Deck 5: Legal Liability
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/114
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 5: Legal Liability
1
Distinguish between what is meant by business failure and audit failure.
Business failure occurs when a business is unable to repay its lenders or meet expectations of its investors because of economic or business conditions, such as recession, poor management decisions, or unexpected competition in the industry. Audit failure occurs when the auditor issues an incorrect audit opinion because it failed to comply with the requirements of auditing standards.
2
Auditors may be liable to their clients for:
A)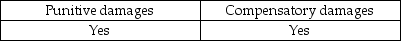
B)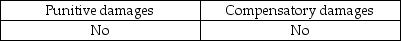
C)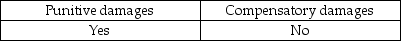
D)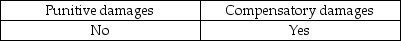
A)

B)

C)

D)

A
3
Which of the following most accurately describes constructive fraud?
A) Absence of reasonable care
B) Lack of slight care
C) Knowledge and intent to deceive
D) Extreme or unusual negligence without the intent to deceive
A) Absence of reasonable care
B) Lack of slight care
C) Knowledge and intent to deceive
D) Extreme or unusual negligence without the intent to deceive
D
4
An example of a breach of contract would likely include:
A) an auditor's refusal to return the client's general ledger book until the client paid last year's audit fees.
B) a bank's claim that an auditor had a duty to uncover material errors in financial statements that had been relied on in making a loan.
C) a CPA firm's failure to complete an audit on the agreed-upon date because the firm had a backlog of other work which was more lucrative.
D) an auditor's claim that the client staff is unqualified.
A) an auditor's refusal to return the client's general ledger book until the client paid last year's audit fees.
B) a bank's claim that an auditor had a duty to uncover material errors in financial statements that had been relied on in making a loan.
C) a CPA firm's failure to complete an audit on the agreed-upon date because the firm had a backlog of other work which was more lucrative.
D) an auditor's claim that the client staff is unqualified.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Under the laws of agency, partners of a CPA firm may be liable for the work of others on whom they rely. This would not include:
A) employees of the CPA firm.
B) employees of the audit client.
C) other CPA firms engaged to do part of the audit work.
D) specialists employed by the CPA firm to provide technical advice on the audit.
A) employees of the CPA firm.
B) employees of the audit client.
C) other CPA firms engaged to do part of the audit work.
D) specialists employed by the CPA firm to provide technical advice on the audit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Audit fraud occurs when:
A) a misstatement is made and there is both knowledge of its falsity and the intent to deceive.
B) a misstatement is made and there is knowledge of its falsity but no intent to deceive.
C) the auditor lacks even slight care in the performance in performing the audit.
D) the auditor has an absence of reasonable care in the performance of the audit.
A) a misstatement is made and there is both knowledge of its falsity and the intent to deceive.
B) a misstatement is made and there is knowledge of its falsity but no intent to deceive.
C) the auditor lacks even slight care in the performance in performing the audit.
D) the auditor has an absence of reasonable care in the performance of the audit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The standard of due care to which the auditor is expected to adhere to in the performance of the audit is referred to as the:
A) prudent person concept.
B) common law doctrine.
C) due care concept.
D) vigilant person concept.
A) prudent person concept.
B) common law doctrine.
C) due care concept.
D) vigilant person concept.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
An individual who is not party to the contract between a CPA and the client, but who is known by both and is intended to receive certain benefits from the contract is known as:
A) a third party.
B) a common law inheritor.
C) a tort.
D) a third-party beneficiary.
A) a third party.
B) a common law inheritor.
C) a tort.
D) a third-party beneficiary.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Discuss three major factors that have contributed to the recent increase in the number of lawsuits against auditors and the size of awards to plaintiffs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The assessment against a defendant of the full loss suffered by a plaintiff regardless of the extent to which other parties shared in the wrongdoing is called:
A) separate and proportionate liability.
B) shared liability.
C) unitary liability.
D) joint and several liability.
A) separate and proportionate liability.
B) shared liability.
C) unitary liability.
D) joint and several liability.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Audit risk is the risk there will be an audit failure for a given audit engagement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A(n) ________ failure occurs when an auditor issues an erroneous opinion because it failed to comply with requirements of auditing standards.
A) business
B) audit
C) ethics
D) process
A) business
B) audit
C) ethics
D) process

