Deck 5: Light
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/87
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 5: Light
1
If the wavelength of a beam of light were to double, how would that affect its frequency?
A) The frequency would be four times larger.
B) The frequency would be two times larger.
C) The frequency would be two times smaller
D) The frequency would be four times smaller.
E) There is no relationship between wavelength and frequency.
A) The frequency would be four times larger.
B) The frequency would be two times larger.
C) The frequency would be two times smaller
D) The frequency would be four times smaller.
E) There is no relationship between wavelength and frequency.
The frequency would be two times smaller
2
Cooler objects radiate more of their total light at shorter wavelengths than hotter objects.
False
3
The speed of light in a vacuum is:
A) 300,000 m/s
B) 300,000 mph
C) 300,000 km/s
D) 300,000,000 mph
E) infinite
A) 300,000 m/s
B) 300,000 mph
C) 300,000 km/s
D) 300,000,000 mph
E) infinite
300,000 km/s
4
A light-year is a unit that is used to measure:
A) time
B) wavelength
C) speed
D) energy
E) distance
A) time
B) wavelength
C) speed
D) energy
E) distance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A thin cloud of cool gas on top of a hotter blackbody will radiate an emission spectrum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
If the frequency of a beam of light were to increase, its period would _________ and its wavelength would _________?
A) decrease; increase
B) increase; decrease
C) increase; increase
D) decrease; decrease
E) stay the same; stay the same
A) decrease; increase
B) increase; decrease
C) increase; increase
D) decrease; decrease
E) stay the same; stay the same

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
How does the speed of light traveling through a medium (such as air or glass) compare to the speed of light in a vacuum?
A) It is the same as the speed of light in a vacuum.
B) It is always less than the speed of light in a vacuum.
C) It is always greater than the speed of light in a vacuum.
D) Sometimes it is greater than the speed of light in a vacuum, and sometimes it is less, depending on the medium.
E) Light can't travel through a medium, it only can go through a vacuum.
A) It is the same as the speed of light in a vacuum.
B) It is always less than the speed of light in a vacuum.
C) It is always greater than the speed of light in a vacuum.
D) Sometimes it is greater than the speed of light in a vacuum, and sometimes it is less, depending on the medium.
E) Light can't travel through a medium, it only can go through a vacuum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The speed of light was first determined by which scientist?
A) Galileo
B) Newton
C) Kepler
D) Rømer
E) Einstein
A) Galileo
B) Newton
C) Kepler
D) Rømer
E) Einstein

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
If an object is moving toward you, the light you see from it will be blueshifted.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Use the figure below to answer the following question: 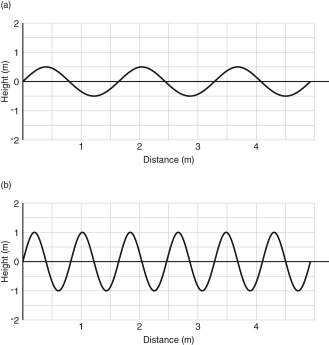 Which of these statements about the amplitude and wavelength of the two waves shown is correct?
Which of these statements about the amplitude and wavelength of the two waves shown is correct?
A) Wave A has a larger amplitude and a larger wavelength.
B) Wave B has a larger amplitude and a larger wavelength.
C) Wave A has a larger amplitude, and Wave B has a larger wavelength.
D) Wave B has a larger amplitude, and Wave A has a larger wavelength.
E) Wave A and B have the same amplitude and wavelength.
 Which of these statements about the amplitude and wavelength of the two waves shown is correct?
Which of these statements about the amplitude and wavelength of the two waves shown is correct?A) Wave A has a larger amplitude and a larger wavelength.
B) Wave B has a larger amplitude and a larger wavelength.
C) Wave A has a larger amplitude, and Wave B has a larger wavelength.
D) Wave B has a larger amplitude, and Wave A has a larger wavelength.
E) Wave A and B have the same amplitude and wavelength.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The luminosity of an object is independent of its distance from you.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The period of a wave is inversely proportional to the frequency of that wave.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The fact that the speed of light is constant as it travels through a vacuum means that:
A) photons with longer wavelengths have lower frequencies
B) radio wave photons have shorter wavelengths than gamma ray photons
C) X-rays can be transmitted through the atmosphere around the world
D) ultraviolet photons have less energy than visible photons
E) all of the above are true
A) photons with longer wavelengths have lower frequencies
B) radio wave photons have shorter wavelengths than gamma ray photons
C) X-rays can be transmitted through the atmosphere around the world
D) ultraviolet photons have less energy than visible photons
E) all of the above are true

