Deck 29: Challenging the Postwar Order 1960-1991
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/77
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 29: Challenging the Postwar Order 1960-1991
1
Between 1981 and 1989, Ronald Reagan and the U.S. Congress
A)increased taxes on the wealthy.
B)cut defense spending.
C)increased taxes and government-provided social services.
D)cut taxes and ballooned the government deficit.
A)increased taxes on the wealthy.
B)cut defense spending.
C)increased taxes and government-provided social services.
D)cut taxes and ballooned the government deficit.
cut taxes and ballooned the government deficit.
2
Why did OPEC declare an oil embargo on the United States in 1973?
A)The United States had attacked Iran in response to Iran's seizure of American hostages during its revolution.
B)The United States had intervened in Saudi Arabian elections in order to prevent a radical Islamic party from gaining authority.
C)The United States had refused to join the boycott against the apartheid regime in South Africa.
D)The United States had aided Israel in its war with Egypt and Syria in 1973.
A)The United States had attacked Iran in response to Iran's seizure of American hostages during its revolution.
B)The United States had intervened in Saudi Arabian elections in order to prevent a radical Islamic party from gaining authority.
C)The United States had refused to join the boycott against the apartheid regime in South Africa.
D)The United States had aided Israel in its war with Egypt and Syria in 1973.
The United States had aided Israel in its war with Egypt and Syria in 1973.
3
Who wrote Divided Heaven (1963), a classic example of a novel that provided a critical view of life in East Germany but did not directly oppose communism?
A)Helmut Kohl
B)Willy Brandt
C)Christa Wolf
D)Betty Friedan
A)Helmut Kohl
B)Willy Brandt
C)Christa Wolf
D)Betty Friedan
Christa Wolf
4
What was the result of Margaret Thatcher's effort to encourage low- and moderate-income renters to buy their apartments?
A)It failed miserably.
B)It led to destructive debt levels for poorer people.
C)It created a new class of property owners.
D)It led to accusations that Thatcher was a socialist.
A)It failed miserably.
B)It led to destructive debt levels for poorer people.
C)It created a new class of property owners.
D)It led to accusations that Thatcher was a socialist.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
What did the leaders of the Prague Spring hope to accomplish in Czechoslovakia?
A)To establish nationwide, multiparty electoral politics in support of free markets and individual liberties
B)To reconcile socialism with internal party democracy, in which local decision by trade unions, managers, and consumers would replace rigid bureaucratic planning
C)To overthrow Soviet domination and join NATO
D)To overturn the recent liberal reforms that had challenged the position of the Communist Party and to restore centralized planning and economic controls
A)To establish nationwide, multiparty electoral politics in support of free markets and individual liberties
B)To reconcile socialism with internal party democracy, in which local decision by trade unions, managers, and consumers would replace rigid bureaucratic planning
C)To overthrow Soviet domination and join NATO
D)To overturn the recent liberal reforms that had challenged the position of the Communist Party and to restore centralized planning and economic controls

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
In 1992, Francis Fukuyama declared that the world had arrived at
A)"a bridge to a new tomorrow."
B)"the first day of a new era."
C)"the beginning of the end."
D)"the end of history."
A)"a bridge to a new tomorrow."
B)"the first day of a new era."
C)"the beginning of the end."
D)"the end of history."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The essence of Willy Brandt's policies toward the Eastern Bloc was
A)to seek peace and reconciliation.
B)to reduce the influence of NATO in Germany.
C)to establish German neutrality in the Cold War.
D)to reassert German claims to majority-German areas of eastern Europe.
A)to seek peace and reconciliation.
B)to reduce the influence of NATO in Germany.
C)to establish German neutrality in the Cold War.
D)to reassert German claims to majority-German areas of eastern Europe.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
What did the New Left advocate?
A)The establishment of socialism in newly decolonized states before capitalism took hold
B)The restoration of classical liberalism with an emphasis on individual rights and economic freedom
C)A return to anarchism and the formation of communes as the basis of a new life
D)The establishment of socialism with a human face that would avoid the worst excesses of capitalism or Soviet-style communism
A)The establishment of socialism in newly decolonized states before capitalism took hold
B)The restoration of classical liberalism with an emphasis on individual rights and economic freedom
C)A return to anarchism and the formation of communes as the basis of a new life
D)The establishment of socialism with a human face that would avoid the worst excesses of capitalism or Soviet-style communism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Poland differed from the other Eastern Bloc states in the 1970s and 1980s because
A)its economy was managed effectively.
B)it retained an independent military.
C)of its independent agriculture and vigorous church.
D)of its refusal to borrow from the West.
A)its economy was managed effectively.
B)it retained an independent military.
C)of its independent agriculture and vigorous church.
D)of its refusal to borrow from the West.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
In the 1960s and 1970s, what was the purpose of eastern European economic policies such as Hungary's New Economic Mechanism and East Germany's New Economic System?
A)To focus economic production on military needs in order to maintain pace in the arms race with NATO
B)To establish five-year plans to surpass economic production in western European countries
C)To introduce some economic liberalization and encourage the production of consumer products
D)To fully adopt free-trade practices and principles within an authoritarian political system
A)To focus economic production on military needs in order to maintain pace in the arms race with NATO
B)To establish five-year plans to surpass economic production in western European countries
C)To introduce some economic liberalization and encourage the production of consumer products
D)To fully adopt free-trade practices and principles within an authoritarian political system

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Following the failure of his program of nationalization and public investment in the early 1980s, French president François Mitterrand
A)resigned.
B)failed to win reelection.
C)was forced to introduce austerity measures.
D)withdrew France from the Common Market.
A)resigned.
B)failed to win reelection.
C)was forced to introduce austerity measures.
D)withdrew France from the Common Market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The Helsinki Accords of 1975 called for
A)the nonproliferation of nuclear weapons.
B)the reunification of eastern and western Europe.
C)respect for human rights and the recognition of existing political boundaries.
D)American de-escalation in Vietnam and Soviet withdrawal from Afghanistan.
A)the nonproliferation of nuclear weapons.
B)the reunification of eastern and western Europe.
C)respect for human rights and the recognition of existing political boundaries.
D)American de-escalation in Vietnam and Soviet withdrawal from Afghanistan.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
What did Richard Nixon do following his election to the U.S. presidency in 1968?
A)Immediately withdrew American troops from Vietnam
B)Gradually reduced American involvement in the Vietnam War
C)Increased the number of American troops in Vietnam
D)Halted U.S. bombing of Vietnam
A)Immediately withdrew American troops from Vietnam
B)Gradually reduced American involvement in the Vietnam War
C)Increased the number of American troops in Vietnam
D)Halted U.S. bombing of Vietnam

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
How did the role of Christian churches change in postwar Europe?
A)Church membership and attendance declined significantly.
B)Churches committed themselves to defending traditional beliefs and practices.
C)Churches became politically active institutions for the first time.
D)Church doctrines embraced literal interpretations of Scripture.
A)Church membership and attendance declined significantly.
B)Churches committed themselves to defending traditional beliefs and practices.
C)Churches became politically active institutions for the first time.
D)Church doctrines embraced literal interpretations of Scripture.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Who was the founder of the National Organization for Women?
A)Simone de Beauvoir
B)Betty Friedan
C)Phyllis Schlafly
D)Gloria Steinem
A)Simone de Beauvoir
B)Betty Friedan
C)Phyllis Schlafly
D)Gloria Steinem