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The term "audit failure" refers to the situation when the auditor has followed auditing standards yet still fails to discover that the client's financial statements are materially misstated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Laws that have been passed by the U.S. Congress and other governmental units are:
A) statutory laws.
B) judicial laws.
C) federal laws.
D) common laws.
A) statutory laws.
B) judicial laws.
C) federal laws.
D) common laws.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Privity of contract exists between:
A) auditor and the federal government.
B) auditor and third parties.
C) auditor and client.
D) auditor and client attorney.
A) auditor and the federal government.
B) auditor and third parties.
C) auditor and client.
D) auditor and client attorney.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Recklessness in the case of an audit is present if the auditor knew an adequate audit was not done but still issued an opinion, even though there was no intent to deceive financial statement users. This description is the legal term for:
A) ordinary negligence.
B) gross negligence.
C) constructive fraud.
D) fraud.
A) ordinary negligence.
B) gross negligence.
C) constructive fraud.
D) fraud.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
In the performance of an audit, a CPA:
A) is legally liable for not detecting client fraud.
B) must strictly follow GAAS for privately held clients.
C) must strictly follow PCAOB auditing standards for publicly held clients.
D) must exercise due professional care in the performance of their audit responsibilities.
A) is legally liable for not detecting client fraud.
B) must strictly follow GAAS for privately held clients.
C) must strictly follow PCAOB auditing standards for publicly held clients.
D) must exercise due professional care in the performance of their audit responsibilities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Auditors who fail to exercise due care in their performance of professional services may be liable for:
A) punitive liability.
B) breach of contract.
C) excess liability.
D) criminal charges.
A) punitive liability.
B) breach of contract.
C) excess liability.
D) criminal charges.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The assessment against a defendant of that portion of the damage caused by the defendant's negligence is called:
A) separate and proportionate liability.
B) joint and several liability.
C) shared liability.
D) unitary liability.
A) separate and proportionate liability.
B) joint and several liability.
C) shared liability.
D) unitary liability.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
"Absence of reasonable care that can be expected of a person in a set of circumstances" defines:
A) pecuniary negligence.
B) gross negligence.
C) extreme negligence.
D) ordinary negligence.
A) pecuniary negligence.
B) gross negligence.
C) extreme negligence.
D) ordinary negligence.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
In a CPA firm operating as a limited liability partnership (LLP), the liability for one partner's actions does extend to the firm's assets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Match seven of the legal terms (a-j) with the definitions provided below (1-7):
a. Common law
b. Constructive fraud
c. Breach of contract
d. Joint and several liability
e. Ordinary negligence
f. Third-party beneficiary
g. Gross negligence
h. Statutory law
i. Fraud
j. Separate and proportionate liability
________ 1. Laws that have been passed by the U.S. Congress and other governmental units.
________ 2. Absence of reasonable care that can be expected of a person in a set of circumstances.
________ 3. Lack of even slight care, tantamount to reckless behavior that can be expected of a person.
________ 4. The assessment against a defendant of that portion of the damage caused by the defendant's negligence.
________ 5. Failure of one or both parties in a contract to fulfill the requirements of the contract.
________ 6. The assessment against a defendant of the full loss suffered by a plaintiff regardless of the extent to which other parties shared in the wrongdoing.
________ 7. Existence of extreme or unusual negligence even though there was no intent to deceive or do harm; also termed recklessness.
a. Common law
b. Constructive fraud
c. Breach of contract
d. Joint and several liability
e. Ordinary negligence
f. Third-party beneficiary
g. Gross negligence
h. Statutory law
i. Fraud
j. Separate and proportionate liability
________ 1. Laws that have been passed by the U.S. Congress and other governmental units.
________ 2. Absence of reasonable care that can be expected of a person in a set of circumstances.
________ 3. Lack of even slight care, tantamount to reckless behavior that can be expected of a person.
________ 4. The assessment against a defendant of that portion of the damage caused by the defendant's negligence.
________ 5. Failure of one or both parties in a contract to fulfill the requirements of the contract.
________ 6. The assessment against a defendant of the full loss suffered by a plaintiff regardless of the extent to which other parties shared in the wrongdoing.
________ 7. Existence of extreme or unusual negligence even though there was no intent to deceive or do harm; also termed recklessness.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following, if present, would most likely support a finding of constructive fraud on the part of a CPA?
A) Gross negligence in applying GAAS
B) Ordinary negligence in applying GAAS
C) Lack of duty to perform
D) Contributory negligence
A) Gross negligence in applying GAAS
B) Ordinary negligence in applying GAAS
C) Lack of duty to perform
D) Contributory negligence

