Deck 16: Amino Acids, proteins, and Enzymes
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/90
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 16: Amino Acids, proteins, and Enzymes
1
The one letter abbreviation for the amino acid tyrosine is ________.
A)T
B)R
C)Y
D)W
E)P
A)T
B)R
C)Y
D)W
E)P
Y
2
The structural formulas of amino acids are the same except for the ________.
A)carboxylate group
B)alpha carbon
C)ammonium group
D)R group
E)hydrogen bonding
A)carboxylate group
B)alpha carbon
C)ammonium group
D)R group
E)hydrogen bonding
R group
3
Which of the following would be most likely to be deficient in at least one essential amino acid?
A)eggs
B)milk
C)beans
D)steak
E)ham
A)eggs
B)milk
C)beans
D)steak
E)ham
beans
4
The one letter abbreviation for the amino acid tryptophan is ________.
A)T
B)R
C)Y
D)W
E)P
A)T
B)R
C)Y
D)W
E)P

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Sucrase,the protein that facilitates the hydrolysis of sucrose,would be classified as a ________ protein.
A)transport
B)hormonal
C)catalytic
D)structural
E)contractile
A)transport
B)hormonal
C)catalytic
D)structural
E)contractile

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
In the ionized form of an amino acid,the carboxylic acid end is ________.
A)positively charged
B)negatively charged
C)neutral
D)soluble in a nonpolar solvent
E)attached to an amine
A)positively charged
B)negatively charged
C)neutral
D)soluble in a nonpolar solvent
E)attached to an amine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The following amino acid side chain is ________. -CH-C 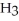 |
| 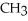
A)polar
B)hydrophobic
C)hydrophilic
D)acidic
E)basic
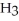 |
| 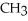
A)polar
B)hydrophobic
C)hydrophilic
D)acidic
E)basic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following is not a function of proteins?
A)provide structural components
B)stores the genetic information of a living organism
C)movement of muscles
D)catalyze reactions in the cells
E)transport substances through the bloodstream
A)provide structural components
B)stores the genetic information of a living organism
C)movement of muscles
D)catalyze reactions in the cells
E)transport substances through the bloodstream

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Methionine is an amino acid that contains ________.
A)a sulfur atom
B)a chlorine atom
C)a sodium atom
D)a phenyl ring
E)a heterocyclic ring
A)a sulfur atom
B)a chlorine atom
C)a sodium atom
D)a phenyl ring
E)a heterocyclic ring

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A completely vegetarian diet will contain all the essential amino acids if it includes ________.
A)wheat and rice
B)rice and beans
C)almonds and walnuts
D)corn and beans
E)wheat and corn
A)wheat and rice
B)rice and beans
C)almonds and walnuts
D)corn and beans
E)wheat and corn

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following functional groups of an amino acid would be in the ionized state at high pH?
A) O
-C-OH
B)-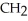 -OH
-OH
C)-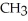
D) O
-C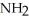
E)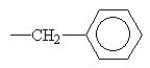
A) O

-C-OH
B)-
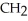 -OH
-OHC)-
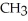
D) O

-C
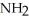
E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The side chain for histidine is classified as a ________ side chain.
A)basic
B)neutral
C)acidic
D)nonpolar
E)polar
A)basic
B)neutral
C)acidic
D)nonpolar
E)polar

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
In the peptide STFNA,the N-terminus is ________.
A)alanine
B)phenylalanine
C)tryptophan
D)aspartate
E)serine
A)alanine
B)phenylalanine
C)tryptophan
D)aspartate
E)serine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The peptide bonds that link amino acids in a protein are ________.
A)ester bonds
B)ether bonds
C)amide bonds
D)glycosidic bonds
E)sulfide bonds
A)ester bonds
B)ether bonds
C)amide bonds
D)glycosidic bonds
E)sulfide bonds

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A basic amino acid has a side chain that contains ________.
A)an ammonium group
B)a carboxyl ate group
C)a methyl group
D)an alcohol group
E)a thiol group
A)an ammonium group
B)a carboxyl ate group
C)a methyl group
D)an alcohol group
E)a thiol group

