Deck 13: Fluids
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/91
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 13: Fluids
1
Which of the following are the SI units for specific gravity?
A) kg/m3
B) g/cm3
C) lb/ft3
D) lb · s2/ft4
E) specific gravity has no units
A) kg/m3
B) g/cm3
C) lb/ft3
D) lb · s2/ft4
E) specific gravity has no units
specific gravity has no units
2
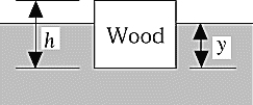 A piece of wood is floating at the surface of some water as illustrated. The wood has a circular cross section and a height h = 3.0 cm. The density of the wood is 0.41 g/cm3. The distance y from the surface of the water to the bottom of the wood is
A piece of wood is floating at the surface of some water as illustrated. The wood has a circular cross section and a height h = 3.0 cm. The density of the wood is 0.41 g/cm3. The distance y from the surface of the water to the bottom of the wood isA) impossible to determine because the area of the cross section is not given.
B) 0.81 cm
C) 3.2 cm
D) 1.2 cm
E) None of these is correct.
1.2 cm
3
What is the gauge pressure at a depth of 6 cm in a glass filled with 4 cm of mercury and
4 cm of water? Water has a density of 1000 kg/m3, and mercury has a density 13.6 times as great.
A) 3.1 kPa
B) 5.6 kPa
C) 5.8 kP
D) 310 kPa
E) 560 kPa
4 cm of water? Water has a density of 1000 kg/m3, and mercury has a density 13.6 times as great.
A) 3.1 kPa
B) 5.6 kPa
C) 5.8 kP
D) 310 kPa
E) 560 kPa
3.1 kPa
4
A block of material has a density . A second block of equal volume has three times the mass of the first. What is the density of the second block?
A)
B) 3
C) /3
D) 9
E) /9
A)
B) 3
C) /3
D) 9
E) /9

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
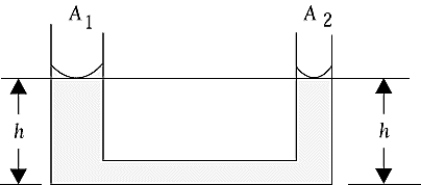 An open U-tube has water to a height h on both sides, as shown. The cross-sectional area of the left-hand tube is A1 = 1.50 cm2, and that of the right-hand tube is A2 = 0.50 cm2. A light oil (which does not mix with water) with a density of 0.83 g/cm3 is added to the right-hand side. When equilibrium is reached, which of the following is correct?
An open U-tube has water to a height h on both sides, as shown. The cross-sectional area of the left-hand tube is A1 = 1.50 cm2, and that of the right-hand tube is A2 = 0.50 cm2. A light oil (which does not mix with water) with a density of 0.83 g/cm3 is added to the right-hand side. When equilibrium is reached, which of the following is correct?A) The level on the right-hand side is higher than that on the left.
B) The level on the right-hand side is lower than that on the left.
C) The levels of the two sides are the same.
D) The difference in the heights depends on A1 and A2.
E) None of these is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A glass is filled with water. The gauge pressure at the top of the glass is zero and the gauge pressure at the bottom is P. A second glass with three times the height and twice the diameter is also filled with water. What is the pressure at the bottom of the second glass?
A) P
B) 2P
C) 3P
D) 3P/2
E) 3P/4
A) P
B) 2P
C) 3P
D) 3P/2
E) 3P/4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A tube with a radius of 4.2 cm is holding oil that has a density of 0.92 g/cm3. The pressure in the oil at a depth of 64 cm from the top of the surface is
A) 5.8 102 Pa
B) 5.8 103 Pa
C) 1.0 102 Pa
D) 1.0 106 Pa
E) 1.7 103 Pa
A) 5.8 102 Pa
B) 5.8 103 Pa
C) 1.0 102 Pa
D) 1.0 106 Pa
E) 1.7 103 Pa

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Your blood pressure is reported as 50 mm of Hg. The density of mercury is 13.6 g/cm3. Your pressure is equivalent to
A) 6.7 106 Pa
B) 6.8 Pa
C) 6.8 102 Pa
D) 6.7 103 Pa
E) 3.2 102 Pa
A) 6.7 106 Pa
B) 6.8 Pa
C) 6.8 102 Pa
D) 6.7 103 Pa
E) 3.2 102 Pa

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
At what depth in sea water is the gauge pressure equal to 1 atm? The density of sea water is 1.03 103 kg/m3.
A) 5 m
B) 7.5 m
C) 10 m
D) 15 m
E) 20 m
A) 5 m
B) 7.5 m
C) 10 m
D) 15 m
E) 20 m

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
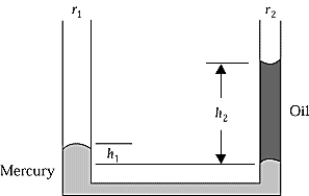 The left-hand side of an open U-tube has a radius r1 = 0.82 cm, and the right-hand side has a radius r2 = 0.41 cm. Mercury and oil are poured into the U-tube. The density of mercury is 13.6 g/cm3. The heights shown in the diagram are h1 = 3.50 cm and h2 = 57.3 cm. The density of the oil is approximately
The left-hand side of an open U-tube has a radius r1 = 0.82 cm, and the right-hand side has a radius r2 = 0.41 cm. Mercury and oil are poured into the U-tube. The density of mercury is 13.6 g/cm3. The heights shown in the diagram are h1 = 3.50 cm and h2 = 57.3 cm. The density of the oil is approximatelyA) 0.83 g/cm3
B) 110 g/cm3
C) 7.9 g/cm3
D) 6.9 g/cm3
E) 1.82 g/cm3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which gas has the lowest density under standard temperature and pressure?
A) hydrogen
B) helium
C) oxygen
D) nitrogen
E) carbon dioxide
A) hydrogen
B) helium
C) oxygen
D) nitrogen
E) carbon dioxide