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Statutory laws are laws that have been developed through court decisions rather than through the U.S. Congress and other governmental units.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of the following most accurately describes fraud?
A) Absence of reasonable care
B) Lack of slight care
C) Knowledge and intent to deceive
D) Extreme or unusual negligence without the intent to deceive
A) Absence of reasonable care
B) Lack of slight care
C) Knowledge and intent to deceive
D) Extreme or unusual negligence without the intent to deceive

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Several states have statutes that permit privileged communication between the client and auditor, allowing a CPA to refuse to testify in state and federal courts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Distinguish between constructive fraud and fraud.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
An important concept in contract law for accountants to understand is the "third-party beneficiary doctrine". Explain and give an example.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
If the CPA negligently failed to properly prepare and file a client's tax return, the CPA may be liable for:
A) the penalties the client owes the IRS.
B) the penalties and interest the client owes.
C) the penalties and interest the client owes, plus the tax preparation fee the CPA charged.
D) the penalties and interest, the tax preparation fee, and the amount of tax that was underpaid.
A) the penalties the client owes the IRS.
B) the penalties and interest the client owes.
C) the penalties and interest the client owes, plus the tax preparation fee the CPA charged.
D) the penalties and interest, the tax preparation fee, and the amount of tax that was underpaid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Gross negligence is the existence of extreme or unusual negligence with the intent to deceive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
When performing an audit the CPA is required to:
A) exercise the level of care of a reasonably prudent CPA.
B) strictly adhere of GAAS.
C) strictly be liable for detection of material misstatements in the financial statements.
D) avoid gross negligence in the performance of their duties.
A) exercise the level of care of a reasonably prudent CPA.
B) strictly adhere of GAAS.
C) strictly be liable for detection of material misstatements in the financial statements.
D) avoid gross negligence in the performance of their duties.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Distinguish between "joint and several liability" and "separate and proportionate liability."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of the following statements is true?
A)
B)
C)
D)
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A third-party beneficiary is one which:
A) has failed to establish legal standing before the court.
B) does not have privity of contract and is unknown to the contracting parties.
C) does not have privity of contract, but is known to the contracting parties and intended to benefit under the contract.
D) may establish legal standing before the court after a contract has been consummated.
A) has failed to establish legal standing before the court.
B) does not have privity of contract and is unknown to the contracting parties.
C) does not have privity of contract, but is known to the contracting parties and intended to benefit under the contract.
D) may establish legal standing before the court after a contract has been consummated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The doctrine of joint and several liability is one factor that has contributed to the recent increase in the number of lawsuits against auditors and the size of awards to plaintiffs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Gregory & Hedrick, a medium-sized CPA firm, employed Elise as a staff accountant. Elise was negligent while auditing several of the firm's clients. Under these circumstances, which of the following statements is true?
A) Elise would have no personal liability for negligence.
B) Gregory & Hedrick is not liable for Elise's negligence because CPAs are generally considered to be independent contractors.
C) Gregory & Hedrick would not be liable for Elise's negligence if Winters disobeyed specific instructions in the performance of the audits.
D) Gregory & Hedrick can recover against its insurer on its malpractice policy even if one of the partners was also negligent in reviewing Elise's work.
A) Elise would have no personal liability for negligence.
B) Gregory & Hedrick is not liable for Elise's negligence because CPAs are generally considered to be independent contractors.
C) Gregory & Hedrick would not be liable for Elise's negligence if Winters disobeyed specific instructions in the performance of the audits.
D) Gregory & Hedrick can recover against its insurer on its malpractice policy even if one of the partners was also negligent in reviewing Elise's work.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
In a CPA firm operating as a limited liability partnership (LLP), the liability for one partner's actions does not extend to another partner's personal assets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Define ordinary negligence, gross negligence, and constructive fraud.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The standard of due care to which the auditor is expected to be held is referred to as the prudent person concept.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Audit contracts (engagement letters):
A) may be either oral or written.
B) must be written.
C) must be written and notarized.
D) must be written if the client is regulated by the Securities and Exchange Commission.
A) may be either oral or written.
B) must be written.
C) must be written and notarized.
D) must be written if the client is regulated by the Securities and Exchange Commission.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
A CPA firm normally uses one or a combination of four defenses when there are legal claims by clients. Which one of the following is generally not a defense?
A) Lack of duty
B) Non-negligent performance
C) Contributory negligence
D) Foreseeable users
A) Lack of duty
B) Non-negligent performance
C) Contributory negligence
D) Foreseeable users

