Deck 12: European Society in the Age of the Renaissance 1350-1550
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/75
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 12: European Society in the Age of the Renaissance 1350-1550
1
Which of the following was one of the central components of the Italian Renaissance?
A)Christian humility
B)A concern for the improvement of society in general
C)A glorification of individual genius
D)The attempt to use art to educate the urban masses
A)Christian humility
B)A concern for the improvement of society in general
C)A glorification of individual genius
D)The attempt to use art to educate the urban masses
A glorification of individual genius
2
How did Pico della Mirandola understand the uniqueness of humankind?
A)As creatures in the image of God, humans were superior to the rest of creation, including the angels and other heavenly beings.
B)Humans, lacking a fixed place, were the one part of the created world that could freely choose to rise to the heavens or sink into the realm of animals.
C)Lacking a specific role in God's creation, humans were actually below animals but had the potential for greatness denied to animals.
D)Humans were established by God as just below the angels and given to rule over everything on earth.
A)As creatures in the image of God, humans were superior to the rest of creation, including the angels and other heavenly beings.
B)Humans, lacking a fixed place, were the one part of the created world that could freely choose to rise to the heavens or sink into the realm of animals.
C)Lacking a specific role in God's creation, humans were actually below animals but had the potential for greatness denied to animals.
D)Humans were established by God as just below the angels and given to rule over everything on earth.
Humans, lacking a fixed place, were the one part of the created world that could freely choose to rise to the heavens or sink into the realm of animals.
3
Which of the following did Francesco Petrarch believe?
A)A new era would dawn as writers stripped Christianity of the classical Roman influences that had polluted the church's teachings.
B)The writers of ancient Greece had reached a perfection in literature and philosophy that the writers of ancient Rome had corrupted.
C)The recovery of classical texts would bring about a new golden age of intellectual achievement.
D)The barbarian invaders had brought a new, vigorous energy to Western culture that needed to be integrated into the classical tradition.
A)A new era would dawn as writers stripped Christianity of the classical Roman influences that had polluted the church's teachings.
B)The writers of ancient Greece had reached a perfection in literature and philosophy that the writers of ancient Rome had corrupted.
C)The recovery of classical texts would bring about a new golden age of intellectual achievement.
D)The barbarian invaders had brought a new, vigorous energy to Western culture that needed to be integrated into the classical tradition.
The recovery of classical texts would bring about a new golden age of intellectual achievement.
4
Which of the following best defines the term race as it was used in the Renaissance?
A)Groupings of people based on skin color
B)Groupings of people based on noble lineage
C)Groupings of people based on geographic origins
D)Groupings of people based on ethnic, national, or religious factors
A)Groupings of people based on skin color
B)Groupings of people based on noble lineage
C)Groupings of people based on geographic origins
D)Groupings of people based on ethnic, national, or religious factors

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following characterizes Girolamo Savonarola?
A)He came to power in Florence as a general suppressing a popular revolt but lost authority when the merchants rejected his efforts to restrict their wealth.
B)He came to power in Florence denouncing vice and corruption, but as people tired of his moral denunciations, he lost authority.
C)He was appointed ruler in Florence by the pope but lost authority when he challenged papal interference in Florence's banking industry.
D)He was appointed chief administrator in Florence by the ruling oligarchs but lost power when he failed to defeat the French invasion.
A)He came to power in Florence as a general suppressing a popular revolt but lost authority when the merchants rejected his efforts to restrict their wealth.
B)He came to power in Florence denouncing vice and corruption, but as people tired of his moral denunciations, he lost authority.
C)He was appointed ruler in Florence by the pope but lost authority when he challenged papal interference in Florence's banking industry.
D)He was appointed chief administrator in Florence by the ruling oligarchs but lost power when he failed to defeat the French invasion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following inhibited women's success as painters in the Renaissance?
A)They were allowed to study the male nude.
B)They could not work in public, a requirement of the fresco technique.
C)They were permitted to join groups of male artists for informal practice.
D)They were permitted to attend artistic academies.
A)They were allowed to study the male nude.
B)They could not work in public, a requirement of the fresco technique.
C)They were permitted to join groups of male artists for informal practice.
D)They were permitted to attend artistic academies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
What role did the idea of "fate" play in Machiavelli's analysis in The Prince?
A)Fate marked the sheer random movement of nature and people that was beyond the ability of any ruler to control.
B)The most skilled and prepared ruler could not fully escape the operations of fate that might cause a prince to lose his realm.
C)The idea of fate was but a metaphor for the favor that God randomly bestows on some rulers and denies to others.
D)The skilled ruler can overcome the operations of fate if he is willing to abandon all moral limitations and scruples.
A)Fate marked the sheer random movement of nature and people that was beyond the ability of any ruler to control.
B)The most skilled and prepared ruler could not fully escape the operations of fate that might cause a prince to lose his realm.
C)The idea of fate was but a metaphor for the favor that God randomly bestows on some rulers and denies to others.
D)The skilled ruler can overcome the operations of fate if he is willing to abandon all moral limitations and scruples.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following was a wealthy Florentine, the political leader of his city, and a patron of Renaissance artists?
A)Cesare Borgia
B)Cosimo de Medici
C)Giovanni Sforza
D)Gerolama Orsini
A)Cesare Borgia
B)Cosimo de Medici
C)Giovanni Sforza
D)Gerolama Orsini

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Who was the most prominent metalsmith who helped develop metal movable print?
A)Leonardo da Vinci
B)Johann Gutenberg
C)Johann Fust
D)Desiderius Erasmus
A)Leonardo da Vinci
B)Johann Gutenberg
C)Johann Fust
D)Desiderius Erasmus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
What was the Star Chamber?
A)A court that dealt with noble threats to royal power in England
B)A court dominated by the great nobles of England
C)A court that was the English equivalent of the Spanish Inquisition
D)A court that dealt with the finances of the English government
A)A court that dealt with noble threats to royal power in England
B)A court dominated by the great nobles of England
C)A court that was the English equivalent of the Spanish Inquisition
D)A court that dealt with the finances of the English government