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Who began the wave of social unrest that almost toppled Charles de Gaulle's Fifth Republic?
A)Workers
B)Students
C)Civil servants
D)Soldiers
A)Workers
B)Students
C)Civil servants
D)Soldiers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Why did the August 1991 attempted coup by the Communist old guard in the Soviet Union fail?
A)Massive popular resistance rallied around Boris Yeltsin.
B)Gorbachev used the Red Army to crush the rebels.
C)NATO threatened to intervene.
D)The old guard was unable to decide on a new leader.
A)Massive popular resistance rallied around Boris Yeltsin.
B)Gorbachev used the Red Army to crush the rebels.
C)NATO threatened to intervene.
D)The old guard was unable to decide on a new leader.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The postindustrial society that emerged at the end of the 1970s
A)idolized Rachel Carson's Silent Spring and worked to reduce industrial pollution substantially.
B)relied on high-tech and service-oriented jobs for economic growth rather than on heavy industry and manufacturing jobs.
C)emphasized a back-to-the-land movement that included moving out of the cities and growing one's own food.
D)worked to establish a better balance between industry and agriculture.
A)idolized Rachel Carson's Silent Spring and worked to reduce industrial pollution substantially.
B)relied on high-tech and service-oriented jobs for economic growth rather than on heavy industry and manufacturing jobs.
C)emphasized a back-to-the-land movement that included moving out of the cities and growing one's own food.
D)worked to establish a better balance between industry and agriculture.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
What was the policy of détente that Social Democrats in Europe pursued?
A)The reunification of East and West Germany
B)A political unification of Europe into a single state
C)A progressive relaxation of Cold War tensions
D)The creation of a Europe-wide free-trade zone
A)The reunification of East and West Germany
B)A political unification of Europe into a single state
C)A progressive relaxation of Cold War tensions
D)The creation of a Europe-wide free-trade zone

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
How was the Tet Offensive, launched by the Vietcong in January 1968, perceived in the United States?
A)As a sign that the war was not close to ending
B)As a sign that the North Vietnamese were at the end of their tether
C)As a sign of Soviet direction of the Vietcong and North Vietnamese war effort
D)As a sign that more U.S. troops were needed to crush the Communist insurgency
A)As a sign that the war was not close to ending
B)As a sign that the North Vietnamese were at the end of their tether
C)As a sign of Soviet direction of the Vietcong and North Vietnamese war effort
D)As a sign that more U.S. troops were needed to crush the Communist insurgency

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The Brezhnev Doctrine stated that the Soviet Union and its allies
A)would soon catch up to and surpass the West economically.
B)were pursuing a policy of peaceful coexistence.
C)had the right to intervene in any East Bloc country if necessary to preserve Communist rule.
D)wanted to explore space with the United States and its allies.
A)would soon catch up to and surpass the West economically.
B)were pursuing a policy of peaceful coexistence.
C)had the right to intervene in any East Bloc country if necessary to preserve Communist rule.
D)wanted to explore space with the United States and its allies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
What did Rachel Carson seek to expose in her book Silent Spring?
A)The rampant overuse of pesticides
B)The consequences of the use of nuclear weapons
C)The discrimination faced by colonial migrants to European nations
D)The failures of the educational system to prepare future workers
A)The rampant overuse of pesticides
B)The consequences of the use of nuclear weapons
C)The discrimination faced by colonial migrants to European nations
D)The failures of the educational system to prepare future workers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Throughout the 1970s and 1980s, Spain faced terrorist actions by an insurgent movement of
A)Catholic radicals.
B)Basque separatists.
C)Muslim revivalists.
D)former colonial expatriates.
A)Catholic radicals.
B)Basque separatists.
C)Muslim revivalists.
D)former colonial expatriates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following describes Eastern Bloc living standards in the 1970s?
A)Equal with those in the West and well above those in the developing world
B)Below those of the West and equal with those in the developing world
C)Well below those in the West but well above those in the developing world
D)Far below those of the West and even below those of most of the developing world
A)Equal with those in the West and well above those in the developing world
B)Below those of the West and equal with those in the developing world
C)Well below those in the West but well above those in the developing world
D)Far below those of the West and even below those of most of the developing world

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The neoliberal policies of the 1980s promoted which of the following?
A)Increased spending on social services
B)Government subsidies to businesses
C)Privatization of state-owned businesses
D)Increase in regulations on industry
A)Increased spending on social services
B)Government subsidies to businesses
C)Privatization of state-owned businesses
D)Increase in regulations on industry

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Who was Poland's first non-Communist prime minister in 1989?
A)Lech WaÇêsa
B)Tadeusz Mazowiecki
C)Karol Wojtyla
D)Yuri Andropov
A)Lech WaÇêsa
B)Tadeusz Mazowiecki
C)Karol Wojtyla
D)Yuri Andropov

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
What was Mikhail Gorbachev's goal in bringing reforms to Russia?
A)To revitalize the Soviet system in order to save it
B)To secure the power of the Communist Party through more sophisticated systems of control
C)To merge capitalism and communism into a new economic system
D)To prepare for a the collapse of Communist authority
A)To revitalize the Soviet system in order to save it
B)To secure the power of the Communist Party through more sophisticated systems of control
C)To merge capitalism and communism into a new economic system
D)To prepare for a the collapse of Communist authority

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
How did the Solidarity trade union in Poland understand its goals in the early 1980s?
A)It sought to force the government out of economic planning so that the free market could direct economic activity.
B)It sought to establish open democratic elections in which the Communist Party would have to compete for power.
C)It sought a self-limiting revolution to defend freedoms won in previous agreements with the Communist government.
D)It sought to overthrow the government and drive the Communist Party out of Poland.
A)It sought to force the government out of economic planning so that the free market could direct economic activity.
B)It sought to establish open democratic elections in which the Communist Party would have to compete for power.
C)It sought a self-limiting revolution to defend freedoms won in previous agreements with the Communist government.
D)It sought to overthrow the government and drive the Communist Party out of Poland.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The experience of women in the socialist systems of the East Bloc countries of the 1970s included
A)the domination of the judicial system as lawyers and judges.
B)the creation of independent groups dedicated to feminist reform.
C)an extensive system of state-supported childcare that freed women to work outside the home.
D)an end of the double burden of work in the office and at home.
A)the domination of the judicial system as lawyers and judges.
B)the creation of independent groups dedicated to feminist reform.
C)an extensive system of state-supported childcare that freed women to work outside the home.
D)an end of the double burden of work in the office and at home.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
What happened in 1989 when the Hungarians tore down the barbed-wire curtain separating it from Austria?
A)Austrians flooded into Hungary to take advantage of low prices on food and other goods.
B)Hungarians set up lucrative smuggling routes for illegal drugs.
C)Large numbers of dissatisfied East German "vacationers" crossed from Hungary into Austria and from there on to West Germany.
D)Unemployed residents of the Central Asian republics of the Soviet Union crossed into Austria in search of jobs.
A)Austrians flooded into Hungary to take advantage of low prices on food and other goods.
B)Hungarians set up lucrative smuggling routes for illegal drugs.
C)Large numbers of dissatisfied East German "vacationers" crossed from Hungary into Austria and from there on to West Germany.
D)Unemployed residents of the Central Asian republics of the Soviet Union crossed into Austria in search of jobs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Samizdat literature referred to books, periodicals, pamphlets, and newspapers that were
A)published secretly and passed from hand to hand.
B)available only at special stores for Communist party members.
C)smuggled in from the West.
D)regarded as pornographic by the Communist government.
A)published secretly and passed from hand to hand.
B)available only at special stores for Communist party members.
C)smuggled in from the West.
D)regarded as pornographic by the Communist government.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
How did many Soviet citizens receive lessons in open political discussion, critical thinking, and representative government?
A)From participation in local councils in each neighborhood that resolved local political grievances through elected officers
B)From illegally watching banned U.S. television shows that depicted electoral activity
C)From following political activity in new democracies that emerged with decolonization and were widely reported on by the Soviet press
D)From watching the Congress of People's Deputies, whose deputies had been chosen in free elections in 1989
A)From participation in local councils in each neighborhood that resolved local political grievances through elected officers
B)From illegally watching banned U.S. television shows that depicted electoral activity
C)From following political activity in new democracies that emerged with decolonization and were widely reported on by the Soviet press
D)From watching the Congress of People's Deputies, whose deputies had been chosen in free elections in 1989

