Deck 16: Accounting for Income Taxes
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/145
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 16: Accounting for Income Taxes
1
The classification of deferred tax assets is sometimes dependent on when the benefit will be realized.
True
2
Expenditures currently deducted in the tax return but not included with expenses in the income statement until subsequent years create deferred tax liabilities.
True
3
A deferred tax asset represents the tax effect of the temporary difference between the financial carrying value of an asset or liability and its tax basis.
True
4
Revenues from installment sales of property reported on financial statements in prior years and currently reported in the tax return create deferred tax assets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
For its first year of operations, Tringali Corporation's reconciliation of pretax accounting income to taxable income is as follows: 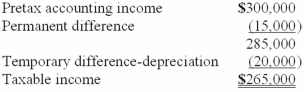 Tringali's tax rate is 40%. What should Tringali report as its income tax expense for its first year of operations?
Tringali's tax rate is 40%. What should Tringali report as its income tax expense for its first year of operations?
A)$120,000.
B)$114,000.
C)$106,000.
D)$8,000.
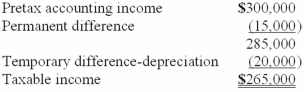 Tringali's tax rate is 40%. What should Tringali report as its income tax expense for its first year of operations?
Tringali's tax rate is 40%. What should Tringali report as its income tax expense for its first year of operations?A)$120,000.
B)$114,000.
C)$106,000.
D)$8,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The basic issue in deciding whether to record a valuation allowance for a deferred tax asset is if probable taxable income is anticipated to be insufficient to realize the tax benefit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following circumstances creates a future taxable amount?
A)Service fees collected in advance from customers: taxable when received, recognized for financial reporting when earned.
B)Accrued compensation costs for future payments.
C)Straight-line depreciation for financial reporting and accelerated depreciation for tax reporting.
D)Investment expenses incurred to obtain tax-exempt income (not tax deductible).
A)Service fees collected in advance from customers: taxable when received, recognized for financial reporting when earned.
B)Accrued compensation costs for future payments.
C)Straight-line depreciation for financial reporting and accelerated depreciation for tax reporting.
D)Investment expenses incurred to obtain tax-exempt income (not tax deductible).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following causes a temporary difference between taxable and pretax accounting income?
A)Investment expenses incurred to generate tax-exempt income.
B)MACRS used for depreciating equipment.
C)The dividends received deduction.
D)Life insurance proceeds received due to the death of an executive.
A)Investment expenses incurred to generate tax-exempt income.
B)MACRS used for depreciating equipment.
C)The dividends received deduction.
D)Life insurance proceeds received due to the death of an executive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A result of inter-period tax allocation is that:
A)Large fluctuations in a company's tax liability are eliminated.
B)The income tax expense is allocated among the income statement items that caused the expense.
C)The income tax expense in the income statement is the sum of the income taxes payable for the year and the changes in deferred tax asset or liability balances for the year.
D)The income tax expense shown in the income statement is equal to the deferred taxes for the year.
A)Large fluctuations in a company's tax liability are eliminated.
B)The income tax expense is allocated among the income statement items that caused the expense.
C)The income tax expense in the income statement is the sum of the income taxes payable for the year and the changes in deferred tax asset or liability balances for the year.
D)The income tax expense shown in the income statement is equal to the deferred taxes for the year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following differences between financial accounting and tax accounting ordinarily creates a deferred tax liability?
A)Interest income on municipal bonds.
B)Proceeds from life insurance received due to death of an executive.
C)Prepaid rent.
D)None of the above.
A)Interest income on municipal bonds.
B)Proceeds from life insurance received due to death of an executive.
C)Prepaid rent.
D)None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Future taxable amounts result in deferred tax assets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
For its first year of operations, Tringali Corporation's reconciliation of pretax accounting income to taxable income is as follows: 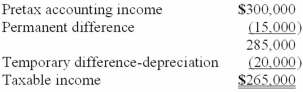 Tringali's tax rate is 40%. What should Tringali report as its deferred income tax liability as of the end of its first year of operations?
Tringali's tax rate is 40%. What should Tringali report as its deferred income tax liability as of the end of its first year of operations?
A)$35,000.
B)$20,000.
C)$14,000.
D)$8,000.
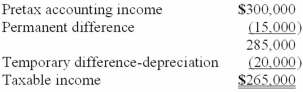 Tringali's tax rate is 40%. What should Tringali report as its deferred income tax liability as of the end of its first year of operations?
