would eventually produce a new equilibrium at point:
Refer to the graph above. Assume that the economy is in initial equilibrium where AD1 intersects ASLR1. If the economy experiences a change in technology that increases productivity and resources, then real-business-cycle theory would suggest that this macroeconomic instability would eventually produce a new equilibrium at point:A) B
B) C
C) D
D) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
In the view of real-business-cycle theory, an increase in the long-run aggregate supply would lead to a(n):
A) Increase in aggregate demand by an equal amount, so real output would increase and the price level would be unchanged
B) Increase in aggregate demand by an equal amount, so real output and the price level would increase
C) Decrease in aggregate demand, so real output would increase and the price level would decrease
D) Decrease in aggregate demand, so real output and the price level would increase
A) Increase in aggregate demand by an equal amount, so real output would increase and the price level would be unchanged
B) Increase in aggregate demand by an equal amount, so real output and the price level would increase
C) Decrease in aggregate demand, so real output would increase and the price level would decrease
D) Decrease in aggregate demand, so real output and the price level would increase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
If nominal GDP is $848 billion and the velocity of money is 4, then the:
A) Money supply is $170 billion
B) Money supply is $212 billion
C) Consumer price index is 340
D) Average level of prices is $170 billion
A) Money supply is $170 billion
B) Money supply is $212 billion
C) Consumer price index is 340
D) Average level of prices is $170 billion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Coordination failures occur when people lack some way to jointly coordinate their actions to reach a(n):
A) Unanticipated price level change
B) Fully-anticipated price level change
C) Mutually beneficial equilibrium
D) Insider-outsider relationship
A) Unanticipated price level change
B) Fully-anticipated price level change
C) Mutually beneficial equilibrium
D) Insider-outsider relationship

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Monetarists would argue that the severe recession of 2007-2009 was primarily caused by:
A) Adverse aggregate-supply shocks causing tremendous unemployment
B) Wide swings in investment expenditures driving erratic fluctuations in aggregate demand
C) Excessive money supply creating a bubble in some sectors of the economy
D) Too much deregulation of the financial sector in previous years
A) Adverse aggregate-supply shocks causing tremendous unemployment
B) Wide swings in investment expenditures driving erratic fluctuations in aggregate demand
C) Excessive money supply creating a bubble in some sectors of the economy
D) Too much deregulation of the financial sector in previous years

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
If the economy diverges from its full-employment output, new classical economics would suggest that:
A) A change in the velocity of money would be all that is needed to return it to its full-employment output
B) An improvement in insider-outsider relationships is all that is needed to return it to its full-employment output
C) An efficiency wage in the economy would return it to its full-employment output
D) Internal mechanisms within the economy would automatically return it to its full-employment output
A) A change in the velocity of money would be all that is needed to return it to its full-employment output
B) An improvement in insider-outsider relationships is all that is needed to return it to its full-employment output
C) An efficiency wage in the economy would return it to its full-employment output
D) Internal mechanisms within the economy would automatically return it to its full-employment output

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
If the money supply rises from $600 billion to $800 billion and nominal GDP stays unchanged at $4,800 billion, then the income velocity of money:
A) Rises by 33 percent
B) Falls by 33 percent
C) Rises from 6 to 8
D) Falls from 8 to 6
A) Rises by 33 percent
B) Falls by 33 percent
C) Rises from 6 to 8
D) Falls from 8 to 6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
If households and firms cut back on spending because they expect other households and firms to do so, and this self-fulfilling prophecy causes a recession, then this would be an example of:
A) Insider-outsider relationships
B) Efficiency wage theory
C) A coordination failure
D) A price-level surprise
A) Insider-outsider relationships
B) Efficiency wage theory
C) A coordination failure
D) A price-level surprise

