Deck 13: Policy Effects and Costs Shocks in the Asad Model
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/102
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 13: Policy Effects and Costs Shocks in the Asad Model
1
The Fed will raise the interest rate by the greatest amount when the economy is on the ________ part of the AS curve and there is ________.
A)flat; a decrease in taxes
B)flat; an increase in taxes
C)steep; a decrease in taxes
D)steep; an increase in taxes
A)flat; a decrease in taxes
B)flat; an increase in taxes
C)steep; a decrease in taxes
D)steep; an increase in taxes
C
2
If the economy is on the flat portion of the AS curve,
A)there is little crowding out of planned investment.
B)there is almost complete crowding out of planned investment.
C)consumption,but not government spending,crowds out planned investment.
D)government spending,but not consumption,crowds out planned investment.
A)there is little crowding out of planned investment.
B)there is almost complete crowding out of planned investment.
C)consumption,but not government spending,crowds out planned investment.
D)government spending,but not consumption,crowds out planned investment.
A
3
The objective of an expansionary fiscal policy is to
A)reduce unemployment.
B)reduce inflation.
C)reduce growth in output.
D)reduce growth in international trade.
A)reduce unemployment.
B)reduce inflation.
C)reduce growth in output.
D)reduce growth in international trade.
A
4
Aggregate demand increases if
A)the government decreases spending.
B)the Fed sells government bonds.
C)the government decreases taxes.
D)the Fed increases the required reserve ratio.
A)the government decreases spending.
B)the Fed sells government bonds.
C)the government decreases taxes.
D)the Fed increases the required reserve ratio.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The objective of a contractionary fiscal policy is to
A)reduce unemployment.
B)increase growth in output.
C)reduce inflation.
D)increase stagflation.
A)reduce unemployment.
B)increase growth in output.
C)reduce inflation.
D)increase stagflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Refer to the information provided in Figure 13.1 below to answer the questions that follow.
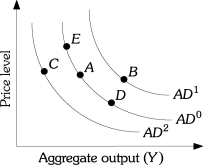 Figure 13.1
Figure 13.1
Refer to Figure 13.1.Suppose the economy is at Point A,a decrease in taxes can cause a movement to Point
A)E.
B)B.
C)C.
D)D.
 Figure 13.1
Figure 13.1Refer to Figure 13.1.Suppose the economy is at Point A,a decrease in taxes can cause a movement to Point
A)E.
B)B.
C)C.
D)D.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
If the economy is on the steep portion of the AS curve and taxes decrease,________ crowds out ________.
A)consumption; planned investment
B)government spending; planned investment
C)planned investment; consumption
D)planned investment; government spending
A)consumption; planned investment
B)government spending; planned investment
C)planned investment; consumption
D)planned investment; government spending

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Refer to the information provided in Figure 13.1 below to answer the questions that follow.
 Figure 13.1
Figure 13.1
Refer to Figure 13.1.Suppose the economy is at Point A an increase in government purchases can cause a movement to Point
A)E.
B)B.
C)C.
D)D.
 Figure 13.1
Figure 13.1Refer to Figure 13.1.Suppose the economy is at Point A an increase in government purchases can cause a movement to Point
A)E.
B)B.
C)C.
D)D.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following is an example of an expansionary fiscal policy?
A)the Fed selling government securities in the open market
B)the federal government increasing the marginal tax rate on incomes above $200,000
C)the federal government increasing the amount of money spent on public health programs
D)the federal government reducing pollution standards to allow firms to produce more output
A)the Fed selling government securities in the open market
B)the federal government increasing the marginal tax rate on incomes above $200,000
C)the federal government increasing the amount of money spent on public health programs
D)the federal government reducing pollution standards to allow firms to produce more output