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Why did a unified Italian state fail to develop in the fifteenth century?
A)Political loyalty and feeling centered on a passionate attachment to the individual city-state.
B)The papacy prevented any movement toward unification, fearing a threat to its political authority.
C)France and the Holy Roman Empire had too many land claims in the region to permit any unification.
D)Italians were too culturally and linguistically diverse to realistically contemplate unification.
A)Political loyalty and feeling centered on a passionate attachment to the individual city-state.
B)The papacy prevented any movement toward unification, fearing a threat to its political authority.
C)France and the Holy Roman Empire had too many land claims in the region to permit any unification.
D)Italians were too culturally and linguistically diverse to realistically contemplate unification.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following characterizes the intersection of the hierarchies of wealth and orders in the Renaissance?
A)The nobility retained its status by blocking the newly wealthy from political positions and from marriage into the nobility.
B)The newly wealthy used their resources to establish new forms of social prestige that the nobility could not copy and which discredited the nobility as social leaders.
C)The newly wealthy rejected the claims of the nobility to moral superiority of landed wealth.
D)The nobility retained its status by taking in and integrating the new social elite of wealth.
A)The nobility retained its status by blocking the newly wealthy from political positions and from marriage into the nobility.
B)The newly wealthy used their resources to establish new forms of social prestige that the nobility could not copy and which discredited the nobility as social leaders.
C)The newly wealthy rejected the claims of the nobility to moral superiority of landed wealth.
D)The nobility retained its status by taking in and integrating the new social elite of wealth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Italian humanists stressed the
A)study of the classics for what they could reveal about human nature.
B)study of the classics in order to understand the divine nature of God.
C)absolute authority of classical texts.
D)role of the church in the reform of society.
A)study of the classics for what they could reveal about human nature.
B)study of the classics in order to understand the divine nature of God.
C)absolute authority of classical texts.
D)role of the church in the reform of society.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The marriage of Ferdinand of Aragon and Isabella of Castile
A)permitted the monarchs to undermine the provincial elite by unifying the two states into a single, unified kingdom.
B)unified all of the Iberian Peninsula.
C)created a dynastic union but did not unify the separate kingdoms into a single state.
D)undermined the claims of the Holy Roman emperor to be the defender of the church.
A)permitted the monarchs to undermine the provincial elite by unifying the two states into a single, unified kingdom.
B)unified all of the Iberian Peninsula.
C)created a dynastic union but did not unify the separate kingdoms into a single state.
D)undermined the claims of the Holy Roman emperor to be the defender of the church.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Most male Renaissance humanists argued that
A)men and women were equals in intellectual pursuits.
B)the status of women had improved since the Middle Ages.
C)women's sphere of activity was private and domestic.
D)women were asexual beings.
A)men and women were equals in intellectual pursuits.
B)the status of women had improved since the Middle Ages.
C)women's sphere of activity was private and domestic.
D)women were asexual beings.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
According to Machiavelli, government should be judged on whether it
A)provided the necessary public services.
B)was based on Christian morality.
C)protected the liberty of its citizens.
D)provided order, security, and safety for the populace.
A)provided the necessary public services.
B)was based on Christian morality.
C)protected the liberty of its citizens.
D)provided order, security, and safety for the populace.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
What purposes were served by sumptuary laws?
A)Sumptuary laws sought to prevent all forms of luxury, reinforce ascetic piety, and undermine the growing wealth of merchants.
B)Sumptuary laws attacked social inequalities by rejecting luxury products and sought to protect local industries by requiring the use of certain materials.
C)Sumptuary laws attempted to impose moral standards and challenged the efforts of the clergy to express their status through clothing styles.
D)Sumptuary laws reinforced social hierarchies, attempted to impose moral standards, and sought to protect local industries.
A)Sumptuary laws sought to prevent all forms of luxury, reinforce ascetic piety, and undermine the growing wealth of merchants.
B)Sumptuary laws attacked social inequalities by rejecting luxury products and sought to protect local industries by requiring the use of certain materials.
C)Sumptuary laws attempted to impose moral standards and challenged the efforts of the clergy to express their status through clothing styles.
D)Sumptuary laws reinforced social hierarchies, attempted to impose moral standards, and sought to protect local industries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
According to the text, Thomas More's Utopia was remarkable for its time because it asserted that
A)the problems plaguing society could be solved by a beneficent government.
B)North America would one day be the site of the greatest power in world history.
C)Native Americans could be saved through conversion to Christianity.
D)flaws in the divine nature were responsible for human corruption.
A)the problems plaguing society could be solved by a beneficent government.
B)North America would one day be the site of the greatest power in world history.
C)Native Americans could be saved through conversion to Christianity.
D)flaws in the divine nature were responsible for human corruption.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following best characterizes the Renaissance idea of virtù?
A)The ability to shape the world around oneself according to one's will
B)The expression of perfection in the life lived in balance and simplicity
C)Moral goodness as set out in the Christian Scriptures
D)The serenity achieved through contemplation and acceptance of life's hardships
A)The ability to shape the world around oneself according to one's will
B)The expression of perfection in the life lived in balance and simplicity
C)Moral goodness as set out in the Christian Scriptures
D)The serenity achieved through contemplation and acceptance of life's hardships

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
In early Renaissance Italy, art
A)manifested corporate power.
B)was commissioned by nobles only.
C)was seen as subversive by the church.
D)did not depict living people.
A)manifested corporate power.
B)was commissioned by nobles only.
C)was seen as subversive by the church.
D)did not depict living people.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
What Florentine artist was commissioned by Pope Julius II to build his tomb and paint the Sistine Chapel?
A)Botticelli
B)Da Vinci
C)Raphael
D)Michelangelo
A)Botticelli
B)Da Vinci
C)Raphael
D)Michelangelo

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The following is an excerpt from the Florentine merchant and historian Benedetto Dei's description of his home city: "Our beautiful Florence contains within the city in this present year two hundred seventy shops belonging to the wool merchants' guild . . . eighty-three rich and splendid warehouses of the silk merchants' guild. . . . The number of banks amounts to thirty-three; the shops of the cabinet-makers, whose business is carving and inlaid work, to eighty-four . . . there are forty-four goldsmiths' and jewellers' shops."
What does this passage suggest about Florence?
A)That Florentines were uncomfortable with borrowing and lending money at interest
B)That the pottery industry was very important to the city
C)That the city's economy was built around agriculture
D)That there was high demand for luxury items in the city
What does this passage suggest about Florence?
A)That Florentines were uncomfortable with borrowing and lending money at interest
B)That the pottery industry was very important to the city
C)That the city's economy was built around agriculture
D)That there was high demand for luxury items in the city

