Deck 14: Our Starthe Sun
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/88
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 14: Our Starthe Sun
1
The fact that the surface of the Sun rings like a bell lets us understand its interior better.
True
2
In the radiative zone inside the Sun, photons are transported from the core to the convective zone in a matter of seconds.
False
3
In our Sun, hydrostatic equilibrium exists only in the core, where energy production via fusion can balance gravity.
False
4
If the Sun stopped nuclear fusion in its core, it would take 1,000 years for its luminosity to change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Our Sun is unique compared to the other stars in our galaxy because of its:
A) temperature
B) size
C) evolutionary stage
D) proximity
E) mass
A) temperature
B) size
C) evolutionary stage
D) proximity
E) mass

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following curves best matches the shape of a graph of the density of material inside the Sun (in thousands of kg/m3) as you move further away from the center? 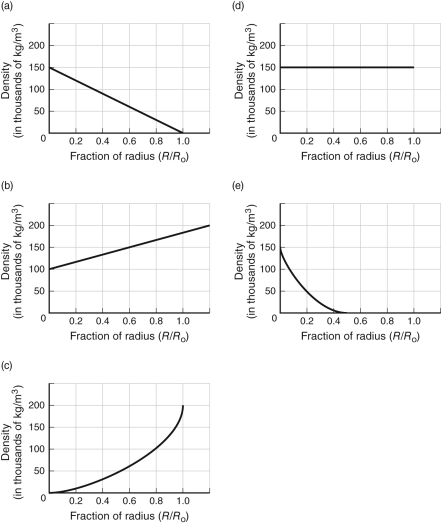
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The Sun has a mass of:
A) 2 * 1010 kg
B) 2 * 1025 kg
C) 2 * 1030 kg
D) 2 *1035 kg
E) 2 * 1045 kg
A) 2 * 1010 kg
B) 2 * 1025 kg
C) 2 * 1030 kg
D) 2 *1035 kg
E) 2 * 1045 kg

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The solar neutrino problem was solved by postulating that neutrinos have a small mass and oscillate between three different types of neutrino.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Neutrinos are particles with small masses that interact easily with normal matter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Density, temperature, and pressure increase as you move inward in the interior of the Sun. This means that the force of gravity, (Fg = GMm/r2), _________ as you move inward toward the core.
A) increases
B) decreases
C) stays the same
D) There is not enough information to answer.
A) increases
B) decreases
C) stays the same
D) There is not enough information to answer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Hydrostatic equilibrium is a balance between:
A) heat and centrifugal force
B) core temperature and surface temperature
C) pressure and gravity
D) radiation and heat
E) centrifugal force and gravity
A) heat and centrifugal force
B) core temperature and surface temperature
C) pressure and gravity
D) radiation and heat
E) centrifugal force and gravity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
If coronal holes covered a larger fraction of the Sun's surface, the solar wind would contain a higher density of particles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which force is responsible for holding the protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom together?
A) gravity
B) strong nuclear force
C) electric force
D) magnetic force
E) Electrons push them together.
A) gravity
B) strong nuclear force
C) electric force
D) magnetic force
E) Electrons push them together.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Nuclei of atoms are held together by gravity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The solar magnetic field switches polarity every 11 years.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The balance of energy in the solar interior means that:
A) energy production rate in the core equals the rate of radiation escaping the Sun's surface
B) the source of energy in the core is stable and will sustain the Sun for millions of years
C) the outer layers of the Sun absorb and re-emit the radiation from the core at increasingly longer wavelengths
D) radiation pressure balances the weight of the overlying solar layers
E) the core of the Sun has higher pressure than the outer layers
A) energy production rate in the core equals the rate of radiation escaping the Sun's surface
B) the source of energy in the core is stable and will sustain the Sun for millions of years
C) the outer layers of the Sun absorb and re-emit the radiation from the core at increasingly longer wavelengths
D) radiation pressure balances the weight of the overlying solar layers
E) the core of the Sun has higher pressure than the outer layers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The net result of the proton-proton chain of nuclear reactions is that four protons are converted into one helium nucleus and energy, electrons, and neutrinos are released.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The temperature of the corona is much hotter than any other layer in the solar atmosphere.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
At the center of the Sun, the temperature is roughly 15 million K.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
In a sunspot, the umbra is cooler than the penumbra.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Why is hydrogen burning the main energy source for main-sequence stars?
A) Hydrogen is the most common element in stars.
B) Hydrogen nuclei have the smallest positive charge.
C) Hydrogen burning is the most efficient of all fusion or fission reactions.
D) Hydrogen can fuse at temperatures lower than other elements.
E) All the above are valid reasons.
A) Hydrogen is the most common element in stars.
B) Hydrogen nuclei have the smallest positive charge.
C) Hydrogen burning is the most efficient of all fusion or fission reactions.
D) Hydrogen can fuse at temperatures lower than other elements.
E) All the above are valid reasons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The interior zones of the Sun are distinguished by:
A) jumps in density between zones
B) their temperature profiles
C) pressure differences inside each zone
D) their modes of energy transport
E) all of the above
A) jumps in density between zones
B) their temperature profiles
C) pressure differences inside each zone
D) their modes of energy transport
E) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Light from the Sun's photosphere reaches Earth approximately _________ times faster than photons released in fusion in the core.
A) 1,000
B) 600,000
C) 1 million
D) 6 billion
E) 10 billion
A) 1,000
B) 600,000
C) 1 million
D) 6 billion
E) 10 billion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
If the Sun converts 5 * 1011 kg of H to He per second and the mass of a single hydrogen nucleus is 1.7 *10-27 kg, how many net proton-proton reactions go on per second in the Sun? What is the luminosity produced if the mass difference between a single helium nucleus and four hydrogen nuclei is 4 *10-29 kg? Note that 1 Watt * 1 m2 kg/s3.
A) 7 *1037 reactions per sec; 3 * 1026 Watt
B) 3*1038 reactions per sec; 1027 Watt
C) 3 * 1038 reactions per sec; 4 * 1026 Watt
D) 7 *1037 reactions per sec; 5 * 1025 Watt
E) 3 * 1037 reactions per sec; 6* 1024 Watt
A) 7 *1037 reactions per sec; 3 * 1026 Watt
B) 3*1038 reactions per sec; 1027 Watt
C) 3 * 1038 reactions per sec; 4 * 1026 Watt
D) 7 *1037 reactions per sec; 5 * 1025 Watt
E) 3 * 1037 reactions per sec; 6* 1024 Watt

