Deck 24: Amino Acids and Proteins
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/135
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 24: Amino Acids and Proteins
1
Which of these natural amino acids contains an indole ring?
A)Phenylalanine
B)Tyrosine
C)Tryptophan
D)4-Hydroxyproline
E)Asparigine
A)Phenylalanine
B)Tyrosine
C)Tryptophan
D)4-Hydroxyproline
E)Asparigine
Tryptophan
2
Which of these natural amino acids contains a phenolic group?
A)Phenylalanine
B)Tyrosine
C)Tryptophan
D)4-Hydroxyproline
E)Serine
A)Phenylalanine
B)Tyrosine
C)Tryptophan
D)4-Hydroxyproline
E)Serine
Tyrosine
3
Which of these natural amino acids,when present in a polypeptide,is not likely to exhibit significant hydrogen bonding through its side chain?
A)Leucine
B)Threonine
C)Tyrosine
D)Serine
E)All of these are likely to exhibit significant hydrogen bonding through the side chain.
A)Leucine
B)Threonine
C)Tyrosine
D)Serine
E)All of these are likely to exhibit significant hydrogen bonding through the side chain.
Leucine
4
Which of these amino acids has the R configuration at the stereogenic center but,nonetheless,is an L amino acid? 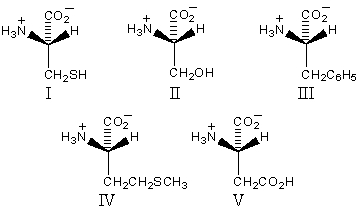
A)I
B)II
C)III
D)IV
E)V

A)I
B)II
C)III
D)IV
E)V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following amino acids is theoretically capable of existing in diastereomeric forms? 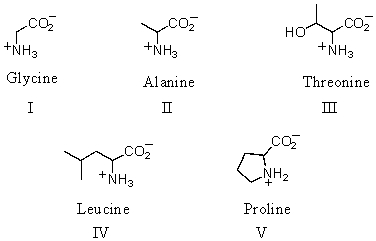
A)I
B)II
C)III
D)IV
E)V

A)I
B)II
C)III
D)IV
E)V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which amino acid is achiral? 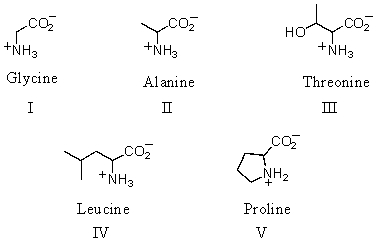
A)I
B)II
C)III
D)IV
E)V

A)I
B)II
C)III
D)IV
E)V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of these natural amino acids contains two carboxylic acid groups?
A)Aspartic acid
B)Cysteine
C)Glutamic acid
D)Cystine and cysteine
E)Aspartic acidand glutamic acid
A)Aspartic acid
B)Cysteine
C)Glutamic acid
D)Cystine and cysteine
E)Aspartic acidand glutamic acid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of these natural amino acids contains an amide function?
A)Asparagine
B)Proline
C)Arginine
D)Histidine
E)None of these choices.
A)Asparagine
B)Proline
C)Arginine
D)Histidine
E)None of these choices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of these natural amino acids,when present in a polypeptide,is likely to exhibit significant hydrogen bonding through its side chain?
A)Serine
B)Threonine
C)Tyrosine
D)Two of these choices.
E)All of these choices.
A)Serine
B)Threonine
C)Tyrosine
D)Two of these choices.
E)All of these choices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of these amino acids is(are)R amino acid(s)? 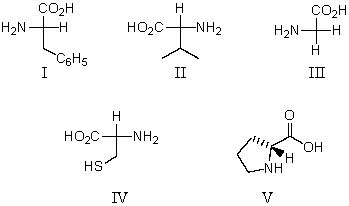
A)II and IV
B)IV and V
C)I and III
D)V
E)All of these are R amino acids.

A)II and IV
B)IV and V
C)I and III
D)V
E)All of these are R amino acids.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of these natural amino acids contains a pyrrolidine ring?
A)Phenylalanine
B)Tyrosine
C)Tryptophan
D)4-Hydroxyproline
E)Serine
A)Phenylalanine
B)Tyrosine
C)Tryptophan
D)4-Hydroxyproline
E)Serine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of these natural amino acids contains an imidazole ring?
A)Histidine
B)Lysine
C)Tryptophan
D)4-Hydroxyproline
E)Two of these choices.
A)Histidine
B)Lysine
C)Tryptophan
D)4-Hydroxyproline
E)Two of these choices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of these natural amino acids contains an -OH group?
A)Serine
B)Threonine
C)Tyrosine
D)Two of these.
E)All of these choices.
A)Serine
B)Threonine
C)Tyrosine
D)Two of these.
E)All of these choices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of these natural amino acids contains an amide function?
A)Asparagine
B)Glutamine
C)Methionine
D)Cysteine
E)Two of these
A)Asparagine
B)Glutamine
C)Methionine
D)Cysteine
E)Two of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of these amino acids cannot be described as an l-amino acid? 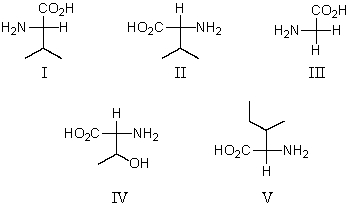
A)I
B)II,IV and V
C)I and III
D)II and IV
E)III and V

