Deck 17: Live Fast,die Younghigh-Mass Stellar Evolution
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/70
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 17: Live Fast,die Younghigh-Mass Stellar Evolution
1
Most of the uranium 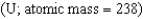 found on the Earth was formed in Type II supernova explosions.
found on the Earth was formed in Type II supernova explosions.
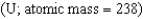 found on the Earth was formed in Type II supernova explosions.
found on the Earth was formed in Type II supernova explosions.True
2
High-mass stars differ from low-mass stars in that they burn helium to carbon when on the main sequence.
False
3
We can determine the age of a star cluster by measuring the color of the reddest red giant stars in the cluster.
False
4
Black holes emit no light whatsoever.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
All evolutionary differences between high- and low-mass stars can be attributed to differences in the amount of gravity each star possesses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Gravitational lensing allows us to see distant objects that would otherwise be blocked by a star or galaxy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Einstein's special theory of relativity implies that if a person standing at the front of a train traveling at 0.1 km/s shines a flashlight out in front of the train,the emitted photons will travel at a speed of 300,000.1 km/s.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Fusion reactions that create chemical elements heavier than oxygen require energy input,thus these reactions cannot provide a star with power.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The densest state of matter found in nature occurs inside a white dwarf star.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The production of large numbers of neutrons in nuclear reactions at the core of a massive star helps rob the core of energy and speeds its eventual collapse.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
As a high-mass main-sequence star evolves off the main sequence,it follows a __________ on the H-R diagram.
A) nearly vertical path
B) path of constant radius
C) roughly horizontal path
D) None of the above answers is correct.
A) nearly vertical path
B) path of constant radius
C) roughly horizontal path
D) None of the above answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A Cepheid star varies in luminosity because
A) the entire star pulsates from its core to its surface.
B) the outer envelope of the star pulsates.
C) the star rotates too quickly.
D) the star is too massive to be stable.
A) the entire star pulsates from its core to its surface.
B) the outer envelope of the star pulsates.
C) the star rotates too quickly.
D) the star is too massive to be stable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Hydrogen burns through the CNO cycle only in high-mass main-sequence stars because of the greater __________ in their cores.
A) concentration of heavy elements like carbon
B) densities
C) abundance of hydrogen
D) temperatures
A) concentration of heavy elements like carbon
B) densities
C) abundance of hydrogen
D) temperatures

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Special relativity says that moving clocks run slower.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Every pulsar is a neutron star,but not every neutron star is a pulsar.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Gravity is nothing more than a curvature in the fabric of spacetime.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
An 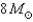 star will eventually die as a Type I supernova.
star will eventually die as a Type I supernova.
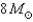 star will eventually die as a Type I supernova.
star will eventually die as a Type I supernova.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Pulsating variable stars are more commonly known as pulsars.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Black holes have an infinitely small radius,but a finite event horizon.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Type I and Type II supernovae are approximately equal in luminosity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Using the Hubble Space Telescope,you discover a Cepheid variable star in a nearby galaxy that has a period of 10 days and an apparent magnitude of 20.If nearby Cepheids follow a period-luminosity relationship that says the luminosity of the star is 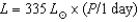 then what is this Cepheid's absolute magnitude and distance? Note that the Sun's absolute magnitude is 5.
then what is this Cepheid's absolute magnitude and distance? Note that the Sun's absolute magnitude is 5.
A) -13 and 60 kpc
B) -13 and 10 Mpc
C) -4 and 600 kpc
D) -4 and 1 Mpc
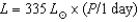 then what is this Cepheid's absolute magnitude and distance? Note that the Sun's absolute magnitude is 5.
then what is this Cepheid's absolute magnitude and distance? Note that the Sun's absolute magnitude is 5.A) -13 and 60 kpc
B) -13 and 10 Mpc
C) -4 and 600 kpc
D) -4 and 1 Mpc

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
When the core of a massive star collapses,a neutron star forms because
A) all the charged particles are ejected in the resulting explosion.
B) protons and electrons combine to minimize electromagnetic forces.
C) iron nuclei disintegrate into neutrons.
D) neutrinos escaping from the core carry away most of the electromagnetic charge.
A) all the charged particles are ejected in the resulting explosion.
B) protons and electrons combine to minimize electromagnetic forces.
C) iron nuclei disintegrate into neutrons.