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
What did the era of stagflation in the 1970s demonstrate about the social welfare states in western Europe?
A)The welfare state was vastly insufficient to respond to the personal difficulties created by a failing economy.
B)The welfare state was capable of preventing mass suffering and sustaining political stability and democracy.
C)The welfare state was highly inefficient in its operations and resulted primarily in wasted funds.
D)The welfare state encouraged individuals to freeload on society and inhibited economic recovery.
A)The welfare state was vastly insufficient to respond to the personal difficulties created by a failing economy.
B)The welfare state was capable of preventing mass suffering and sustaining political stability and democracy.
C)The welfare state was highly inefficient in its operations and resulted primarily in wasted funds.
D)The welfare state encouraged individuals to freeload on society and inhibited economic recovery.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
How did Helmut Kohl's neoliberal policies in Germany in the 1980s affect the Germany economy?
A)The policies reenergized German industry, resulting in low unemployment rates.
B)The policies undermined economic stability, which led to a revival of socialist parties.
C)The policies increased unemployment in heavy industry but led to solid economic growth.
D)The policies failed to revive Germany's economy but resulted in a more equitable distribution of wealth.
A)The policies reenergized German industry, resulting in low unemployment rates.
B)The policies undermined economic stability, which led to a revival of socialist parties.
C)The policies increased unemployment in heavy industry but led to solid economic growth.
D)The policies failed to revive Germany's economy but resulted in a more equitable distribution of wealth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
How did the West German chancellor Helmut Kohl build support for German reunification in East Germany?
A)He promised East Germany's business leaders that they would hold similar roles in the new, unified Germany.
B)He immediately forced all Soviet troops to leave East Germany.
C)He invited many high-ranking Communist officials into government ministries in the unified Germany.
D)He offered the East Germans an economically advantageous swap of East German currency for West German currency.
A)He promised East Germany's business leaders that they would hold similar roles in the new, unified Germany.
B)He immediately forced all Soviet troops to leave East Germany.
C)He invited many high-ranking Communist officials into government ministries in the unified Germany.
D)He offered the East Germans an economically advantageous swap of East German currency for West German currency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Charter 77 was a manifesto signed by a small group of Czech citizens that called on Communist leaders to
A)improve the benefits offered by the state welfare system.
B)take Czechoslovakia out of the Warsaw Pact.
C)respect civil and political liberties.
D)establish trade relations with western Europe.
A)improve the benefits offered by the state welfare system.
B)take Czechoslovakia out of the Warsaw Pact.
C)respect civil and political liberties.
D)establish trade relations with western Europe.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
How was the revolution in Romania in 1989 different from the revolutions in the rest of eastern Europe?
A)A strong Catholic Church served as negotiator between Romania's Communist regime and the rebels.
B)It became violent and bloody when Communist leaders ordered security forces to slaughter thousands.
C)It began as the Communist Party removed reform Communists leading the country and reestablished Stalinist leadership.
D)The Romanian Communist Party initiated political reforms in order to build its legitimacy before elections that seemed inevitable.
A)A strong Catholic Church served as negotiator between Romania's Communist regime and the rebels.
B)It became violent and bloody when Communist leaders ordered security forces to slaughter thousands.
C)It began as the Communist Party removed reform Communists leading the country and reestablished Stalinist leadership.
D)The Romanian Communist Party initiated political reforms in order to build its legitimacy before elections that seemed inevitable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Boris Yeltsin's role in the disintegration of the Soviet Union included
A)working as an ally of Gorbachev to save the Communist Party by opening party institutions to electoral politics.
B)leading the old guard Communists who sought to kidnap Gorbachev and seize power in the Soviet Union in order to crush the reform movement.
C)emerging as a radical reform Communist who embraced the democratic movement and led Russia to declare independence from the Soviet Union.
D)directing the Soviet effort to quash Lithuanian claims of independence.
A)working as an ally of Gorbachev to save the Communist Party by opening party institutions to electoral politics.
B)leading the old guard Communists who sought to kidnap Gorbachev and seize power in the Soviet Union in order to crush the reform movement.
C)emerging as a radical reform Communist who embraced the democratic movement and led Russia to declare independence from the Soviet Union.
D)directing the Soviet effort to quash Lithuanian claims of independence.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
In response to the growing power of Solidarity in Poland, Wojciech Jaruzelski, a general and head of the Polish government, suddenly
A)resigned in favor of the leader of Solidarity, Lech WaÇêsa.
B)called on the Soviet Union to come to the aid of the government.
C)appealed to the United Nations to resolve the crisis.
D)proclaimed martial law and arrested Solidarity's leaders.
A)resigned in favor of the leader of Solidarity, Lech WaÇêsa.
B)called on the Soviet Union to come to the aid of the government.
C)appealed to the United Nations to resolve the crisis.
D)proclaimed martial law and arrested Solidarity's leaders.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Mikhail Gorbachev, who became the leader of the Soviet Union in 1985, tried to reform the Communist system through perestroika, or
A)a newfound openness in government and the media.
B)democratization, which led to the first free elections since 1917.
C)new thinking, particularly in the area of foreign policy.
D)economic restructuring.
A)a newfound openness in government and the media.
B)democratization, which led to the first free elections since 1917.
C)new thinking, particularly in the area of foreign policy.
D)economic restructuring.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
In the following excerpt from The Second Sex (Evaluating the Evidence 29.2), Simone de Beauvoir offers her views on traditional marriage: "The drama of marriage is not that it does not guarantee the wife the promised happiness-there is no guarantee of happiness-it is that it mutilates her; it dooms her to repetition and routine. The first twenty years of a woman's life are extraordinarily rich; she experiences menstruation, sexuality, marriage, and motherhood; she discovers the world and her destiny. She is mistress of a home at twenty, linked from then on to one man, a child in her arms, now her life is finished forever. Real activity, real work, are the privilege of man: her only occupations are sometimes exhausting but never fulfill her. . ."
In Beauvoir's view,
A)traditional marriage is a kind of death for women.
B)traditional marriage is very satisfying for some women.
C)traditional marriage is the foundation of society.
D)traditional marriage is harder on men than on women.
In Beauvoir's view,
A)traditional marriage is a kind of death for women.
B)traditional marriage is very satisfying for some women.
C)traditional marriage is the foundation of society.
D)traditional marriage is harder on men than on women.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
What was the central argument of Simone de Beauvoir's The Second Sex?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
What led to the collapse of the international monetary system in the early 1970s?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
What structural weaknesses help explain the revolutions of 1989 in the East Bloc?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Why is Margaret Thatcher seen as such a significant political figure in the 1980s?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The following is an excerpt from Rachel Carson's Silent Spring (Thinking Like a Historian): "For each of us, as for the robin in Michigan or the Salmon in the Miramichi, this is a problem of ecology, of interrelationships, of interdependence. We poison the caddis flies in a stream and the salmon runs dwindle and die. We poison the gnats in a lake and the poison travels from link to link of the food chain and soon the birds of the lake margins become its victims. We spray our elms and the following springs are silent of robin song, not because we sprayed the robins directly but because the poison traveled, step by step, through the now familiar elm leaf-earthworm-robin cycle. These are matters of record, observable, part of the visible world around us. They reflect the web of life-or death-that scientists know as ecology. . . ."
Carson wanted her readers to understand that
A)the use of pesticides affected much more than the targeted insects.
B)insect infestations were on the rise.
C)environmental policies could result in economic growth.
D)the planet was doomed.
Carson wanted her readers to understand that
A)the use of pesticides affected much more than the targeted insects.
B)insect infestations were on the rise.
C)environmental policies could result in economic growth.
D)the planet was doomed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
What did the Second Vatican Council accomplish?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
According to Map 29.2: Democratic Movements in Eastern Europe, 1989, which country was the first to display a democratic movement? 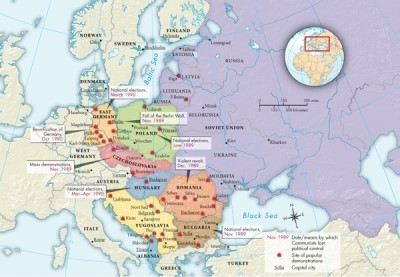
A)Poland
B)Czechoslovakia
C)East Germany
D)Yugoslavia