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Aggregate demand increases if
A)the government increases spending.
B)the Fed sells government bonds.
C)the government increases taxes.
D)the Fed raises the discount rate.
A)the government increases spending.
B)the Fed sells government bonds.
C)the government increases taxes.
D)the Fed raises the discount rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Refer to the information provided in Figure 13.1 below to answer the questions that follow.
 Figure 13.1
Figure 13.1
Refer to Figure 13.1.Suppose the economy is at Point A,a decrease in the price level can cause a movement to Point
A)E.
B)B.
C)C.
D)D.
 Figure 13.1
Figure 13.1Refer to Figure 13.1.Suppose the economy is at Point A,a decrease in the price level can cause a movement to Point
A)E.
B)B.
C)C.
D)D.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
If a decrease in net taxes in the United States resulted in a very large increase in aggregate output and a very small increase in the price level,then the U.S.economy must have been
A)on the very steep part of the short-run aggregate supply curve.
B)on the very flat part of the short-run aggregate supply curve.
C)on the very steep part of the short-run aggregate demand curve.
D)on the very flat part of the short-run aggregate demand curve.
A)on the very steep part of the short-run aggregate supply curve.
B)on the very flat part of the short-run aggregate supply curve.
C)on the very steep part of the short-run aggregate demand curve.
D)on the very flat part of the short-run aggregate demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A decrease in net taxes at a given price level leads to
A)no change in aggregate demand.
B)an increase in aggregate demand.
C)a decrease in aggregate demand.
D)a decrease in aggregate supply.
A)no change in aggregate demand.
B)an increase in aggregate demand.
C)a decrease in aggregate demand.
D)a decrease in aggregate supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
An increase in government spending will completely crowd out investment if
A)money supply is increased at the same time.
B)money demand is not sensitive to the interest rate.
C)the economy is operating at capacity.
D)the economy is operating well below capacity.
A)money supply is increased at the same time.
B)money demand is not sensitive to the interest rate.
C)the economy is operating at capacity.
D)the economy is operating well below capacity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Fiscal policy affects the goods market through
A)changes in money supply.
B)changes in taxes and money supply.
C)changes in government spending and money supply.
D)changes in taxes and government spending.
A)changes in money supply.
B)changes in taxes and money supply.
C)changes in government spending and money supply.
D)changes in taxes and government spending.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Refer to the information provided in Figure 13.1 below to answer the questions that follow.
 Figure 13.1
Figure 13.1
Refer to Figure 13.1.Suppose the economy is at Point A,an decrease in government purchases can cause a movement to Point
A)E.
B)B.
C)C.
D)D.
 Figure 13.1
Figure 13.1Refer to Figure 13.1.Suppose the economy is at Point A,an decrease in government purchases can cause a movement to Point
A)E.
B)B.
C)C.
D)D.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Refer to the information provided in Figure 13.1 below to answer the questions that follow.
 Figure 13.1
Figure 13.1
Refer to Figure 13.1.An aggregate demand shift from AD2 to AD0 can be caused by
A)a decrease in the price level.
B)an increase in the price level.
C)a decrease in taxes.
D)a decrease in money supply.
 Figure 13.1
Figure 13.1Refer to Figure 13.1.An aggregate demand shift from AD2 to AD0 can be caused by
A)a decrease in the price level.
B)an increase in the price level.
C)a decrease in taxes.
D)a decrease in money supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Refer to the information provided in Figure 13.1 below to answer the questions that follow.
 Figure 13.1
Figure 13.1
Refer to Figure 13.1.Suppose the economy is at Point A,an increase in the price level can cause a movement to Point
A)E.
B)B.
C)C.
D)D.
 Figure 13.1
Figure 13.1Refer to Figure 13.1.Suppose the economy is at Point A,an increase in the price level can cause a movement to Point
A)E.
B)B.
C)C.
D)D.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The aggregate demand curve would shift to the left if
A)government spending were increased.
B)net taxes were increased.
C)the money supply were increased.
