Deck 6: The Roman Empire 27 Bce-284 CE
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/76
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 6: The Roman Empire 27 Bce-284 CE
1
Roman poetry and prose during the "golden age" was characterized by which of the following?
A)Focus on the divine
B)Celebration of the dignity of humanity
C)Advocacy of a life of austerity and hardship
D)Criticism of mankind
A)Focus on the divine
B)Celebration of the dignity of humanity
C)Advocacy of a life of austerity and hardship
D)Criticism of mankind
Focus on the divine
2
What was Pontius Pilate's main objective?
A)Crushing all religious challenges to Judaism
B)Suppressing the Jews
C)Reforming the provincial administration
D)Maintaining law and order
A)Crushing all religious challenges to Judaism
B)Suppressing the Jews
C)Reforming the provincial administration
D)Maintaining law and order
Maintaining law and order
3
Before Augustus, the term imperator
A)originally meant "emperor."
B)was an honorific for a victorious general.
C)referred to the chief officer of the Senate.
D)meant "ruler of the East."
A)originally meant "emperor."
B)was an honorific for a victorious general.
C)referred to the chief officer of the Senate.
D)meant "ruler of the East."
was an honorific for a victorious general.
4
Which of the following describes the structure of Augustus's settlement?
A)The emperor served at the pleasure of the Senate, which retained full authority over the military and the city of Rome.
B)Authority was balanced between the emperor, who controlled the military, and the Senate, which controlled the civil bureaucracy.
C)The emperor held all executive authority over the civil government and the military leadership, while the Senate remained a prestigious advisory body.
D)The Senate held authority over Rome and its close Italian allies, while the emperor had authority over the imperial lands outside of Italy.
A)The emperor served at the pleasure of the Senate, which retained full authority over the military and the city of Rome.
B)Authority was balanced between the emperor, who controlled the military, and the Senate, which controlled the civil bureaucracy.
C)The emperor held all executive authority over the civil government and the military leadership, while the Senate remained a prestigious advisory body.
D)The Senate held authority over Rome and its close Italian allies, while the emperor had authority over the imperial lands outside of Italy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
During the age of the five good emperors, the Roman army was
A)a source of economic stability and Romanization.
B)the cause of ongoing political unrest in the provinces.
C)composed of citizen-soldiers from Italy, with Roman officers.
D)greatly reduced in size and political influence.
A)a source of economic stability and Romanization.
B)the cause of ongoing political unrest in the provinces.
C)composed of citizen-soldiers from Italy, with Roman officers.
D)greatly reduced in size and political influence.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Why did the emperor's power increase during the era of the five good emperors?
A)The expansion of the military required a single source of authority, which only the emperor could provide.
B)The people of Rome demanded that one figure be placed in a position to protect their interests, whom they could hold accountable for failure.
C)The five emperors were capable and efficient administrators, and the easiest way to manage the empire was to expand their authority.
D)The imperial lands were held as personal property of the emperor, giving him a decisive advantage over all political rivals.
A)The expansion of the military required a single source of authority, which only the emperor could provide.
B)The people of Rome demanded that one figure be placed in a position to protect their interests, whom they could hold accountable for failure.
C)The five emperors were capable and efficient administrators, and the easiest way to manage the empire was to expand their authority.
D)The imperial lands were held as personal property of the emperor, giving him a decisive advantage over all political rivals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Augustus encouraged the cult of Roma et Augustus
A)to attempt to erase Judaism from Palestine.
B)to unify the Senate under his rule.
C)to increase the donations to his personal cult.
D)to create a spiritual bond between the provinces and Rome.
A)to attempt to erase Judaism from Palestine.
B)to unify the Senate under his rule.
C)to increase the donations to his personal cult.
D)to create a spiritual bond between the provinces and Rome.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following characterizes the relationship between Romans in provincial towns and the people they ruled over?
A)The Romans required local peoples to fully adopt Roman religion, culture, and lifestyles, including food and clothing.
B)The Romans forbade conquered peoples from adopting any aspect of Roman culture or religion, believing that Roman values would be degraded by such an act.
C)The Romans only permitted those local peoples who became Roman citizens to worship Roman deities and participate in civic festivals.
D)The Romans did not force their adaptable culture on local peoples but allowed local peoples to adopt the aspects of Roman culture that they found appealing.
A)The Romans required local peoples to fully adopt Roman religion, culture, and lifestyles, including food and clothing.
B)The Romans forbade conquered peoples from adopting any aspect of Roman culture or religion, believing that Roman values would be degraded by such an act.
C)The Romans only permitted those local peoples who became Roman citizens to worship Roman deities and participate in civic festivals.
D)The Romans did not force their adaptable culture on local peoples but allowed local peoples to adopt the aspects of Roman culture that they found appealing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
How did Vespasian transform the political system?
A)He turned the political system into a military dictatorship in which leading generals served as his chief advisors.
B)He restored powers to the Senate in an effort to contain the growing authority of the military.
C)He transformed the system into an open and admitted monarchy and expanded his power by increasing the size of the bureaucracy.
D)He expanded the size of the military in order to undermine efforts by the bureaucracy, under Senate control, to seize control over the imperial system.
A)He turned the political system into a military dictatorship in which leading generals served as his chief advisors.
B)He restored powers to the Senate in an effort to contain the growing authority of the military.
C)He transformed the system into an open and admitted monarchy and expanded his power by increasing the size of the bureaucracy.
D)He expanded the size of the military in order to undermine efforts by the bureaucracy, under Senate control, to seize control over the imperial system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The bureaucracy created by the emperor Claudius was made up of
A)ex-officers and soldiers of the army.
B)professional administrators.
C)Greek immigrants.
D)patricians.
A)ex-officers and soldiers of the army.
B)professional administrators.
C)Greek immigrants.
D)patricians.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Hadrian's reforms were designed to deal with
A)the problem of barbarian invasions.
B)the organization of the imperial bureaucracy.
C)the spread of Christianity.
D)the spread of prostitution.
A)the problem of barbarian invasions.
B)the organization of the imperial bureaucracy.
C)the spread of Christianity.
D)the spread of prostitution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
What was the most important source of information on the life of Jesus?
A)A biography written by Paul of Tarsus
B)Roman census records
C)Oral tradition of early Christianity
D)Four Gospels of the New Testament
A)A biography written by Paul of Tarsus
B)Roman census records
C)Oral tradition of early Christianity
D)Four Gospels of the New Testament