A)Poland
B)Czechoslovakia
C)East Germany
D)Yugoslavia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The following is an excerpt from "Some Preconditions for Resolving the Ecology Crisis" (Thinking Like a Historian) by Rudolf Bahro, a founding member of the West German Green Party: "The ecology crisis is insoluble unless we work at the same time at overcoming the confrontation of military blocs. It is insoluble without a resolute policy of détente and disarmament, one that renounces all demands for subverting other countries. . . .
The ecology crisis is insoluble without a world order on the North-South axis. And we must realize that our entire standard of living [in the North] is largely based on the exploitation and suppression of the rest of humanity. . . ."
In this excerpt, Bahrosuggests that a solution to the ecology crisis will require
A)aid programs for impoverished countries.
B)military blockades along the North-South axis.
C)undermining the authority of other countries.
D)an easing of hostility between countries.
The ecology crisis is insoluble without a world order on the North-South axis. And we must realize that our entire standard of living [in the North] is largely based on the exploitation and suppression of the rest of humanity. . . ."
In this excerpt, Bahrosuggests that a solution to the ecology crisis will require
A)aid programs for impoverished countries.
B)military blockades along the North-South axis.
C)undermining the authority of other countries.
D)an easing of hostility between countries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
What was the effect of the invention of the birth control pill?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
According to Map 29.2: Democratic Movements in Eastern Europe, 1989, which country had the most popular demonstrations? 
A)Yugoslavia
B)East Germany
C)Romania
D)Poland

A)Yugoslavia
B)East Germany
C)Romania
D)Poland

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
What was the importance of the Catholic Church to the Polish reform movement in the 1980s?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
What was the result of the "May Events" of 1968?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
What was the Velvet Revolution in 1989?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
What was the Paris Accord, signed in 1990 by twenty-two European countries, the United States, and the Soviet Union?
A)An agreement to respect the environment and a pledge to undo the damage that had been done up to that point
B)A formal recognition of the superiority of democratic political systems
C)Essentially a general peace treaty that brought an end to both World War II and the Cold War
D)A pledge to create an economic organization that would include all European countries and replace the European Community
A)An agreement to respect the environment and a pledge to undo the damage that had been done up to that point
B)A formal recognition of the superiority of democratic political systems
C)Essentially a general peace treaty that brought an end to both World War II and the Cold War
D)A pledge to create an economic organization that would include all European countries and replace the European Community

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Map 29.2: Democratic Movements in Eastern Europe, 1989 shows that most of the events of the Velvet Revolution took place in what capital city? 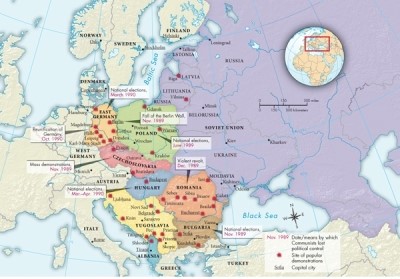
A)Berlin
B)Leipzig
C)Prague
D)Bratislava