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
What French word was coined by historian Giorgio Vasari to describe the "rebirth" of the culture of classical antiquity?
A)Renaissance
B)Detente
C)Ancien Régime
D)Reconnaissance
A)Renaissance
B)Detente
C)Ancien Régime
D)Reconnaissance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The most important factor in the emergence of the Italian Renaissance was the
A)decline of religious feeling.
B)political disunity of Italy.
C)great commercial revival in Italy.
D)creation of powerful, centralized monarchies.
A)decline of religious feeling.
B)political disunity of Italy.
C)great commercial revival in Italy.
D)creation of powerful, centralized monarchies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The Concordat of Bologna, between Francis I of France and Pope Leo X, gave the French monarch the authority to
A)administer monasteries in Italy.
B)select bishops and abbots.
C)select the pope.
D)administer Italian city-states.
A)administer monasteries in Italy.
B)select bishops and abbots.
C)select the pope.
D)administer Italian city-states.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The Spanish conversos were which of the following?
A)American Indians who returned to Spain to demonstrate that they could and would embrace Christianity
B)Jewish Christians, some of whom held prominent positions in the state, church, and business
C)Albigensian heretics who had fled to Spain to avoid the Inquisition in France
D)Muslim converts to Christianity following the fall of Granada
A)American Indians who returned to Spain to demonstrate that they could and would embrace Christianity
B)Jewish Christians, some of whom held prominent positions in the state, church, and business
C)Albigensian heretics who had fled to Spain to avoid the Inquisition in France
D)Muslim converts to Christianity following the fall of Granada

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The Spanish Inquisition was an attempt to
A)root out insincere Jewish converts to Christianity.
B)inventory and secure the wealth of Europe.
C)regulate university curricula.
D)counteract the influence of the mendicant orders.
A)root out insincere Jewish converts to Christianity.
B)inventory and secure the wealth of Europe.
C)regulate university curricula.
D)counteract the influence of the mendicant orders.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
On the Iberian Peninsula, who were the people referred to as the "New Christians"?
A)Germanic and Scandinavian converts
B)Orthodox Byzantine mercenaries
C)Jewish and Muslim converts
D)Christians who had been re-baptized
A)Germanic and Scandinavian converts
B)Orthodox Byzantine mercenaries
C)Jewish and Muslim converts
D)Christians who had been re-baptized

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
On the Iberian Peninsula, what was the social position of African slaves?
A)They intermingled with the people they lived among and sometimes intermarried with them.
B)They were socially segregated as a lesser class lacking any rights.
C)They isolated themselves into tight-knit communities that sought to achieve independence from their masters.
D)They were kept in guarded, military-style barracks that limited their ability to move within the society.
A)They intermingled with the people they lived among and sometimes intermarried with them.
B)They were socially segregated as a lesser class lacking any rights.
C)They isolated themselves into tight-knit communities that sought to achieve independence from their masters.
D)They were kept in guarded, military-style barracks that limited their ability to move within the society.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
According to Map 12.3: The Unification of Spain and the Expulsion of the Jews, Fifteenth Century, where did the Jewish population of the Spanish kingdom migrate to after their ordered expulsion by Isabella and Ferdinand? 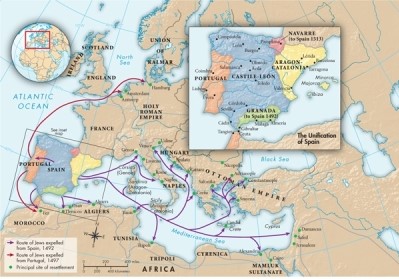
A)Ireland
B)Scandinavia
C)Rural France
D)Cities in the Mediterranean and southern Europe

A)Ireland
B)Scandinavia
C)Rural France
D)Cities in the Mediterranean and southern Europe

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
"Assiduous in the science and skill of dealing with arms and horses and musical instruments, as well as in the pursuit of letters and the fine arts." Who authored this quote about his own important qualities?
A)Leon Battista Alberti
B)Niccolo Machiavelli
C)Giorgio Vasari
D)Desiderius Erasmus
A)Leon Battista Alberti
B)Niccolo Machiavelli
C)Giorgio Vasari
D)Desiderius Erasmus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Why did a woman's work receive less compensation than a man's work during the Renaissance?
A)The traditional work associated with women was unskilled and, therefore, more widely performed.
B)Women were largely secluded in their homes; therefore, their work was seen as strictly domestic and not worthy of compensation.
C)Women did not seek to organize in guilds so that they could better influence wages and prices for their work.
D)It was understood that a woman was either married or to be married and, therefore, not responsible for supporting a family.
A)The traditional work associated with women was unskilled and, therefore, more widely performed.
B)Women were largely secluded in their homes; therefore, their work was seen as strictly domestic and not worthy of compensation.
C)Women did not seek to organize in guilds so that they could better influence wages and prices for their work.
D)It was understood that a woman was either married or to be married and, therefore, not responsible for supporting a family.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
What educational book by Baldassare Castiglione provided a treatise on training a young man in the discipline and fashion needed for the courtly ideal of being a gentleman?
A)The Prince
B)Education of a Christian Prince
C)Utopia
D)The Courtier
A)The Prince
B)Education of a Christian Prince
C)Utopia
D)The Courtier

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which of the following was the most important source of patronage for Renaissance artists?
A)Monasteries
B)Art guilds
C)Universities and academic institutions
D)Wealthy individuals and rulers
A)Monasteries
B)Art guilds
C)Universities and academic institutions
D)Wealthy individuals and rulers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
"[T]he city in this present year [contains] two hundred seventy shops belonging to the wool merchants' guild . . . eighty-three rich and splendid warehouses of the silk merchants' guild. . . . The number of banks amounts to thirty-three; the shops of the cabinet-makers, whose business is carving and inlaid work, to eighty-four . . . there are forty-four goldsmiths' and jewellers' shops." What city is Benedetto Dei describing in this quote?
A)Venice
B)Naples
C)Rome
D)Florence
A)Venice
B)Naples
C)Rome
D)Florence