A)I
B)II,IV and V
C)I and III
D)II and IV
E)III and V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Disulfide bonds in proteins:
A)result from an oxidation of thiols.
B)help to maintain the shape of proteins.
C)can be broken by reduction.
D)can link two cysteine amino acid residues.
E)All of these choices.
A)result from an oxidation of thiols.
B)help to maintain the shape of proteins.
C)can be broken by reduction.
D)can link two cysteine amino acid residues.
E)All of these choices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of these amino acids contains a hydrophobic side chain?
A)Lysine
B)Serine
C)Methionine
D)Arginine
E)Cysteine
A)Lysine
B)Serine
C)Methionine
D)Arginine
E)Cysteine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of these amino acids is a D amino acid? 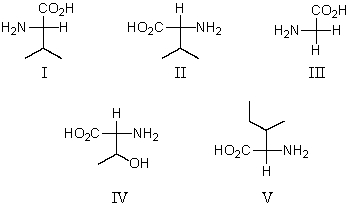
A)I
B)II
C)III
D)IV
E)V

A)I
B)II
C)III
D)IV
E)V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of these natural amino acids contains a heterocyclic ring?
A)Asparagine
B)Proline
C)Arginine
D)Histidine
E)Proline and histidine
A)Asparagine
B)Proline
C)Arginine
D)Histidine
E)Proline and histidine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which amino acid is unlikely to be found in a natural protein? 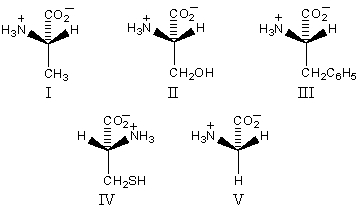
A)IV
B)III
C)II
D)V
E)I

A)IV
B)III
C)II
D)V
E)I

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which amino acid would have its isoelectric point near pH 10? 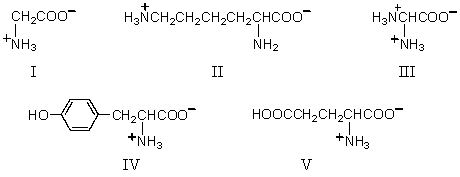
A)I
B)II
C)III
D)IV
E)V

A)I
B)II
C)III
D)IV
E)V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
What might be concluded upon determining that an unknown amino acid has its isoelectric point near pH 10?
A)It must have a hydrophobic side chain.
B)It must have a hydrophilic side chain.
C)Its side chain must contain more basic groups then acidic groups.
D)Its side chain must contain an acidic group.
E)None of these choices is a valid conclusion.
A)It must have a hydrophobic side chain.
B)It must have a hydrophilic side chain.
C)Its side chain must contain more basic groups then acidic groups.
D)Its side chain must contain an acidic group.
E)None of these choices is a valid conclusion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The pH at which the concentration of the dipolar ion (zwitterion)form of an amino acid is at a maximum and the cationic and anionic forms are at equal concentrations is termed the
A)end point.
B)equivalence point.
C)neutral point.
D)isoelectric point.
E)dipolar point.
A)end point.
B)equivalence point.
C)neutral point.
D)isoelectric point.
E)dipolar point.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
What might be concluded upon determining that an unknown amino acid has its isoelectric point near pH 3?
A)It must have a hydrophobic side chain.
B)It must have a hydrophilic side chain.
C)Its side chain must contain a basic group.
D)Its side chain must contain more acidic groups then basic groups.
E)None of these choices is a valid conclusion.
A)It must have a hydrophobic side chain.
B)It must have a hydrophilic side chain.
C)Its side chain must contain a basic group.
D)Its side chain must contain more acidic groups then basic groups.
E)None of these choices is a valid conclusion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Logically,the following "unnatural" amino acid would be substituted for which natural amino acid in the synthesis of peptide analogs? 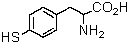
A)Methionine
B)Cysteine
C)Cystine
D)Tyrosine
E)It could be substituted for all of these amino acids.

