Deck 20: Thermal Properties and Processes
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/54
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 20: Thermal Properties and Processes
1
In operation an aluminum flywheel within an engine gearbox increases its temperature by 40 C. Assuming the flywheel to be a uniform circular disk, calculate the percentage change in the moment of inertia of the flywheel.
(Coefficient of linear expansion for Al = 24 10-6/K.)
A) 0.002%
B) 0.2%
C) 0.1%
D) 0.001%
E) 1.0%
(Coefficient of linear expansion for Al = 24 10-6/K.)
A) 0.002%
B) 0.2%
C) 0.1%
D) 0.001%
E) 1.0%
0.2%
2
A well-known technique for achieving a very tight fit between two components is to "expand by heating and then cool to shrink fit." For example, an aluminum ring of inner radius 5.98 cm needs to be firmly bonded to a cylindrical shaft of radius 6.00 cm (Measurements are at 20 C). Calculate the minimum temperature to which the aluminum ring needs to be heated before it can be slipped over the shaft for fitting.
(Coefficient of linear expansion for Al = 24 10-6/K.)
A) 140 C
B) 850 C
C) 120 C
D) 160 C
E) 180 C
(Coefficient of linear expansion for Al = 24 10-6/K.)
A) 140 C
B) 850 C
C) 120 C
D) 160 C
E) 180 C
160 C
3
The amount of linear expansion of a rod does not depend on
A) the original length of the rod.
B) the specific heat of the rod.
C) the change in the absolute temperature of the rod.
D) the coefficient of linear expansion.
E) the material from which the rod is made.
A) the original length of the rod.
B) the specific heat of the rod.
C) the change in the absolute temperature of the rod.
D) the coefficient of linear expansion.
E) the material from which the rod is made.
the specific heat of the rod.
4
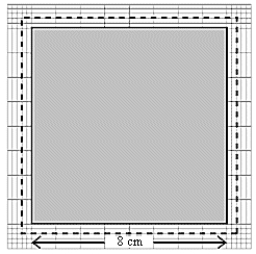 A change in temperature of 100º C causes a square plate to expand as shown in the figure. The coefficient of linear expansion of the plate is approximately
A change in temperature of 100º C causes a square plate to expand as shown in the figure. The coefficient of linear expansion of the plate is approximatelyA) 0.0020/Cº
B) 0.0010/Cº
C) 0.0005/Cº
D) 0.0040/Cº
E) 0.0017/Cº

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A glass rod that is 1.0 m long at 0ºC increases its length by 0.68 mm when heated to 80ºC. The coefficient of linear expansion of this glass is approximately
A) 8.5 10-6/Cº
B) 6.8 10-4/Cº
C) 0.013/Cº
D) 1.0/Cº
E) 80/Cº
A) 8.5 10-6/Cº
B) 6.8 10-4/Cº
C) 0.013/Cº
D) 1.0/Cº
E) 80/Cº

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The coefficient of thermal expansion of water at 20ºC is 0.207 x 10-3 K-1 A thin glass tube contains a 75.0 cm column of water at 20ºC. If the thermal expansion of the glass tube is negligible, by how much does the length of the column of water expand when it is heated to 80ºC?
A) 3.1 mm
B) 9.3 mm
C) 12.4 mm
D) 4.1 mm
E) 28 mm
A) 3.1 mm
B) 9.3 mm
C) 12.4 mm
D) 4.1 mm
E) 28 mm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
If is the coefficient of linear expansion of a material at 0ºC, the volume thermal-expansion coefficient of this material at 0ºC is
A) ~
B) ~3
C) ~ 3
D) ~ 1/3
E) None of these is correct.
A) ~
B) ~3
C) ~ 3
D) ~ 1/3
E) None of these is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
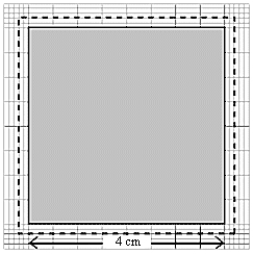 A change in temperature of 100º C causes a square plate to expand as shown in the figure. The coefficient of linear expansion of the plate is approximately
A change in temperature of 100º C causes a square plate to expand as shown in the figure. The coefficient of linear expansion of the plate is approximatelyA) 0.0020/Cº
B) 0.0010/Cº
C) 0.0005/Cº
D) 0.0040/Cº
E) 0.0017/Cº

