Deck 12: Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/152
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 12: Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply
1
The foreign purchases effect on aggregate demand suggests that a:
A) Fall in our domestic price level will increase our imports and reduce our exports, thereby reducing the net exports component of aggregate demand
B) Fall in our domestic price level will decrease our imports and increase our exports, thereby reducing the net exports component of aggregate demand
C) Rise in our domestic price level will increase our imports and reduce our exports, thereby reducing the net exports component of aggregate demand
D) Rise in our domestic price level will decrease our imports and increase our exports, thereby reducing the net exports component of aggregate demand
A) Fall in our domestic price level will increase our imports and reduce our exports, thereby reducing the net exports component of aggregate demand
B) Fall in our domestic price level will decrease our imports and increase our exports, thereby reducing the net exports component of aggregate demand
C) Rise in our domestic price level will increase our imports and reduce our exports, thereby reducing the net exports component of aggregate demand
D) Rise in our domestic price level will decrease our imports and increase our exports, thereby reducing the net exports component of aggregate demand
Rise in our domestic price level will increase our imports and reduce our exports, thereby reducing the net exports component of aggregate demand
2
The aggregate demand curve shows the:
A) Inverse relationship between the price level and the quantity of real GDP purchased
B) Direct relationship between the price level and the quantity of real GDP produced
C) Inverse relationship between interest rates and the quantity of real GDP produced
D) Direct relationship between real-balances and the quantity of real GDP purchased
A) Inverse relationship between the price level and the quantity of real GDP purchased
B) Direct relationship between the price level and the quantity of real GDP produced
C) Inverse relationship between interest rates and the quantity of real GDP produced
D) Direct relationship between real-balances and the quantity of real GDP purchased
Inverse relationship between the price level and the quantity of real GDP purchased
3
The aggregate demand curve or schedule shows the relationship between the total demand for output and the:
A) Income level
B) Interest rate
C) Price level
D) Real GDP
A) Income level
B) Interest rate
C) Price level
D) Real GDP
Price level
4
When the price level decreases:
A) The demand for money falls and the interest rate falls
B) Holders of financial assets with fixed money values decrease their spending
C) Holders of financial assets with fixed money values have less purchasing power
D) There is a decrease in consumer spending that is sensitive to changes in interest rates
A) The demand for money falls and the interest rate falls
B) Holders of financial assets with fixed money values decrease their spending
C) Holders of financial assets with fixed money values have less purchasing power
D) There is a decrease in consumer spending that is sensitive to changes in interest rates

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
In the aggregate demand-aggregate supply model, the economy's price level is assumed to be:
A) Constant, just like in the aggregate expenditures model
B) Variable, just like in the aggregate expenditures model
C) Constant, unlike in the aggregate expenditures model
D) Variable, unlike in the aggregate expenditures model
A) Constant, just like in the aggregate expenditures model
B) Variable, just like in the aggregate expenditures model
C) Constant, unlike in the aggregate expenditures model
D) Variable, unlike in the aggregate expenditures model

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
An increase in personal income tax rates will cause a(n):
A) Decrease (or shift left) in aggregate demand
B) Increase (or shift right) in aggregate demand
C) Decrease in the quantity of real output demanded (or movement up along AD)
D) Increase in the quantity of real output demanded (or movement down along AD)
A) Decrease (or shift left) in aggregate demand
B) Increase (or shift right) in aggregate demand
C) Decrease in the quantity of real output demanded (or movement up along AD)
D) Increase in the quantity of real output demanded (or movement down along AD)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The real-balances effect on aggregate demand suggests that a:
A) Lower price level will decrease the demand for money, decrease interest rates, and increase consumption and investment spending
B) Lower price level will decrease the real value of many financial assets and therefore cause an increase in spending
C) Lower price level will increase the real value of many financial assets and therefore cause an increase in spending
D) Higher price level will increase the real value of many financial assets and therefore cause an increase in spending
A) Lower price level will decrease the demand for money, decrease interest rates, and increase consumption and investment spending
B) Lower price level will decrease the real value of many financial assets and therefore cause an increase in spending
C) Lower price level will increase the real value of many financial assets and therefore cause an increase in spending
D) Higher price level will increase the real value of many financial assets and therefore cause an increase in spending