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Some restaurants place food under infrared heat lamps so that it stays warm after it has been cooked. This is an example of energy being transported by:
A) radiation
B) convection
C) conduction
D) convection and conduction
E) radiation and conduction
A) radiation
B) convection
C) conduction
D) convection and conduction
E) radiation and conduction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Approximately how long does it take the photons released in nuclear reactions in the core of the Sun to exit the photosphere?
A) 8 minutes
B) 16 hours
C) 1,000 years
D) 100,000 years
E) 4.6 billion years
A) 8 minutes
B) 16 hours
C) 1,000 years
D) 100,000 years
E) 4.6 billion years

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The majority of the Sun's energy comes from:
A) gravitational contraction
B) nuclear fission of uranium
C) hydrogen fusion
D) helium burning
E) burning material as in a fire
A) gravitational contraction
B) nuclear fission of uranium
C) hydrogen fusion
D) helium burning
E) burning material as in a fire

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The detection of solar neutrinos confirms that:
A) the Sun's core is powered by proton-proton fusion
B) energy transport by radiation occurs throughout much of the solar interior
C) magnetic fields are responsible for surface activity on the Sun
D) convection churns the base of the solar atmosphere
E) sunspots are cooler than the rest of the photosphere
A) the Sun's core is powered by proton-proton fusion
B) energy transport by radiation occurs throughout much of the solar interior
C) magnetic fields are responsible for surface activity on the Sun
D) convection churns the base of the solar atmosphere
E) sunspots are cooler than the rest of the photosphere

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
If neutrinos oscillated between five different types of neutrino during their transit from the Sun to Earth, then how many neutrinos would we have detected compared to what was emitted by the Sun?
A) one-half as many
B) one-third as many
C) one-fourth as many
D) one-fifth as many
E) We would detect no neutrinos.
A) one-half as many
B) one-third as many
C) one-fourth as many
D) one-fifth as many
E) We would detect no neutrinos.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The net effect of the proton-proton chain is that four hydrogen nuclei are converted to one helium nucleus and _________ are released.
A) visible wavelength photons
B) gamma ray photons, positrons, and neutrinos
C) ultraviolet photons and neutrinos
D) X-ray photons, electrons, and neutrinos
E) infrared photons and positrons
A) visible wavelength photons
B) gamma ray photons, positrons, and neutrinos
C) ultraviolet photons and neutrinos
D) X-ray photons, electrons, and neutrinos
E) infrared photons and positrons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
If the Sun converts 5*1011 kg of H to He per second and 10 percent of the Sun's total mass is available for nuclear burning, how long might we expect the Sun to live?
A) 104 years
B) 108 years
C) 1010 years
D) 1011 years
E) 1014 years
A) 104 years
B) 108 years
C) 1010 years
D) 1011 years
E) 1014 years