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
"Everyone gets a fair share, so there are never any poor men or beggars. Nobody owns anything, but everyone is rich-for what greater wealth can there be than cheerfulness, peace of mind, and freedom from anxiety? Instead of being worried about his food supply, upset by the plaintive demands of his wife, afraid of poverty for his son." This quote (from Evaluating the Evidence 12.2) describes the ideal society depicted in what humanist's work?
A)Desiderius Erasmus
B)Thomas More
C)Niccolo Machiavelli
D)John Locke
A)Desiderius Erasmus
B)Thomas More
C)Niccolo Machiavelli
D)John Locke

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
According to Map 12.1: The Italian City-States, ca. 1494, which European monarch invaded multiple Italian city-states in 1494? 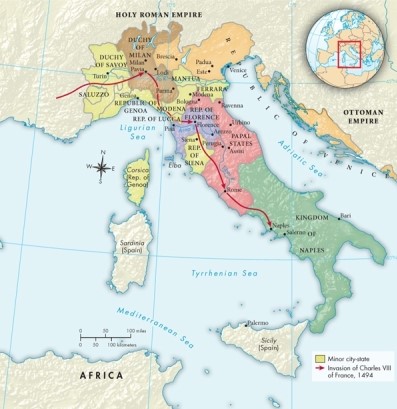
A)Henry VII of England
B)Ferdinand of Spain
C)Charles VIII of France
D)Maximilian I of the Holy Roman Empire

A)Henry VII of England
B)Ferdinand of Spain
C)Charles VIII of France
D)Maximilian I of the Holy Roman Empire

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The following is an excerpt from sixteenth-century regulations for vineyard workers: "Men who work in the vineyards, doing work that is skilled, are to be paid 16 pence per day; in addition, they are to receive soup and wine in the morning, at midday beer, vegetables and meat, and in the evening soup, vegetables and wine. Young boys are to be paid 10 pence per day. Women who work as haymakers are to be given 6 pence a day. If the employer wants to have them doing other work, he may make an agreement with them to pay them 7 or 8 pence. He may also give them soup and vegetables to eat in the morning but no wine-milk and bread at midday, but nothing in the evening."
This passage provides evidence in support of which of the following claims?
A)Vineyard work was difficult, dangerous, and poorly paid.
B)Vineyard workers were paid an hourly wage and received no other compensation.
C)Vineyard work was an exclusively male profession.
D)Women were the lowest paid vineyard workers.
This passage provides evidence in support of which of the following claims?
A)Vineyard work was difficult, dangerous, and poorly paid.
B)Vineyard workers were paid an hourly wage and received no other compensation.
C)Vineyard work was an exclusively male profession.
D)Women were the lowest paid vineyard workers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
What individuals believed the merging of Christian and classical traditions could provide reform for the church and deepen the spiritual lives of people?
A)Patricians
B)Conversos
C)Christian humanists
D)Jacobites
A)Patricians
B)Conversos
C)Christian humanists
D)Jacobites

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The Tudor Henry VII of England won broad, popular support by
A)reforming the church.
B)promoting peace and social order at the local level.
C)restricting the wages of the working classes.
D)lowering taxes and subsidizing the wool industry.
A)reforming the church.
B)promoting peace and social order at the local level.
C)restricting the wages of the working classes.
D)lowering taxes and subsidizing the wool industry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
What were the goals of the Inquisition in fifteenth-century Spain?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
What political powers dominated fifteenth-century Italy?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
How did the Renaissance humanists understand the roles of Julius Caesar and Cicero in the development of Rome?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
In Renaissance Italy, what purposes were served by merchant oligarchs who transformed their homes into courts?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Educated fifteenth-century Italians believed that
A)the world was coming to an end.
B)they were living in a new era of human history.
C)they had much to learn from the culture of the Middle Ages.
D)their society was in the midst of inevitable and unstoppable decline.
A)the world was coming to an end.
B)they were living in a new era of human history.
C)they had much to learn from the culture of the Middle Ages.
D)their society was in the midst of inevitable and unstoppable decline.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
What was the "debate about women"?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
_________________ led the way in the great commercial revival of the eleventh century.
A)Northern Italian cities
B)Southern Italian cities
C)The cities of southern France
D)The cities of central Europe
A)Northern Italian cities
B)Southern Italian cities
C)The cities of southern France
D)The cities of central Europe

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Describe the political and socioeconomic makeup of the Italian city-states.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Piero della Francesca and Andrea Mantegna pioneered
A)the fresco technique.
B)the use of metal type in printing.
C)marble sculpture.
D)perspective in painting.
A)the fresco technique.
B)the use of metal type in printing.
C)marble sculpture.
D)perspective in painting.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
What impact did the War of the Roses have on the development of the English state?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
What benefits did humanists claim would come from the education system they proposed?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
How is the praise of the Renaissance artist as a "man of genius" somewhat misleading?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which of the following gained control of papal banking toward the end of the thirteenth century?
A)French dukes
B)Spanish nobles
C)Florentine merchants
D)The Knights Templar
A)French dukes
B)Spanish nobles
C)Florentine merchants
D)The Knights Templar

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The _____________ emerged as a distinct artistic genre during the Renaissance.
A)individual portrait
B)landscape
C)religious allegory
D)history painting
A)individual portrait
B)landscape
C)religious allegory
D)history painting

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
What were the main sources of Florentine wealth?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Under Henry VII of England, the center of royal authority was
A)the London Guild Hall.
B)the archdiocese of Canterbury.
C)the royal council.
D)Parliament.
A)the London Guild Hall.
B)the archdiocese of Canterbury.
C)the royal council.
D)Parliament.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
How did the content and style of Renaissance art differ from that of medieval art?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
What did Petrarch do to help bring about a new golden age in Italy?
A)He entered the service of the lords of Florence.
B)He devoted himself to prayer and fasting.
C)He proposed a new kind of education.
D)He donated all of his wealth to the church.
A)He entered the service of the lords of Florence.
B)He devoted himself to prayer and fasting.
C)He proposed a new kind of education.
D)He donated all of his wealth to the church.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Charles VII of France created the first __________________ anywhere in Europe.
A)permanent royal army
B)national bank
C)public library
D)art museum
A)permanent royal army
B)national bank
C)public library
D)art museum