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The labels for the axes of the aggregate demand graph should be:
A) Quantity of a product on the vertical axis and the price of a product on the horizontal axis
B) Price of a product on the vertical axis and quantity of a product on the horizontal axis
C) Real domestic output on the vertical axis and the price level on the horizontal axis
D) Real domestic output on the horizontal axis and the price level on the vertical axis
A) Quantity of a product on the vertical axis and the price of a product on the horizontal axis
B) Price of a product on the vertical axis and quantity of a product on the horizontal axis
C) Real domestic output on the vertical axis and the price level on the horizontal axis
D) Real domestic output on the horizontal axis and the price level on the vertical axis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
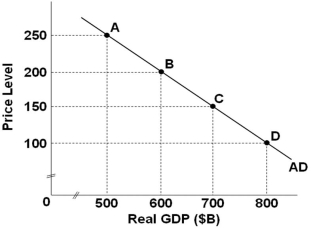 Refer to the graph above, which shows an aggregate demand curve. If the price level decreases from 200 to 100, the real output demanded will:
Refer to the graph above, which shows an aggregate demand curve. If the price level decreases from 200 to 100, the real output demanded will:A) Increase by $800 billion
B) Increase by $200 billion
C) Decrease by $600 billion
D) Decrease by $200 billion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A decrease in interest rates caused by a change in the price level would cause a(n):
A) Decrease (or shift left) in aggregate demand
B) Increase (or shift right) in aggregate demand
C) Decrease in the quantity of real output demanded (or movement up along AD)
D) Increase in the quantity of real output demanded (or movement down along AD)
A) Decrease (or shift left) in aggregate demand
B) Increase (or shift right) in aggregate demand
C) Decrease in the quantity of real output demanded (or movement up along AD)
D) Increase in the quantity of real output demanded (or movement down along AD)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
An expected increase in the prices of consumer goods in the near future will:
A) Decrease (or shift left) in aggregate demand now
B) Increase (or shift right) in aggregate demand now
C) Decrease in the quantity of real output demanded (or movement up along AD)
D) Increase in the quantity of real output demanded (or movement down along AD)
A) Decrease (or shift left) in aggregate demand now
B) Increase (or shift right) in aggregate demand now
C) Decrease in the quantity of real output demanded (or movement up along AD)
D) Increase in the quantity of real output demanded (or movement down along AD)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
An increase in personal income taxes would shift AD to the:
A) Right because C will increase
B) Left because C will decrease
C) Right because G will increase
D) Left because G will decrease
A) Right because C will increase
B) Left because C will decrease
C) Right because G will increase
D) Left because G will decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
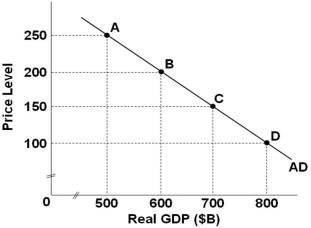 Refer to the graph above, which shows an aggregate demand. If the economy is at point C and the price level increases by 100, then the wealth, interest-rate, and foreign purchases effects will:
Refer to the graph above, which shows an aggregate demand. If the economy is at point C and the price level increases by 100, then the wealth, interest-rate, and foreign purchases effects will:A) Move the economy to point A
B) Move the economy to point B
C) Move the economy to point D
D) Shift the AD curve to the left

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A decrease in expected returns on investment will most likely shift the AD curve to the:
A) Right because C will increase
B) Left because C will decrease
C) Right because Ig will increase
D) Left because Ig will decrease
A) Right because C will increase
B) Left because C will decrease
C) Right because Ig will increase
D) Left because Ig will decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The interest rate effect on aggregate demand indicates that a(n):
A) Decrease in the price level will increase the demand for money, increase interest rates, and decrease consumption and investment spending
B) Decrease in the price level will decrease the demand for money, decrease interest rates, and increase consumption and investment spending
C) Increase in the price level will increase the demand for money, reduce interest rates, and decrease consumption and investment spending
D) Increase in the supply of money will increase interest rates and decrease interest-sensitive consumption and investment spending
A) Decrease in the price level will increase the demand for money, increase interest rates, and decrease consumption and investment spending
B) Decrease in the price level will decrease the demand for money, decrease interest rates, and increase consumption and investment spending
C) Increase in the price level will increase the demand for money, reduce interest rates, and decrease consumption and investment spending
D) Increase in the supply of money will increase interest rates and decrease interest-sensitive consumption and investment spending

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The following factors explain the inverse relationship between the price level and the total demand for output, except:
A) A substitution effect
B) A real-balances effect
C) An interest-rate effect
D) A foreign-purchases effect
A) A substitution effect
B) A real-balances effect
C) An interest-rate effect
D) A foreign-purchases effect