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A radio photon travels slower than a gamma ray photon.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
An emission line is produced when an atom absorbs a photon of a specific energy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
What is the difference between visible light and X-rays?
A) Speed; X-rays go faster than visible light.
B) Speed; X-rays go slower than visible light.
C) Wavelength; X-rays have a shorter wavelength than visible light.
D) Wavelength; X-rays have a longer wavelength than visible light.
E) X-rays are made up of particles, while visible light is made up of waves.
A) Speed; X-rays go faster than visible light.
B) Speed; X-rays go slower than visible light.
C) Wavelength; X-rays have a shorter wavelength than visible light.
D) Wavelength; X-rays have a longer wavelength than visible light.
E) X-rays are made up of particles, while visible light is made up of waves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Your average body temperature is approximately 310 K, thus most of the light you radiate is at ultraviolet wavelengths.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
If the Sun instantaneously stopped giving off light, what would happen on Earth?
A) It would immediately get dark.
B) It would get dark 8 minutes later.
C) It would get dark 27 minutes later.
D) It would get dark 1 hour later.
E) It would get dark 24 hours later.
A) It would immediately get dark.
B) It would get dark 8 minutes later.
C) It would get dark 27 minutes later.
D) It would get dark 1 hour later.
E) It would get dark 24 hours later.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The emission lines of a given atom occur at the exact same energies as that atom's absorption lines.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The emission spectrum of a helium atom is identical to that of a carbon atom.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of these objects would emit an absorption spectrum?
A) an incandescent light bulb
B) a fluorescent light bulb
C) an isolated hot gas cloud
D) a hot, solid object
E) a thin, cool gas cloud that lies in front of a hotter blackbody
A) an incandescent light bulb
B) a fluorescent light bulb
C) an isolated hot gas cloud
D) a hot, solid object
E) a thin, cool gas cloud that lies in front of a hotter blackbody

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
As wavelength increases, the energy of a photon _________ and its frequency _________.
A) increases; decreases
B) increases; increases
C) decreases; decreases
D) decreases; increases
A) increases; decreases
B) increases; increases
C) decreases; decreases
D) decreases; increases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
In the quantum mechanical view of the atom, an electron is best thought of as:
A) a cloud that is centered on the nucleus
B) a particle orbiting the nucleus
C) free to orbit at any distance from the nucleus
D) a particle inside the nucleus
E) All of the above are true.
A) a cloud that is centered on the nucleus
B) a particle orbiting the nucleus
C) free to orbit at any distance from the nucleus
D) a particle inside the nucleus
E) All of the above are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following photons carry the smallest amount of energy?
A) a blue photon of the visible spectrum, whose wavelength is 450 nm
B) an infrared photon, whose wavelength is 10-5 m
C) a red photon in the visible spectrum, whose wavelength is 700 nm
D) a microwave photon, whose wavelength is 10-2 m
E) an ultraviolet photon, whose wavelength is 300 nm
A) a blue photon of the visible spectrum, whose wavelength is 450 nm
B) an infrared photon, whose wavelength is 10-5 m
C) a red photon in the visible spectrum, whose wavelength is 700 nm
D) a microwave photon, whose wavelength is 10-2 m
E) an ultraviolet photon, whose wavelength is 300 nm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which formula denotes how the speed of light is related to its wavelength and frequency?
A) c = f
B) c= /f
C) c = f/
D) c= 1/ f
E) There is no relationship between wavelength and frequency.
A) c = f
B) c= /f
C) c = f/
D) c= 1/ f
E) There is no relationship between wavelength and frequency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
How do the wavelength and frequency of red light compare to the wavelength and frequency of blue light?
A) Red light has a longer wavelength and higher frequency than blue light.
B) Red light has a longer wavelength and lower frequency than blue light.
C) Red light has a shorter wavelength and higher frequency than blue light.
D) Red light has a shorter wavelength and lower frequency than blue light.
A) Red light has a longer wavelength and higher frequency than blue light.
B) Red light has a longer wavelength and lower frequency than blue light.
C) Red light has a shorter wavelength and higher frequency than blue light.
D) Red light has a shorter wavelength and lower frequency than blue light.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The color of visible light is determined by its:
A) speed
B) wavelength
C) mass
D) distance from you
E) size
A) speed
B) wavelength
C) mass
D) distance from you
E) size

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Saying that something is quantized means that it:
A) is a wave
B) is a particle
C) travels at the speed of light
D) can only have discrete quantities
E) is smaller than an atom
A) is a wave
B) is a particle
C) travels at the speed of light
D) can only have discrete quantities
E) is smaller than an atom