D) neutrinos escaping from the core carry away most of the electromagnetic charge.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Essentially all the elements heavier than iron in our galaxy were formed
A) by supernovae.
B) during the formation of black holes.
C) by fusion in the cores of the most massive main-sequence stars.
D) during the formation of planetary nebulae.
A) by supernovae.
B) during the formation of black holes.
C) by fusion in the cores of the most massive main-sequence stars.
D) during the formation of planetary nebulae.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The Type II supernova that created the Crab Nebula was seen by Chinese and Arab astronomers in the year A.D.1054.Because the star is 6,500 light-years away from us,we know the star exploded in the year
A) A.D.7554
B) A.D.1054
C) 5446 B.C.
D) 7554 B.C.
A) A.D.7554
B) A.D.1054
C) 5446 B.C.
D) 7554 B.C.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
What characteristic of a star cluster is used to determine its age?
A) The chemical composition of stars in the cluster
B) The luminosity of the faintest stars in the cluster
C) The color of the main sequence turnoff in the cluster
D) The total number of stars in the cluster
A) The chemical composition of stars in the cluster
B) The luminosity of the faintest stars in the cluster
C) The color of the main sequence turnoff in the cluster
D) The total number of stars in the cluster

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Why does the luminosity of a high-mass star remain nearly constant as the star burns heavy elements in its core,even though it is producing millions of times more energy per second than it did on the main sequence?
A) Most of the energy is trapped in the core,increasing the core's temperature.
B) All of the extra energy goes into heating the shells of fusion surrounding the core.
C) Most of the energy is absorbed by the outer layers of the star,increasing the star's radius but leaving its luminosity unchanged.
D) Most of the energy is carried out of the star by escaping neutrinos.
A) Most of the energy is trapped in the core,increasing the core's temperature.
B) All of the extra energy goes into heating the shells of fusion surrounding the core.
C) Most of the energy is absorbed by the outer layers of the star,increasing the star's radius but leaving its luminosity unchanged.
D) Most of the energy is carried out of the star by escaping neutrinos.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the following is NOT a common characteristic of a neutron star?
A) Extremely high density
B) Enormous magnetic field
C) Very short rotation period
D) All of these are common characteristics of a neutron star.
A) Extremely high density
B) Enormous magnetic field
C) Very short rotation period
D) All of these are common characteristics of a neutron star.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
An iron core cannot support a massive main-sequence star because
A) iron has poor nuclear binding energy.
B) iron cannot fuse with other nuclei to produce energy.
C) iron supplies too much pressure.
D) iron fusion only occurs in a degenerate core.
A) iron has poor nuclear binding energy.
B) iron cannot fuse with other nuclei to produce energy.
C) iron supplies too much pressure.
D) iron fusion only occurs in a degenerate core.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
If a 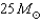 main-sequence star loses mass at a rate of
main-sequence star loses mass at a rate of 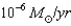 then how much mass will it lose in its 3-million-year lifetime?
then how much mass will it lose in its 3-million-year lifetime?
A)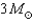
B)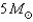
C)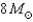
D)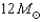
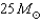 main-sequence star loses mass at a rate of
main-sequence star loses mass at a rate of 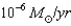 then how much mass will it lose in its 3-million-year lifetime?
then how much mass will it lose in its 3-million-year lifetime?A)
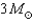
B)
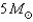
C)
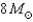
D)
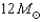

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
If you measure the average brightness and pulsation period of a Cepheid variable star,you can also determine its
A) age.
B) rotation period.
C) distance.
D) mass.
A) age.
B) rotation period.
C) distance.
D) mass.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The main difference between Cepheid variable stars and RR Lyrae stars is
A) their pulsation mechanisms.
B) their masses.
C) that Cepheids form at much greater distances from Earth.
D) that RR Lyrae were discovered much earlier than Cepheids.
A) their pulsation mechanisms.
B) their masses.
C) that Cepheids form at much greater distances from Earth.
D) that RR Lyrae were discovered much earlier than Cepheids.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
During the main-sequence evolution of a massive star,increasingly heavier elements are fused in the core,giving the core support for
A) decreasingly shorter times.
B) increasingly longer times.
C) an approximately equal amount of time.
D) approximately 10,000 years.
A) decreasingly shorter times.
B) increasingly longer times.
