Deck 7: Sources of the Magnetic Field
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/115
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 7: Sources of the Magnetic Field
1
A particle with charge q = 5 C is moving with velocity 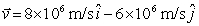 . At t = 0, it is located at the origin. The magnetic field at
. At t = 0, it is located at the origin. The magnetic field at 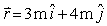 at t = 0 is
at t = 0 is
A)
B)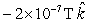
C)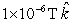
D)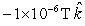
E) None of these is correct.
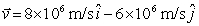 . At t = 0, it is located at the origin. The magnetic field at
. At t = 0, it is located at the origin. The magnetic field at 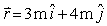 at t = 0 is
at t = 0 isA)

B)
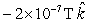
C)
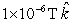
D)
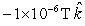
E) None of these is correct.

2
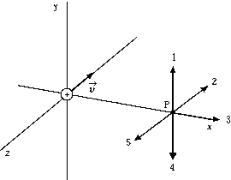
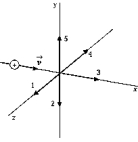 A positively charged body is moving in the positive x direction as shown. The direction of the magnetic field at the origin due to the motion of this charged body is
A positively charged body is moving in the positive x direction as shown. The direction of the magnetic field at the origin due to the motion of this charged body isA) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) None of these is correct, as this charged body does not create a magnetic field along the axis of its motion.
4
3
The magnitude of the magnetic field due to the presence of a charged body
A) varies directly with the speed of the body.
B) varies directly with the charge carried by the body.
C) varies inversely with the square of the distance between the charged body and the field point.
D) depends on the magnetic properties of the space between the charged body and the field point.
E) is described by all of these.
A) varies directly with the speed of the body.
B) varies directly with the charge carried by the body.
C) varies inversely with the square of the distance between the charged body and the field point.
D) depends on the magnetic properties of the space between the charged body and the field point.
E) is described by all of these.
is described by all of these.
4
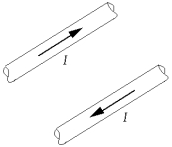 Two wires lying in the plane of this page carry equal currents in opposite directions, as shown. At a point midway between the wires, the magnetic field is
Two wires lying in the plane of this page carry equal currents in opposite directions, as shown. At a point midway between the wires, the magnetic field isA) zero.
B) into the page.
C) out of the page.
D) toward the top or bottom of the page.
E) toward one of the two wires.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A point charge is moving with speed 2 *107 m/s along the x axis. At t = 0, the charge is at x = 0 m and the magnitude of the magnetic field at x = 4 m is B0. The magnitude of the magnetic field at x = 4m when t = 0.1 s is
A) B0/2
B) B0
C) B0/4
D) 2B0
E) 4B0
A) B0/2
B) B0
C) B0/4
D) 2B0
E) 4B0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
 A positively charged body is moving in the negative z direction as shown. The direction of the magnetic field due to the motion of this charged body at point P is
A positively charged body is moving in the negative z direction as shown. The direction of the magnetic field due to the motion of this charged body at point P isA) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The top diagram shows the velocity of a positively charged particle. The direction of the magnetic field due to the moving charge at r is best represented by 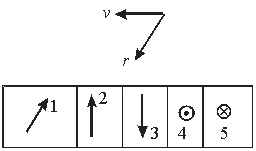
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5

A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
At a certain instant of time a particle with charge q = 25 C is located at x = 4.0 m, y = 2.0 m; its velocity at that time is v = -20 m/s 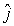 . If you are at the origin, what do you measure as the magnitude of the magnetic field due to this moving point charge?
. If you are at the origin, what do you measure as the magnitude of the magnetic field due to this moving point charge?
A) 6.8 pT
B) 1.1 pT
C) 5.6 pT
D) 2.2 pT
E) 4.4 pT
 . If you are at the origin, what do you measure as the magnitude of the magnetic field due to this moving point charge?
. If you are at the origin, what do you measure as the magnitude of the magnetic field due to this moving point charge?A) 6.8 pT
B) 1.1 pT
C) 5.6 pT
D) 2.2 pT
E) 4.4 pT

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
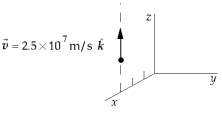 A point charge of q1 = 5.8 nC is moving with speed 2.5 * 107 m/s parallel to the z axis along the line x = 3 m. The magnetic field produced by this charge at the origin when it is at the point x = 3 m, z = 4 m is approximately
A point charge of q1 = 5.8 nC is moving with speed 2.5 * 107 m/s parallel to the z axis along the line x = 3 m. The magnetic field produced by this charge at the origin when it is at the point x = 3 m, z = 4 m is approximatelyA) 0.70 nT
B) -0.70 nT
C) 3.2 nT
D) -1.6 nT
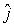
E) -0.35 nT