D)the cost of energy were to decrease.
A)government spending were increased.
B)net taxes were increased.
C)the money supply were increased.
D)the cost of energy were to decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Refer to the information provided in Figure 13.1 below to answer the questions that follow.
 Figure 13.1
Figure 13.1
Refer to Figure 13.1.An aggregate demand shift from AD1 to AD0 can be caused by
A)a decrease in government spending.
B)an increase in money supply.
C)a decrease in the price level.
D)an increase in the price level.
 Figure 13.1
Figure 13.1Refer to Figure 13.1.An aggregate demand shift from AD1 to AD0 can be caused by
A)a decrease in government spending.
B)an increase in money supply.
C)a decrease in the price level.
D)an increase in the price level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
An increase in AD will primarily increase the price level when the economy is on the steep part of the AS curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
A decrease in net taxes will result in consumption crowding out planned investment when the economy is on the steep part of the AS curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
If wages adjust fully to price increases in the long run,fiscal policy will
A)have no affect on the price level.
B)have no affect on output.
C)have no affect on either output or the price level.
D)affect both output and the price level.
A)have no affect on the price level.
B)have no affect on output.
C)have no affect on either output or the price level.
D)affect both output and the price level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
When the economy is on the flat part of the AS curve,there is very little crowding out of planned investment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Refer to the information provided in Figure 13.2 below to answer the questions that follow.
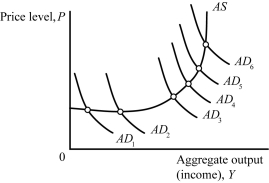 Figure 13.2
Figure 13.2
Refer to Figure 13.2.In response to a decrease in net taxes,the Fed would increase the interest rate by the least amount when the aggregate demand curve shifts from
A)AD1 to AD2.
B)AD3 to AD4.
C)AD5 to AD6.
D)AD1 to AD6.
 Figure 13.2
Figure 13.2Refer to Figure 13.2.In response to a decrease in net taxes,the Fed would increase the interest rate by the least amount when the aggregate demand curve shifts from
A)AD1 to AD2.
B)AD3 to AD4.
C)AD5 to AD6.
D)AD1 to AD6.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Expansionary economic policies are things the government can do to decrease aggregate demand or aggregate supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Refer to the information provided in Figure 13.2 below to answer the questions that follow.
 Figure 13.2
Figure 13.2
Refer to Figure 13.2.The tax multiplier is smallest (in absolute value)when the aggregate demand curve shifts from
A)AD1 to AD2.
B)AD3 to AD4.
C)AD5 to AD6.
D)The output multiplier is the same for all AD curve shifts shown in the figure.
 Figure 13.2
Figure 13.2Refer to Figure 13.2.The tax multiplier is smallest (in absolute value)when the aggregate demand curve shifts from
A)AD1 to AD2.
B)AD3 to AD4.
C)AD5 to AD6.
D)The output multiplier is the same for all AD curve shifts shown in the figure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Economic policies are effective at changing output when
A)the economy is not producing at capacity.
B)the economy is producing at its potential output.
C)the unemployment rate is at the natural rate.
D)the aggregate supply curve is vertical.
A)the economy is not producing at capacity.
B)the economy is producing at its potential output.
C)the unemployment rate is at the natural rate.
D)the aggregate supply curve is vertical.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Refer to the information provided in Figure 13.2 below to answer the questions that follow.
 Figure 13.2
Figure 13.2
Refer to Figure 13.2.In response to an increase in government spending,the Fed would increase the interest rate by the greatest amount when the aggregate demand curve shifts from
A)AD1 to AD2.
B)AD3 to AD4.
C)AD5 to AD6.
D)AD6 to AD1.
 Figure 13.2
Figure 13.2Refer to Figure 13.2.In response to an increase in government spending,the Fed would increase the interest rate by the greatest amount when the aggregate demand curve shifts from
A)AD1 to AD2.
B)AD3 to AD4.
C)AD5 to AD6.
D)AD6 to AD1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Economic policies are ineffective concerning quantities of output directly when
A)the aggregate supply curve is flat.