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
What is the main theme of Livy's Ab Urbe Condita?
A)The disastrous impact of Christianity
B)The greatness of the republic
C)The usurpation of the republic by Augustus
D)The beauty and fulfillment of rural life
A)The disastrous impact of Christianity
B)The greatness of the republic
C)The usurpation of the republic by Augustus
D)The beauty and fulfillment of rural life

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The early followers of Jesus, before the conversion of Paul of Tarsus, were mostly
A)Gentiles.
B)Essenes.
C)Jews.
D)Phoenicians.
A)Gentiles.
B)Essenes.
C)Jews.
D)Phoenicians.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
What was the worst defect of the Augustan settlement?
A)The use of slaves in the bureaucracy
B)The army's ability to interfere in politics
C)The establishment of a monarchical form of government
D)The suppression of Christianity
A)The use of slaves in the bureaucracy
B)The army's ability to interfere in politics
C)The establishment of a monarchical form of government
D)The suppression of Christianity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
What is the premise of the Aeneid by the Roman poet Virgil?
A)It provides a mythological account of the founding of Rome.
B)It documents the defeat of Roman legions in Teutoburger Forest.
C)It traces the genealogy of Jupiter, chief god of the Romans and analogue of the Greek god Zeus.
D)It describes Julius Caesar's conquest of Gaul.
A)It provides a mythological account of the founding of Rome.
B)It documents the defeat of Roman legions in Teutoburger Forest.
C)It traces the genealogy of Jupiter, chief god of the Romans and analogue of the Greek god Zeus.
D)It describes Julius Caesar's conquest of Gaul.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Who were the Zealots?
A)Christians who believed that Jesus was the Messiah
B)Jews who wanted to expel the Romans from Judea
C)Followers of a new mystery religion
D)Followers of Asclepius
A)Christians who believed that Jesus was the Messiah
B)Jews who wanted to expel the Romans from Judea
C)Followers of a new mystery religion
D)Followers of Asclepius

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
How did Augustus seek to promote childbearing?
A)A cash reward was paid to the husband for every child born to his wife.
B)After the birth of a fourth child, a husband was released from all military service.
C)Women were provided with a house servant for one year after the birth of each child.
D)Free women were released from male guardianship if they gave birth to a certain number of children.
A)A cash reward was paid to the husband for every child born to his wife.
B)After the birth of a fourth child, a husband was released from all military service.
C)Women were provided with a house servant for one year after the birth of each child.
D)Free women were released from male guardianship if they gave birth to a certain number of children.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Paul of Tarsus believed that
A)Christ's teachings should be proclaimed to all.
B)Christianity should be used to defeat Rome.
C)Christ's message applied only to Jews.
D)Christians should avoid contact with pagans.
A)Christ's teachings should be proclaimed to all.
B)Christianity should be used to defeat Rome.
C)Christ's message applied only to Jews.
D)Christians should avoid contact with pagans.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
After the death of Nero, which Flavian Roman emperor appointed his son Titus to command Roman forces in Judea, in order to put down a revolt among the Jews?
A)Marcus Aurelius
B)Vespasian
C)Nerva
D)Trajan
A)Marcus Aurelius
B)Vespasian
C)Nerva
D)Trajan

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
"You, Roman, remember-these are your arts: To rule nations, and to impose the ways of peace,
To spare the humble and to conquer the proud."
What Roman writer defined the mission of Rome in these terms?
A)Quintilian
B)Ovid
C)Virgil
D)Horace
To spare the humble and to conquer the proud."
What Roman writer defined the mission of Rome in these terms?
A)Quintilian
B)Ovid
C)Virgil
D)Horace