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A block of material has a density . A second block of equal mass has twice the volume of the first. What is the density of the second block?
A)
B) 2
C) /2
D) 4
E) /4
A)
B) 2
C) /2
D) 4
E) /4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A flat plate with a negligible mass and an area of 1.0 cm2 is placed in a horizontal position well beneath the surface in a liquid that is not moving. The pressure at the location of the plate is P Pa. The total force that arises from the pressure of the liquid on this plate is
A) P N, directed down.
B) P 10-4 N, directed down.
C) P N, directed up.
D) P 10-4 N, directed up.
E) zero.
A) P N, directed down.
B) P 10-4 N, directed down.
C) P N, directed up.
D) P 10-4 N, directed up.
E) zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The atmospheric pressure deceases exponentially with height. At 5.5 km, the pressure is half that at sea level. At what height is the pressure one eighth that of sea level?
A) 7.5 km
B) 11 km
C) 16.5 km
D) 22 km
E) 27.5 km
A) 7.5 km
B) 11 km
C) 16.5 km
D) 22 km
E) 27.5 km

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
If the atmosphere were compressed until it had the density of water, it would cover Earth to a depth of about
A) 0.81 km
B) 4.6 m
C) 1.6 km
D) 76 cm
E) 10 m
A) 0.81 km
B) 4.6 m
C) 1.6 km
D) 76 cm
E) 10 m

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A penny has a mass of 3.0 g, a diameter of 1.9 cm, and a thickness of 0.15 cm. What is the density of the metal of which it is made?
A) 1.8 g/cm3
B) 3.4 g/cm3
C) 3.5 g/cm3
D) 7.1 g/cm3
E) 4.5 g/cm3
A) 1.8 g/cm3
B) 3.4 g/cm3
C) 3.5 g/cm3
D) 7.1 g/cm3
E) 4.5 g/cm3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
A small sphere of wood with a density = 0.40 g/cm3 is held at rest well under the surface of a pool of water. The magnitude of the initial acceleration of the sphere when it is released is
A) 15 m/s2
B) 9.8 m/s2
C) 33 m/s2
D) 23 m/s2
E) 3.4 m/s2
A) 15 m/s2
B) 9.8 m/s2
C) 33 m/s2
D) 23 m/s2
E) 3.4 m/s2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following is the mass density of a material?
A) the material's weight per unit volume
B) the material's mass per unit volume
C) the material's specific gravity
D) the material's volume per unit weight
E) the material's volume per unit mass
A) the material's weight per unit volume
B) the material's mass per unit volume
C) the material's specific gravity
D) the material's volume per unit weight
E) the material's volume per unit mass

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
If the gauge pressure is doubled, the absolute pressure is
A) halved.
B) doubled.
C) unchanged.
D) squared.
E) Not enough information is given to determine the answer.
A) halved.
B) doubled.
C) unchanged.
D) squared.
E) Not enough information is given to determine the answer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A container of height, h, is filled with water of density , and sealed with a flexible membrane. The container is placed in the space shuttle in orbit. If the air pressure in the shuttle is Po, the pressure in the middle of the container is
A) Po
B) Po + gh
gh
C) gh
gh
D) gh
E) depends how fast the shuttle is moving
A) Po
B) Po +
 gh
ghC)
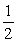 gh
ghD) gh
E) depends how fast the shuttle is moving

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Use the figure to the right to answer the next problems. A beaker is filled with water. A small plastic container contains a solid bar of aluminum, which has a mass of 40 g, and is placed on the water so that it floats. The water level reads 60 ml. Next, the bar of aluminum is taken out of the container and placed in the water so that it sinks to the bottom. 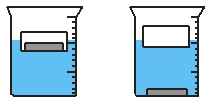
-The water level in the beaker _____
A) drops.
B) stays unchanged.
C) rises.
D) depends on the type of container
E) unable to tell

-The water level in the beaker _____
A) drops.
B) stays unchanged.
C) rises.
D) depends on the type of container
E) unable to tell

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Is it possible to float an object that is less dense that water when the amount of the water is less than the weight of the object? 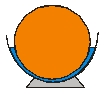
A) No, the weight of the water must at least equal the weight of the object.
B) Yes, as long as the container that holds the water allows the water to rise so that the volume of water displaced is equal to the weight of the object.
C) It is not possible to determine the answer.
D) It depends on the density of the object.
E) It depends on the mass of the object.

