Deck 6: Making War and Republican Governments, 1776-1789
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/81
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 6: Making War and Republican Governments, 1776-1789
1
Which of the following statements characterizes events at Valley Forge in the winter of 1777-1778?
A) The Continental army was ill-equipped,but the British troops in nearby Philadelphia also struggled to find adequate food and shelter during the harsh winter.
B) Through the training of Baron von Steuben,the Continental army emerged as a much tougher and better-disciplined force.
C) Of the 30,000 troops encamped at Valley Forge,one-third deserted and another third died of malnutrition or disease before the winter was over.
D) The sufferings of the Continental army were largely a myth,disseminated to win greater sympathy for the Patriot cause.
A) The Continental army was ill-equipped,but the British troops in nearby Philadelphia also struggled to find adequate food and shelter during the harsh winter.
B) Through the training of Baron von Steuben,the Continental army emerged as a much tougher and better-disciplined force.
C) Of the 30,000 troops encamped at Valley Forge,one-third deserted and another third died of malnutrition or disease before the winter was over.
D) The sufferings of the Continental army were largely a myth,disseminated to win greater sympathy for the Patriot cause.
Through the training of Baron von Steuben,the Continental army emerged as a much tougher and better-disciplined force.
2
France gave serious consideration to an alliance with the rebel colonies primarily because it regarded the war as an opportunity to
A) exact revenge on Britain for defeat in the French and Indian War and the loss of Canada.
B) defend Catholics in Maryland and Quebec against the potentially hostile Protestant Patriots.
C) annex Maine and regain the province of Quebec that it had lost during the Great War for Empire.
D) persuade the Americans to accept King Louis XVI's younger brother as their new constitutional monarch.
A) exact revenge on Britain for defeat in the French and Indian War and the loss of Canada.
B) defend Catholics in Maryland and Quebec against the potentially hostile Protestant Patriots.
C) annex Maine and regain the province of Quebec that it had lost during the Great War for Empire.
D) persuade the Americans to accept King Louis XVI's younger brother as their new constitutional monarch.
exact revenge on Britain for defeat in the French and Indian War and the loss of Canada.
3
Why was the Battle of Saratoga historically significant?
A) It lulled the British into a false sense of security.
B) The victory ensured the French would join in an alliance with the Americans.
C) The British captured more than 5,000 American troops.
D) The loss showed the need for better training for the Patriot troops.
A) It lulled the British into a false sense of security.
B) The victory ensured the French would join in an alliance with the Americans.
C) The British captured more than 5,000 American troops.
D) The loss showed the need for better training for the Patriot troops.
The victory ensured the French would join in an alliance with the Americans.
4
Which of the following statements characterizes the relative military strengths of the British and Patriot forces during the Revolutionary War?
A) The Patriots could count on more help from Indians than could the British.
B) The Americans relied mostly on a standing army of about 48,000 men.
C) Due to American shipbuilding,American naval strength roughly matched that of the British Navy.
D) The British could expect support from thousands of Loyalists in the colonies and many Indian tribes.
A) The Patriots could count on more help from Indians than could the British.
B) The Americans relied mostly on a standing army of about 48,000 men.
C) Due to American shipbuilding,American naval strength roughly matched that of the British Navy.
D) The British could expect support from thousands of Loyalists in the colonies and many Indian tribes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
How did the finances of the Continental Congress compare to those of the states during the first two years of the Revolutionary War?
A) While states suffered from the lack of funds,the Continental Congress achieved financial solvency through tax collection.
B) Like the states,the Continental Congress lacked income and issued paper money in an effort to sustain itself.
C) The states collected sufficient revenue through tax collection,but the Continental Congress lacked the authority to tax.
D) Because they benefitted from both land and excise taxes,neither the states nor the Continental Congress experienced financial burdens at this time.
A) While states suffered from the lack of funds,the Continental Congress achieved financial solvency through tax collection.
B) Like the states,the Continental Congress lacked income and issued paper money in an effort to sustain itself.
C) The states collected sufficient revenue through tax collection,but the Continental Congress lacked the authority to tax.
D) Because they benefitted from both land and excise taxes,neither the states nor the Continental Congress experienced financial burdens at this time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Through which of the following actions did Sir Henry Clinton launch his southern campaign in 1778?
A) Capturing Savannah,Georgia,and mobilizing hundreds of blacks
B) Advancing his troops from Philadelphia toward Virginia to entrap Washington's army
C) Issuing the Philipsburg Proclamation,promising freedom to rebel slaves
D) Fortifying his position at Philadelphia and daring Washington to attack him
A) Capturing Savannah,Georgia,and mobilizing hundreds of blacks
B) Advancing his troops from Philadelphia toward Virginia to entrap Washington's army
C) Issuing the Philipsburg Proclamation,promising freedom to rebel slaves
D) Fortifying his position at Philadelphia and daring Washington to attack him

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following factors posed a major problem for the colonies during the American Revolution?
A) The absence of allies
B) Slave insurrections
C) The high price and scarcity of goods
D) A depressed economy
A) The absence of allies
B) Slave insurrections
C) The high price and scarcity of goods
D) A depressed economy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following statements describes the American Revolution's impact on civilians in areas that saw military conflicts?
A) Wartime violence was limited to the battlefield and nearby civilians were left unharmed.
B) British troops frequently attacked civilian targets despite Patriots' efforts to protect them.
C) British troops followed the laws of war,but Americans frequently targeted Loyalist civilians.
D) Both British and American troops were known to loot farms and harass and rape civilian women.
A) Wartime violence was limited to the battlefield and nearby civilians were left unharmed.
B) British troops frequently attacked civilian targets despite Patriots' efforts to protect them.
C) British troops followed the laws of war,but Americans frequently targeted Loyalist civilians.
D) Both British and American troops were known to loot farms and harass and rape civilian women.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
What spurred the British Parliament to repeal the Tea Act in 1778?
A) The British East India Tea Company had resurged and the American market was no longer needed.
B) British tea merchants finally succeeded in convincing members of Parliament that they needed the American market.
C) The British blockade of the Atlantic coast prevented trade and the Tea Act was no longer necessary.
D) Parliament hoped it would aid Britain's efforts to seek a negotiated peace with the Continental Congress.
A) The British East India Tea Company had resurged and the American market was no longer needed.
B) British tea merchants finally succeeded in convincing members of Parliament that they needed the American market.
C) The British blockade of the Atlantic coast prevented trade and the Tea Act was no longer necessary.
D) Parliament hoped it would aid Britain's efforts to seek a negotiated peace with the Continental Congress.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of these events occurred at the Battle of Long Island in August 1776?
A) General Howe and his British troops forced the Americans to retreat to Manhattan Island.
B) General Washington and the Continental army won their first major victory over British forces.
C) The Continental troops quickly surrendered and General Washington barely escaped.
D) Benedict Arnold surrendered a strategic fort to the British,helping them to win the battle.
A) General Howe and his British troops forced the Americans to retreat to Manhattan Island.
B) General Washington and the Continental army won their first major victory over British forces.
C) The Continental troops quickly surrendered and General Washington barely escaped.
D) Benedict Arnold surrendered a strategic fort to the British,helping them to win the battle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
How did the British respond after their loss at the Battle of Saratoga in 1777?
A) The British doubled the size of its army in the colonies.
B) They tried to broker a negotiated settlement with the Americans.
C) Britain attempted to bolster its forces by a military alliance with Spain.
D) The British retreated to ships in New York Harbor to consider their options.
A) The British doubled the size of its army in the colonies.
B) They tried to broker a negotiated settlement with the Americans.
C) Britain attempted to bolster its forces by a military alliance with Spain.
D) The British retreated to ships in New York Harbor to consider their options.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following statements describes British military strategy during the first two years of the Revolutionary War?
A) The British were content to demonstrate their superior power and tactics in the hopes of convincing the rebels to surrender.
B) The British harassed the Continental army ruthlessly,but with great luck,Washington and his troops repeatedly escaped.
C) With the Atlantic standing between them and their country,the British relied on the Loyalists for supplies.
D) The British used guerrilla tactics instead of conventional warfare,attempting to outmaneuver the rebels and force their surrender.
A) The British were content to demonstrate their superior power and tactics in the hopes of convincing the rebels to surrender.
B) The British harassed the Continental army ruthlessly,but with great luck,Washington and his troops repeatedly escaped.
C) With the Atlantic standing between them and their country,the British relied on the Loyalists for supplies.
D) The British used guerrilla tactics instead of conventional warfare,attempting to outmaneuver the rebels and force their surrender.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following was an advantage for the English at the outset of the American Revolution?
A) Fighting a defensive war
B) A more motivated military
C) Outdated weaponry
D) Experienced and well-trained recruits
A) Fighting a defensive war
B) A more motivated military
C) Outdated weaponry
D) Experienced and well-trained recruits

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following was a consequence of the large increase in paper currency in circulation in the states during the Revolutionary War years?
A) Paper currency made it easier for American families to buy goods.
B) It caused many Loyalists to switch their allegiance to the Patriot cause.
C) The printing of additional bills allowed most Americans to become very wealthy.
D) The paper bills quickly fell in value,becoming nearly worthless.
A) Paper currency made it easier for American families to buy goods.
B) It caused many Loyalists to switch their allegiance to the Patriot cause.
C) The printing of additional bills allowed most Americans to become very wealthy.
D) The paper bills quickly fell in value,becoming nearly worthless.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following describes the Continental army during the Revolutionary War?
A) Although it grew slowly,the force numbered 75,000 men at its peak.
B) It consisted mainly of yeomen farmers and well-to-do young Patriots.
C) Most of its recruits were poor native-born youths and older foreign-born men.
D) Its morale and discipline exceeded the British army's because it was fighting for a patriotic cause.
A) Although it grew slowly,the force numbered 75,000 men at its peak.
B) It consisted mainly of yeomen farmers and well-to-do young Patriots.
C) Most of its recruits were poor native-born youths and older foreign-born men.
D) Its morale and discipline exceeded the British army's because it was fighting for a patriotic cause.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The Treaty of Alliance that the French and Americans signed in 1778 included which of the following stipulations?
A) American generals would not interfere with French troops' weekly Catholic mass attendance.
B) The French would aid the Americans but refrain from seeking new territory in the West Indies.
C) If the Americans won,they would never interfere with French territory west of the Mississippi.
D) Neither side would sign a separate peace that failed to recognize American independence.
A) American generals would not interfere with French troops' weekly Catholic mass attendance.
B) The French would aid the Americans but refrain from seeking new territory in the West Indies.
C) If the Americans won,they would never interfere with French territory west of the Mississippi.
D) Neither side would sign a separate peace that failed to recognize American independence.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
What was significant about George Washington's leading of his troops across the Delaware River on Christmas night in 1776?
A) It was the first time Washington had shown decisive leadership and it saved his job.
B) Washington's action surprised the enemy and gave the Americans their first real victory.
C) His failed effort to cross the frozen river resulted in the deaths of 200 American troops.
D) The event allowed the Continental Army to retake New Jersey and most of Long Island.
A) It was the first time Washington had shown decisive leadership and it saved his job.
B) Washington's action surprised the enemy and gave the Americans their first real victory.
C) His failed effort to cross the frozen river resulted in the deaths of 200 American troops.
D) The event allowed the Continental Army to retake New Jersey and most of Long Island.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The British strategy in its military campaign in the South in 1778 relied on which of the following factors?
A) A plan to use Loyalists to fight backcountry Patriots
B) Their refusal to exploit racial divisions,fearing that such a strategy might backfire
C) A plan to use Loyalists to administer the territories they expected to capture
D) Quick and easy victory in Virginia,which they viewed as the most important southern colony
A) A plan to use Loyalists to fight backcountry Patriots
B) Their refusal to exploit racial divisions,fearing that such a strategy might backfire
C) A plan to use Loyalists to administer the territories they expected to capture
D) Quick and easy victory in Virginia,which they viewed as the most important southern colony

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
To finance the war during its first two years,the new American state governments relied primarily on
A) raising taxes to unprecedented levels.
B) forced requisitions from the wealthy.
C) selling public landholdings.
D) printing large quantities of paper money.
A) raising taxes to unprecedented levels.
B) forced requisitions from the wealthy.
C) selling public landholdings.
D) printing large quantities of paper money.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Patriot women contributed to the war effort in the 1770s by
A) increasing production of homespun cloth.
B) joining the women's regiment.
C) working as government officials.
D) working in army offices to free men to fight.
A) increasing production of homespun cloth.
B) joining the women's regiment.
C) working as government officials.
D) working in army offices to free men to fight.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Why did British and American diplomats take nearly two years to conclude a peace treaty after the British surrendered at Yorktown?
A) American negotiators sought delays so that state governments could coordinate their demands.
B) France and Spain stalled,hoping for some major naval victory or territorial conquest before the official peace.
C) Members of Parliament could not reach agreement on the concessions that they were willing to make.
D) The lengthy periods necessary for transatlantic travel and communications required a long process.
A) American negotiators sought delays so that state governments could coordinate their demands.
B) France and Spain stalled,hoping for some major naval victory or territorial conquest before the official peace.
C) Members of Parliament could not reach agreement on the concessions that they were willing to make.
D) The lengthy periods necessary for transatlantic travel and communications required a long process.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Why were the land ordinances of the 1780s considered a great accomplishment of the Confederation Congress?
A) The ordinances provided for orderly settlement and created a fair process for those areas to eventually become fully equal states.
B) The laws funded the building of roads and canals to encourage white settlement throughout the old Northwest.
C) They prevented the formation of larger western states that might one day dominate smaller eastern states.
D) Ordinances limited foreign immigration to the West,ensuring that those areas retained a traditional American culture.
A) The ordinances provided for orderly settlement and created a fair process for those areas to eventually become fully equal states.
B) The laws funded the building of roads and canals to encourage white settlement throughout the old Northwest.
C) They prevented the formation of larger western states that might one day dominate smaller eastern states.
D) Ordinances limited foreign immigration to the West,ensuring that those areas retained a traditional American culture.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following issues formed the basis for the major political and economic challenges that faced postrevolutionary state governments in the 1780s?
A) Conflicts between property owners and those who had nothing
B) Plentiful but worthless paper currency and big debts
C) Wealthy citizens' demands for low taxes and the repudiation of state debts
D) Poor citizens' demands for government assistance in finding jobs
A) Conflicts between property owners and those who had nothing
B) Plentiful but worthless paper currency and big debts
C) Wealthy citizens' demands for low taxes and the repudiation of state debts
D) Poor citizens' demands for government assistance in finding jobs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following factors explains George Washington's success as an American military leader?
A) His ability to maintain the support and morale of the Continental Congress,state governments,and the Continental army.
B) His strong personality,which enabled him to keep persistent pressure on the Continental Congress to supply the army.
C) The advanced military training he gained during his years fighting with the British Navy in the North Atlantic.
D) His willingness to overlook the actions of discontented soldiers,which endeared him to his troops.
A) His ability to maintain the support and morale of the Continental Congress,state governments,and the Continental army.
B) His strong personality,which enabled him to keep persistent pressure on the Continental Congress to supply the army.
C) The advanced military training he gained during his years fighting with the British Navy in the North Atlantic.
D) His willingness to overlook the actions of discontented soldiers,which endeared him to his troops.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
What happened to the property of Loyalists during the Revolution?
A) The Continental Congress auctioned off most Loyalists' lands to pay for war debts.
B) State governments seized Loyalist lands and redistributed them among Patriot landowners.
C) Most of the lands of wealthy Loyalists were seized by local governments and redistributed among Patriot tenant farmers.
D) Most Loyalist property was not seized because doing so would have violated America's republican principles.
A) The Continental Congress auctioned off most Loyalists' lands to pay for war debts.
B) State governments seized Loyalist lands and redistributed them among Patriot landowners.
C) Most of the lands of wealthy Loyalists were seized by local governments and redistributed among Patriot tenant farmers.
D) Most Loyalist property was not seized because doing so would have violated America's republican principles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following battles marked the end of the American Revolution in 1781?
A) Saratoga
B) New York
C) Yorktown
D) Quebec
A) Saratoga
B) New York
C) Yorktown
D) Quebec

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which event turned the tide of the war after Britain's series of victories in the South in the late 1770s?
A) The American troops' seizure of Augusta,Georgia,in 1779
B) French troops' arrival in Newport,Rhode Island,in 1780
C) King Louis XVI's decision to embrace republican ideas
D) British troops' accidental killing of a group of slaves seeking refuge
A) The American troops' seizure of Augusta,Georgia,in 1779
B) French troops' arrival in Newport,Rhode Island,in 1780
C) King Louis XVI's decision to embrace republican ideas
D) British troops' accidental killing of a group of slaves seeking refuge

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Why was the Northwest Ordinance of 1787 significant?
A) The land ordinance recognized the newly organized states of Kentucky and Tennessee as members of the Confederation.
B) The ordinance mandated the forced removal of Native Americans from the Confederation's new western lands.
C) It prohibited slavery in the territory and earmarked funds from land sales for public schools.
D) It created the Bank of North America and charged it with overseeing the sales of western lands.
A) The land ordinance recognized the newly organized states of Kentucky and Tennessee as members of the Confederation.
B) The ordinance mandated the forced removal of Native Americans from the Confederation's new western lands.
C) It prohibited slavery in the territory and earmarked funds from land sales for public schools.
D) It created the Bank of North America and charged it with overseeing the sales of western lands.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
What did Shays's Rebellion,which took place in Massachusetts in the winter of 1786-1787,demonstrate to American political leaders?
A) The institution of slavery posed a threat to the American republic.
B) A stronger national government was needed to solve the nation's monetary problems.
C) Patriots in Massachusetts had always been more radical than those in the other states.
D) Unless they gained the right to vote,propertyless men would destroy the American republic.