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Wool is primarily made up of ________.
A)protein
B)carbohydrate
C)globin
D)triacylglycerols
E)enkephalin
A)protein
B)carbohydrate
C)globin
D)triacylglycerols
E)enkephalin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The side chain for valine is classified as a ________ side chain.
A)basic
B)neutral
C)acidic
D)nonpolar
E)polar
A)basic
B)neutral
C)acidic
D)nonpolar
E)polar

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Amino acids that are not synthesized in the body and must be obtained from the diet are called ________.
A)essential
B)polar
C)nonpolar
D)complete
E)incomplete
A)essential
B)polar
C)nonpolar
D)complete
E)incomplete

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Collagen,a protein found in tendons and cartilage,would be classified as a ________ protein.
A)catalytic
B)structural
C)transport
D)storage
E)hormone
A)catalytic
B)structural
C)transport
D)storage
E)hormone

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The R group for serine is - 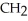 -OH.In the ionized form,serine has the structural formula ________.
-OH.In the ionized form,serine has the structural formula ________.
A)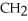 -OH
-OH 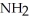 -
- 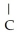 H-COOH
H-COOH
B)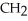 -OH
-OH 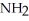 -
- 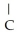 H-COO-
H-COO-
C)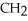
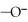 H3
H3 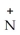 -
- 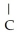 H-COOH
H-COOH
D)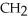 -OH H3
-OH H3 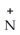 -
- 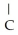 H-COOH
H-COOH
E)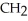 -OH H3
-OH H3 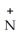 -
- 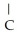 H-COO-
H-COO-
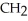 -OH.In the ionized form,serine has the structural formula ________.
-OH.In the ionized form,serine has the structural formula ________.A)
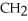 -OH
-OH 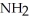 -
- 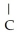 H-COOH
H-COOHB)
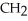 -OH
-OH 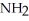 -
- 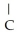 H-COO-
H-COO-C)
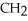
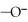 H3
H3 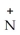 -
- 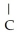 H-COOH
H-COOHD)
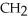 -OH H3
-OH H3 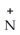 -
- 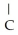 H-COOH
H-COOHE)
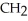 -OH H3
-OH H3 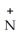 -
- 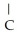 H-COO-
H-COO-
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Heat denatures a protein by disrupting ________.
A)salt bridges and peptide bonds
B)hydrophobic interactions and hydrogen bonds
C)peptide bonds and hydrophobic interactions
D)disulfide bonds and peptide bonds
E)hydrogen bonds and disulfide bonds
A)salt bridges and peptide bonds
B)hydrophobic interactions and hydrogen bonds
C)peptide bonds and hydrophobic interactions
D)disulfide bonds and peptide bonds
E)hydrogen bonds and disulfide bonds

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Enkephalins are polypeptides that have ________.
A)a sweet taste
B)a bitter taste
C)extra caloric value
D)pain-killing properties
E)hormone activity
A)a sweet taste
B)a bitter taste
C)extra caloric value
D)pain-killing properties
E)hormone activity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The attractive forces that are important in the secondary structure of a protein are ________.
A)hydrogen bonds
B)hydrophobic interactions
C)disulfide bonds
D)salt bridges
E)peptide bonds
A)hydrogen bonds
B)hydrophobic interactions
C)disulfide bonds
D)salt bridges
E)peptide bonds

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The α helix of the secondary structure of a protein is held together by ________ between two widely separated parts of a protein chain.
A)hydrogen bonds
B)disulfide bridges
C)salt bridges
D)hydrophilic interactions
E)hydrophobic interactions
A)hydrogen bonds
B)disulfide bridges
C)salt bridges
D)hydrophilic interactions
E)hydrophobic interactions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Denaturation of a protein ________.
A)changes the primary structure of a protein
B)disrupts the secondary,tertiary,or quaternary structure of a protein
C)is always irreversible
D)hydrolyzes peptide bonds
E)can only occur in a protein with quaternary structure
A)changes the primary structure of a protein
B)disrupts the secondary,tertiary,or quaternary structure of a protein
C)is always irreversible
D)hydrolyzes peptide bonds
E)can only occur in a protein with quaternary structure