B)the aggregate demand is flat.
C)the aggregate supply is vertical.
D)the economy is not producing at capacity.
A)the aggregate supply curve is flat.
B)the aggregate demand is flat.
C)the aggregate supply is vertical.
D)the economy is not producing at capacity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
When the economy is near capacity,the Fed would lower the interest rate in response to an increase in government spending.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Refer to the information provided in Figure 13.2 below to answer the questions that follow.
 Figure 13.2
Figure 13.2
Refer to Figure 13.2.The output multiplier is largest when the aggregate demand curve shifts from
A)AD1 to AD2.
B)AD3 to AD4.
C)AD5 to AD6.
D)The output multiplier is the same for all AD curve shifts shown in the figure.
 Figure 13.2
Figure 13.2Refer to Figure 13.2.The output multiplier is largest when the aggregate demand curve shifts from
A)AD1 to AD2.
B)AD3 to AD4.
C)AD5 to AD6.
D)The output multiplier is the same for all AD curve shifts shown in the figure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Refer to the information provided in Figure 13.2 below to answer the questions that follow.
 Figure 13.2
Figure 13.2
Refer to Figure 13.2.Firms respond to a decrease in net taxes by mostly increasing output when the aggregate demand curve shifts from
A)AD1 to AD2.
B)AD3 to AD4.
C)AD5 to AD6.
D)AD6 to AD1.
 Figure 13.2
Figure 13.2Refer to Figure 13.2.Firms respond to a decrease in net taxes by mostly increasing output when the aggregate demand curve shifts from
A)AD1 to AD2.
B)AD3 to AD4.
C)AD5 to AD6.
D)AD6 to AD1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A decrease in net taxation increases aggregate demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Refer to the information provided in Figure 13.2 below to answer the questions that follow.
 Figure 13.2
Figure 13.2
Refer to Figure 13.2.Firms respond to an increase in government spending by mostly raising their prices when the aggregate demand curve shifts from
A)AD1 to AD2.
B)AD3 to AD4.
C)AD5 to AD6.
D)AD6 to AD1.
 Figure 13.2
Figure 13.2Refer to Figure 13.2.Firms respond to an increase in government spending by mostly raising their prices when the aggregate demand curve shifts from
A)AD1 to AD2.
B)AD3 to AD4.
C)AD5 to AD6.
D)AD6 to AD1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
If the economy is on the steep part of its aggregate supply curve,expansionary policy will mostly increase the price level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
An increase in AD will primarily increase output when the economy is on the flat part of the AS curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Refer to the information provided in Figure 13.2 below to answer the questions that follow.
 Figure 13.2
Figure 13.2
Refer to Figure 13.2.An expansionary fiscal policy would be most effective in raising output with little or no inflation when the aggregate demand curve shifts from
A)AD1 to AD2.
B)AD3 to AD4.
C)AD5 to AD6.
D)AD1 to AD6.
 Figure 13.2
Figure 13.2Refer to Figure 13.2.An expansionary fiscal policy would be most effective in raising output with little or no inflation when the aggregate demand curve shifts from
A)AD1 to AD2.
B)AD3 to AD4.
C)AD5 to AD6.
D)AD1 to AD6.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
If the long-run aggregate supply curve is vertical,the multiplier effect of a change in net taxes on aggregate output in the long run
A)depends on the price level.
B)is one.
C)is zero.
D)is infinitely large.
A)depends on the price level.
B)is one.
C)is zero.
D)is infinitely large.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Refer to the information provided in Figure 13.2 below to answer the questions that follow.
 Figure 13.2
Figure 13.2
Refer to Figure 13.2.Planned investment would experience the greatest amount of crowding out when the aggregate demand curve shifts from
A)AD1 to AD2.
B)AD3 to AD4.
C)AD5 to AD6.
D)The amount of crowding out is the same for all AD curve shifts shown in the figure.
 Figure 13.2
Figure 13.2Refer to Figure 13.2.Planned investment would experience the greatest amount of crowding out when the aggregate demand curve shifts from
A)AD1 to AD2.
B)AD3 to AD4.
C)AD5 to AD6.
D)The amount of crowding out is the same for all AD curve shifts shown in the figure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
In a binding situation,the ________ curve is ________.
A)AD; horizontal
B)AD; vertical
C)AS; horizontal
D)AS; vertical
A)AD; horizontal
B)AD; vertical
C)AS; horizontal
D)AS; vertical