A)Berlin
B)Leipzig
C)Prague
D)Bratislava

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which of the following helps explain the revolutions in the East Bloc in 1989?
A)East Bloc economies never really recovered from the economic catastrophe of the 1970s.
B)A series of bad harvests led to mass starvation.
C)Large cuts to government spending undermined social welfare programs.
D)Economic growth fueled rising expectations about political reform.
A)East Bloc economies never really recovered from the economic catastrophe of the 1970s.
B)A series of bad harvests led to mass starvation.
C)Large cuts to government spending undermined social welfare programs.
D)Economic growth fueled rising expectations about political reform.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
What were perestroika and glasnost?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The following is an excerpt from the Manifesto of the Czechoslovak dissident group Charter 77 (Evaluating the Evidence 29.3): "Responsibility for the maintenance of rights in our country naturally devolves in the first place on the political and state authorities. Yet not only on them: everyone bears his share of responsibility for the conditions that prevail and accordingly also for the observance of legally enshrined agreements, binding upon all individuals as well as upon governments.
It is this sense of co-responsibility, our belief in the importance of its conscious public acceptance and the general need to give it new and more effective expression that led us to the idea of creating Charter 77, whose inception we today publicly announce. . . ."
The authors of Charter 77 were inspired by
A)events in South Africa.
B)a sense of their own responsibility for the maintenance of human rights.
C)the American Revolution.
D)a sense that the Czech government was close to collapse.
It is this sense of co-responsibility, our belief in the importance of its conscious public acceptance and the general need to give it new and more effective expression that led us to the idea of creating Charter 77, whose inception we today publicly announce. . . ."
The authors of Charter 77 were inspired by
A)events in South Africa.
B)a sense of their own responsibility for the maintenance of human rights.
C)the American Revolution.
D)a sense that the Czech government was close to collapse.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
In the following excerpt from The Second Sex (Evaluating the Evidence 29.2), Simone de Beauvoir offers her views on marriage: "Marriage must combine two autonomous existences, not be a withdrawal, an annexation, an escape, a remedy. . . . The couple should not consider itself a community, a closed cell: instead, the individual as individual has to be integrated into a society in which he can thrive without assistance; he will then be able to create links in pure generosity with another individual equally adapted to the group, links founded on the recognition of two freedoms."
In Beauvoir's view,
A)marriage should be abolished.
B)men and women have very different roles in marriage.
C)both partners in a marriage must maintain their autonomy.
D)marriage is the union of souls.
In Beauvoir's view,
A)marriage should be abolished.
B)men and women have very different roles in marriage.
C)both partners in a marriage must maintain their autonomy.
D)marriage is the union of souls.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Answer the following questions:
Velvet Revolution
A)Doctrine that held that the Soviet Union had the right to intervene in any East Bloc country whenever it saw the need.
B)Society that relies on high-tech and service-oriented jobs for economic growth rather than heavy industry and manufacturing jobs.
C)Term coined in the early 1980s to describe the combination of low growth and high inflation that led to a worldwide recession.
D)A term used by Communist leaders to describe the socialist accomplishments of their societies, such as nationalized industry, collective agriculture, and extensive social welfare programs.
E)Philosophy of 1980s conservatives who argued for decreased government spending on social services and privatization of state-run industries.
F)The term given to the relatively peaceful overthrow of communism in Czechoslovakia; the label came to signify the collapse of the East Bloc in general in 1989 to 1990.
G)The progressive relaxation of Cold War tensions that emerged in the early 1970s.
H)Independent Polish trade union that worked for workers' rights and political reform throughout the 1980s.
I)A 1960s counterculture movement that embraced updated forms of Marxism to challenge both Western capitalism and Soviet-style communism.
J)Economic restructuring and reform implemented by Premier Mikhail Gorbachev in the Soviet Union in 1985.
K)Soviet premier Mikhail Gorbachev's popular campaign for openness in government and the media.
Velvet Revolution
A)Doctrine that held that the Soviet Union had the right to intervene in any East Bloc country whenever it saw the need.
B)Society that relies on high-tech and service-oriented jobs for economic growth rather than heavy industry and manufacturing jobs.
C)Term coined in the early 1980s to describe the combination of low growth and high inflation that led to a worldwide recession.
D)A term used by Communist leaders to describe the socialist accomplishments of their societies, such as nationalized industry, collective agriculture, and extensive social welfare programs.
E)Philosophy of 1980s conservatives who argued for decreased government spending on social services and privatization of state-run industries.
F)The term given to the relatively peaceful overthrow of communism in Czechoslovakia; the label came to signify the collapse of the East Bloc in general in 1989 to 1990.
G)The progressive relaxation of Cold War tensions that emerged in the early 1970s.
H)Independent Polish trade union that worked for workers' rights and political reform throughout the 1980s.
I)A 1960s counterculture movement that embraced updated forms of Marxism to challenge both Western capitalism and Soviet-style communism.
J)Economic restructuring and reform implemented by Premier Mikhail Gorbachev in the Soviet Union in 1985.
K)Soviet premier Mikhail Gorbachev's popular campaign for openness in government and the media.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Answer the following questions:
Solidarity
A)Doctrine that held that the Soviet Union had the right to intervene in any East Bloc country whenever it saw the need.
B)Society that relies on high-tech and service-oriented jobs for economic growth rather than heavy industry and manufacturing jobs.
C)Term coined in the early 1980s to describe the combination of low growth and high inflation that led to a worldwide recession.
D)A term used by Communist leaders to describe the socialist accomplishments of their societies, such as nationalized industry, collective agriculture, and extensive social welfare programs.
E)Philosophy of 1980s conservatives who argued for decreased government spending on social services and privatization of state-run industries.
F)The term given to the relatively peaceful overthrow of communism in Czechoslovakia; the label came to signify the collapse of the East Bloc in general in 1989 to 1990.
G)The progressive relaxation of Cold War tensions that emerged in the early 1970s.
H)Independent Polish trade union that worked for workers' rights and political reform throughout the 1980s.
I)A 1960s counterculture movement that embraced updated forms of Marxism to challenge both Western capitalism and Soviet-style communism.
J)Economic restructuring and reform implemented by Premier Mikhail Gorbachev in the Soviet Union in 1985.
K)Soviet premier Mikhail Gorbachev's popular campaign for openness in government and the media.
Solidarity
A)Doctrine that held that the Soviet Union had the right to intervene in any East Bloc country whenever it saw the need.
B)Society that relies on high-tech and service-oriented jobs for economic growth rather than heavy industry and manufacturing jobs.
C)Term coined in the early 1980s to describe the combination of low growth and high inflation that led to a worldwide recession.
D)A term used by Communist leaders to describe the socialist accomplishments of their societies, such as nationalized industry, collective agriculture, and extensive social welfare programs.
E)Philosophy of 1980s conservatives who argued for decreased government spending on social services and privatization of state-run industries.
F)The term given to the relatively peaceful overthrow of communism in Czechoslovakia; the label came to signify the collapse of the East Bloc in general in 1989 to 1990.
G)The progressive relaxation of Cold War tensions that emerged in the early 1970s.
H)Independent Polish trade union that worked for workers' rights and political reform throughout the 1980s.
I)A 1960s counterculture movement that embraced updated forms of Marxism to challenge both Western capitalism and Soviet-style communism.
J)Economic restructuring and reform implemented by Premier Mikhail Gorbachev in the Soviet Union in 1985.
K)Soviet premier Mikhail Gorbachev's popular campaign for openness in government and the media.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Answer the following questions:
détente
A)Doctrine that held that the Soviet Union had the right to intervene in any East Bloc country whenever it saw the need.
B)Society that relies on high-tech and service-oriented jobs for economic growth rather than heavy industry and manufacturing jobs.
C)Term coined in the early 1980s to describe the combination of low growth and high inflation that led to a worldwide recession.
D)A term used by Communist leaders to describe the socialist accomplishments of their societies, such as nationalized industry, collective agriculture, and extensive social welfare programs.
E)Philosophy of 1980s conservatives who argued for decreased government spending on social services and privatization of state-run industries.
F)The term given to the relatively peaceful overthrow of communism in Czechoslovakia; the label came to signify the collapse of the East Bloc in general in 1989 to 1990.
G)The progressive relaxation of Cold War tensions that emerged in the early 1970s.
H)Independent Polish trade union that worked for workers' rights and political reform throughout the 1980s.
I)A 1960s counterculture movement that embraced updated forms of Marxism to challenge both Western capitalism and Soviet-style communism.
J)Economic restructuring and reform implemented by Premier Mikhail Gorbachev in the Soviet Union in 1985.
K)Soviet premier Mikhail Gorbachev's popular campaign for openness in government and the media.
détente
A)Doctrine that held that the Soviet Union had the right to intervene in any East Bloc country whenever it saw the need.
B)Society that relies on high-tech and service-oriented jobs for economic growth rather than heavy industry and manufacturing jobs.
C)Term coined in the early 1980s to describe the combination of low growth and high inflation that led to a worldwide recession.
D)A term used by Communist leaders to describe the socialist accomplishments of their societies, such as nationalized industry, collective agriculture, and extensive social welfare programs.
E)Philosophy of 1980s conservatives who argued for decreased government spending on social services and privatization of state-run industries.
F)The term given to the relatively peaceful overthrow of communism in Czechoslovakia; the label came to signify the collapse of the East Bloc in general in 1989 to 1990.
G)The progressive relaxation of Cold War tensions that emerged in the early 1970s.
H)Independent Polish trade union that worked for workers' rights and political reform throughout the 1980s.
I)A 1960s counterculture movement that embraced updated forms of Marxism to challenge both Western capitalism and Soviet-style communism.
J)Economic restructuring and reform implemented by Premier Mikhail Gorbachev in the Soviet Union in 1985.
K)Soviet premier Mikhail Gorbachev's popular campaign for openness in government and the media.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Answer the following questions:
New Left
A)Doctrine that held that the Soviet Union had the right to intervene in any East Bloc country whenever it saw the need.
B)Society that relies on high-tech and service-oriented jobs for economic growth rather than heavy industry and manufacturing jobs.
C)Term coined in the early 1980s to describe the combination of low growth and high inflation that led to a worldwide recession.
D)A term used by Communist leaders to describe the socialist accomplishments of their societies, such as nationalized industry, collective agriculture, and extensive social welfare programs.
E)Philosophy of 1980s conservatives who argued for decreased government spending on social services and privatization of state-run industries.
F)The term given to the relatively peaceful overthrow of communism in Czechoslovakia; the label came to signify the collapse of the East Bloc in general in 1989 to 1990.
G)The progressive relaxation of Cold War tensions that emerged in the early 1970s.
H)Independent Polish trade union that worked for workers' rights and political reform throughout the 1980s.
I)A 1960s counterculture movement that embraced updated forms of Marxism to challenge both Western capitalism and Soviet-style communism.
J)Economic restructuring and reform implemented by Premier Mikhail Gorbachev in the Soviet Union in 1985.
K)Soviet premier Mikhail Gorbachev's popular campaign for openness in government and the media.
New Left
A)Doctrine that held that the Soviet Union had the right to intervene in any East Bloc country whenever it saw the need.
B)Society that relies on high-tech and service-oriented jobs for economic growth rather than heavy industry and manufacturing jobs.
C)Term coined in the early 1980s to describe the combination of low growth and high inflation that led to a worldwide recession.
D)A term used by Communist leaders to describe the socialist accomplishments of their societies, such as nationalized industry, collective agriculture, and extensive social welfare programs.
E)Philosophy of 1980s conservatives who argued for decreased government spending on social services and privatization of state-run industries.
F)The term given to the relatively peaceful overthrow of communism in Czechoslovakia; the label came to signify the collapse of the East Bloc in general in 1989 to 1990.
G)The progressive relaxation of Cold War tensions that emerged in the early 1970s.
H)Independent Polish trade union that worked for workers' rights and political reform throughout the 1980s.
I)A 1960s counterculture movement that embraced updated forms of Marxism to challenge both Western capitalism and Soviet-style communism.
J)Economic restructuring and reform implemented by Premier Mikhail Gorbachev in the Soviet Union in 1985.
K)Soviet premier Mikhail Gorbachev's popular campaign for openness in government and the media.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Answer the following questions:
neoliberalism
A)Doctrine that held that the Soviet Union had the right to intervene in any East Bloc country whenever it saw the need.
B)Society that relies on high-tech and service-oriented jobs for economic growth rather than heavy industry and manufacturing jobs.
C)Term coined in the early 1980s to describe the combination of low growth and high inflation that led to a worldwide recession.
D)A term used by Communist leaders to describe the socialist accomplishments of their societies, such as nationalized industry, collective agriculture, and extensive social welfare programs.
E)Philosophy of 1980s conservatives who argued for decreased government spending on social services and privatization of state-run industries.
F)The term given to the relatively peaceful overthrow of communism in Czechoslovakia; the label came to signify the collapse of the East Bloc in general in 1989 to 1990.
G)The progressive relaxation of Cold War tensions that emerged in the early 1970s.
H)Independent Polish trade union that worked for workers' rights and political reform throughout the 1980s.
I)A 1960s counterculture movement that embraced updated forms of Marxism to challenge both Western capitalism and Soviet-style communism.
J)Economic restructuring and reform implemented by Premier Mikhail Gorbachev in the Soviet Union in 1985.
K)Soviet premier Mikhail Gorbachev's popular campaign for openness in government and the media.
neoliberalism
A)Doctrine that held that the Soviet Union had the right to intervene in any East Bloc country whenever it saw the need.
B)Society that relies on high-tech and service-oriented jobs for economic growth rather than heavy industry and manufacturing jobs.
C)Term coined in the early 1980s to describe the combination of low growth and high inflation that led to a worldwide recession.
D)A term used by Communist leaders to describe the socialist accomplishments of their societies, such as nationalized industry, collective agriculture, and extensive social welfare programs.
E)Philosophy of 1980s conservatives who argued for decreased government spending on social services and privatization of state-run industries.
F)The term given to the relatively peaceful overthrow of communism in Czechoslovakia; the label came to signify the collapse of the East Bloc in general in 1989 to 1990.
G)The progressive relaxation of Cold War tensions that emerged in the early 1970s.
H)Independent Polish trade union that worked for workers' rights and political reform throughout the 1980s.
I)A 1960s counterculture movement that embraced updated forms of Marxism to challenge both Western capitalism and Soviet-style communism.
J)Economic restructuring and reform implemented by Premier Mikhail Gorbachev in the Soviet Union in 1985.
K)Soviet premier Mikhail Gorbachev's popular campaign for openness in government and the media.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Answer the following questions:
perestroika
A)Doctrine that held that the Soviet Union had the right to intervene in any East Bloc country whenever it saw the need.
B)Society that relies on high-tech and service-oriented jobs for economic growth rather than heavy industry and manufacturing jobs.
C)Term coined in the early 1980s to describe the combination of low growth and high inflation that led to a worldwide recession.
D)A term used by Communist leaders to describe the socialist accomplishments of their societies, such as nationalized industry, collective agriculture, and extensive social welfare programs.