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
In the peptide Ala-Try-Gly-Phe,the N-terminus is ________.
A)alanine
B)phenylalanine
C)tryptophan
D)aspartate
E)glycine
A)alanine
B)phenylalanine
C)tryptophan
D)aspartate
E)glycine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
In insulin,two peptide chains are held together in a single unit by ________.
A)disulfide bridges
B)hydrogen bonds
C)salt bridges
D)a prosthetic group
E)a β-pleated sheet
A)disulfide bridges
B)hydrogen bonds
C)salt bridges
D)a prosthetic group
E)a β-pleated sheet

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
What type of interaction would you expect between the following R groups in the tertiary structure of a protein? O
-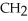
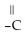
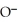 and -
and - 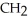
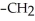
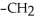
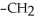 -
- 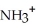
A)disulfide bonds
B)salt bridges
C)hydrogen bonds
D)hydrophobic interactions
E)peptide bonds
-
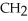
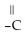
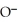 and -
and - 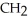
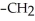
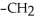
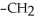 -
- 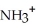
A)disulfide bonds
B)salt bridges
C)hydrogen bonds
D)hydrophobic interactions
E)peptide bonds

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
In the peptide Ser-Cys-Ala-Gly,the C-terminus is ________.
A)serine
B)serotonin
C)glycine
D)glycerine
E)alanine
A)serine
B)serotonin
C)glycine
D)glycerine
E)alanine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
What type of interaction would you expect between the following R groups in the tertiary structure of a protein? 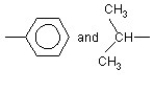
A)disulfide bonds
B)salt bridges
C)hydrogen bonds
D)hydrophobic interactions
E)peptide bonds

A)disulfide bonds
B)salt bridges
C)hydrogen bonds
D)hydrophobic interactions
E)peptide bonds

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following is a secondary protein structure?
A)α-helix
B)Ser-Met-Ala-Gly-Ile
C)disulfide bond
D)salt bridges
E)hydrophobic interactions
A)α-helix
B)Ser-Met-Ala-Gly-Ile
C)disulfide bond
D)salt bridges
E)hydrophobic interactions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The structure of collagen consists of ________.
A)single α-helix strands
B)double α-helix strands
C)many α-helixes wound into fibrils
D)a braided triple helix
E)many glycoside links
A)single α-helix strands
B)double α-helix strands
C)many α-helixes wound into fibrils
D)a braided triple helix
E)many glycoside links

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Acids and bases denature a protein by disrupting ________.
A)peptide bonds and salt bridges
B)amide bonds and alkene bonds
C)hydrophobic interactions and peptide bonds
D)salt bridges and hydrophobic interactions
E)salt bridges and hydrogen bonds
A)peptide bonds and salt bridges
B)amide bonds and alkene bonds
C)hydrophobic interactions and peptide bonds
D)salt bridges and hydrophobic interactions
E)salt bridges and hydrogen bonds

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
In sickle-cell anemia,the hemoglobin molecules ________.
A)come apart into separate chains
B)enlarge to twice normal size
C)clump together into insoluble fibers
D)dissolve in the plasma
E)undergo crenation
A)come apart into separate chains
B)enlarge to twice normal size
C)clump together into insoluble fibers
D)dissolve in the plasma
E)undergo crenation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which R group would most likely be found in a hydrophobic area of the tertiary structure of a globular protein?
A)-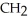 -OH
-OH
B)-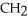 - COO-
- COO-
C)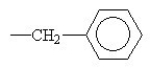
D)-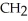 -
- 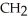 -
- 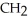 -
- 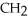 -
- 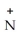 H3
H3
E)O -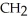 -
- 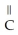 -
- 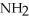
A)-
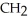 -OH
-OHB)-
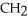 - COO-
- COO-C)

D)-
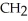 -
- 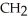 -
- 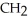 -
- 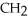 -
- 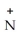 H3
H3E)O -
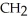 -
- 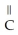 -
- 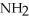