A)Methionine
B)Cysteine
C)Cystine
D)Tyrosine
E)It could be substituted for all of these amino acids.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which amino acid would not have its isoelectric point in the pH range 5-7?
A)Glycine
B)Proline
C)Cysteine
D)Glutamine
E)All of these amino acids have isoelectric point in the pH range 5-7
A)Glycine
B)Proline
C)Cysteine
D)Glutamine
E)All of these amino acids have isoelectric point in the pH range 5-7

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which amino acid would not have its isoelectric point in the pH range 5-7?
A)Leucine
B)Threonine
C)Methionine
D)Arginine
E)Cysteine
A)Leucine
B)Threonine
C)Methionine
D)Arginine
E)Cysteine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Logically,the following "unnatural" amino acid would be substituted for which natural amino acid in the synthesis of peptide analogs? 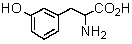
A)Tyrosine
B)Proline
C)Tryptophan
D)Phenylalanine
E)Histidine

A)Tyrosine
B)Proline
C)Tryptophan
D)Phenylalanine
E)Histidine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Pipecolic acid logically would be substituted for which natural amino acid in the synthesis of peptide analogs? 
A)Histidine
B)Proline
C)Tryptophan
D)Phenylalanine
E)Tyrosine

A)Histidine
B)Proline
C)Tryptophan
D)Phenylalanine
E)Tyrosine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
What is the name of the aminoacids F; E; R,respectively:
A)Proline,aspartic acid,asparagine.
B)Proline,methionine,cysteine.
C)Phenylalanine,glutamic acid,arginine.
D)Proline,glutamic acid,glutamine.
E)Phenylalanine,asparagine,glutamine.
A)Proline,aspartic acid,asparagine.
B)Proline,methionine,cysteine.
C)Phenylalanine,glutamic acid,arginine.
D)Proline,glutamic acid,glutamine.
E)Phenylalanine,asparagine,glutamine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of these amino acids is formed from a precursor amino acid only after the latter has been incorporated into a polypeptide chain?
A)Serine
B)Arginine
C)Isoleucine
D)Tryptophan
E)Hydroxyproline
A)Serine
B)Arginine
C)Isoleucine
D)Tryptophan
E)Hydroxyproline

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of these amino acids is described as an "essential" amino acid?
A)Threonine
B)Glycine
C)Tyrosine
D)Serine
E)All of these are "essential" amino acids.
A)Threonine
B)Glycine
C)Tyrosine
D)Serine
E)All of these are "essential" amino acids.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Logically,the following "unnatural" amino acid would be substituted for which natural amino acid in the synthesis of peptide analogs? 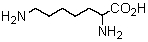
A)Leucine
B)Lysine
C)Arginine
D)Alanine
E)Valine

A)Leucine
B)Lysine
C)Arginine
D)Alanine
E)Valine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
What is the pI of the following amino acid? 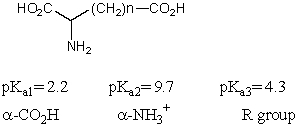
A)2.1
B)5.9
C)3.2
D)6.5
E)7.0
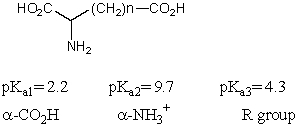
A)2.1
B)5.9
C)3.2
D)6.5
E)7.0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Logically,the following "unnatural" amino acid would be substituted for which natural amino acid in the synthesis of peptide analogs? 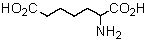
A)Aspartic acid
B)Glutamine
C)Lysine
D)Asparagine
E)Glutamic acid

A)Aspartic acid
B)Glutamine
C)Lysine
D)Asparagine
E)Glutamic acid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following sets of amino acids are essential amino acids:
A)Lysine,glutamic acid,asparagine.
B)Phenylalanine,threonine,lysine.
C)Threonine,tyrosine,tryptophan.
D)Proline,cysteine,hydroxyproline.
E)Arginine,histidine,lysine.
A)Lysine,glutamic acid,asparagine.
B)Phenylalanine,threonine,lysine.
C)Threonine,tyrosine,tryptophan.
D)Proline,cysteine,hydroxyproline.
E)Arginine,histidine,lysine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which amino acid would have its isoelectric point near pH 3? 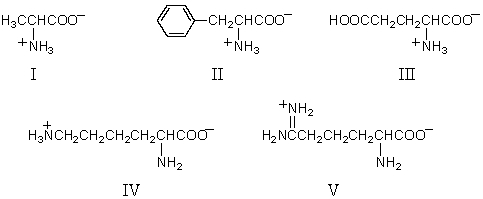
A)I
B)II
C)III
D)IV
E)V