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following method(s) is (are) NOT used to transport energy from the core of the Sun to its surface?
A) radiation
B) convection
C) conduction
D) All of the above are important in the solar interior.
E) None of the above are important in the solar interior.
A) radiation
B) convection
C) conduction
D) All of the above are important in the solar interior.
E) None of the above are important in the solar interior.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The energy that fuels the Sun is generated:
A) only on its surface
B) only in its core
C) only in the solar wind
D) both in its core and on its surface
E) in its core, on the surface, and in the solar wind
A) only on its surface
B) only in its core
C) only in the solar wind
D) both in its core and on its surface
E) in its core, on the surface, and in the solar wind

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
When two atomic nuclei come together to form a new species of atom, this is called:
A) nuclear fission
B) nuclear recombination
C) nuclear splitting
D) nuclear fusion
E) ionization
A) nuclear fission
B) nuclear recombination
C) nuclear splitting
D) nuclear fusion
E) ionization

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
If you hold on to one end of a metal spoon while placing the other end in a pot of boiling water, you will burn your hand. This is an example of energy being transported by:
A) radiation
B) convection
C) conduction
D) convection and radiation
E) radiation and conduction
A) radiation
B) convection
C) conduction
D) convection and radiation
E) radiation and conduction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
When you turn on the heater in a car, the passengers in the front seat warm up first, then eventually the warm air gets to the passengers in the back seat. This is an example of energy being transported by:
A) radiation
B) convection
C) conduction
D) convection and conduction
E) radiation and conduction
A) radiation
B) convection
C) conduction
D) convection and conduction
E) radiation and conduction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of these can travel directly from the center of the Sun to Earth in about 8 minutes?
A) photons
B) electrons
C) protons
D) neutrons
E) neutrinos
A) photons
B) electrons
C) protons
D) neutrons
E) neutrinos

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
What do astronomers mean when they say that the Sun makes energy by hydrogen burning?
A) The Sun is combusting hydrogen in a fire and releasing energy.
B) The Sun is fusing hydrogen into uranium and releasing energy.
C) The Sun is made of mostly hydrogen at very high temperature.
D) The Sun is fusing hydrogen into helium and releasing energy.
E) The Sun is accumulating hydrogen from the solar wind and releasing energy.
A) The Sun is combusting hydrogen in a fire and releasing energy.
B) The Sun is fusing hydrogen into uranium and releasing energy.
C) The Sun is made of mostly hydrogen at very high temperature.
D) The Sun is fusing hydrogen into helium and releasing energy.
E) The Sun is accumulating hydrogen from the solar wind and releasing energy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
If the core of the Sun were hotter than it is now, how would the Sun's energy production change?
A) It would produce less energy per second than it does now.
B) It would produce more energy per second than it does now.
C) Its energy production would vary more than it does now.
D) Its energy production would be more stable than it is now.
E) The Sun's energy production would not change.
A) It would produce less energy per second than it does now.
B) It would produce more energy per second than it does now.
C) Its energy production would vary more than it does now.
D) Its energy production would be more stable than it is now.
E) The Sun's energy production would not change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following layers of the Sun makes up the majority of its interior?
A) the core
B) the radiative zone
C) the convective zone
D) the photosphere
E) the chromosphere
A) the core
B) the radiative zone
C) the convective zone
D) the photosphere
E) the chromosphere