A) The institution of slavery posed a threat to the American republic.
B) A stronger national government was needed to solve the nation's monetary problems.
C) Patriots in Massachusetts had always been more radical than those in the other states.
D) Unless they gained the right to vote,propertyless men would destroy the American republic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following was true under the Articles of Confederation?
A) Bills required a unanimous vote to become laws.
B) Congress could tax the states and individuals,if necessary.
C) Amendments could be passed with a majority of states approving.
D) Most of the power remained with the states.
A) Bills required a unanimous vote to become laws.
B) Congress could tax the states and individuals,if necessary.
C) Amendments could be passed with a majority of states approving.
D) Most of the power remained with the states.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following factors made a critical contribution to the outcome of the Battle of Yorktown in 1781?
A) The long-awaited arrival of Admiral Rochambeau's fleet in the Chesapeake Bay
B) Americans' discovery,capture,and execution of the traitor Benedict Arnold
C) Washington's feigned attack on Manhattan while French troops set out for Virginia
D) The arrival of General Nathanael Greene's Patriot troops from South Carolina
A) The long-awaited arrival of Admiral Rochambeau's fleet in the Chesapeake Bay
B) Americans' discovery,capture,and execution of the traitor Benedict Arnold
C) Washington's feigned attack on Manhattan while French troops set out for Virginia
D) The arrival of General Nathanael Greene's Patriot troops from South Carolina

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Why did it take the Continental Congress several years to ratify the Articles of Confederation?
A) Fighting the war was a higher priority than creating a new national government.
B) Many Patriots feared that any national government,no matter how weak,would eventually abuse its power.
C) There was disagreement over how many votes each state should have in the new Congress.
D) Disputes over western land claims led some states to block ratification.
A) Fighting the war was a higher priority than creating a new national government.
B) Many Patriots feared that any national government,no matter how weak,would eventually abuse its power.
C) There was disagreement over how many votes each state should have in the new Congress.
D) Disputes over western land claims led some states to block ratification.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of the following statements characterizes postwar trends in American trade?
A) The war had crippled American shipping,which reduced the export of tobacco and other farm goods.
B) In the absence of British trade restrictions,the production of tobacco boomed.
C) Domestic industries supplied products unavailable from Britain during the war and flourished after the war's end.
D) Economic growth spurred by western land sales stimulated American manufacturing and increased exports.
A) The war had crippled American shipping,which reduced the export of tobacco and other farm goods.
B) In the absence of British trade restrictions,the production of tobacco boomed.
C) Domestic industries supplied products unavailable from Britain during the war and flourished after the war's end.
D) Economic growth spurred by western land sales stimulated American manufacturing and increased exports.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which of the following statements explains the Patriots' successful revolution against Great Britain?
A) British officers were inexperienced in combat and committed an incredible series of blunders.
B) Guerrilla fighters in the Patriot militias wore down British troops,even though the Continental army rarely won a battle.
C) About one-third of the population strongly supported the war and was willing to finance the fighting through inflation.
D) The number of Loyalists and Indians who supported the British was never large enough to provide critical support.
A) British officers were inexperienced in combat and committed an incredible series of blunders.
B) Guerrilla fighters in the Patriot militias wore down British troops,even though the Continental army rarely won a battle.
C) About one-third of the population strongly supported the war and was willing to finance the fighting through inflation.
D) The number of Loyalists and Indians who supported the British was never large enough to provide critical support.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Although women made few gains in the eighteenth century,they did achieve a degree of progress in 1790 when they won which of the following?
A) Suffrage in New York State
B) Equal access to public education in Massachusetts
C) The right of entry into college in Virginia
D) The right to hold office in Rhode Island
A) Suffrage in New York State
B) Equal access to public education in Massachusetts
C) The right of entry into college in Virginia
D) The right to hold office in Rhode Island

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
For this question,refer to the following map,"Land Division in the Northwest Territory." 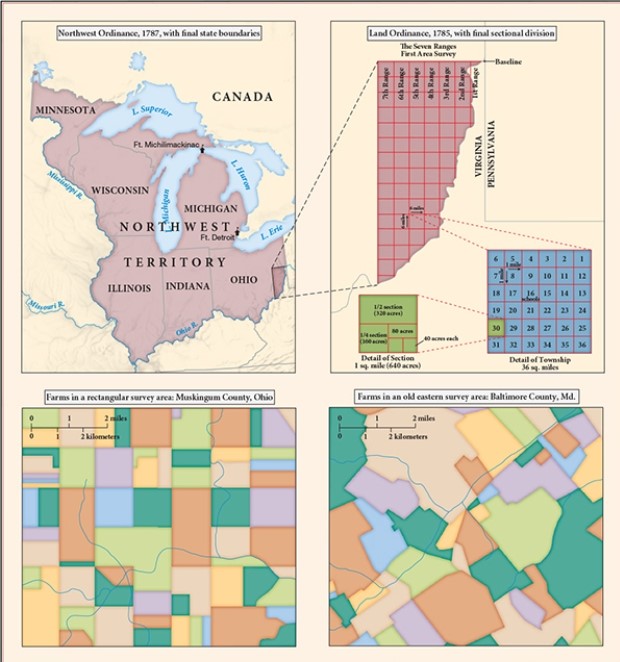 This map best serves as evidence of
This map best serves as evidence of
A) the creation of new settlements in the West,with distinctive backcountry cultures.
B) the enactment of policies that began to encourage orderly incorporation of new territories into the nation.
C) the challenges that the United States faced in safeguarding its borders from European powers.
D) states manifesting republican fears of both centralized power and excessive popular influence.
 This map best serves as evidence of
This map best serves as evidence ofA) the creation of new settlements in the West,with distinctive backcountry cultures.
B) the enactment of policies that began to encourage orderly incorporation of new territories into the nation.
C) the challenges that the United States faced in safeguarding its borders from European powers.
D) states manifesting republican fears of both centralized power and excessive popular influence.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Despite the favorable terms Americans achieved in the 1783 Treaty of Paris,they could not ultimately secure which of the following?
A) The lands between the Appalachian Mountains and the Mississippi River
B) Rights to fish off the coast of British Newfoundland
C) Britain's formal recognition of the thirteen colonies' independence
D) Forgiveness of their debts to British merchants
A) The lands between the Appalachian Mountains and the Mississippi River
B) Rights to fish off the coast of British Newfoundland
C) Britain's formal recognition of the thirteen colonies' independence
D) Forgiveness of their debts to British merchants

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which of the following statements characterized Pennsylvania's democratic constitution of 1776?
A) Patriots greatly admired it,but they also expressed reluctance to adopt all of its features.
B) It reflected the ideas John Adams articulated in his book,Thoughts on Government.
C) Its radicalism went unnoticed by leading Patriots in other states,whose attention was focused on local concerns.
D) Many leading Patriots found its radically democratic elements quite alarming.
A) Patriots greatly admired it,but they also expressed reluctance to adopt all of its features.
B) It reflected the ideas John Adams articulated in his book,Thoughts on Government.
C) Its radicalism went unnoticed by leading Patriots in other states,whose attention was focused on local concerns.
D) Many leading Patriots found its radically democratic elements quite alarming.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Why did the British surrender to the Americans in the Battle of Yorktown in 1781?
A) The British were outnumbered and cut off from reinforcement or retreat by sea.
B) The army was depleted after sending reinforcement troops to General Benedict Arnold.
C) General Cornwallis had already suffered a number of defeats as his army moved through Virginia.
D) The British planned to continue the war on the American mainland as soon as they had additional supplies.
A) The British were outnumbered and cut off from reinforcement or retreat by sea.
B) The army was depleted after sending reinforcement troops to General Benedict Arnold.
C) General Cornwallis had already suffered a number of defeats as his army moved through Virginia.
D) The British planned to continue the war on the American mainland as soon as they had additional supplies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Why was Abigail Adams a notable figure in the Revolutionary era?
A) She publicly denounced most Patriot leaders as tyrants because they held power over women.
B) Adams was married to the Patriot John Adams and helped him with his work.
C) She criticized Patriots like her husband John and insisted on equal legal rights for married women.
D) She became the only woman to take part in the deliberations of the Continental Congress.
A) She publicly denounced most Patriot leaders as tyrants because they held power over women.
B) Adams was married to the Patriot John Adams and helped him with his work.
C) She criticized Patriots like her husband John and insisted on equal legal rights for married women.
D) She became the only woman to take part in the deliberations of the Continental Congress.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
To persuade Massachusetts,Virginia,and New York to ratify the Constitution,leading Federalists promised that
A) George Washington would become the first president.
B) a bill of rights would be added to the Constitution.
C) New York City would be the national capital.
D) New York and Virginia would regain their former western claims.
A) George Washington would become the first president.
B) a bill of rights would be added to the Constitution.
C) New York City would be the national capital.
D) New York and Virginia would regain their former western claims.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Answer the following questions :
Battle of Long Island (1776)
A)First major engagement of the new Continental army,defending against 32,000 British troops outside of New York City.
B)A multistage battle in New York ending with the surrender of British general John Burgoyne.The victory ensured the diplomatic success of American representatives in Paris,who won a military alliance with France.
C)A military camp in which George Washington's army of 12,000 soldiers and hundreds of camp followers suffered horribly in the winter of 1777-1778.
D)A 1779 proclamation that declared that any slave who deserted a rebel master would receive protection,freedom,and land from Great Britain.
E)A battle in which French and American troops and a French fleet trapped the British army under the command of General Charles Cornwallis.The Franco-American victory broke the resolve of the British government.
F)A hidden tax on the farmers and artisans who accepted Continental bills in payment for supplies and on the thousands of soldiers who took them as pay.Because of rampant inflation,Continental currency lost much of its value during the war;thus,the implicit tax on those who accepted it as payment.
G)The treaty that ended the Revolutionary War.In the treaty,Great Britain formally recognized American independence and relinquished its claims to lands south of the Great Lakes and east of the Mississippi River.
H)A constitution that granted all taxpaying men the right to vote and hold office and created a unicameral (one-house)legislature with complete power;there was no governor to exercise a veto.Other provisions mandated a system of elementary education and protected citizens from imprisonment for debt.
I)John Adams's theory from Thoughts on Government (1776),which called for three branches of government,each representing one function: executive,legislative,and judicial.This system of dispersed authority was devised to maintain a balance of power and ensure the legitimacy of governmental procedures.
J)The written document defining the structure of the government from 1781 to 1788,under which the Union was a confederation of equal states,with no executive and limited powers,existing mainly to foster a common defense.
K)A land act that provided for orderly settlement and established a process by which settled territories would become the states of Ohio,Indiana,Illinois,Michigan,and Wisconsin.It also banned slavery in the Northwest Territory.
L)A 1786-1787 uprising led by dissident farmers in western Massachusetts,many of them Revolutionary War veterans,protesting the taxation policies of the eastern elites who controlled the state's government.
M)A plan drafted by James Madison that was presented at the Philadelphia Constitutional Convention.It designed a powerful three-branch government,with representation in both houses of the congress tied to population;this plan would have eclipsed the voice of small states in the national government.
N)Alternative to the Virginia Plan drafted by delegates from small states,retaining the confederation's single-house congress with one vote per state.It shared with the Virginia Plan enhanced congressional powers to raise revenue,control commerce,and make binding requisitions on the states.
O)Supporters of the Constitution of 1787,which created a strong central government;their opponents,the Antifederalists,feared that a strong central government would corrupt the nation's newly won liberty.
P)Opponents of ratification of the Constitution.This party feared that a powerful and distant central government would be out of touch with the needs of citizens.They also complained that it failed to guarantee individual liberties in a bill of rights.
Q)An essay by James Madison in The Federalist (1787-1788)that challenged the view that republican governments only worked in small polities;it argued that a geographically expansive national government would better protect republican liberty.
Battle of Long Island (1776)
A)First major engagement of the new Continental army,defending against 32,000 British troops outside of New York City.
B)A multistage battle in New York ending with the surrender of British general John Burgoyne.The victory ensured the diplomatic success of American representatives in Paris,who won a military alliance with France.
C)A military camp in which George Washington's army of 12,000 soldiers and hundreds of camp followers suffered horribly in the winter of 1777-1778.
D)A 1779 proclamation that declared that any slave who deserted a rebel master would receive protection,freedom,and land from Great Britain.
E)A battle in which French and American troops and a French fleet trapped the British army under the command of General Charles Cornwallis.The Franco-American victory broke the resolve of the British government.
F)A hidden tax on the farmers and artisans who accepted Continental bills in payment for supplies and on the thousands of soldiers who took them as pay.Because of rampant inflation,Continental currency lost much of its value during the war;thus,the implicit tax on those who accepted it as payment.
G)The treaty that ended the Revolutionary War.In the treaty,Great Britain formally recognized American independence and relinquished its claims to lands south of the Great Lakes and east of the Mississippi River.
H)A constitution that granted all taxpaying men the right to vote and hold office and created a unicameral (one-house)legislature with complete power;there was no governor to exercise a veto.Other provisions mandated a system of elementary education and protected citizens from imprisonment for debt.
I)John Adams's theory from Thoughts on Government (1776),which called for three branches of government,each representing one function: executive,legislative,and judicial.This system of dispersed authority was devised to maintain a balance of power and ensure the legitimacy of governmental procedures.
J)The written document defining the structure of the government from 1781 to 1788,under which the Union was a confederation of equal states,with no executive and limited powers,existing mainly to foster a common defense.
K)A land act that provided for orderly settlement and established a process by which settled territories would become the states of Ohio,Indiana,Illinois,Michigan,and Wisconsin.It also banned slavery in the Northwest Territory.
L)A 1786-1787 uprising led by dissident farmers in western Massachusetts,many of them Revolutionary War veterans,protesting the taxation policies of the eastern elites who controlled the state's government.
M)A plan drafted by James Madison that was presented at the Philadelphia Constitutional Convention.It designed a powerful three-branch government,with representation in both houses of the congress tied to population;this plan would have eclipsed the voice of small states in the national government.
N)Alternative to the Virginia Plan drafted by delegates from small states,retaining the confederation's single-house congress with one vote per state.It shared with the Virginia Plan enhanced congressional powers to raise revenue,control commerce,and make binding requisitions on the states.
O)Supporters of the Constitution of 1787,which created a strong central government;their opponents,the Antifederalists,feared that a strong central government would corrupt the nation's newly won liberty.
P)Opponents of ratification of the Constitution.This party feared that a powerful and distant central government would be out of touch with the needs of citizens.They also complained that it failed to guarantee individual liberties in a bill of rights.
Q)An essay by James Madison in The Federalist (1787-1788)that challenged the view that republican governments only worked in small polities;it argued that a geographically expansive national government would better protect republican liberty.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
For this question,refer to the following excerpt. Mr.Martin proposed to vary article 7,sect.4 so as to allow a prohibition or tax on the importation of slaves....[He believed] it was inconsistent with the principles of the Revolution,and dishonorable to the American character,to have such a feature [promoting the slave trade] in the Constitution....
Mr)[Oliver] Ellsworth [of Connecticut] was for leaving the clause as it stands.Let every state import what it pleases.The morality or wisdom of slavery are considerations belonging to the states themselves....
Col)[George] Mason [of Virginia stated that] this infernal trade originated in the avarice of British merchants.The British government constantly checked the attempts of Virginia to put a stop to it.The Western people are already calling out for slaves for their new lands,and will fill that country with slaves,if they can be got through South Carolina and Georgia.Slavery discourages arts and manufactures.The poor despise labor when performed by slaves.They prevent the immigration of whites,who really enrich and strengthen a country....
Every master of slaves is born a petty tyrant.They bring the judgment of Heaven on a country.As nations cannot be rewarded or punished in the next world,they must be in this.By an inevitable chain of causes and effects,Providence punishes national sins by national calamities....He held it essential,in every point of view,that the general government should have power to prevent the increase of slavery....
Gen)[Charles C.] Pinckney [argued that] South Carolina and Georgia cannot do without slaves....He contended that the importation of slaves would be for the interest of the whole Union.The more slaves,the more produce to employ the carrying trade;the more consumption also;and the more of this,the more revenue for the common treasury....
The Records of the Federal Convention of 1787
The excerpt quoted above would be most useful to historians analyzing
A) the series of compromises worked through to form a national government.
B) how calls for greater guarantees of rights resulted in the addition of the Bill of Rights.
C) the debates among American political leaders about politics and society,religion,and governance.
D) why difficulties over trade,interstate relations,and internal unrest led to calls for a stronger central government.
Mr)[Oliver] Ellsworth [of Connecticut] was for leaving the clause as it stands.Let every state import what it pleases.The morality or wisdom of slavery are considerations belonging to the states themselves....
Col)[George] Mason [of Virginia stated that] this infernal trade originated in the avarice of British merchants.The British government constantly checked the attempts of Virginia to put a stop to it.The Western people are already calling out for slaves for their new lands,and will fill that country with slaves,if they can be got through South Carolina and Georgia.Slavery discourages arts and manufactures.The poor despise labor when performed by slaves.They prevent the immigration of whites,who really enrich and strengthen a country....
Every master of slaves is born a petty tyrant.They bring the judgment of Heaven on a country.As nations cannot be rewarded or punished in the next world,they must be in this.By an inevitable chain of causes and effects,Providence punishes national sins by national calamities....He held it essential,in every point of view,that the general government should have power to prevent the increase of slavery....
Gen)[Charles C.] Pinckney [argued that] South Carolina and Georgia cannot do without slaves....He contended that the importation of slaves would be for the interest of the whole Union.The more slaves,the more produce to employ the carrying trade;the more consumption also;and the more of this,the more revenue for the common treasury....
The Records of the Federal Convention of 1787
The excerpt quoted above would be most useful to historians analyzing
A) the series of compromises worked through to form a national government.