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
A chain made of more than 50 amino acids that has biological activity is referred to as a(n)________.
A)peptide
B)protein
C)enzyme
D)globulin
E)hormone
A)peptide
B)protein
C)enzyme
D)globulin
E)hormone

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Hemoglobin has a total of ________ protein chains in its quaternary structure.
A)one
B)two
C)three
D)four
E)five
A)one
B)two
C)three
D)four
E)five

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
In the peptide GLVIW,the C-terminus is ________.
A)tryptophan
B)serotonin
C)glycine
D)glycerine
E)alanine
A)tryptophan
B)serotonin
C)glycine
D)glycerine
E)alanine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
In the β-pleated sheet secondary structure of a protein,two or more amino acid sequences in separate parts of the protein are held together ________.
A)in a coil,by hydrogen bonding
B)in random order,due to hydrophobic interactions
C)in a triple helix
D)in a double helix
E)by hydrogen bonding between different sections of the polypeptide chain
A)in a coil,by hydrogen bonding
B)in random order,due to hydrophobic interactions
C)in a triple helix
D)in a double helix
E)by hydrogen bonding between different sections of the polypeptide chain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
What kinds of interactions are not part of tertiary protein structure?
A)peptide bonds
B)disulfide bonds
C)hydrophilic interactions
D)salt bridges
E)hydrophobic interactions
A)peptide bonds
B)disulfide bonds
C)hydrophilic interactions
D)salt bridges
E)hydrophobic interactions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The hydrolysis of ester bonds in triacylglycerols is catalyzed by a ________.
A)lipase
B)lyase
C)isomerase
D)peptidase
E)oxidoreductase
A)lipase
B)lyase
C)isomerase
D)peptidase
E)oxidoreductase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Heavy metals denature proteins by ________.
A)releasing amino acids
B)disrupting hydrophobic interactions
C)changing the pH of the protein solution
D)changing the temperature of the protein solution
E)disrupting disulfide bonds
A)releasing amino acids
B)disrupting hydrophobic interactions
C)changing the pH of the protein solution
D)changing the temperature of the protein solution
E)disrupting disulfide bonds

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
To what main class of enzymes does the enzyme that catalyzes the following reaction belong? O OH 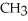 -
- 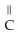 - COO- →
- COO- → 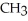 -
- 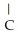 H- COO-
H- COO-
A)oxidoreductase
B)transferase
C)hydrolase
D)lyase
E)isomerase
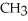 -
- 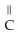 - COO- →
- COO- → 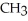 -
- 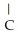 H- COO-
H- COO-A)oxidoreductase
B)transferase
C)hydrolase
D)lyase
E)isomerase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The optimum temperature for sucrase activity is 37 °C.The hydrolysis of sucrose is slowest at which temperature in the choices below?
A)0 °C
B)10 °C
C)20 °C
D)25 °C
E)45 °C
A)0 °C
B)10 °C
C)20 °C
D)25 °C
E)45 °C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
A biological catalyst is called a(n)________.
A)lipid
B)enzyme
C)steroid
D)coenzyme
E)substrate
A)lipid
B)enzyme
C)steroid
D)coenzyme
E)substrate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The purpose of the many chemical reactions in our bodies is to ________.
A)store chemical energy in the body for future use
B)produce the amino acids
C)produce the lipids
D)release chemical energy for the production of macromolecules
E)all of the above
A)store chemical energy in the body for future use
B)produce the amino acids
C)produce the lipids
D)release chemical energy for the production of macromolecules
E)all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The general function of an enzyme in the body is to ________.
A)catalyze chemical reactions
B)maintain a neutral pH
C)act as a reactant in carbohydrate storage
D)maintain homeostasis
E)eliminate waste products from the blood
A)catalyze chemical reactions
B)maintain a neutral pH
C)act as a reactant in carbohydrate storage
D)maintain homeostasis
E)eliminate waste products from the blood

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Disulfide bonds in a protein chain connect ________.
A)an amine and a carboxylic acid group
B)an alcohol and a carboxylic acid group
C)tryptophan and alanine residues
D)two cysteine residues
E)two asparagine residues
A)an amine and a carboxylic acid group
B)an alcohol and a carboxylic acid group
C)tryptophan and alanine residues
D)two cysteine residues
E)two asparagine residues