E)Philosophy of 1980s conservatives who argued for decreased government spending on social services and privatization of state-run industries.
F)The term given to the relatively peaceful overthrow of communism in Czechoslovakia; the label came to signify the collapse of the East Bloc in general in 1989 to 1990.
G)The progressive relaxation of Cold War tensions that emerged in the early 1970s.
H)Independent Polish trade union that worked for workers' rights and political reform throughout the 1980s.
I)A 1960s counterculture movement that embraced updated forms of Marxism to challenge both Western capitalism and Soviet-style communism.
J)Economic restructuring and reform implemented by Premier Mikhail Gorbachev in the Soviet Union in 1985.
K)Soviet premier Mikhail Gorbachev's popular campaign for openness in government and the media.
perestroika
A)Doctrine that held that the Soviet Union had the right to intervene in any East Bloc country whenever it saw the need.
B)Society that relies on high-tech and service-oriented jobs for economic growth rather than heavy industry and manufacturing jobs.
C)Term coined in the early 1980s to describe the combination of low growth and high inflation that led to a worldwide recession.
D)A term used by Communist leaders to describe the socialist accomplishments of their societies, such as nationalized industry, collective agriculture, and extensive social welfare programs.
E)Philosophy of 1980s conservatives who argued for decreased government spending on social services and privatization of state-run industries.
F)The term given to the relatively peaceful overthrow of communism in Czechoslovakia; the label came to signify the collapse of the East Bloc in general in 1989 to 1990.
G)The progressive relaxation of Cold War tensions that emerged in the early 1970s.
H)Independent Polish trade union that worked for workers' rights and political reform throughout the 1980s.
I)A 1960s counterculture movement that embraced updated forms of Marxism to challenge both Western capitalism and Soviet-style communism.
J)Economic restructuring and reform implemented by Premier Mikhail Gorbachev in the Soviet Union in 1985.
K)Soviet premier Mikhail Gorbachev's popular campaign for openness in government and the media.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
How did the women's movement in the 1970s seek to realize Simone de Beauvoir's call for women to "reach out beyond themselves, transcend themselves, toward society in production and action"?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The year 1989 witnessed an almost unbelievable turn of events in the Eastern Bloc. Discuss those changes. What were the long-term causes? What new problems were created?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Describe Willy Brandt's attempt to answer the German question. What role did the United States and NATO play in Brandt's policies? What was the impact of those policies on the Cold War?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The revolutionary surge of the 1960s was primarily a youth movement. Describe this movement. What factors caused it to gain momentum and then explode in the late 1960s and early 1970s? What were the consequences of this movement?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Answer the following questions:
postindustrial society
A)Doctrine that held that the Soviet Union had the right to intervene in any East Bloc country whenever it saw the need.
B)Society that relies on high-tech and service-oriented jobs for economic growth rather than heavy industry and manufacturing jobs.
C)Term coined in the early 1980s to describe the combination of low growth and high inflation that led to a worldwide recession.
D)A term used by Communist leaders to describe the socialist accomplishments of their societies, such as nationalized industry, collective agriculture, and extensive social welfare programs.
E)Philosophy of 1980s conservatives who argued for decreased government spending on social services and privatization of state-run industries.
F)The term given to the relatively peaceful overthrow of communism in Czechoslovakia; the label came to signify the collapse of the East Bloc in general in 1989 to 1990.
G)The progressive relaxation of Cold War tensions that emerged in the early 1970s.
H)Independent Polish trade union that worked for workers' rights and political reform throughout the 1980s.
I)A 1960s counterculture movement that embraced updated forms of Marxism to challenge both Western capitalism and Soviet-style communism.
J)Economic restructuring and reform implemented by Premier Mikhail Gorbachev in the Soviet Union in 1985.
K)Soviet premier Mikhail Gorbachev's popular campaign for openness in government and the media.
postindustrial society
A)Doctrine that held that the Soviet Union had the right to intervene in any East Bloc country whenever it saw the need.
B)Society that relies on high-tech and service-oriented jobs for economic growth rather than heavy industry and manufacturing jobs.
C)Term coined in the early 1980s to describe the combination of low growth and high inflation that led to a worldwide recession.
D)A term used by Communist leaders to describe the socialist accomplishments of their societies, such as nationalized industry, collective agriculture, and extensive social welfare programs.
E)Philosophy of 1980s conservatives who argued for decreased government spending on social services and privatization of state-run industries.
F)The term given to the relatively peaceful overthrow of communism in Czechoslovakia; the label came to signify the collapse of the East Bloc in general in 1989 to 1990.
G)The progressive relaxation of Cold War tensions that emerged in the early 1970s.
H)Independent Polish trade union that worked for workers' rights and political reform throughout the 1980s.
I)A 1960s counterculture movement that embraced updated forms of Marxism to challenge both Western capitalism and Soviet-style communism.
J)Economic restructuring and reform implemented by Premier Mikhail Gorbachev in the Soviet Union in 1985.
K)Soviet premier Mikhail Gorbachev's popular campaign for openness in government and the media.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Answer the following questions:
stagflation
A)Doctrine that held that the Soviet Union had the right to intervene in any East Bloc country whenever it saw the need.
B)Society that relies on high-tech and service-oriented jobs for economic growth rather than heavy industry and manufacturing jobs.
C)Term coined in the early 1980s to describe the combination of low growth and high inflation that led to a worldwide recession.
D)A term used by Communist leaders to describe the socialist accomplishments of their societies, such as nationalized industry, collective agriculture, and extensive social welfare programs.
E)Philosophy of 1980s conservatives who argued for decreased government spending on social services and privatization of state-run industries.
F)The term given to the relatively peaceful overthrow of communism in Czechoslovakia; the label came to signify the collapse of the East Bloc in general in 1989 to 1990.
G)The progressive relaxation of Cold War tensions that emerged in the early 1970s.
H)Independent Polish trade union that worked for workers' rights and political reform throughout the 1980s.
I)A 1960s counterculture movement that embraced updated forms of Marxism to challenge both Western capitalism and Soviet-style communism.
J)Economic restructuring and reform implemented by Premier Mikhail Gorbachev in the Soviet Union in 1985.
K)Soviet premier Mikhail Gorbachev's popular campaign for openness in government and the media.
stagflation
A)Doctrine that held that the Soviet Union had the right to intervene in any East Bloc country whenever it saw the need.
B)Society that relies on high-tech and service-oriented jobs for economic growth rather than heavy industry and manufacturing jobs.
C)Term coined in the early 1980s to describe the combination of low growth and high inflation that led to a worldwide recession.
D)A term used by Communist leaders to describe the socialist accomplishments of their societies, such as nationalized industry, collective agriculture, and extensive social welfare programs.
E)Philosophy of 1980s conservatives who argued for decreased government spending on social services and privatization of state-run industries.
F)The term given to the relatively peaceful overthrow of communism in Czechoslovakia; the label came to signify the collapse of the East Bloc in general in 1989 to 1990.
G)The progressive relaxation of Cold War tensions that emerged in the early 1970s.
H)Independent Polish trade union that worked for workers' rights and political reform throughout the 1980s.
I)A 1960s counterculture movement that embraced updated forms of Marxism to challenge both Western capitalism and Soviet-style communism.
J)Economic restructuring and reform implemented by Premier Mikhail Gorbachev in the Soviet Union in 1985.
K)Soviet premier Mikhail Gorbachev's popular campaign for openness in government and the media.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