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following was true of the Roman government under Augustus?
A)It had the appearance of a republic.
B)It was dominated by rival warlords.
C)It divided power between the Senate, Augustus, and the people.
D)It was an avowed monarchy.
A)It had the appearance of a republic.
B)It was dominated by rival warlords.
C)It divided power between the Senate, Augustus, and the people.
D)It was an avowed monarchy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
"Take heed not to be transformed into a Caesar. . . . Keep yourself therefore simple, good, pure, grave, unaffected, the friend of justice, religious, kind, affectionate, strong for your proper work." What emperor extols this advice in his collection Meditations?
A)Augustus
B)Vespasian
C)Marcus Aurelius
D)Titus
A)Augustus
B)Vespasian
C)Marcus Aurelius
D)Titus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
What emperor established colonies of Roman military veterans?
A)Hadrian
B)Trajan
C)Caligula
D)Augustus
A)Hadrian
B)Trajan
C)Caligula
D)Augustus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
How did Roman rule in Asia Minor differ from that in northern Europe?
A)In northern Europe, the villa or country estate was the primary unit of political life, while in Asia Minor, it was the city.
B)In northern Europe, clans controlled local politics under the umbrella of Roman authority, while in Asia Minor, the Romans ruled directly.
C)In Asia Minor, local princes were retained as symbols of authority to quell any local uprisings, while in northern Europe, the Romans ruled directly.
D)In Asia Minor, the mountainous terrain made it impossible for the Romans to dominate the landscape, so they settled for controlling the sea coasts and a few major cities.
A)In northern Europe, the villa or country estate was the primary unit of political life, while in Asia Minor, it was the city.
B)In northern Europe, clans controlled local politics under the umbrella of Roman authority, while in Asia Minor, the Romans ruled directly.
C)In Asia Minor, local princes were retained as symbols of authority to quell any local uprisings, while in northern Europe, the Romans ruled directly.
D)In Asia Minor, the mountainous terrain made it impossible for the Romans to dominate the landscape, so they settled for controlling the sea coasts and a few major cities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The Roman official Pontius Pilate
A)was Jewish.
B)was sympathetic to Jesus's message.
C)sought to stamp out all non-Roman religions.
D)knew little of Jesus's teachings.
A)was Jewish.
B)was sympathetic to Jesus's message.
C)sought to stamp out all non-Roman religions.
D)knew little of Jesus's teachings.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Refer to Map 6.1: Roman Expansion Under the Empire, 44 B.C.E.-180 C.E. With the loss of territory in Caledonia in 105 C.E., what emperor would build a massive wall from the Irish Sea to the North Sea to protect Roman interests? 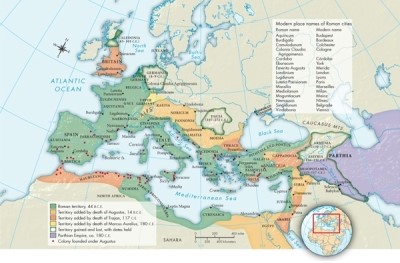
A)Nero
B)Hadrian
C)Titus
D)Vespasian

A)Nero
B)Hadrian
C)Titus
D)Vespasian

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
According to Map 6.1: Roman Expansion Under the Empire, 44 B.C.E.-180 C.E., what part of the Roman Empire was conquered in 4 C.E. and lost in 9 C.E.? 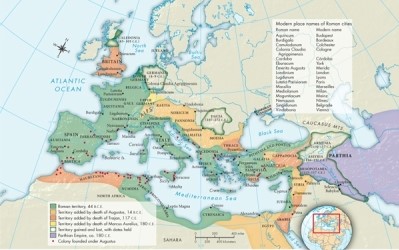
A)Dacia
B)Germania
C)Lycia
D)Armenia

A)Dacia
B)Germania
C)Lycia
D)Armenia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
In Evaluating the Evidence 6.2: Ovid, The Art of Love, Ovid states that "Hunters know where to spread their nets for the stag in his covert, Hunters know where the boar gnashes his teeth in the glade." What is his goal in this passage?
A)To instruct the reader on conducting business by comparing it to hunting
B)To instruct the reader on pursuing a lover by comparing it to hunting
C)To compare the skills of hunting stags and boars
D)To compare political skills to hunting
A)To instruct the reader on conducting business by comparing it to hunting
B)To instruct the reader on pursuing a lover by comparing it to hunting
C)To compare the skills of hunting stags and boars
D)To compare political skills to hunting

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
What does British historian Edward Gibbon's term "pax Romana" mean?
A)The Scourge of Rome
B)The Peace of Rome
C)The Age of Rome
D)The Growth of Rome
A)The Scourge of Rome
B)The Peace of Rome
C)The Age of Rome
D)The Growth of Rome

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
What was the population of the city of Rome during the golden age?
A)Between 100,000 and 250,000
B)Two million
C)Between three million and four million
D)Nearly one million
A)Between 100,000 and 250,000
B)Two million
C)Between three million and four million
D)Nearly one million

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
What belief did the Roman Empire and early Christianity share?
A)Both believed that the state must be a religious entity.
B)Both believed that there must be only one religious system to which all must adhere.
C)Both believed that political authorities must be submissive to religious authorities.
D)Both believed themselves participants in a universal enterprise.
A)Both believed that the state must be a religious entity.
B)Both believed that there must be only one religious system to which all must adhere.
C)Both believed that political authorities must be submissive to religious authorities.
D)Both believed themselves participants in a universal enterprise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
"Look, the bull, shining under the rough plough, falls to the ground . . . and releases his dying groan. Sadly moves the ploughman, unharnessing the young steer grieving for the death of his brother." This quote from Georgics is the work of which golden age poet?
A)Ovid
B)Horace
C)Virgil
D)Pliny
A)Ovid
B)Horace
C)Virgil
D)Pliny

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Map 6.2: Production and Trade in the Pax Romana, ca. 27 B.C.E.-180 C.E. illustrates Rome's massive trade routes and roads, which facilitated what movement during the principate? 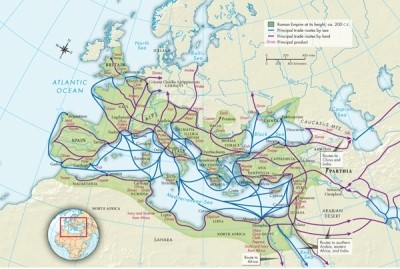
A)The arts
B)Migration
C)Democracy
D)Christianity

A)The arts
B)Migration
C)Democracy
D)Christianity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
What type of slave was most likely to be given freedom?
A)Slaves trained in skilled crafts
B)Household slaves
C)Military slaves
D)Gladiatorial slaves
A)Slaves trained in skilled crafts
B)Household slaves
C)Military slaves
D)Gladiatorial slaves