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The 1136 Tenants case was a criminal case concerning a CPA's failure to uncover fraud during a financial statement audit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Matthews & Co., CPAs, issued an unqualified opinion on Dodgers Corporation. Millennium Bank, which relied on the audited financial statements, granted a loan of $200,00,000 to Dodgers Corporation. Dodgers subsequently defaulted on the loan. To succeed in an action against Matthews & Co., Millennium Bank must prove that the bank was:
A) in privity of contract with Dodgers.
B) in privity of contract with Millennium.
C) free from contributory negligence.
D) justified in relying on the financial statements in granting the loan.
A) in privity of contract with Dodgers.
B) in privity of contract with Millennium.
C) free from contributory negligence.
D) justified in relying on the financial statements in granting the loan.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Tort actions against CPAs are more common than breach of contract actions because:
A) there are more torts than contracts.
B) the burden of proof is on the auditor rather than on the person suing.
C) the person suing need prove only negligence.
D) the amounts recoverable are normally larger.
A) there are more torts than contracts.
B) the burden of proof is on the auditor rather than on the person suing.
C) the person suing need prove only negligence.
D) the amounts recoverable are normally larger.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Which of the following is an illustration of liability to clients under common law?
A) Client sues auditor for not discovering a theft of assets by an employee.
B) Bank sues auditor for not discovering that borrower's financial statements are misstated.
C) Combined group of stockholders sue auditor for not discovering materially misstated financial statements.
D) Federal government prosecutes auditor for knowingly issuing an incorrect audit report.
A) Client sues auditor for not discovering a theft of assets by an employee.
B) Bank sues auditor for not discovering that borrower's financial statements are misstated.
C) Combined group of stockholders sue auditor for not discovering materially misstated financial statements.
D) Federal government prosecutes auditor for knowingly issuing an incorrect audit report.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which of the following is an illustration of liability under the federal securities acts?
A) Client sues auditor for not discovering a theft of assets by an employee.
B) Bank sues auditor for not discovering that borrower's financial statements are misstated.
C) Combined group of stockholders sue auditor for not discovering materially misstated financial statements.
D) auditor sues client for not cooperating during engagement.
A) Client sues auditor for not discovering a theft of assets by an employee.
B) Bank sues auditor for not discovering that borrower's financial statements are misstated.
C) Combined group of stockholders sue auditor for not discovering materially misstated financial statements.
D) auditor sues client for not cooperating during engagement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
In the auditing environment, failure to meet auditing standards is often:
A) an accepted practice.
B) a suggestion of negligence.
C) conclusive evidence of negligence.
D) tantamount to criminal behavior.
A) an accepted practice.
B) a suggestion of negligence.
C) conclusive evidence of negligence.
D) tantamount to criminal behavior.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The principal issue to be resolved in cases involving alleged negligence is usually:
A) the amount of the damages suffered by plaintiff.
B) whether to impose punitive damages on defendant.
C) the level of care exercised by the CPA.
D) whether defendant was involved in fraud.
A) the amount of the damages suffered by plaintiff.
B) whether to impose punitive damages on defendant.
C) the level of care exercised by the CPA.
D) whether defendant was involved in fraud.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
One of the changes in auditing procedure which was brought about as a result of the 1136 Tenants case was that auditors were encouraged to begin using:
A) letters of representation.
B) confirmation letters.
C) engagement letters.
D) billet doux letters.
A) letters of representation.
B) confirmation letters.
C) engagement letters.
D) billet doux letters.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
There are four major sources of an auditor's legal liability. One source is liability to the audit client. List the other three sources.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995 reduced potential damages in securities-related litigation, but because the act applied only to federal courts, attorneys began taking cases to state courts. Which of the following eliminated this loophole?
A) Private Securities Litigation Reform Amendment
B) Securities Litigation Uniform Standards Act of 1998
C) Racketeer Influenced and Corrupt Organization Act
D) U.S. Securities Claims Reform Act
A) Private Securities Litigation Reform Amendment
B) Securities Litigation Uniform Standards Act of 1998
C) Racketeer Influenced and Corrupt Organization Act
D) U.S. Securities Claims Reform Act