B) how calls for greater guarantees of rights resulted in the addition of the Bill of Rights.
C) the debates among American political leaders about politics and society,religion,and governance.
D) why difficulties over trade,interstate relations,and internal unrest led to calls for a stronger central government.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Answer the following questions :
Antifederalists
A)First major engagement of the new Continental army,defending against 32,000 British troops outside of New York City.
B)A multistage battle in New York ending with the surrender of British general John Burgoyne.The victory ensured the diplomatic success of American representatives in Paris,who won a military alliance with France.
C)A military camp in which George Washington's army of 12,000 soldiers and hundreds of camp followers suffered horribly in the winter of 1777-1778.
D)A 1779 proclamation that declared that any slave who deserted a rebel master would receive protection,freedom,and land from Great Britain.
E)A battle in which French and American troops and a French fleet trapped the British army under the command of General Charles Cornwallis.The Franco-American victory broke the resolve of the British government.
F)A hidden tax on the farmers and artisans who accepted Continental bills in payment for supplies and on the thousands of soldiers who took them as pay.Because of rampant inflation,Continental currency lost much of its value during the war;thus,the implicit tax on those who accepted it as payment.
G)The treaty that ended the Revolutionary War.In the treaty,Great Britain formally recognized American independence and relinquished its claims to lands south of the Great Lakes and east of the Mississippi River.
H)A constitution that granted all taxpaying men the right to vote and hold office and created a unicameral (one-house)legislature with complete power;there was no governor to exercise a veto.Other provisions mandated a system of elementary education and protected citizens from imprisonment for debt.
I)John Adams's theory from Thoughts on Government (1776),which called for three branches of government,each representing one function: executive,legislative,and judicial.This system of dispersed authority was devised to maintain a balance of power and ensure the legitimacy of governmental procedures.
J)The written document defining the structure of the government from 1781 to 1788,under which the Union was a confederation of equal states,with no executive and limited powers,existing mainly to foster a common defense.
K)A land act that provided for orderly settlement and established a process by which settled territories would become the states of Ohio,Indiana,Illinois,Michigan,and Wisconsin.It also banned slavery in the Northwest Territory.
L)A 1786-1787 uprising led by dissident farmers in western Massachusetts,many of them Revolutionary War veterans,protesting the taxation policies of the eastern elites who controlled the state's government.
M)A plan drafted by James Madison that was presented at the Philadelphia Constitutional Convention.It designed a powerful three-branch government,with representation in both houses of the congress tied to population;this plan would have eclipsed the voice of small states in the national government.
N)Alternative to the Virginia Plan drafted by delegates from small states,retaining the confederation's single-house congress with one vote per state.It shared with the Virginia Plan enhanced congressional powers to raise revenue,control commerce,and make binding requisitions on the states.
O)Supporters of the Constitution of 1787,which created a strong central government;their opponents,the Antifederalists,feared that a strong central government would corrupt the nation's newly won liberty.
P)Opponents of ratification of the Constitution.This party feared that a powerful and distant central government would be out of touch with the needs of citizens.They also complained that it failed to guarantee individual liberties in a bill of rights.
Q)An essay by James Madison in The Federalist (1787-1788)that challenged the view that republican governments only worked in small polities;it argued that a geographically expansive national government would better protect republican liberty.
Antifederalists
A)First major engagement of the new Continental army,defending against 32,000 British troops outside of New York City.
B)A multistage battle in New York ending with the surrender of British general John Burgoyne.The victory ensured the diplomatic success of American representatives in Paris,who won a military alliance with France.
C)A military camp in which George Washington's army of 12,000 soldiers and hundreds of camp followers suffered horribly in the winter of 1777-1778.
D)A 1779 proclamation that declared that any slave who deserted a rebel master would receive protection,freedom,and land from Great Britain.
E)A battle in which French and American troops and a French fleet trapped the British army under the command of General Charles Cornwallis.The Franco-American victory broke the resolve of the British government.
F)A hidden tax on the farmers and artisans who accepted Continental bills in payment for supplies and on the thousands of soldiers who took them as pay.Because of rampant inflation,Continental currency lost much of its value during the war;thus,the implicit tax on those who accepted it as payment.
G)The treaty that ended the Revolutionary War.In the treaty,Great Britain formally recognized American independence and relinquished its claims to lands south of the Great Lakes and east of the Mississippi River.
H)A constitution that granted all taxpaying men the right to vote and hold office and created a unicameral (one-house)legislature with complete power;there was no governor to exercise a veto.Other provisions mandated a system of elementary education and protected citizens from imprisonment for debt.
I)John Adams's theory from Thoughts on Government (1776),which called for three branches of government,each representing one function: executive,legislative,and judicial.This system of dispersed authority was devised to maintain a balance of power and ensure the legitimacy of governmental procedures.
J)The written document defining the structure of the government from 1781 to 1788,under which the Union was a confederation of equal states,with no executive and limited powers,existing mainly to foster a common defense.
K)A land act that provided for orderly settlement and established a process by which settled territories would become the states of Ohio,Indiana,Illinois,Michigan,and Wisconsin.It also banned slavery in the Northwest Territory.
L)A 1786-1787 uprising led by dissident farmers in western Massachusetts,many of them Revolutionary War veterans,protesting the taxation policies of the eastern elites who controlled the state's government.
M)A plan drafted by James Madison that was presented at the Philadelphia Constitutional Convention.It designed a powerful three-branch government,with representation in both houses of the congress tied to population;this plan would have eclipsed the voice of small states in the national government.
N)Alternative to the Virginia Plan drafted by delegates from small states,retaining the confederation's single-house congress with one vote per state.It shared with the Virginia Plan enhanced congressional powers to raise revenue,control commerce,and make binding requisitions on the states.
O)Supporters of the Constitution of 1787,which created a strong central government;their opponents,the Antifederalists,feared that a strong central government would corrupt the nation's newly won liberty.
P)Opponents of ratification of the Constitution.This party feared that a powerful and distant central government would be out of touch with the needs of citizens.They also complained that it failed to guarantee individual liberties in a bill of rights.
Q)An essay by James Madison in The Federalist (1787-1788)that challenged the view that republican governments only worked in small polities;it argued that a geographically expansive national government would better protect republican liberty.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
For this question,refer to the following excerpt. Mr.Martin proposed to vary article 7,sect.4 so as to allow a prohibition or tax on the importation of slaves....[He believed] it was inconsistent with the principles of the Revolution,and dishonorable to the American character,to have such a feature [promoting the slave trade] in the Constitution....
Mr)[Oliver] Ellsworth [of Connecticut] was for leaving the clause as it stands.Let every state import what it pleases.The morality or wisdom of slavery are considerations belonging to the states themselves....
Col)[George] Mason [of Virginia stated that] this infernal trade originated in the avarice of British merchants.The British government constantly checked the attempts of Virginia to put a stop to it.The Western people are already calling out for slaves for their new lands,and will fill that country with slaves,if they can be got through South Carolina and Georgia.Slavery discourages arts and manufactures.The poor despise labor when performed by slaves.They prevent the immigration of whites,who really enrich and strengthen a country....
Every master of slaves is born a petty tyrant.They bring the judgment of Heaven on a country.As nations cannot be rewarded or punished in the next world,they must be in this.By an inevitable chain of causes and effects,Providence punishes national sins by national calamities....He held it essential,in every point of view,that the general government should have power to prevent the increase of slavery....
Gen)[Charles C.] Pinckney [argued that] South Carolina and Georgia cannot do without slaves....He contended that the importation of slaves would be for the interest of the whole Union.The more slaves,the more produce to employ the carrying trade;the more consumption also;and the more of this,the more revenue for the common treasury....
The Records of the Federal Convention of 1787
The passage above best serves as evidence of
A) continued debates about the proper balance between liberty and order.
B) an increased awareness of the inequalities in society.
C) the ways in which U.S.policies encouraged western migration.
D) debates leading to the creation of political parties.
Mr)[Oliver] Ellsworth [of Connecticut] was for leaving the clause as it stands.Let every state import what it pleases.The morality or wisdom of slavery are considerations belonging to the states themselves....
Col)[George] Mason [of Virginia stated that] this infernal trade originated in the avarice of British merchants.The British government constantly checked the attempts of Virginia to put a stop to it.The Western people are already calling out for slaves for their new lands,and will fill that country with slaves,if they can be got through South Carolina and Georgia.Slavery discourages arts and manufactures.The poor despise labor when performed by slaves.They prevent the immigration of whites,who really enrich and strengthen a country....
Every master of slaves is born a petty tyrant.They bring the judgment of Heaven on a country.As nations cannot be rewarded or punished in the next world,they must be in this.By an inevitable chain of causes and effects,Providence punishes national sins by national calamities....He held it essential,in every point of view,that the general government should have power to prevent the increase of slavery....
Gen)[Charles C.] Pinckney [argued that] South Carolina and Georgia cannot do without slaves....He contended that the importation of slaves would be for the interest of the whole Union.The more slaves,the more produce to employ the carrying trade;the more consumption also;and the more of this,the more revenue for the common treasury....
The Records of the Federal Convention of 1787
The passage above best serves as evidence of
A) continued debates about the proper balance between liberty and order.
B) an increased awareness of the inequalities in society.
C) the ways in which U.S.policies encouraged western migration.
D) debates leading to the creation of political parties.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Answer the following questions :
currency tax
A)First major engagement of the new Continental army,defending against 32,000 British troops outside of New York City.
B)A multistage battle in New York ending with the surrender of British general John Burgoyne.The victory ensured the diplomatic success of American representatives in Paris,who won a military alliance with France.
C)A military camp in which George Washington's army of 12,000 soldiers and hundreds of camp followers suffered horribly in the winter of 1777-1778.
D)A 1779 proclamation that declared that any slave who deserted a rebel master would receive protection,freedom,and land from Great Britain.
E)A battle in which French and American troops and a French fleet trapped the British army under the command of General Charles Cornwallis.The Franco-American victory broke the resolve of the British government.
F)A hidden tax on the farmers and artisans who accepted Continental bills in payment for supplies and on the thousands of soldiers who took them as pay.Because of rampant inflation,Continental currency lost much of its value during the war;thus,the implicit tax on those who accepted it as payment.
G)The treaty that ended the Revolutionary War.In the treaty,Great Britain formally recognized American independence and relinquished its claims to lands south of the Great Lakes and east of the Mississippi River.
H)A constitution that granted all taxpaying men the right to vote and hold office and created a unicameral (one-house)legislature with complete power;there was no governor to exercise a veto.Other provisions mandated a system of elementary education and protected citizens from imprisonment for debt.
I)John Adams's theory from Thoughts on Government (1776),which called for three branches of government,each representing one function: executive,legislative,and judicial.This system of dispersed authority was devised to maintain a balance of power and ensure the legitimacy of governmental procedures.
J)The written document defining the structure of the government from 1781 to 1788,under which the Union was a confederation of equal states,with no executive and limited powers,existing mainly to foster a common defense.
K)A land act that provided for orderly settlement and established a process by which settled territories would become the states of Ohio,Indiana,Illinois,Michigan,and Wisconsin.It also banned slavery in the Northwest Territory.
L)A 1786-1787 uprising led by dissident farmers in western Massachusetts,many of them Revolutionary War veterans,protesting the taxation policies of the eastern elites who controlled the state's government.
M)A plan drafted by James Madison that was presented at the Philadelphia Constitutional Convention.It designed a powerful three-branch government,with representation in both houses of the congress tied to population;this plan would have eclipsed the voice of small states in the national government.
N)Alternative to the Virginia Plan drafted by delegates from small states,retaining the confederation's single-house congress with one vote per state.It shared with the Virginia Plan enhanced congressional powers to raise revenue,control commerce,and make binding requisitions on the states.
O)Supporters of the Constitution of 1787,which created a strong central government;their opponents,the Antifederalists,feared that a strong central government would corrupt the nation's newly won liberty.
P)Opponents of ratification of the Constitution.This party feared that a powerful and distant central government would be out of touch with the needs of citizens.They also complained that it failed to guarantee individual liberties in a bill of rights.
Q)An essay by James Madison in The Federalist (1787-1788)that challenged the view that republican governments only worked in small polities;it argued that a geographically expansive national government would better protect republican liberty.
currency tax
A)First major engagement of the new Continental army,defending against 32,000 British troops outside of New York City.
B)A multistage battle in New York ending with the surrender of British general John Burgoyne.The victory ensured the diplomatic success of American representatives in Paris,who won a military alliance with France.
C)A military camp in which George Washington's army of 12,000 soldiers and hundreds of camp followers suffered horribly in the winter of 1777-1778.
D)A 1779 proclamation that declared that any slave who deserted a rebel master would receive protection,freedom,and land from Great Britain.
E)A battle in which French and American troops and a French fleet trapped the British army under the command of General Charles Cornwallis.The Franco-American victory broke the resolve of the British government.
F)A hidden tax on the farmers and artisans who accepted Continental bills in payment for supplies and on the thousands of soldiers who took them as pay.Because of rampant inflation,Continental currency lost much of its value during the war;thus,the implicit tax on those who accepted it as payment.
G)The treaty that ended the Revolutionary War.In the treaty,Great Britain formally recognized American independence and relinquished its claims to lands south of the Great Lakes and east of the Mississippi River.
H)A constitution that granted all taxpaying men the right to vote and hold office and created a unicameral (one-house)legislature with complete power;there was no governor to exercise a veto.Other provisions mandated a system of elementary education and protected citizens from imprisonment for debt.
I)John Adams's theory from Thoughts on Government (1776),which called for three branches of government,each representing one function: executive,legislative,and judicial.This system of dispersed authority was devised to maintain a balance of power and ensure the legitimacy of governmental procedures.
J)The written document defining the structure of the government from 1781 to 1788,under which the Union was a confederation of equal states,with no executive and limited powers,existing mainly to foster a common defense.
K)A land act that provided for orderly settlement and established a process by which settled territories would become the states of Ohio,Indiana,Illinois,Michigan,and Wisconsin.It also banned slavery in the Northwest Territory.
L)A 1786-1787 uprising led by dissident farmers in western Massachusetts,many of them Revolutionary War veterans,protesting the taxation policies of the eastern elites who controlled the state's government.
M)A plan drafted by James Madison that was presented at the Philadelphia Constitutional Convention.It designed a powerful three-branch government,with representation in both houses of the congress tied to population;this plan would have eclipsed the voice of small states in the national government.
N)Alternative to the Virginia Plan drafted by delegates from small states,retaining the confederation's single-house congress with one vote per state.It shared with the Virginia Plan enhanced congressional powers to raise revenue,control commerce,and make binding requisitions on the states.
O)Supporters of the Constitution of 1787,which created a strong central government;their opponents,the Antifederalists,feared that a strong central government would corrupt the nation's newly won liberty.
P)Opponents of ratification of the Constitution.This party feared that a powerful and distant central government would be out of touch with the needs of citizens.They also complained that it failed to guarantee individual liberties in a bill of rights.
Q)An essay by James Madison in The Federalist (1787-1788)that challenged the view that republican governments only worked in small polities;it argued that a geographically expansive national government would better protect republican liberty.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
American Antifederalist Patrick Henry opposed the ratification of the Constitution for which of the following reasons?
A) Henry objected to provisions that protected the interests of slaveholders.
B) He feared high taxes,a large bureaucracy,and a standing army.
C) As an American from Virginia,he objected to provisions that ran counter to the interests of slaveholders.
D) He was concerned that it would deprive the central government of necessary powers.
A) Henry objected to provisions that protected the interests of slaveholders.
B) He feared high taxes,a large bureaucracy,and a standing army.
C) As an American from Virginia,he objected to provisions that ran counter to the interests of slaveholders.
D) He was concerned that it would deprive the central government of necessary powers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Answer the following questions :
mixed government
A)First major engagement of the new Continental army,defending against 32,000 British troops outside of New York City.
B)A multistage battle in New York ending with the surrender of British general John Burgoyne.The victory ensured the diplomatic success of American representatives in Paris,who won a military alliance with France.
C)A military camp in which George Washington's army of 12,000 soldiers and hundreds of camp followers suffered horribly in the winter of 1777-1778.
D)A 1779 proclamation that declared that any slave who deserted a rebel master would receive protection,freedom,and land from Great Britain.
E)A battle in which French and American troops and a French fleet trapped the British army under the command of General Charles Cornwallis.The Franco-American victory broke the resolve of the British government.
F)A hidden tax on the farmers and artisans who accepted Continental bills in payment for supplies and on the thousands of soldiers who took them as pay.Because of rampant inflation,Continental currency lost much of its value during the war;thus,the implicit tax on those who accepted it as payment.
G)The treaty that ended the Revolutionary War.In the treaty,Great Britain formally recognized American independence and relinquished its claims to lands south of the Great Lakes and east of the Mississippi River.
H)A constitution that granted all taxpaying men the right to vote and hold office and created a unicameral (one-house)legislature with complete power;there was no governor to exercise a veto.Other provisions mandated a system of elementary education and protected citizens from imprisonment for debt.
I)John Adams's theory from Thoughts on Government (1776),which called for three branches of government,each representing one function: executive,legislative,and judicial.This system of dispersed authority was devised to maintain a balance of power and ensure the legitimacy of governmental procedures.
J)The written document defining the structure of the government from 1781 to 1788,under which the Union was a confederation of equal states,with no executive and limited powers,existing mainly to foster a common defense.
K)A land act that provided for orderly settlement and established a process by which settled territories would become the states of Ohio,Indiana,Illinois,Michigan,and Wisconsin.It also banned slavery in the Northwest Territory.
L)A 1786-1787 uprising led by dissident farmers in western Massachusetts,many of them Revolutionary War veterans,protesting the taxation policies of the eastern elites who controlled the state's government.