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Einstein showed that the _________ could be explained if photons carried quantized amounts of energy.
A) warping of space and time
B) Heisenberg uncertainty principle
C) photoelectric effect
D) theory of special relativity
E) Bohr model of the atom
A) warping of space and time
B) Heisenberg uncertainty principle
C) photoelectric effect
D) theory of special relativity
E) Bohr model of the atom

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
If you observe an isolated hot cloud of gas, you will see:
A) an absorption spectrum
B) a continuous spectrum
C) an emission spectrum
D) a rainbow spectrum
E) a dark spectrum
A) an absorption spectrum
B) a continuous spectrum
C) an emission spectrum
D) a rainbow spectrum
E) a dark spectrum

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Light with a wavelength of 600 nm has a frequency of:
A) 2* 105 Hz
B) 5 * 107 Hz
C) 2 * 1010 Hz
D) 5 * 1012 Hz
E) 5 * 1014 Hz
A) 2* 105 Hz
B) 5 * 107 Hz
C) 2 * 1010 Hz
D) 5 * 1012 Hz
E) 5 * 1014 Hz

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Why is an iron atom a different element than a carbon atom?
A) A carbon atom has fewer neutrons in its nucleus than an iron atom.
B) An iron atom has more protons in its nucleus than a carbon atom.
C) An iron atom has more electrons than a carbon atom.
D) A carbon atom is bigger than an iron atom.
E) All of the above are true.
A) A carbon atom has fewer neutrons in its nucleus than an iron atom.
B) An iron atom has more protons in its nucleus than a carbon atom.
C) An iron atom has more electrons than a carbon atom.
D) A carbon atom is bigger than an iron atom.
E) All of the above are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
When an electron moves from a higher energy level in an atom to a lower energy level:
A) the atom is ionized
B) a continuous spectrum is emitted
C) a photon is emitted
D) a photon is absorbed
E) the electron loses mass
A) the atom is ionized
B) a continuous spectrum is emitted
C) a photon is emitted
D) a photon is absorbed
E) the electron loses mass

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The n = 5 electronic energy level in a hydrogen atom is 1.5 *10 - 19 J higher than the n = 3 level. If an electron moves from the n = 5 level to the n = 3 level, then a photon of wavelength:
A) 1.3 nm, which is in the ultraviolet region, is emitted
B) 1.3 nm, which is in the ultraviolet region, is absorbed
C) 1,300 nm, which is in the infrared region, is absorbed
D) 1,300 nm, which is in the infrared region, is emitted
E) no light will be absorbed or emitted
A) 1.3 nm, which is in the ultraviolet region, is emitted
B) 1.3 nm, which is in the ultraviolet region, is absorbed
C) 1,300 nm, which is in the infrared region, is absorbed
D) 1,300 nm, which is in the infrared region, is emitted
E) no light will be absorbed or emitted

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The Doppler shift can be used to determine the _________ of an object.
A) energy
B) temperature
C) radial velocity
D) color
E) three-dimensional velocity
A) energy
B) temperature
C) radial velocity
D) color
E) three-dimensional velocity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
If you observe a star, you will see:
A) an absorption spectrum
B) a continuous spectrum
C) an emission spectrum
D) a rainbow spectrum
E) a dark spectrum
A) an absorption spectrum
B) a continuous spectrum
C) an emission spectrum
D) a rainbow spectrum
E) a dark spectrum

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
A red photon has a wavelength of 650 nm. An ultraviolet photon has a wavelength of 250 nm. The energy of an ultraviolet photon is _________ the energy of a red photon.
A) 2.6 times larger than
B) 6.8 times larger than
C) 2.6 times smaller than
D) 6.8 times smaller than
E) the same as
A) 2.6 times larger than
B) 6.8 times larger than
C) 2.6 times smaller than
D) 6.8 times smaller than
E) the same as

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which of the following lists different types of electromagnetic radiation in order from the smallest wavelength to the largest wavelength?
A) radio waves, infrared, visible, ultraviolet, X-rays
B) gamma rays, ultraviolet, visible, infrared, radio waves
C) gamma rays, X-rays, infrared, visible, ultraviolet
D) X-rays, infrared, visible, ultraviolet, radio waves
E) radio waves, ultraviolet, visible, infrared, gamma rays
A) radio waves, infrared, visible, ultraviolet, X-rays
B) gamma rays, ultraviolet, visible, infrared, radio waves
C) gamma rays, X-rays, infrared, visible, ultraviolet
D) X-rays, infrared, visible, ultraviolet, radio waves
E) radio waves, ultraviolet, visible, infrared, gamma rays

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Light is:
A) a wave
B) a particle
C) both a particle and a wave
D) neither a particle nor a wave
A) a wave
B) a particle
C) both a particle and a wave
D) neither a particle nor a wave