A) No, the weight of the water must at least equal the weight of the object.
B) Yes, as long as the container that holds the water allows the water to rise so that the volume of water displaced is equal to the weight of the object.
C) It is not possible to determine the answer.
D) It depends on the density of the object.
E) It depends on the mass of the object.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Use the figure to the right to answer the next problems. A beaker is filled with water. A small plastic container contains a solid bar of aluminum, which has a mass of 40 g, and is placed on the water so that it floats. The water level reads 60 ml. Next, the bar of aluminum is taken out of the container and placed in the water so that it sinks to the bottom. 
-By how much does the water level change? (density of Al is 2.7 g/cm3)
A) 40 ml
B) 14.8 ml
C) 25.2 ml
D) 0 ml
E) 30 ml

-By how much does the water level change? (density of Al is 2.7 g/cm3)
A) 40 ml
B) 14.8 ml
C) 25.2 ml
D) 0 ml
E) 30 ml

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A block of wood of relative density 0.750 and dimensions 20.3 cm 30.5 cm 40.6 cm is tossed into a choppy freshwater lake. After a reasonable time, the approximate vertical dimension above the water will be
A) 2.54 cm
B) 5.08 cm
C) 7.62 cm
D) 10.2 cm
E) 12.7 cm
A) 2.54 cm
B) 5.08 cm
C) 7.62 cm
D) 10.2 cm
E) 12.7 cm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A stone of volume 1.42 10-2 m3 lies at the bottom of a freshwater lake. If the rock's specific gravity is 3.5, the work required to lift it 1 m through the water is approximately
A) 487 J
B) 139 J
C) 348 J
D) 223 J
E) 469 J
A) 487 J
B) 139 J
C) 348 J
D) 223 J
E) 469 J

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
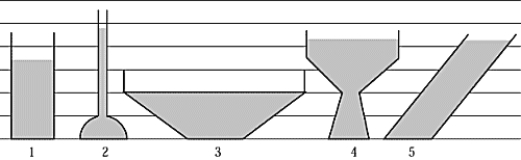 The vessels in the figure contain liquids of the same density. The vessel that has the greatest pressure at its base is
The vessels in the figure contain liquids of the same density. The vessel that has the greatest pressure at its base isA) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Pressure as a function of depth for a certain liquid is plotted on the graph. What is the density of the liquid? 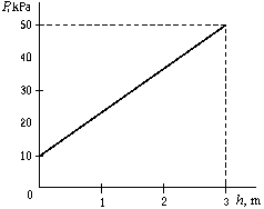
A) 1.76 g/cm3
B) 1.36 g/cm3
C) 0.340 g/cm3
D) 1.70 g/cm3
E) 3.27 g/cm3

A) 1.76 g/cm3
B) 1.36 g/cm3
C) 0.340 g/cm3
D) 1.70 g/cm3
E) 3.27 g/cm3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
If a column of liquid 52 cm high supports a column of mercury ( = 13.6 g/cm3) 10 cm high, the density of the liquid is
A) 6.0 g/cm3
B) 2.6 g/cm3
C) 3.8 g/cm3
D) 4.9 g/cm3
E) 5.0 g/cm3
A) 6.0 g/cm3
B) 2.6 g/cm3
C) 3.8 g/cm3
D) 4.9 g/cm3
E) 5.0 g/cm3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Two objects with different volumes have the same apparent weight when submerged in water. If they are placed in a vacuum,
A) both weigh less than before.
B) the one with the smaller volume weighs less than the other.
C) the one with the smaller volume weighs more than the other.
D) they weigh the same.
E) both weigh more than before.
A) both weigh less than before.
B) the one with the smaller volume weighs less than the other.
C) the one with the smaller volume weighs more than the other.
D) they weigh the same.
E) both weigh more than before.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The force exerted by a stationary liquid on an inclined rectangular surface at rest in the liquid
A) acts normally to the surface.
B) is exerted equally at all points on the surface.
C) acts parallel to the surface.
D) is independent of the density of the liquid.
E) varies inversely as the depth.
A) acts normally to the surface.
B) is exerted equally at all points on the surface.
C) acts parallel to the surface.
D) is independent of the density of the liquid.
E) varies inversely as the depth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
According to Pascal's principle, the pressure at every point in a confined liquid
A) depends only on the density of the liquid.
B) is equal to the weight of the liquid.
C) is the same.
D) is changed the same amount by an externally applied pressure.
E) is equal to the externally applied pressure.
A) depends only on the density of the liquid.
B) is equal to the weight of the liquid.
C) is the same.
D) is changed the same amount by an externally applied pressure.
E) is equal to the externally applied pressure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A beaker is filled with water. A ball of mass m and density < water is tied to a string. The other end of the string is then tied to the bottom of the beaker so that the ball is completely submerged. What is the tension in the string? 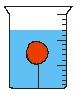
A)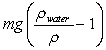
B)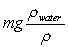
C) mg
D)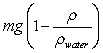
E)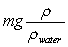

A)
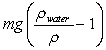
B)
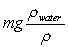
C) mg
D)
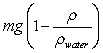
E)
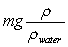

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The U-tube in the figure is sealed at both ends. It contains a gas in A, another gas in B, and mercury in C. The heights of the mercury in the two arms are as shown. The density of mercury is 13.6 g/cm3. If the pressure in A is 1 104 dyn/cm2, the pressure in B is 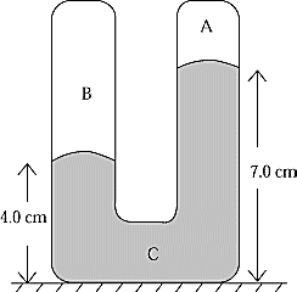
A) 1 104 dyn/cm2
B) 2 104 dyn/cm2
C) 3 104 dyn/cm2
D) 4 104 dyn/cm2
E) 5 104 dyn/cm2