A)I
B)II
C)III
D)IV
E)V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which amino acid would have its isoelectric point near pH 10?
A)Glycine
B)Tryptophan
C)Serine
D)Proline
E)Lysine
A)Glycine
B)Tryptophan
C)Serine
D)Proline
E)Lysine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of these amino acids is described as an "essential" amino acid?
A)Methionine
B)Phenylalanine
C)Isoleucine
D)Tryptophan
E)All of these are "essential" amino acids.
A)Methionine
B)Phenylalanine
C)Isoleucine
D)Tryptophan
E)All of these are "essential" amino acids.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
What is the pI of the following amino acid? 
A)1.2
B)3.2
C)5.5
D)6.2
E)7.0

A)1.2
B)3.2
C)5.5
D)6.2
E)7.0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
What methods can be used for the identification of amino acids?
A)Amino acid analyzer using cation-exchange resin
B)Cation-exchange resin packed column in an HPLC instrument
C)Column chromatography on normal phase silica gel
D)Reaction with ninhydrin followed by IR spectroscopy
E)Two of these choices.
A)Amino acid analyzer using cation-exchange resin
B)Cation-exchange resin packed column in an HPLC instrument
C)Column chromatography on normal phase silica gel
D)Reaction with ninhydrin followed by IR spectroscopy
E)Two of these choices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which is an isolable intermediate in the Strecker synthesis of an amino acid? 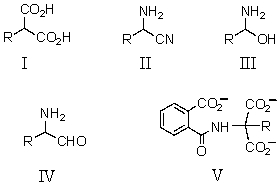
A)I
B)II
C)III
D)IV
E)V

A)I
B)II
C)III
D)IV
E)V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
What is the pI of the following amino acid? 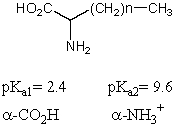
A)12.0
B)3.6
C)4.8
D)6.0
E)7.2
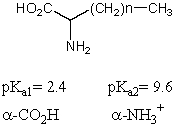
A)12.0
B)3.6
C)4.8
D)6.0
E)7.2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
What is the product of the treatment of a racemic form of dl-phenylalanine with acetic anhydride followed by treatment with deacylase enzyme?
A)S-Phenylalanine
B)R-Phenylalanine
C)d-Phenylalanine
D)Both are hydrolyzed
E)The mixture is not affected by this enzyme.
A)S-Phenylalanine
B)R-Phenylalanine
C)d-Phenylalanine
D)Both are hydrolyzed
E)The mixture is not affected by this enzyme.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The purple color of the anion formed in the ninhydrin test for α-amino acids is due to:
A)the attraction of the anion to a metal in a pi-complex.
B)intermolecular hydrogen bonding.
C)molecular vibrations.
D)the highly conjugated nature of the anion.
E)the color of the ninhydrin.
A)the attraction of the anion to a metal in a pi-complex.
B)intermolecular hydrogen bonding.
C)molecular vibrations.
D)the highly conjugated nature of the anion.
E)the color of the ninhydrin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
What is the pKa of the carboxylic acids present in the following compounds in the given order: 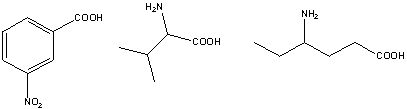
A)10.1; 2.32; 4.45
B)2.32; 2.32; 5.00
C)4.45; 3.22; 4.75
D)2.32; 4.50; 4.75
E)3.47; 2.32; 4.45