Tringali's tax rate is 40%. What should Tringali report as its deferred income tax liability as of the end of its first year of operations?A)$35,000.
B)$20,000.
C)$14,000.
D)$8,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following creates a deferred tax liability?
A)An unrealized loss from recording inventory at lower of cost or market.
B)Accelerated depreciation in the tax return.
C)Estimated warranty expense.
D)Subscriptions collected in advance.
A)An unrealized loss from recording inventory at lower of cost or market.
B)Accelerated depreciation in the tax return.
C)Estimated warranty expense.
D)Subscriptions collected in advance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
For its first year of operations, Tringali Corporation's reconciliation of pretax accounting income to taxable income is as follows: 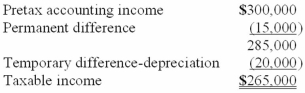 Tringali's tax rate is 40%. Assume that no estimated taxes have been paid. What should Tringali report as income tax payable for its first year of operations?
Tringali's tax rate is 40%. Assume that no estimated taxes have been paid. What should Tringali report as income tax payable for its first year of operations?
A)$120,000.
B)$114,000.
C)$106,000.
D)$8,000.
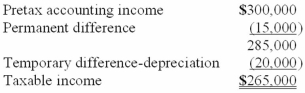 Tringali's tax rate is 40%. Assume that no estimated taxes have been paid. What should Tringali report as income tax payable for its first year of operations?
Tringali's tax rate is 40%. Assume that no estimated taxes have been paid. What should Tringali report as income tax payable for its first year of operations?A)$120,000.
B)$114,000.
C)$106,000.
D)$8,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The tax benefit of a net operating loss carried back two years represents a current receivable for income tax to be refunded.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Changes in enacted tax rates that do not become effective in the current period affect deferred tax accounts only after the new rates take effect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following usually results in an increase in a deferred tax liability?
A)Accrual of estimated operating expenses.
B)Revenue collected in advance.
C)Prepaid operating expenses, currently deductible.
D)All of the above are correct.
A)Accrual of estimated operating expenses.
B)Revenue collected in advance.
C)Prepaid operating expenses, currently deductible.
D)All of the above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
GAAP regarding accounting for income taxes requires the following procedure:
A)Computation of deferred tax assets and liabilities based on temporary differences.
B)Computation of deferred income tax based on permanent differences.
C)Computation of income tax expense based on taxable income.
D)Computation of deferred income tax based on temporary and permanent differences.
A)Computation of deferred tax assets and liabilities based on temporary differences.
B)Computation of deferred income tax based on permanent differences.
C)Computation of income tax expense based on taxable income.
D)Computation of deferred income tax based on temporary and permanent differences.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
A temporary difference originates in one period and reverses, or turns around, in one or more later periods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A net operating loss (NOL) carryforward creates a deferred tax liability that should be classified as current to the extent that the NOL will be recovered in the following year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the following must Franklin Freightways disclose related to the income tax expense reported in the income statement ($ in millions)?
A)Only the current portion of tax expense of $66.
B)Only the total tax expense of $82.
C)Both the current portion of the tax expense of $66 and the deferred portion of the tax expense of $16.
D)None of the above.
A)Only the current portion of tax expense of $66.
B)Only the total tax expense of $82.
C)Both the current portion of the tax expense of $66 and the deferred portion of the tax expense of $16.
D)None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
In the statement of cash flows, by using the indirect method for determining cash flows from operating activities, a decrease in deferred tax liabilities is:
A)Added to net income.
B)Subtracted from net income.
C)Ignored.
D)Included under financing activities.
A)Added to net income.
B)Subtracted from net income.
C)Ignored.
D)Included under financing activities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
What would Kent's income tax expense be in the year 2013?
A)$42,300.
B)$45,900.
C)$49,500.
D)None of the above is correct.
A)$42,300.
B)$45,900.
C)$49,500.
D)None of the above is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Ignoring operating expenses, what deferred tax liability would Isaac report in its year-end 2013 balance sheet?
A)$18 million
B)$162 million
C)$180 million
D)$540 million
A)$18 million
B)$162 million
C)$180 million
D)$540 million

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
During the current year, Stern Company had pretax accounting income of $45 million. Stern's only temporary difference for the year was rent received for the following year in the amount of $15 million. Stern's taxable income for the year would be:
A)$30 million.
B)$60 million.
C)$50 million.
D)$45 million.
A)$30 million.
B)$60 million.