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The fall of ____________ to Christian forces in 1492 signaled the completion of the reconquista.
A)Navarre
B)Granada
C)Portugal
D)Catalonia
A)Navarre
B)Granada
C)Portugal
D)Catalonia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Answer the following questions:
New Christians
A)Debate among writers and thinkers in the Renaissance about women's qualities and proper role in society.
B)Sworn associations of free men in Italian cities led by merchant guilds that sought political and economic independence from local nobles.
C)A program of study designed by Italians that emphasized the critical study of Latin and Greek literature with the goal of understanding human nature.
D)Disenfranchised common people in Italian cities who resented their exclusion from power.
E)A French word meaning "rebirth," used to describe the rebirth of the culture of classical antiquity in Italy during the fourteenth to sixteenth centuries.
F)Northern humanists who interpreted Italian ideas about and attitudes toward classical antiquity and humanism in terms of their own religious traditions.
G)A term for Jews and Muslims in the Iberian Peninsula who accepted Christianity; in many cases, they included Christians whose families had converted centuries earlier.
H)Magnificent households and palaces where signori and other rulers lived, conducted business, and supported the arts.
I)Financial support of writers and artists by cities, groups, and individuals, often to produce specific works or works in specific styles.
J)Government by one-man rule in Italian cities such as Milan; also refers to these rulers.
K)The quality of being able to shape the world according to one's own will.
New Christians
A)Debate among writers and thinkers in the Renaissance about women's qualities and proper role in society.
B)Sworn associations of free men in Italian cities led by merchant guilds that sought political and economic independence from local nobles.
C)A program of study designed by Italians that emphasized the critical study of Latin and Greek literature with the goal of understanding human nature.
D)Disenfranchised common people in Italian cities who resented their exclusion from power.
E)A French word meaning "rebirth," used to describe the rebirth of the culture of classical antiquity in Italy during the fourteenth to sixteenth centuries.
F)Northern humanists who interpreted Italian ideas about and attitudes toward classical antiquity and humanism in terms of their own religious traditions.
G)A term for Jews and Muslims in the Iberian Peninsula who accepted Christianity; in many cases, they included Christians whose families had converted centuries earlier.
H)Magnificent households and palaces where signori and other rulers lived, conducted business, and supported the arts.
I)Financial support of writers and artists by cities, groups, and individuals, often to produce specific works or works in specific styles.
J)Government by one-man rule in Italian cities such as Milan; also refers to these rulers.
K)The quality of being able to shape the world according to one's own will.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Answer the following questions:
courts
A)Debate among writers and thinkers in the Renaissance about women's qualities and proper role in society.
B)Sworn associations of free men in Italian cities led by merchant guilds that sought political and economic independence from local nobles.
C)A program of study designed by Italians that emphasized the critical study of Latin and Greek literature with the goal of understanding human nature.
D)Disenfranchised common people in Italian cities who resented their exclusion from power.
E)A French word meaning "rebirth," used to describe the rebirth of the culture of classical antiquity in Italy during the fourteenth to sixteenth centuries.
F)Northern humanists who interpreted Italian ideas about and attitudes toward classical antiquity and humanism in terms of their own religious traditions.
G)A term for Jews and Muslims in the Iberian Peninsula who accepted Christianity; in many cases, they included Christians whose families had converted centuries earlier.
H)Magnificent households and palaces where signori and other rulers lived, conducted business, and supported the arts.
I)Financial support of writers and artists by cities, groups, and individuals, often to produce specific works or works in specific styles.
J)Government by one-man rule in Italian cities such as Milan; also refers to these rulers.
K)The quality of being able to shape the world according to one's own will.
courts
A)Debate among writers and thinkers in the Renaissance about women's qualities and proper role in society.
B)Sworn associations of free men in Italian cities led by merchant guilds that sought political and economic independence from local nobles.
C)A program of study designed by Italians that emphasized the critical study of Latin and Greek literature with the goal of understanding human nature.
D)Disenfranchised common people in Italian cities who resented their exclusion from power.
E)A French word meaning "rebirth," used to describe the rebirth of the culture of classical antiquity in Italy during the fourteenth to sixteenth centuries.
F)Northern humanists who interpreted Italian ideas about and attitudes toward classical antiquity and humanism in terms of their own religious traditions.
G)A term for Jews and Muslims in the Iberian Peninsula who accepted Christianity; in many cases, they included Christians whose families had converted centuries earlier.
H)Magnificent households and palaces where signori and other rulers lived, conducted business, and supported the arts.
I)Financial support of writers and artists by cities, groups, and individuals, often to produce specific works or works in specific styles.
J)Government by one-man rule in Italian cities such as Milan; also refers to these rulers.
K)The quality of being able to shape the world according to one's own will.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Answer the following questions:
signori
A)Debate among writers and thinkers in the Renaissance about women's qualities and proper role in society.
B)Sworn associations of free men in Italian cities led by merchant guilds that sought political and economic independence from local nobles.
C)A program of study designed by Italians that emphasized the critical study of Latin and Greek literature with the goal of understanding human nature.
D)Disenfranchised common people in Italian cities who resented their exclusion from power.
E)A French word meaning "rebirth," used to describe the rebirth of the culture of classical antiquity in Italy during the fourteenth to sixteenth centuries.
F)Northern humanists who interpreted Italian ideas about and attitudes toward classical antiquity and humanism in terms of their own religious traditions.
G)A term for Jews and Muslims in the Iberian Peninsula who accepted Christianity; in many cases, they included Christians whose families had converted centuries earlier.
H)Magnificent households and palaces where signori and other rulers lived, conducted business, and supported the arts.
I)Financial support of writers and artists by cities, groups, and individuals, often to produce specific works or works in specific styles.
J)Government by one-man rule in Italian cities such as Milan; also refers to these rulers.
K)The quality of being able to shape the world according to one's own will.
signori
A)Debate among writers and thinkers in the Renaissance about women's qualities and proper role in society.
B)Sworn associations of free men in Italian cities led by merchant guilds that sought political and economic independence from local nobles.
C)A program of study designed by Italians that emphasized the critical study of Latin and Greek literature with the goal of understanding human nature.
D)Disenfranchised common people in Italian cities who resented their exclusion from power.
E)A French word meaning "rebirth," used to describe the rebirth of the culture of classical antiquity in Italy during the fourteenth to sixteenth centuries.