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
What wavelengths of light can the human eye see?
A) 3.8 m to 7.5 m
B) 3.8 nm to 7.5 nm
C) 380 cm to 750 cm
D) 380 nm to 750 nm
E) 3.8 m to 7.5 m
A) 3.8 m to 7.5 m
B) 3.8 nm to 7.5 nm
C) 380 cm to 750 cm
D) 380 nm to 750 nm
E) 3.8 m to 7.5 m

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Star A and star B appear equally bright in the sky. Star A is twice as far away from Earth as star B. How do the luminosities of stars A and B compare?
A) Star A is twice as luminous as star B.
B) Star B is twice as luminous as star A.
C) Star A is four times as luminous as star B.
D) Star B is four times as luminous as star A.
E) Stars A and B have the same luminosity.
A) Star A is twice as luminous as star B.
B) Star B is twice as luminous as star A.
C) Star A is four times as luminous as star B.
D) Star B is four times as luminous as star A.
E) Stars A and B have the same luminosity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The spaceship shown in the figure below is traveling at a speed of 15,000 km/s to the left while it sends out a signal with a wavelength of 4 meters. 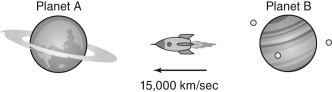 If astronomers living on planets A and B measure the radio waves coming from the space ship, what wavelengths will they measure?
If astronomers living on planets A and B measure the radio waves coming from the space ship, what wavelengths will they measure?
A) Planet A measures 6 meters, and planet B measures 2 meters.
B) Planet A measures 2 meters, and planet B measures 6 meters.
C) Planet A measures 4.2 meters, and planet B measures 3.8 meters.
D) Planet A measures 3.8 meters, and Planet B measures 4.2 meters.
E) Both Planet A and Planet B measure 4 meters.
 If astronomers living on planets A and B measure the radio waves coming from the space ship, what wavelengths will they measure?
If astronomers living on planets A and B measure the radio waves coming from the space ship, what wavelengths will they measure?A) Planet A measures 6 meters, and planet B measures 2 meters.
B) Planet A measures 2 meters, and planet B measures 6 meters.
C) Planet A measures 4.2 meters, and planet B measures 3.8 meters.
D) Planet A measures 3.8 meters, and Planet B measures 4.2 meters.
E) Both Planet A and Planet B measure 4 meters.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
What does it mean to say that an object is in thermal equilibrium?
A) It isn't absorbing any energy.
B) It isn't radiating any energy.
C) It is radiating more energy than it is absorbing.
D) It is absorbing more energy than it is radiating.
E) It is absorbing the same amount of energy that it is radiating.
A) It isn't absorbing any energy.
B) It isn't radiating any energy.
C) It is radiating more energy than it is absorbing.
D) It is absorbing more energy than it is radiating.
E) It is absorbing the same amount of energy that it is radiating.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
If you find that the H-alpha line in a star's spectrum occurs at a wavelength of 656.45 nm, what is the star's radial velocity? Note that the rest wavelength of this line is 656.30 nm.
A) 150 km/s away from you
B) 150 km/s toward you
C) 350 km/s toward you
D) 70 km/s away from you
E) 70 km/s toward you
A) 150 km/s away from you
B) 150 km/s toward you
C) 350 km/s toward you
D) 70 km/s away from you
E) 70 km/s toward you

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
You are driving on the freeway when a police officer records a shift of -7 nm when he or she hits you with a radar gun that operates at a wavelength of 0.1 m. How fast were you going?
A) 43 mph
B) 83 mph
C) 21 mph
D) 65 mph
E) 47 mph
A) 43 mph
B) 83 mph
C) 21 mph
D) 65 mph
E) 47 mph

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
You observe a red star and a blue star and are able to determine that they are the same size. Which star is hotter, and which star is more luminous?
A) The red star is hotter and more luminous.
B) The red star is hotter, and the blue star is more luminous.
C) The blue star is hotter and more luminous.
D) The blue star is hotter, and the red star is more luminous.
E) They have the same luminosities and temperatures.
A) The red star is hotter and more luminous.
B) The red star is hotter, and the blue star is more luminous.
C) The blue star is hotter and more luminous.
D) The blue star is hotter, and the red star is more luminous.
E) They have the same luminosities and temperatures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
At what temperature does water freeze?
A) 0 K
B) 32 K
C) 100 K
D) 273 K
E) 373 K
A) 0 K
B) 32 K
C) 100 K
D) 273 K
E) 373 K