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Other things equal,a decrease in the Z factors will ________ the equilibrium price level and ________ equilibrium output.
A)increase; increase
B)increase; decrease
C)decrease; increase
D)decrease; decrease
A)increase; increase
B)increase; decrease
C)decrease; increase
D)decrease; decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
If wages adjust fully to price increases,fiscal policy will have no effect on output in the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
An intended goal of contractionary fiscal policy and a tightening of monetary policy is
A)an increase in interest rates.
B)an increase in the price level.
C)a decrease in the unemployment rate.
D)a decrease in the level of aggregate output.
A)an increase in interest rates.
B)an increase in the price level.
C)a decrease in the unemployment rate.
D)a decrease in the level of aggregate output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
When the AD curve is vertical,
A)fiscal policy can be used to increase output.
B)monetary policy can be used to increase output.
C)both fiscal policy and monetary policy can be used to increase output.
D)neither fiscal policy nor monetary policy can be used to increase output.
A)fiscal policy can be used to increase output.
B)monetary policy can be used to increase output.
C)both fiscal policy and monetary policy can be used to increase output.
D)neither fiscal policy nor monetary policy can be used to increase output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
An increase in the Z factors represents
A)a tightening of monetary policy.
B)an easing of monetary policy.
C)an expansionary fiscal policy.
D)a contractionary fiscal policy.
A)a tightening of monetary policy.
B)an easing of monetary policy.
C)an expansionary fiscal policy.
D)a contractionary fiscal policy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
In a binding situation,the AD curve is vertical.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
If the AD curve is relatively flat,the Fed is willing to accept large changes in output to keep the price level stable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
In a binding situation,an increase in net taxes
A)shifts the AD curve to the right.
B)shifts the AD curve to the left.
C)does not shift the AD curve.
D)causes the AD curve to become horizontal.
A)shifts the AD curve to the right.
B)shifts the AD curve to the left.
C)does not shift the AD curve.
D)causes the AD curve to become horizontal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
If a decrease in the Z factors resulted in a very large change in the price level and a very small change in aggregate output,
A)then in the U.S.economy investment demand must not be sensitive to the interest rate.
B)then the U.S.economy must have been on the very steep part of its short-run aggregate supply curve.
C)then the U.S.economy must have been on the very flat part of its short-run aggregate supply curve.
D)then the U.S.aggregate demand curve must be very steep.
A)then in the U.S.economy investment demand must not be sensitive to the interest rate.
B)then the U.S.economy must have been on the very steep part of its short-run aggregate supply curve.
C)then the U.S.economy must have been on the very flat part of its short-run aggregate supply curve.
D)then the U.S.aggregate demand curve must be very steep.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
In a binding situation,there is ________ crowding out of planned investment when government spending increases.
A)complete
B)partial
C)no
D)negative
A)complete
B)partial
C)no
D)negative