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The length of an object varies with temperature according to
L = 6 + 2T + 5T2
The coefficient of linear expansion of this object is
A) 2 + 10T
B) 2/L
C) 10T/L
D) T/L
E) (2 + 10T)/L
L = 6 + 2T + 5T2
The coefficient of linear expansion of this object is
A) 2 + 10T
B) 2/L
C) 10T/L
D) T/L
E) (2 + 10T)/L

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The coefficient of linear expansion of the steel in a certain bridge is 1.10 10-5/Cº. If at a minimum winter temperature of -30ºC the bridge is 30.5 m long, at the summer maximum of 40ºC its length is increased about
A) 2.54 cm
B) 2.54 mm
C) 0.254 mm
D) 25.4 µm
E) 2.54 µm
A) 2.54 cm
B) 2.54 mm
C) 0.254 mm
D) 25.4 µm
E) 2.54 µm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The coefficient of linear expansion for most materials
A) is much less than 1 K-1.
B) is much greater than 1 K-1.
C) is approximately 1 K-1.
D) can be less than, greater than, or about equal to 1 K-1.
E) is described by none of these.
A) is much less than 1 K-1.
B) is much greater than 1 K-1.
C) is approximately 1 K-1.
D) can be less than, greater than, or about equal to 1 K-1.
E) is described by none of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The coefficient of linear expansion for a certain metal is . The coefficient of area expansion for a square plate made of the same metal is approximately
A)
B) /2
C) 2
D)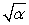
E) 2
A)
B) /2
C) 2
D)
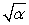
E) 2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A common trick to open the lid of a jar that is stuck is to put the lid under hot running water. Suppose the diameter of the lid of a jar of strawberry jam is 6 cm, by how much does the circumference change if the temperature is increased by 30 C? Assume the lid is made of steel.
A) 2.0 10 -3 cm
B) 3.1 10 -3 cm
C) 4.1 10 -3 cm
D) 6.2 10 -3 cm
E) 5.2 10 -3 cm
A) 2.0 10 -3 cm
B) 3.1 10 -3 cm
C) 4.1 10 -3 cm
D) 6.2 10 -3 cm
E) 5.2 10 -3 cm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Modern railway tracks consist of continuous welded-steel rails of 1.0-km lengths. If the coefficient of linear expansion of steel is 11 10-6 K-1, by how much would such a rail change in length between the highest summer temperature (40ºC) and the lowest winter temperature (-40ºC)?
A) 44 cm
B) 88 cm
C) 0.88 mm
D) 1.8 mm
E) 4.4 cm
A) 44 cm
B) 88 cm
C) 0.88 mm
D) 1.8 mm
E) 4.4 cm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
You have cut a hole in the middle of a large sheet of metal. When the sheet is heated, the area of the hole
A) does not change.
B) always increases.
C) always decreases.
D) increases if the hole is not in the exact center of the sheet.
E) decreases only if the hole is in the exact center of the sheet.
A) does not change.
B) always increases.
C) always decreases.
D) increases if the hole is not in the exact center of the sheet.
E) decreases only if the hole is in the exact center of the sheet.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A sheet of metal has a star shaped hole. What happens to the distance, d, when the temperature of the sheet is increased? 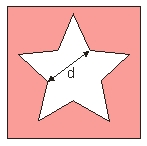
A) does not change
B) always increases
C) always decreases
D) unable to tell
E) depends on the thickness of the metal sheet.