F)Northern humanists who interpreted Italian ideas about and attitudes toward classical antiquity and humanism in terms of their own religious traditions.
G)A term for Jews and Muslims in the Iberian Peninsula who accepted Christianity; in many cases, they included Christians whose families had converted centuries earlier.
H)Magnificent households and palaces where signori and other rulers lived, conducted business, and supported the arts.
I)Financial support of writers and artists by cities, groups, and individuals, often to produce specific works or works in specific styles.
J)Government by one-man rule in Italian cities such as Milan; also refers to these rulers.
K)The quality of being able to shape the world according to one's own will.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Answer the following questions:
communes
A)Debate among writers and thinkers in the Renaissance about women's qualities and proper role in society.
B)Sworn associations of free men in Italian cities led by merchant guilds that sought political and economic independence from local nobles.
C)A program of study designed by Italians that emphasized the critical study of Latin and Greek literature with the goal of understanding human nature.
D)Disenfranchised common people in Italian cities who resented their exclusion from power.
E)A French word meaning "rebirth," used to describe the rebirth of the culture of classical antiquity in Italy during the fourteenth to sixteenth centuries.
F)Northern humanists who interpreted Italian ideas about and attitudes toward classical antiquity and humanism in terms of their own religious traditions.
G)A term for Jews and Muslims in the Iberian Peninsula who accepted Christianity; in many cases, they included Christians whose families had converted centuries earlier.
H)Magnificent households and palaces where signori and other rulers lived, conducted business, and supported the arts.
I)Financial support of writers and artists by cities, groups, and individuals, often to produce specific works or works in specific styles.
J)Government by one-man rule in Italian cities such as Milan; also refers to these rulers.
K)The quality of being able to shape the world according to one's own will.
communes
A)Debate among writers and thinkers in the Renaissance about women's qualities and proper role in society.
B)Sworn associations of free men in Italian cities led by merchant guilds that sought political and economic independence from local nobles.
C)A program of study designed by Italians that emphasized the critical study of Latin and Greek literature with the goal of understanding human nature.
D)Disenfranchised common people in Italian cities who resented their exclusion from power.
E)A French word meaning "rebirth," used to describe the rebirth of the culture of classical antiquity in Italy during the fourteenth to sixteenth centuries.
F)Northern humanists who interpreted Italian ideas about and attitudes toward classical antiquity and humanism in terms of their own religious traditions.
G)A term for Jews and Muslims in the Iberian Peninsula who accepted Christianity; in many cases, they included Christians whose families had converted centuries earlier.
H)Magnificent households and palaces where signori and other rulers lived, conducted business, and supported the arts.
I)Financial support of writers and artists by cities, groups, and individuals, often to produce specific works or works in specific styles.
J)Government by one-man rule in Italian cities such as Milan; also refers to these rulers.
K)The quality of being able to shape the world according to one's own will.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Answer the following questions:
debate about women
A)Debate among writers and thinkers in the Renaissance about women's qualities and proper role in society.
B)Sworn associations of free men in Italian cities led by merchant guilds that sought political and economic independence from local nobles.
C)A program of study designed by Italians that emphasized the critical study of Latin and Greek literature with the goal of understanding human nature.
D)Disenfranchised common people in Italian cities who resented their exclusion from power.
E)A French word meaning "rebirth," used to describe the rebirth of the culture of classical antiquity in Italy during the fourteenth to sixteenth centuries.
F)Northern humanists who interpreted Italian ideas about and attitudes toward classical antiquity and humanism in terms of their own religious traditions.
G)A term for Jews and Muslims in the Iberian Peninsula who accepted Christianity; in many cases, they included Christians whose families had converted centuries earlier.
H)Magnificent households and palaces where signori and other rulers lived, conducted business, and supported the arts.
I)Financial support of writers and artists by cities, groups, and individuals, often to produce specific works or works in specific styles.
J)Government by one-man rule in Italian cities such as Milan; also refers to these rulers.
K)The quality of being able to shape the world according to one's own will.
debate about women
A)Debate among writers and thinkers in the Renaissance about women's qualities and proper role in society.
B)Sworn associations of free men in Italian cities led by merchant guilds that sought political and economic independence from local nobles.
C)A program of study designed by Italians that emphasized the critical study of Latin and Greek literature with the goal of understanding human nature.
D)Disenfranchised common people in Italian cities who resented their exclusion from power.
E)A French word meaning "rebirth," used to describe the rebirth of the culture of classical antiquity in Italy during the fourteenth to sixteenth centuries.
F)Northern humanists who interpreted Italian ideas about and attitudes toward classical antiquity and humanism in terms of their own religious traditions.
G)A term for Jews and Muslims in the Iberian Peninsula who accepted Christianity; in many cases, they included Christians whose families had converted centuries earlier.
H)Magnificent households and palaces where signori and other rulers lived, conducted business, and supported the arts.
I)Financial support of writers and artists by cities, groups, and individuals, often to produce specific works or works in specific styles.
J)Government by one-man rule in Italian cities such as Milan; also refers to these rulers.
K)The quality of being able to shape the world according to one's own will.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Answer the following questions:
Christian humanists
A)Debate among writers and thinkers in the Renaissance about women's qualities and proper role in society.
B)Sworn associations of free men in Italian cities led by merchant guilds that sought political and economic independence from local nobles.
C)A program of study designed by Italians that emphasized the critical study of Latin and Greek literature with the goal of understanding human nature.
D)Disenfranchised common people in Italian cities who resented their exclusion from power.
E)A French word meaning "rebirth," used to describe the rebirth of the culture of classical antiquity in Italy during the fourteenth to sixteenth centuries.
F)Northern humanists who interpreted Italian ideas about and attitudes toward classical antiquity and humanism in terms of their own religious traditions.
G)A term for Jews and Muslims in the Iberian Peninsula who accepted Christianity; in many cases, they included Christians whose families had converted centuries earlier.
H)Magnificent households and palaces where signori and other rulers lived, conducted business, and supported the arts.
I)Financial support of writers and artists by cities, groups, and individuals, often to produce specific works or works in specific styles.
J)Government by one-man rule in Italian cities such as Milan; also refers to these rulers.
K)The quality of being able to shape the world according to one's own will.
Christian humanists
A)Debate among writers and thinkers in the Renaissance about women's qualities and proper role in society.
B)Sworn associations of free men in Italian cities led by merchant guilds that sought political and economic independence from local nobles.