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
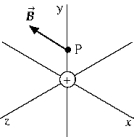 At the instant the positively charged body is at the origin, the magnetic field at point P due to the motion of this charged body is in the negative x direction. The charged body must be moving
At the instant the positively charged body is at the origin, the magnetic field at point P due to the motion of this charged body is in the negative x direction. The charged body must be movingA) in the negative z direction.
B) in the positive y direction.
C) in the positive x direction.
D) in the negative y direction.
E) in the positive z direction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
In a simple picture of the hydrogen atom, the electron moves in circular orbits around the central proton attracted by the Coulomb force. The lowest (n = 1) energy orbit that is allowed for the electron is at a radius of 5.29*10-11 m and the second (n = 2) lowest allowed orbit is at 4 times this radius. Calculate the magnetic field strength at the proton due to the orbital motion of the electron in the n = 2 state.
A) 0 T
B) 6.3 T
C) 0.39 T
D) 12.5 T
E) None of the above
A) 0 T
B) 6.3 T
C) 0.39 T
D) 12.5 T
E) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The Biot-Savart law is similar to Coulomb's law in that both
A) are inverse square laws.
B) include the permeability of free space.
C) deal with excess charges.
D) are not electrical in nature.
E) are described by none of the above.
A) are inverse square laws.
B) include the permeability of free space.
C) deal with excess charges.
D) are not electrical in nature.
E) are described by none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The magnetic field due to the presence of a charged body
A) depends on whether the charged body is moving.
B) depends on the direction the charged body is moving in relationship to the location of the field point.
C) varies inversely with the square of the distance between the charged body and the field point.
D) depends on the magnetic properties of the space between the charged body and the field point.
E) is described by all of these.
A) depends on whether the charged body is moving.
B) depends on the direction the charged body is moving in relationship to the location of the field point.
C) varies inversely with the square of the distance between the charged body and the field point.
D) depends on the magnetic properties of the space between the charged body and the field point.
E) is described by all of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
In a simple picture of the hydrogen atom, the electron moves in circular orbits around the central proton attracted by the Coulomb force. The lowest (n = 1) energy orbit that is allowed for the electron is at a radius of 5.29 *10-11 m and the second (n = 2) lowest allowed orbit is at 4 times this radius. How many times stronger is the magnetic field strength at the proton due to the orbital motion of the electron in the n = 1 state than the n = 2 state?
A) 64
B) 16
C) 4
D) 1
E) 32
A) 64
B) 16
C) 4
D) 1
E) 32

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
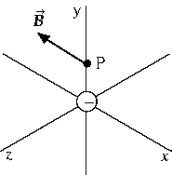 At the instant the negatively charged body is at the origin, the magnetic field at point P due to its motion is in the negative x direction. The charged body must be moving
At the instant the negatively charged body is at the origin, the magnetic field at point P due to its motion is in the negative x direction. The charged body must be movingA) in the negative z direction.
B) in the positive y direction.
C) in the positive x direction.
D) in the negative y direction.
E) in the positive z direction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A wire carries an electric current straight upward. What is the direction of the magnetic field due to the current north of the wire?
A) north
B) east
C) west
D) south
E) upward
A) north
B) east
C) west
D) south
E) upward

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
What is the direction of the magnetic field around a wire carrying a current perpendicularly into this page?
A) The field is parallel to and in the same direction as the current flow.
B) It is parallel to but directed opposite to the current flow.
C) It is counterclockwise around the wire in the plane of the page.
D) It is clockwise around the wire in the plane of the page.
E) None of these is correct.
A) The field is parallel to and in the same direction as the current flow.
B) It is parallel to but directed opposite to the current flow.
C) It is counterclockwise around the wire in the plane of the page.
D) It is clockwise around the wire in the plane of the page.
E) None of these is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
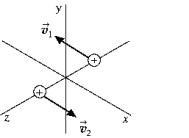 Two positively charged bodies are moving in opposite directions on parallel paths that lie in the xz plane. Their speeds are equal and their trajectories are equidistant from the x axis. The magnetic field at the origin, due to the motion of these charged bodies will be
Two positively charged bodies are moving in opposite directions on parallel paths that lie in the xz plane. Their speeds are equal and their trajectories are equidistant from the x axis. The magnetic field at the origin, due to the motion of these charged bodies will beA) in the x direction.
B) in the y direction.
C) in all directions.
D) in the z direction.
E) zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
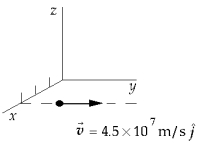 A point charge of q1 = 3.6 nC is moving with speed 4.5 * 107 m/s parallel to the y axis along the line x = 3 m. The magnetic field produced by this charge at the origin when it is at the point x = 3 m, y = 4 m is approximately
A point charge of q1 = 3.6 nC is moving with speed 4.5 * 107 m/s parallel to the y axis along the line x = 3 m. The magnetic field produced by this charge at the origin when it is at the point x = 3 m, y = 4 m is approximatelyA) 0.39 nT
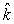
B) -0.78 nT
C) -0.39 nT
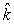
D) 0.78 nT
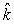
E) 2.0 nT