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
When the general price level in our economy increases, the following effects occur except:
A) The purchasing power of people's savings will increase
B) The interest rate will also tend to increase
C) Foreign buyers will buy less of our output, and we tend to import more
D) Our net exports will tend to decrease
A) The purchasing power of people's savings will increase
B) The interest rate will also tend to increase
C) Foreign buyers will buy less of our output, and we tend to import more
D) Our net exports will tend to decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
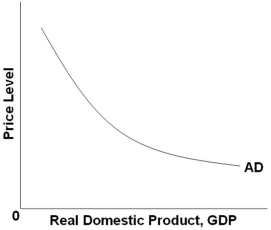 Refer to the graph above. Which of the following factors does not explain a movement along the AD curve?
Refer to the graph above. Which of the following factors does not explain a movement along the AD curve?A) The expenditure multiplier effect
B) The real-balances effect
C) The interest-rate effect
D) The foreign purchases effect

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following effects best explains the downward slope of the aggregate demand curve?
A) A multiplier effect
B) An expectations effect
C) A substitution effect
D) An interest-rate effect
A) A multiplier effect
B) An expectations effect
C) A substitution effect
D) An interest-rate effect

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The foreign purchases, interest rate, and real-balances effects explain why the:
A) Aggregate demand curve is downward-sloping
B) Aggregate demand curve may shift to the left or right
C) Economy will adjust towards equilibrium
D) Aggregate expenditures schedule may shift up or down
A) Aggregate demand curve is downward-sloping
B) Aggregate demand curve may shift to the left or right
C) Economy will adjust towards equilibrium
D) Aggregate expenditures schedule may shift up or down

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Changes in the national incomes of our trading partners would directly impact our:
A) Consumption
B) Exports
C) Imports
D) Government spending
A) Consumption
B) Exports
C) Imports
D) Government spending

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
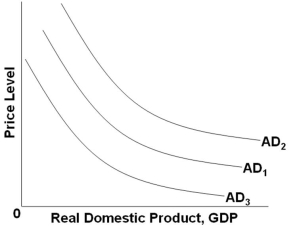 Refer to the graph above. Which of the following changes will shift AD1 to AD2?
Refer to the graph above. Which of the following changes will shift AD1 to AD2?A) A cut in personal and business taxes
B) An increase in the value of the dollar relative to other currencies
C) A shrinkage in the value of stocks and other financial assets
D) An increase in real interest rates

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
When the excess capacity of business expands unintentionally, aggregate:
A) Demand will increase
B) Demand will decrease
C) Supply will increase
D) Supply will decrease
A) Demand will increase
B) Demand will decrease
C) Supply will increase
D) Supply will decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
If the dollar appreciates in value relative to foreign currencies:
A) Aggregate demand decreases because C decreases
B) Aggregate demand increases because C increases
C) Aggregate demand decreases because net exports decrease
D) Aggregate demand increases because net exports increase
A) Aggregate demand decreases because C decreases
B) Aggregate demand increases because C increases
C) Aggregate demand decreases because net exports decrease
D) Aggregate demand increases because net exports increase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of the following events would most likely reduce aggregate demand?
A) A reduction in the amount of existing capital stock
B) A reduction in business and personal tax rates
C) An increase in expected returns on investment
D) An increase in real interest rates
A) A reduction in the amount of existing capital stock
B) A reduction in business and personal tax rates
C) An increase in expected returns on investment
D) An increase in real interest rates

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
When the dollar appreciates relative to foreign currencies, it means that:
A) We need more dollars to buy each unit of another currency
B) We can buy less foreign currency with a given amount of dollars
C) The value of foreign currencies decreased relative to our dollar
D) Foreigners need less of their currency to buy one dollar
A) We need more dollars to buy each unit of another currency
B) We can buy less foreign currency with a given amount of dollars
C) The value of foreign currencies decreased relative to our dollar
D) Foreigners need less of their currency to buy one dollar

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the following would not shift the aggregate demand curve? Changes in:
A) Productivity rates
B) Foreign-exchange rates
C) Real interest rates
D) Income tax rates
A) Productivity rates
B) Foreign-exchange rates
C) Real interest rates
D) Income tax rates

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
If the dollar appreciates relative to foreign currencies, then:
A) U.S. goods will look cheaper to foreign buyers
B) Foreign goods will look more expensive to U.S. buyers
C) Net exports of the U.S. will increase
D) Foreign buyers will find U.S. goods become more expensive
A) U.S. goods will look cheaper to foreign buyers
B) Foreign goods will look more expensive to U.S. buyers
C) Net exports of the U.S. will increase
D) Foreign buyers will find U.S. goods become more expensive