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
In general, the relationship between Christians and Rome was characterized by
A)phases of toleration, with sporadic outbursts of persecution.
B)unrelenting persecution until the late fourth century.
C)mutual respect and toleration.
D)the failure of the Romans to distinguish between Judaism and Christianity.
A)phases of toleration, with sporadic outbursts of persecution.
B)unrelenting persecution until the late fourth century.
C)mutual respect and toleration.
D)the failure of the Romans to distinguish between Judaism and Christianity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Following the death of Marcus Aurelius, the empire
A)entered into a long period of fighting and misrule.
B)underwent a cultural and intellectual renaissance.
C)was ruled by a series of competent and resourceful leaders.
D)collapsed entirely and succumbed to barbarian rule.
A)entered into a long period of fighting and misrule.
B)underwent a cultural and intellectual renaissance.
C)was ruled by a series of competent and resourceful leaders.
D)collapsed entirely and succumbed to barbarian rule.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Around the first century C.E., which of the following was a prediction associated with the Jewish tradition of militant apocalypticism?
A)The Messiah would soon overthrow the Jewish tradition of law found in the Torah and establish a new worship of God based on faith.
B)The Jewish state would be destroyed by the Roman legions but then reformed as a heavenly empire in the next world.
C)The Messiah would soon return, destroy the Roman legions, and bring happiness and plenty to the Jews.
D)The Messiah would arrive as a spiritual teacher and lead the true believers into the desert so that they would be saved from the coming wars.
A)The Messiah would soon overthrow the Jewish tradition of law found in the Torah and establish a new worship of God based on faith.
B)The Jewish state would be destroyed by the Roman legions but then reformed as a heavenly empire in the next world.
C)The Messiah would soon return, destroy the Roman legions, and bring happiness and plenty to the Jews.
D)The Messiah would arrive as a spiritual teacher and lead the true believers into the desert so that they would be saved from the coming wars.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Why did non-Christians distrust Christianity?
A)Christians' refusal to participate in public rituals linked to the good of the state led non-Christians to question their loyalty to Rome.
B)Christianity preached a message of peace that contradicted the military foundations of the Roman Empire.
C)The rejection of slavery by Christians challenged the economic foundations of the Roman economy.
D)The aggressiveness and public visibility with which early Christians practiced their faith led many to see Christianity as a subversive force.
A)Christians' refusal to participate in public rituals linked to the good of the state led non-Christians to question their loyalty to Rome.
B)Christianity preached a message of peace that contradicted the military foundations of the Roman Empire.
C)The rejection of slavery by Christians challenged the economic foundations of the Roman economy.
D)The aggressiveness and public visibility with which early Christians practiced their faith led many to see Christianity as a subversive force.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following was true of Jesus's teachings?
A)His teachings constituted a rejection of Judaism.
B)His teachings were based on Hebrew scriptures.
C)His teachings were entirely new and original.
D)His teachings were consistent with Jewish orthodoxy in every way.
A)His teachings constituted a rejection of Judaism.
B)His teachings were based on Hebrew scriptures.
C)His teachings were entirely new and original.
D)His teachings were consistent with Jewish orthodoxy in every way.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
In the aftermath of the civil wars that brought him to power, what was Augustus's first and perhaps most important challenge?
A)To dismantle the Senate
B)To defeat rebellious generals
C)To fend off challenges to Roman rule in the east
D)To reconstruct the institutions and organs of government
A)To dismantle the Senate
B)To defeat rebellious generals
C)To fend off challenges to Roman rule in the east
D)To reconstruct the institutions and organs of government

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
How did Virgil's Aeneid reinforce fundamental Roman values?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The army that Augustus created was
A)loyal to him as a person.
B)loyal to him as head of the state.
C)weak and disorganized.
D)unable to sustain itself after his demise.
A)loyal to him as a person.
B)loyal to him as head of the state.
C)weak and disorganized.
D)unable to sustain itself after his demise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
What does the city of Aspendos demonstrate about the Roman Empire in Asia Minor?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Who was Galen, and why was he important?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
What was the "crisis of the third century"?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Describe Nero's reign and its consequences.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Who did Augustus name as his heir?
A)Nero
B)Tiberius
C)Caligula
D)Claudius
A)Nero
B)Tiberius
C)Caligula
D)Claudius

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
What kind of education did most Roman children receive?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
What kinds of Roman religious practices were included under the term "pagan"?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
"Do not lay up for yourselves treasures on earth, where moth and rust consume and where thieves break in and steal, but lay up for yourselves treasures in heaven, where neither moth nor rust consumes and where thieves do not break in and steal." Who offered this advice?
A)Horace
B)Marcus Aurelius
C)Virgil
D)Jesus
A)Horace
B)Marcus Aurelius
C)Virgil
D)Jesus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Augustus encouraged the development of poets and writers, with the exception of Ovid, who he banished to a city on the Black Sea in 8 B.C.E. Why did Augustus punish Ovid?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
According to Quintilian, what was the most important skill for an elite Roman man to master?
A)Good manners
B)Dissimilation
C)Public speaking
D)Hand-to-hand combat
A)Good manners
B)Dissimilation
C)Public speaking
D)Hand-to-hand combat