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
At a certain instant of time a particle with charge q = 15 C is located at x = 2.0 m, y = 5.0 m; its velocity at that time is v = 40 m/s 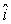 . If you are at the origin, what do you measure as the magnitude of the magnetic field due to this moving point charge?
. If you are at the origin, what do you measure as the magnitude of the magnetic field due to this moving point charge?
A) 1.9 pT
B) 3.8 pT
C) 2.7 pT
D) 4.1 pT
E) 5.9 pT
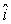 . If you are at the origin, what do you measure as the magnitude of the magnetic field due to this moving point charge?
. If you are at the origin, what do you measure as the magnitude of the magnetic field due to this moving point charge?A) 1.9 pT
B) 3.8 pT
C) 2.7 pT
D) 4.1 pT
E) 5.9 pT

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
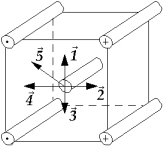 Four wires carry equal currents along the four parallel edges of a cube. A parallel current-carrying wire through the center of the cube is free to move. The vector that might represent the direction in which the center wire will move is
Four wires carry equal currents along the four parallel edges of a cube. A parallel current-carrying wire through the center of the cube is free to move. The vector that might represent the direction in which the center wire will move isA)
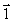
B)
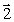
C)
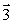
D)
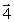
E)
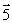

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The magnetic field at a distance of 50 cm from a long, straight wire carrying a current of 5.0 A is approximately
A) 10 T
B) 50 T
C) 5.0 T
D) 32 T
E) 2.0 T
A) 10 T
B) 50 T
C) 5.0 T
D) 32 T
E) 2.0 T

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
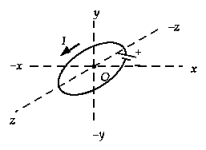 The sketch shows a circular coil in the xz plane carrying a current I. The direction of the magnetic field at point O is
The sketch shows a circular coil in the xz plane carrying a current I. The direction of the magnetic field at point O isA) x
B) -x
C) y
D) -y
E) -z

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
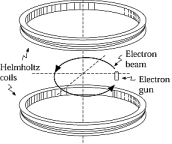
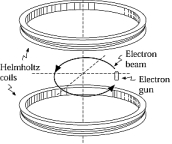 An electron beam travels counterclockwise in a circle in the magnetic field produced by the Helmholtz coils, as shown. Assuming that Earth's field is downward, one can conclude that
An electron beam travels counterclockwise in a circle in the magnetic field produced by the Helmholtz coils, as shown. Assuming that Earth's field is downward, one can conclude thatA) the Helmholtz field equals Earth's field.
B) the current in the coils moves in the same direction as the electron beam.
C) the current in the coils moves in the direction opposite to the electron beam.
D) the Helmholtz field curves in the direction of the electron beam.
E) the Helmholtz field curves in a direction opposite to the electron beam.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
At great axial distances x from a current-carrying loop the magnetic field varies as
A) x2
B) x-3
C) x-2
D) x3
E) x-1
A) x2
B) x-3
C) x-2
D) x3
E) x-1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
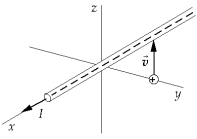 The current in a wire along the x axis flows in the positive x direction. If a proton, located as shown in the figure, has an initial velocity in the positive z direction, it experiences
The current in a wire along the x axis flows in the positive x direction. If a proton, located as shown in the figure, has an initial velocity in the positive z direction, it experiencesA) a force in the direction of positive x.
B) a force in the direction of negative x.
C) a force in the direction of positive z.
D) a force in the direction of positive y.
E) no force.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A circular loop of wire 10 cm in radius carries a current of 20 A. The axial magnetic field 15 cm from the center of the loop is approximately
A) 37 T
B) 13 T
C) 21 T
D) 41 T
E) 18 T
A) 37 T
B) 13 T
C) 21 T
D) 41 T
E) 18 T

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
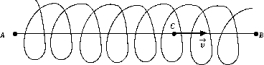 A solenoid carries a current I. An electron is injected with velocity
A solenoid carries a current I. An electron is injected with velocity 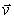 along the axis AB of the solenoid. When the electron is at C, it experiences a force that is
along the axis AB of the solenoid. When the electron is at C, it experiences a force that isA) zero.
B) not zero and along AB.
C) not zero and along BA.
D) not zero and perpendicular to the page.
E) None of these is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
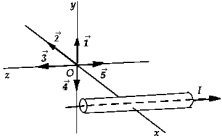 A long conductor carrying current I lies in the xz plane parallel to the z axis. The current travels in the negative z direction, as shown in the figure. The vector that represents the magnetic field at the origin O is
A long conductor carrying current I lies in the xz plane parallel to the z axis. The current travels in the negative z direction, as shown in the figure. The vector that represents the magnetic field at the origin O isA)
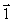
B)
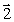
C)
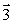
D)
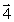
E)
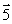