A) does not change
B) always increases
C) always decreases
D) unable to tell
E) depends on the thickness of the metal sheet.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
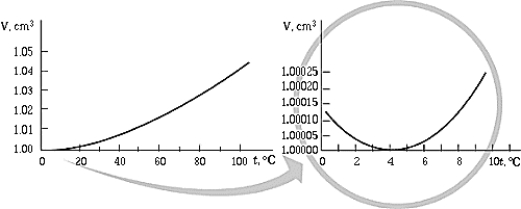 The graph shows the volume occupied by 1 g of water as a function of temperature. The graph shows that
The graph shows the volume occupied by 1 g of water as a function of temperature. The graph shows thatA) for temperatures greater than 4ºC, the volume decreases with temperature.
B) the volume of the water is a minimum at 4ºC.
C) for temperatures less than 4ºC, the volume increases as the temperature decreases.
D) for temperatures greater than 4ºC, water becomes denser as it cools.
E) All of these statements are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A clock pendulum made of aluminum, which has a coefficient of linear expansion of 24 10-6/K, has a period of exactly 1 s at 20ºC. Before a homeowner leaves town for one week, he turns the thermostat down to 10ºC. When he returns, the clock is
A) fast by about 73 s.
B) fast by about 7.6 min.
C) exactly on time.
D) slow by about 7.6 min.
E) slow by about 73 s.
A) fast by about 73 s.
B) fast by about 7.6 min.
C) exactly on time.
D) slow by about 7.6 min.
E) slow by about 73 s.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
A square hole, 30 cm on each edge, is cut in the center of a square aluminum plate 1 m on a side. The coefficient of linear expansion of aluminum is 2.4 10-5/Cº. If the plate is heated 25 ºC above the starting temperature, the area of the hole
A) increases by 1.1 cm2.
B) increases by 0.54 cm2.
C) increases by 0.00060 cm2.
D) decreases by 0.54 cm2.
E) decreases by 0.00060 cm2.
A) increases by 1.1 cm2.
B) increases by 0.54 cm2.
C) increases by 0.00060 cm2.
D) decreases by 0.54 cm2.
E) decreases by 0.00060 cm2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The length of an object varies with temperature according to
L = -5T + 3T3
The coefficient of linear expansion of this object is
A) (-5 + 9T2)/L
B) -5/L
C) (-5 + 6T2)/L
D) 9T2
E) 9T2/L
L = -5T + 3T3
The coefficient of linear expansion of this object is
A) (-5 + 9T2)/L
B) -5/L
C) (-5 + 6T2)/L
D) 9T2
E) 9T2/L

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Mountaineers say that you cannot hardboil an egg on the top of Mount Rainier. This is true because
A) the air is too cold to boil water.
B) the air pressure is too low for stoves to burn.
C) boiling water is not hot enough to hardboil the egg.
D) the oxygen content of the air is too low.
E) eggs always break in their backpacks.
A) the air is too cold to boil water.
B) the air pressure is too low for stoves to burn.
C) boiling water is not hot enough to hardboil the egg.
D) the oxygen content of the air is too low.
E) eggs always break in their backpacks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The axes on a phase diagram are
A) temperature and volume.
B) pressure and volume.
C) isotherms and pressure.
D) temperature and pressure.
E) solid, liquid, and vapor.
A) temperature and volume.
B) pressure and volume.
C) isotherms and pressure.
D) temperature and pressure.
E) solid, liquid, and vapor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The critical temperature of any gas is
A) the temperature above which the gas cannot be liquefied.
B) the temperature at which solid, liquid, and gas coexist.
C) the temperature below which the gas cannot exist as a liquid.
D) the temperature at which the gas has a maximum volume.
E) 374ºC.
A) the temperature above which the gas cannot be liquefied.
B) the temperature at which solid, liquid, and gas coexist.
C) the temperature below which the gas cannot exist as a liquid.
D) the temperature at which the gas has a maximum volume.
E) 374ºC.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following processes of heat transfer is independent of the area exposed?
A) conduction
B) convection
C) radiation
D) All of these are independent of the area exposed.
E) None of these is independent of the area exposed.
A) conduction
B) convection
C) radiation
D) All of these are independent of the area exposed.
E) None of these is independent of the area exposed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The gas tank of your car can hold 60 L of gasoline. Do you get more gasoline in terms of the number of moles when you fill your tank when the gasoline is cold or hot? The coefficient of volume expansion for gasoline = 930 10-6/K and that of steel is 33 10-6/K.
A) Gasoline is sold by volume so it does not make any difference.
B) Gasoline expands when the temperature increases, so you get more when it is hot.
C) Gasoline expands when the temperature increases, so you get less when it is hot.
D) Both gasoline and the tank expand so they cancel each other out.
E) It depends on whether it is regular or premium gasoline.
A) Gasoline is sold by volume so it does not make any difference.
B) Gasoline expands when the temperature increases, so you get more when it is hot.
C) Gasoline expands when the temperature increases, so you get less when it is hot.
D) Both gasoline and the tank expand so they cancel each other out.
E) It depends on whether it is regular or premium gasoline.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
A scuba tank of volume 40 L is filled with 200 moles of compressed air at a pressure of 100 atm. What is the value of an2/V2 due to O2?
A) 1.52 atm
B) 34.6 atm
C) 21.6 atm
D) 3.23 atm
E) 10.4 atm
A) 1.52 atm
B) 34.6 atm
C) 21.6 atm
D) 3.23 atm
E) 10.4 atm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The pressure of a saturated vapor depends on the
A) volume of the vapor.
B) mass of liquid vaporized.
C) density of the liquid only.
D) temperature only.
E) combined volume of liquid and vapor.
A) volume of the vapor.
B) mass of liquid vaporized.
C) density of the liquid only.
D) temperature only.
E) combined volume of liquid and vapor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
If the absolute temperature of the filament of a lamp were doubled, the energy radiated per second by the filament would
A) remain the same.
B) increase by a factor of 2.
C) increase by a factor of 4.
D) increase by a factor of 8.
E) increase by a factor of 16.
A) remain the same.
B) increase by a factor of 2.
C) increase by a factor of 4.
D) increase by a factor of 8.
E) increase by a factor of 16.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
If the thickness of a uniform wall is doubled, the rate at which heat is conducted through the wall is
A) doubled.
B) increased by a factor of four.
C) decreased by a factor of four.
D) cut in half.
E) unchanged.
A) doubled.
B) increased by a factor of four.
C) decreased by a factor of four.
D) cut in half.
E) unchanged.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Under some conditions, real gases depart from Boyle's law due to
A) low partial pressures.
B) high molecular speeds.
C) the presence of diatomic molecules.
D) Brownian motion.
E) forces between molecules.
A) low partial pressures.
B) high molecular speeds.
C) the presence of diatomic molecules.
D) Brownian motion.
E) forces between molecules.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
If the temperature on the warmer side of a wall is doubled, the rate at which heat is conducted through the wall
A) doubles.
B) increases by a factor of 4.
C) decreases by a factor of 4.
D) is cut in half.
E) increases but the rate cannot be determined.
A) doubles.
B) increases by a factor of 4.
C) decreases by a factor of 4.
D) is cut in half.
E) increases but the rate cannot be determined.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The wall of a house consists of three layers: a wooden outer wall with an R factor of 1.0, a 3-in layer of fiberglass insulation with an R factor of 11, and a gypsum-board inner wall with an R factor of 0.33 (all R factors are in h · ft2 · Fº/Btu). When the temperature is 68ºF inside the house and - 4.0ºF outside, what is the rate of heat loss through an 8-ft by 15-ft section of this wall?
A) 700 Btu/h
B) 780 Btu/h
C) 5.8 Btu/h
D) 130 Btu/h
E) 350 Btu/h
A) 700 Btu/h
B) 780 Btu/h
C) 5.8 Btu/h
D) 130 Btu/h
E) 350 Btu/h