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The names of many enzymes can be recognized by the suffix ________.
A)ate
B)ite
C)ose
D)ine
E)ase
A)ate
B)ite
C)ose
D)ine
E)ase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Most enzymes are ________.
A)fluid-mosaic proteins
B)induced proteins
C)substrate proteins
D)fibrous proteins
E)globular proteins
A)fluid-mosaic proteins
B)induced proteins
C)substrate proteins
D)fibrous proteins
E)globular proteins

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which of the following is not true for a competitive inhibitor?
A)It occupies the active site.
B)It cannot be converted to products.
C)It has a structure similar to the substrate.
D)Increasing the substrate concentration can reverse competitive inhibition.
E)It binds to the enzyme at a site remote from the active site.
A)It occupies the active site.
B)It cannot be converted to products.
C)It has a structure similar to the substrate.
D)Increasing the substrate concentration can reverse competitive inhibition.
E)It binds to the enzyme at a site remote from the active site.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Compared to an uncatalyzed reaction,an enzyme-catalyzed reaction ________.
A)uses less substrate
B)produces different products
C)occurs at a faster rate
D)requires more energy
E)requires a higher temperature
A)uses less substrate
B)produces different products
C)occurs at a faster rate
D)requires more energy
E)requires a higher temperature

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The formation of an enzyme-substrate complex is the ________ step in enzyme action.
A)first
B)second
C)third
D)fourth
E)last
A)first
B)second
C)third
D)fourth
E)last

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
An acid can denature a protein by ________.
A)agitating the protein chains
B)disrupting hydrogen bonds between side chains
C)disrupting hydrophobic interactions within a protein chain
D)removing helping molecules such as heme
E)breaking disulfide bridges
A)agitating the protein chains
B)disrupting hydrogen bonds between side chains
C)disrupting hydrophobic interactions within a protein chain
D)removing helping molecules such as heme
E)breaking disulfide bridges

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The presence of enzymes to catalyze bioreactions in our bodies allows ________.
A)us to eat non-nutritious substances without consequence
B)the activation energy of a reaction to be raised
C)the rate of a desired chemical reaction to slow down
D)bioreactions to occur under extreme conditions of temperature and pH
E)bioreactions to take place under mild conditions
A)us to eat non-nutritious substances without consequence
B)the activation energy of a reaction to be raised
C)the rate of a desired chemical reaction to slow down
D)bioreactions to occur under extreme conditions of temperature and pH
E)bioreactions to take place under mild conditions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
One heavy metal that can cause denaturation of a protein is ________.
A)silver
B)sodium
C)barium
D)iron
E)calcium
A)silver
B)sodium
C)barium
D)iron
E)calcium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
To what main class of enzymes does the enzyme that catalyzes the following reaction belong? ser-ala → ser + ala
A)oxidoreductase
B)transferase
C)hydrolase
D)lyase
E)isomerase
A)oxidoreductase
B)transferase
C)hydrolase
D)lyase
E)isomerase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The full name of the enzyme LDH is ________.
A)lactate dehydrogenase
B)liver decompensation hexase
C)lactate dehydrase
D)liver dihydrogen kinase
E)lipase dehydrogenase
A)lactate dehydrogenase
B)liver decompensation hexase
C)lactate dehydrase
D)liver dihydrogen kinase
E)lipase dehydrogenase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
To what main class of enzymes does the enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of lactose to galactose and glucose belong?
A)oxidoreductase
B)transferase
C)hydrolase
D)lyase
E)isomerase
A)oxidoreductase
B)transferase
C)hydrolase
D)lyase
E)isomerase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The active site of an enzyme ________.
A)is remote from the site of substrate attachment
B)is converted to a product
C)is the region where the reaction takes place
D)increases the energy of reaction
E)includes the entire enzyme
A)is remote from the site of substrate attachment
B)is converted to a product
C)is the region where the reaction takes place
D)increases the energy of reaction
E)includes the entire enzyme