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
You observe the spectrum of two stars. A section of these spectra are shown below. The spectra are different because star A is: 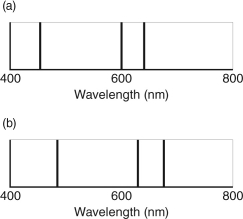
A) cooler than star B
B) farther away from us than star B
C) moving toward us faster than star B
D) made of different elements than star B
E) larger than star B

A) cooler than star B
B) farther away from us than star B
C) moving toward us faster than star B
D) made of different elements than star B
E) larger than star B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
At what wavelength does your body radiate the most given that your temperature is approximately that of the Earth, which is 300 K?
A) 10-5 m
B) 10-3 m
C) 10-2 m
D) 10 m
E) 1,000 m
A) 10-5 m
B) 10-3 m
C) 10-2 m
D) 10 m
E) 1,000 m

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
As a blackbody becomes hotter, it also becomes _________ and _________.
A) more luminous; redder
B) more luminous; bluer
C) less luminous; redder
D) less luminous; bluer
E) more luminous; stays the same color
A) more luminous; redder
B) more luminous; bluer
C) less luminous; redder
D) less luminous; bluer
E) more luminous; stays the same color

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
You record the spectrum of a star and find that a calcium absorption line has an observed wavelength of 394.0 nm. This calcium absorption line has a rest wavelength is 393.3 nm; what is the radial velocity of this star?
A) 5,000 km/s
B) 500 km/s
C) 50 km/s
D) 5 km/s
E) 0.5 km/s
A) 5,000 km/s
B) 500 km/s
C) 50 km/s
D) 5 km/s
E) 0.5 km/s

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which of these stars would have the biggest redshift?
A) a star moving slowly toward you
B) a star moving fast toward you
C) a star moving slowly away from you
D) a star moving fast away from you
E) a star that is not moving away from you or toward you
A) a star moving slowly toward you
B) a star moving fast toward you
C) a star moving slowly away from you
D) a star moving fast away from you
E) a star that is not moving away from you or toward you

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
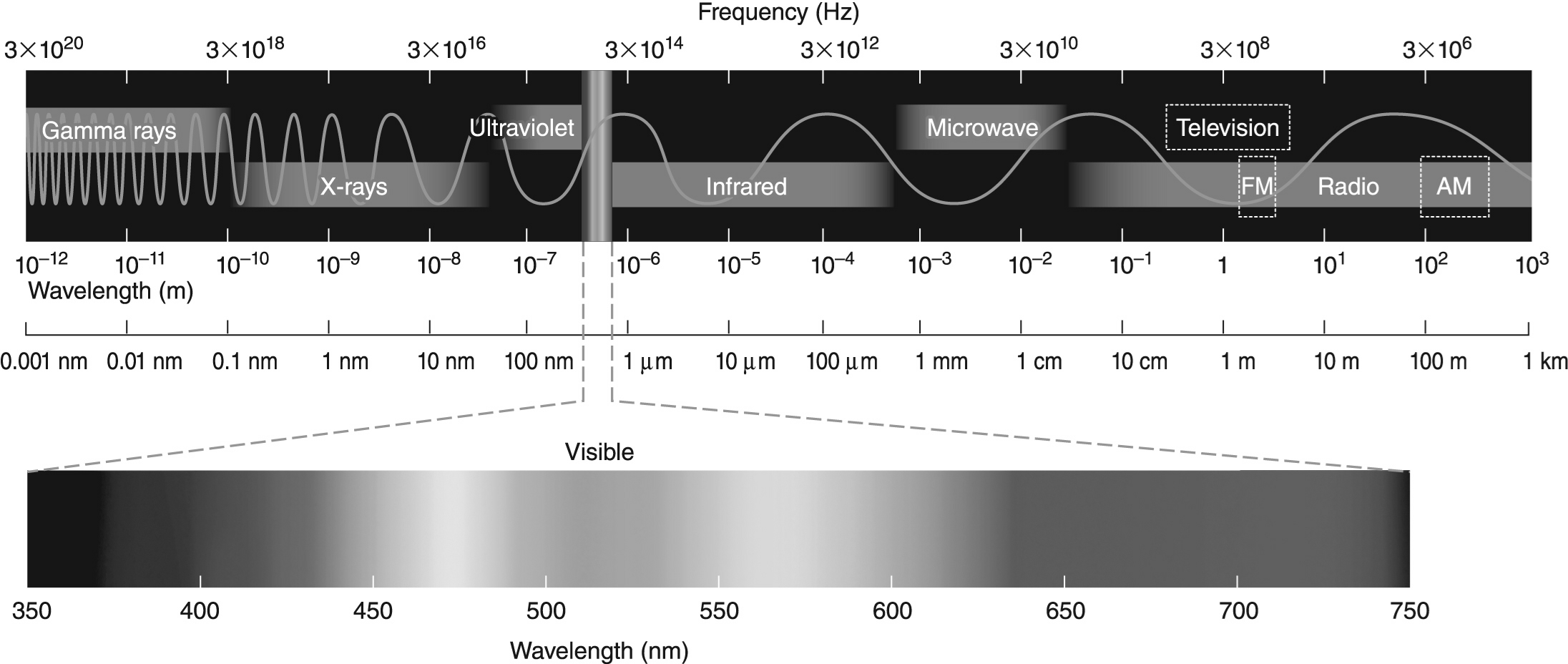 Figure 1
Figure 1-If the typical temperature of a red giant is 3000 K, at what wavelength is its radiation the brightest? Use the electromagnetic spectrum in Figure 1 to help you answer this question.
A) 1 m-infrared wavelengths
B) 1 m-red visible wavelengths
C) 20 m-infrared wavelengths
D) 20 m-red visible wavelengths
E) 700 nm-red visible wavelengths