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
If the national incomes of our trading partners increase, then our:
A) Aggregate demand decreases because C decreases
B) Aggregate demand increases because C increases
C) Aggregate demand decreases because net exports decrease
D) Aggregate demand increases because net exports increase
A) Aggregate demand decreases because C decreases
B) Aggregate demand increases because C increases
C) Aggregate demand decreases because net exports decrease
D) Aggregate demand increases because net exports increase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
An increase in aggregate demand is most likely to be caused by:
A) An increase in real interest rates
B) A decrease in government spending
C) A decrease in expected returns on investment
D) A decrease in the tax rates on household income
A) An increase in real interest rates
B) A decrease in government spending
C) A decrease in expected returns on investment
D) A decrease in the tax rates on household income

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
In the Great Recession of 2007-2009, the stock market values shrank, causing a reverse:
A) Wealth effect
B) Real-balances effect
C) Interest-rate effect
D) Expectations effect
A) Wealth effect
B) Real-balances effect
C) Interest-rate effect
D) Expectations effect

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
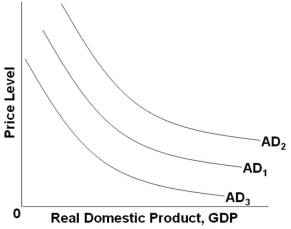 Refer to the graph above. Which of the following factors will shift AD1 to AD3?
Refer to the graph above. Which of the following factors will shift AD1 to AD3?A) An increase in expected returns on investment
B) An increase in productivity
C) A decrease in real interest rates
D) A decrease in consumer wealth

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The expenditure multiplier concept of the aggregate-expenditures model:
A) Is not at all relevant in the AD-AS model
B) Magnifies the shifts of the aggregate demand curve
C) Explains movement up or down the aggregate demand curve
D) Reverses the shift of the aggregate demand curve
A) Is not at all relevant in the AD-AS model
B) Magnifies the shifts of the aggregate demand curve
C) Explains movement up or down the aggregate demand curve
D) Reverses the shift of the aggregate demand curve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
An increase in expected future income will:
A) Increase aggregate demand and aggregate supply
B) Decrease aggregate demand and aggregate supply
C) Increase aggregate supply
D) Increase aggregate demand
A) Increase aggregate demand and aggregate supply
B) Decrease aggregate demand and aggregate supply
C) Increase aggregate supply
D) Increase aggregate demand

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
A decrease in government spending will cause a(n):
A) Increase in the quantity of real output demanded
B) Decrease in the quantity of real output demanded
C) Decrease in aggregate demand
D) Increase in aggregate demand
A) Increase in the quantity of real output demanded
B) Decrease in the quantity of real output demanded
C) Decrease in aggregate demand
D) Increase in aggregate demand

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
When national income in other nations decreases, aggregate demand in our economy:
A) Increases because our exports will increase
B) Decreases because our exports will decrease
C) Increases because our imports will decrease
D) Decreases because our imports will increase
A) Increases because our exports will increase
B) Decreases because our exports will decrease
C) Increases because our imports will decrease
D) Decreases because our imports will increase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
If the dollar depreciates in value relative to foreign currencies, then aggregate:
A) Demand decreases
B) Demand increases
C) Supply and aggregate demand increase
D) Supply and aggregate demand decrease
A) Demand decreases
B) Demand increases
C) Supply and aggregate demand increase
D) Supply and aggregate demand decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A sharp rise in the real value of stock prices, which is independent of a change in the price level, would best be an example of:
A) The interest-rate effect
B) The real-balances effect
C) A change in the degree of excess capacity
D) A change in real value of consumer wealth
A) The interest-rate effect
B) The real-balances effect
C) A change in the degree of excess capacity
D) A change in real value of consumer wealth

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
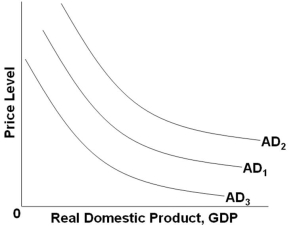 Refer to the graph above. Which of the following factors will shift AD1 to AD2?
Refer to the graph above. Which of the following factors will shift AD1 to AD2?A) A decrease in the general price level
B) An increase in real interest rates
C) An increase in national incomes abroad
D) A decrease in the value of financial assets