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
How did Augustus transform the Roman army?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The Parthians served as a link between Rome and
A)Britain.
B)Spain.
C)Egypt.
D)China.
A)Britain.
B)Spain.
C)Egypt.
D)China.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Under Augustus, Rome
A)was officially transformed into an monarchy.
B)remained officially a republic.
C)became increasingly politically decentralized.
D)experienced a prolonged economic downturn.
A)was officially transformed into an monarchy.
B)remained officially a republic.
C)became increasingly politically decentralized.
D)experienced a prolonged economic downturn.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Who were the "five good emperors," and why were they identified as such by Machiavelli?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The most important medical researcher and physician working in imperial Rome was
A)Ovid.
B)Paracelsus.
C)Galen.
D)Hippocrates.
A)Ovid.
B)Paracelsus.
C)Galen.
D)Hippocrates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which of the following policies was put into place by Augustus?
A)Adultery was made a crime.
B)Slavery was abolished in the city of Rome.
C)Christianity was outlawed.
D)All Roman men were required to perform military service.
A)Adultery was made a crime.
B)Slavery was abolished in the city of Rome.
C)Christianity was outlawed.
D)All Roman men were required to perform military service.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
What were the Praetorians?
A)An elite group of Senators
B)An imperial bodyguard
C)Members of a religious cult
D)A group of poets and playwrights
A)An elite group of Senators
B)An imperial bodyguard
C)Members of a religious cult
D)A group of poets and playwrights