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
"Physiological conditions" for reactions within the body are approximately ________.
A)pH 3.0 and 37 °C
B)pH 7.4 and 37 °C
C)pH 7.4 and 37 °F
D)pH 8.7 and 273 °C
E)pH 7.4 and 273 K
A)pH 3.0 and 37 °C
B)pH 7.4 and 37 °C
C)pH 7.4 and 37 °F
D)pH 8.7 and 273 °C
E)pH 7.4 and 273 K

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Hydrophobic interactions help to stabilize the ________ structure(s)of a protein.
A)primary
B)secondary
C)secondary and tertiary
D)tertiary and quaternary
E)secondary and quaternary
A)primary
B)secondary
C)secondary and tertiary
D)tertiary and quaternary
E)secondary and quaternary

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
A compound that binds to an enzyme,and changes its shape so that a substrate cannot enter the active site,is called a(n)________.
A)coenzyme
B)proenzyme
C)steroid
D)noncompetitive inhibitor
E)competitive inhibitor
A)coenzyme
B)proenzyme
C)steroid
D)noncompetitive inhibitor
E)competitive inhibitor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
In an enzyme,the polypeptide chain folds into a compact shape known as the ________ structure.
A)pleated
B)primary
C)secondary
D)tertiary
E)quaternary
A)pleated
B)primary
C)secondary
D)tertiary
E)quaternary

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
An enzyme that removes H atoms to form a double is a (an)________.
A)lyase
B)isomerase
C)hydrolase
D)oxidoreductase
E)transferase
A)lyase
B)isomerase
C)hydrolase
D)oxidoreductase
E)transferase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
A competitive inhibitor is one that ________.
A)binds to the enzyme at a site far from the active site
B)binds to the active site in place of the substrate
C)destroys the substrate
D)binds to the allosteric site on an enzyme
E)forms a complex with the substrate
A)binds to the enzyme at a site far from the active site
B)binds to the active site in place of the substrate
C)destroys the substrate
D)binds to the allosteric site on an enzyme
E)forms a complex with the substrate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
When two protein chains combine to form an active protein,the structural level is ________.
A)pleated
B)primary
C)secondary
D)tertiary
E)quaternary
A)pleated
B)primary
C)secondary
D)tertiary
E)quaternary

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
"Physiological pH," the pH for optimum activity for most enzymes,is a pH equal to about ________.
A)3.0
B)5.4
C)7.4
D)8.6
E)9.0
A)3.0
B)5.4
C)7.4
D)8.6
E)9.0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Most enzymes are deactivated permanently above a temperature of about ________.
A)25 °C
B)37 °F
C)40 °C
D)45 °F
E)50 °C
A)25 °C
B)37 °F
C)40 °C
D)45 °F
E)50 °C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
What type of amino acids has polar side chains that are attracted to water?
A)hydrophilic
B)hydrophobic
C)nonpolar
D)aromatic
E)hydrocarbon
A)hydrophilic
B)hydrophobic
C)nonpolar
D)aromatic
E)hydrocarbon

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Consider the R groups of the following amino acids: cysteine: - 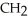 SH; alanine: -
SH; alanine: - 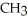 ; serine: -
; serine: - 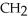 OH
OH
The name for the dipeptide shown below is ________.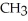 O
O 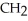 OH
OH 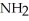
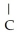 H -
H - 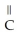 - NH
- NH 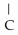 HCOOH
HCOOH
A)alanylcysteine
B)alanylserine
C)serylalanine
D)serylcysteine
E)serinealanine
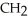 SH; alanine: -
SH; alanine: - 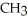 ; serine: -
; serine: - 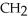 OH
OHThe name for the dipeptide shown below is ________.
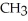 O
O 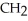 OH
OH 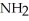
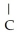 H -
H - 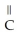 - NH
- NH 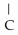 HCOOH
HCOOHA)alanylcysteine
B)alanylserine
C)serylalanine
D)serylcysteine
E)serinealanine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
In the lock-and-key model of enzyme action,the enzyme active site is thought of as ________.
A)a rigid,nonflexible shape that fits the substrate exactly
B)an area of the enzyme that can adjust to fit the substrate shape
C)a key-like shape that fits into a pocket of the substrate surface
D)a hydrophilic area on the enzyme surface
E)a lock that bars a noncompetitive inhibitor from reacting
A)a rigid,nonflexible shape that fits the substrate exactly
B)an area of the enzyme that can adjust to fit the substrate shape
C)a key-like shape that fits into a pocket of the substrate surface
D)a hydrophilic area on the enzyme surface
E)a lock that bars a noncompetitive inhibitor from reacting