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which combination of factors would most likely increase aggregate demand?
A) An increase in household indebtedness and a decrease in net exports
B) An increase in consumer wealth and a decrease in interest rates
C) An increase in personal taxes and a decrease in government spending
D) An increase in business taxes and a decrease in profit expectations
A) An increase in household indebtedness and a decrease in net exports
B) An increase in consumer wealth and a decrease in interest rates
C) An increase in personal taxes and a decrease in government spending
D) An increase in business taxes and a decrease in profit expectations

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The long-run aggregate supply analysis assumes that:
A) Input prices are fixed while product prices are variable
B) Input prices are variable while product prices are fixed
C) Both input and product prices are variable
D) Both input and product prices are fixed
A) Input prices are fixed while product prices are variable
B) Input prices are variable while product prices are fixed
C) Both input and product prices are variable
D) Both input and product prices are fixed

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
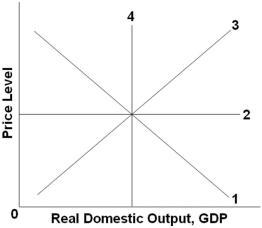 Refer to the graph above. The long-run aggregate supply curve would be represented by which line?
Refer to the graph above. The long-run aggregate supply curve would be represented by which line?A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
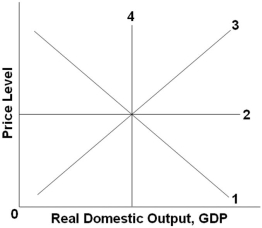 Refer to the graph above. Which line might represent an aggregate demand curve?
Refer to the graph above. Which line might represent an aggregate demand curve?A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Answer the question based on the following list of factors that are related to the aggregate demand curve.  Which of the above factors best explain the downward slope of aggregate demand curve?
Which of the above factors best explain the downward slope of aggregate demand curve?
A) 2, 4, and 6
B) 7, 9, and 10
C) 1, 3, and 8
D) 4, 6, and 7
 Which of the above factors best explain the downward slope of aggregate demand curve?
Which of the above factors best explain the downward slope of aggregate demand curve?A) 2, 4, and 6
B) 7, 9, and 10
C) 1, 3, and 8
D) 4, 6, and 7

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Answer the question based on the following list of factors that are related to the aggregate demand curve.  Refer to the list above. A change in net export spending would most likely be caused by changes in:
Refer to the list above. A change in net export spending would most likely be caused by changes in:
A) 2 and 3
B) 5 and 6
C) 7 and 8
D) 6 and 9
 Refer to the list above. A change in net export spending would most likely be caused by changes in:
Refer to the list above. A change in net export spending would most likely be caused by changes in:A) 2 and 3
B) 5 and 6
C) 7 and 8
D) 6 and 9

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The short-run aggregate supply curve:
A) Becomes flatter at output levels above the full-employment output
B) Becomes steep at output levels above the full-employment output
C) Is upward-sloping with a constant slope
D) Is horizontal
A) Becomes flatter at output levels above the full-employment output
B) Becomes steep at output levels above the full-employment output
C) Is upward-sloping with a constant slope
D) Is horizontal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The short-run aggregate supply curve shows the:
A) Inverse relationship between the price level and real GDP purchased
B) Inverse relationship between the price level and real GDP produced
C) Direct relationship between the price level and real GDP produced
D) Direct relationship between the price level and real GDP purchased
A) Inverse relationship between the price level and real GDP purchased
B) Inverse relationship between the price level and real GDP produced
C) Direct relationship between the price level and real GDP produced
D) Direct relationship between the price level and real GDP purchased

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The short-run version of aggregate supply assumes that product prices are:
A) Fixed while resource prices are flexible
B) Flexible while resource prices are fixed
C) Both input and product prices are flexible
D) Both input and product prices are fixed
A) Fixed while resource prices are flexible
B) Flexible while resource prices are fixed
C) Both input and product prices are flexible
D) Both input and product prices are fixed

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The version of aggregate supply that allows for changes in both product prices and resource prices is the:
A) Immediate short-run
B) Short run
C) Immediate long-run
D) Long run
A) Immediate short-run
B) Short run
C) Immediate long-run
D) Long run

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The slope of the immediate-short-run aggregate supply curve is based on the assumption that:
A) Both input and output prices are fixed
B) Neither input nor output prices are fixed
C) Input prices are flexible but output prices are fixed
D) Input prices are fixed but output prices are flexible
A) Both input and output prices are fixed
B) Neither input nor output prices are fixed
C) Input prices are flexible but output prices are fixed
D) Input prices are fixed but output prices are flexible

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
A fall in the prices of inputs will shift the aggregate:
A) Demand curve leftward
B) Demand curve rightward
C) Supply curve rightward
D) Supply curve leftward
A) Demand curve leftward
B) Demand curve rightward
C) Supply curve rightward
D) Supply curve leftward