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
We know the Sun's corona is very hot because:
A) we observe it emitting radiation at visible wavelengths
B) the chromosphere and the photosphere are that hot, too
C) we observe absorption from highly ionized atoms of iron and calcium in its spectrum
D) the gas emits most of its radiation at radio wavelengths
E) all of the above
A) we observe it emitting radiation at visible wavelengths
B) the chromosphere and the photosphere are that hot, too
C) we observe absorption from highly ionized atoms of iron and calcium in its spectrum
D) the gas emits most of its radiation at radio wavelengths
E) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The surface of the Sun appears sharp when we look at it in visible light because:
A) the photosphere is cooler than the layers below it
B) the photosphere is thin compared to the other layers in the Sun
C) the photosphere is much less dense than the convection zone
D) the photosphere is transparent to radiation
E) the Sun has a distinct surface
A) the photosphere is cooler than the layers below it
B) the photosphere is thin compared to the other layers in the Sun
C) the photosphere is much less dense than the convection zone
D) the photosphere is transparent to radiation
E) the Sun has a distinct surface

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which of the following is NOT a result of an increase in solar activity?
A) The altitudes of orbiting satellites decrease.
B) Airplanes have trouble navigating.
C) Stronger auroras are seen.
D) Power grids can be damaged.
E) All of the above can be caused by increased solar activity.
A) The altitudes of orbiting satellites decrease.
B) Airplanes have trouble navigating.
C) Stronger auroras are seen.
D) Power grids can be damaged.
E) All of the above can be caused by increased solar activity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which of the following are created by solar magnetic activity?
A) sunspots
B) prominences
C) coronal mass ejections
D) solar flares
E) all of the above
A) sunspots
B) prominences
C) coronal mass ejections
D) solar flares
E) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
By studying how the surface of the Sun vibrates like a struck bell we can determine its:
A) age
B) interior density
C) total mass
D) size
E) temperature
A) age
B) interior density
C) total mass
D) size
E) temperature

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The darkest part of a sunspot is called the:
A) penumbra
B) umbra
C) granule
D) photosphere
E) magnetic field
A) penumbra
B) umbra
C) granule
D) photosphere
E) magnetic field

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Sunspots appear dark because they have _________ than the surrounding gas.
A) higher densities
B) lower densities
C) higher pressures
D) lower temperatures
E) higher temperatures
A) higher densities
B) lower densities
C) higher pressures
D) lower temperatures
E) higher temperatures

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Imagine that you observed the Sun and measured the brightness of the face of the Sun at the locations marked in this image: 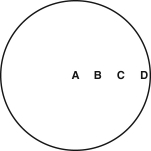 At which of these locations would you measure the lowest brightness?
At which of these locations would you measure the lowest brightness?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) They would all have the same brightness.
 At which of these locations would you measure the lowest brightness?
At which of these locations would you measure the lowest brightness?A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) They would all have the same brightness.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The Sun's corona has a temperature of approximately 1 million degrees. At what wavelength and in what part of the electromagnetic spectrum does its radiation peak?
A) 550 nm, visible
B) 2 *10-5 m, infrared
C) 4 *10-7 m, ultraviolet
D) 3 *10-9 m, X-rays
E) 6 m, radio
A) 550 nm, visible
B) 2 *10-5 m, infrared
C) 4 *10-7 m, ultraviolet
D) 3 *10-9 m, X-rays
E) 6 m, radio

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which of the layers of the Sun is located the furthest from the center of the Sun?
A) chromosphere
B) photosphere
C) radiative zone
D) convective zone
E) corona
A) chromosphere
B) photosphere
C) radiative zone
D) convective zone
E) corona

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The Sun's chromosphere appears red because:
A) it is hotter than the photosphere
B) as the Sun rotates, the chromosphere appears to move away from us radially
C) it has a higher concentration of heavy metals
D) it is made of mostly helium
E) its spectrum is dominated by H emission
A) it is hotter than the photosphere
B) as the Sun rotates, the chromosphere appears to move away from us radially
C) it has a higher concentration of heavy metals
D) it is made of mostly helium
E) its spectrum is dominated by H emission

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
If a sunspot appears one-quarter as bright as the surrounding photosphere, and the average temperature of the photosphere is 5800 K, what is the temperature of the gas in this sunspot?
A) 3625 K
B) 4100 K
C) 4500 K
D) 5200 K
E) 5500 K
A) 3625 K
B) 4100 K
C) 4500 K
D) 5200 K
E) 5500 K

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The best wavelength to use to observe a solar prominence is:
A) 550 nm, green visible light
B) 656 nm, a red hydrogen emission line
C) 16 mm, an ultraviolet emission line
D) 21 cm, microwave emission
E) 0.02 nm, X-ray emission
A) 550 nm, green visible light
B) 656 nm, a red hydrogen emission line
C) 16 mm, an ultraviolet emission line
D) 21 cm, microwave emission
E) 0.02 nm, X-ray emission