C)$50 million.
D)$45 million.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Woody Corp. had taxable income of $8,000 in the current year. The amount of MACRS depreciation was $3,000, while the amount of depreciation reported in the income statement was $1,000. Assuming no other differences between tax and accounting income, Woody's pretax accounting income was:
A)$5,000.
B)$6,000.
C)$10,000.
D)$11,000.
A)$5,000.
B)$6,000.
C)$10,000.
D)$11,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Alamo Inc. had $300 million in taxable income for the current year. Alamo also had a decrease in deferred tax assets of $30 million and an increase in deferred tax liabilities of $60 million. The company is subject to a tax rate of 40%. The total income tax expense for the year was:
A)$390 million.
B)$210 million.
C)$150 million.
D)$180 million.
A)$390 million.
B)$210 million.
C)$150 million.
D)$180 million.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Franklin Freightways experienced ($ in millions) a current:
A)Tax liability of $66.
B)Tax liability of $36.
C)Tax liability of $70.6.
D)Tax benefit of $10 due to the NOL.
A)Tax liability of $66.
B)Tax liability of $36.
C)Tax liability of $70.6.
D)Tax benefit of $10 due to the NOL.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Franklin's net income ($ in millions) is:
A)$134.
B)$124.
C)$119.4.
D)$118.
A)$134.
B)$124.
C)$119.4.
D)$118.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Franklin's taxable income ($ in millions) is:
A)$40.
B)$165.
C)$110.
D)$160.
A)$40.
B)$165.
C)$110.
D)$160.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
What should Kent report as the current portion of its income tax expense in the year 2013?
A)$45,900.
B)$49,500.
C)$54,000.
D)None of the above is correct.
A)$45,900.
B)$49,500.
C)$54,000.
D)None of the above is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following statements is true as to GAAP regarding accounting for income taxes, and its use of the asset and liability approach?
A)Considerable flexibility is permitted in the balance sheet classification of deferred tax amounts.
B)The approach recognizes the time value of money.
C)The approach is consistent with a balance sheet emphasis of U.S.GAAP and the International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS).
D)The approach is consistent with cash basis accounting.
A)Considerable flexibility is permitted in the balance sheet classification of deferred tax amounts.
B)The approach recognizes the time value of money.
C)The approach is consistent with a balance sheet emphasis of U.S.GAAP and the International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS).
D)The approach is consistent with cash basis accounting.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A deferred tax asset represents a:
A)Future income tax benefit.
B)Future cash collection.
C)Future tax refund.
D)Future amount of money to be paid out.
A)Future income tax benefit.
B)Future cash collection.
C)Future tax refund.
D)Future amount of money to be paid out.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Ignoring operating expenses and additional sales in 2014, what deferred tax liability would Isaac report in its year-end 2014 balance sheet?
A)$54 million
B)$144 million
C)$126 million
D)$180 million.
A)$54 million
B)$144 million
C)$126 million
D)$180 million.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Of the following temporary differences, which one ordinarily creates a deferred tax asset?
A)Intangible drilling costs.
B)MACRS depreciation.
C)Rent received in advance.
D)Installment sales.
A)Intangible drilling costs.
B)MACRS depreciation.
C)Rent received in advance.
D)Installment sales.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Franklin's balance sheet at the end of its first year would report:
A)A deferred tax liability of $16 among noncurrent liabilities.
B)A deferred tax liability of $16 among current liabilities.
C)A deferred tax asset of $16 among noncurrent assets.
D)A deferred tax asset of $16 among current assets.
A)A deferred tax liability of $16 among noncurrent liabilities.
B)A deferred tax liability of $16 among current liabilities.
C)A deferred tax asset of $16 among noncurrent assets.
D)A deferred tax asset of $16 among current assets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Of the following temporary differences, which one ordinarily creates a deferred tax asset?
A)Completed-contract method for long-term construction contracts for tax reporting.
B)Installment sales for tax reporting.
C)Accrued warranty expense.
D)Accelerated depreciation for tax reporting.
A)Completed-contract method for long-term construction contracts for tax reporting.
B)Installment sales for tax reporting.
C)Accrued warranty expense.
D)Accelerated depreciation for tax reporting.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Using straight-line depreciation for financial reporting purposes and MACRS for tax purposes in the first year of an asset's life creates a:
A)Future deductible amount.
B)Permanent difference not requiring inter-period tax allocation.
C)Deferred tax asset.
D)Deferred tax liability.