M)A plan drafted by James Madison that was presented at the Philadelphia Constitutional Convention.It designed a powerful three-branch government,with representation in both houses of the congress tied to population;this plan would have eclipsed the voice of small states in the national government.
N)Alternative to the Virginia Plan drafted by delegates from small states,retaining the confederation's single-house congress with one vote per state.It shared with the Virginia Plan enhanced congressional powers to raise revenue,control commerce,and make binding requisitions on the states.
O)Supporters of the Constitution of 1787,which created a strong central government;their opponents,the Antifederalists,feared that a strong central government would corrupt the nation's newly won liberty.
P)Opponents of ratification of the Constitution.This party feared that a powerful and distant central government would be out of touch with the needs of citizens.They also complained that it failed to guarantee individual liberties in a bill of rights.
Q)An essay by James Madison in The Federalist (1787-1788)that challenged the view that republican governments only worked in small polities;it argued that a geographically expansive national government would better protect republican liberty.
mixed government
A)First major engagement of the new Continental army,defending against 32,000 British troops outside of New York City.
B)A multistage battle in New York ending with the surrender of British general John Burgoyne.The victory ensured the diplomatic success of American representatives in Paris,who won a military alliance with France.
C)A military camp in which George Washington's army of 12,000 soldiers and hundreds of camp followers suffered horribly in the winter of 1777-1778.
D)A 1779 proclamation that declared that any slave who deserted a rebel master would receive protection,freedom,and land from Great Britain.
E)A battle in which French and American troops and a French fleet trapped the British army under the command of General Charles Cornwallis.The Franco-American victory broke the resolve of the British government.
F)A hidden tax on the farmers and artisans who accepted Continental bills in payment for supplies and on the thousands of soldiers who took them as pay.Because of rampant inflation,Continental currency lost much of its value during the war;thus,the implicit tax on those who accepted it as payment.
G)The treaty that ended the Revolutionary War.In the treaty,Great Britain formally recognized American independence and relinquished its claims to lands south of the Great Lakes and east of the Mississippi River.
H)A constitution that granted all taxpaying men the right to vote and hold office and created a unicameral (one-house)legislature with complete power;there was no governor to exercise a veto.Other provisions mandated a system of elementary education and protected citizens from imprisonment for debt.
I)John Adams's theory from Thoughts on Government (1776),which called for three branches of government,each representing one function: executive,legislative,and judicial.This system of dispersed authority was devised to maintain a balance of power and ensure the legitimacy of governmental procedures.
J)The written document defining the structure of the government from 1781 to 1788,under which the Union was a confederation of equal states,with no executive and limited powers,existing mainly to foster a common defense.
K)A land act that provided for orderly settlement and established a process by which settled territories would become the states of Ohio,Indiana,Illinois,Michigan,and Wisconsin.It also banned slavery in the Northwest Territory.
L)A 1786-1787 uprising led by dissident farmers in western Massachusetts,many of them Revolutionary War veterans,protesting the taxation policies of the eastern elites who controlled the state's government.
M)A plan drafted by James Madison that was presented at the Philadelphia Constitutional Convention.It designed a powerful three-branch government,with representation in both houses of the congress tied to population;this plan would have eclipsed the voice of small states in the national government.
N)Alternative to the Virginia Plan drafted by delegates from small states,retaining the confederation's single-house congress with one vote per state.It shared with the Virginia Plan enhanced congressional powers to raise revenue,control commerce,and make binding requisitions on the states.
O)Supporters of the Constitution of 1787,which created a strong central government;their opponents,the Antifederalists,feared that a strong central government would corrupt the nation's newly won liberty.
P)Opponents of ratification of the Constitution.This party feared that a powerful and distant central government would be out of touch with the needs of citizens.They also complained that it failed to guarantee individual liberties in a bill of rights.
Q)An essay by James Madison in The Federalist (1787-1788)that challenged the view that republican governments only worked in small polities;it argued that a geographically expansive national government would better protect republican liberty.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Answer the following questions :
Federalists
A)First major engagement of the new Continental army,defending against 32,000 British troops outside of New York City.
B)A multistage battle in New York ending with the surrender of British general John Burgoyne.The victory ensured the diplomatic success of American representatives in Paris,who won a military alliance with France.
C)A military camp in which George Washington's army of 12,000 soldiers and hundreds of camp followers suffered horribly in the winter of 1777-1778.
D)A 1779 proclamation that declared that any slave who deserted a rebel master would receive protection,freedom,and land from Great Britain.
E)A battle in which French and American troops and a French fleet trapped the British army under the command of General Charles Cornwallis.The Franco-American victory broke the resolve of the British government.
F)A hidden tax on the farmers and artisans who accepted Continental bills in payment for supplies and on the thousands of soldiers who took them as pay.Because of rampant inflation,Continental currency lost much of its value during the war;thus,the implicit tax on those who accepted it as payment.
G)The treaty that ended the Revolutionary War.In the treaty,Great Britain formally recognized American independence and relinquished its claims to lands south of the Great Lakes and east of the Mississippi River.
H)A constitution that granted all taxpaying men the right to vote and hold office and created a unicameral (one-house)legislature with complete power;there was no governor to exercise a veto.Other provisions mandated a system of elementary education and protected citizens from imprisonment for debt.
I)John Adams's theory from Thoughts on Government (1776),which called for three branches of government,each representing one function: executive,legislative,and judicial.This system of dispersed authority was devised to maintain a balance of power and ensure the legitimacy of governmental procedures.
J)The written document defining the structure of the government from 1781 to 1788,under which the Union was a confederation of equal states,with no executive and limited powers,existing mainly to foster a common defense.
K)A land act that provided for orderly settlement and established a process by which settled territories would become the states of Ohio,Indiana,Illinois,Michigan,and Wisconsin.It also banned slavery in the Northwest Territory.
L)A 1786-1787 uprising led by dissident farmers in western Massachusetts,many of them Revolutionary War veterans,protesting the taxation policies of the eastern elites who controlled the state's government.
M)A plan drafted by James Madison that was presented at the Philadelphia Constitutional Convention.It designed a powerful three-branch government,with representation in both houses of the congress tied to population;this plan would have eclipsed the voice of small states in the national government.
N)Alternative to the Virginia Plan drafted by delegates from small states,retaining the confederation's single-house congress with one vote per state.It shared with the Virginia Plan enhanced congressional powers to raise revenue,control commerce,and make binding requisitions on the states.
O)Supporters of the Constitution of 1787,which created a strong central government;their opponents,the Antifederalists,feared that a strong central government would corrupt the nation's newly won liberty.
P)Opponents of ratification of the Constitution.This party feared that a powerful and distant central government would be out of touch with the needs of citizens.They also complained that it failed to guarantee individual liberties in a bill of rights.
Q)An essay by James Madison in The Federalist (1787-1788)that challenged the view that republican governments only worked in small polities;it argued that a geographically expansive national government would better protect republican liberty.
Federalists
A)First major engagement of the new Continental army,defending against 32,000 British troops outside of New York City.
B)A multistage battle in New York ending with the surrender of British general John Burgoyne.The victory ensured the diplomatic success of American representatives in Paris,who won a military alliance with France.
C)A military camp in which George Washington's army of 12,000 soldiers and hundreds of camp followers suffered horribly in the winter of 1777-1778.
D)A 1779 proclamation that declared that any slave who deserted a rebel master would receive protection,freedom,and land from Great Britain.
E)A battle in which French and American troops and a French fleet trapped the British army under the command of General Charles Cornwallis.The Franco-American victory broke the resolve of the British government.
F)A hidden tax on the farmers and artisans who accepted Continental bills in payment for supplies and on the thousands of soldiers who took them as pay.Because of rampant inflation,Continental currency lost much of its value during the war;thus,the implicit tax on those who accepted it as payment.
G)The treaty that ended the Revolutionary War.In the treaty,Great Britain formally recognized American independence and relinquished its claims to lands south of the Great Lakes and east of the Mississippi River.
H)A constitution that granted all taxpaying men the right to vote and hold office and created a unicameral (one-house)legislature with complete power;there was no governor to exercise a veto.Other provisions mandated a system of elementary education and protected citizens from imprisonment for debt.
I)John Adams's theory from Thoughts on Government (1776),which called for three branches of government,each representing one function: executive,legislative,and judicial.This system of dispersed authority was devised to maintain a balance of power and ensure the legitimacy of governmental procedures.
J)The written document defining the structure of the government from 1781 to 1788,under which the Union was a confederation of equal states,with no executive and limited powers,existing mainly to foster a common defense.
K)A land act that provided for orderly settlement and established a process by which settled territories would become the states of Ohio,Indiana,Illinois,Michigan,and Wisconsin.It also banned slavery in the Northwest Territory.
L)A 1786-1787 uprising led by dissident farmers in western Massachusetts,many of them Revolutionary War veterans,protesting the taxation policies of the eastern elites who controlled the state's government.
M)A plan drafted by James Madison that was presented at the Philadelphia Constitutional Convention.It designed a powerful three-branch government,with representation in both houses of the congress tied to population;this plan would have eclipsed the voice of small states in the national government.
N)Alternative to the Virginia Plan drafted by delegates from small states,retaining the confederation's single-house congress with one vote per state.It shared with the Virginia Plan enhanced congressional powers to raise revenue,control commerce,and make binding requisitions on the states.
O)Supporters of the Constitution of 1787,which created a strong central government;their opponents,the Antifederalists,feared that a strong central government would corrupt the nation's newly won liberty.
P)Opponents of ratification of the Constitution.This party feared that a powerful and distant central government would be out of touch with the needs of citizens.They also complained that it failed to guarantee individual liberties in a bill of rights.
Q)An essay by James Madison in The Federalist (1787-1788)that challenged the view that republican governments only worked in small polities;it argued that a geographically expansive national government would better protect republican liberty.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Answer the following questions :
Valley Forge
A)First major engagement of the new Continental army,defending against 32,000 British troops outside of New York City.
B)A multistage battle in New York ending with the surrender of British general John Burgoyne.The victory ensured the diplomatic success of American representatives in Paris,who won a military alliance with France.
C)A military camp in which George Washington's army of 12,000 soldiers and hundreds of camp followers suffered horribly in the winter of 1777-1778.
D)A 1779 proclamation that declared that any slave who deserted a rebel master would receive protection,freedom,and land from Great Britain.
E)A battle in which French and American troops and a French fleet trapped the British army under the command of General Charles Cornwallis.The Franco-American victory broke the resolve of the British government.
F)A hidden tax on the farmers and artisans who accepted Continental bills in payment for supplies and on the thousands of soldiers who took them as pay.Because of rampant inflation,Continental currency lost much of its value during the war;thus,the implicit tax on those who accepted it as payment.
G)The treaty that ended the Revolutionary War.In the treaty,Great Britain formally recognized American independence and relinquished its claims to lands south of the Great Lakes and east of the Mississippi River.
H)A constitution that granted all taxpaying men the right to vote and hold office and created a unicameral (one-house)legislature with complete power;there was no governor to exercise a veto.Other provisions mandated a system of elementary education and protected citizens from imprisonment for debt.
I)John Adams's theory from Thoughts on Government (1776),which called for three branches of government,each representing one function: executive,legislative,and judicial.This system of dispersed authority was devised to maintain a balance of power and ensure the legitimacy of governmental procedures.
J)The written document defining the structure of the government from 1781 to 1788,under which the Union was a confederation of equal states,with no executive and limited powers,existing mainly to foster a common defense.
K)A land act that provided for orderly settlement and established a process by which settled territories would become the states of Ohio,Indiana,Illinois,Michigan,and Wisconsin.It also banned slavery in the Northwest Territory.
L)A 1786-1787 uprising led by dissident farmers in western Massachusetts,many of them Revolutionary War veterans,protesting the taxation policies of the eastern elites who controlled the state's government.
M)A plan drafted by James Madison that was presented at the Philadelphia Constitutional Convention.It designed a powerful three-branch government,with representation in both houses of the congress tied to population;this plan would have eclipsed the voice of small states in the national government.
N)Alternative to the Virginia Plan drafted by delegates from small states,retaining the confederation's single-house congress with one vote per state.It shared with the Virginia Plan enhanced congressional powers to raise revenue,control commerce,and make binding requisitions on the states.
O)Supporters of the Constitution of 1787,which created a strong central government;their opponents,the Antifederalists,feared that a strong central government would corrupt the nation's newly won liberty.
P)Opponents of ratification of the Constitution.This party feared that a powerful and distant central government would be out of touch with the needs of citizens.They also complained that it failed to guarantee individual liberties in a bill of rights.
Q)An essay by James Madison in The Federalist (1787-1788)that challenged the view that republican governments only worked in small polities;it argued that a geographically expansive national government would better protect republican liberty.
Valley Forge
A)First major engagement of the new Continental army,defending against 32,000 British troops outside of New York City.
B)A multistage battle in New York ending with the surrender of British general John Burgoyne.The victory ensured the diplomatic success of American representatives in Paris,who won a military alliance with France.
C)A military camp in which George Washington's army of 12,000 soldiers and hundreds of camp followers suffered horribly in the winter of 1777-1778.
D)A 1779 proclamation that declared that any slave who deserted a rebel master would receive protection,freedom,and land from Great Britain.
E)A battle in which French and American troops and a French fleet trapped the British army under the command of General Charles Cornwallis.The Franco-American victory broke the resolve of the British government.
F)A hidden tax on the farmers and artisans who accepted Continental bills in payment for supplies and on the thousands of soldiers who took them as pay.Because of rampant inflation,Continental currency lost much of its value during the war;thus,the implicit tax on those who accepted it as payment.
G)The treaty that ended the Revolutionary War.In the treaty,Great Britain formally recognized American independence and relinquished its claims to lands south of the Great Lakes and east of the Mississippi River.
H)A constitution that granted all taxpaying men the right to vote and hold office and created a unicameral (one-house)legislature with complete power;there was no governor to exercise a veto.Other provisions mandated a system of elementary education and protected citizens from imprisonment for debt.
I)John Adams's theory from Thoughts on Government (1776),which called for three branches of government,each representing one function: executive,legislative,and judicial.This system of dispersed authority was devised to maintain a balance of power and ensure the legitimacy of governmental procedures.
J)The written document defining the structure of the government from 1781 to 1788,under which the Union was a confederation of equal states,with no executive and limited powers,existing mainly to foster a common defense.
K)A land act that provided for orderly settlement and established a process by which settled territories would become the states of Ohio,Indiana,Illinois,Michigan,and Wisconsin.It also banned slavery in the Northwest Territory.
L)A 1786-1787 uprising led by dissident farmers in western Massachusetts,many of them Revolutionary War veterans,protesting the taxation policies of the eastern elites who controlled the state's government.
M)A plan drafted by James Madison that was presented at the Philadelphia Constitutional Convention.It designed a powerful three-branch government,with representation in both houses of the congress tied to population;this plan would have eclipsed the voice of small states in the national government.
N)Alternative to the Virginia Plan drafted by delegates from small states,retaining the confederation's single-house congress with one vote per state.It shared with the Virginia Plan enhanced congressional powers to raise revenue,control commerce,and make binding requisitions on the states.
O)Supporters of the Constitution of 1787,which created a strong central government;their opponents,the Antifederalists,feared that a strong central government would corrupt the nation's newly won liberty.
P)Opponents of ratification of the Constitution.This party feared that a powerful and distant central government would be out of touch with the needs of citizens.They also complained that it failed to guarantee individual liberties in a bill of rights.
Q)An essay by James Madison in The Federalist (1787-1788)that challenged the view that republican governments only worked in small polities;it argued that a geographically expansive national government would better protect republican liberty.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Answer the following questions :
Philipsburg Proclamation
A)First major engagement of the new Continental army,defending against 32,000 British troops outside of New York City.
B)A multistage battle in New York ending with the surrender of British general John Burgoyne.The victory ensured the diplomatic success of American representatives in Paris,who won a military alliance with France.
C)A military camp in which George Washington's army of 12,000 soldiers and hundreds of camp followers suffered horribly in the winter of 1777-1778.
D)A 1779 proclamation that declared that any slave who deserted a rebel master would receive protection,freedom,and land from Great Britain.
E)A battle in which French and American troops and a French fleet trapped the British army under the command of General Charles Cornwallis.The Franco-American victory broke the resolve of the British government.
F)A hidden tax on the farmers and artisans who accepted Continental bills in payment for supplies and on the thousands of soldiers who took them as pay.Because of rampant inflation,Continental currency lost much of its value during the war;thus,the implicit tax on those who accepted it as payment.
G)The treaty that ended the Revolutionary War.In the treaty,Great Britain formally recognized American independence and relinquished its claims to lands south of the Great Lakes and east of the Mississippi River.
H)A constitution that granted all taxpaying men the right to vote and hold office and created a unicameral (one-house)legislature with complete power;there was no governor to exercise a veto.Other provisions mandated a system of elementary education and protected citizens from imprisonment for debt.
I)John Adams's theory from Thoughts on Government (1776),which called for three branches of government,each representing one function: executive,legislative,and judicial.This system of dispersed authority was devised to maintain a balance of power and ensure the legitimacy of governmental procedures.
J)The written document defining the structure of the government from 1781 to 1788,under which the Union was a confederation of equal states,with no executive and limited powers,existing mainly to foster a common defense.
K)A land act that provided for orderly settlement and established a process by which settled territories would become the states of Ohio,Indiana,Illinois,Michigan,and Wisconsin.It also banned slavery in the Northwest Territory.
L)A 1786-1787 uprising led by dissident farmers in western Massachusetts,many of them Revolutionary War veterans,protesting the taxation policies of the eastern elites who controlled the state's government.
M)A plan drafted by James Madison that was presented at the Philadelphia Constitutional Convention.It designed a powerful three-branch government,with representation in both houses of the congress tied to population;this plan would have eclipsed the voice of small states in the national government.