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Answer the question based on the following list of factors that are related to the aggregate demand curve.  Refer to the list above. Investment spending would most likely be influenced by changes in:
Refer to the list above. Investment spending would most likely be influenced by changes in:
A) 1 and 3
B) 4 and 6
C) 5 and 10
D) 8 and 9
 Refer to the list above. Investment spending would most likely be influenced by changes in:
Refer to the list above. Investment spending would most likely be influenced by changes in:A) 1 and 3
B) 4 and 6
C) 5 and 10
D) 8 and 9

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The upward slope of the short-run aggregate supply curve is based on the assumption that:
A) Wages and other resource prices do not respond to price level changes
B) Wages and other resource prices do respond to price level changes
C) Prices of output do not respond to price level changes
D) Prices of inputs flexible while prices of outputs are fixed
A) Wages and other resource prices do not respond to price level changes
B) Wages and other resource prices do respond to price level changes
C) Prices of output do not respond to price level changes
D) Prices of inputs flexible while prices of outputs are fixed

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
An aggregate supply curve represents the relationship between the:
A) Price level and the buying of real domestic output
B) Price level and the production of real domestic output
C) Real domestic output bought and the real domestic output sold
D) Price level that producers are willing to accept and the price level buyers are willing to pay
A) Price level and the buying of real domestic output
B) Price level and the production of real domestic output
C) Real domestic output bought and the real domestic output sold
D) Price level that producers are willing to accept and the price level buyers are willing to pay

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The labels for the axes of an aggregate supply curve should be:
A) Real domestic output for the vertical axis and price level for the horizontal axis
B) Real domestic output for the horizontal axis and price level for the vertical axis
C) Real employment for the vertical axis and price level for the horizontal axis
D) Aggregate demand for the vertical axis and real national output for the horizontal axis
A) Real domestic output for the vertical axis and price level for the horizontal axis
B) Real domestic output for the horizontal axis and price level for the vertical axis
C) Real employment for the vertical axis and price level for the horizontal axis
D) Aggregate demand for the vertical axis and real national output for the horizontal axis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Answer the question based on the following list of factors that are related to the aggregate demand curve.  Changes in which two of the factors in the list above would most likely cause a shift in aggregate demand due to a change in consumer spending?
Changes in which two of the factors in the list above would most likely cause a shift in aggregate demand due to a change in consumer spending?
A) 1 and 3
B) 2 and 4
C) 5 and 10
D) 8 and 9
 Changes in which two of the factors in the list above would most likely cause a shift in aggregate demand due to a change in consumer spending?
Changes in which two of the factors in the list above would most likely cause a shift in aggregate demand due to a change in consumer spending?A) 1 and 3
B) 2 and 4
C) 5 and 10
D) 8 and 9

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The real-balance effect pertains to the effect of:
A) Consumer spending on the price level, while the wealth effect refers to the impact of changes in wealth on consumer spending
B) Wealth-changes on aggregate demand, while the wealth effect refers to the impact of changes in the price level on the real value of wealth
C) Changes in interest rate on aggregate demand, while the wealth effect refers to the impact of changes aggregate demand on people's wealth
D) Price-changes on aggregate demand, while the wealth effect refers to the impact of changes in wealth on aggregate demand
A) Consumer spending on the price level, while the wealth effect refers to the impact of changes in wealth on consumer spending
B) Wealth-changes on aggregate demand, while the wealth effect refers to the impact of changes in the price level on the real value of wealth
C) Changes in interest rate on aggregate demand, while the wealth effect refers to the impact of changes aggregate demand on people's wealth
D) Price-changes on aggregate demand, while the wealth effect refers to the impact of changes in wealth on aggregate demand

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The long-run aggregate supply curve is:
A) Upward-sloping and becomes steeper at output levels above the full-employment output
B) Upward-sloping and becomes flatter at output levels above the full-employment output
C) Horizontal
D) Vertical
A) Upward-sloping and becomes steeper at output levels above the full-employment output
B) Upward-sloping and becomes flatter at output levels above the full-employment output
C) Horizontal
D) Vertical

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
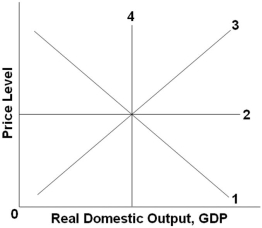 Refer to the graph above. Which line might represent an immediate-short-run aggregate supply curve?
Refer to the graph above. Which line might represent an immediate-short-run aggregate supply curve?A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The immediate-short-run aggregate supply curve is:
A) Vertical
B) Horizontal
C) Upward-sloping
D) Downward-sloping
A) Vertical
B) Horizontal
C) Upward-sloping
D) Downward-sloping