A)Future deductible amount.
B)Permanent difference not requiring inter-period tax allocation.
C)Deferred tax asset.
D)Deferred tax liability.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
What should be the balance in Kent's deferred tax liability account as of December 31, 2013?
A)$5,200.
B)$7,500.
C)$25,000.
D)None of the above is correct.
A)$5,200.
B)$7,500.
C)$25,000.
D)None of the above is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Suppose that, in 2014, legislation revised the income tax rates so that Isaac would be taxed in 2015 and beyond at 40%, rather than 30%. Assume that there were no other differences in income for financial statement and tax purposes. Ignoring operating expenses and additional sales in 2014, what deferred tax liability would Isaac report in its year-end 2014 balance sheet?
A)$168 million
B)$144 million
C)$126 million
D)$240 million.
A)$168 million
B)$144 million
C)$126 million
D)$240 million.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which of the following creates a deferred tax asset?
A)An unrealized loss from recording investments at fair value.
B)Prepaid insurance.
C)An unrealized gain from recording investments at fair value.
D)Accelerated depreciation in the tax return.
A)An unrealized loss from recording investments at fair value.
B)Prepaid insurance.
C)An unrealized gain from recording investments at fair value.
D)Accelerated depreciation in the tax return.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
In 2012, HD had reported a deferred tax asset of $90 million with no valuation allowance. At December 31, 2013, the account balances of HD Services showed a deferred tax asset of $120 million before assessing the need for a valuation allowance and income taxes payable of $80 million. HD determined that it was more likely than not that 30% of the deferred tax asset ultimately would not be realized. HD made no estimated tax payments during 2013. What amount should HD report as income tax expense in its 2013 income statement?
A)$50 million.
B)$80 million.
C)$86 million.
D)$116 million.
A)$50 million.
B)$80 million.
C)$86 million.
D)$116 million.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The valuation allowance account that is used in conjunction with deferred taxes relates:
A)Only to deferred tax liabilities.
B)To both deferred tax assets and liabilities.
C)Only to deferred tax assets.
D)Only to income taxes receivable due to net operating loss carrybacks.
A)Only to deferred tax liabilities.
B)To both deferred tax assets and liabilities.
C)Only to deferred tax assets.
D)Only to income taxes receivable due to net operating loss carrybacks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Pretax accounting income for the year ended December 31, 2013, was $50 million for Truffles Company. Truffles' taxable income was $60 million. This was a result of differences between straight-line depreciation for financial reporting purposes and MACRS for tax purposes. The enacted tax rate is 30% for 2013 and 40% thereafter. What amount should Truffles report as the current portion of income tax expense for 2013?
A)$15 million.
B)$18 million.
C)$20 million.
D)$24 million.
A)$15 million.
B)$18 million.
C)$20 million.
D)$24 million.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The valuation allowance account that is used in conjunction with deferred tax assets is a(n):
A)Liability.
B)Component of shareholders' equity.
C)Asset.
D)Contra asset.
A)Liability.
B)Component of shareholders' equity.
C)Asset.
D)Contra asset.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
If a company's deferred tax asset is not reduced by a valuation allowance, the company believes it is:
A)Probable that sufficient taxable income will be generated in future years to realize the full tax benefit.
B)Probable that sufficient financial income will be generated in future years to realize the full tax benefit.
C)More likely than not that sufficient taxable income will be generated in future years to realize the full tax benefit.
D)More likely than not that sufficient financial income will be generated in future years to realize the full tax benefit.
A)Probable that sufficient taxable income will be generated in future years to realize the full tax benefit.
B)Probable that sufficient financial income will be generated in future years to realize the full tax benefit.
C)More likely than not that sufficient taxable income will be generated in future years to realize the full tax benefit.
D)More likely than not that sufficient financial income will be generated in future years to realize the full tax benefit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Which of the following causes a permanent difference between taxable income and pretax accounting income?
A)Advance collections of revenues.
B)MACRS depreciation method used for equipment.
C)The installment method used for sales of merchandise.
D)Interest earned on municipal securities.
A)Advance collections of revenues.
B)MACRS depreciation method used for equipment.
C)The installment method used for sales of merchandise.
D)Interest earned on municipal securities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
At the end of the current year, Newsmax Inc. has $400,000 of subscriptions received in advance included in its balance sheet. A disclosure note reveals that the entire $400,000 will be earned in the next year. In the absence of other temporary differences, in the balance sheet one would also expect to find a:
A)Noncurrent deferred tax liability.