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The legal term for when an auditor issues an opinion of an audit, knowing that an adequate audit was not performed is called?
A) breach of contract
B) tort action for negligence
C) constructive fraud
D) fraud
A) breach of contract
B) tort action for negligence
C) constructive fraud
D) fraud

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Discuss each of the four defenses a CPA firm can normally use when facing legal claims by clients. Which of these defenses is ordinarily not available against third-party suits?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
To succeed in an action against the auditor, the client must be able to show that:
A) the auditor was fraudulent.
B) the auditor was grossly negligent.
C) there was a written contract.
D) there is a close causal connection between the auditor's behavior and the damages suffered by the client.
A) the auditor was fraudulent.
B) the auditor was grossly negligent.
C) there was a written contract.
D) there is a close causal connection between the auditor's behavior and the damages suffered by the client.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
In third-party suits, which of the auditor's defenses contends lack of privity of contract?
A) Lack of duty
B) Non-negligent performance
C) Contributory negligence
D) Absence of causal connections
A) Lack of duty
B) Non-negligent performance
C) Contributory negligence
D) Absence of causal connections

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
An example of auditor legal liability to third parties under common law would be the federal government prosecuting an auditor for knowingly issuing an incorrect audit report.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The preferred defense in third-party suits is absence of causal connection.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
A common way for a CPA firm to demonstrate its lack of duty to perform is by use of a(n):
A) expert witness' testimony.
B) audit contract, or engagement letter.
C) management representation letter.
D) confirmation letter.
A) expert witness' testimony.
B) audit contract, or engagement letter.
C) management representation letter.
D) confirmation letter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The King Surety Company wrote a general fidelity bond covering thefts of assets by the employees of Wilson, Inc. Thereafter, Cooney, an employee of Wilson, embezzled $17,200 of company funds. When the activities were discovered, King paid Wilson the full amount in accordance with the terms of the fidelity bond, and then sought recovery against Wilson's auditors, Lynch & Merritt, CPAs. Which of the following would be Lynch & Merritt's best defense?
A) King is not in privity of contract.
B) The shortages were the result of clever forgeries and collusive fraud which would not be detected by an examination made in accordance with generally accepted auditing standards.
C) Lynch & Merritt were not guilty either of gross negligence or fraud.
D) Lynch & Merritt were not aware of the King-Wilson surety relationship.
A) King is not in privity of contract.
B) The shortages were the result of clever forgeries and collusive fraud which would not be detected by an examination made in accordance with generally accepted auditing standards.
C) Lynch & Merritt were not guilty either of gross negligence or fraud.
D) Lynch & Merritt were not aware of the King-Wilson surety relationship.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
In connection with the audit of financial statements, an independent auditor could be responsible for failure to detect a material fraud if:
A) statistical sampling techniques were not used on the audit engagement.
B) the auditor planned the audit in a negligent manner.
C) accountants performing important parts of the work failed to discover a close relationship between the treasurer and the cashier.
D) the fraud was perpetrated by one employee who circumvented the existing internal controls.
A) statistical sampling techniques were not used on the audit engagement.
B) the auditor planned the audit in a negligent manner.
C) accountants performing important parts of the work failed to discover a close relationship between the treasurer and the cashier.
D) the fraud was perpetrated by one employee who circumvented the existing internal controls.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The preferred defense in third-party suits is:
A) lack of duty to perform.
B) non-negligent performance.
C) absence of causal connection.
D) client fraud.
A) lack of duty to perform.
B) non-negligent performance.
C) absence of causal connection.
D) client fraud.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The Credit Alliance approach to the concept of foreseen users states that to be liable to third parties, an auditor (1) must know and intend that the work product would be used by the third-party for a specific purpose, and (2) the knowledge and intent must be evidenced by the auditor's conduct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The partnership of Booth & Haynes, CPAs, has been engaged to examine the financial statements of Paul, Inc., in connection with the registration of Paul's securities with the Securities and Exchange Commission. Under these circumstances, which of the following statements is true?