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
When the positive current in a long wire is flowing in a direction from S to N, it creates a magnetic field below the wire that is directed
A) from E to W.
B) from N to S.
C) from NE to SW.
D) from S to N.
E) from W to E.
A) from E to W.
B) from N to S.
C) from NE to SW.
D) from S to N.
E) from W to E.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
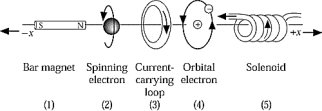 Each of the figures shown is the source of a magnetic field. In which figure does the magnetic dipole vector (
Each of the figures shown is the source of a magnetic field. In which figure does the magnetic dipole vector ( 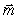 ) point in the direction of the negative x axis?
) point in the direction of the negative x axis?A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
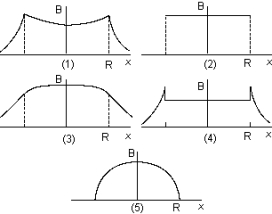 The graph that best represents the magnetic field B between the coils of radius R of a Helmholtz pair as a function of distance along the axis of the pair is
The graph that best represents the magnetic field B between the coils of radius R of a Helmholtz pair as a function of distance along the axis of the pair isA) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
In a circular loop of wire lying on a horizontal floor, the current is constant and, to a person looking downward, has a clockwise direction. The accompanying magnetic field at the center of the circle is directed
A) horizontally and to the east.
B) horizontally and to the north.
C) vertically upward.
D) parallel to the floor.
E) vertically downward.
A) horizontally and to the east.
B) horizontally and to the north.
C) vertically upward.
D) parallel to the floor.
E) vertically downward.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
 An electron beam travels counterclockwise in a circle of radius R in the magnetic field produced by the Helmholtz coils as shown. If you increase the current in the Helmholtz coils, the electron beam will
An electron beam travels counterclockwise in a circle of radius R in the magnetic field produced by the Helmholtz coils as shown. If you increase the current in the Helmholtz coils, the electron beam willA) increase its radius.
B) decrease its radius.
C) maintain the same radius.
D) reverse and travel clockwise with the same radius.
E) reverse and travel clockwise with a larger radius.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
What is the magnetic field at the center of a circular loop with a diameter of 15.0 cm that carries a current of 1.50 A?
A) zero
B) 6.28 *10-6 T
C) 1.26 * 10-5 T
D) 2.51* 10-5 T
E) 1.68* 10-4 T
A) zero
B) 6.28 *10-6 T
C) 1.26 * 10-5 T
D) 2.51* 10-5 T
E) 1.68* 10-4 T

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
A circular loop of wire of radius 6.0 cm has 30 turns and lies in the xy plane. It carries a current of 5 A in such a direction that the magnetic moment of the loop is along the x axis. The magnetic field on the x axis at x = 6.0 cm is approximately
A) 19 T
B) 0.56 mT
C) 0.11 mT
D) 47 T
E) 0.88 mT
A) 19 T
B) 0.56 mT
C) 0.11 mT
D) 47 T
E) 0.88 mT

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
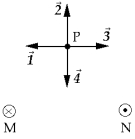 Two straight wires perpendicular to the plane of this page are shown in the figure. The currents in the wires are the same. The current in M is into the page and the current in N is out of the page. The vector that represents the resultant magnetic field at point P is
Two straight wires perpendicular to the plane of this page are shown in the figure. The currents in the wires are the same. The current in M is into the page and the current in N is out of the page. The vector that represents the resultant magnetic field at point P isA)
B)
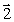
C)
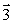
D)
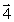
E) None of these is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Two current-carrying wires are perpendicular to each other. The current in one flows vertically upward and the current in the other flows horizontally toward the east. The horizontal wire is 1 m south of the vertical wire. What is the direction of the net magnetic force on the horizontal wire?
A) north
B) east
C) west
D) south
E) There is no net magnetic force on the horizontal wire.
A) north
B) east
C) west
D) south
E) There is no net magnetic force on the horizontal wire.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
A 1000-turn solenoid is 50 cm long and has a radius of 2.0 cm. It carries a current of 8.0 A. What is the magnetic field inside the solenoid near its center?
A) 2.0 * 10-2 T
B) 3.2 * 10-3 T
C) 4.0 * 10-4 T
D) 1.0 T
E) 2.0 * 10-4 T
A) 2.0 * 10-2 T
B) 3.2 * 10-3 T
C) 4.0 * 10-4 T
D) 1.0 T
E) 2.0 * 10-4 T

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
A circular loop of wire 1.0 cm in radius carries a current of 30 A. The magnetic field at the center of the loop is
A) 1.9 mT
B) 2.4 mT
C) 3.8 mT
D) 12 T
E) 48 T
A) 1.9 mT
B) 2.4 mT
C) 3.8 mT
D) 12 T
E) 48 T

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
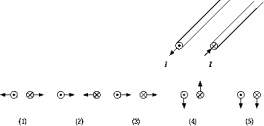 Two very long, parallel conducting wires carry equal currents in opposite directions. The numbered diagrams show end views of the wires and the resultant force vectors due to current flow in each wire. Which diagram best represents the direction of the forces?
Two very long, parallel conducting wires carry equal currents in opposite directions. The numbered diagrams show end views of the wires and the resultant force vectors due to current flow in each wire. Which diagram best represents the direction of the forces?A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Two straight rods 60 cm long and 2.0 mm apart in a current balance carry currents of 18 A each in opposite directions. What mass must be placed on the upper rod to balance the magnetic force of repulsion?
A) 0.50 g
B) 0.99 g
C) 9.7 g
D) 4.3 g
E) 1.6 g
A) 0.50 g
B) 0.99 g
C) 9.7 g
D) 4.3 g
E) 1.6 g