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
If the price of crude oil decreases, then this would most likely:
A) Decrease aggregate supply in the U.S.
B) Increase aggregate supply in the U.S.
C) Increase aggregate demand in the U.S.
D) Decrease aggregate demand in the U.S.
A) Decrease aggregate supply in the U.S.
B) Increase aggregate supply in the U.S.
C) Increase aggregate demand in the U.S.
D) Decrease aggregate demand in the U.S.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Which would be considered to be one of the factors that shift the aggregate supply curve in the short run? A change in:
A) Personal income taxes
B) Consumer spending
C) Government regulation
D) Profit expectations on investment projects
A) Personal income taxes
B) Consumer spending
C) Government regulation
D) Profit expectations on investment projects

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
If Congress passed new laws significantly increasing the regulation of business, this action would tend to:
A) Increase per-unit production costs and shift the aggregate supply curve to the left
B) Increase per-unit production costs and shift the aggregate supply curve to the right
C) Increase per-unit production costs and shift the aggregate demand curve to the left
D) Decrease per-unit production costs and shift the aggregate supply curve to the left
A) Increase per-unit production costs and shift the aggregate supply curve to the left
B) Increase per-unit production costs and shift the aggregate supply curve to the right
C) Increase per-unit production costs and shift the aggregate demand curve to the left
D) Decrease per-unit production costs and shift the aggregate supply curve to the left

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Answer the question based on the following list of items that are related to aggregate demand and/or aggregate supply.  Refer to the list above. Changes in which combination of factors best explain why the aggregate supply curve would shift?
Refer to the list above. Changes in which combination of factors best explain why the aggregate supply curve would shift?
A) 1 and 2
B) 2 and 10
C) 3 and 6
D) 7 and 8
 Refer to the list above. Changes in which combination of factors best explain why the aggregate supply curve would shift?
Refer to the list above. Changes in which combination of factors best explain why the aggregate supply curve would shift?A) 1 and 2
B) 2 and 10
C) 3 and 6
D) 7 and 8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
A decrease in business taxes will tend to:
A) Increase aggregate demand but not change aggregate supply
B) Increase aggregate supply but not change aggregate demand
C) Increase aggregate demand and increase aggregate supply
D) Decrease aggregate supply and decrease aggregate demand
A) Increase aggregate demand but not change aggregate supply
B) Increase aggregate supply but not change aggregate demand
C) Increase aggregate demand and increase aggregate supply
D) Decrease aggregate supply and decrease aggregate demand

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Answer the question based on the following list of items that are related to aggregate demand and/or aggregate supply.  Refer to the list above. Changes in which of the above two factors would most likely cause a change in aggregate demand?
Refer to the list above. Changes in which of the above two factors would most likely cause a change in aggregate demand?
A) 1 and 5
B) 3 and 10
C) 5 and 7
D) 8 and 9
 Refer to the list above. Changes in which of the above two factors would most likely cause a change in aggregate demand?
Refer to the list above. Changes in which of the above two factors would most likely cause a change in aggregate demand?A) 1 and 5
B) 3 and 10
C) 5 and 7
D) 8 and 9

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Which would most likely increase aggregate supply?
A) An increase in the prices of imported products
B) An increase in productivity
C) A decrease in business subsidies
D) A decrease in personal income taxes
A) An increase in the prices of imported products
B) An increase in productivity
C) A decrease in business subsidies
D) A decrease in personal income taxes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Suppose that an economy produces 2400 units of output, employing the 60 units of input, and the price of the input is $30 per unit. Refer to the information above. The level of productivity in this economy is:
A) 20
B) 30
C) 40
D) 50
A) 20
B) 30
C) 40
D) 50

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
A fall in labor costs will cause aggregate:
A) Supply to increase
B) Demand to increase
C) Supply to decrease
D) Demand to decrease
A) Supply to increase
B) Demand to increase
C) Supply to decrease
D) Demand to decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
An increase in productivity will:
A) Increase aggregate demand
B) Increase aggregate supply
C) Increase aggregate supply and aggregate demand
D) Decrease aggregate supply and aggregate demand
A) Increase aggregate demand
B) Increase aggregate supply
C) Increase aggregate supply and aggregate demand
D) Decrease aggregate supply and aggregate demand