A) 1 104 dyn/cm2
B) 2 104 dyn/cm2
C) 3 104 dyn/cm2
D) 4 104 dyn/cm2
E) 5 104 dyn/cm2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Two pistons of a hydraulic lift have radii of 2.67 cm and 20.0 cm. The downward force on the 2.67-cm piston that is required to lift a mass of 2000 kg supported by the 20-cm piston is
A) 350 N
B) 270 N
C) 36 N
D) 1.5 103 N
E) 2.6 103 N
A) 350 N
B) 270 N
C) 36 N
D) 1.5 103 N
E) 2.6 103 N

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
A ball bearing that has a density of 5.16 g/cm3 is held at rest under the surface of a liquid that has a density of 2.50 g/cm3. The magnitude of the acceleration of the ball bearing just after it is released is
A) 5.0 m/s2
B) 14 m/s2
C) 10 m/s2
D) 6.5 m/s2
E) 1.6 m/s2
A) 5.0 m/s2
B) 14 m/s2
C) 10 m/s2
D) 6.5 m/s2
E) 1.6 m/s2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
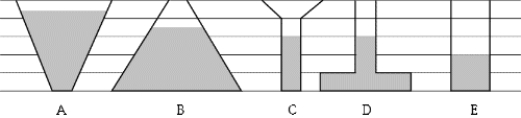 If the same fluid fills the containers shown, the pressures at the bases are related according to which of the following expressions?
If the same fluid fills the containers shown, the pressures at the bases are related according to which of the following expressions?A) PC < PA < PE < PD < PB
B) PE < PD < PC < PB < PA
C) PA < PB < PC < PD < PE
D) PE < PD = PC < PB < PA
E) None of these is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Two identical beakers are filled with the same amount of water. A ball of mass m is placed in the first beaker so that it floats on the surface while a second identical ball is placed in the second beaker but tied with a string of negligible mass so that the ball is completely submerged. Each beaker is then placed on a scale. Which scale has a higher reading? 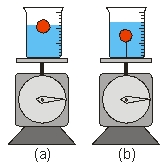
A) (a)
B) (b)
C) the same
D) depends on how far the ball is submerged in (b)
E) unable to tell

A) (a)
B) (b)
C) the same
D) depends on how far the ball is submerged in (b)
E) unable to tell

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A block of ice 30.5 cm thick floating in fresh water just supports a man weighing 801 N. If the specific gravity of ice is 0.917, the smallest area the block can have is
A) 3.25 m2
B) 3.57 m2
C) 2.88 m2
D) 1.45 m2
E) 0.269 m2
A) 3.25 m2
B) 3.57 m2
C) 2.88 m2
D) 1.45 m2
E) 0.269 m2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
A solid wooden sphere of volume 0.0100 m3 floats freely exactly one-half submerged in a liquid of density 800 kg/m3. A lightweight cord is now tied to the sphere and is used to pull the sphere under the surface and hold it completely submerged. What is the tension in the cord?
A) zero
B) 2.00 N
C) 39.2 N
D) 4.00 N
E) 78.4 N
A) zero
B) 2.00 N
C) 39.2 N
D) 4.00 N
E) 78.4 N

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which curve best represents the variation in pressure with depth in a fluid, assuming constant density? 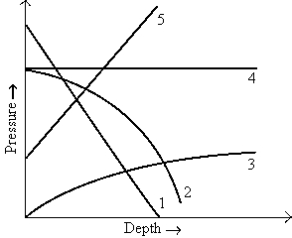
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5