B)Noncurrent deferred tax asset.
C)Current deferred tax liability.
D)Current deferred tax asset.
A)Noncurrent deferred tax liability.
B)Noncurrent deferred tax asset.
C)Current deferred tax liability.
D)Current deferred tax asset.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
In reconciling net income to taxable income, interest earned on municipal bonds is:
A)Ignored.
B)A temporary difference.
C)A reversing difference.
D)A permanent difference.
A)Ignored.
B)A temporary difference.
C)A reversing difference.
D)A permanent difference.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which of the following causes a permanent difference between taxable income and pretax accounting income?
A)The installment method used for sales of property.
B)MACRS depreciation method used for equipment.
C)Interest income on municipal bonds.
D)Percentage-of-completion method for long-term construction contracts.
A)The installment method used for sales of property.
B)MACRS depreciation method used for equipment.
C)Interest income on municipal bonds.
D)Percentage-of-completion method for long-term construction contracts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which of the following would never require reporting deferred tax assets or deferred tax liabilities?
A)Depreciation on equipment.
B)Accrual of warranty expense.
C)Life insurance premiums for the payer's benefit.
D)Rent revenue received in advance.
A)Depreciation on equipment.
B)Accrual of warranty expense.
C)Life insurance premiums for the payer's benefit.
D)Rent revenue received in advance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which of the following differences between financial accounting and tax accounting ordinarily creates a deferred tax asset?
A)Tax depreciation in excess of book depreciation.
B)Revenue collected in advance.
C)The installment sales method for tax purposes.
D)None of the above.
A)Tax depreciation in excess of book depreciation.
B)Revenue collected in advance.
C)The installment sales method for tax purposes.
D)None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Estimated employee compensation expenses earned during the current period but expected to be paid in the next period causes:
A)An increase in a deferred tax asset.
B)A decrease in a deferred tax asset.
C)An increase in a deferred tax liability.
D)A decrease in a deferred tax liability.
A)An increase in a deferred tax asset.
B)A decrease in a deferred tax asset.
C)An increase in a deferred tax liability.
D)A decrease in a deferred tax liability.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
A magazine publisher collects one year in advance for subscription revenue. In the year of providing the magazines to customers, the company would record:
A)An increase in a deferred tax asset.
B)A decrease in a deferred tax asset.
C)An increase in a deferred tax liability.
D)A decrease in a deferred tax liability.
A)An increase in a deferred tax asset.
B)A decrease in a deferred tax asset.
C)An increase in a deferred tax liability.
D)A decrease in a deferred tax liability.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
In 2013, Magic Table Inc. decides to add a 36-month warranty on its new product sales. Warranty costs are tax deductible when claims are settled. In its financial statements for 2013, Magic Table Inc incurs:
A)An increase in a deferred tax asset.
B)A decrease in a deferred tax asset.
C)An increase in a deferred tax liability.
D)A decrease in a deferred tax liability.
A)An increase in a deferred tax asset.
B)A decrease in a deferred tax asset.
C)An increase in a deferred tax liability.
D)A decrease in a deferred tax liability.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which of the following circumstances creates a future deductible amount?
A)Earning of non-taxable interest on municipal bonds.
B)Sales of property (installment method for tax purposes).
C)Prepaid advertising expense.
D)Accrued warranty expenses.
A)Earning of non-taxable interest on municipal bonds.
B)Sales of property (installment method for tax purposes).
C)Prepaid advertising expense.
D)Accrued warranty expenses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
When tax rates are changed subsequent to the creation of a deferred tax asset or liability, GAAP requires that:
A)All deferred tax accounts be adjusted to reflect the new tax rates.
B)The beginning deferred tax accounts are left unchanged.
C)Only the current deferred tax accounts are adjusted to reflect the new tax rates.
D)Only the noncurrent deferred tax accounts are adjusted to reflect the new tax rates.
A)All deferred tax accounts be adjusted to reflect the new tax rates.
B)The beginning deferred tax accounts are left unchanged.
C)Only the current deferred tax accounts are adjusted to reflect the new tax rates.
D)Only the noncurrent deferred tax accounts are adjusted to reflect the new tax rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
For classification purposes, a valuation allowance:
A)Is allocated proportionately between deferred tax assets and deferred tax liabilities.
B)Is allocated proportionately between the current and noncurrent portions of the deferred tax asset.
C)Is allocated proportionately between the current and noncurrent portions of the deferred tax liability.