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
If the Fed has a strong preference for stable prices relative to output,it responds to a price ________ with a ________ increase in the interest rate.
A)increase; large
B)increase; small
C)decrease; large
D)decrease; small
A)increase; large
B)increase; small
C)decrease; large
D)decrease; small

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
If the Fed has a strong preference for stable prices relative to output,the ________ curve is relatively ________.
A)AD; steep
B)AD; flat
C)AS; steep
D)AS; flat
A)AD; steep
B)AD; flat
C)AS; steep
D)AS; flat

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
In a binding situation,an increase in government spending
A)shifts the AD curve to the right.
B)shifts the AD curve to the left.
C)does not shift the AD curve.
D)causes the AD curve to become horizontal.
A)shifts the AD curve to the right.
B)shifts the AD curve to the left.
C)does not shift the AD curve.
D)causes the AD curve to become horizontal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
When the AD curve is relatively flat,the Fed
A)is only willing to accept small changes in output to keep the price level stable.
B)is willing to accept large changes in the price level to keep output stable.
C)is not willing to accept any changes in output to keep the price level stable.
D)is willing to accept large changes in output to keep the price level stable.
A)is only willing to accept small changes in output to keep the price level stable.
B)is willing to accept large changes in the price level to keep output stable.
C)is not willing to accept any changes in output to keep the price level stable.
D)is willing to accept large changes in output to keep the price level stable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
A decrease in the Z factors represents an easing of monetary policy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
In a binding situation,
A)planned investment increases when the price level decreases.
B)output increases when the price level decreases.
C)planned investment and output both increase when the price level decreases.
D)neither planned investment nor output change when the price level decreases.
A)planned investment increases when the price level decreases.
B)output increases when the price level decreases.
C)planned investment and output both increase when the price level decreases.
D)neither planned investment nor output change when the price level decreases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The economy is in a binding situation when the Fed rule calls for a very high interest rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
In a binding situation,
A)only changes in the price level change the interest rate.
B)only changes in the Z factors change the interest rate.
C)changes in both the price level and in the Z factors change the interest rate.
D)the interest rate is always zero.
A)only changes in the price level change the interest rate.
B)only changes in the Z factors change the interest rate.
C)changes in both the price level and in the Z factors change the interest rate.
D)the interest rate is always zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
In a binding situation,an increase in the Z factors
A)shifts the AD curve to the right.
B)shifts the AD curve to the left.
C)does not shift the AD curve.
D)causes the AD curve to become horizontal.
A)shifts the AD curve to the right.
B)shifts the AD curve to the left.
C)does not shift the AD curve.
D)causes the AD curve to become horizontal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
When analyzing the effects of cost shocks,what primarily matters is the shape of
A)the AD curve.
B)the AS curve.
C)both the AD curve and the AS curve.
D)neither the AD curve nor the AS curve.
A)the AD curve.
B)the AS curve.
C)both the AD curve and the AS curve.
D)neither the AD curve nor the AS curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Refer to the information provided in Figure 13.3 below to answer the questions that follow.
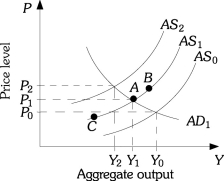 Figure 13.3
Figure 13.3
Refer to Figure 13.3.Cost-push inflation occurs if
A)the economy moves from Point A to Point B on aggregate supply curve AS1.
B)the economy moves from Point A to Point C on the aggregate supply curve AS1.
C)the aggregate supply curve shifts from AS1 to AS0.
D)the aggregate supply curve shifts from AS1 to AS2.
 Figure 13.3
Figure 13.3Refer to Figure 13.3.Cost-push inflation occurs if
A)the economy moves from Point A to Point B on aggregate supply curve AS1.
B)the economy moves from Point A to Point C on the aggregate supply curve AS1.
C)the aggregate supply curve shifts from AS1 to AS0.
D)the aggregate supply curve shifts from AS1 to AS2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Refer to the information provided in Figure 13.3 below to answer the questions that follow.
 Figure 13.3
Figure 13.3
Refer to Figure 13.3.Assume the economy is at Point A.Higher oil prices shift the aggregate supply curve to AS2.If the government decides to counter the effects of higher oil prices by increasing government spending,then the price level will be ________ than P2 and output will be ________ than Y2.
A)greater; greater
B)greater; less
C)less; less
D)less; greater
 Figure 13.3
Figure 13.3Refer to Figure 13.3.Assume the economy is at Point A.Higher oil prices shift the aggregate supply curve to AS2.If the government decides to counter the effects of higher oil prices by increasing government spending,then the price level will be ________ than P2 and output will be ________ than Y2.
A)greater; greater
B)greater; less
C)less; less
D)less; greater

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
When analyzing the effects of government spending,net taxes,and the Z factors,what primarily matters is the shape of
A)the AD curve.
B)the AS curve.
C)both the AD curve and the AS curve.
D)neither the AD curve nor the AS curve.
A)the AD curve.
B)the AS curve.
C)both the AD curve and the AS curve.
D)neither the AD curve nor the AS curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
An economic condition characterized by high unemployment and excessive inflation is called
A)stagflation.
B)recessionary downturn.
C)expansionary growth.
D)depression.
A)stagflation.
B)recessionary downturn.
C)expansionary growth.
D)depression.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
In a binding situation,a positive cost shock will cause ________ in output and ________ in the price level.
A)no change; no change
B)a decrease; an increase
C)no change; an increase
D)a decrease; no change
A)no change; no change
B)a decrease; an increase
C)no change; an increase
D)a decrease; no change

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
For an economy to experience both a recession and inflation at the same time,
A)the aggregate supply curve must shift to the right.
B)the aggregate supply curve must shift to the left.
C)the aggregate demand curve must shift to the left.
D)the aggregate demand curve must shift to the right.
A)the aggregate supply curve must shift to the right.
B)the aggregate supply curve must shift to the left.
C)the aggregate demand curve must shift to the left.
D)the aggregate demand curve must shift to the right.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
With a cost shock,a large decrease in output relative to the increase in the price level would occur if the ________ curve is relatively ________.
A)AS; flat
B)AS; steep
C)AD; flat
D)AD; steep
A)AS; flat
B)AS; steep
C)AD; flat
D)AD; steep