A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
You are floating in a boat in a swimming pool. There are some large stones, with a density of 2.5 g/cm3, in the boat. You throw the stones out of the boat and they sink to the bottom of the pool. The water level h, measured vertically at the end of the pool __________ as the stones are thrown out.
A) decreases
B) increases
C) There is not enough information to solve the problem.
D) stays the same
E) None of these is correct.
A) decreases
B) increases
C) There is not enough information to solve the problem.
D) stays the same
E) None of these is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
A metal block suspended from a spring balance is submerged in water. You observe that the block displaces 55 cm3 of water and that the balance reads 4.3 N. What is the density of the block?
A) 7.0 g/cm3
B) 8.0 g/cm3
C) 9.0 g/cm3
D) 1.1 g/cm3
E) 1.2 g/cm3
A) 7.0 g/cm3
B) 8.0 g/cm3
C) 9.0 g/cm3
D) 1.1 g/cm3
E) 1.2 g/cm3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
You are floating in a boat in a swimming pool. The boat contains some blocks of wood. The specific gravity of the wood is 0.66. You throw the wood blocks into the pool. When the waves settle, the depth of the water in the pool
A) has increased.
B) is the same as before.
C) has decreased.
D) is impossible to determine from the information given
E) is none of these
A) has increased.
B) is the same as before.
C) has decreased.
D) is impossible to determine from the information given
E) is none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
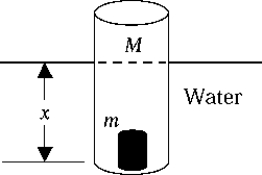 A cylindrical piece of wood has a mass M = 0.235 kg. A small piece of lead with a mass m = 0.021 kg is fixed in the wood at the bottom of the cylinder so that the cylinder floats in water in a stable position, as shown. The radius of the cylinder is 1.65 cm. The depth x of the cylinder below the surface of the water is
A cylindrical piece of wood has a mass M = 0.235 kg. A small piece of lead with a mass m = 0.021 kg is fixed in the wood at the bottom of the cylinder so that the cylinder floats in water in a stable position, as shown. The radius of the cylinder is 1.65 cm. The depth x of the cylinder below the surface of the water isA) 0.38 m
B) 0.57 m
C) 0.22 m
D) 0.42 m
E) None of these is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
![<strong> A tank is filled with water to a height H. A small hole is punched in one of the walls at a depth h below the water's surface. The water leaves the hole in a horizontal direction. The stream of water strikes the floor at a distance x, as shown. Neglecting viscosity, you can calculate the value of x from</strong> A) x = H - h B) x = [2h(H - h)]<sup>1/2 </sup> C) x = h D) x = 2[h(H - h)]<sup>1/2 </sup> E) None of these is correct.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6080/11eaa4be_851c_0991_9e4a_dbbe17e348bb_TB6080_00.jpg) A tank is filled with water to a height H. A small hole is punched in one of the walls at a depth h below the water's surface. The water leaves the hole in a horizontal direction. The stream of water strikes the floor at a distance x, as shown. Neglecting viscosity, you can calculate the value of x from
A tank is filled with water to a height H. A small hole is punched in one of the walls at a depth h below the water's surface. The water leaves the hole in a horizontal direction. The stream of water strikes the floor at a distance x, as shown. Neglecting viscosity, you can calculate the value of x fromA) x = H - h
B) x = [2h(H - h)]1/2
C) x = h
D) x = 2[h(H - h)]1/2
E) None of these is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Bernoulli's equation for nonviscous flow can be stated as
P1 + gy1 +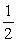 v12 = P2 + gy2 +
v12 = P2 + gy2 + 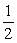 v22
v22
A fluid is flowing through a horizontal tube that changes in cross-sectional area from
A1= 0.75 cm2 to A2 = 0.030 cm2.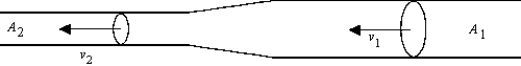 When v1 = 3.5 cm/s, = 1.4 g/cm3, and viscosity is neglected, the difference between pressure P2 at A2 and P1 at A1 is
When v1 = 3.5 cm/s, = 1.4 g/cm3, and viscosity is neglected, the difference between pressure P2 at A2 and P1 at A1 is
A) 54 103 dyn/cm2, with P1 higher.
B) 59 dyn/cm2, with P2 higher.
C) 59 dyn/cm2, with P1 higher.
D) 8.3 102 dyn/cm2, with P2 higher.
E) None of these is correct.
P1 + gy1 +
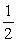 v12 = P2 + gy2 +
v12 = P2 + gy2 + 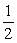 v22
v22A fluid is flowing through a horizontal tube that changes in cross-sectional area from
A1= 0.75 cm2 to A2 = 0.030 cm2.
 When v1 = 3.5 cm/s, = 1.4 g/cm3, and viscosity is neglected, the difference between pressure P2 at A2 and P1 at A1 is
When v1 = 3.5 cm/s, = 1.4 g/cm3, and viscosity is neglected, the difference between pressure P2 at A2 and P1 at A1 isA) 54 103 dyn/cm2, with P1 higher.
B) 59 dyn/cm2, with P2 higher.
C) 59 dyn/cm2, with P1 higher.
D) 8.3 102 dyn/cm2, with P2 higher.
E) None of these is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A horizontal pipe narrows from a diameter of 10 to 5 cm. For a nonviscous fluid flowing from the larger diameter to the smaller,
A) the velocity and pressure both increase.
B) the velocity increases and the pressure decreases.
C) the velocity decreases and the pressure increases.
D) the velocity and pressure both decrease.
E) either the velocity or the pressure changes but not both.
A) the velocity and pressure both increase.
B) the velocity increases and the pressure decreases.
C) the velocity decreases and the pressure increases.
D) the velocity and pressure both decrease.
E) either the velocity or the pressure changes but not both.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which conservation law governs the Bernoulli's equation?
A) Conservation of energy
B) Conservation of linear momentum
C) Conservation of angular momentum
D) Newton's universal law of gravitation
E) Bernoulli's equation does not follow from any conservation law.
A) Conservation of energy
B) Conservation of linear momentum
C) Conservation of angular momentum
D) Newton's universal law of gravitation
E) Bernoulli's equation does not follow from any conservation law.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
A block of wood of mass 300 g and density 0.75 g/cm3 is floating on the surface of a liquid of density 1.1 g/cm3. What mass of lead (density = 11.3 g/cm3) must be added to the block in order for the combination just to be submerged?
A) 440 g
B) 820 g
C) 140 g
D) 155 g
E) none of the above
A) 440 g
B) 820 g
C) 140 g
D) 155 g
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
A raft of density 700 kg/m3 has a surface area of 7.0 m2 and a volume of 0.7 m3. What depth does it sink into water of density 1000 kg/m3?
A) 10 cm
B) 0.7 cm
C) 0.7 m
D) 7 m
E) 7 cm
A) 10 cm
B) 0.7 cm
C) 0.7 m
D) 7 m
E) 7 cm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The drag force on a plane is proportional to the density of the air. By what factor does the drag force change if a plane goes from an altitude 5.5 km to 11 km? The atmospheric pressure goes from 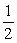 to
to 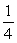 atm in going from 5.5 km to 11 km. Assume that the plane is at level flight and flies at the same speed.
atm in going from 5.5 km to 11 km. Assume that the plane is at level flight and flies at the same speed.
A)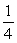
B)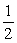
C)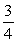
D) 1
E) 2
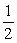 to
to 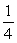 atm in going from 5.5 km to 11 km. Assume that the plane is at level flight and flies at the same speed.
atm in going from 5.5 km to 11 km. Assume that the plane is at level flight and flies at the same speed.A)
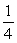
B)
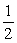
C)
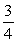
D) 1
E) 2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Water from a tap is flowing at a uniform rate of 24 cm3/s into a cylindrical container. An exit tube is mounted on the side of the container at height h/2 from the base. The height h of the water remains constant. The volume flow at which the water leaves the container is
A) 12 cm3/s
B) 24 cm3/s
C) 36 cm3/s
D) 48 cm3/s
E) 72 cm3/s
A) 12 cm3/s
B) 24 cm3/s
C) 36 cm3/s
D) 48 cm3/s
E) 72 cm3/s