C)A program of study designed by Italians that emphasized the critical study of Latin and Greek literature with the goal of understanding human nature.
D)Disenfranchised common people in Italian cities who resented their exclusion from power.
E)A French word meaning "rebirth," used to describe the rebirth of the culture of classical antiquity in Italy during the fourteenth to sixteenth centuries.
F)Northern humanists who interpreted Italian ideas about and attitudes toward classical antiquity and humanism in terms of their own religious traditions.
G)A term for Jews and Muslims in the Iberian Peninsula who accepted Christianity; in many cases, they included Christians whose families had converted centuries earlier.
H)Magnificent households and palaces where signori and other rulers lived, conducted business, and supported the arts.
I)Financial support of writers and artists by cities, groups, and individuals, often to produce specific works or works in specific styles.
J)Government by one-man rule in Italian cities such as Milan; also refers to these rulers.
K)The quality of being able to shape the world according to one's own will.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Answer the following questions:
patronage
A)Debate among writers and thinkers in the Renaissance about women's qualities and proper role in society.
B)Sworn associations of free men in Italian cities led by merchant guilds that sought political and economic independence from local nobles.
C)A program of study designed by Italians that emphasized the critical study of Latin and Greek literature with the goal of understanding human nature.
D)Disenfranchised common people in Italian cities who resented their exclusion from power.
E)A French word meaning "rebirth," used to describe the rebirth of the culture of classical antiquity in Italy during the fourteenth to sixteenth centuries.
F)Northern humanists who interpreted Italian ideas about and attitudes toward classical antiquity and humanism in terms of their own religious traditions.
G)A term for Jews and Muslims in the Iberian Peninsula who accepted Christianity; in many cases, they included Christians whose families had converted centuries earlier.
H)Magnificent households and palaces where signori and other rulers lived, conducted business, and supported the arts.
I)Financial support of writers and artists by cities, groups, and individuals, often to produce specific works or works in specific styles.
J)Government by one-man rule in Italian cities such as Milan; also refers to these rulers.
K)The quality of being able to shape the world according to one's own will.
patronage
A)Debate among writers and thinkers in the Renaissance about women's qualities and proper role in society.
B)Sworn associations of free men in Italian cities led by merchant guilds that sought political and economic independence from local nobles.
C)A program of study designed by Italians that emphasized the critical study of Latin and Greek literature with the goal of understanding human nature.
D)Disenfranchised common people in Italian cities who resented their exclusion from power.
E)A French word meaning "rebirth," used to describe the rebirth of the culture of classical antiquity in Italy during the fourteenth to sixteenth centuries.
F)Northern humanists who interpreted Italian ideas about and attitudes toward classical antiquity and humanism in terms of their own religious traditions.
G)A term for Jews and Muslims in the Iberian Peninsula who accepted Christianity; in many cases, they included Christians whose families had converted centuries earlier.
H)Magnificent households and palaces where signori and other rulers lived, conducted business, and supported the arts.
I)Financial support of writers and artists by cities, groups, and individuals, often to produce specific works or works in specific styles.
J)Government by one-man rule in Italian cities such as Milan; also refers to these rulers.
K)The quality of being able to shape the world according to one's own will.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
How did anti-Semitism in Spain contribute to the development of modern theories of race?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Answer the following questions:
humanism
A)Debate among writers and thinkers in the Renaissance about women's qualities and proper role in society.
B)Sworn associations of free men in Italian cities led by merchant guilds that sought political and economic independence from local nobles.
C)A program of study designed by Italians that emphasized the critical study of Latin and Greek literature with the goal of understanding human nature.
D)Disenfranchised common people in Italian cities who resented their exclusion from power.
E)A French word meaning "rebirth," used to describe the rebirth of the culture of classical antiquity in Italy during the fourteenth to sixteenth centuries.
F)Northern humanists who interpreted Italian ideas about and attitudes toward classical antiquity and humanism in terms of their own religious traditions.
G)A term for Jews and Muslims in the Iberian Peninsula who accepted Christianity; in many cases, they included Christians whose families had converted centuries earlier.
H)Magnificent households and palaces where signori and other rulers lived, conducted business, and supported the arts.
I)Financial support of writers and artists by cities, groups, and individuals, often to produce specific works or works in specific styles.
J)Government by one-man rule in Italian cities such as Milan; also refers to these rulers.
K)The quality of being able to shape the world according to one's own will.
humanism
A)Debate among writers and thinkers in the Renaissance about women's qualities and proper role in society.
B)Sworn associations of free men in Italian cities led by merchant guilds that sought political and economic independence from local nobles.
C)A program of study designed by Italians that emphasized the critical study of Latin and Greek literature with the goal of understanding human nature.
D)Disenfranchised common people in Italian cities who resented their exclusion from power.
E)A French word meaning "rebirth," used to describe the rebirth of the culture of classical antiquity in Italy during the fourteenth to sixteenth centuries.
F)Northern humanists who interpreted Italian ideas about and attitudes toward classical antiquity and humanism in terms of their own religious traditions.
G)A term for Jews and Muslims in the Iberian Peninsula who accepted Christianity; in many cases, they included Christians whose families had converted centuries earlier.
H)Magnificent households and palaces where signori and other rulers lived, conducted business, and supported the arts.
I)Financial support of writers and artists by cities, groups, and individuals, often to produce specific works or works in specific styles.
J)Government by one-man rule in Italian cities such as Milan; also refers to these rulers.
K)The quality of being able to shape the world according to one's own will.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
What were the most important components of the intellectual movement that underlay the Renaissance?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
How did people define race, class, and gender during the Renaissance? How do Renaissance definitions of these terms differ from contemporary definitions?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Answer the following questions:
popolo
A)Debate among writers and thinkers in the Renaissance about women's qualities and proper role in society.
B)Sworn associations of free men in Italian cities led by merchant guilds that sought political and economic independence from local nobles.
C)A program of study designed by Italians that emphasized the critical study of Latin and Greek literature with the goal of understanding human nature.
D)Disenfranchised common people in Italian cities who resented their exclusion from power.
E)A French word meaning "rebirth," used to describe the rebirth of the culture of classical antiquity in Italy during the fourteenth to sixteenth centuries.