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
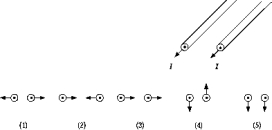 Two very long, parallel conducting wires carry equal currents in the same direction, as shown. The numbered diagrams show end views of the wires and the resultant force vectors due to current flow in each wire. Which diagram best represents the direction of the forces?
Two very long, parallel conducting wires carry equal currents in the same direction, as shown. The numbered diagrams show end views of the wires and the resultant force vectors due to current flow in each wire. Which diagram best represents the direction of the forces?A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The force per unit length between two current-carrying wires is expressed as
F/l = ( 0/2 d)I2
Where I is the current, d the separation of the wires, and l the length of each wire. A plot of force per unit length versus I2 gives a straight line, the slope of which is
A) 0
B) F/l
C) (2 d/ 0)1/2
D) 0/2 d
E) FI2/l
F/l = ( 0/2 d)I2
Where I is the current, d the separation of the wires, and l the length of each wire. A plot of force per unit length versus I2 gives a straight line, the slope of which is
A) 0
B) F/l
C) (2 d/ 0)1/2
D) 0/2 d
E) FI2/l

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Two long, straight parallel wires 9.3 cm apart carry currents of equal magnitude I. They repel each other with a force per unit length of 5.8 nN/m. The current I is approximately
A) 27 mA
B) 65 mA
C) 43 mA
D) 52 mA
E) 2.7 mA
A) 27 mA
B) 65 mA
C) 43 mA
D) 52 mA
E) 2.7 mA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
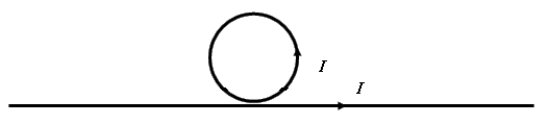 Calculate the magnetic field at the center of a circular current loop of radius R divided by the magnetic field at a distance R away from a very long straight wire carrying the same current value I. (Note the loop and wire are not in electrical contact.)
Calculate the magnetic field at the center of a circular current loop of radius R divided by the magnetic field at a distance R away from a very long straight wire carrying the same current value I. (Note the loop and wire are not in electrical contact.)A) 3.14
B) 1.00
C) 2.00
D) 0.318
E) 0.500

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Calculate the magnetic field at the center of a circular current loop of area 0.200 m2 divided by the magnetic field at the center of a square current loop of the same inside area for the same current I value.
A) 1.00
B) 1.02
C) 0.246
D) 0.985
E) 0.785
A) 1.00
B) 1.02
C) 0.246
D) 0.985
E) 0.785

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
If the magnetic field at the center of a square current loop of side L = 40 cm is
2)4 *10-6 T calculate the current flowing around the loop.
A) 11 A
B) 3.4 A
C) 0.85 A
D) 0.21 A
E) 1.7 A
2)4 *10-6 T calculate the current flowing around the loop.
A) 11 A
B) 3.4 A
C) 0.85 A
D) 0.21 A
E) 1.7 A

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
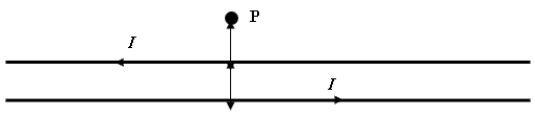 Calculate the magnetic field and its direction at point P, which is 2.0 cm away from the top wire and 4.0 cm from the bottom wire. Assume both wires are infinitely long and each carries a current of 1.5 A.
Calculate the magnetic field and its direction at point P, which is 2.0 cm away from the top wire and 4.0 cm from the bottom wire. Assume both wires are infinitely long and each carries a current of 1.5 A.A) 2.3 *10-5 T directed OUT of the page
B) 7.5 *10-6 T directed INTO the page
C) 2.3 *10-5 T directed INTO the page
D) 7.5 * 10-6 T directed OUT of the page
E) 1.1 * 10-5 T directed OUT of the page

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Use the following to answer the next question: 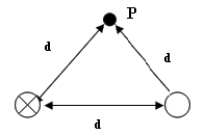
-Two long parallel wires are a distance d apart (d = 6 cm) and carry equal and opposite currents of 5 A. Point P is distance d from each of the wires. Calculate the magnitude of the magnetic field strength at point P.
A) 2.9 * 10-5 T
B) 8.5*10-6 T
C) 3.3 *10-5 T
D) 1.7* 10-5 T
E) none of the above

-Two long parallel wires are a distance d apart (d = 6 cm) and carry equal and opposite currents of 5 A. Point P is distance d from each of the wires. Calculate the magnitude of the magnetic field strength at point P.
A) 2.9 * 10-5 T
B) 8.5*10-6 T
C) 3.3 *10-5 T
D) 1.7* 10-5 T
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The two wires in a DC adapter cable are 5 mm apart and carry a current of 4 A. If the cable is 1.5 m long, calculate the force between the wires and state if this force is attractive or not.
A) 9.6 *10-4 N, attractive
B) 9.6 * 10-7 N, attractive
C) 1.1 * 10-8 N, attractive
D) 9.6 *10-4 N, repulsive
E) 1.1 *10-8 N, repulsive
A) 9.6 *10-4 N, attractive
B) 9.6 * 10-7 N, attractive
C) 1.1 * 10-8 N, attractive
D) 9.6 *10-4 N, repulsive
E) 1.1 *10-8 N, repulsive