C) an approximately equal amount of time.
D) approximately 10,000 years.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Neutron stars have masses that range from
A)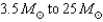 .
.
B)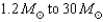 .
.
C)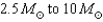 .
.
D)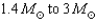 .
.
A)
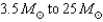 .
.B)
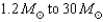 .
.C)
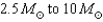 .
.D)
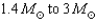 .
.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Once silicon burning begins to fuse iron in the core of a high-mass main-sequence star,it only has a few __________ left to live.
A) seconds
B) days
C) months
D) years
A) seconds
B) days
C) months
D) years

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
What is the minimum mass main-sequence star that becomes a Type II supernova?
A)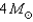
B)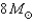
C)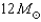
D)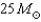
A)
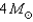
B)
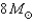
C)
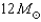
D)
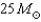

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The collapse of the core of a high-mass star at the end of its life lasts approximately
A) one second.
B) one hour.
C) one week.
D) one year.
A) one second.
B) one hour.
C) one week.
D) one year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
A neutron star contains a mass of up to 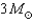 in a sphere with a diameter approximately the size of
in a sphere with a diameter approximately the size of
A) an atomic nucleus.
B) a school bus.
C) a city.
D) the Earth.
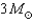 in a sphere with a diameter approximately the size of
in a sphere with a diameter approximately the size ofA) an atomic nucleus.
B) a school bus.
C) a city.
D) the Earth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
We can identify only a small fraction of all the pulsars that exist in our galaxy because
A) gas and dust efficiently block radio photons.
B) few swing their beam of synchrotron emission in our direction.
C) most have evolved to become black holes,which emit no light.
D) massive stars are very rare.
A) gas and dust efficiently block radio photons.
B) few swing their beam of synchrotron emission in our direction.
C) most have evolved to become black holes,which emit no light.
D) massive stars are very rare.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Suppose you measured H-R diagrams for the two star clusters pictured below.Which of the following statements is TRUE? 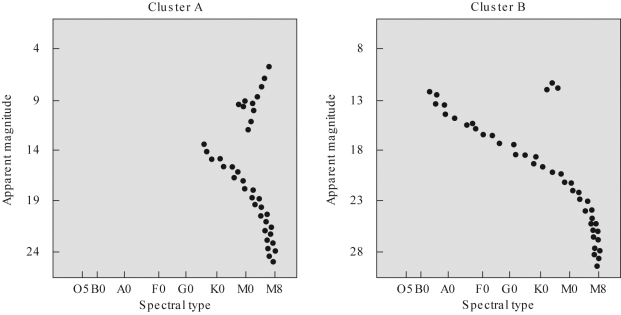
A) Cluster A is younger than Cluster B.
B) Cluster A is closer to us than Cluster B.
C) Both a and b are TRUE.
D) Both a and b are FALSE.

A) Cluster A is younger than Cluster B.
B) Cluster A is closer to us than Cluster B.
C) Both a and b are TRUE.
D) Both a and b are FALSE.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
You observed three different star clusters and found that the main-sequence turnoff stars in Cluster 1 had spectral type A,the main-sequence turnoff stars in Cluster 2 had spectral type B,and the main-sequence turnoff stars in Cluster 3 had spectral type G.Which star cluster is the youngest?
A) Cluster 1
B) Cluster 2
C) Cluster 3
D) It is impossible to determine their ages given only the spectral types.
A) Cluster 1
B) Cluster 2
C) Cluster 3
D) It is impossible to determine their ages given only the spectral types.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Name two processes that speed the collapse of the core of a dying high-mass star.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
If an 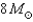 star loses mass at an average rate of
star loses mass at an average rate of 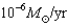 in a stellar wind,how many years would it take for its mass be reduced to
in a stellar wind,how many years would it take for its mass be reduced to 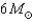 ? Would this amount of mass loss be possible in the star's lifetime?
? Would this amount of mass loss be possible in the star's lifetime?
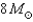 star loses mass at an average rate of
star loses mass at an average rate of 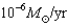 in a stellar wind,how many years would it take for its mass be reduced to
in a stellar wind,how many years would it take for its mass be reduced to 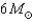 ? Would this amount of mass loss be possible in the star's lifetime?
? Would this amount of mass loss be possible in the star's lifetime?
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Gravitational lensing occurs when __________ distorts the fabric of spacetime.