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
A mainstream criticism of the rational expectations theory is that:
A) The theorists confuse correlation with causation in interpreting the empirical evidence
B) People do not make consistent forecasting errors which can be exploited by policy makers
C) Many markets are not purely competitive and do not adjust rapidly to changing market conditions
D) The data indicate that economic policy does not affect real GDP and employment
A) The theorists confuse correlation with causation in interpreting the empirical evidence
B) People do not make consistent forecasting errors which can be exploited by policy makers
C) Many markets are not purely competitive and do not adjust rapidly to changing market conditions
D) The data indicate that economic policy does not affect real GDP and employment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
From a rational expectations perspective, an easy money policy is likely to be completely:
A) Ineffective unless the increase in the money supply is unanticipated
B) Effective unless the increase in the money supply is unanticipated
C) Ineffective unless the increase in the money supply is anticipated
D) Effective unless the increase in the money supply is anticipated
A) Ineffective unless the increase in the money supply is unanticipated
B) Effective unless the increase in the money supply is unanticipated
C) Ineffective unless the increase in the money supply is anticipated
D) Effective unless the increase in the money supply is anticipated

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
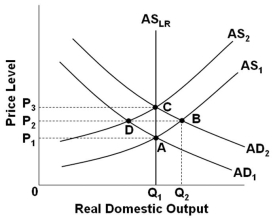 Refer to the graph above. Assume that the economy is in initial equilibrium where AD1 intersects AS1. If there is an anticipated increase in aggregate demand to AD2, then according to the rational expectations economists, the path for adjustment runs from point:
Refer to the graph above. Assume that the economy is in initial equilibrium where AD1 intersects AS1. If there is an anticipated increase in aggregate demand to AD2, then according to the rational expectations economists, the path for adjustment runs from point:A) A to B to C
B) A to D to C
C) A directly to C
D) A directly to B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Mainstream economists think that:
A) Market participants change their actions in response to anticipated price-level changes such that no change in real output occurs
B) The economy self-corrects when unanticipated events divert it from its full-employment level of real output
C) The downward inflexibility of wages and prices may leave the economy stuck in a costly recession for long periods
D) Significant changes in technology and resource availability cause macroeconomic instability
A) Market participants change their actions in response to anticipated price-level changes such that no change in real output occurs
B) The economy self-corrects when unanticipated events divert it from its full-employment level of real output
C) The downward inflexibility of wages and prices may leave the economy stuck in a costly recession for long periods
D) Significant changes in technology and resource availability cause macroeconomic instability

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
One of the basic assumptions of rational expectations theory is that:
A) People can anticipate the future effects of policy changes and the actions they take may offset the effects of economic policy
B) People are not able to assess the future effects of policy changes, so government can use economic policy effectively
C) Markets are not very competitive and fail to adjust very quickly to changes in demand and supply
D) People expect government to solve the major unemployment and inflation problems facing the nation and behave accordingly
A) People can anticipate the future effects of policy changes and the actions they take may offset the effects of economic policy
B) People are not able to assess the future effects of policy changes, so government can use economic policy effectively
C) Markets are not very competitive and fail to adjust very quickly to changes in demand and supply
D) People expect government to solve the major unemployment and inflation problems facing the nation and behave accordingly

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
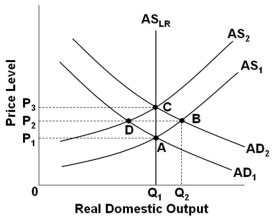 Refer to the graph above. Assume that the economy is in initial equilibrium where AD1 intersects AS1. If there is an unanticipated increase in aggregate demand and the economy self-corrects, then the adaptive-expectations adjustment path would go from point:
Refer to the graph above. Assume that the economy is in initial equilibrium where AD1 intersects AS1. If there is an unanticipated increase in aggregate demand and the economy self-corrects, then the adaptive-expectations adjustment path would go from point:A) A directly to B
B) A to B to C
C) B to A to D
D) A to B to C to D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
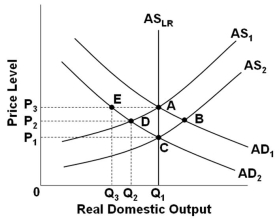 Refer to the graph above. Assume that the economy is in initial equilibrium where AD1 intersects AS1. If there is an anticipated decrease in aggregate demand to AD2, then according to rational expectations theory, the path for adjustment runs from point:
Refer to the graph above. Assume that the economy is in initial equilibrium where AD1 intersects AS1. If there is an anticipated decrease in aggregate demand to AD2, then according to rational expectations theory, the path for adjustment runs from point:A) A to B to C
B) A to D to C
C) A directly to C
D) A directly to D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Rational expectations theory considers the aggregate:
A) Demand curve to be vertical
B) Supply curve to be vertical
C) Supply curve to be horizontal
D) Demand curve to be horizontal
A) Demand curve to be vertical
B) Supply curve to be vertical
C) Supply curve to be horizontal
D) Demand curve to be horizontal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Which economic perspective typically views the market system as less than fully competitive, and therefore subject to macroeconomic instability?
A) Monetarism
B) Mainstream economics
C) Real business cycle theory
D) Rational expectations theory
A) Monetarism
B) Mainstream economics
C) Real business cycle theory
D) Rational expectations theory