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Two long, parallel wires are spaced 1 m apart in air, and you have established a current of 1 A in each. The force per unit length that each wire exerts on the other is
A) 4 0
B) 2 0
C) 0
D) 0/4
E) 0/2
A) 4 0
B) 2 0
C) 0
D) 0/4
E) 0/2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Two long, straight parallel wires 7.6 cm apart carry currents of equal magnitude I. They attract each other with a force per unit length of 4.3 nN/m. The current I is approximately
A) 1.6 mA
B) 40 mA
C) 37 mA
D) 59 mA
E) 4.0 mA
A) 1.6 mA
B) 40 mA
C) 37 mA
D) 59 mA
E) 4.0 mA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
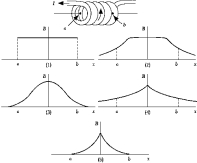 The graph that best represents the magnetic field on the axis inside a solenoid as a function of position x on the axis is
The graph that best represents the magnetic field on the axis inside a solenoid as a function of position x on the axis isA) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
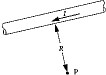 The magnetic field at point P, due to the current in the very long wire, varies with distance R according to
The magnetic field at point P, due to the current in the very long wire, varies with distance R according toA) R2
B) R-3
C) R-2
D) R3
E) R-1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
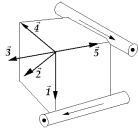 Current-carrying wires are located along two edges of a cube with the directions of the currents as indicated. The vector that indicates the resultant magnetic field at the corner of the cube is
Current-carrying wires are located along two edges of a cube with the directions of the currents as indicated. The vector that indicates the resultant magnetic field at the corner of the cube isA)
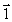
B)
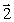
C)
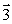
D)
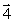
E)
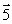

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Two straight rods 55 cm long and 1.4 mm apart in a current balance carry current I, each in opposite directions. If a mass of 1.3 g when placed on the upper rod balances the magnetic force of repulsion between the rods, then calculate the current I.
A) 160 A
B) 18 A
C) 13 A
D) 3.6 A
E) 9.0 A
A) 160 A
B) 18 A
C) 13 A
D) 3.6 A
E) 9.0 A

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Two long, parallel wires are spaced 1 m apart in air, and you have established a current of 1 A in each. The force per unit length that each wire exerts on the other is approximately
A) 2 * 10-6 N/m
B) 2 * 10-5 N/m
C) 2 * 10-7 N/m
D) 2 * 10-5 N/m
E) 2 * 10-6 N/m
A) 2 * 10-6 N/m
B) 2 * 10-5 N/m
C) 2 * 10-7 N/m
D) 2 * 10-5 N/m
E) 2 * 10-6 N/m

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Two parallel wires carry currents I1 and I2 = 2I1 in the same direction. Which of the following expressions shows the relationship of the forces on the wires?
A) F1 = F2
B) F1 = 2F2
C) 2F1 = F2
D) F1 = 4F2
E) 4F1 = F2
A) F1 = F2
B) F1 = 2F2
C) 2F1 = F2
D) F1 = 4F2
E) 4F1 = F2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Use the following to answer the next question: 
Two long parallel wires are a distance d apart and carry equal and opposite currents. Point P is distance d from each of the wires. Which diagram best represents the direction of the magnetic field at point P?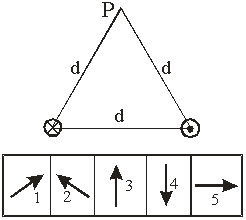
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5

Two long parallel wires are a distance d apart and carry equal and opposite currents. Point P is distance d from each of the wires. Which diagram best represents the direction of the magnetic field at point P?

A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
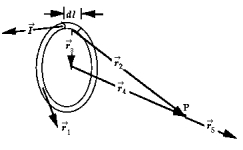 If the Biot-Savart relationship d
If the Biot-Savart relationship d  = ( 0/4 )(
= ( 0/4 )(  *
* 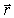 d
d 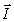 )/r3
)/r3Is used to determine the magnetic field at the point P on the axis of a circular current-carrying loop, the vector
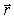 is correctly represented by
is correctly represented byA)
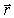 1
1 B)
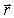 2
2 C)
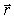 3
3 D)
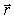 4
4 E)
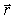 5
5 
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
A long straight wire of radius R carries a current density J = kr A/m2 where k is a constant. The magnetic field for r < R is (Hint: Current enclosed 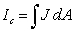 .)
.)
A) 0kr2/2
B) 0kr2/3
C) 2 0kr
D) 2 0kr/2
E) none of the above
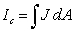 .)
.)A) 0kr2/2
B) 0kr2/3
C) 2 0kr
D) 2 0kr/2
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
A coaxial cable consists of a solid inner cylindrical conductor of radius 2 mm and an outer cylindrical shell of inner radius 3 mm and outer radius 3.5 mm. A current of 15 A flows down the inner wire and an equal return current flows in the outer conductor. If we assume that the currents are uniform over the cross section of the conductors, then calculate the magnitude of the enclosed current for use in Ampere's Law at a radius of 3.25 mm.
A) 7.2 A
B) 3.8 A
C) 7.8 A
D) 11.2 A
E) 7.5 A
A) 7.2 A
B) 3.8 A
C) 7.8 A
D) 11.2 A
E) 7.5 A