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The image below taken at visible wavelengths shows a section of the Sun with sunspots visible. 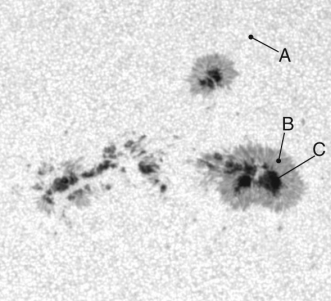 Which of the labeled regions is the lowest temperature?
Which of the labeled regions is the lowest temperature?
A) region A
B) region B
C) region C
D) They are all the same temperature.
E) There is not enough information to determine their relative temperatures.
 Which of the labeled regions is the lowest temperature?
Which of the labeled regions is the lowest temperature?A) region A
B) region B
C) region C
D) They are all the same temperature.
E) There is not enough information to determine their relative temperatures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
What keeps the gas in the Sun's corona from flying away from the Sun?
A) gravity
B) strong nuclear force
C) the Sun's magnetic field
D) the solar wind
E) sunspots
A) gravity
B) strong nuclear force
C) the Sun's magnetic field
D) the solar wind
E) sunspots

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
We can determine how the density changes with radius in the Sun using:
A) radar observations
B) neutrino detections
C) high-energy (gamma ray) observations
D) helioseismology
E) infrared observations
A) radar observations
B) neutrino detections
C) high-energy (gamma ray) observations
D) helioseismology
E) infrared observations

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The magnetic field of the Sun is continuously produced and deformed by:
A) its differential rotation
B) the solar wind
C) changes in the rate of nuclear fusion in the core
D) a liquid conducting layer in the interior
E) This is a trick question. The solar magnetic field is primordial.
A) its differential rotation
B) the solar wind
C) changes in the rate of nuclear fusion in the core
D) a liquid conducting layer in the interior
E) This is a trick question. The solar magnetic field is primordial.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The solar spectrum is an example of a(n) _________ spectrum.
A) emission
B) absorption
C) continuum
D) blackbody
E) X-ray
A) emission
B) absorption
C) continuum
D) blackbody
E) X-ray

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The solar neutrino problem was solved by:
A) adjusting the rate of hydrogen burning in solar models
B) improving detector efficiencies so more neutrinos were observed
C) postulating that neutrinos had mass and oscillated between three different types
D) lowering the percentage of helium in models of solar composition
E) correctly measuring the density of the Sun's interior
A) adjusting the rate of hydrogen burning in solar models
B) improving detector efficiencies so more neutrinos were observed
C) postulating that neutrinos had mass and oscillated between three different types
D) lowering the percentage of helium in models of solar composition
E) correctly measuring the density of the Sun's interior

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The image below shows the Sun during a solar eclipse at visible wavelengths. 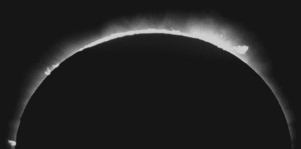 Which part of the Sun is visible around the shadow of the Moon?
Which part of the Sun is visible around the shadow of the Moon?
A) chromosphere
B) photosphere
C) radiative zone
D) convective zone
E) corona
 Which part of the Sun is visible around the shadow of the Moon?
Which part of the Sun is visible around the shadow of the Moon?A) chromosphere
B) photosphere
C) radiative zone
D) convective zone
E) corona

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Solar wind particles hit the surface of the Moon, but they don't make it to the surface of the Earth because the Earth:
A) is larger than the Moon
B) is warmer than the Moon
C) has an atmosphere while the Moon does not
D) has a magnetic field while the Moon does not
E) is further from the Sun than the Moon
A) is larger than the Moon
B) is warmer than the Moon
C) has an atmosphere while the Moon does not
D) has a magnetic field while the Moon does not
E) is further from the Sun than the Moon