A)10.1; 2.32; 4.45
B)2.32; 2.32; 5.00
C)4.45; 3.22; 4.75
D)2.32; 4.50; 4.75
E)3.47; 2.32; 4.45

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Which of the following would provide a synthesis of leucine?
A)(CH3)2C=CHCH2OH,HBr/peroxides; then CrO3/H2SO4/H2O; then excess NH3
B)Potassium phthalimide,BrCH(CO2C2H5)2; then (CH3)2CHCHClCO2C2H5,NaOEt; then KOH/H2O; then HCl,heat
C)Potassium phthalimide,BrCH(CO2C2H5)2; then (CH3)2CHCH2Br,NaOEt; then KOH/H2O; then HCl,heat
D)(CH3)2CHCOOH,PCl5; then NH3
E)Two of these choices.
A)(CH3)2C=CHCH2OH,HBr/peroxides; then CrO3/H2SO4/H2O; then excess NH3
B)Potassium phthalimide,BrCH(CO2C2H5)2; then (CH3)2CHCHClCO2C2H5,NaOEt; then KOH/H2O; then HCl,heat
C)Potassium phthalimide,BrCH(CO2C2H5)2; then (CH3)2CHCH2Br,NaOEt; then KOH/H2O; then HCl,heat
D)(CH3)2CHCOOH,PCl5; then NH3
E)Two of these choices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which of the following would provide a synthesis of phenylalanine?
A)Phenylacetaldehyde,NH3,HCN; then H3O+ and heat
B)Potassium phthalimide,BrCH(CO2C2H5)2; C6H5CH2Br,NaOEt; then NaOH; then HCl,heat
C)Potassium phthalimide,(C6H5)CH2CH2Br; then KOH/H2O; then HCl,heat
D)C6H5CH2COOH,SOCl2; then NH3
E)Two of these choices.
A)Phenylacetaldehyde,NH3,HCN; then H3O+ and heat
B)Potassium phthalimide,BrCH(CO2C2H5)2; C6H5CH2Br,NaOEt; then NaOH; then HCl,heat
C)Potassium phthalimide,(C6H5)CH2CH2Br; then KOH/H2O; then HCl,heat
D)C6H5CH2COOH,SOCl2; then NH3
E)Two of these choices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
What would be the predominant form of lysine in water at pH 14? 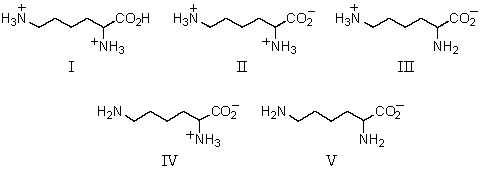
A)I
B)II
C)III
D)IV
E)V

A)I
B)II
C)III
D)IV
E)V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
What is the pI of phenylalanine (pKa1 = 1.8; pKa2= 9.1)?
A)2.3
B)1.8
C)5.5
D)9.1
E)10.9
A)2.3
B)1.8
C)5.5
D)9.1
E)10.9

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
A heptapeptide Ala2,Glu,Phe,Pro,Tyr,Val gives labeled alanine when heated with DNFB followed by hydrolysis.On partial hydrolysis the unlabeled heptapeptide gives the following: Ala·Glu,Pro·Tyr,Ala·Val,Tyr·Ala,Val·Phe·Pro.
What is the amino acid sequence of the heptapeptide?
A)Ala·Phe·Pro·Tyr·Ala·Glu·Val
B)Ala·Val·Phe·Pro·Tyr·Ala·Glu
C)Ala·Val·Phe·Pro·Tyr·Glu·Ala
D)Ala·Val·Phe·Tyr·Pro·Ala·Glu
E)Val·Ala·Phe·Tyr·Pro·Ala·Glu
What is the amino acid sequence of the heptapeptide?
A)Ala·Phe·Pro·Tyr·Ala·Glu·Val
B)Ala·Val·Phe·Pro·Tyr·Ala·Glu
C)Ala·Val·Phe·Pro·Tyr·Glu·Ala
D)Ala·Val·Phe·Tyr·Pro·Ala·Glu
E)Val·Ala·Phe·Tyr·Pro·Ala·Glu

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which one of these amino acids does not give the usual purple color with ninhydrin?
A)Histidine
B)Proline
C)Tryptophan
D)Leucine
E)Aspartic acid
A)Histidine
B)Proline
C)Tryptophan
D)Leucine
E)Aspartic acid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The predominant form of aspartic acid in water at pH 1 would be: 
A)I
B)II
C)III
D)IV
E)V

A)I
B)II
C)III
D)IV
E)V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which of the following would provide a synthesis of valine?
A)Potassium phthalimide,(CH3)2CHCHClCO2C2H5; then KOH/H2O; then HCl
B)(CH3)2C=CHCH2OH,HBr/peroxides; then CrO3/H2SO4/H2O; then excess NH3
C)Potassium phthalimide,(CH3)2CHCH2Br; then KOH/H2O; then CO2,H3O+
D)CH3CH2COOH,(C6H5)3CNa; then NH3
E)Two of these choices.
A)Potassium phthalimide,(CH3)2CHCHClCO2C2H5; then KOH/H2O; then HCl
B)(CH3)2C=CHCH2OH,HBr/peroxides; then CrO3/H2SO4/H2O; then excess NH3
C)Potassium phthalimide,(CH3)2CHCH2Br; then KOH/H2O; then CO2,H3O+
D)CH3CH2COOH,(C6H5)3CNa; then NH3
E)Two of these choices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
For the accompanying fully-protonated amino acid,what is the arrangement of pKa values in order of increasing magnitude? 
A)I < II < III
B)II < I < III
C)III < I < II
D)III < II < I
E)II < III < I