N)Alternative to the Virginia Plan drafted by delegates from small states,retaining the confederation's single-house congress with one vote per state.It shared with the Virginia Plan enhanced congressional powers to raise revenue,control commerce,and make binding requisitions on the states.
O)Supporters of the Constitution of 1787,which created a strong central government;their opponents,the Antifederalists,feared that a strong central government would corrupt the nation's newly won liberty.
P)Opponents of ratification of the Constitution.This party feared that a powerful and distant central government would be out of touch with the needs of citizens.They also complained that it failed to guarantee individual liberties in a bill of rights.
Q)An essay by James Madison in The Federalist (1787-1788)that challenged the view that republican governments only worked in small polities;it argued that a geographically expansive national government would better protect republican liberty.
Philipsburg Proclamation
A)First major engagement of the new Continental army,defending against 32,000 British troops outside of New York City.
B)A multistage battle in New York ending with the surrender of British general John Burgoyne.The victory ensured the diplomatic success of American representatives in Paris,who won a military alliance with France.
C)A military camp in which George Washington's army of 12,000 soldiers and hundreds of camp followers suffered horribly in the winter of 1777-1778.
D)A 1779 proclamation that declared that any slave who deserted a rebel master would receive protection,freedom,and land from Great Britain.
E)A battle in which French and American troops and a French fleet trapped the British army under the command of General Charles Cornwallis.The Franco-American victory broke the resolve of the British government.
F)A hidden tax on the farmers and artisans who accepted Continental bills in payment for supplies and on the thousands of soldiers who took them as pay.Because of rampant inflation,Continental currency lost much of its value during the war;thus,the implicit tax on those who accepted it as payment.
G)The treaty that ended the Revolutionary War.In the treaty,Great Britain formally recognized American independence and relinquished its claims to lands south of the Great Lakes and east of the Mississippi River.
H)A constitution that granted all taxpaying men the right to vote and hold office and created a unicameral (one-house)legislature with complete power;there was no governor to exercise a veto.Other provisions mandated a system of elementary education and protected citizens from imprisonment for debt.
I)John Adams's theory from Thoughts on Government (1776),which called for three branches of government,each representing one function: executive,legislative,and judicial.This system of dispersed authority was devised to maintain a balance of power and ensure the legitimacy of governmental procedures.
J)The written document defining the structure of the government from 1781 to 1788,under which the Union was a confederation of equal states,with no executive and limited powers,existing mainly to foster a common defense.
K)A land act that provided for orderly settlement and established a process by which settled territories would become the states of Ohio,Indiana,Illinois,Michigan,and Wisconsin.It also banned slavery in the Northwest Territory.
L)A 1786-1787 uprising led by dissident farmers in western Massachusetts,many of them Revolutionary War veterans,protesting the taxation policies of the eastern elites who controlled the state's government.
M)A plan drafted by James Madison that was presented at the Philadelphia Constitutional Convention.It designed a powerful three-branch government,with representation in both houses of the congress tied to population;this plan would have eclipsed the voice of small states in the national government.
N)Alternative to the Virginia Plan drafted by delegates from small states,retaining the confederation's single-house congress with one vote per state.It shared with the Virginia Plan enhanced congressional powers to raise revenue,control commerce,and make binding requisitions on the states.
O)Supporters of the Constitution of 1787,which created a strong central government;their opponents,the Antifederalists,feared that a strong central government would corrupt the nation's newly won liberty.
P)Opponents of ratification of the Constitution.This party feared that a powerful and distant central government would be out of touch with the needs of citizens.They also complained that it failed to guarantee individual liberties in a bill of rights.
Q)An essay by James Madison in The Federalist (1787-1788)that challenged the view that republican governments only worked in small polities;it argued that a geographically expansive national government would better protect republican liberty.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
In Federalist No.10,James Madison maintained that the constitutional government would accomplish which of the following ends?
A) Eliminate the need for political parties
B) Protect the rights of individual states against abuses by the central government
C) Prevent any one faction from becoming dominant
D) Bring focus and order to American foreign policy
A) Eliminate the need for political parties
B) Protect the rights of individual states against abuses by the central government
C) Prevent any one faction from becoming dominant
D) Bring focus and order to American foreign policy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
For this question,refer to the following excerpt. Mr.Martin proposed to vary article 7,sect.4 so as to allow a prohibition or tax on the importation of slaves....[He believed] it was inconsistent with the principles of the Revolution,and dishonorable to the American character,to have such a feature [promoting the slave trade] in the Constitution....
Mr)[Oliver] Ellsworth [of Connecticut] was for leaving the clause as it stands.Let every state import what it pleases.The morality or wisdom of slavery are considerations belonging to the states themselves....
Col)[George] Mason [of Virginia stated that] this infernal trade originated in the avarice of British merchants.The British government constantly checked the attempts of Virginia to put a stop to it.The Western people are already calling out for slaves for their new lands,and will fill that country with slaves,if they can be got through South Carolina and Georgia.Slavery discourages arts and manufactures.The poor despise labor when performed by slaves.They prevent the immigration of whites,who really enrich and strengthen a country....
Every master of slaves is born a petty tyrant.They bring the judgment of Heaven on a country.As nations cannot be rewarded or punished in the next world,they must be in this.By an inevitable chain of causes and effects,Providence punishes national sins by national calamities....He held it essential,in every point of view,that the general government should have power to prevent the increase of slavery....
Gen)[Charles C.] Pinckney [argued that] South Carolina and Georgia cannot do without slaves....He contended that the importation of slaves would be for the interest of the whole Union.The more slaves,the more produce to employ the carrying trade;the more consumption also;and the more of this,the more revenue for the common treasury....
The Records of the Federal Convention of 1787
Which of the following resulted most directly from the debate described in the passage above?
A) Property qualifications were established for voting and citizenship.
B) Greater political democracy was called for in new state and national governments.
C) A solution to the slave issue was postponed,setting the stage for recurring conflicts.
D) The ideals set forth in the excerpt had reverberations in France,Haiti,and Latin America,inspiring future rebellions.
Mr)[Oliver] Ellsworth [of Connecticut] was for leaving the clause as it stands.Let every state import what it pleases.The morality or wisdom of slavery are considerations belonging to the states themselves....
Col)[George] Mason [of Virginia stated that] this infernal trade originated in the avarice of British merchants.The British government constantly checked the attempts of Virginia to put a stop to it.The Western people are already calling out for slaves for their new lands,and will fill that country with slaves,if they can be got through South Carolina and Georgia.Slavery discourages arts and manufactures.The poor despise labor when performed by slaves.They prevent the immigration of whites,who really enrich and strengthen a country....
Every master of slaves is born a petty tyrant.They bring the judgment of Heaven on a country.As nations cannot be rewarded or punished in the next world,they must be in this.By an inevitable chain of causes and effects,Providence punishes national sins by national calamities....He held it essential,in every point of view,that the general government should have power to prevent the increase of slavery....
Gen)[Charles C.] Pinckney [argued that] South Carolina and Georgia cannot do without slaves....He contended that the importation of slaves would be for the interest of the whole Union.The more slaves,the more produce to employ the carrying trade;the more consumption also;and the more of this,the more revenue for the common treasury....
The Records of the Federal Convention of 1787
Which of the following resulted most directly from the debate described in the passage above?
A) Property qualifications were established for voting and citizenship.
B) Greater political democracy was called for in new state and national governments.
C) A solution to the slave issue was postponed,setting the stage for recurring conflicts.
D) The ideals set forth in the excerpt had reverberations in France,Haiti,and Latin America,inspiring future rebellions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The Great Compromise led to which of the following outcomes?
A) A bicameral legislature with a House of Representatives and a Senate
B) The separation of powers among the executive,legislative,and judicial branches
C) A division of powers between the states and the national government
D) Interstate and foreign trade controlled by the national government
A) A bicameral legislature with a House of Representatives and a Senate
B) The separation of powers among the executive,legislative,and judicial branches
C) A division of powers between the states and the national government
D) Interstate and foreign trade controlled by the national government

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The three-fifths compromise dealt with which of the following issues?
A) Interstate trade
B) Presidential terms
C) Slavery
D) Voting qualifications
A) Interstate trade
B) Presidential terms
C) Slavery
D) Voting qualifications

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Answer the following questions :
Treaty of Paris of 1783
A)First major engagement of the new Continental army,defending against 32,000 British troops outside of New York City.
B)A multistage battle in New York ending with the surrender of British general John Burgoyne.The victory ensured the diplomatic success of American representatives in Paris,who won a military alliance with France.
C)A military camp in which George Washington's army of 12,000 soldiers and hundreds of camp followers suffered horribly in the winter of 1777-1778.
D)A 1779 proclamation that declared that any slave who deserted a rebel master would receive protection,freedom,and land from Great Britain.
E)A battle in which French and American troops and a French fleet trapped the British army under the command of General Charles Cornwallis.The Franco-American victory broke the resolve of the British government.
F)A hidden tax on the farmers and artisans who accepted Continental bills in payment for supplies and on the thousands of soldiers who took them as pay.Because of rampant inflation,Continental currency lost much of its value during the war;thus,the implicit tax on those who accepted it as payment.
G)The treaty that ended the Revolutionary War.In the treaty,Great Britain formally recognized American independence and relinquished its claims to lands south of the Great Lakes and east of the Mississippi River.
H)A constitution that granted all taxpaying men the right to vote and hold office and created a unicameral (one-house)legislature with complete power;there was no governor to exercise a veto.Other provisions mandated a system of elementary education and protected citizens from imprisonment for debt.
I)John Adams's theory from Thoughts on Government (1776),which called for three branches of government,each representing one function: executive,legislative,and judicial.This system of dispersed authority was devised to maintain a balance of power and ensure the legitimacy of governmental procedures.
J)The written document defining the structure of the government from 1781 to 1788,under which the Union was a confederation of equal states,with no executive and limited powers,existing mainly to foster a common defense.
K)A land act that provided for orderly settlement and established a process by which settled territories would become the states of Ohio,Indiana,Illinois,Michigan,and Wisconsin.It also banned slavery in the Northwest Territory.
L)A 1786-1787 uprising led by dissident farmers in western Massachusetts,many of them Revolutionary War veterans,protesting the taxation policies of the eastern elites who controlled the state's government.
M)A plan drafted by James Madison that was presented at the Philadelphia Constitutional Convention.It designed a powerful three-branch government,with representation in both houses of the congress tied to population;this plan would have eclipsed the voice of small states in the national government.
N)Alternative to the Virginia Plan drafted by delegates from small states,retaining the confederation's single-house congress with one vote per state.It shared with the Virginia Plan enhanced congressional powers to raise revenue,control commerce,and make binding requisitions on the states.
O)Supporters of the Constitution of 1787,which created a strong central government;their opponents,the Antifederalists,feared that a strong central government would corrupt the nation's newly won liberty.
P)Opponents of ratification of the Constitution.This party feared that a powerful and distant central government would be out of touch with the needs of citizens.They also complained that it failed to guarantee individual liberties in a bill of rights.
Q)An essay by James Madison in The Federalist (1787-1788)that challenged the view that republican governments only worked in small polities;it argued that a geographically expansive national government would better protect republican liberty.
Treaty of Paris of 1783
A)First major engagement of the new Continental army,defending against 32,000 British troops outside of New York City.
B)A multistage battle in New York ending with the surrender of British general John Burgoyne.The victory ensured the diplomatic success of American representatives in Paris,who won a military alliance with France.
C)A military camp in which George Washington's army of 12,000 soldiers and hundreds of camp followers suffered horribly in the winter of 1777-1778.
D)A 1779 proclamation that declared that any slave who deserted a rebel master would receive protection,freedom,and land from Great Britain.
E)A battle in which French and American troops and a French fleet trapped the British army under the command of General Charles Cornwallis.The Franco-American victory broke the resolve of the British government.
F)A hidden tax on the farmers and artisans who accepted Continental bills in payment for supplies and on the thousands of soldiers who took them as pay.Because of rampant inflation,Continental currency lost much of its value during the war;thus,the implicit tax on those who accepted it as payment.
G)The treaty that ended the Revolutionary War.In the treaty,Great Britain formally recognized American independence and relinquished its claims to lands south of the Great Lakes and east of the Mississippi River.
H)A constitution that granted all taxpaying men the right to vote and hold office and created a unicameral (one-house)legislature with complete power;there was no governor to exercise a veto.Other provisions mandated a system of elementary education and protected citizens from imprisonment for debt.
I)John Adams's theory from Thoughts on Government (1776),which called for three branches of government,each representing one function: executive,legislative,and judicial.This system of dispersed authority was devised to maintain a balance of power and ensure the legitimacy of governmental procedures.
J)The written document defining the structure of the government from 1781 to 1788,under which the Union was a confederation of equal states,with no executive and limited powers,existing mainly to foster a common defense.
K)A land act that provided for orderly settlement and established a process by which settled territories would become the states of Ohio,Indiana,Illinois,Michigan,and Wisconsin.It also banned slavery in the Northwest Territory.
L)A 1786-1787 uprising led by dissident farmers in western Massachusetts,many of them Revolutionary War veterans,protesting the taxation policies of the eastern elites who controlled the state's government.
M)A plan drafted by James Madison that was presented at the Philadelphia Constitutional Convention.It designed a powerful three-branch government,with representation in both houses of the congress tied to population;this plan would have eclipsed the voice of small states in the national government.
N)Alternative to the Virginia Plan drafted by delegates from small states,retaining the confederation's single-house congress with one vote per state.It shared with the Virginia Plan enhanced congressional powers to raise revenue,control commerce,and make binding requisitions on the states.
O)Supporters of the Constitution of 1787,which created a strong central government;their opponents,the Antifederalists,feared that a strong central government would corrupt the nation's newly won liberty.
P)Opponents of ratification of the Constitution.This party feared that a powerful and distant central government would be out of touch with the needs of citizens.They also complained that it failed to guarantee individual liberties in a bill of rights.
Q)An essay by James Madison in The Federalist (1787-1788)that challenged the view that republican governments only worked in small polities;it argued that a geographically expansive national government would better protect republican liberty.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The Constitution,as completed on September 17,1787,gave the national government which of the following?
A) Powers equal to those that were granted to the states
B) A weak chief executive with carefully limited powers
C) Fewer powers than those reserved to the states
D) Broad powers over taxation,military defense,and commerce
A) Powers equal to those that were granted to the states
B) A weak chief executive with carefully limited powers
C) Fewer powers than those reserved to the states
D) Broad powers over taxation,military defense,and commerce

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
For this question,refer to the following map,"Land Division in the Northwest Territory." 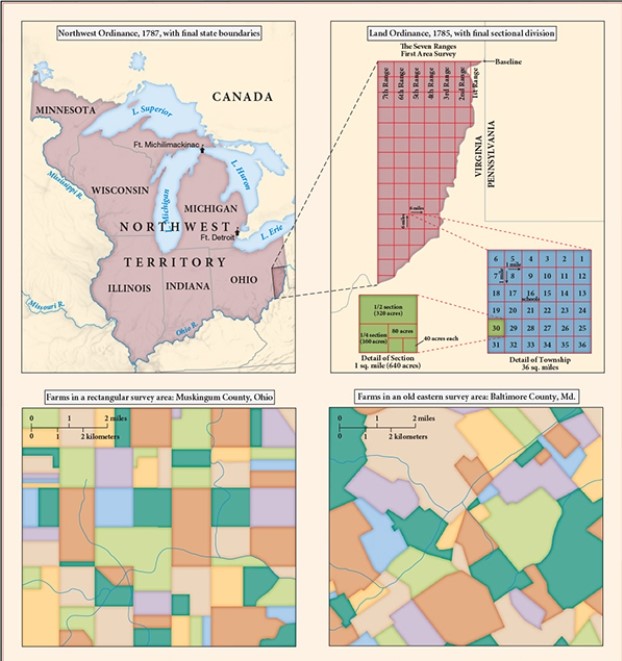 The map above reflects most directly which of the following continuities in U.S.history?
The map above reflects most directly which of the following continuities in U.S.history?
A) The concept of Manifest Destiny and the sense of a unique national mission
B) The tendency to cling to regional identities
C) Debates over the proper relationship between the federal and state governments
D) The failure to define precisely the relationship between American Indian tribes and the national government
 The map above reflects most directly which of the following continuities in U.S.history?
The map above reflects most directly which of the following continuities in U.S.history?A) The concept of Manifest Destiny and the sense of a unique national mission
B) The tendency to cling to regional identities
C) Debates over the proper relationship between the federal and state governments
D) The failure to define precisely the relationship between American Indian tribes and the national government

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Answer the following questions :
Shays's Rebellion
A)First major engagement of the new Continental army,defending against 32,000 British troops outside of New York City.
B)A multistage battle in New York ending with the surrender of British general John Burgoyne.The victory ensured the diplomatic success of American representatives in Paris,who won a military alliance with France.
C)A military camp in which George Washington's army of 12,000 soldiers and hundreds of camp followers suffered horribly in the winter of 1777-1778.
D)A 1779 proclamation that declared that any slave who deserted a rebel master would receive protection,freedom,and land from Great Britain.
E)A battle in which French and American troops and a French fleet trapped the British army under the command of General Charles Cornwallis.The Franco-American victory broke the resolve of the British government.
F)A hidden tax on the farmers and artisans who accepted Continental bills in payment for supplies and on the thousands of soldiers who took them as pay.Because of rampant inflation,Continental currency lost much of its value during the war;thus,the implicit tax on those who accepted it as payment.
G)The treaty that ended the Revolutionary War.In the treaty,Great Britain formally recognized American independence and relinquished its claims to lands south of the Great Lakes and east of the Mississippi River.