From the early 1970s well into the 1980s, North American and western European economies stagnated. Explain the causes of this stagnation and discuss its consequences for politics in the West.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Answer the following questions:
glasnost
A)Doctrine that held that the Soviet Union had the right to intervene in any East Bloc country whenever it saw the need.
B)Society that relies on high-tech and service-oriented jobs for economic growth rather than heavy industry and manufacturing jobs.
C)Term coined in the early 1980s to describe the combination of low growth and high inflation that led to a worldwide recession.
D)A term used by Communist leaders to describe the socialist accomplishments of their societies, such as nationalized industry, collective agriculture, and extensive social welfare programs.
E)Philosophy of 1980s conservatives who argued for decreased government spending on social services and privatization of state-run industries.
F)The term given to the relatively peaceful overthrow of communism in Czechoslovakia; the label came to signify the collapse of the East Bloc in general in 1989 to 1990.
G)The progressive relaxation of Cold War tensions that emerged in the early 1970s.
H)Independent Polish trade union that worked for workers' rights and political reform throughout the 1980s.
I)A 1960s counterculture movement that embraced updated forms of Marxism to challenge both Western capitalism and Soviet-style communism.
J)Economic restructuring and reform implemented by Premier Mikhail Gorbachev in the Soviet Union in 1985.
K)Soviet premier Mikhail Gorbachev's popular campaign for openness in government and the media.
glasnost
A)Doctrine that held that the Soviet Union had the right to intervene in any East Bloc country whenever it saw the need.
B)Society that relies on high-tech and service-oriented jobs for economic growth rather than heavy industry and manufacturing jobs.
C)Term coined in the early 1980s to describe the combination of low growth and high inflation that led to a worldwide recession.
D)A term used by Communist leaders to describe the socialist accomplishments of their societies, such as nationalized industry, collective agriculture, and extensive social welfare programs.
E)Philosophy of 1980s conservatives who argued for decreased government spending on social services and privatization of state-run industries.
F)The term given to the relatively peaceful overthrow of communism in Czechoslovakia; the label came to signify the collapse of the East Bloc in general in 1989 to 1990.
G)The progressive relaxation of Cold War tensions that emerged in the early 1970s.
H)Independent Polish trade union that worked for workers' rights and political reform throughout the 1980s.
I)A 1960s counterculture movement that embraced updated forms of Marxism to challenge both Western capitalism and Soviet-style communism.
J)Economic restructuring and reform implemented by Premier Mikhail Gorbachev in the Soviet Union in 1985.
K)Soviet premier Mikhail Gorbachev's popular campaign for openness in government and the media.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Historians use the term détente to describe relations between the Soviet bloc and the Western democracies in the 1970s. How did the policy evolve? What were the key elements of this diplomatic change? What were the limits of détente? What impact did détente have on the subsequent end of the Cold War?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Answer the following questions:
Brezhnev Doctrine
A)Doctrine that held that the Soviet Union had the right to intervene in any East Bloc country whenever it saw the need.
B)Society that relies on high-tech and service-oriented jobs for economic growth rather than heavy industry and manufacturing jobs.
C)Term coined in the early 1980s to describe the combination of low growth and high inflation that led to a worldwide recession.
D)A term used by Communist leaders to describe the socialist accomplishments of their societies, such as nationalized industry, collective agriculture, and extensive social welfare programs.
E)Philosophy of 1980s conservatives who argued for decreased government spending on social services and privatization of state-run industries.
F)The term given to the relatively peaceful overthrow of communism in Czechoslovakia; the label came to signify the collapse of the East Bloc in general in 1989 to 1990.
G)The progressive relaxation of Cold War tensions that emerged in the early 1970s.
H)Independent Polish trade union that worked for workers' rights and political reform throughout the 1980s.
I)A 1960s counterculture movement that embraced updated forms of Marxism to challenge both Western capitalism and Soviet-style communism.
J)Economic restructuring and reform implemented by Premier Mikhail Gorbachev in the Soviet Union in 1985.
K)Soviet premier Mikhail Gorbachev's popular campaign for openness in government and the media.
Brezhnev Doctrine
A)Doctrine that held that the Soviet Union had the right to intervene in any East Bloc country whenever it saw the need.
B)Society that relies on high-tech and service-oriented jobs for economic growth rather than heavy industry and manufacturing jobs.
C)Term coined in the early 1980s to describe the combination of low growth and high inflation that led to a worldwide recession.
D)A term used by Communist leaders to describe the socialist accomplishments of their societies, such as nationalized industry, collective agriculture, and extensive social welfare programs.
E)Philosophy of 1980s conservatives who argued for decreased government spending on social services and privatization of state-run industries.
F)The term given to the relatively peaceful overthrow of communism in Czechoslovakia; the label came to signify the collapse of the East Bloc in general in 1989 to 1990.
G)The progressive relaxation of Cold War tensions that emerged in the early 1970s.
H)Independent Polish trade union that worked for workers' rights and political reform throughout the 1980s.
I)A 1960s counterculture movement that embraced updated forms of Marxism to challenge both Western capitalism and Soviet-style communism.
J)Economic restructuring and reform implemented by Premier Mikhail Gorbachev in the Soviet Union in 1985.
K)Soviet premier Mikhail Gorbachev's popular campaign for openness in government and the media.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Answer the following questions:
developed socialism
A)Doctrine that held that the Soviet Union had the right to intervene in any East Bloc country whenever it saw the need.
B)Society that relies on high-tech and service-oriented jobs for economic growth rather than heavy industry and manufacturing jobs.
C)Term coined in the early 1980s to describe the combination of low growth and high inflation that led to a worldwide recession.
D)A term used by Communist leaders to describe the socialist accomplishments of their societies, such as nationalized industry, collective agriculture, and extensive social welfare programs.
E)Philosophy of 1980s conservatives who argued for decreased government spending on social services and privatization of state-run industries.
F)The term given to the relatively peaceful overthrow of communism in Czechoslovakia; the label came to signify the collapse of the East Bloc in general in 1989 to 1990.
G)The progressive relaxation of Cold War tensions that emerged in the early 1970s.
H)Independent Polish trade union that worked for workers' rights and political reform throughout the 1980s.
I)A 1960s counterculture movement that embraced updated forms of Marxism to challenge both Western capitalism and Soviet-style communism.
J)Economic restructuring and reform implemented by Premier Mikhail Gorbachev in the Soviet Union in 1985.
K)Soviet premier Mikhail Gorbachev's popular campaign for openness in government and the media.
developed socialism
A)Doctrine that held that the Soviet Union had the right to intervene in any East Bloc country whenever it saw the need.
B)Society that relies on high-tech and service-oriented jobs for economic growth rather than heavy industry and manufacturing jobs.
C)Term coined in the early 1980s to describe the combination of low growth and high inflation that led to a worldwide recession.
D)A term used by Communist leaders to describe the socialist accomplishments of their societies, such as nationalized industry, collective agriculture, and extensive social welfare programs.
E)Philosophy of 1980s conservatives who argued for decreased government spending on social services and privatization of state-run industries.
F)The term given to the relatively peaceful overthrow of communism in Czechoslovakia; the label came to signify the collapse of the East Bloc in general in 1989 to 1990.
G)The progressive relaxation of Cold War tensions that emerged in the early 1970s.
H)Independent Polish trade union that worked for workers' rights and political reform throughout the 1980s.
I)A 1960s counterculture movement that embraced updated forms of Marxism to challenge both Western capitalism and Soviet-style communism.
J)Economic restructuring and reform implemented by Premier Mikhail Gorbachev in the Soviet Union in 1985.
K)Soviet premier Mikhail Gorbachev's popular campaign for openness in government and the media.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