A)I < II < III
B)II < I < III
C)III < I < II
D)III < II < I
E)II < III < I

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
A pentapeptide has the molecular formula: Asp,Glu,His,Phe,Val.Partial hydrolysis of the pentapeptide gives: Val·Asp,Glu·His,Phe·Val,and Asp·Glu.What is the amino acid sequence of the pentapeptide?
A)Phe·Val·Asp·Glu·His
B)His·Glu·Asp·Val·Phe
C)Asp·Glu·His·Phe·Val
D)Phe·Val·Glu·His·Asp
E)Glu·His·Phe·Val·Asp
A)Phe·Val·Asp·Glu·His
B)His·Glu·Asp·Val·Phe
C)Asp·Glu·His·Phe·Val
D)Phe·Val·Glu·His·Asp
E)Glu·His·Phe·Val·Asp

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which of the following would provide a synthesis of alanine?
A)CH2=CHCH2OH,HBr; then CrO3/H2SO4/H2O; then excess NH3
B)Potassium phthalimide,ClCH2CO2C2H5; then KOH/H2O; then HCl
C)Potassium phthalimide,C6H5CH2Br; then KOH/H2O; then CO2,H3O+
D)CH3CH2COOH,(C6H5)3CNa; then NH3
E)Two of these choices.
A)CH2=CHCH2OH,HBr; then CrO3/H2SO4/H2O; then excess NH3
B)Potassium phthalimide,ClCH2CO2C2H5; then KOH/H2O; then HCl
C)Potassium phthalimide,C6H5CH2Br; then KOH/H2O; then CO2,H3O+
D)CH3CH2COOH,(C6H5)3CNa; then NH3
E)Two of these choices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Why is this sequence,CH2=CHCH2OH + HBr,then CrO3/H2SO4/H2O,finally excess NH3,not a good method for the preparation of l-alanine?
A)NH3 is not sufficiently nucleophilic to perform the final step.
B)HBr does not add to substituted alkenes.
C)1° alcohols are not oxidized by CrO3 in acidic solution.
D)Initial HBr addition produces a racemic intermediate which leads to racemic product.
E)Steric hindrance precludes nucleophilic substitution at a 2° carbon atom.
A)NH3 is not sufficiently nucleophilic to perform the final step.
B)HBr does not add to substituted alkenes.
C)1° alcohols are not oxidized by CrO3 in acidic solution.
D)Initial HBr addition produces a racemic intermediate which leads to racemic product.
E)Steric hindrance precludes nucleophilic substitution at a 2° carbon atom.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
What product(s)would you expect from the following reaction? 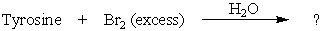
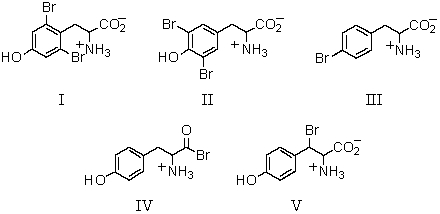
A)I
B)II
C)III
D)IV
E)V