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
A wire of radius 0.35 cm carries a current of 75 A that is uniformly distributed over its cross-sectional area. The magnetic field 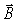 at the surface of the wire is approximately
at the surface of the wire is approximately
A) 8.4 mT
B) 4.3 mT
C) 6.7 mT
D) 2.3 mT
E) 5.7 mT
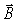 at the surface of the wire is approximately
at the surface of the wire is approximatelyA) 8.4 mT
B) 4.3 mT
C) 6.7 mT
D) 2.3 mT
E) 5.7 mT

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Use the following to answer the next question: 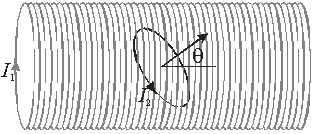
-A coil of radius R = 5 cm lies inside a long solenoid which carries a current I1 = 10 A and has 800 turns/m. The coil carries a current I2 = 4 A and the normal of the plane of the coil is at an angle = 30 with the axis of the solenoid. The magnitude of the torque on the coil is
A) 1.56 * 10-4 N . m
B) 2.74 * 10-4 N . m
C) 5.03 * 10-5 N . m
D) 3.16 * 10-4 N . m
E) none of the above

-A coil of radius R = 5 cm lies inside a long solenoid which carries a current I1 = 10 A and has 800 turns/m. The coil carries a current I2 = 4 A and the normal of the plane of the coil is at an angle = 30 with the axis of the solenoid. The magnitude of the torque on the coil is
A) 1.56 * 10-4 N . m
B) 2.74 * 10-4 N . m
C) 5.03 * 10-5 N . m
D) 3.16 * 10-4 N . m
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
A wire of radius 0.6 cm carries a current of 10 A that is uniformly distributed over its cross section. Calculate the magnetic field strength at r = 0.2 cm divided by that at r = 0.4 cm.
A) 1.0
B) 0.75
C) 0.50
D) 2.0
E) 3.0
A) 1.0
B) 0.75
C) 0.50
D) 2.0
E) 3.0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
A toroid has 200 turns of wire with a current of 3 A passing through the wire. The inner radius of the toroid is 3 cm and the outer radius is 5 cm. Calculate the magnetic field strength at a radius of 2 cm.
A) 6.0 * 10-3 T
B) 3.0 * 10-3 T
C) 1.2* 10-2 T
D) 4.8 F*10-4 T
E) none of the above
A) 6.0 * 10-3 T
B) 3.0 * 10-3 T
C) 1.2* 10-2 T
D) 4.8 F*10-4 T
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Use the following figure to answer the next problem: 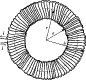
-The tightly wound toroid shown consists of 100 turns of wire, each carrying a current
I = 3 A. If a = 12 cm and b = 15 cm, the magnetic field at r = 13 cm, due to the current in this toroid, is (µ0 = 4 *10-7 N/A2)
A) 333 µT
B) 462 µT
C) 500 µT
D) 600
E) zero

-The tightly wound toroid shown consists of 100 turns of wire, each carrying a current
I = 3 A. If a = 12 cm and b = 15 cm, the magnetic field at r = 13 cm, due to the current in this toroid, is (µ0 = 4 *10-7 N/A2)
A) 333 µT
B) 462 µT
C) 500 µT
D) 600
E) zero

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Use the following figure to answer the next problem: 
-The tightly wound toroid shown consists of 100 turns of wire, each carrying a current
I = 3 A. If a = 12 cm and b = 15 cm, the magnetic field at r = 18 cm, due to the current in this toroid, is (µ0 = 4 *10-7 N/A2)
A) 333 µT
B) 400 µT
C) 500 µT
D) 600
E) zero

-The tightly wound toroid shown consists of 100 turns of wire, each carrying a current
I = 3 A. If a = 12 cm and b = 15 cm, the magnetic field at r = 18 cm, due to the current in this toroid, is (µ0 = 4 *10-7 N/A2)
A) 333 µT
B) 400 µT
C) 500 µT
D) 600
E) zero

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
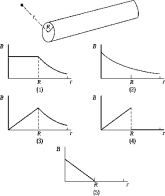 The graph that best represents B as a function of r for a wire of radius R carrying a current I uniformly distributed over its cross-sectional area is
The graph that best represents B as a function of r for a wire of radius R carrying a current I uniformly distributed over its cross-sectional area isA) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
A wire of radius 0.35 cm carries a current of 75 A that is uniformly distributed over its cross-sectional area. The magnetic field 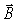 at a distance of 5.0 cm from the center of the wire is approximately
at a distance of 5.0 cm from the center of the wire is approximately
A) 0.47 mT
B) 1.5 mT
C) 0.30 mT
D) 0.56 mT
E) 0.24 mT
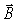 at a distance of 5.0 cm from the center of the wire is approximately
at a distance of 5.0 cm from the center of the wire is approximatelyA) 0.47 mT
B) 1.5 mT
C) 0.30 mT
D) 0.56 mT
E) 0.24 mT