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Earth receives approximately 1.7 1017 J of energy from the sun each second through a process called
A) conduction.
B) convection.
C) radiation.
D) sublimation.
E) evaporation.
A) conduction.
B) convection.
C) radiation.
D) sublimation.
E) evaporation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Two types of wall separate a refrigerated room from the rest of a building. Wall 1 has half the thermal conductivity of wall 2. Wall 2 is half as thick as wall 1. The two walls have the same area. The rate of heat flow through wall 2 compared with the rate of heat flow through wall 1 is
A) four times greater.
B) twice as great.
C) the same.
D) half as great.
E) one-quarter as great.
A) four times greater.
B) twice as great.
C) the same.
D) half as great.
E) one-quarter as great.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
If the thickness of a uniform wall is halved, the rate at which heat is conducted through the wall is
A) doubled.
B) increased by a factor of four.
C) decreased by a factor of four.
D) cut in half.
E) unchanged.
A) doubled.
B) increased by a factor of four.
C) decreased by a factor of four.
D) cut in half.
E) unchanged.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The triple point of a substance gas is
A) the temperature above which the gas cannot be liquefied.
B) the temperature at which solid, liquid, and gas coexist.
C) the temperature below which the gas cannot exist as a liquid.
D) the temperature at which the gas has a maximum volume.
E) the temperature above which there is not distinction between liquid and solid.
A) the temperature above which the gas cannot be liquefied.
B) the temperature at which solid, liquid, and gas coexist.
C) the temperature below which the gas cannot exist as a liquid.
D) the temperature at which the gas has a maximum volume.
E) the temperature above which there is not distinction between liquid and solid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
A scuba tank of volume 40 L is filled with 200 moles of compressed air at a pressure of 100 atm. What is the volume occupied by O2?
A) 6.37 L
B) 1.34 L
C) 0.67 L
D) 5.03 L
E) 2.68 L
A) 6.37 L
B) 1.34 L
C) 0.67 L
D) 5.03 L
E) 2.68 L