A)I
B)II
C)III
D)IV
E)V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
What is the pI of the following amino acid? 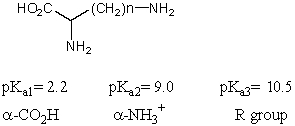
A)1.5
B)6.3
C)5.6
D)9.8
E)7.2
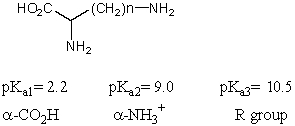
A)1.5
B)6.3
C)5.6
D)9.8
E)7.2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Which one is the correct reaction sequence for the attachment of valine on the N-terminus of a growing peptide?
A)Amino group deprotection,addition of Val and base,heating.
B)Amino group cleavage on Val,activation of carboxylic acid functionality on growing peptide chain,reaction between the two.
C)Amino group protection on the growing peptide chain,activation of the carboxylic acid functionality on Val,reaction with growing peptide.
D)Amino group deprotection on growing peptide,activation of the carboxylic acid functionality on Val,reaction with growing peptide.
E)Mix Val and growing peptide,add base and incubate the two for a period of time.
A)Amino group deprotection,addition of Val and base,heating.
B)Amino group cleavage on Val,activation of carboxylic acid functionality on growing peptide chain,reaction between the two.
C)Amino group protection on the growing peptide chain,activation of the carboxylic acid functionality on Val,reaction with growing peptide.
D)Amino group deprotection on growing peptide,activation of the carboxylic acid functionality on Val,reaction with growing peptide.
E)Mix Val and growing peptide,add base and incubate the two for a period of time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The Edman degradation uses this reagent to identify the N-terminal amino acid of a peptide or protein.
A)C6H5NHNH2
B)C6H5NH2
C)C6H5N=C=S
D)C6H5N=C=O
E)Aminopeptidase
A)C6H5NHNH2
B)C6H5NH2
C)C6H5N=C=S
D)C6H5N=C=O
E)Aminopeptidase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
What is lysozyme?
A)It is a hydrolytic DNA.
B)It is an enzyme that breaches the cell wall of gram-positive bacteria.
C)It is a protein that causes DNA hydrolysis.
D)It is an enzymatic protein contained in the nucleous.
E)It is a protein that can bind and hydrolyze esters.
A)It is a hydrolytic DNA.
B)It is an enzyme that breaches the cell wall of gram-positive bacteria.
C)It is a protein that causes DNA hydrolysis.
D)It is an enzymatic protein contained in the nucleous.
E)It is a protein that can bind and hydrolyze esters.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Which of the following statements are correct:
(I)Lysozyme produces hydrolysis of specific acetal linkages in peptidoglycan polymers.
(II)Lysozyme binds the cell wall substrate in a cleft within its tertiary structure.
(III)Evidence suggests sequential SN2 reactions and a covalent enzyme-substrate intermediate.
(IV)One product of the hydrolytic reaction shows inversion of configuration.
(V)The entire lysozyme molecule acts as a leaving group in the cleavage reaction.
A)I,II
B)III,IV
C)I,II,III,IV
D)I,II,V
E)All are correct.
(I)Lysozyme produces hydrolysis of specific acetal linkages in peptidoglycan polymers.
(II)Lysozyme binds the cell wall substrate in a cleft within its tertiary structure.
(III)Evidence suggests sequential SN2 reactions and a covalent enzyme-substrate intermediate.
(IV)One product of the hydrolytic reaction shows inversion of configuration.
(V)The entire lysozyme molecule acts as a leaving group in the cleavage reaction.
A)I,II
B)III,IV
C)I,II,III,IV
D)I,II,V
E)All are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
When the pentapeptide below is heated first with 2,4-dinitrofluorobenzene (and base)and then subjected to acidic hydrolysis,which amino acid will bear the dinitrophenyl group? Leu·Val·Gly·Phe·Ile
A)Leucine
B)Valine
C)Glycine
D)Phenylalanine
E)Isoleucine
A)Leucine
B)Valine
C)Glycine
D)Phenylalanine
E)Isoleucine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Which of these are methods to determine the sequence of amino acids in a peptide?
A)Ladder sequencing; partial hydrolysis and sequence comparison.
B)Partial hydrolysis; tandem mass spectrometry and IR.
C)Partial hydrogenolysis and mass spectrometry.
D)Edman's degradation and NMR.
E)DNFB in acid,Edman's degradation and labeling.
A)Ladder sequencing; partial hydrolysis and sequence comparison.
B)Partial hydrolysis; tandem mass spectrometry and IR.
C)Partial hydrogenolysis and mass spectrometry.
D)Edman's degradation and NMR.
E)DNFB in acid,Edman's degradation and labeling.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
What statements are true about enzymes?
(I)They are biological catalysts,non-specific,that increase the reaction rate by 1000 times.
(II)They are catalysts that increase reaction rates by a factor or 1 million or more.
(III)Enzymes are remarkably specific,leading Fischer to formulate a lock-and-key hypothesis.
(IV)Enzymes undergo an induced fit upon binding the substrate.
(V)Enzyme and substrate form a complex
A)I,III,V
B)II,III,V
C)I,III,IV,V
D)II,III,IV,V
E)III,V
(I)They are biological catalysts,non-specific,that increase the reaction rate by 1000 times.
(II)They are catalysts that increase reaction rates by a factor or 1 million or more.
(III)Enzymes are remarkably specific,leading Fischer to formulate a lock-and-key hypothesis.
(IV)Enzymes undergo an induced fit upon binding the substrate.
(V)Enzyme and substrate form a complex
A)I,III,V
B)II,III,V
C)I,III,IV,V
D)II,III,IV,V
E)III,V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
It is known that enzymes vary considerably in their geometric specificity because:
A)All enzymes bind only one compound as substrate.
B)All enzymes can bind any type of substrate.
C)Only a few enzymes can bind only one compound as substrate.
D)Some enzymes bind only one compound as substrate but others recognize a range of compounds with similar chemical groups.
E)The enzymes will recognize only one type of geometrical shape in the substrate.
A)All enzymes bind only one compound as substrate.
B)All enzymes can bind any type of substrate.
C)Only a few enzymes can bind only one compound as substrate.
D)Some enzymes bind only one compound as substrate but others recognize a range of compounds with similar chemical groups.
E)The enzymes will recognize only one type of geometrical shape in the substrate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The secondary structure of proteins is derived from:
A)peptide linkages.
B)disulfide linkages.
C)hydrogen bond formation.
D)hydrophobic interactions.
E)acid-base interactions.
A)peptide linkages.
B)disulfide linkages.
C)hydrogen bond formation.
D)hydrophobic interactions.
E)acid-base interactions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
This reagent is used to "protect" the amino group of an amino acid which is to be joined to a second amino acid by a peptide bond.
A)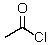
B)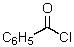
C)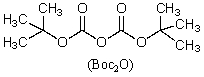
D)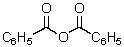
E)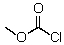
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
What is the induced fit in an enzyme?
A)It is the formation of hydrogen bonding between the enzyme and substrate.
B)It is a change of secondary structure of the enzyme before binding the substrate.
C)It is a conformational change produced upon binding of the substrate.
D)It is a change in quaternary structure of the enzyme to produce the catalysis.
E)It is the change in the substrate after the catalytic reaction took place.
A)It is the formation of hydrogen bonding between the enzyme and substrate.
B)It is a change of secondary structure of the enzyme before binding the substrate.
C)It is a conformational change produced upon binding of the substrate.
D)It is a change in quaternary structure of the enzyme to produce the catalysis.
E)It is the change in the substrate after the catalytic reaction took place.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
The occurrence of this amino acid in a polypeptide chain disrupts an α-helix:
A)Proline
B)Alanine
C)Methionine
D)Histidine
E)Tyrosine
A)Proline
B)Alanine
C)Methionine
D)Histidine
E)Tyrosine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Which amino acid of a polypeptide would become labeled when the polypeptide is treated with 2,4-dinitrofluorobenzene in base,even though the amino acid is not a terminal amino acid?
A)Lysine
B)Glycine
C)Alanine
D)Phenylalanine
E)Leucine
A)Lysine
B)Glycine
C)Alanine
D)Phenylalanine
E)Leucine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
What product would be obtained upon treating alanine with the following reagent? 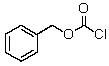
A)I
B)II
C)III
D)IV
E)V