A) a star
B) dark matter
C) a black hole
D) any massive object
A) a star
B) dark matter
C) a black hole
D) any massive object

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
An indestructible robot would feel __________ as it crossed the event horizon of a black hole.
A) incredibly strong tidal forces
B) intense heating
C) intense gravitational stretching
D) nothing
A) incredibly strong tidal forces
B) intense heating
C) intense gravitational stretching
D) nothing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Photons have no mass,and Einstein's theory of general relativity says
A) their paths through spacetime are curved in the presence of a massive body.
B) their apparent speeds depend on the observer's frame of reference.
C) they should not be attracted to a massive object.
D) their wavelengths must remain the same as they travel through spacetime.
A) their paths through spacetime are curved in the presence of a massive body.
B) their apparent speeds depend on the observer's frame of reference.
C) they should not be attracted to a massive object.
D) their wavelengths must remain the same as they travel through spacetime.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
If the Earth were to be condensed down in size until it became a black hole,its Schwarzschild radius would be
A) 1 cm.
B) 1 m.
C) 1 km.
D) 10 km.
A) 1 cm.
B) 1 m.
C) 1 km.
D) 10 km.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Light is increasingly redshifted near a black hole because
A) the photons are moving away from us very quickly as they are sucked into the black hole.
B) the photons are moving increasingly faster in order to escape the pull of the black hole.
C) time is moving increasingly slower in the observer's frame of reference.
D) the curvature of spacetime is increasingly stretched near the black hole,which in turn stretches the wavelengths of the photons.
A) the photons are moving away from us very quickly as they are sucked into the black hole.
B) the photons are moving increasingly faster in order to escape the pull of the black hole.
C) time is moving increasingly slower in the observer's frame of reference.
D) the curvature of spacetime is increasingly stretched near the black hole,which in turn stretches the wavelengths of the photons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Why do large,high-mass main-sequence stars never become red giants?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
While traveling the galaxy in a spacecraft,you and a colleague set out to investigate the 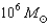 black hole at the center of our galaxy.Your colleague hops aboard an escape pod and drops into a circular orbit around the black hole,maintaining a distance of 1 AU,while you remain much farther away in the spacecraft.After doing some experiments to measure the strength of gravity,your colleague signals his/her results back to you using a green laser.What would you see?
black hole at the center of our galaxy.Your colleague hops aboard an escape pod and drops into a circular orbit around the black hole,maintaining a distance of 1 AU,while you remain much farther away in the spacecraft.After doing some experiments to measure the strength of gravity,your colleague signals his/her results back to you using a green laser.What would you see?
A) His/her signals,because he/she is orbiting well outside the event horizon that lies 0.02 AU from the black hole.
B) His/her signals,but shifted to a much redder wavelength because he/she is close to the event horizon that lies 0.8 AU from the black hole.
C) Nothing,because your colleague has crossed the event horizon that lies 8 AU from the black hole.
D) Nothing,because no light can escape the gravitational pull of a black hole no matter how close he/she is to it.
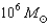 black hole at the center of our galaxy.Your colleague hops aboard an escape pod and drops into a circular orbit around the black hole,maintaining a distance of 1 AU,while you remain much farther away in the spacecraft.After doing some experiments to measure the strength of gravity,your colleague signals his/her results back to you using a green laser.What would you see?
black hole at the center of our galaxy.Your colleague hops aboard an escape pod and drops into a circular orbit around the black hole,maintaining a distance of 1 AU,while you remain much farther away in the spacecraft.After doing some experiments to measure the strength of gravity,your colleague signals his/her results back to you using a green laser.What would you see?A) His/her signals,because he/she is orbiting well outside the event horizon that lies 0.02 AU from the black hole.
B) His/her signals,but shifted to a much redder wavelength because he/she is close to the event horizon that lies 0.8 AU from the black hole.
C) Nothing,because your colleague has crossed the event horizon that lies 8 AU from the black hole.
D) Nothing,because no light can escape the gravitational pull of a black hole no matter how close he/she is to it.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which of the following is a consequence of Einstein's special theory of relativity?
A) Moving clocks run quicker.
B) The velocity of light depends on the speed of the observer.
C) Distances appear shorter when traveling near the speed of light.
D) Gravity arises because mass distorts spacetime.
A) Moving clocks run quicker.