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
A large spherical air balloon is filled with helium. If the balloon is to lift three people, each approximately 80 kg, plus a basket and balloon outer covering material of mass
50 kg, calculate the minimum radius of the balloon. Assume values of the density of air and helium to be 1.29 kg/m3 and 0.18 kg/m3 respectively.
A) 62 m
B) 8.0 m
C) 4.0 m
D) 20 m
E) 5.0 m
50 kg, calculate the minimum radius of the balloon. Assume values of the density of air and helium to be 1.29 kg/m3 and 0.18 kg/m3 respectively.
A) 62 m
B) 8.0 m
C) 4.0 m
D) 20 m
E) 5.0 m

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
A block of wood of mass 400 g and density 0.8 g/cm3 is floating on the surface of a liquid of density 1.3 g/cm3. What is the difference in mass of stone (density = 1.9 g/cm3) that must be added to the block in order for the combination (wood and stone) to be just submerged rather than only the wood to be submerged?
A) 250 g
B) 540 g
C) 170 g
D) 790 g
E) none of the above
A) 250 g
B) 540 g
C) 170 g
D) 790 g
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
A block of wood of length L = 21.0 cm, width w = 9.53 cm, and height h = 5.92 cm is just barely immersed in water by placing a mass m on the top of the block. The density of the wood is = 0.390 g/cm3. The value of m is
A) 0.72 kg
B) 7.1 kg
C) 1.2 kg
D) 1.6 kg
E) 0.36 kg
A) 0.72 kg
B) 7.1 kg
C) 1.2 kg
D) 1.6 kg
E) 0.36 kg

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
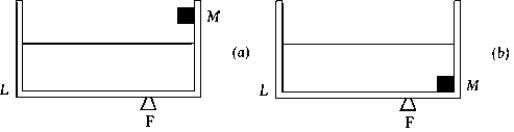 A large tub is half full of water. A mass M = 25.0 kg, which has a specific gravity of 2.5, is attached to the right-hand side of the tub, out of the water. The entire apparatus balances perfectly horizontally on a fulcrum at F, as in (a). The tub is clamped in place and M is lowered to the bottom, completely submerged, as in (b). When the clamps are removed, the tub
A large tub is half full of water. A mass M = 25.0 kg, which has a specific gravity of 2.5, is attached to the right-hand side of the tub, out of the water. The entire apparatus balances perfectly horizontally on a fulcrum at F, as in (a). The tub is clamped in place and M is lowered to the bottom, completely submerged, as in (b). When the clamps are removed, the tubA) remains balanced.
B) tips, with point L going down.
C) tips, with point L going up.
D) There is not enough information to solve the problem.
E) None of these is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
A rock of mass M with a density twice that of water is sitting on the bottom of an aquarium tank filled with water. The normal force exerted on the rock by the bottom of the tank is
A) 2Mg
B) Mg
C) Mg/2
D) zero
E) impossible to determine from the information given.
A) 2Mg
B) Mg
C) Mg/2
D) zero
E) impossible to determine from the information given.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
A uniform cylinder of wood of length 25 cm is floating vertically upright in a dual layered fluid. An oil layer (of density 0.9 g/cm3) that is 9 cm deep lies above a depth of water. If only 5 cm of wood lies above the oil surface calculate the density of the wood.
A) 0.76 g/ cm3
B) 0.80 g/ cm3
C) 0.70 g/ cm3
D) 0.66 g/ cm3
E) none of the above
A) 0.76 g/ cm3
B) 0.80 g/ cm3
C) 0.70 g/ cm3
D) 0.66 g/ cm3
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
A rock of mass M, that has a density twice that of water, is suspended in water by a thin, massless cord. The tension in the cord is
A) 2Mg
B) Mg
C) Mg/2
D) zero
E) impossible to determine from the information given.
A) 2Mg
B) Mg
C) Mg/2
D) zero
E) impossible to determine from the information given.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
A rock is thrown into a swimming pool that is filled with water at a uniform temperature. Which of the following statements is true?
A) The buoyant force on the rock is zero as it sinks.
B) The buoyant force on the rock increases as it sinks.
C) The buoyant force on the rock decreases as it sinks.
D) The buoyant force on the rock is constant as it sinks.
E) The buoyant force on the rock as it sinks is nonzero at first but becomes zero once the terminal velocity is reached.
A) The buoyant force on the rock is zero as it sinks.
B) The buoyant force on the rock increases as it sinks.
C) The buoyant force on the rock decreases as it sinks.
D) The buoyant force on the rock is constant as it sinks.
E) The buoyant force on the rock as it sinks is nonzero at first but becomes zero once the terminal velocity is reached.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
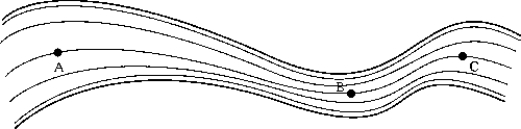
The figure represents the streamline flow of an incompressible fluid. Which of the following statements is true of the velocity and/or pressure at the indicated points?
A) vA = vB = vC
B) vA = vB = vC; pA pB pC
C) vA vB vC; pA = pB = pC
D) vA vB vC; pA pB pC
E) vA = vB = vC; pA > pB > pC