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The Sun's internal magnetic field becomes tangled up over time because of:
A) coronal holes
B) coronal mass ejections
C) differential rotation
D) temperature changes in the Sun's core
E) all of the above
A) coronal holes
B) coronal mass ejections
C) differential rotation
D) temperature changes in the Sun's core
E) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
In the proton-proton chain, the net reaction is that 4 protons are converted into 1 helium nucleus. What other byproducts are released in this reaction, and why?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Explain why magnetic fields trap coronal gas over much of the solar surface but allow it to escape in coronal holes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
In the text we considered the case of a "too-large" Sun. Show that a star with the same mass, composition, radius, and luminosity as the Sun, but with a higher temperature (that is, a "too-hot" Sun), also leads to a contradiction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
What is "limb darkening"? Explain why limb darkening occurs in the Sun.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The Sun's magnetic field reverses direction every:
A) 24 hours
B) 27 days
C) 12 months
D) 11 years
E) 22 years
A) 24 hours
B) 27 days
C) 12 months
D) 11 years
E) 22 years

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Through hydrogen fusion, the Sun loses approximately 4 million tons of mass each second. If it burns hydrogen at this rate for 10 billion years, what percentage of its original mass will it lose in all? (Note: The mass of the Sun is 1.99*1030 kg, and 1 ton = 1,000 kg.)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The Maunder Minimum was a 60-year period when:
A) debris thrown up in a comet collision blanketed the Sun
B) almost no sunspots occurred on the Sun
C) the Voyager 2 spacecraft traversed the heliopause
D) very few dust storms occurred on Mars
E) very few volcanic eruptions occurred on Mars
A) debris thrown up in a comet collision blanketed the Sun
B) almost no sunspots occurred on the Sun
C) the Voyager 2 spacecraft traversed the heliopause
D) very few dust storms occurred on Mars
E) very few volcanic eruptions occurred on Mars

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Calculate the amount of energy released by converting four hydrogen atoms into one helium atom. The mass of a hydrogen atom is 1.67 * 10-24g; the mass of a helium atom is 6.65 *10-24
g. The speed of light is 3 * 108 m/s.
g. The speed of light is 3 * 108 m/s.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The picture below shows a diagram of the Sun with zones labeled A, B, and C. 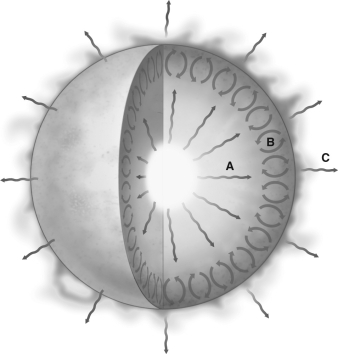 Explain how energy is being transferred in each of the three regions.
Explain how energy is being transferred in each of the three regions.
 Explain how energy is being transferred in each of the three regions.
Explain how energy is being transferred in each of the three regions.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
If a coronal mass ejection occurs on the Sun that expels material at a speed of 800 km/s, how long will it take these charged particles to reach the Earth?
A) 0.7 day
B) 1.4 days
C) 1.8 days
D) 2.2 days
E) 3.5 days
A) 0.7 day
B) 1.4 days
C) 1.8 days
D) 2.2 days
E) 3.5 days

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Explain why hydrostatic equilibrium results in the center of the Sun having the highest pressure and temperature.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
If you observe a maximum number of sunspots right now, how long would you have to wait to see the next solar maximum?
A) 24 hours
B) 6 months
C) 1 year
D) 11 years
E) 22 years
A) 24 hours
B) 6 months
C) 1 year
D) 11 years
E) 22 years

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
When solar activity is very high, the Earth's atmosphere will:
A) expand
B) contract
C) remain approximately the same
D) repel charged particles
E) block out sunlight
A) expand
B) contract
C) remain approximately the same
D) repel charged particles
E) block out sunlight

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Why is hydrogen burning the main energy source for main-sequence stars? Give at least two reasons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
In addition to the laws of physics and chemistry, what information do we need to know about our Sun to calculate its internal structure and radius?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Explain why the solution to the solar neutrino problem is an excellent example of how observations drive the evolution of science.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
When is the Sun most luminous?
A) when there are a maximum number of sunspots
B) when there are a average number of sunspots
C) where there a minimum number of sunspots
D) the Sun's luminosity does not change
E) the Sun's luminosity changes, but it has no relation to the number of sunspots
A) when there are a maximum number of sunspots
B) when there are a average number of sunspots
C) where there a minimum number of sunspots
D) the Sun's luminosity does not change
E) the Sun's luminosity changes, but it has no relation to the number of sunspots

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
List three methods of energy transport in nature and explain how the energy is being transferred in each of those methods. Which two are means by which energy is transported inside the Sun?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