F)Northern humanists who interpreted Italian ideas about and attitudes toward classical antiquity and humanism in terms of their own religious traditions.
G)A term for Jews and Muslims in the Iberian Peninsula who accepted Christianity; in many cases, they included Christians whose families had converted centuries earlier.
H)Magnificent households and palaces where signori and other rulers lived, conducted business, and supported the arts.
I)Financial support of writers and artists by cities, groups, and individuals, often to produce specific works or works in specific styles.
J)Government by one-man rule in Italian cities such as Milan; also refers to these rulers.
K)The quality of being able to shape the world according to one's own will.
popolo
A)Debate among writers and thinkers in the Renaissance about women's qualities and proper role in society.
B)Sworn associations of free men in Italian cities led by merchant guilds that sought political and economic independence from local nobles.
C)A program of study designed by Italians that emphasized the critical study of Latin and Greek literature with the goal of understanding human nature.
D)Disenfranchised common people in Italian cities who resented their exclusion from power.
E)A French word meaning "rebirth," used to describe the rebirth of the culture of classical antiquity in Italy during the fourteenth to sixteenth centuries.
F)Northern humanists who interpreted Italian ideas about and attitudes toward classical antiquity and humanism in terms of their own religious traditions.
G)A term for Jews and Muslims in the Iberian Peninsula who accepted Christianity; in many cases, they included Christians whose families had converted centuries earlier.
H)Magnificent households and palaces where signori and other rulers lived, conducted business, and supported the arts.
I)Financial support of writers and artists by cities, groups, and individuals, often to produce specific works or works in specific styles.
J)Government by one-man rule in Italian cities such as Milan; also refers to these rulers.
K)The quality of being able to shape the world according to one's own will.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Answer the following questions:
Renaissance
A)Debate among writers and thinkers in the Renaissance about women's qualities and proper role in society.
B)Sworn associations of free men in Italian cities led by merchant guilds that sought political and economic independence from local nobles.
C)A program of study designed by Italians that emphasized the critical study of Latin and Greek literature with the goal of understanding human nature.
D)Disenfranchised common people in Italian cities who resented their exclusion from power.
E)A French word meaning "rebirth," used to describe the rebirth of the culture of classical antiquity in Italy during the fourteenth to sixteenth centuries.
F)Northern humanists who interpreted Italian ideas about and attitudes toward classical antiquity and humanism in terms of their own religious traditions.
G)A term for Jews and Muslims in the Iberian Peninsula who accepted Christianity; in many cases, they included Christians whose families had converted centuries earlier.
H)Magnificent households and palaces where signori and other rulers lived, conducted business, and supported the arts.
I)Financial support of writers and artists by cities, groups, and individuals, often to produce specific works or works in specific styles.
J)Government by one-man rule in Italian cities such as Milan; also refers to these rulers.
K)The quality of being able to shape the world according to one's own will.
Renaissance
A)Debate among writers and thinkers in the Renaissance about women's qualities and proper role in society.
B)Sworn associations of free men in Italian cities led by merchant guilds that sought political and economic independence from local nobles.
C)A program of study designed by Italians that emphasized the critical study of Latin and Greek literature with the goal of understanding human nature.
D)Disenfranchised common people in Italian cities who resented their exclusion from power.
E)A French word meaning "rebirth," used to describe the rebirth of the culture of classical antiquity in Italy during the fourteenth to sixteenth centuries.
F)Northern humanists who interpreted Italian ideas about and attitudes toward classical antiquity and humanism in terms of their own religious traditions.
G)A term for Jews and Muslims in the Iberian Peninsula who accepted Christianity; in many cases, they included Christians whose families had converted centuries earlier.
H)Magnificent households and palaces where signori and other rulers lived, conducted business, and supported the arts.
I)Financial support of writers and artists by cities, groups, and individuals, often to produce specific works or works in specific styles.
J)Government by one-man rule in Italian cities such as Milan; also refers to these rulers.
K)The quality of being able to shape the world according to one's own will.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Ideas about gender and status for both women and men were modified during the Renaissance. What was the status of women, both upper class and common, in this era? What does this reveal about Renaissance society in general?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Answer the following questions:
virtù
A)Debate among writers and thinkers in the Renaissance about women's qualities and proper role in society.
B)Sworn associations of free men in Italian cities led by merchant guilds that sought political and economic independence from local nobles.
C)A program of study designed by Italians that emphasized the critical study of Latin and Greek literature with the goal of understanding human nature.
D)Disenfranchised common people in Italian cities who resented their exclusion from power.
E)A French word meaning "rebirth," used to describe the rebirth of the culture of classical antiquity in Italy during the fourteenth to sixteenth centuries.
F)Northern humanists who interpreted Italian ideas about and attitudes toward classical antiquity and humanism in terms of their own religious traditions.
G)A term for Jews and Muslims in the Iberian Peninsula who accepted Christianity; in many cases, they included Christians whose families had converted centuries earlier.
H)Magnificent households and palaces where signori and other rulers lived, conducted business, and supported the arts.
I)Financial support of writers and artists by cities, groups, and individuals, often to produce specific works or works in specific styles.
J)Government by one-man rule in Italian cities such as Milan; also refers to these rulers.
K)The quality of being able to shape the world according to one's own will.
virtù
A)Debate among writers and thinkers in the Renaissance about women's qualities and proper role in society.
B)Sworn associations of free men in Italian cities led by merchant guilds that sought political and economic independence from local nobles.
C)A program of study designed by Italians that emphasized the critical study of Latin and Greek literature with the goal of understanding human nature.
D)Disenfranchised common people in Italian cities who resented their exclusion from power.
E)A French word meaning "rebirth," used to describe the rebirth of the culture of classical antiquity in Italy during the fourteenth to sixteenth centuries.
F)Northern humanists who interpreted Italian ideas about and attitudes toward classical antiquity and humanism in terms of their own religious traditions.
G)A term for Jews and Muslims in the Iberian Peninsula who accepted Christianity; in many cases, they included Christians whose families had converted centuries earlier.
H)Magnificent households and palaces where signori and other rulers lived, conducted business, and supported the arts.
I)Financial support of writers and artists by cities, groups, and individuals, often to produce specific works or works in specific styles.
J)Government by one-man rule in Italian cities such as Milan; also refers to these rulers.
K)The quality of being able to shape the world according to one's own will.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