A) Booth & Haynes is assuming much greater third-party liability than it assumes on engagements under common law.
B) If its examination is not fraudulent, Booth & Haynes may issue an appropriate disclaimer to the financial statements and thereby avoid liability.
C) Booth & Haynes must incorporate if they wish to practice before the SEC.
D) Booth & Haynes must be a large interstate firm if they wish to practice before the SEC.
A) Booth & Haynes is assuming much greater third-party liability than it assumes on engagements under common law.
B) If its examination is not fraudulent, Booth & Haynes may issue an appropriate disclaimer to the financial statements and thereby avoid liability.
C) Booth & Haynes must incorporate if they wish to practice before the SEC.
D) Booth & Haynes must be a large interstate firm if they wish to practice before the SEC.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The basic legal concept which was affirmed in the 1985 New York case, Credit Alliance, was that:
A) the auditor's defense of privity of contract is still valid against third parties.
B) the auditor is liable for ordinary negligence to specifically foreseen third parties.
C) the auditor is liable for ordinary negligence to reasonably foreseeable third parties.
D) the auditor's defense of contributory negligence is no longer valid.
A) the auditor's defense of privity of contract is still valid against third parties.
B) the auditor is liable for ordinary negligence to specifically foreseen third parties.
C) the auditor is liable for ordinary negligence to reasonably foreseeable third parties.
D) the auditor's defense of contributory negligence is no longer valid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
As a consequence of his failure to adhere to generally accepted auditing standards in the course of his examination of the Lamp Corp., Harrison, CPA, did not detect the embezzlement of a material amount of funds by the company's controller. As a matter of common law, to what extent would Harrison be liable to the Lamp Corp. for losses attributable to the theft?
A) He would have no liability, since the ordinary examination cannot be relied upon to detect thefts of assets by employees.
B) He would have no liability because privity of contract is lacking.
C) He would be liable for losses attributable to his negligence.
D) He would be liable only if it could be proven that he was grossly negligent.
A) He would have no liability, since the ordinary examination cannot be relied upon to detect thefts of assets by employees.
B) He would have no liability because privity of contract is lacking.
C) He would be liable for losses attributable to his negligence.
D) He would be liable only if it could be proven that he was grossly negligent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
In an action against a CPA in a jurisdiction that follows the Ultramares doctrine, lack of privity is a viable defense provided the plaintiff:
A) is the client's creditor who sued the CPA for negligence.
B) can prove gross negligence.
C) violated the Securities Act of 1933.
D) violated the Securities Act of 1934.
A) is the client's creditor who sued the CPA for negligence.
B) can prove gross negligence.
C) violated the Securities Act of 1933.
D) violated the Securities Act of 1934.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
A broad interpretation of the rights of third-party beneficiaries holds that users that the auditor should have been able to foresee as being likely users of financial statements have the same rights as those with privity of contract. This is known as the concept of:
A) foreseen users.
B) foreseeable users.
C) expected users.
D) four-party contracts.
A) foreseen users.
B) foreseeable users.
C) expected users.
D) four-party contracts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The major conclusion of the 1931 Ultramares case was that:
A) ordinary negligence is insufficient for liability to third parties.
B) ordinary negligence is sufficient for liability to third-party beneficiaries.
C) fraud or gross negligence is sufficient for liability to third parties.
D) auditors have no liabilities to third parties.
A) ordinary negligence is insufficient for liability to third parties.
B) ordinary negligence is sufficient for liability to third-party beneficiaries.
C) fraud or gross negligence is sufficient for liability to third parties.
D) auditors have no liabilities to third parties.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Which of the following required an adequate system of internal control for SEC registrants?
A) Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002
B) Securities Act of 1933
C) Foreign Corrupt Practices Act of 1977
D) Securities Act of 1934
A) Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002
B) Securities Act of 1933
C) Foreign Corrupt Practices Act of 1977
D) Securities Act of 1934