D)Is added to the deferred tax asset.
A)Is allocated proportionately between deferred tax assets and deferred tax liabilities.
B)Is allocated proportionately between the current and noncurrent portions of the deferred tax asset.
C)Is allocated proportionately between the current and noncurrent portions of the deferred tax liability.
D)Is added to the deferred tax asset.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The financial reporting carrying value of Boze Music's only depreciable asset exceeded its tax basis by $150,000 at December 31, 2013. This was a result of differences between straight-line depreciation for financial reporting purposes and MACRS for tax purposes. The asset was acquired earlier in the year. Boze has no other temporary differences. The enacted tax rate is 30% for 2013 and 40% thereafter. Boze should report the deferred tax effect of this difference in its December 31, 2013, balance sheet as:
A)A liability of $45,000.
B)A liability of $60,000.
C)An asset of $45,000.
D)An asset of $60,000.
A)A liability of $45,000.
B)A liability of $60,000.
C)An asset of $45,000.
D)An asset of $60,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Which of the following usually results in an increase in a deferred tax asset?
A)Accelerated depreciation for tax reporting and straight-line depreciation for financial reporting.
B)Prepaid insurance.
C)Subscriptions delivered for which customers had paid in advance.
D)None of the above is correct.
A)Accelerated depreciation for tax reporting and straight-line depreciation for financial reporting.
B)Prepaid insurance.
C)Subscriptions delivered for which customers had paid in advance.
D)None of the above is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Puritan Corp. reported the following pretax accounting income and taxable income for its first three years of operations: 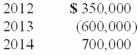 Puritan's tax rate is 40% for all years. Puritan elected a loss carryback. Puritan was certain it would recover the full tax benefit of the NOL. What did it report on December 31, 2013, as the deferred tax asset for the NOL carryforward?
Puritan's tax rate is 40% for all years. Puritan elected a loss carryback. Puritan was certain it would recover the full tax benefit of the NOL. What did it report on December 31, 2013, as the deferred tax asset for the NOL carryforward?
A)$280,000.
B)$200,000.
C)$100,000.
D)$0.
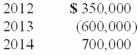 Puritan's tax rate is 40% for all years. Puritan elected a loss carryback. Puritan was certain it would recover the full tax benefit of the NOL. What did it report on December 31, 2013, as the deferred tax asset for the NOL carryforward?
Puritan's tax rate is 40% for all years. Puritan elected a loss carryback. Puritan was certain it would recover the full tax benefit of the NOL. What did it report on December 31, 2013, as the deferred tax asset for the NOL carryforward?A)$280,000.
B)$200,000.
C)$100,000.
D)$0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
According to GAAP for accounting for income taxes, when a company has a net operating loss carryforward:
A)A deferred tax liability is recognized.
B)A receivable is created.
C)A deferred tax equity account is created.
D)A deferred tax asset is recorded along with any applicable valuation allowance.
A)A deferred tax liability is recognized.
B)A receivable is created.
C)A deferred tax equity account is created.
D)A deferred tax asset is recorded along with any applicable valuation allowance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Under current tax law a net operating loss may be carried forward up to:
A)5 years.
B)10 years.
C)15 years.
D)20 years.
A)5 years.
B)10 years.
C)15 years.
D)20 years.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
In its first four years of operations Peridot Jewelers reported the following operating income (loss) amounts:  There were no other deferred income taxes in any year. In 2012, Peridot elected to carry back its operating loss. The enacted income tax rate was 40%. In its 2013 income statement, what amount should Peridot report as current income tax payable?
There were no other deferred income taxes in any year. In 2012, Peridot elected to carry back its operating loss. The enacted income tax rate was 40%. In its 2013 income statement, what amount should Peridot report as current income tax payable?
A)$80,000.
B)$110,000.
C)$170,000.
D)$180,000.
 There were no other deferred income taxes in any year. In 2012, Peridot elected to carry back its operating loss. The enacted income tax rate was 40%. In its 2013 income statement, what amount should Peridot report as current income tax payable?
There were no other deferred income taxes in any year. In 2012, Peridot elected to carry back its operating loss. The enacted income tax rate was 40%. In its 2013 income statement, what amount should Peridot report as current income tax payable?A)$80,000.
B)$110,000.
C)$170,000.
D)$180,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
If a company's deferred tax asset is not reduced by a valuation allowance, the company believes it is more likely than not that:
A)Sufficient accounting income will be generated in future years to realize the full tax benefit.