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
 Figure 1
Figure 1If Jupiter has a temperature of 165 K, then at what wavelength does its spectrum peak? Use the electromagnetic spectrum in Figure 1 to answer this question.
A) 18 nm-orange visible wavelengths
B) 1,800 mm-microwave wavelengths
C) 1,800 nm-infrared wavelengths
D) 18,000 nm-ultraviolet wavelengths
E) 18,000 nm-infrared wavelengths

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
If a star has a peak wavelength of 290 nm, what is its surface temperature?
A) 1000 K
B) 2000 K
C) 5000 K
D) 10,000 K
E) 100,000 K
A) 1000 K
B) 2000 K
C) 5000 K
D) 10,000 K
E) 100,000 K

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The Kelvin temperature scale is used in astronomy because:
A) at 0 K an object has absolutely zero energy
B) water freezes at 0 K
C) water boils at 100 K
D) hydrogen freezes at 0 K
E) the highest temperature possible is 1000 K
A) at 0 K an object has absolutely zero energy
B) water freezes at 0 K
C) water boils at 100 K
D) hydrogen freezes at 0 K
E) the highest temperature possible is 1000 K

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Consider an incandescent light bulb. If you wanted to turn a 10 W light bulb into a 100 W light bulb, how would you change the temperature of the filament inside the bulb?
A) Raise its temperature by a factor of 3.2.
B) Raise its temperature by a factor of 1.8.
C) Raise its temperature by a factor of 10.
D) Lower its temperature by a factor of 2.6.
E) Lower its temperature by a factor of 5.4.
A) Raise its temperature by a factor of 3.2.
B) Raise its temperature by a factor of 1.8.
C) Raise its temperature by a factor of 10.
D) Lower its temperature by a factor of 2.6.
E) Lower its temperature by a factor of 5.4.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Compare two blackbody objects, one at 200 K and one at 400 K. How much larger is the flux from the 400 K object, compared to the flux from the 200 K object?
A) two times larger
B) four times larger
C) eight times larger
D) sixteen times larger
E) They have the same flux.
A) two times larger
B) four times larger
C) eight times larger
D) sixteen times larger
E) They have the same flux.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Why do some stars in the sky appear blue, while other stars appear red?
A) The red stars are hotter on their surfaces than the blue stars.
B) The blue stars are hotter on their surfaces than the red stars.
C) The blue stars are closer to us than the red stars.
D) The red stars are closer to us than the blue stars.
E) The blue stars are moving away from us faster than the red stars.
A) The red stars are hotter on their surfaces than the blue stars.
B) The blue stars are hotter on their surfaces than the red stars.
C) The blue stars are closer to us than the red stars.
D) The red stars are closer to us than the blue stars.
E) The blue stars are moving away from us faster than the red stars.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
A spaceship is traveling toward Earth while giving off a constant radio signal with a wavelength of 1 meter. What will the signal look like to people on Earth?
A) a signal with a wavelength less than 1 m
B) a signal with a wavelength more than 1 m
C) a signal moving faster than the speed of light
D) a signal moving slower than the speed of light
E) a signal with a wavelength of 1 m, moving the normal speed of light
A) a signal with a wavelength less than 1 m
B) a signal with a wavelength more than 1 m
C) a signal moving faster than the speed of light
D) a signal moving slower than the speed of light
E) a signal with a wavelength of 1 m, moving the normal speed of light