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
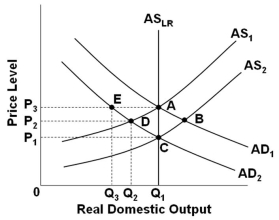 Refer to the graph above. Assume that the economy is in initial equilibrium where AD1 intersects AS1. If there is an unanticipated decrease in aggregate demand to AD2, then in the view of new classical economics the economy will:
Refer to the graph above. Assume that the economy is in initial equilibrium where AD1 intersects AS1. If there is an unanticipated decrease in aggregate demand to AD2, then in the view of new classical economics the economy will:A) Self-correct through a shift in AS, which brings output back to Q1
B) Self-correct through a shift in AD, which brings output back to Q1
C) Need the government to implement expansionary policy in order to bring output back to Q1
D) Need the government to implement contractionary policy in order to bring output back to Q1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Within the aggregate demand-aggregate supply framework, a strict interpretation of rational expectations theory suggests that a change in aggregate:
A) Demand will have a large effect on the price level, but a small effect on output
B) Demand will have a small effect on the price level, but a large effect on output
C) Demand will have a large effect on the price level, but no effect on output
D) Supply will have a large effect on the price level, but no effect on output
A) Demand will have a large effect on the price level, but a small effect on output
B) Demand will have a small effect on the price level, but a large effect on output
C) Demand will have a large effect on the price level, but no effect on output
D) Supply will have a large effect on the price level, but no effect on output

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
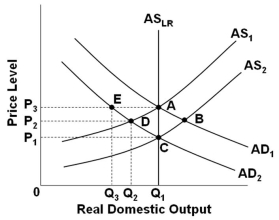 Refer to the graph above. Assume that the economy is in initial equilibrium where AD1 intersects AS1. If there is a decrease in aggregate demand to AD2, then according to mainstream economists, if prices are flexible and wages are not, this will result in an equilibrium at point:
Refer to the graph above. Assume that the economy is in initial equilibrium where AD1 intersects AS1. If there is a decrease in aggregate demand to AD2, then according to mainstream economists, if prices are flexible and wages are not, this will result in an equilibrium at point:A) B
B) C
C) D
D) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
In the rational expectations theory, a temporary change in real output could result from:
A) Anticipated price-level changes
B) A price-level surprise
C) A coordination failure
D) Insider-outsider relationships
A) Anticipated price-level changes
B) A price-level surprise
C) A coordination failure
D) Insider-outsider relationships

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
An efficiency wage is one that:
A) Increases the velocity of money
B) Minimizes the firm's labor cost per unit of output
C) Results from significant changes in technology and labor
D) Is imposed by government to guarantee workers a living wage
A) Increases the velocity of money
B) Minimizes the firm's labor cost per unit of output
C) Results from significant changes in technology and labor
D) Is imposed by government to guarantee workers a living wage

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which of the following contributes to the downward inflexibility of wages, according to mainstream economists?
A) Efficiency wages
B) A monetary rule
C) Price-level surprises
D) Coordination failures
A) Efficiency wages
B) A monetary rule
C) Price-level surprises
D) Coordination failures

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which view of the macro economy suggests that the speed of adjustment for self-correction would be very quick?
A) Monetarism
B) Mainstream economics
C) Supply-side economics
D) Rational expectations theory
A) Monetarism
B) Mainstream economics
C) Supply-side economics
D) Rational expectations theory

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Monetarists base their assessment of the speed of adjustment for self-correction in the economy on:
A) Adaptive expectations
B) Rational expectations
C) Coordination failures
D) Efficiency wages
A) Adaptive expectations
B) Rational expectations
C) Coordination failures
D) Efficiency wages