H)A constitution that granted all taxpaying men the right to vote and hold office and created a unicameral (one-house)legislature with complete power;there was no governor to exercise a veto.Other provisions mandated a system of elementary education and protected citizens from imprisonment for debt.
I)John Adams's theory from Thoughts on Government (1776),which called for three branches of government,each representing one function: executive,legislative,and judicial.This system of dispersed authority was devised to maintain a balance of power and ensure the legitimacy of governmental procedures.
J)The written document defining the structure of the government from 1781 to 1788,under which the Union was a confederation of equal states,with no executive and limited powers,existing mainly to foster a common defense.
K)A land act that provided for orderly settlement and established a process by which settled territories would become the states of Ohio,Indiana,Illinois,Michigan,and Wisconsin.It also banned slavery in the Northwest Territory.
L)A 1786-1787 uprising led by dissident farmers in western Massachusetts,many of them Revolutionary War veterans,protesting the taxation policies of the eastern elites who controlled the state's government.
M)A plan drafted by James Madison that was presented at the Philadelphia Constitutional Convention.It designed a powerful three-branch government,with representation in both houses of the congress tied to population;this plan would have eclipsed the voice of small states in the national government.
N)Alternative to the Virginia Plan drafted by delegates from small states,retaining the confederation's single-house congress with one vote per state.It shared with the Virginia Plan enhanced congressional powers to raise revenue,control commerce,and make binding requisitions on the states.
O)Supporters of the Constitution of 1787,which created a strong central government;their opponents,the Antifederalists,feared that a strong central government would corrupt the nation's newly won liberty.
P)Opponents of ratification of the Constitution.This party feared that a powerful and distant central government would be out of touch with the needs of citizens.They also complained that it failed to guarantee individual liberties in a bill of rights.
Q)An essay by James Madison in The Federalist (1787-1788)that challenged the view that republican governments only worked in small polities;it argued that a geographically expansive national government would better protect republican liberty.
Shays's Rebellion
A)First major engagement of the new Continental army,defending against 32,000 British troops outside of New York City.
B)A multistage battle in New York ending with the surrender of British general John Burgoyne.The victory ensured the diplomatic success of American representatives in Paris,who won a military alliance with France.
C)A military camp in which George Washington's army of 12,000 soldiers and hundreds of camp followers suffered horribly in the winter of 1777-1778.
D)A 1779 proclamation that declared that any slave who deserted a rebel master would receive protection,freedom,and land from Great Britain.
E)A battle in which French and American troops and a French fleet trapped the British army under the command of General Charles Cornwallis.The Franco-American victory broke the resolve of the British government.
F)A hidden tax on the farmers and artisans who accepted Continental bills in payment for supplies and on the thousands of soldiers who took them as pay.Because of rampant inflation,Continental currency lost much of its value during the war;thus,the implicit tax on those who accepted it as payment.
G)The treaty that ended the Revolutionary War.In the treaty,Great Britain formally recognized American independence and relinquished its claims to lands south of the Great Lakes and east of the Mississippi River.
H)A constitution that granted all taxpaying men the right to vote and hold office and created a unicameral (one-house)legislature with complete power;there was no governor to exercise a veto.Other provisions mandated a system of elementary education and protected citizens from imprisonment for debt.
I)John Adams's theory from Thoughts on Government (1776),which called for three branches of government,each representing one function: executive,legislative,and judicial.This system of dispersed authority was devised to maintain a balance of power and ensure the legitimacy of governmental procedures.
J)The written document defining the structure of the government from 1781 to 1788,under which the Union was a confederation of equal states,with no executive and limited powers,existing mainly to foster a common defense.
K)A land act that provided for orderly settlement and established a process by which settled territories would become the states of Ohio,Indiana,Illinois,Michigan,and Wisconsin.It also banned slavery in the Northwest Territory.
L)A 1786-1787 uprising led by dissident farmers in western Massachusetts,many of them Revolutionary War veterans,protesting the taxation policies of the eastern elites who controlled the state's government.
M)A plan drafted by James Madison that was presented at the Philadelphia Constitutional Convention.It designed a powerful three-branch government,with representation in both houses of the congress tied to population;this plan would have eclipsed the voice of small states in the national government.
N)Alternative to the Virginia Plan drafted by delegates from small states,retaining the confederation's single-house congress with one vote per state.It shared with the Virginia Plan enhanced congressional powers to raise revenue,control commerce,and make binding requisitions on the states.
O)Supporters of the Constitution of 1787,which created a strong central government;their opponents,the Antifederalists,feared that a strong central government would corrupt the nation's newly won liberty.
P)Opponents of ratification of the Constitution.This party feared that a powerful and distant central government would be out of touch with the needs of citizens.They also complained that it failed to guarantee individual liberties in a bill of rights.
Q)An essay by James Madison in The Federalist (1787-1788)that challenged the view that republican governments only worked in small polities;it argued that a geographically expansive national government would better protect republican liberty.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Answer the following questions :
Pennsylvania constitution of 1776
A)First major engagement of the new Continental army,defending against 32,000 British troops outside of New York City.
B)A multistage battle in New York ending with the surrender of British general John Burgoyne.The victory ensured the diplomatic success of American representatives in Paris,who won a military alliance with France.
C)A military camp in which George Washington's army of 12,000 soldiers and hundreds of camp followers suffered horribly in the winter of 1777-1778.
D)A 1779 proclamation that declared that any slave who deserted a rebel master would receive protection,freedom,and land from Great Britain.
E)A battle in which French and American troops and a French fleet trapped the British army under the command of General Charles Cornwallis.The Franco-American victory broke the resolve of the British government.
F)A hidden tax on the farmers and artisans who accepted Continental bills in payment for supplies and on the thousands of soldiers who took them as pay.Because of rampant inflation,Continental currency lost much of its value during the war;thus,the implicit tax on those who accepted it as payment.
G)The treaty that ended the Revolutionary War.In the treaty,Great Britain formally recognized American independence and relinquished its claims to lands south of the Great Lakes and east of the Mississippi River.
H)A constitution that granted all taxpaying men the right to vote and hold office and created a unicameral (one-house)legislature with complete power;there was no governor to exercise a veto.Other provisions mandated a system of elementary education and protected citizens from imprisonment for debt.
I)John Adams's theory from Thoughts on Government (1776),which called for three branches of government,each representing one function: executive,legislative,and judicial.This system of dispersed authority was devised to maintain a balance of power and ensure the legitimacy of governmental procedures.
J)The written document defining the structure of the government from 1781 to 1788,under which the Union was a confederation of equal states,with no executive and limited powers,existing mainly to foster a common defense.
K)A land act that provided for orderly settlement and established a process by which settled territories would become the states of Ohio,Indiana,Illinois,Michigan,and Wisconsin.It also banned slavery in the Northwest Territory.
L)A 1786-1787 uprising led by dissident farmers in western Massachusetts,many of them Revolutionary War veterans,protesting the taxation policies of the eastern elites who controlled the state's government.
M)A plan drafted by James Madison that was presented at the Philadelphia Constitutional Convention.It designed a powerful three-branch government,with representation in both houses of the congress tied to population;this plan would have eclipsed the voice of small states in the national government.
N)Alternative to the Virginia Plan drafted by delegates from small states,retaining the confederation's single-house congress with one vote per state.It shared with the Virginia Plan enhanced congressional powers to raise revenue,control commerce,and make binding requisitions on the states.
O)Supporters of the Constitution of 1787,which created a strong central government;their opponents,the Antifederalists,feared that a strong central government would corrupt the nation's newly won liberty.
P)Opponents of ratification of the Constitution.This party feared that a powerful and distant central government would be out of touch with the needs of citizens.They also complained that it failed to guarantee individual liberties in a bill of rights.
Q)An essay by James Madison in The Federalist (1787-1788)that challenged the view that republican governments only worked in small polities;it argued that a geographically expansive national government would better protect republican liberty.
Pennsylvania constitution of 1776
A)First major engagement of the new Continental army,defending against 32,000 British troops outside of New York City.
B)A multistage battle in New York ending with the surrender of British general John Burgoyne.The victory ensured the diplomatic success of American representatives in Paris,who won a military alliance with France.
C)A military camp in which George Washington's army of 12,000 soldiers and hundreds of camp followers suffered horribly in the winter of 1777-1778.
D)A 1779 proclamation that declared that any slave who deserted a rebel master would receive protection,freedom,and land from Great Britain.
E)A battle in which French and American troops and a French fleet trapped the British army under the command of General Charles Cornwallis.The Franco-American victory broke the resolve of the British government.
F)A hidden tax on the farmers and artisans who accepted Continental bills in payment for supplies and on the thousands of soldiers who took them as pay.Because of rampant inflation,Continental currency lost much of its value during the war;thus,the implicit tax on those who accepted it as payment.
G)The treaty that ended the Revolutionary War.In the treaty,Great Britain formally recognized American independence and relinquished its claims to lands south of the Great Lakes and east of the Mississippi River.
H)A constitution that granted all taxpaying men the right to vote and hold office and created a unicameral (one-house)legislature with complete power;there was no governor to exercise a veto.Other provisions mandated a system of elementary education and protected citizens from imprisonment for debt.
I)John Adams's theory from Thoughts on Government (1776),which called for three branches of government,each representing one function: executive,legislative,and judicial.This system of dispersed authority was devised to maintain a balance of power and ensure the legitimacy of governmental procedures.
J)The written document defining the structure of the government from 1781 to 1788,under which the Union was a confederation of equal states,with no executive and limited powers,existing mainly to foster a common defense.
K)A land act that provided for orderly settlement and established a process by which settled territories would become the states of Ohio,Indiana,Illinois,Michigan,and Wisconsin.It also banned slavery in the Northwest Territory.
L)A 1786-1787 uprising led by dissident farmers in western Massachusetts,many of them Revolutionary War veterans,protesting the taxation policies of the eastern elites who controlled the state's government.
M)A plan drafted by James Madison that was presented at the Philadelphia Constitutional Convention.It designed a powerful three-branch government,with representation in both houses of the congress tied to population;this plan would have eclipsed the voice of small states in the national government.
N)Alternative to the Virginia Plan drafted by delegates from small states,retaining the confederation's single-house congress with one vote per state.It shared with the Virginia Plan enhanced congressional powers to raise revenue,control commerce,and make binding requisitions on the states.
O)Supporters of the Constitution of 1787,which created a strong central government;their opponents,the Antifederalists,feared that a strong central government would corrupt the nation's newly won liberty.
P)Opponents of ratification of the Constitution.This party feared that a powerful and distant central government would be out of touch with the needs of citizens.They also complained that it failed to guarantee individual liberties in a bill of rights.
Q)An essay by James Madison in The Federalist (1787-1788)that challenged the view that republican governments only worked in small polities;it argued that a geographically expansive national government would better protect republican liberty.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
What were the causes of Shays's Rebellion?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Why were British forces militarily superior to American forces in the first years of the war? How did the Americans sustain the Revolution between 1776 and 1778? What accounted for the American victory by 1783?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
To what extent was there a consensus among different social groups about the meaning of America's republican revolution? What evidence does the chapter provide?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Why did Britain switch to a southern military strategy? Why did that strategy ultimately fail?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Why was the Constitution a controversial document even as it was being written?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Answer the following questions :
Articles of Confederation
A)First major engagement of the new Continental army,defending against 32,000 British troops outside of New York City.
B)A multistage battle in New York ending with the surrender of British general John Burgoyne.The victory ensured the diplomatic success of American representatives in Paris,who won a military alliance with France.
C)A military camp in which George Washington's army of 12,000 soldiers and hundreds of camp followers suffered horribly in the winter of 1777-1778.
D)A 1779 proclamation that declared that any slave who deserted a rebel master would receive protection,freedom,and land from Great Britain.
E)A battle in which French and American troops and a French fleet trapped the British army under the command of General Charles Cornwallis.The Franco-American victory broke the resolve of the British government.
F)A hidden tax on the farmers and artisans who accepted Continental bills in payment for supplies and on the thousands of soldiers who took them as pay.Because of rampant inflation,Continental currency lost much of its value during the war;thus,the implicit tax on those who accepted it as payment.
G)The treaty that ended the Revolutionary War.In the treaty,Great Britain formally recognized American independence and relinquished its claims to lands south of the Great Lakes and east of the Mississippi River.
H)A constitution that granted all taxpaying men the right to vote and hold office and created a unicameral (one-house)legislature with complete power;there was no governor to exercise a veto.Other provisions mandated a system of elementary education and protected citizens from imprisonment for debt.
I)John Adams's theory from Thoughts on Government (1776),which called for three branches of government,each representing one function: executive,legislative,and judicial.This system of dispersed authority was devised to maintain a balance of power and ensure the legitimacy of governmental procedures.
J)The written document defining the structure of the government from 1781 to 1788,under which the Union was a confederation of equal states,with no executive and limited powers,existing mainly to foster a common defense.
K)A land act that provided for orderly settlement and established a process by which settled territories would become the states of Ohio,Indiana,Illinois,Michigan,and Wisconsin.It also banned slavery in the Northwest Territory.
L)A 1786-1787 uprising led by dissident farmers in western Massachusetts,many of them Revolutionary War veterans,protesting the taxation policies of the eastern elites who controlled the state's government.
M)A plan drafted by James Madison that was presented at the Philadelphia Constitutional Convention.It designed a powerful three-branch government,with representation in both houses of the congress tied to population;this plan would have eclipsed the voice of small states in the national government.
N)Alternative to the Virginia Plan drafted by delegates from small states,retaining the confederation's single-house congress with one vote per state.It shared with the Virginia Plan enhanced congressional powers to raise revenue,control commerce,and make binding requisitions on the states.
O)Supporters of the Constitution of 1787,which created a strong central government;their opponents,the Antifederalists,feared that a strong central government would corrupt the nation's newly won liberty.
P)Opponents of ratification of the Constitution.This party feared that a powerful and distant central government would be out of touch with the needs of citizens.They also complained that it failed to guarantee individual liberties in a bill of rights.
Q)An essay by James Madison in The Federalist (1787-1788)that challenged the view that republican governments only worked in small polities;it argued that a geographically expansive national government would better protect republican liberty.
Articles of Confederation
A)First major engagement of the new Continental army,defending against 32,000 British troops outside of New York City.
B)A multistage battle in New York ending with the surrender of British general John Burgoyne.The victory ensured the diplomatic success of American representatives in Paris,who won a military alliance with France.
C)A military camp in which George Washington's army of 12,000 soldiers and hundreds of camp followers suffered horribly in the winter of 1777-1778.
D)A 1779 proclamation that declared that any slave who deserted a rebel master would receive protection,freedom,and land from Great Britain.
E)A battle in which French and American troops and a French fleet trapped the British army under the command of General Charles Cornwallis.The Franco-American victory broke the resolve of the British government.
F)A hidden tax on the farmers and artisans who accepted Continental bills in payment for supplies and on the thousands of soldiers who took them as pay.Because of rampant inflation,Continental currency lost much of its value during the war;thus,the implicit tax on those who accepted it as payment.
G)The treaty that ended the Revolutionary War.In the treaty,Great Britain formally recognized American independence and relinquished its claims to lands south of the Great Lakes and east of the Mississippi River.
H)A constitution that granted all taxpaying men the right to vote and hold office and created a unicameral (one-house)legislature with complete power;there was no governor to exercise a veto.Other provisions mandated a system of elementary education and protected citizens from imprisonment for debt.
I)John Adams's theory from Thoughts on Government (1776),which called for three branches of government,each representing one function: executive,legislative,and judicial.This system of dispersed authority was devised to maintain a balance of power and ensure the legitimacy of governmental procedures.
J)The written document defining the structure of the government from 1781 to 1788,under which the Union was a confederation of equal states,with no executive and limited powers,existing mainly to foster a common defense.
K)A land act that provided for orderly settlement and established a process by which settled territories would become the states of Ohio,Indiana,Illinois,Michigan,and Wisconsin.It also banned slavery in the Northwest Territory.
L)A 1786-1787 uprising led by dissident farmers in western Massachusetts,many of them Revolutionary War veterans,protesting the taxation policies of the eastern elites who controlled the state's government.
M)A plan drafted by James Madison that was presented at the Philadelphia Constitutional Convention.It designed a powerful three-branch government,with representation in both houses of the congress tied to population;this plan would have eclipsed the voice of small states in the national government.
N)Alternative to the Virginia Plan drafted by delegates from small states,retaining the confederation's single-house congress with one vote per state.It shared with the Virginia Plan enhanced congressional powers to raise revenue,control commerce,and make binding requisitions on the states.
O)Supporters of the Constitution of 1787,which created a strong central government;their opponents,the Antifederalists,feared that a strong central government would corrupt the nation's newly won liberty.
P)Opponents of ratification of the Constitution.This party feared that a powerful and distant central government would be out of touch with the needs of citizens.They also complained that it failed to guarantee individual liberties in a bill of rights.
Q)An essay by James Madison in The Federalist (1787-1788)that challenged the view that republican governments only worked in small polities;it argued that a geographically expansive national government would better protect republican liberty.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Answer the following questions :
Battle of Saratoga (1777)
A)First major engagement of the new Continental army,defending against 32,000 British troops outside of New York City.
B)A multistage battle in New York ending with the surrender of British general John Burgoyne.The victory ensured the diplomatic success of American representatives in Paris,who won a military alliance with France.
C)A military camp in which George Washington's army of 12,000 soldiers and hundreds of camp followers suffered horribly in the winter of 1777-1778.
D)A 1779 proclamation that declared that any slave who deserted a rebel master would receive protection,freedom,and land from Great Britain.
E)A battle in which French and American troops and a French fleet trapped the British army under the command of General Charles Cornwallis.The Franco-American victory broke the resolve of the British government.