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The optimum pH for the activity of pepsin is about ________.
A)2.0
B)4.0
C)6.5
D)7.4
E)7.6
A)2.0
B)4.0
C)6.5
D)7.4
E)7.6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
A noncompetitive inhibitor ________.
A)binds at the active site of the enzyme
B)alters the three-dimensional structure of the enzyme
C)increases the rate of the enzyme-catalyzed reaction
D)has a structure similar to the substrate
E)has its effect reversed by adding more substrate
A)binds at the active site of the enzyme
B)alters the three-dimensional structure of the enzyme
C)increases the rate of the enzyme-catalyzed reaction
D)has a structure similar to the substrate
E)has its effect reversed by adding more substrate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Urea is converted to ammonia and carbon dioxide by the action of urease.What will be the effect on the rate if the temperature of the reaction is lowered from 37 °C (the optimum temperature)to 27 °C? O 
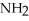 -C-
-C- 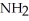 +
+ 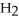 O
O 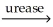 2N
2N 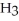 +
+ 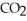
A)There will be no effect.
B)The rate will slow down.
C)The rate will double.
D)The rate will triple.
E)The rate will slow down,then speed up again.

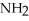 -C-
-C- 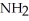 +
+ 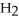 O
O 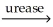 2N
2N 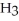 +
+ 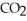
A)There will be no effect.
B)The rate will slow down.
C)The rate will double.
D)The rate will triple.
E)The rate will slow down,then speed up again.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Immunoglobulin,a protein that stimulates immune responses,would be classified as a ________ protein.
A)transport
B)structural
C)storage
D)protection
E)catalytic
A)transport
B)structural
C)storage
D)protection
E)catalytic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Enzymes that catalyze the same reactions but have slightly different structures are called ________.
A)coenzymes
B)cofactors
C)isoenzymes
D)competitive
E)noncompetitive
A)coenzymes
B)cofactors
C)isoenzymes
D)competitive
E)noncompetitive

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
The function of the enzyme-substrate complex is to provide an alternative reaction pathway that ________.
A)lowers the energy of the products
B)lowers the energy of the substrate
C)changes the concentration of the substrate
D)lowers the activation energy for the reaction
E)changes the possible product formed
A)lowers the energy of the products
B)lowers the energy of the substrate
C)changes the concentration of the substrate
D)lowers the activation energy for the reaction
E)changes the possible product formed

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
A noncompetitive inhibitor has a structure that ________.
A)does not resemble the substrate structure
B)resembles the active site of the enzyme
C)can bind to the active site of the enzyme
D)does not interfere with the enzyme-substrate complex formation
E)causes a change in the shape of the substrate
A)does not resemble the substrate structure
B)resembles the active site of the enzyme
C)can bind to the active site of the enzyme
D)does not interfere with the enzyme-substrate complex formation
E)causes a change in the shape of the substrate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
In the induced-fit model of enzyme action,the enzyme active site ________.
A)stays the same shape during substrate binding
B)adjusts shape to adapt to the shape of the substrate
C)stays the same shape while causing a change in the shape of the substrate
D)uses an inhibitor to adjust its shape for the substrate
E)uses a cofactor to change the shape of a substrate
A)stays the same shape during substrate binding
B)adjusts shape to adapt to the shape of the substrate
C)stays the same shape while causing a change in the shape of the substrate
D)uses an inhibitor to adjust its shape for the substrate
E)uses a cofactor to change the shape of a substrate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