B) The velocity of light depends on the speed of the observer.
C) Distances appear shorter when traveling near the speed of light.
D) Gravity arises because mass distorts spacetime.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
__________ is the result of mass distorting the fabric of spacetime.
A) Energy
B) Radiation
C) Fusion
D) Gravity
A) Energy
B) Radiation
C) Fusion
D) Gravity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The event horizon of a black hole is defined as
A) the point of maximum gravity.
B) the radius of the original neutron star before it became a black hole.
C) the point at which shock waves emanate from the strong gravitational distortion the black hole creates in the fabric of spacetime.
D) the radius at which the escape speed equals the speed of light.
A) the point of maximum gravity.
B) the radius of the original neutron star before it became a black hole.
C) the point at which shock waves emanate from the strong gravitational distortion the black hole creates in the fabric of spacetime.
D) the radius at which the escape speed equals the speed of light.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
With the Hubble Space Telescope,you discover a Cepheid variable star in a nearby galaxy that has a period of 30 days.If nearby Cepheids follow a period-luminosity relationship that says the luminosity of the star is 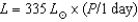 ,then what is this Cepheid's luminosity and absolute magnitude? Recall that the Sun's absolute magnitude is
,then what is this Cepheid's luminosity and absolute magnitude? Recall that the Sun's absolute magnitude is 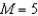 .If the apparent magnitude of the Cepheid is 25,what is this galaxy's distance in Mpc?
.If the apparent magnitude of the Cepheid is 25,what is this galaxy's distance in Mpc?
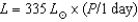 ,then what is this Cepheid's luminosity and absolute magnitude? Recall that the Sun's absolute magnitude is
,then what is this Cepheid's luminosity and absolute magnitude? Recall that the Sun's absolute magnitude is 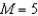 .If the apparent magnitude of the Cepheid is 25,what is this galaxy's distance in Mpc?
.If the apparent magnitude of the Cepheid is 25,what is this galaxy's distance in Mpc?
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
How do Cepheid variable stars differ from RR Lyrae variable stars in their masses,luminosities,and periods?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
If the Sun were to be instantly replaced by a 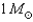 black hole,the gravitational pull of the black hole on Earth would be
black hole,the gravitational pull of the black hole on Earth would be
A) much greater than it is now.
B) the same as it is now.
C) much smaller than it is now.
D) irrelevant because Earth would be quickly obliterated by the strong tidal force of the black hole.
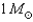 black hole,the gravitational pull of the black hole on Earth would be
black hole,the gravitational pull of the black hole on Earth would beA) much greater than it is now.
B) the same as it is now.
C) much smaller than it is now.
D) irrelevant because Earth would be quickly obliterated by the strong tidal force of the black hole.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The equivalence principle says that
A) being stationary in a gravitational field is the same as being in an accelerated reference frame.
B) the universe is homogeneous and isotropic.
C) at any radius inside a star the outward gas pressure must balance the weight of the material on top.
D) mass and energy are interchangeable and neither can be destroyed.
A) being stationary in a gravitational field is the same as being in an accelerated reference frame.
B) the universe is homogeneous and isotropic.
C) at any radius inside a star the outward gas pressure must balance the weight of the material on top.
D) mass and energy are interchangeable and neither can be destroyed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Hawking radiation is emitted by a black hole when
A) the black hole rotates quickly.
B) the black hole accretes material.
C) a virtual pair of particles is created from the vacuum of space.
D) synchrotron radiation is emitted by infalling charged particles.
A) the black hole rotates quickly.
B) the black hole accretes material.
C) a virtual pair of particles is created from the vacuum of space.
D) synchrotron radiation is emitted by infalling charged particles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Black holes that are stellar remnants can be found by searching for
A) dark regions at the centers of galaxies.
B) variable X-ray sources.
C) extremely luminous infrared objects.
D) objects that emit very faint radio emission.
A) dark regions at the centers of galaxies.
B) variable X-ray sources.
C) extremely luminous infrared objects.
D) objects that emit very faint radio emission.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
What would happen if mass were continually added to a 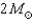 neutron star?
neutron star?
A) The star's radius would increase.
B) The star would eventually become a black hole.
C) The star would erupt as a nova.
D) All of the above would occur.
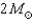 neutron star?
neutron star?A) The star's radius would increase.