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Answer the following questions:
imperator
A)In Jewish belief, a savior who would bring a period of peace and happiness for Jews.
B)The "Roman peace," a period during the first and second centuries C.E. of political stability and relative peace.
C)Originally referring to those who lived in the countryside, this term came to mean those who practiced religions other than Judaism or Christianity.
D)Imperial bodyguard created by Augustus.
E)Canals, channels, and pipes that brought freshwater into cities.
F)Christian church officials with jurisdiction over certain areas and the power to determine the correct interpretation of Christian teachings.
G)Emperors of the middle of the third century, so called because they were military commanders.
H)The five Roman emperors (Nerva, Trajan, Hadrian, Antoninus Pius, and Marcus Aurelius) of the second century whose reigns were relatively prosperous and stable.
I)Official title of Augustus's form of government, taken from princeps, meaning "first citizen."
J)Title given to a Roman general after a major victory that came to mean "emperor."
K)A religious practice or belief judged unacceptable by church officials.
imperator
A)In Jewish belief, a savior who would bring a period of peace and happiness for Jews.
B)The "Roman peace," a period during the first and second centuries C.E. of political stability and relative peace.
C)Originally referring to those who lived in the countryside, this term came to mean those who practiced religions other than Judaism or Christianity.
D)Imperial bodyguard created by Augustus.
E)Canals, channels, and pipes that brought freshwater into cities.
F)Christian church officials with jurisdiction over certain areas and the power to determine the correct interpretation of Christian teachings.
G)Emperors of the middle of the third century, so called because they were military commanders.
H)The five Roman emperors (Nerva, Trajan, Hadrian, Antoninus Pius, and Marcus Aurelius) of the second century whose reigns were relatively prosperous and stable.
I)Official title of Augustus's form of government, taken from princeps, meaning "first citizen."
J)Title given to a Roman general after a major victory that came to mean "emperor."
K)A religious practice or belief judged unacceptable by church officials.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Answer the following questions:
bishops
A)In Jewish belief, a savior who would bring a period of peace and happiness for Jews.
B)The "Roman peace," a period during the first and second centuries C.E. of political stability and relative peace.
C)Originally referring to those who lived in the countryside, this term came to mean those who practiced religions other than Judaism or Christianity.
D)Imperial bodyguard created by Augustus.
E)Canals, channels, and pipes that brought freshwater into cities.
F)Christian church officials with jurisdiction over certain areas and the power to determine the correct interpretation of Christian teachings.
G)Emperors of the middle of the third century, so called because they were military commanders.
H)The five Roman emperors (Nerva, Trajan, Hadrian, Antoninus Pius, and Marcus Aurelius) of the second century whose reigns were relatively prosperous and stable.
I)Official title of Augustus's form of government, taken from princeps, meaning "first citizen."
J)Title given to a Roman general after a major victory that came to mean "emperor."
K)A religious practice or belief judged unacceptable by church officials.
bishops
A)In Jewish belief, a savior who would bring a period of peace and happiness for Jews.
B)The "Roman peace," a period during the first and second centuries C.E. of political stability and relative peace.
C)Originally referring to those who lived in the countryside, this term came to mean those who practiced religions other than Judaism or Christianity.
D)Imperial bodyguard created by Augustus.
E)Canals, channels, and pipes that brought freshwater into cities.
F)Christian church officials with jurisdiction over certain areas and the power to determine the correct interpretation of Christian teachings.
G)Emperors of the middle of the third century, so called because they were military commanders.
H)The five Roman emperors (Nerva, Trajan, Hadrian, Antoninus Pius, and Marcus Aurelius) of the second century whose reigns were relatively prosperous and stable.
I)Official title of Augustus's form of government, taken from princeps, meaning "first citizen."
J)Title given to a Roman general after a major victory that came to mean "emperor."
K)A religious practice or belief judged unacceptable by church officials.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
How did the Roman army serve as a vehicle for the spread of Roman culture throughout the empire?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Answer the following questions:
principate
A)In Jewish belief, a savior who would bring a period of peace and happiness for Jews.
B)The "Roman peace," a period during the first and second centuries C.E. of political stability and relative peace.
C)Originally referring to those who lived in the countryside, this term came to mean those who practiced religions other than Judaism or Christianity.
D)Imperial bodyguard created by Augustus.
E)Canals, channels, and pipes that brought freshwater into cities.
F)Christian church officials with jurisdiction over certain areas and the power to determine the correct interpretation of Christian teachings.
G)Emperors of the middle of the third century, so called because they were military commanders.
H)The five Roman emperors (Nerva, Trajan, Hadrian, Antoninus Pius, and Marcus Aurelius) of the second century whose reigns were relatively prosperous and stable.
I)Official title of Augustus's form of government, taken from princeps, meaning "first citizen."
J)Title given to a Roman general after a major victory that came to mean "emperor."
K)A religious practice or belief judged unacceptable by church officials.
principate
A)In Jewish belief, a savior who would bring a period of peace and happiness for Jews.
B)The "Roman peace," a period during the first and second centuries C.E. of political stability and relative peace.
C)Originally referring to those who lived in the countryside, this term came to mean those who practiced religions other than Judaism or Christianity.
D)Imperial bodyguard created by Augustus.
E)Canals, channels, and pipes that brought freshwater into cities.
F)Christian church officials with jurisdiction over certain areas and the power to determine the correct interpretation of Christian teachings.
G)Emperors of the middle of the third century, so called because they were military commanders.
H)The five Roman emperors (Nerva, Trajan, Hadrian, Antoninus Pius, and Marcus Aurelius) of the second century whose reigns were relatively prosperous and stable.
I)Official title of Augustus's form of government, taken from princeps, meaning "first citizen."
J)Title given to a Roman general after a major victory that came to mean "emperor."
K)A religious practice or belief judged unacceptable by church officials.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The relationship between Rome and the provinces was complex and would have an impact long after the empire in the West had ceased to exist. Describe this relationship, being sure to note regional differences. How pervasive was "Romanization"? What were the long-term consequences of this relationship?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Answer the following questions:
heresy
A)In Jewish belief, a savior who would bring a period of peace and happiness for Jews.
B)The "Roman peace," a period during the first and second centuries C.E. of political stability and relative peace.
C)Originally referring to those who lived in the countryside, this term came to mean those who practiced religions other than Judaism or Christianity.
D)Imperial bodyguard created by Augustus.
E)Canals, channels, and pipes that brought freshwater into cities.
F)Christian church officials with jurisdiction over certain areas and the power to determine the correct interpretation of Christian teachings.
G)Emperors of the middle of the third century, so called because they were military commanders.
H)The five Roman emperors (Nerva, Trajan, Hadrian, Antoninus Pius, and Marcus Aurelius) of the second century whose reigns were relatively prosperous and stable.
I)Official title of Augustus's form of government, taken from princeps, meaning "first citizen."
J)Title given to a Roman general after a major victory that came to mean "emperor."
K)A religious practice or belief judged unacceptable by church officials.
heresy
A)In Jewish belief, a savior who would bring a period of peace and happiness for Jews.
B)The "Roman peace," a period during the first and second centuries C.E. of political stability and relative peace.