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
A group typically included as "third parties" in common law is:
A)
B)
C)
D)
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Of the three approaches to applying the concept of foreseen users (Credit Alliance approach, restatement of torts approach, and foreseeable user approach), the approach followed by the most states is the Credit Alliance approach.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Under the Securities Act of 1933, the auditor's responsibility for making sure the financial statements were fairly stated extends to:
A) the date of the financial statements.
B) the date the registration statement becomes effective.
C) the date of the audit report.
D) one year beyond the date of the financial statements.
A) the date of the financial statements.
B) the date the registration statement becomes effective.
C) the date of the audit report.
D) one year beyond the date of the financial statements.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
According to the principle established by the Restatement of Torts case, foreseen users must be members of:
A) any potential user group.
B) a legally protected class.
C) a reasonably limited and identifiable user group.
D) a reasonably limited and established user group.
A) any potential user group.
B) a legally protected class.
C) a reasonably limited and identifiable user group.
D) a reasonably limited and established user group.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The increased litigation under the federal securities laws has resulted from:
A)
B)
C)
D)
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Which of the auditor's defenses is ordinarily not available when lawsuits are filed by a third party?
A) Absence of causal connections
B) Contributory negligence
C) Non-negligent performance
D) Lack of duty
A) Absence of causal connections
B) Contributory negligence
C) Non-negligent performance
D) Lack of duty

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The restatement of torts approach to the concept of foreseen users states that any users that the auditor should have reasonably been able to foresee as being likely users of financial statements have the same rights as those with privity of contract.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Three approaches to the application of the foreseen users' concept are (1) the Credit Alliance approach, (2) the restatement of torts approach, and (3) the foreseeable user approach. Summarize each of these three approaches.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Under common law, an individual or company that (1) does not have a contract with an auditor, (2) is known by the auditor in advance of the audit, and (3) will use the auditor's report to make decisions about the client company has:
A) no rights unless an auditor is grossly negligent.
B) no rights unless an auditor is fraudulent.
C) no rights against an auditor.
D) the same rights against an auditor as a client.
A) no rights unless an auditor is grossly negligent.
B) no rights unless an auditor is fraudulent.
C) no rights against an auditor.
D) the same rights against an auditor as a client.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
A financial institution sues the audit firm for failure to discover that a borrower's financial statements are materially misstated. This is an example of which of the following legal liability concepts?
A) Liability to clients
B) Liability to 3rd parties under common law
C) Civil liability under federal securities law
D) Criminal liability
A) Liability to clients
B) Liability to 3rd parties under common law
C) Civil liability under federal securities law
D) Criminal liability

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Which of the following auditor's defenses usually means non-reliance on the financial statements by the user?
A) Lack of duty
B) Non-negligent performance
C) Absence of causal connections
D) Contributory negligence
A) Lack of duty
B) Non-negligent performance
C) Absence of causal connections
D) Contributory negligence

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