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
During the evening the partial pressure of water vapor in the air remains constant. As the temperature decreases, the relative humidity
A) stays the same.
B) increases.
C) decreases.
D) increases or decreases depending on the temperature.
E) More information is needed to answer this question.
A) stays the same.
B) increases.
C) decreases.
D) increases or decreases depending on the temperature.
E) More information is needed to answer this question.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
A certain blackbody radiates 100 W at a temperature of 2000 K. How much power would this body radiate at 3000 K?
A) 150 W
B) 225 W
C) 338 W
D) 506 W
E) 759 W
A) 150 W
B) 225 W
C) 338 W
D) 506 W
E) 759 W

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
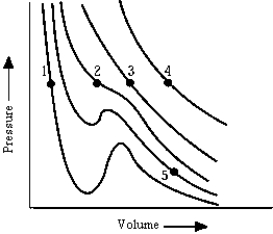 The graph shows isotherms of a gas plotted from van der Waal's equation. At which point is a mixture of liquid and vapor likely to be found?
The graph shows isotherms of a gas plotted from van der Waal's equation. At which point is a mixture of liquid and vapor likely to be found?A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
You are testing thermal conduction through two different materials, A and B, of the same cross-sectional area. Material A is twice as thick as material B, and the thermal conductivity of material A is three times higher than that of material B. What is the thermal resistance of A divided by the thermal resistance of B?
A) 6.0
B) 1.5
C) 5.0
D) 0.67
E) 0.17
A) 6.0
B) 1.5
C) 5.0
D) 0.67
E) 0.17

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
If the absolute temperature of an object is tripled, the rate at which it radiates thermal energy
A) triples.
B) increases by a factor of 9.
C) increases by a factor of 27.
D) increases by a factor of 81.
E) depends on whether the absolute temperature is above or below zero.
A) triples.
B) increases by a factor of 9.
C) increases by a factor of 27.
D) increases by a factor of 81.
E) depends on whether the absolute temperature is above or below zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
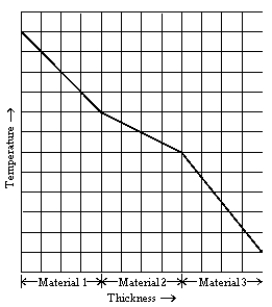 The graph shows temperature as a function of thickness in three adjacent slabs of material of equal thickness. Assuming the heat transfer through the compound slabs is in a steady state, what can you say of these materials?
The graph shows temperature as a function of thickness in three adjacent slabs of material of equal thickness. Assuming the heat transfer through the compound slabs is in a steady state, what can you say of these materials?A) material 1 is the best insulator
B) material 2 is the best insulator
C) material 3 is the best insulator
D) all are equally good insulators
E) It is impossible to determine which is the best insulator.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
You are trying to decide what the change in heat loss would be if you put a
100 cm 150 cm and 5-mm thick glass window in an outside wall. The thickness of the wall is 15 cm. If the thermal conductivities of the glass and wall are 0.90 W/m·K and 0.15 W/m·K respectively, calculate the difference in heat loss through thermal conductivity with and without the window when the outside temperature is -10 C and the inside temperature is 15 C.
A) 1.34 103 J/s
B) 6.7 103 J/s
C) 5.53 103 J/s
D) 6.75 103 J/s
E) none of the above
100 cm 150 cm and 5-mm thick glass window in an outside wall. The thickness of the wall is 15 cm. If the thermal conductivities of the glass and wall are 0.90 W/m·K and 0.15 W/m·K respectively, calculate the difference in heat loss through thermal conductivity with and without the window when the outside temperature is -10 C and the inside temperature is 15 C.
A) 1.34 103 J/s
B) 6.7 103 J/s
C) 5.53 103 J/s
D) 6.75 103 J/s
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The main process by which heat is transferred to your home when it is heated by solar energy is
A) conduction.
B) convection.
C) radiation.
D) latent heat transfer.
E) insulation.
A) conduction.
B) convection.
C) radiation.
D) latent heat transfer.
E) insulation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
If the absolute temperature of an object is doubled, the rate at which it radiates thermal energy
A) doubles.
B) increases by a factor of 4.
C) increases by a factor of 8.
D) increases by a factor of 16.
E) increases by a factor of 32.
A) doubles.
B) increases by a factor of 4.
C) increases by a factor of 8.
D) increases by a factor of 16.
E) increases by a factor of 32.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A thermo keeps a hot drink hot and a cold drink cold for a long time. Shown below is a cut-away section of a thermo with the important features labeled. The reason for the silvered double-wall vacuum chamber is 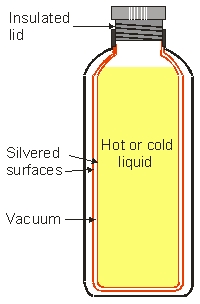
A) the silvered surfaces reflect any radiation while the vacuum suppresses heat losses by convection and heat conductivity.
B) people like silvery thing so it is a marketing tool. The vacuum keeps the container clean.
C) the silvered surfaces suppresses heat conduction and convection and the vacuum prevents radiated heat.
D) because putting silvery surface is easy to manufacture, and while they are at it, might as well put a vacuum in between.
E) none of the above