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
In the view of rational expectations theory:
A) People make economic forecasts that are based on insider-outsider relationships and self-fulfilling prophecies
B) People form beliefs about future economic outcomes that accurately reflect the likelihood that those outcomes will occur
C) People form their expectations on present realities and only gradually change their expectations as experience unfolds
D) The economy does not respond quickly to changes in prices, which causes a mis-allocation of economic resources
A) People make economic forecasts that are based on insider-outsider relationships and self-fulfilling prophecies
B) People form beliefs about future economic outcomes that accurately reflect the likelihood that those outcomes will occur
C) People form their expectations on present realities and only gradually change their expectations as experience unfolds
D) The economy does not respond quickly to changes in prices, which causes a mis-allocation of economic resources

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
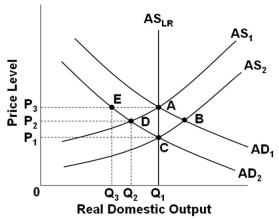 Refer to the above graph. Assume that the economy is in initial equilibrium where AD1 intersects AS1. If there is a decrease in aggregate demand to AD2, then according to mainstream economists, if prices and wages are not flexible, this will result in an equilibrium at point:
Refer to the above graph. Assume that the economy is in initial equilibrium where AD1 intersects AS1. If there is a decrease in aggregate demand to AD2, then according to mainstream economists, if prices and wages are not flexible, this will result in an equilibrium at point:A) E
B) B
C) C
D) D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
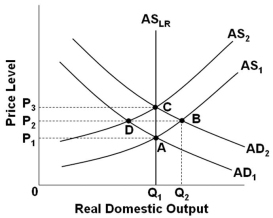 Refer to the graph above. Assume that the economy is in initial equilibrium where AD1 intersects AS1. If there is an unanticipated increase in aggregate demand, then according to new classical economics the economy will self-correct with a:
Refer to the graph above. Assume that the economy is in initial equilibrium where AD1 intersects AS1. If there is an unanticipated increase in aggregate demand, then according to new classical economics the economy will self-correct with a:A) Movement from point B to point A
B) Movement from point A to point B
C) Shift from AS1 to AS2
D) Shift from AD2 to AD1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Crowding-out results from:
A) An increase in the supply of money and a decrease in the velocity of money
B) A decrease in the supply of money and an increase in the velocity of money
C) The inverse relationship between the supply of money and nominal GDP
D) Deficit financing which increases interest rates and reduces investment
A) An increase in the supply of money and a decrease in the velocity of money
B) A decrease in the supply of money and an increase in the velocity of money
C) The inverse relationship between the supply of money and nominal GDP
D) Deficit financing which increases interest rates and reduces investment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The key implication for macroeconomic instability is that efficiency wages:
A) Contribute to the downward inflexibility of wages
B) Help reduce the downward inflexibility of wages
C) Increase the velocity of money
D) Reduce the velocity of money
A) Contribute to the downward inflexibility of wages
B) Help reduce the downward inflexibility of wages
C) Increase the velocity of money
D) Reduce the velocity of money

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
According to rational expectations theory, instantaneous market adjustments make:
A) Expansionary economic policy more effective in increasing output
B) Expansionary economic policy ineffective in increasing output
C) Economic policy more rational and more stable
D) Economic policy less rational and less stable
A) Expansionary economic policy more effective in increasing output
B) Expansionary economic policy ineffective in increasing output
C) Economic policy more rational and more stable
D) Economic policy less rational and less stable

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
If the economy's real output is growing by 2.5 percent a year, then in order to maintain price stability a monetarist would most likely recommend that money supply should be:
A) Held constant
B) Decreased by 1 percent a year
C) Increased by 2.5 percent a year
D) Increased by 7.5 percent a year
A) Held constant
B) Decreased by 1 percent a year
C) Increased by 2.5 percent a year
D) Increased by 7.5 percent a year