A)I
B)II
C)III
D)IV
E)V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Which attractive force is responsible for maintaining the tertiary structure of a protein?
A)Disulfide linkages
B)Hydrogen bonds
C)van der Waals forces
D)Hydrophobic interactions
E)All of these choices.
A)Disulfide linkages
B)Hydrogen bonds
C)van der Waals forces
D)Hydrophobic interactions
E)All of these choices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
The primary structure of a protein refers to its:
A)sequence of amino acid residues.
B)disulfide bonds.
C)helical structure.
D)hydrogen bonding.
E)All of these choices.
A)sequence of amino acid residues.
B)disulfide bonds.
C)helical structure.
D)hydrogen bonding.
E)All of these choices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Enzymes catalyze stereospecific reactions.Stereospecific reactions are those that:
A)Lead to different stereoisomers from different stereoisomeric substrates.
B)Lead to the same stereoisomer despite starting with different stereoisomeric substrates.
C)Both stereoisomers,cis or trans can produce identical products.
D)Transform different substrates.
E)Transform one conformer into another conformer by rotation of the bonds.
A)Lead to different stereoisomers from different stereoisomeric substrates.
B)Lead to the same stereoisomer despite starting with different stereoisomeric substrates.
C)Both stereoisomers,cis or trans can produce identical products.
D)Transform different substrates.
E)Transform one conformer into another conformer by rotation of the bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
A prosthetic group is a
A)peptide chain linked to a protein
B)nonprotein group part of a conjugated protein
C)protein
D)smaller protein part of a bigger one
E)protein unit forming part of a protein
A)peptide chain linked to a protein
B)nonprotein group part of a conjugated protein
C)protein
D)smaller protein part of a bigger one
E)protein unit forming part of a protein

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Why is dicyclohexylcarbodiimide (DCC)used in peptide synthesis?
A)DCC "protects" the amino group of the intended N-terminal amino acid.
B)DCC activates the carboxyl group of one amino acid so that this amino acid reacts more readily with a second amino acid.
C)DCC cleaves the blocking groups from the final peptide.
D)DCC is the resin used in the automated synthesis of peptides.
E)DCC removes the peptide from the resin at the conclusion of the synthesis.
A)DCC "protects" the amino group of the intended N-terminal amino acid.
B)DCC activates the carboxyl group of one amino acid so that this amino acid reacts more readily with a second amino acid.
C)DCC cleaves the blocking groups from the final peptide.
D)DCC is the resin used in the automated synthesis of peptides.
E)DCC removes the peptide from the resin at the conclusion of the synthesis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
How many different tripeptides can exist,each containing one residue of glycine,one of l-threonine,and one of l-arginine?
A)2
B)3
C)6
D)8
E)9
A)2
B)3
C)6
D)8
E)9

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