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
A small portion of an incompressible liquid in steady flow through a pipe of variable cross section, if friction is negligible, has at each point throughout its path a constant
A) kinetic energy.
B) velocity.
C) potential energy.
D) total energy.
E) momentum.
A) kinetic energy.
B) velocity.
C) potential energy.
D) total energy.
E) momentum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
When Bernoulli's equation is written in the form
P/ +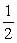 v2 + U = C,
v2 + U = C,
The constant C represents the
A) energy per unit mass.
B) energy per unit volume.
C) net work done by outside forces.
D) power supplied by outside sources.
E) mass flow per unit time.
P/ +
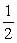 v2 + U = C,
v2 + U = C,The constant C represents the
A) energy per unit mass.
B) energy per unit volume.
C) net work done by outside forces.
D) power supplied by outside sources.
E) mass flow per unit time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
A smooth stone is falling with its constant terminal velocity in a viscous liquid. The density of the stone is 2.89 103 kg/m3, and the density of the liquid is 1.34 103 kg/m3. The volume of the stone is 2.15 10-6 m3. The drag force F of the liquid on the stone is given by F = 3.52v in SI units, where v is the terminal velocity. The value of v is
A) 8.5 10-3 m/s
B) 1.1 10-2 m/s
C) 3.2 10-2 m/s
D) 1.7 10-2 m/s
E) 1.7 10-3 m/s
A) 8.5 10-3 m/s
B) 1.1 10-2 m/s
C) 3.2 10-2 m/s
D) 1.7 10-2 m/s
E) 1.7 10-3 m/s

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
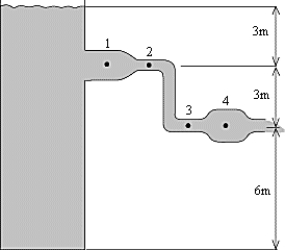 Water is discharged from the tank in the manner shown. At which point is the pressure the least?
Water is discharged from the tank in the manner shown. At which point is the pressure the least?A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) The pressure is the same at all points.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
A pipe of 2.54 cm inside diameter has a constriction in which the inside diameter is 1.27 cm. If water is flowing through this pipe with a velocity of 1.22 m/s in the main section, the velocity in the constricted section is
A) 0.305 m/s
B) 0.610 m/s
C) 2.44 m/s
D) 1.22 m/s
E) 4.88 m/s
A) 0.305 m/s
B) 0.610 m/s
C) 2.44 m/s
D) 1.22 m/s
E) 4.88 m/s

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Cities across the U.S. supply fresh water to the residents at constant pressure by the use of water towers. If the diameter, d2, of the pipe coming out of the tower is 25 cm, and the diameter, d1, of the pipe at your home is 2.0 cm, what is the ratio of the velocity of the water at d1 compared to d2? Assume that all the taps are off except yours.
A) 12.5
B) 156
C) 0.0064
D) 0.08
E) 25
A) 12.5
B) 156
C) 0.0064
D) 0.08
E) 25

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
A fish model that is 5.08 cm in diameter is placed in a pipe 25.4 cm in diameter and aligned along the axis of the pipe. If the water must flow past the fish at 2.44 m/s, the water in the unconstricted part of the pipe must flow at
A) 9.75 cm/s
B) 2.84 m/s
C) 2.35 m/s
D) 2.44 m/s
E) 6.10 m/s
A) 9.75 cm/s
B) 2.84 m/s
C) 2.35 m/s
D) 2.44 m/s
E) 6.10 m/s

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
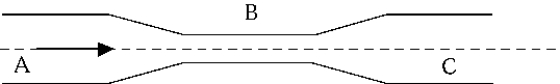 A liquid, such as water, with a low but not negligible viscosity is flowing from A to C with no turbulence through the horizontal tube, as shown in the figure. The cross-sectional area at A is equal to that at C. Which of the following is observed?
A liquid, such as water, with a low but not negligible viscosity is flowing from A to C with no turbulence through the horizontal tube, as shown in the figure. The cross-sectional area at A is equal to that at C. Which of the following is observed?A) The pressure at A is the same as the pressure at C, and this pressure is smaller than the pressure at B.
B) The pressure at A is somewhat larger than that at C, and the pressures at both A and C are larger than the pressure at B.
C) The pressures at A and C are the same, and this pressure is larger than the pressure at B.
D) The pressure at A is larger than the pressure at B, which is larger than the pressure at C.
E) None of these is observed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
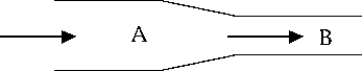 Water flows through the pipe shown in the figure. The pressure
Water flows through the pipe shown in the figure. The pressureA) is greater at A than at B.
B) at A equals that at B.
C) is less at A than at B.
D) at A is unrelated to that at B.
E) at A can be greater or less than that at B depending on the rate of flow.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Sea water of density 1.03 103 kg/m3 is in streamline flow through a Venturi meter. The pressure difference between the main pipe and the constriction is 20.7 kPa, and the flow velocity in the constriction is 7.32 m/s. The flow velocity in the main pipe is
A) 2.44 m/s
B) 3.66 m/s
C) 7.32 m/s
D) 14.6 m/s
E) 29.3 m/s
A) 2.44 m/s
B) 3.66 m/s
C) 7.32 m/s
D) 14.6 m/s
E) 29.3 m/s