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
To stabilize the economy, monetarists and rational-expectations economists:
A) Would like a monetary rule to be adopted
B) Would like to see coordination failures eliminated
C) Recommend the use of discretionary fiscal policy
D) Recommend the use of discretionary monetary policy
A) Would like a monetary rule to be adopted
B) Would like to see coordination failures eliminated
C) Recommend the use of discretionary fiscal policy
D) Recommend the use of discretionary monetary policy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Monetarists take the position that monetary policy:
A) Is limited by the crowding-out effect on investment
B) Is enhanced by the crowding-out effect on investment
C) Should be based on rules rather than discretion
D) Should be based on discretion rather than rules
A) Is limited by the crowding-out effect on investment
B) Is enhanced by the crowding-out effect on investment
C) Should be based on rules rather than discretion
D) Should be based on discretion rather than rules

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Monetarists argue that when expansionary fiscal policy is financed through borrowing:
A) Monetary policy becomes tight
B) Private investment spending will be crowded out
C) The demand for money and interest rates both decrease
D) The investment demand curve becomes relatively steep
A) Monetary policy becomes tight
B) Private investment spending will be crowded out
C) The demand for money and interest rates both decrease
D) The investment demand curve becomes relatively steep

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The theory of rational expectations calls for monetary policy rules because:
A) Of past policy errors
B) Policy tends to be countercyclical
C) Of the inability to time policy decisions
D) Of the reaction of the public to the expected effects of policy
A) Of past policy errors
B) Policy tends to be countercyclical
C) Of the inability to time policy decisions
D) Of the reaction of the public to the expected effects of policy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Which of the following is a likely result of firms paying efficiency wages?
A) Lesser work effort
B) A lower wage rate
C) Increased job turnover
D) Reduced supervision costs
A) Lesser work effort
B) A lower wage rate
C) Increased job turnover
D) Reduced supervision costs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
One reason why the lowest wage rate is not necessarily the same as the efficiency wage is that workers might:
A) Be more productive at a higher wage rate
B) Have more incentive to shirk at higher wage rates
C) Be tempted to switch jobs more frequently at higher wage rates
D) Be less inclined to work well at a higher wage rate
A) Be more productive at a higher wage rate
B) Have more incentive to shirk at higher wage rates
C) Be tempted to switch jobs more frequently at higher wage rates
D) Be less inclined to work well at a higher wage rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
From a monetarist perspective, an expansionary fiscal policy's effect on aggregate demand would be offset by:
A) The buying of government securities by the Treasury
B) The selling of government securities by the Treasury
C) A cut in the Federal funds rate
D) A cut in the discount rate
A) The buying of government securities by the Treasury
B) The selling of government securities by the Treasury
C) A cut in the Federal funds rate
D) A cut in the discount rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
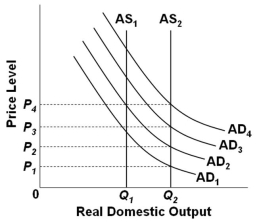 Refer to the graph above. Assume that the economy is initially in equilibrium at the intersection of AD1 and AS1. Suppose that there is economic growth which shifts AS1 to AS2. Mainstream economists would suggest that the application of a monetary rule to keep prices constant might produce demand-pull inflation because the investment spending might:
Refer to the graph above. Assume that the economy is initially in equilibrium at the intersection of AD1 and AS1. Suppose that there is economic growth which shifts AS1 to AS2. Mainstream economists would suggest that the application of a monetary rule to keep prices constant might produce demand-pull inflation because the investment spending might:A) Increase and cause the aggregate demand curve to shift from AD1 to AD4
B) Decrease and cause the investment demand curve to shift from AD1 to AD4
C) Increase and cause the aggregate demand curve to shift from AD1 to AD2
D) Decrease and cause the investment demand curve to shift from AD1 to AD2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
According to rational expectations theory, discretionary monetary and fiscal policy will be ineffective primarily because of the:
A) Successes of macroeconomic policy makers
B) Inability of policy makers to time decisions properly
C) Reaction of the public to the expected effects of policy changes
D) Slow impact of policy to stimulate changes in real output and employment
A) Successes of macroeconomic policy makers
B) Inability of policy makers to time decisions properly
C) Reaction of the public to the expected effects of policy changes
D) Slow impact of policy to stimulate changes in real output and employment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The policy rule recommended by monetarists is that the money supply should be increased at the same rate as the potential growth in:
A) Real GDP
B) Population
C) The level of prices
D) The velocity of money
A) Real GDP
B) Population
C) The level of prices
D) The velocity of money