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
In a binding situation,changes in government spending do not shift the AD curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
If the aggregate supply curve is vertical in the long-run,then neither monetary nor fiscal policy will affect aggregate output in the long-run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
A rightward shift in the aggregate demand curve generates a ________ inflation and ________ output.
A)demand-pull; lower
B)cost-push; higher
C)demand-pull; higher
D)cost-push; lower
A)demand-pull; lower
B)cost-push; higher
C)demand-pull; higher
D)cost-push; lower

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
An increase in inflationary expectations that causes firms to increase their prices shifts the
A)aggregate supply curve to the left.
B)aggregate demand curve to the left.
C)aggregate supply curve to the right.
D)aggregate demand curve to the right.
A)aggregate supply curve to the left.
B)aggregate demand curve to the left.
C)aggregate supply curve to the right.
D)aggregate demand curve to the right.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
A sudden increase in the price of oil causes a ________ inflation and ________ output.
A)demand-pull; lower
B)cost-push; higher
C)demand-pull; higher
D)cost-push; lower
A)demand-pull; lower
B)cost-push; higher
C)demand-pull; higher
D)cost-push; lower

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Refer to the information provided in Figure 13.3 below to answer the questions that follow.
 Figure 13.3
Figure 13.3
Refer to Figure 13.3.Assume the economy is currently at Point A on aggregate supply curve AS1.An increase in inflationary expectations that causes firms to increase their prices
A)shifts the aggregate supply curve to AS0.
B)shifts the aggregate supply curve to AS2.
C)moves the economy to Point C on aggregate supply curve AS1.
D)moves the economy to Point B on aggregate supply curve AS1.
 Figure 13.3
Figure 13.3Refer to Figure 13.3.Assume the economy is currently at Point A on aggregate supply curve AS1.An increase in inflationary expectations that causes firms to increase their prices
A)shifts the aggregate supply curve to AS0.
B)shifts the aggregate supply curve to AS2.
C)moves the economy to Point C on aggregate supply curve AS1.
D)moves the economy to Point B on aggregate supply curve AS1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
A(n)________ in inflationary expectations that causes firms to decrease their prices shifts the aggregate supply curve to the ________.
A)increase; right
B)increase; left
C)decrease; right
D)decrease; left
A)increase; right
B)increase; left
C)decrease; right
D)decrease; left

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
An earthquake destroyed 50% of the Moldovian manufacturing base.The Moldovian government decided to use a contractionary fiscal policy to counter the effects of the earthquake on the economy.The use of the contractionary fiscal policy would have caused
A)the price level to be lower and the output level to be higher than they would have been without the policy action.
B)both the price level and the output level to be higher than they would have been without the policy action.
C)both the price level and output level to be lower than what they would have been without the policy action.
D)the price level to be higher and the output level to be lower than they would have been without the policy action.
A)the price level to be lower and the output level to be higher than they would have been without the policy action.
B)both the price level and the output level to be higher than they would have been without the policy action.
C)both the price level and output level to be lower than what they would have been without the policy action.
D)the price level to be higher and the output level to be lower than they would have been without the policy action.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
In a binding situation,the interest rate is always zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Refer to the information provided in Figure 13.3 below to answer the questions that follow.
 Figure 13.3
Figure 13.3
Refer to Figure 13.3.Assume the economy is at Point A.Higher oil prices shift the aggregate supply curve to AS2.If the government decides to counter the effects of higher oil prices by increasing net taxes,then the price level will be ________ than P2 and output will be ________ than Y2.
A)greater; greater
B)greater; less
C)less; less
D)less; greater
 Figure 13.3
Figure 13.3Refer to Figure 13.3.Assume the economy is at Point A.Higher oil prices shift the aggregate supply curve to AS2.If the government decides to counter the effects of higher oil prices by increasing net taxes,then the price level will be ________ than P2 and output will be ________ than Y2.
A)greater; greater
B)greater; less
C)less; less
D)less; greater

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Decreases in net taxes,increases in the Z factors,and increases in government spending are contractionary policies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Cost-push inflation corresponds to ________ output and demand-pull inflation corresponds to ________ output.
A)higher; higher
B)higher; lower
C)lower; higher
D)lower; lower
A)higher; higher
B)higher; lower
C)lower; higher
D)lower; lower

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