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
For a star that lies in the plane of Earth's orbit around the Sun, how does the observed wavelength of the hydrogen absorption line at 656.28 nm in its spectrum change in wavelength (if at all) with the time of year?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
A black car left in the sunlight becomes hotter than a white car left in the sunlight under the same conditions because:
A) the white car absorbs more sunlight than the black car
B) the white car reflects more sunlight than the black car
C) the black car absorbs only blue photons and reflects red photons, whereas the white car absorbs only red photons and reflects blue photons
D) the atoms in the black car are smaller than the atoms in the white car
A) the white car absorbs more sunlight than the black car
B) the white car reflects more sunlight than the black car
C) the black car absorbs only blue photons and reflects red photons, whereas the white car absorbs only red photons and reflects blue photons
D) the atoms in the black car are smaller than the atoms in the white car

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The figure below shows an energy level diagram for a hydrogen atom, with the electron in the n = 4 level. 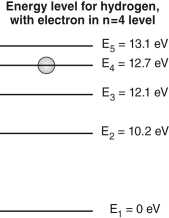 If this atom emitted a photon, what energies could this photon have?
If this atom emitted a photon, what energies could this photon have?
 If this atom emitted a photon, what energies could this photon have?
If this atom emitted a photon, what energies could this photon have?
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
An asteroid with an albedo of 0.1 and a comet with an albedo of 0.6 are orbiting at roughly the same distance from the Sun. How do their temperatures compare?
A) They both have the same temperature.
B) The comet is hotter than the asteroid.
C) The asteroid is hotter than the comet.
D) You must know their sizes to compare their temperatures.
E) You must know their compositions to compare their temperatures.
A) They both have the same temperature.
B) The comet is hotter than the asteroid.
C) The asteroid is hotter than the comet.
D) You must know their sizes to compare their temperatures.
E) You must know their compositions to compare their temperatures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Name four physical properties of an object that we can determine by analyzing the radiation that it emits, and briefly describe how these properties are determined. Cite the names of any laws that apply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Suppose you observe a star emitting a certain emission line of helium at 584.8 nm. The rest wavelength of this line is 587.6 nm. How fast is the star moving? Is it moving toward you or away from you?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Which of these planets would be expected to have the highest average temperature?
A) a light-colored planet close to the Sun
B) a dark-colored planet close to the Sun
C) a light-colored planet far from the Sun
D) a dark-colored planet far from the Sun
E) There is not enough information to know which would be hotter.
A) a light-colored planet close to the Sun
B) a dark-colored planet close to the Sun
C) a light-colored planet far from the Sun
D) a dark-colored planet far from the Sun
E) There is not enough information to know which would be hotter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Which of the following factors does NOT directly influence the temperature of a planet?
A) the luminosity of the Sun
B) the distance of the planet from the Sun
C) the albedo of the planet
D) the size of the planet
E) the atmosphere of the planet
A) the luminosity of the Sun
B) the distance of the planet from the Sun
C) the albedo of the planet
D) the size of the planet
E) the atmosphere of the planet