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
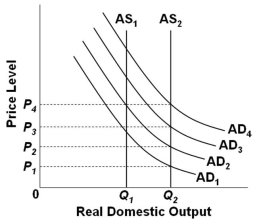 Refer to the graph above. Assume that the economy is initially in equilibrium at the intersection of AD1 and AS1. Suppose that there is economic growth which shifts AS1 to AS2. Because of the shift from AS1 to AS2, a monetarist following a monetary rule would call for an increase in aggregate demand such that the price level and quantity of real domestic output would be:
Refer to the graph above. Assume that the economy is initially in equilibrium at the intersection of AD1 and AS1. Suppose that there is economic growth which shifts AS1 to AS2. Because of the shift from AS1 to AS2, a monetarist following a monetary rule would call for an increase in aggregate demand such that the price level and quantity of real domestic output would be:A) P4 and Q2
B) P3 and Q2
C) P2 and Q2
D) P1 and Q2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
The key implication for macroeconomic instability is that insider-outside relationships in the labor market:
A) Contribute to the downward inflexibility of wages
B) Help reduce the downward inflexibility of wages
C) Increase the velocity of money
D) Reduce the velocity of money
A) Contribute to the downward inflexibility of wages
B) Help reduce the downward inflexibility of wages
C) Increase the velocity of money
D) Reduce the velocity of money

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
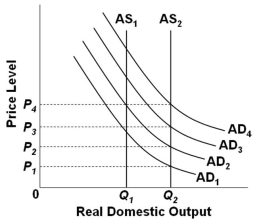 Refer to the graph above. Assume that the economy is initially in equilibrium at the intersection of AD1 and AS1. Suppose that there is economic growth which shifts AS1 to AS2. If the application of a monetary rule is designed to shift AD1 to AD3, but because of pessimistic business expectations AD1 only shifts to AD2, then mainstream economists would suggest that the actions to be taken to avoid deflation would be to implement a(n):
Refer to the graph above. Assume that the economy is initially in equilibrium at the intersection of AD1 and AS1. Suppose that there is economic growth which shifts AS1 to AS2. If the application of a monetary rule is designed to shift AD1 to AD3, but because of pessimistic business expectations AD1 only shifts to AD2, then mainstream economists would suggest that the actions to be taken to avoid deflation would be to implement a(n):A) Expansionary fiscal policy and a tight money policy
B) Contractionary fiscal policy and a tight money policy
C) Expansionary fiscal policy and an easy money policy
D) Contractionary fiscal policy and an easy money policy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
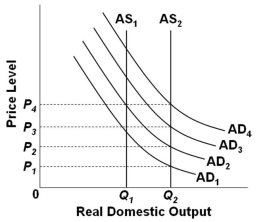 Refer to the graph above. Assume that the economy is initially in equilibrium at the intersection of AD1 and AS1. Suppose that there is economic growth which shifts AS1 to AS2. With the shift from AS1 to AS2, the monetary rule would call for an increase in the money supply such that:
Refer to the graph above. Assume that the economy is initially in equilibrium at the intersection of AD1 and AS1. Suppose that there is economic growth which shifts AS1 to AS2. With the shift from AS1 to AS2, the monetary rule would call for an increase in the money supply such that:A) AD1 would shift to AD2
B) AD1 would shift to AD3
C) AD1 would shift to AD4
D) AS2 would shift to AS1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
The notion that the annual rate of increase in the money supply should be equal to the potential annual growth rate of real GDP best describes the:
A) Monetary rule
B) Velocity of money
C) Equation of exchange
D) Crowding-out effect
A) Monetary rule
B) Velocity of money
C) Equation of exchange
D) Crowding-out effect

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
In the rational expectations view:
A) Wages are flexible downward but prices are inflexible downward
B) Prices are flexible downward but wages are inflexible downward
C) Discretionary policy tends to be countercyclical
D) Discretionary policy tends to be ineffective
A) Wages are flexible downward but prices are inflexible downward
B) Prices are flexible downward but wages are inflexible downward
C) Discretionary policy tends to be countercyclical
D) Discretionary policy tends to be ineffective

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 134 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