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Suppose that an economy produces 2400 units of output, employing the 60 units of input, and the price of the input is $30 per unit. Refer to the information above. All else equal, if the price of each unit of input decreased from $30 to $20, then productivity would:
A) Increase from $40 to $90 and aggregate supply would decrease
B) Increase from $50 to $60 and aggregate supply would decrease
C) Increase from $60 to $70 and aggregate supply would increase
D) Remain unchanged but aggregate supply would increase
A) Increase from $40 to $90 and aggregate supply would decrease
B) Increase from $50 to $60 and aggregate supply would decrease
C) Increase from $60 to $70 and aggregate supply would increase
D) Remain unchanged but aggregate supply would increase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Suppose that an economy produces 2400 units of output, employing the 60 units of input, and the price of the input is $30 per unit. Refer to the information above. If productivity increased such that 3000 units are now produced with the quantity of inputs still equal to 60, then per-unit production costs would:
A) Decrease and aggregate supply would decrease
B) Decrease and aggregate supply would increase
C) Increase and aggregate supply would decrease
D) Remain unchanged and aggregate supply would remain unchanged
A) Decrease and aggregate supply would decrease
B) Decrease and aggregate supply would increase
C) Increase and aggregate supply would decrease
D) Remain unchanged and aggregate supply would remain unchanged

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Suppose that an economy produces 2400 units of output, employing the 60 units of input, and the price of the input is $30 per unit. Refer to the information above. The per-unit cost of production is:
A) $0.25
B) $0.50
C) $0.75
D) $2.00
A) $0.25
B) $0.50
C) $0.75
D) $2.00

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
If personal income taxes and business taxes increase, then this will:
A) Increase aggregate demand and aggregate supply
B) Decrease aggregate demand and aggregate supply
C) Decrease aggregate demand and increase aggregate supply
D) Increase aggregate demand and decrease aggregate supply
A) Increase aggregate demand and aggregate supply
B) Decrease aggregate demand and aggregate supply
C) Decrease aggregate demand and increase aggregate supply
D) Increase aggregate demand and decrease aggregate supply

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Suppose that an economy produces 500 units of output. It takes 10 units of labor at $15 a unit and 4 units of capital at $50 a unit to produce this amount of output. The per unit cost of production is:
A) $1.42
B) $1.24
C) $0.70
D) $0.40
A) $1.42
B) $1.24
C) $0.70
D) $0.40

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
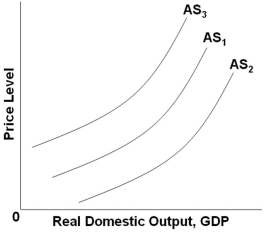 Refer to the graph above. Which of the following factors will shift AS1 to AS3?
Refer to the graph above. Which of the following factors will shift AS1 to AS3?A) An increase in productivity
B) An increase in input prices
C) A decrease in business taxes
D) A decrease in household indebtedness

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
In an economy it costs $1,500 to produce 2,000 units of output. If the costs increase to $2,500, then the per unit cost of production will have increased from:
A) $0.75 to $1.25
B) $0.75 to $1.00
C) $1.33 to $1.75
D) $0.80 to $1.33
A) $0.75 to $1.25
B) $0.75 to $1.00
C) $1.33 to $1.75
D) $0.80 to $1.33

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Which would most likely shift the aggregate supply curve? A change in the prices of:
A) Domestic products
B) Foreign products
C) Financial assets
D) Resources
A) Domestic products
B) Foreign products
C) Financial assets
D) Resources

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
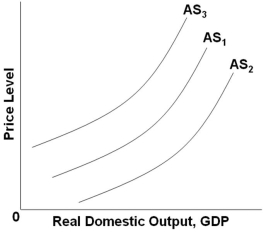 Refer to the graph above. Which of the following factors will shift AS1 to AS2?
Refer to the graph above. Which of the following factors will shift AS1 to AS2?A) An increase in real interest rates
B) A decrease in business subsidies
C) An increase in input prices
D) A decrease in business taxes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
If the U.S. dollar appreciates in value relative to foreign currencies, then this will:
A) Increase aggregate demand and aggregate supply
B) Decrease aggregate demand and aggregate supply
C) Decrease aggregate demand and increase aggregate supply
D) Increase aggregate demand and decrease aggregate supply
A) Increase aggregate demand and aggregate supply
B) Decrease aggregate demand and aggregate supply
C) Decrease aggregate demand and increase aggregate supply
D) Increase aggregate demand and decrease aggregate supply

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 152 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