C)Originally referring to those who lived in the countryside, this term came to mean those who practiced religions other than Judaism or Christianity.
D)Imperial bodyguard created by Augustus.
E)Canals, channels, and pipes that brought freshwater into cities.
F)Christian church officials with jurisdiction over certain areas and the power to determine the correct interpretation of Christian teachings.
G)Emperors of the middle of the third century, so called because they were military commanders.
H)The five Roman emperors (Nerva, Trajan, Hadrian, Antoninus Pius, and Marcus Aurelius) of the second century whose reigns were relatively prosperous and stable.
I)Official title of Augustus's form of government, taken from princeps, meaning "first citizen."
J)Title given to a Roman general after a major victory that came to mean "emperor."
K)A religious practice or belief judged unacceptable by church officials.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Answer the following questions:
barracks emperors
A)In Jewish belief, a savior who would bring a period of peace and happiness for Jews.
B)The "Roman peace," a period during the first and second centuries C.E. of political stability and relative peace.
C)Originally referring to those who lived in the countryside, this term came to mean those who practiced religions other than Judaism or Christianity.
D)Imperial bodyguard created by Augustus.
E)Canals, channels, and pipes that brought freshwater into cities.
F)Christian church officials with jurisdiction over certain areas and the power to determine the correct interpretation of Christian teachings.
G)Emperors of the middle of the third century, so called because they were military commanders.
H)The five Roman emperors (Nerva, Trajan, Hadrian, Antoninus Pius, and Marcus Aurelius) of the second century whose reigns were relatively prosperous and stable.
I)Official title of Augustus's form of government, taken from princeps, meaning "first citizen."
J)Title given to a Roman general after a major victory that came to mean "emperor."
K)A religious practice or belief judged unacceptable by church officials.
barracks emperors
A)In Jewish belief, a savior who would bring a period of peace and happiness for Jews.
B)The "Roman peace," a period during the first and second centuries C.E. of political stability and relative peace.
C)Originally referring to those who lived in the countryside, this term came to mean those who practiced religions other than Judaism or Christianity.
D)Imperial bodyguard created by Augustus.
E)Canals, channels, and pipes that brought freshwater into cities.
F)Christian church officials with jurisdiction over certain areas and the power to determine the correct interpretation of Christian teachings.
G)Emperors of the middle of the third century, so called because they were military commanders.
H)The five Roman emperors (Nerva, Trajan, Hadrian, Antoninus Pius, and Marcus Aurelius) of the second century whose reigns were relatively prosperous and stable.
I)Official title of Augustus's form of government, taken from princeps, meaning "first citizen."
J)Title given to a Roman general after a major victory that came to mean "emperor."
K)A religious practice or belief judged unacceptable by church officials.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The culture and society of the Roman Empire are often portrayed as lascivious, cruel, bloodthirsty, and extravagant. How accurate is this portrayal?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Answer the following questions:
"five good emperors"
A)In Jewish belief, a savior who would bring a period of peace and happiness for Jews.
B)The "Roman peace," a period during the first and second centuries C.E. of political stability and relative peace.
C)Originally referring to those who lived in the countryside, this term came to mean those who practiced religions other than Judaism or Christianity.
D)Imperial bodyguard created by Augustus.
E)Canals, channels, and pipes that brought freshwater into cities.
F)Christian church officials with jurisdiction over certain areas and the power to determine the correct interpretation of Christian teachings.
G)Emperors of the middle of the third century, so called because they were military commanders.
H)The five Roman emperors (Nerva, Trajan, Hadrian, Antoninus Pius, and Marcus Aurelius) of the second century whose reigns were relatively prosperous and stable.
I)Official title of Augustus's form of government, taken from princeps, meaning "first citizen."
J)Title given to a Roman general after a major victory that came to mean "emperor."
K)A religious practice or belief judged unacceptable by church officials.
"five good emperors"
A)In Jewish belief, a savior who would bring a period of peace and happiness for Jews.
B)The "Roman peace," a period during the first and second centuries C.E. of political stability and relative peace.
C)Originally referring to those who lived in the countryside, this term came to mean those who practiced religions other than Judaism or Christianity.
D)Imperial bodyguard created by Augustus.
E)Canals, channels, and pipes that brought freshwater into cities.
F)Christian church officials with jurisdiction over certain areas and the power to determine the correct interpretation of Christian teachings.
G)Emperors of the middle of the third century, so called because they were military commanders.
H)The five Roman emperors (Nerva, Trajan, Hadrian, Antoninus Pius, and Marcus Aurelius) of the second century whose reigns were relatively prosperous and stable.
I)Official title of Augustus's form of government, taken from princeps, meaning "first citizen."
J)Title given to a Roman general after a major victory that came to mean "emperor."
K)A religious practice or belief judged unacceptable by church officials.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Answer the following questions:
Messiah
A)In Jewish belief, a savior who would bring a period of peace and happiness for Jews.
B)The "Roman peace," a period during the first and second centuries C.E. of political stability and relative peace.
C)Originally referring to those who lived in the countryside, this term came to mean those who practiced religions other than Judaism or Christianity.
D)Imperial bodyguard created by Augustus.
E)Canals, channels, and pipes that brought freshwater into cities.
F)Christian church officials with jurisdiction over certain areas and the power to determine the correct interpretation of Christian teachings.
G)Emperors of the middle of the third century, so called because they were military commanders.
H)The five Roman emperors (Nerva, Trajan, Hadrian, Antoninus Pius, and Marcus Aurelius) of the second century whose reigns were relatively prosperous and stable.
I)Official title of Augustus's form of government, taken from princeps, meaning "first citizen."
J)Title given to a Roman general after a major victory that came to mean "emperor."
K)A religious practice or belief judged unacceptable by church officials.
Messiah
A)In Jewish belief, a savior who would bring a period of peace and happiness for Jews.
B)The "Roman peace," a period during the first and second centuries C.E. of political stability and relative peace.
C)Originally referring to those who lived in the countryside, this term came to mean those who practiced religions other than Judaism or Christianity.
D)Imperial bodyguard created by Augustus.
E)Canals, channels, and pipes that brought freshwater into cities.
F)Christian church officials with jurisdiction over certain areas and the power to determine the correct interpretation of Christian teachings.
G)Emperors of the middle of the third century, so called because they were military commanders.
H)The five Roman emperors (Nerva, Trajan, Hadrian, Antoninus Pius, and Marcus Aurelius) of the second century whose reigns were relatively prosperous and stable.
I)Official title of Augustus's form of government, taken from princeps, meaning "first citizen."
J)Title given to a Roman general after a major victory that came to mean "emperor."
K)A religious practice or belief judged unacceptable by church officials.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Answer the following questions:
aqueducts
A)In Jewish belief, a savior who would bring a period of peace and happiness for Jews.
B)The "Roman peace," a period during the first and second centuries C.E. of political stability and relative peace.
C)Originally referring to those who lived in the countryside, this term came to mean those who practiced religions other than Judaism or Christianity.
D)Imperial bodyguard created by Augustus.
E)Canals, channels, and pipes that brought freshwater into cities.
F)Christian church officials with jurisdiction over certain areas and the power to determine the correct interpretation of Christian teachings.
G)Emperors of the middle of the third century, so called because they were military commanders.
H)The five Roman emperors (Nerva, Trajan, Hadrian, Antoninus Pius, and Marcus Aurelius) of the second century whose reigns were relatively prosperous and stable.