B)Sufficient accounting and taxable income will exist in future years to realize the full tax benefit.
C)Sufficient taxable income will be generated in future years to realize the full tax benefit.
D)Tax rates will not change in future years.
A)Sufficient accounting income will be generated in future years to realize the full tax benefit.
B)Sufficient accounting and taxable income will exist in future years to realize the full tax benefit.
C)Sufficient taxable income will be generated in future years to realize the full tax benefit.
D)Tax rates will not change in future years.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Bumble Bee Co. had taxable income of $7,000, MACRS depreciation of $5,000, book depreciation of $2,000, and accrued warranty expense of $400 on the books although no warranty work was performed. What is Bumble Bee's pretax accounting income?
A)$4,400.
B)$3,600.
C)$9,600.
D)$2,600.
A)$4,400.
B)$3,600.
C)$9,600.
D)$2,600.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
A net operating loss (NOL) carryforward cannot result in the balance sheet at the end of the NOL year showing:
A)A receivable under current assets for an income tax refund.
B)A current deferred tax asset.
C)A noncurrent deferred tax asset.
D)Both a current and a noncurrent deferred tax asset.
A)A receivable under current assets for an income tax refund.
B)A current deferred tax asset.
C)A noncurrent deferred tax asset.
D)Both a current and a noncurrent deferred tax asset.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
For the current year ($ in millions), Centipede Corp. had $80 in pretax accounting income. This included warranty expense of $6 and $20 in depreciation expense. Two million of warranty costs were incurred, and MACRS depreciation amounted to $35. In the absence of other temporary or permanent differences, what was Centipede's taxable income?
A)$73 million.
B)$69 million.
C)$63 million.
D)$49 million.
A)$73 million.
B)$69 million.
C)$63 million.
D)$49 million.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
In its first four years of operations Peridot Jewelers reported the following operating income (loss) amounts:  There were no other deferred income taxes in any year. In 2012, Peridot elected to carry back its operating loss. The enacted income tax rate was 40%. In its 2013 income statement, what amount should Peridot report as income tax expense?
There were no other deferred income taxes in any year. In 2012, Peridot elected to carry back its operating loss. The enacted income tax rate was 40%. In its 2013 income statement, what amount should Peridot report as income tax expense?
A)$80,000.
B)$110,000.
C)$170,000.
D)$180,000.
 There were no other deferred income taxes in any year. In 2012, Peridot elected to carry back its operating loss. The enacted income tax rate was 40%. In its 2013 income statement, what amount should Peridot report as income tax expense?
There were no other deferred income taxes in any year. In 2012, Peridot elected to carry back its operating loss. The enacted income tax rate was 40%. In its 2013 income statement, what amount should Peridot report as income tax expense?A)$80,000.
B)$110,000.
C)$170,000.
D)$180,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Under current tax law, generally a net operating loss may be carried back:
A)2 years.
B)5 years.
C)15 years.
D)20 years.
A)2 years.
B)5 years.
C)15 years.
D)20 years.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
In its first year of operations, Woodmount Corporation reported pretax accounting income of $500 million for the current year. Depreciation reported in the tax return in excess of depreciation in the income statement was $60 million. The excess tax will reverse itself evenly over the next three years. The current year's tax rate of 40% will be reduced under the current law to 35% next year and 30% for all subsequent years. At the end of the current year, the deferred tax liability related to the excess depreciation will be:
A)$21 million.
B)$24 million.
C)$18 million.
D)$19 million.
A)$21 million.
B)$24 million.
C)$18 million.
D)$19 million.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Recognizing tax benefits in a loss year due to a net operating loss carryforward requires:
A)Creating a tax refund receivable.
B)Note disclosure only.
C)Creating a deferred tax asset.
D)Creating a deferred tax liability.
A)Creating a tax refund receivable.
B)Note disclosure only.
C)Creating a deferred tax asset.
D)Creating a deferred tax liability.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The effect of a change in tax rates:
A)Results in a prior period adjustment.
B)Is allocated between discontinued operations and continuing operations.
C)Is reported separately after extraordinary items.
D)Is reflected in income from continuing operations.
A)Results in a prior period adjustment.
B)Is allocated between discontinued operations and continuing operations.
C)Is reported separately after extraordinary items.