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
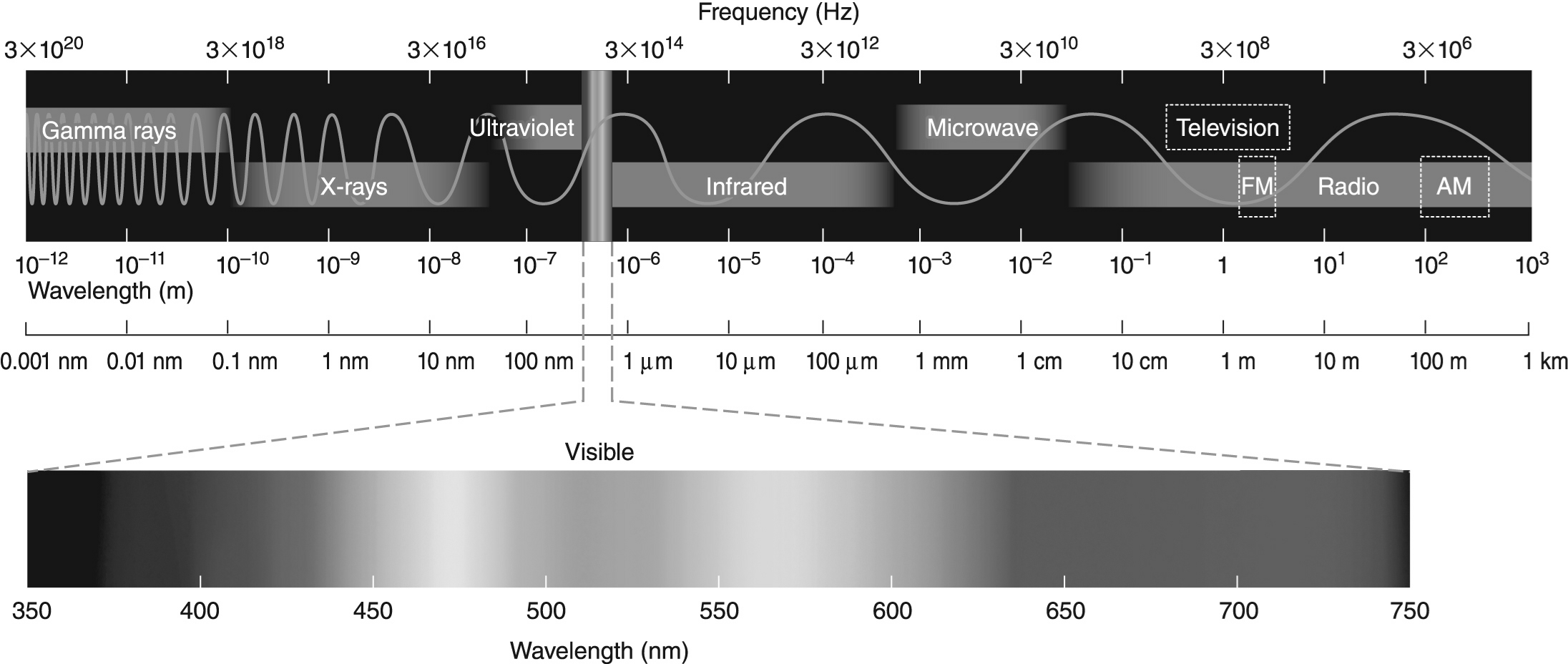 Figure 1
Figure 1-The difference in energy between the n = 2 and n = 1 electronic energy levels in the hydrogen atom is 1.6 * 10-18 J. If an electron moves from the n = 1 level to the n = 2 level, will a photon be emitted or absorbed? What will its energy be, and what type of electromagnetic radiation is it? Use the electromagnetic spectrum shown above to answer this question.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Imagine you observed three different stars: a red star, a blue star, and a yellow star. You are able to determine that each of these stars has the same radius. Answer each question below and explain how you know.
A: Which star is hottest?
B: Which star is the most luminous?
C: Which star is the brightest?
A: Which star is hottest?
B: Which star is the most luminous?
C: Which star is the brightest?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
 Figure 1
Figure 1Describe, in your own words, the fundamental problem with the Bohr model of the atom. (That is, why doesn't an electron orbit a nucleus like a planet does the Sun?)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
The average red giant in the night sky is about 1,000 times more luminous than the average main-sequence star. If both kinds of stars have about the same brightness, how much farther away are the red giants compared to the main-sequence stars?
A) 32 times farther
B) 1,000 times farther
C) 65 times farther
D) 5.6 times farther
E) The red giants and main sequence stars have approximately the same distances.
A) 32 times farther
B) 1,000 times farther
C) 65 times farther
D) 5.6 times farther
E) The red giants and main sequence stars have approximately the same distances.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
If Saturn has a semimajor axis of 10 AU and an albedo of 0.7, what is its expected temperature?
A) 130 K
B) 15 K
C) 35 K
D) 170 K
E) 65 K
A) 130 K
B) 15 K
C) 35 K
D) 170 K
E) 65 K

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Compare and contrast the wavelengths, frequencies, speeds, and energies of red and blue photons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
How much would you have to change the temperature of an object if you wanted to increase its flux by a factor of 100?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Imagine a satellite is orbiting a planet as shown in the image below. This satellite gives off radio waves with a constant wavelength of 1 meter. An observer on Earth then measures the signal from the satellite when it is at the locations labeled A-D. For each of these locations, how does the wavelength received compare to the wavelength that the satellite gave off? 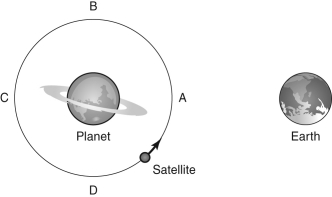


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Why do we see black lines in an absorption spectrum if the absorbed photons are (almost) instantaneously reemitted by the atoms in the cloud?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
How are atoms excited and why do they decay?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Star C and star D have the same luminosity. Star C is twice as far away from Earth as star D. How do the brightnesses of stars C and D compare?
A) Star C appears four times as bright as star D.
B) Star C appears twice as bright as star D.
C) Star D appears twice as bright as star C.
D) Star D appears four times as bright as star C.
E) Stars C and D appear equally bright.
A) Star C appears four times as bright as star D.
B) Star C appears twice as bright as star D.
C) Star D appears twice as bright as star C.
D) Star D appears four times as bright as star C.
E) Stars C and D appear equally bright.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
A spaceship approaches Earth at 0.9 times the speed of light and shines a powerful searchlight onto Earth. How fast will the photons from this searchlight be moving when they hit Earth?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