B) The star would eventually become a black hole.
C) The star would erupt as a nova.
D) All of the above would occur.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Why do main-sequence high-mass stars lose so much mass compared to low-mass stars?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Suppose you measured H-R diagrams for the two star clusters pictured below.Which cluster is older? Which cluster is farther away? Explain why. 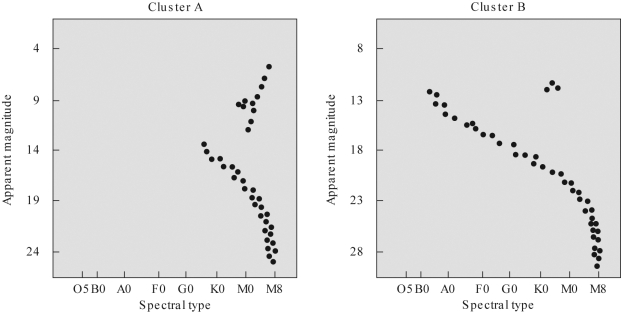


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Galileo supposedly experimented with gravity by dropping two objects of different masses from the leaning tower of Pisa at the same instant and observing that they hit the ground at the same time.If Albert Einstein had done the experiment,how would his conclusion have differed from Galileo's?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Which has a smaller radius,a 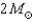 neutron star or a
neutron star or a 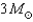 neutron star? What supports each of these stars from collapsing to form a black hole?
neutron star? What supports each of these stars from collapsing to form a black hole?
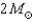 neutron star or a
neutron star or a 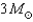 neutron star? What supports each of these stars from collapsing to form a black hole?
neutron star? What supports each of these stars from collapsing to form a black hole?
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
While traveling the galaxy in a spacecraft,you and a colleague set out to investigate a 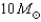 black hole.Your colleague hops aboard an escape pod and drops into a circular orbit around the black hole maintaining a distance of 50 km from it,while you remain much farther away inside the spacecraft.After doing some experiments to measure the strength of gravity,your colleague signals the results back to you using a green laser.What would you see,and why?
black hole.Your colleague hops aboard an escape pod and drops into a circular orbit around the black hole maintaining a distance of 50 km from it,while you remain much farther away inside the spacecraft.After doing some experiments to measure the strength of gravity,your colleague signals the results back to you using a green laser.What would you see,and why?
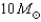 black hole.Your colleague hops aboard an escape pod and drops into a circular orbit around the black hole maintaining a distance of 50 km from it,while you remain much farther away inside the spacecraft.After doing some experiments to measure the strength of gravity,your colleague signals the results back to you using a green laser.What would you see,and why?
black hole.Your colleague hops aboard an escape pod and drops into a circular orbit around the black hole maintaining a distance of 50 km from it,while you remain much farther away inside the spacecraft.After doing some experiments to measure the strength of gravity,your colleague signals the results back to you using a green laser.What would you see,and why?
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
What is the difference between the singularity and the event horizon of a black hole?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Although a Type II supernova shines with a luminosity of 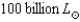 ,most of the energy in the explosion is emitted in another way.What is it,and how much more energy does it carry compared to the light?
,most of the energy in the explosion is emitted in another way.What is it,and how much more energy does it carry compared to the light?
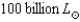 ,most of the energy in the explosion is emitted in another way.What is it,and how much more energy does it carry compared to the light?
,most of the energy in the explosion is emitted in another way.What is it,and how much more energy does it carry compared to the light?
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Explain why Einstein's theory of general relativity predicts the existence of gravitational lensing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Explain why a blue star cluster is likely younger than a red star cluster.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Suppose we discovered radio signals coming from the star Alpha Centauri,whose distance is 4.4 light-years from us,and we sent a crew in a spacecraft to visit it.If the spacecraft used revolutionary technology allowing it to travel at a speed of 0.5 c,how long would it take the spacecraft to get to Alpha Centauri,and how long a time would the astronauts say passed during the trip? (Ignore the time it would take to accelerate the spacecraft to reach a velocity of 0.5 c.)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Suppose you observe three star clusters.Cluster 1 has a main-sequence turnoff point at spectral type G,Cluster 2 has a turnoff point at spectral type A,and Cluster 3 has a turnoff point at spectral type B.Which cluster is youngest and which is oldest? Explain why.What is the approximate age of the oldest cluster?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