A) the silvered surfaces reflect any radiation while the vacuum suppresses heat losses by convection and heat conductivity.
B) people like silvery thing so it is a marketing tool. The vacuum keeps the container clean.
C) the silvered surfaces suppresses heat conduction and convection and the vacuum prevents radiated heat.
D) because putting silvery surface is easy to manufacture, and while they are at it, might as well put a vacuum in between.
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
An object at temperature 227 C radiates energy at a net rate of R J/s.
By what factor would the net rate of energy loss increase if the same object were at a temperature of 427 C? Assume the surrounding temperature is 0 C.
A) 4.1
B) 3.8
C) 12.5
D) 8.3
E) 6.7
By what factor would the net rate of energy loss increase if the same object were at a temperature of 427 C? Assume the surrounding temperature is 0 C.
A) 4.1
B) 3.8
C) 12.5
D) 8.3
E) 6.7

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
A solid sphere at temperature T radiates energy at a rate of R J/s. If the radius of the sphere were doubled (its temperature remains at T), then the rate of radiating energy would go up by a factor of
A) stays the same
B) 2
C) 4
D) 8
E) 16
A) stays the same
B) 2
C) 4
D) 8
E) 16

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The temperature gradient in a wall is 80º C/cm, and the thermal conductivity of this wall is 4.0 10-3 cal/s · cm · Cº. The amount of heat conducted per minute per square centimeter through this wall is approximately
A) 19 cal
B) 27 cal
C) 35 cal
D) 42 cal
E) 0.42 kcal
A) 19 cal
B) 27 cal
C) 35 cal
D) 42 cal
E) 0.42 kcal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
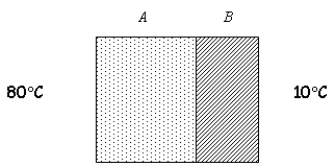
You are testing thermal conduction through a composite material made up of two layers, A and B. Layer A is twice as thick as layer B, and the thermal conductivity of material A is three times higher than that of material B. If the temperature on the outside surface of A is 80 C, and the temperature on the outside surface of B is 10 C, find the temperature at the interface of the two materials once a steady state of heat flow has been established.
A) 44 C
B) 52 C
C) 70 C
D) 12 C
E) 47 C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which of the following statements about electromagnetic radiation is NOT true?
A) Electromagnetic radiation occurs for all objects at all temperatures.
B) Electromagnetic radiation can travel in vacuum.
C) Electromagnetic radiation can travel through glass.
D) A medium is needed for electromagnetic radiation.
E) Electromagnetic radiation transfers energy.
A) Electromagnetic radiation occurs for all objects at all temperatures.
B) Electromagnetic radiation can travel in vacuum.
C) Electromagnetic radiation can travel through glass.
D) A medium is needed for electromagnetic radiation.
E) Electromagnetic radiation transfers energy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
If a piece of iron is exposed to the sun, its temperature rises until
A) it is hot enough to reflect all the energy that strikes it.
B) the heat absorbed exceeds its thermal capacity.
C) the heat absorbed equals its thermal capacity.
D) it loses and gains heat at the same rate.
E) its temperature equals the temperature of its surroundings.
A) it is hot enough to reflect all the energy that strikes it.
B) the heat absorbed exceeds its thermal capacity.
C) the heat absorbed equals its thermal capacity.
D) it loses and gains heat at the same rate.
E) its temperature equals the temperature of its surroundings.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Calculate the rate of heat transfer from a 1.5 m 1.0 m window frame that is made of aluminum. The thickness of the frame is 1 mm and measures 3 cm from inside to outside. The inside room temperature is 25 C and outside temperature is 0 C.
A) 988 W
B) 2964 W
C) 1482 W
D) 494 W
E) none of the above
A) 988 W
B) 2964 W
C) 1482 W
D) 494 W
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