F)A hidden tax on the farmers and artisans who accepted Continental bills in payment for supplies and on the thousands of soldiers who took them as pay.Because of rampant inflation,Continental currency lost much of its value during the war;thus,the implicit tax on those who accepted it as payment.
G)The treaty that ended the Revolutionary War.In the treaty,Great Britain formally recognized American independence and relinquished its claims to lands south of the Great Lakes and east of the Mississippi River.
H)A constitution that granted all taxpaying men the right to vote and hold office and created a unicameral (one-house)legislature with complete power;there was no governor to exercise a veto.Other provisions mandated a system of elementary education and protected citizens from imprisonment for debt.
I)John Adams's theory from Thoughts on Government (1776),which called for three branches of government,each representing one function: executive,legislative,and judicial.This system of dispersed authority was devised to maintain a balance of power and ensure the legitimacy of governmental procedures.
J)The written document defining the structure of the government from 1781 to 1788,under which the Union was a confederation of equal states,with no executive and limited powers,existing mainly to foster a common defense.
K)A land act that provided for orderly settlement and established a process by which settled territories would become the states of Ohio,Indiana,Illinois,Michigan,and Wisconsin.It also banned slavery in the Northwest Territory.
L)A 1786-1787 uprising led by dissident farmers in western Massachusetts,many of them Revolutionary War veterans,protesting the taxation policies of the eastern elites who controlled the state's government.
M)A plan drafted by James Madison that was presented at the Philadelphia Constitutional Convention.It designed a powerful three-branch government,with representation in both houses of the congress tied to population;this plan would have eclipsed the voice of small states in the national government.
N)Alternative to the Virginia Plan drafted by delegates from small states,retaining the confederation's single-house congress with one vote per state.It shared with the Virginia Plan enhanced congressional powers to raise revenue,control commerce,and make binding requisitions on the states.
O)Supporters of the Constitution of 1787,which created a strong central government;their opponents,the Antifederalists,feared that a strong central government would corrupt the nation's newly won liberty.
P)Opponents of ratification of the Constitution.This party feared that a powerful and distant central government would be out of touch with the needs of citizens.They also complained that it failed to guarantee individual liberties in a bill of rights.
Q)An essay by James Madison in The Federalist (1787-1788)that challenged the view that republican governments only worked in small polities;it argued that a geographically expansive national government would better protect republican liberty.
Battle of Saratoga (1777)
A)First major engagement of the new Continental army,defending against 32,000 British troops outside of New York City.
B)A multistage battle in New York ending with the surrender of British general John Burgoyne.The victory ensured the diplomatic success of American representatives in Paris,who won a military alliance with France.
C)A military camp in which George Washington's army of 12,000 soldiers and hundreds of camp followers suffered horribly in the winter of 1777-1778.
D)A 1779 proclamation that declared that any slave who deserted a rebel master would receive protection,freedom,and land from Great Britain.
E)A battle in which French and American troops and a French fleet trapped the British army under the command of General Charles Cornwallis.The Franco-American victory broke the resolve of the British government.
F)A hidden tax on the farmers and artisans who accepted Continental bills in payment for supplies and on the thousands of soldiers who took them as pay.Because of rampant inflation,Continental currency lost much of its value during the war;thus,the implicit tax on those who accepted it as payment.
G)The treaty that ended the Revolutionary War.In the treaty,Great Britain formally recognized American independence and relinquished its claims to lands south of the Great Lakes and east of the Mississippi River.
H)A constitution that granted all taxpaying men the right to vote and hold office and created a unicameral (one-house)legislature with complete power;there was no governor to exercise a veto.Other provisions mandated a system of elementary education and protected citizens from imprisonment for debt.
I)John Adams's theory from Thoughts on Government (1776),which called for three branches of government,each representing one function: executive,legislative,and judicial.This system of dispersed authority was devised to maintain a balance of power and ensure the legitimacy of governmental procedures.
J)The written document defining the structure of the government from 1781 to 1788,under which the Union was a confederation of equal states,with no executive and limited powers,existing mainly to foster a common defense.
K)A land act that provided for orderly settlement and established a process by which settled territories would become the states of Ohio,Indiana,Illinois,Michigan,and Wisconsin.It also banned slavery in the Northwest Territory.
L)A 1786-1787 uprising led by dissident farmers in western Massachusetts,many of them Revolutionary War veterans,protesting the taxation policies of the eastern elites who controlled the state's government.
M)A plan drafted by James Madison that was presented at the Philadelphia Constitutional Convention.It designed a powerful three-branch government,with representation in both houses of the congress tied to population;this plan would have eclipsed the voice of small states in the national government.
N)Alternative to the Virginia Plan drafted by delegates from small states,retaining the confederation's single-house congress with one vote per state.It shared with the Virginia Plan enhanced congressional powers to raise revenue,control commerce,and make binding requisitions on the states.
O)Supporters of the Constitution of 1787,which created a strong central government;their opponents,the Antifederalists,feared that a strong central government would corrupt the nation's newly won liberty.
P)Opponents of ratification of the Constitution.This party feared that a powerful and distant central government would be out of touch with the needs of citizens.They also complained that it failed to guarantee individual liberties in a bill of rights.
Q)An essay by James Madison in The Federalist (1787-1788)that challenged the view that republican governments only worked in small polities;it argued that a geographically expansive national government would better protect republican liberty.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Answer the following questions :
Battle of Yorktown (1781)
A)First major engagement of the new Continental army,defending against 32,000 British troops outside of New York City.
B)A multistage battle in New York ending with the surrender of British general John Burgoyne.The victory ensured the diplomatic success of American representatives in Paris,who won a military alliance with France.
C)A military camp in which George Washington's army of 12,000 soldiers and hundreds of camp followers suffered horribly in the winter of 1777-1778.
D)A 1779 proclamation that declared that any slave who deserted a rebel master would receive protection,freedom,and land from Great Britain.
E)A battle in which French and American troops and a French fleet trapped the British army under the command of General Charles Cornwallis.The Franco-American victory broke the resolve of the British government.
F)A hidden tax on the farmers and artisans who accepted Continental bills in payment for supplies and on the thousands of soldiers who took them as pay.Because of rampant inflation,Continental currency lost much of its value during the war;thus,the implicit tax on those who accepted it as payment.
G)The treaty that ended the Revolutionary War.In the treaty,Great Britain formally recognized American independence and relinquished its claims to lands south of the Great Lakes and east of the Mississippi River.
H)A constitution that granted all taxpaying men the right to vote and hold office and created a unicameral (one-house)legislature with complete power;there was no governor to exercise a veto.Other provisions mandated a system of elementary education and protected citizens from imprisonment for debt.
I)John Adams's theory from Thoughts on Government (1776),which called for three branches of government,each representing one function: executive,legislative,and judicial.This system of dispersed authority was devised to maintain a balance of power and ensure the legitimacy of governmental procedures.
J)The written document defining the structure of the government from 1781 to 1788,under which the Union was a confederation of equal states,with no executive and limited powers,existing mainly to foster a common defense.
K)A land act that provided for orderly settlement and established a process by which settled territories would become the states of Ohio,Indiana,Illinois,Michigan,and Wisconsin.It also banned slavery in the Northwest Territory.
L)A 1786-1787 uprising led by dissident farmers in western Massachusetts,many of them Revolutionary War veterans,protesting the taxation policies of the eastern elites who controlled the state's government.
M)A plan drafted by James Madison that was presented at the Philadelphia Constitutional Convention.It designed a powerful three-branch government,with representation in both houses of the congress tied to population;this plan would have eclipsed the voice of small states in the national government.
N)Alternative to the Virginia Plan drafted by delegates from small states,retaining the confederation's single-house congress with one vote per state.It shared with the Virginia Plan enhanced congressional powers to raise revenue,control commerce,and make binding requisitions on the states.
O)Supporters of the Constitution of 1787,which created a strong central government;their opponents,the Antifederalists,feared that a strong central government would corrupt the nation's newly won liberty.
P)Opponents of ratification of the Constitution.This party feared that a powerful and distant central government would be out of touch with the needs of citizens.They also complained that it failed to guarantee individual liberties in a bill of rights.
Q)An essay by James Madison in The Federalist (1787-1788)that challenged the view that republican governments only worked in small polities;it argued that a geographically expansive national government would better protect republican liberty.
Battle of Yorktown (1781)
A)First major engagement of the new Continental army,defending against 32,000 British troops outside of New York City.
B)A multistage battle in New York ending with the surrender of British general John Burgoyne.The victory ensured the diplomatic success of American representatives in Paris,who won a military alliance with France.
C)A military camp in which George Washington's army of 12,000 soldiers and hundreds of camp followers suffered horribly in the winter of 1777-1778.
D)A 1779 proclamation that declared that any slave who deserted a rebel master would receive protection,freedom,and land from Great Britain.
E)A battle in which French and American troops and a French fleet trapped the British army under the command of General Charles Cornwallis.The Franco-American victory broke the resolve of the British government.
F)A hidden tax on the farmers and artisans who accepted Continental bills in payment for supplies and on the thousands of soldiers who took them as pay.Because of rampant inflation,Continental currency lost much of its value during the war;thus,the implicit tax on those who accepted it as payment.
G)The treaty that ended the Revolutionary War.In the treaty,Great Britain formally recognized American independence and relinquished its claims to lands south of the Great Lakes and east of the Mississippi River.
H)A constitution that granted all taxpaying men the right to vote and hold office and created a unicameral (one-house)legislature with complete power;there was no governor to exercise a veto.Other provisions mandated a system of elementary education and protected citizens from imprisonment for debt.
I)John Adams's theory from Thoughts on Government (1776),which called for three branches of government,each representing one function: executive,legislative,and judicial.This system of dispersed authority was devised to maintain a balance of power and ensure the legitimacy of governmental procedures.
J)The written document defining the structure of the government from 1781 to 1788,under which the Union was a confederation of equal states,with no executive and limited powers,existing mainly to foster a common defense.
K)A land act that provided for orderly settlement and established a process by which settled territories would become the states of Ohio,Indiana,Illinois,Michigan,and Wisconsin.It also banned slavery in the Northwest Territory.
L)A 1786-1787 uprising led by dissident farmers in western Massachusetts,many of them Revolutionary War veterans,protesting the taxation policies of the eastern elites who controlled the state's government.
M)A plan drafted by James Madison that was presented at the Philadelphia Constitutional Convention.It designed a powerful three-branch government,with representation in both houses of the congress tied to population;this plan would have eclipsed the voice of small states in the national government.
N)Alternative to the Virginia Plan drafted by delegates from small states,retaining the confederation's single-house congress with one vote per state.It shared with the Virginia Plan enhanced congressional powers to raise revenue,control commerce,and make binding requisitions on the states.
O)Supporters of the Constitution of 1787,which created a strong central government;their opponents,the Antifederalists,feared that a strong central government would corrupt the nation's newly won liberty.
P)Opponents of ratification of the Constitution.This party feared that a powerful and distant central government would be out of touch with the needs of citizens.They also complained that it failed to guarantee individual liberties in a bill of rights.
Q)An essay by James Madison in The Federalist (1787-1788)that challenged the view that republican governments only worked in small polities;it argued that a geographically expansive national government would better protect republican liberty.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Who was most to blame for Britain's failure to win a quick victory over the American rebels: General Howe,General Burgoyne,or the ministers in London? Explain your answer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Answer the following questions :
Northwest Ordinance of 1787
A)First major engagement of the new Continental army,defending against 32,000 British troops outside of New York City.
B)A multistage battle in New York ending with the surrender of British general John Burgoyne.The victory ensured the diplomatic success of American representatives in Paris,who won a military alliance with France.
C)A military camp in which George Washington's army of 12,000 soldiers and hundreds of camp followers suffered horribly in the winter of 1777-1778.
D)A 1779 proclamation that declared that any slave who deserted a rebel master would receive protection,freedom,and land from Great Britain.
E)A battle in which French and American troops and a French fleet trapped the British army under the command of General Charles Cornwallis.The Franco-American victory broke the resolve of the British government.
F)A hidden tax on the farmers and artisans who accepted Continental bills in payment for supplies and on the thousands of soldiers who took them as pay.Because of rampant inflation,Continental currency lost much of its value during the war;thus,the implicit tax on those who accepted it as payment.
G)The treaty that ended the Revolutionary War.In the treaty,Great Britain formally recognized American independence and relinquished its claims to lands south of the Great Lakes and east of the Mississippi River.
H)A constitution that granted all taxpaying men the right to vote and hold office and created a unicameral (one-house)legislature with complete power;there was no governor to exercise a veto.Other provisions mandated a system of elementary education and protected citizens from imprisonment for debt.
I)John Adams's theory from Thoughts on Government (1776),which called for three branches of government,each representing one function: executive,legislative,and judicial.This system of dispersed authority was devised to maintain a balance of power and ensure the legitimacy of governmental procedures.
J)The written document defining the structure of the government from 1781 to 1788,under which the Union was a confederation of equal states,with no executive and limited powers,existing mainly to foster a common defense.
K)A land act that provided for orderly settlement and established a process by which settled territories would become the states of Ohio,Indiana,Illinois,Michigan,and Wisconsin.It also banned slavery in the Northwest Territory.
L)A 1786-1787 uprising led by dissident farmers in western Massachusetts,many of them Revolutionary War veterans,protesting the taxation policies of the eastern elites who controlled the state's government.
M)A plan drafted by James Madison that was presented at the Philadelphia Constitutional Convention.It designed a powerful three-branch government,with representation in both houses of the congress tied to population;this plan would have eclipsed the voice of small states in the national government.
N)Alternative to the Virginia Plan drafted by delegates from small states,retaining the confederation's single-house congress with one vote per state.It shared with the Virginia Plan enhanced congressional powers to raise revenue,control commerce,and make binding requisitions on the states.
O)Supporters of the Constitution of 1787,which created a strong central government;their opponents,the Antifederalists,feared that a strong central government would corrupt the nation's newly won liberty.
P)Opponents of ratification of the Constitution.This party feared that a powerful and distant central government would be out of touch with the needs of citizens.They also complained that it failed to guarantee individual liberties in a bill of rights.
Q)An essay by James Madison in The Federalist (1787-1788)that challenged the view that republican governments only worked in small polities;it argued that a geographically expansive national government would better protect republican liberty.
Northwest Ordinance of 1787
A)First major engagement of the new Continental army,defending against 32,000 British troops outside of New York City.
B)A multistage battle in New York ending with the surrender of British general John Burgoyne.The victory ensured the diplomatic success of American representatives in Paris,who won a military alliance with France.
C)A military camp in which George Washington's army of 12,000 soldiers and hundreds of camp followers suffered horribly in the winter of 1777-1778.
D)A 1779 proclamation that declared that any slave who deserted a rebel master would receive protection,freedom,and land from Great Britain.
E)A battle in which French and American troops and a French fleet trapped the British army under the command of General Charles Cornwallis.The Franco-American victory broke the resolve of the British government.
F)A hidden tax on the farmers and artisans who accepted Continental bills in payment for supplies and on the thousands of soldiers who took them as pay.Because of rampant inflation,Continental currency lost much of its value during the war;thus,the implicit tax on those who accepted it as payment.
G)The treaty that ended the Revolutionary War.In the treaty,Great Britain formally recognized American independence and relinquished its claims to lands south of the Great Lakes and east of the Mississippi River.
H)A constitution that granted all taxpaying men the right to vote and hold office and created a unicameral (one-house)legislature with complete power;there was no governor to exercise a veto.Other provisions mandated a system of elementary education and protected citizens from imprisonment for debt.
I)John Adams's theory from Thoughts on Government (1776),which called for three branches of government,each representing one function: executive,legislative,and judicial.This system of dispersed authority was devised to maintain a balance of power and ensure the legitimacy of governmental procedures.
J)The written document defining the structure of the government from 1781 to 1788,under which the Union was a confederation of equal states,with no executive and limited powers,existing mainly to foster a common defense.
K)A land act that provided for orderly settlement and established a process by which settled territories would become the states of Ohio,Indiana,Illinois,Michigan,and Wisconsin.It also banned slavery in the Northwest Territory.
L)A 1786-1787 uprising led by dissident farmers in western Massachusetts,many of them Revolutionary War veterans,protesting the taxation policies of the eastern elites who controlled the state's government.
M)A plan drafted by James Madison that was presented at the Philadelphia Constitutional Convention.It designed a powerful three-branch government,with representation in both houses of the congress tied to population;this plan would have eclipsed the voice of small states in the national government.
N)Alternative to the Virginia Plan drafted by delegates from small states,retaining the confederation's single-house congress with one vote per state.It shared with the Virginia Plan enhanced congressional powers to raise revenue,control commerce,and make binding requisitions on the states.
O)Supporters of the Constitution of 1787,which created a strong central government;their opponents,the Antifederalists,feared that a strong central government would corrupt the nation's newly won liberty.
P)Opponents of ratification of the Constitution.This party feared that a powerful and distant central government would be out of touch with the needs of citizens.They also complained that it failed to guarantee individual liberties in a bill of rights.
Q)An essay by James Madison in The Federalist (1787-1788)that challenged the view that republican governments only worked in small polities;it argued that a geographically expansive national government would better protect republican liberty.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
How did the Philadelphia convention resolve three contentious political issues: the representation of large and small states,slavery,and state sovereignty?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
How did the French alliance ensure the success of the American rebellion?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
What were the main differences between conservative state constitutions,like that of Massachusetts,and more democratic constitutions,like Pennsylvania's?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Answer the following questions :
Federalist No.10
A)First major engagement of the new Continental army,defending against 32,000 British troops outside of New York City.
B)A multistage battle in New York ending with the surrender of British general John Burgoyne.The victory ensured the diplomatic success of American representatives in Paris,who won a military alliance with France.