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Ampère's law is valid
A) when there is a high degree of symmetry in the geometry of the situation.
B) when there is no symmetry.
C) when the current is constant.
D) when the magnetic field is constant.
E) for all of these conditions.
A) when there is a high degree of symmetry in the geometry of the situation.
B) when there is no symmetry.
C) when the current is constant.
D) when the magnetic field is constant.
E) for all of these conditions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Use the following to answer the next question: 
-A coil of radius R = 5 cm lies inside a long solenoid which carries a current I1 = 10 A and has 800 turns/m. The coil carries a current I2 = 4 A and the normal of the plane of the coil is at an angle = 30 with the axis of the solenoid. The magnetic field produced by the solenoid at the center is ____ times greater than the magnetic field by the coil at the center.
A) 100
B) 200
C) 1000
D) 2000
E) 8000

-A coil of radius R = 5 cm lies inside a long solenoid which carries a current I1 = 10 A and has 800 turns/m. The coil carries a current I2 = 4 A and the normal of the plane of the coil is at an angle = 30 with the axis of the solenoid. The magnetic field produced by the solenoid at the center is ____ times greater than the magnetic field by the coil at the center.
A) 100
B) 200
C) 1000
D) 2000
E) 8000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
A wire of radius 0.35 cm carries a current of 75 A that is uniformly distributed over its cross-sectional area. The magnetic field 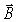 0.20 cm from the center of the wire is approximately
0.20 cm from the center of the wire is approximately
A) 2.5 mT
B) 8.8 T
C) 3.8 mT
D) 15 mT
E) 2.9 T
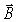 0.20 cm from the center of the wire is approximately
0.20 cm from the center of the wire is approximatelyA) 2.5 mT
B) 8.8 T
C) 3.8 mT
D) 15 mT
E) 2.9 T

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
A long solenoid of radius 3 cm has 1100 turns per m. If the solenoid wire carries a current of 1.5 A, then calculate the magnetic field inside the solenoid.
A) 2.1 * 10-3 T
B) 1.0 *10-3 T
C) 1.7 *10-4 T
D) 7.0 *10-2 T
E) none of the above
A) 2.1 * 10-3 T
B) 1.0 *10-3 T
C) 1.7 *10-4 T
D) 7.0 *10-2 T
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Use the following figure to answer the next problem: 
-The tightly wound toroid shown consists of 100 turns of wire, each carrying a current
I = 3 A. If a = 12 cm and b = 15 cm, the magnetic field at r = 10 cm, due to the current in this toroid, is (µ0 = 4 * 10-7 N/A2)
A) 400 µT
B) 500 µT
C) 600 µT
D) zero
E) impossible to calculate without additional information.

-The tightly wound toroid shown consists of 100 turns of wire, each carrying a current
I = 3 A. If a = 12 cm and b = 15 cm, the magnetic field at r = 10 cm, due to the current in this toroid, is (µ0 = 4 * 10-7 N/A2)
A) 400 µT
B) 500 µT
C) 600 µT
D) zero
E) impossible to calculate without additional information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The orbital magnetic moment of an atomic electron is
A) directly proportional to its angular momentum.
B) directly proportional to the electronic charge.
C) inversely proportional to the mass of the electron.
D) quantized as a consequence of the quantization of angular momentum.
E) described by all of the above.
A) directly proportional to its angular momentum.
B) directly proportional to the electronic charge.
C) inversely proportional to the mass of the electron.
D) quantized as a consequence of the quantization of angular momentum.
E) described by all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
A wire of radius 0.6 cm carries a current of 10 A that is uniformly distributed over its cross section. Calculate the magnetic field strength at r = 0.3 cm divided by that at r = 0.9 cm.
A) 1.0
B) 0.75
C) 0.50
D) 2.0
E) 3.0
A) 1.0
B) 0.75
C) 0.50
D) 2.0
E) 3.0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
A long straight wire of radius R carries a current density J = kr A/m2 where k is a constant. The magnetic field for r > R is (Hint: Current enclosed 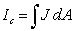 .)
.)
A) 0kR3/3r
B) 2 0kR3/3r
C) 2 0kR2/r
D) 2 0kR/2
E) none of the above
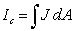 .)
.)A) 0kR3/3r
B) 2 0kR3/3r
C) 2 0kR2/r
D) 2 0kR/2
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Gauss's law for magnetism summarizes the fact(s) that
A) the magnetic flux through a closed surface is zero.
B) the magnetic flux is given by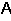 SB dA.
SB dA.
C) the existence of magnetic monopoles has yet to be verified.
D) there is no point in space from which magnetic field lines diverge.
E) all of the above are true.
A) the magnetic flux through a closed surface is zero.
B) the magnetic flux is given by
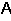 SB dA.
SB dA.C) the existence of magnetic monopoles has yet to be verified.
D) there is no point in space from which magnetic field lines diverge.
E) all of the above are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 115 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