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
An incompressible fluid is in streamline flow through a Venturi meter, as shown. In the graph, one of the curves is a calibration curve for the meter, showing the fluid velocity plotted against the gauge reading. Which curve best represents the calibration data? 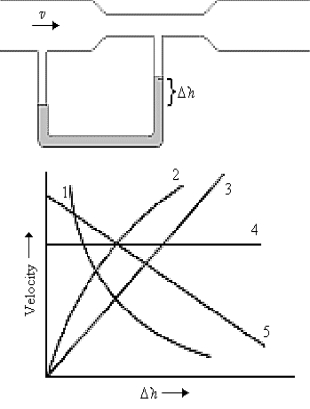
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5

A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Water flows at speed v in a pipe of radius r. Neglecting viscosity, at what speed does the water flow through a constriction in which the radius of the pipe is r/3?
A) v/9
B) v/3
C) v
D) 3v
E) 9v
A) v/9
B) v/3
C) v
D) 3v
E) 9v

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
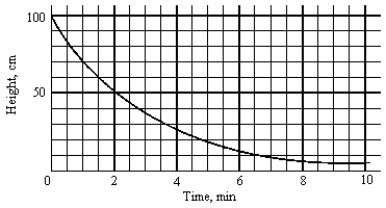 The height of a water column as a function of time is given in the graph. From this graph, the time constant of the process is
The height of a water column as a function of time is given in the graph. From this graph, the time constant of the process isA) 0.85 min
B) 1.4 min
C) 2.0 min
D) 2.9 min
E) infinite

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
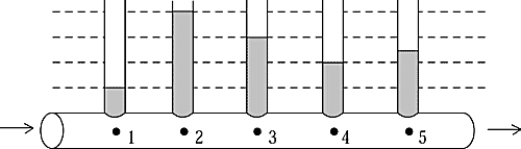 A pipe that appears to be of uniform size has constrictions on the inside. When a liquid flows through the pipe, the pressures at various points are indicated by the heights of the columns in the manometer tubes. If fluid friction is negligible, at which point is the diameter greatest?
A pipe that appears to be of uniform size has constrictions on the inside. When a liquid flows through the pipe, the pressures at various points are indicated by the heights of the columns in the manometer tubes. If fluid friction is negligible, at which point is the diameter greatest?A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Sea water of density 1.03 103 kg/m3 is in streamline flow through a Venturi meter. The cross-sectional areas of the main pipe and the constriction are 0.139 m2 and 0.0464 m2, respectively, and the pressure difference between the two portions is 55.2 kPa. The velocity of flow in the main pipe is
A) 0.305 m/s
B) 1.73 m/s
C) 3.66 m/s
D) 11.0 m/s
E) 20.7 m/s
A) 0.305 m/s
B) 1.73 m/s
C) 3.66 m/s
D) 11.0 m/s
E) 20.7 m/s

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
A wind with speed 45 m/s blows across a roof 20 m long and 12 m wide. The pressure inside the room is 1 atm. What is the net force on this roof due to the pressure difference inside and outside the roof? (The density of air is equal to 1.3 kg/m3.)
A) 3.2 105 N
B) 2.4 107 N
C) 6.3 105 N
D) 7.0 103 N
E) 3.2 108 N
A) 3.2 105 N
B) 2.4 107 N
C) 6.3 105 N
D) 7.0 103 N
E) 3.2 108 N

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
One statement of Bernoulli's law is
At any two points along a pipe in which there is a liquid in steady flow, the sum of the pressure, the kinetic energy per unit volume, and the potential energy per unit volume has the same value.
For this statement to be true, it is not necessary to have
A) streamline flow.
B) frictionless flow.
C) an incompressible fluid.
D) fluid of constant density.
E) constant acceleration of the fluid between the two points.
At any two points along a pipe in which there is a liquid in steady flow, the sum of the pressure, the kinetic energy per unit volume, and the potential energy per unit volume has the same value.
For this statement to be true, it is not necessary to have
A) streamline flow.
B) frictionless flow.
C) an incompressible fluid.
D) fluid of constant density.
E) constant acceleration of the fluid between the two points.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
For the streamlined flow of a viscous liquid, such as water, in a capillary tube, which of the following is correct?
A) The coefficient of viscosity depends on the radius of the inside of the tube raised to the fourth power.
B) The velocity of the liquid is essentially zero at the tube walls and increases toward the center of the tube.
C) There is no pressure difference along the tube provided the tube is less than 10 cm in length.
D) The volume flow rate through the tube can never be constant.
E) None of these is correct.
A) The coefficient of viscosity depends on the radius of the inside of the tube raised to the fourth power.
B) The velocity of the liquid is essentially zero at the tube walls and increases toward the center of the tube.
C) There is no pressure difference along the tube provided the tube is less than 10 cm in length.
D) The volume flow rate through the tube can never be constant.
E) None of these is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Using a motion sensor, Susana finds that the acceleration of a 4-kg rock that has been dropped from the roof of a building is 6 m/s2. She concludes that the magnitude of force of air resistance acting on the rock is approximately
A) 39.2 N
B) 24.0 N
C) 15.2 N
D) 9.81 N
E) None of these is correct.
A) 39.2 N
B) 24.0 N
C) 15.2 N
D) 9.81 N
E) None of these is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