C)A military camp in which George Washington's army of 12,000 soldiers and hundreds of camp followers suffered horribly in the winter of 1777-1778.
D)A 1779 proclamation that declared that any slave who deserted a rebel master would receive protection,freedom,and land from Great Britain.
E)A battle in which French and American troops and a French fleet trapped the British army under the command of General Charles Cornwallis.The Franco-American victory broke the resolve of the British government.
F)A hidden tax on the farmers and artisans who accepted Continental bills in payment for supplies and on the thousands of soldiers who took them as pay.Because of rampant inflation,Continental currency lost much of its value during the war;thus,the implicit tax on those who accepted it as payment.
G)The treaty that ended the Revolutionary War.In the treaty,Great Britain formally recognized American independence and relinquished its claims to lands south of the Great Lakes and east of the Mississippi River.
H)A constitution that granted all taxpaying men the right to vote and hold office and created a unicameral (one-house)legislature with complete power;there was no governor to exercise a veto.Other provisions mandated a system of elementary education and protected citizens from imprisonment for debt.
I)John Adams's theory from Thoughts on Government (1776),which called for three branches of government,each representing one function: executive,legislative,and judicial.This system of dispersed authority was devised to maintain a balance of power and ensure the legitimacy of governmental procedures.
J)The written document defining the structure of the government from 1781 to 1788,under which the Union was a confederation of equal states,with no executive and limited powers,existing mainly to foster a common defense.
K)A land act that provided for orderly settlement and established a process by which settled territories would become the states of Ohio,Indiana,Illinois,Michigan,and Wisconsin.It also banned slavery in the Northwest Territory.
L)A 1786-1787 uprising led by dissident farmers in western Massachusetts,many of them Revolutionary War veterans,protesting the taxation policies of the eastern elites who controlled the state's government.
M)A plan drafted by James Madison that was presented at the Philadelphia Constitutional Convention.It designed a powerful three-branch government,with representation in both houses of the congress tied to population;this plan would have eclipsed the voice of small states in the national government.
N)Alternative to the Virginia Plan drafted by delegates from small states,retaining the confederation's single-house congress with one vote per state.It shared with the Virginia Plan enhanced congressional powers to raise revenue,control commerce,and make binding requisitions on the states.
O)Supporters of the Constitution of 1787,which created a strong central government;their opponents,the Antifederalists,feared that a strong central government would corrupt the nation's newly won liberty.
P)Opponents of ratification of the Constitution.This party feared that a powerful and distant central government would be out of touch with the needs of citizens.They also complained that it failed to guarantee individual liberties in a bill of rights.
Q)An essay by James Madison in The Federalist (1787-1788)that challenged the view that republican governments only worked in small polities;it argued that a geographically expansive national government would better protect republican liberty.
Federalist No.10
A)First major engagement of the new Continental army,defending against 32,000 British troops outside of New York City.
B)A multistage battle in New York ending with the surrender of British general John Burgoyne.The victory ensured the diplomatic success of American representatives in Paris,who won a military alliance with France.
C)A military camp in which George Washington's army of 12,000 soldiers and hundreds of camp followers suffered horribly in the winter of 1777-1778.
D)A 1779 proclamation that declared that any slave who deserted a rebel master would receive protection,freedom,and land from Great Britain.
E)A battle in which French and American troops and a French fleet trapped the British army under the command of General Charles Cornwallis.The Franco-American victory broke the resolve of the British government.
F)A hidden tax on the farmers and artisans who accepted Continental bills in payment for supplies and on the thousands of soldiers who took them as pay.Because of rampant inflation,Continental currency lost much of its value during the war;thus,the implicit tax on those who accepted it as payment.
G)The treaty that ended the Revolutionary War.In the treaty,Great Britain formally recognized American independence and relinquished its claims to lands south of the Great Lakes and east of the Mississippi River.
H)A constitution that granted all taxpaying men the right to vote and hold office and created a unicameral (one-house)legislature with complete power;there was no governor to exercise a veto.Other provisions mandated a system of elementary education and protected citizens from imprisonment for debt.
I)John Adams's theory from Thoughts on Government (1776),which called for three branches of government,each representing one function: executive,legislative,and judicial.This system of dispersed authority was devised to maintain a balance of power and ensure the legitimacy of governmental procedures.
J)The written document defining the structure of the government from 1781 to 1788,under which the Union was a confederation of equal states,with no executive and limited powers,existing mainly to foster a common defense.
K)A land act that provided for orderly settlement and established a process by which settled territories would become the states of Ohio,Indiana,Illinois,Michigan,and Wisconsin.It also banned slavery in the Northwest Territory.
L)A 1786-1787 uprising led by dissident farmers in western Massachusetts,many of them Revolutionary War veterans,protesting the taxation policies of the eastern elites who controlled the state's government.
M)A plan drafted by James Madison that was presented at the Philadelphia Constitutional Convention.It designed a powerful three-branch government,with representation in both houses of the congress tied to population;this plan would have eclipsed the voice of small states in the national government.
N)Alternative to the Virginia Plan drafted by delegates from small states,retaining the confederation's single-house congress with one vote per state.It shared with the Virginia Plan enhanced congressional powers to raise revenue,control commerce,and make binding requisitions on the states.
O)Supporters of the Constitution of 1787,which created a strong central government;their opponents,the Antifederalists,feared that a strong central government would corrupt the nation's newly won liberty.
P)Opponents of ratification of the Constitution.This party feared that a powerful and distant central government would be out of touch with the needs of citizens.They also complained that it failed to guarantee individual liberties in a bill of rights.
Q)An essay by James Madison in The Federalist (1787-1788)that challenged the view that republican governments only worked in small polities;it argued that a geographically expansive national government would better protect republican liberty.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Answer the following questions :
Virginia Plan
A)First major engagement of the new Continental army,defending against 32,000 British troops outside of New York City.
B)A multistage battle in New York ending with the surrender of British general John Burgoyne.The victory ensured the diplomatic success of American representatives in Paris,who won a military alliance with France.
C)A military camp in which George Washington's army of 12,000 soldiers and hundreds of camp followers suffered horribly in the winter of 1777-1778.
D)A 1779 proclamation that declared that any slave who deserted a rebel master would receive protection,freedom,and land from Great Britain.
E)A battle in which French and American troops and a French fleet trapped the British army under the command of General Charles Cornwallis.The Franco-American victory broke the resolve of the British government.
F)A hidden tax on the farmers and artisans who accepted Continental bills in payment for supplies and on the thousands of soldiers who took them as pay.Because of rampant inflation,Continental currency lost much of its value during the war;thus,the implicit tax on those who accepted it as payment.
G)The treaty that ended the Revolutionary War.In the treaty,Great Britain formally recognized American independence and relinquished its claims to lands south of the Great Lakes and east of the Mississippi River.
H)A constitution that granted all taxpaying men the right to vote and hold office and created a unicameral (one-house)legislature with complete power;there was no governor to exercise a veto.Other provisions mandated a system of elementary education and protected citizens from imprisonment for debt.
I)John Adams's theory from Thoughts on Government (1776),which called for three branches of government,each representing one function: executive,legislative,and judicial.This system of dispersed authority was devised to maintain a balance of power and ensure the legitimacy of governmental procedures.
J)The written document defining the structure of the government from 1781 to 1788,under which the Union was a confederation of equal states,with no executive and limited powers,existing mainly to foster a common defense.
K)A land act that provided for orderly settlement and established a process by which settled territories would become the states of Ohio,Indiana,Illinois,Michigan,and Wisconsin.It also banned slavery in the Northwest Territory.
L)A 1786-1787 uprising led by dissident farmers in western Massachusetts,many of them Revolutionary War veterans,protesting the taxation policies of the eastern elites who controlled the state's government.
M)A plan drafted by James Madison that was presented at the Philadelphia Constitutional Convention.It designed a powerful three-branch government,with representation in both houses of the congress tied to population;this plan would have eclipsed the voice of small states in the national government.
N)Alternative to the Virginia Plan drafted by delegates from small states,retaining the confederation's single-house congress with one vote per state.It shared with the Virginia Plan enhanced congressional powers to raise revenue,control commerce,and make binding requisitions on the states.
O)Supporters of the Constitution of 1787,which created a strong central government;their opponents,the Antifederalists,feared that a strong central government would corrupt the nation's newly won liberty.
P)Opponents of ratification of the Constitution.This party feared that a powerful and distant central government would be out of touch with the needs of citizens.They also complained that it failed to guarantee individual liberties in a bill of rights.
Q)An essay by James Madison in The Federalist (1787-1788)that challenged the view that republican governments only worked in small polities;it argued that a geographically expansive national government would better protect republican liberty.
Virginia Plan
A)First major engagement of the new Continental army,defending against 32,000 British troops outside of New York City.
B)A multistage battle in New York ending with the surrender of British general John Burgoyne.The victory ensured the diplomatic success of American representatives in Paris,who won a military alliance with France.
C)A military camp in which George Washington's army of 12,000 soldiers and hundreds of camp followers suffered horribly in the winter of 1777-1778.
D)A 1779 proclamation that declared that any slave who deserted a rebel master would receive protection,freedom,and land from Great Britain.
E)A battle in which French and American troops and a French fleet trapped the British army under the command of General Charles Cornwallis.The Franco-American victory broke the resolve of the British government.
F)A hidden tax on the farmers and artisans who accepted Continental bills in payment for supplies and on the thousands of soldiers who took them as pay.Because of rampant inflation,Continental currency lost much of its value during the war;thus,the implicit tax on those who accepted it as payment.
G)The treaty that ended the Revolutionary War.In the treaty,Great Britain formally recognized American independence and relinquished its claims to lands south of the Great Lakes and east of the Mississippi River.
H)A constitution that granted all taxpaying men the right to vote and hold office and created a unicameral (one-house)legislature with complete power;there was no governor to exercise a veto.Other provisions mandated a system of elementary education and protected citizens from imprisonment for debt.
I)John Adams's theory from Thoughts on Government (1776),which called for three branches of government,each representing one function: executive,legislative,and judicial.This system of dispersed authority was devised to maintain a balance of power and ensure the legitimacy of governmental procedures.
J)The written document defining the structure of the government from 1781 to 1788,under which the Union was a confederation of equal states,with no executive and limited powers,existing mainly to foster a common defense.
K)A land act that provided for orderly settlement and established a process by which settled territories would become the states of Ohio,Indiana,Illinois,Michigan,and Wisconsin.It also banned slavery in the Northwest Territory.
L)A 1786-1787 uprising led by dissident farmers in western Massachusetts,many of them Revolutionary War veterans,protesting the taxation policies of the eastern elites who controlled the state's government.
M)A plan drafted by James Madison that was presented at the Philadelphia Constitutional Convention.It designed a powerful three-branch government,with representation in both houses of the congress tied to population;this plan would have eclipsed the voice of small states in the national government.
N)Alternative to the Virginia Plan drafted by delegates from small states,retaining the confederation's single-house congress with one vote per state.It shared with the Virginia Plan enhanced congressional powers to raise revenue,control commerce,and make binding requisitions on the states.
O)Supporters of the Constitution of 1787,which created a strong central government;their opponents,the Antifederalists,feared that a strong central government would corrupt the nation's newly won liberty.
P)Opponents of ratification of the Constitution.This party feared that a powerful and distant central government would be out of touch with the needs of citizens.They also complained that it failed to guarantee individual liberties in a bill of rights.
Q)An essay by James Madison in The Federalist (1787-1788)that challenged the view that republican governments only worked in small polities;it argued that a geographically expansive national government would better protect republican liberty.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
America's History argues that "it was the American people who decided the outcome" of the war.Based on the evidence presented in the chapter,do you agree? Explain your answer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
What were the central problems of the Articles of Confederation,and how did the delegates to the Philadelphia convention address them?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
How revolutionary was the American Revolution? What political,social,and economic changes did it produce? What stayed the same?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Answer the following questions :
New Jersey Plan
A)First major engagement of the new Continental army,defending against 32,000 British troops outside of New York City.
B)A multistage battle in New York ending with the surrender of British general John Burgoyne.The victory ensured the diplomatic success of American representatives in Paris,who won a military alliance with France.
C)A military camp in which George Washington's army of 12,000 soldiers and hundreds of camp followers suffered horribly in the winter of 1777-1778.
D)A 1779 proclamation that declared that any slave who deserted a rebel master would receive protection,freedom,and land from Great Britain.
E)A battle in which French and American troops and a French fleet trapped the British army under the command of General Charles Cornwallis.The Franco-American victory broke the resolve of the British government.
F)A hidden tax on the farmers and artisans who accepted Continental bills in payment for supplies and on the thousands of soldiers who took them as pay.Because of rampant inflation,Continental currency lost much of its value during the war;thus,the implicit tax on those who accepted it as payment.
G)The treaty that ended the Revolutionary War.In the treaty,Great Britain formally recognized American independence and relinquished its claims to lands south of the Great Lakes and east of the Mississippi River.
H)A constitution that granted all taxpaying men the right to vote and hold office and created a unicameral (one-house)legislature with complete power;there was no governor to exercise a veto.Other provisions mandated a system of elementary education and protected citizens from imprisonment for debt.
I)John Adams's theory from Thoughts on Government (1776),which called for three branches of government,each representing one function: executive,legislative,and judicial.This system of dispersed authority was devised to maintain a balance of power and ensure the legitimacy of governmental procedures.
J)The written document defining the structure of the government from 1781 to 1788,under which the Union was a confederation of equal states,with no executive and limited powers,existing mainly to foster a common defense.
K)A land act that provided for orderly settlement and established a process by which settled territories would become the states of Ohio,Indiana,Illinois,Michigan,and Wisconsin.It also banned slavery in the Northwest Territory.
L)A 1786-1787 uprising led by dissident farmers in western Massachusetts,many of them Revolutionary War veterans,protesting the taxation policies of the eastern elites who controlled the state's government.
M)A plan drafted by James Madison that was presented at the Philadelphia Constitutional Convention.It designed a powerful three-branch government,with representation in both houses of the congress tied to population;this plan would have eclipsed the voice of small states in the national government.
N)Alternative to the Virginia Plan drafted by delegates from small states,retaining the confederation's single-house congress with one vote per state.It shared with the Virginia Plan enhanced congressional powers to raise revenue,control commerce,and make binding requisitions on the states.
O)Supporters of the Constitution of 1787,which created a strong central government;their opponents,the Antifederalists,feared that a strong central government would corrupt the nation's newly won liberty.
P)Opponents of ratification of the Constitution.This party feared that a powerful and distant central government would be out of touch with the needs of citizens.They also complained that it failed to guarantee individual liberties in a bill of rights.
Q)An essay by James Madison in The Federalist (1787-1788)that challenged the view that republican governments only worked in small polities;it argued that a geographically expansive national government would better protect republican liberty.
New Jersey Plan
A)First major engagement of the new Continental army,defending against 32,000 British troops outside of New York City.
B)A multistage battle in New York ending with the surrender of British general John Burgoyne.The victory ensured the diplomatic success of American representatives in Paris,who won a military alliance with France.
C)A military camp in which George Washington's army of 12,000 soldiers and hundreds of camp followers suffered horribly in the winter of 1777-1778.
D)A 1779 proclamation that declared that any slave who deserted a rebel master would receive protection,freedom,and land from Great Britain.
E)A battle in which French and American troops and a French fleet trapped the British army under the command of General Charles Cornwallis.The Franco-American victory broke the resolve of the British government.
F)A hidden tax on the farmers and artisans who accepted Continental bills in payment for supplies and on the thousands of soldiers who took them as pay.Because of rampant inflation,Continental currency lost much of its value during the war;thus,the implicit tax on those who accepted it as payment.
G)The treaty that ended the Revolutionary War.In the treaty,Great Britain formally recognized American independence and relinquished its claims to lands south of the Great Lakes and east of the Mississippi River.
H)A constitution that granted all taxpaying men the right to vote and hold office and created a unicameral (one-house)legislature with complete power;there was no governor to exercise a veto.Other provisions mandated a system of elementary education and protected citizens from imprisonment for debt.
I)John Adams's theory from Thoughts on Government (1776),which called for three branches of government,each representing one function: executive,legislative,and judicial.This system of dispersed authority was devised to maintain a balance of power and ensure the legitimacy of governmental procedures.
J)The written document defining the structure of the government from 1781 to 1788,under which the Union was a confederation of equal states,with no executive and limited powers,existing mainly to foster a common defense.
K)A land act that provided for orderly settlement and established a process by which settled territories would become the states of Ohio,Indiana,Illinois,Michigan,and Wisconsin.It also banned slavery in the Northwest Territory.
L)A 1786-1787 uprising led by dissident farmers in western Massachusetts,many of them Revolutionary War veterans,protesting the taxation policies of the eastern elites who controlled the state's government.
M)A plan drafted by James Madison that was presented at the Philadelphia Constitutional Convention.It designed a powerful three-branch government,with representation in both houses of the congress tied to population;this plan would have eclipsed the voice of small states in the national government.
N)Alternative to the Virginia Plan drafted by delegates from small states,retaining the confederation's single-house congress with one vote per state.It shared with the Virginia Plan enhanced congressional powers to raise revenue,control commerce,and make binding requisitions on the states.
O)Supporters of the Constitution of 1787,which created a strong central government;their opponents,the Antifederalists,feared that a strong central government would corrupt the nation's newly won liberty.
P)Opponents of ratification of the Constitution.This party feared that a powerful and distant central government would be out of touch with the needs of citizens.They also complained that it failed to guarantee individual liberties in a bill of rights.
Q)An essay by James Madison in The Federalist (1787-1788)that challenged the view that republican governments only worked in small polities;it argued that a geographically expansive national government would better protect republican liberty.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
What were the most pressing economic and fiscal problems facing the Patriots at the outset of the war? How successful were they in addressing these problems?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