D)Is reflected in income from continuing operations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Giada Foods reported $940 million in income before income taxes for 2013, its first year of operations. Tax depreciation exceeded depreciation for financial reporting purposes by $100 million. The company also had non-tax-deductible expenses of $80 million relating to permanent differences. The income tax rate for 2013 was 35%, but the enacted rate for years after 2013 is 40%. The balance in the deferred tax liability in the December 31, 2013, balance sheet is:
A)$16 million.
B)$35 million.
C)$40 million.
D)$56 million.
A)$16 million.
B)$35 million.
C)$40 million.
D)$56 million.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The Kelso Company had the following operating results:  What is the income tax refund receivable?
What is the income tax refund receivable?
A)$18,000
B)$19,500
C)$18,750
D)$24,000
 What is the income tax refund receivable?
What is the income tax refund receivable?A)$18,000
B)$19,500
C)$18,750
D)$24,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Puritan Corp. reported the following pretax accounting income and taxable income for its first three years of operations: 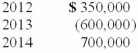 Puritan's tax rate is 40% for all years. As of December 31, 2013, Puritan was certain that it would recover the full tax benefit of the NOL that remained after the operating loss carryback. What would Puritan report as net income for 2014?
Puritan's tax rate is 40% for all years. As of December 31, 2013, Puritan was certain that it would recover the full tax benefit of the NOL that remained after the operating loss carryback. What would Puritan report as net income for 2014?
A)$620,000.
B)$420,000.
C)$250,000.
D)$460,000.
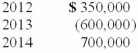 Puritan's tax rate is 40% for all years. As of December 31, 2013, Puritan was certain that it would recover the full tax benefit of the NOL that remained after the operating loss carryback. What would Puritan report as net income for 2014?
Puritan's tax rate is 40% for all years. As of December 31, 2013, Puritan was certain that it would recover the full tax benefit of the NOL that remained after the operating loss carryback. What would Puritan report as net income for 2014?A)$620,000.
B)$420,000.
C)$250,000.
D)$460,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
For the current year ($ in millions), Centipede Corp. had $80 in pretax accounting income. This included warranty expense of $6 and $20 in depreciation expense. Two million of warranty costs were incurred, and MACRS depreciation amounted to $35. In the absence of other temporary or permanent differences, what was Centipede's income tax payable currently, assuming a tax rate of 40%?
A)19.6 million.
B)25.2 million.
C)27.6 million.
D)29.2 million.
A)19.6 million.
B)25.2 million.
C)27.6 million.
D)29.2 million.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
In its first three years of operations Sharp Chairs reported the following operating income (loss) amounts:  There were no deferred income taxes in any year. In 2012, Sharp elected to carry back its operating loss. The enacted income tax rate was 35% in 2011 and 40% thereafter. In its 2013 balance sheet, what amount should Sharp report as current income tax payable?
There were no deferred income taxes in any year. In 2012, Sharp elected to carry back its operating loss. The enacted income tax rate was 35% in 2011 and 40% thereafter. In its 2013 balance sheet, what amount should Sharp report as current income tax payable?
A)$900,000.
B)$1,260,000.
C)$1,440,000.
D)$2,160,000.
 There were no deferred income taxes in any year. In 2012, Sharp elected to carry back its operating loss. The enacted income tax rate was 35% in 2011 and 40% thereafter. In its 2013 balance sheet, what amount should Sharp report as current income tax payable?
There were no deferred income taxes in any year. In 2012, Sharp elected to carry back its operating loss. The enacted income tax rate was 35% in 2011 and 40% thereafter. In its 2013 balance sheet, what amount should Sharp report as current income tax payable?A)$900,000.
B)$1,260,000.
C)$1,440,000.
D)$2,160,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
The tax effect of a net operating loss (NOL) carryback usually:
A)Results in a current receivable at the end of the NOL year.
B)Is subject to a valuation allowance.
C)Is reflected as deferred tax asset at the end of the NOL year.
D)Is reflected as a deferred tax liability at the end of the NOL year.
A)Results in a current receivable at the end of the NOL year.
B)Is subject to a valuation allowance.
C)Is reflected as deferred tax asset at the end of the NOL year.
D)Is reflected as a deferred tax liability at the end of the NOL year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
In 2013, Bodily Corporation reported $300,000 pretax accounting income. The income tax rate for that year was 30%. Bodily had an unused $120,000 net operating loss carryforward from 2011 when the tax rate was 40%. Bodily's income tax payable for 2013 would be
A)$54,000
B)$42,000
C)$90,000
D)$72,000
A)$54,000
B)$42,000
C)$90,000
D)$72,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