I)Official title of Augustus's form of government, taken from princeps, meaning "first citizen."
J)Title given to a Roman general after a major victory that came to mean "emperor."
K)A religious practice or belief judged unacceptable by church officials.
aqueducts
A)In Jewish belief, a savior who would bring a period of peace and happiness for Jews.
B)The "Roman peace," a period during the first and second centuries C.E. of political stability and relative peace.
C)Originally referring to those who lived in the countryside, this term came to mean those who practiced religions other than Judaism or Christianity.
D)Imperial bodyguard created by Augustus.
E)Canals, channels, and pipes that brought freshwater into cities.
F)Christian church officials with jurisdiction over certain areas and the power to determine the correct interpretation of Christian teachings.
G)Emperors of the middle of the third century, so called because they were military commanders.
H)The five Roman emperors (Nerva, Trajan, Hadrian, Antoninus Pius, and Marcus Aurelius) of the second century whose reigns were relatively prosperous and stable.
I)Official title of Augustus's form of government, taken from princeps, meaning "first citizen."
J)Title given to a Roman general after a major victory that came to mean "emperor."
K)A religious practice or belief judged unacceptable by church officials.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
One of the most important events that occurred during the Roman Empire was the birth of Christianity. Describe the evolution of Christianity. How do historians explain its early success?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Answer the following questions:
pagan
A)In Jewish belief, a savior who would bring a period of peace and happiness for Jews.
B)The "Roman peace," a period during the first and second centuries C.E. of political stability and relative peace.
C)Originally referring to those who lived in the countryside, this term came to mean those who practiced religions other than Judaism or Christianity.
D)Imperial bodyguard created by Augustus.
E)Canals, channels, and pipes that brought freshwater into cities.
F)Christian church officials with jurisdiction over certain areas and the power to determine the correct interpretation of Christian teachings.
G)Emperors of the middle of the third century, so called because they were military commanders.
H)The five Roman emperors (Nerva, Trajan, Hadrian, Antoninus Pius, and Marcus Aurelius) of the second century whose reigns were relatively prosperous and stable.
I)Official title of Augustus's form of government, taken from princeps, meaning "first citizen."
J)Title given to a Roman general after a major victory that came to mean "emperor."
K)A religious practice or belief judged unacceptable by church officials.
pagan
A)In Jewish belief, a savior who would bring a period of peace and happiness for Jews.
B)The "Roman peace," a period during the first and second centuries C.E. of political stability and relative peace.
C)Originally referring to those who lived in the countryside, this term came to mean those who practiced religions other than Judaism or Christianity.
D)Imperial bodyguard created by Augustus.
E)Canals, channels, and pipes that brought freshwater into cities.
F)Christian church officials with jurisdiction over certain areas and the power to determine the correct interpretation of Christian teachings.
G)Emperors of the middle of the third century, so called because they were military commanders.
H)The five Roman emperors (Nerva, Trajan, Hadrian, Antoninus Pius, and Marcus Aurelius) of the second century whose reigns were relatively prosperous and stable.
I)Official title of Augustus's form of government, taken from princeps, meaning "first citizen."
J)Title given to a Roman general after a major victory that came to mean "emperor."
K)A religious practice or belief judged unacceptable by church officials.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Answer the following questions:
pax Romana
A)In Jewish belief, a savior who would bring a period of peace and happiness for Jews.
B)The "Roman peace," a period during the first and second centuries C.E. of political stability and relative peace.
C)Originally referring to those who lived in the countryside, this term came to mean those who practiced religions other than Judaism or Christianity.
D)Imperial bodyguard created by Augustus.
E)Canals, channels, and pipes that brought freshwater into cities.
F)Christian church officials with jurisdiction over certain areas and the power to determine the correct interpretation of Christian teachings.
G)Emperors of the middle of the third century, so called because they were military commanders.
H)The five Roman emperors (Nerva, Trajan, Hadrian, Antoninus Pius, and Marcus Aurelius) of the second century whose reigns were relatively prosperous and stable.
I)Official title of Augustus's form of government, taken from princeps, meaning "first citizen."
J)Title given to a Roman general after a major victory that came to mean "emperor."
K)A religious practice or belief judged unacceptable by church officials.
pax Romana
A)In Jewish belief, a savior who would bring a period of peace and happiness for Jews.
B)The "Roman peace," a period during the first and second centuries C.E. of political stability and relative peace.
C)Originally referring to those who lived in the countryside, this term came to mean those who practiced religions other than Judaism or Christianity.
D)Imperial bodyguard created by Augustus.
E)Canals, channels, and pipes that brought freshwater into cities.
F)Christian church officials with jurisdiction over certain areas and the power to determine the correct interpretation of Christian teachings.
G)Emperors of the middle of the third century, so called because they were military commanders.
H)The five Roman emperors (Nerva, Trajan, Hadrian, Antoninus Pius, and Marcus Aurelius) of the second century whose reigns were relatively prosperous and stable.
I)Official title of Augustus's form of government, taken from princeps, meaning "first citizen."
J)Title given to a Roman general after a major victory that came to mean "emperor."
K)A religious practice or belief judged unacceptable by church officials.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Answer the following questions:
Praetorians
A)In Jewish belief, a savior who would bring a period of peace and happiness for Jews.
B)The "Roman peace," a period during the first and second centuries C.E. of political stability and relative peace.
C)Originally referring to those who lived in the countryside, this term came to mean those who practiced religions other than Judaism or Christianity.
D)Imperial bodyguard created by Augustus.
E)Canals, channels, and pipes that brought freshwater into cities.
F)Christian church officials with jurisdiction over certain areas and the power to determine the correct interpretation of Christian teachings.
G)Emperors of the middle of the third century, so called because they were military commanders.
H)The five Roman emperors (Nerva, Trajan, Hadrian, Antoninus Pius, and Marcus Aurelius) of the second century whose reigns were relatively prosperous and stable.
I)Official title of Augustus's form of government, taken from princeps, meaning "first citizen."
J)Title given to a Roman general after a major victory that came to mean "emperor."
K)A religious practice or belief judged unacceptable by church officials.
Praetorians
A)In Jewish belief, a savior who would bring a period of peace and happiness for Jews.
B)The "Roman peace," a period during the first and second centuries C.E. of political stability and relative peace.
C)Originally referring to those who lived in the countryside, this term came to mean those who practiced religions other than Judaism or Christianity.
D)Imperial bodyguard created by Augustus.
E)Canals, channels, and pipes that brought freshwater into cities.
F)Christian church officials with jurisdiction over certain areas and the power to determine the correct interpretation of Christian teachings.
G)Emperors of the middle of the third century, so called because they were military commanders.
H)The five Roman emperors (Nerva, Trajan, Hadrian, Antoninus Pius, and Marcus Aurelius) of the second century whose reigns were relatively prosperous and stable.
I)Official title of Augustus's form of government, taken from princeps, meaning "first citizen."
J)Title given to a Roman general after a major victory that came to mean "emperor."
K)A religious practice or belief judged unacceptable by church officials.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
The history of the Roman Empire is marked by periods of civil war and then reform. How did the reformers-Augustus Caesar and the Antonines-respond to civil wars? Why did civil wars recur?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



