Deck 27: Flowering Plants: Reproduction
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/53
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 27: Flowering Plants: Reproduction
1
Which component of the flowering plant is considered the female portion of the plant?
A) carpel
B) stamen
C) style
D) corolla
A) carpel
B) stamen
C) style
D) corolla
A
2
When a monocot such as corn germinates, the immature leaves are covered by a _____ while the radicle is covered by the _______.
A) hypocotyle; primary root
B) hypocotyle; epicotyl
C) coleoptile; coleorhiza
D) plumule; coleorhiza
A) hypocotyle; primary root
B) hypocotyle; epicotyl
C) coleoptile; coleorhiza
D) plumule; coleorhiza
C
3
Which of the following statements is NOT true about the life cycle of flowering plants?
A) The sporophyte is diploid.
B) The sporophyte produces heterospores.
C) The female gametophyte is the seed.
D) The male gametophyte is the pollen grain.
E) The female gametophyte is retained within the body of the sporophyte parent generation.
A) The sporophyte is diploid.
B) The sporophyte produces heterospores.
C) The female gametophyte is the seed.
D) The male gametophyte is the pollen grain.
E) The female gametophyte is retained within the body of the sporophyte parent generation.
C
4
Match the layers of a pericarp with their correct description.



Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the flowering plant structures is used to attract a specific type of pollinator?
A) petals
B) stamens
C) sepals
D) carpel
A) petals
B) stamens
C) sepals
D) carpel

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Seeds require _____________ for germination to occur.
A) oxygen for increased metabolism
B) adequate warmth
C) adequate water
D) All of the choices are required.
A) oxygen for increased metabolism
B) adequate warmth
C) adequate water
D) All of the choices are required.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The structures in the outermost ring of floral structures that cover and protect the bud are
A) carpels.
B) sepals.
C) receptacles.
D) petals.
E) stamens.
A) carpels.
B) sepals.
C) receptacles.
D) petals.
E) stamens.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Angiosperms have two separate gametophytes because
A) this is normal for alternation of generations.
B) one can survive and fertilize without the need for external water.
C) the microgametophyte is haploid and the megagametophyte is diploid.
D) these two structures allow fertilization without the need for external water.
E) this is normal for all sexually reproducing plants, where sperm are produced by microgametophytes and eggs by megagametophytes.
A) this is normal for alternation of generations.
B) one can survive and fertilize without the need for external water.
C) the microgametophyte is haploid and the megagametophyte is diploid.
D) these two structures allow fertilization without the need for external water.
E) this is normal for all sexually reproducing plants, where sperm are produced by microgametophytes and eggs by megagametophytes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The microspore develops into a
A) megasporocyte.
B) female gametophyte.
C) microsporocyte.
D) male gametophyte.
E) zygote.
A) megasporocyte.
B) female gametophyte.
C) microsporocyte.
D) male gametophyte.
E) zygote.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A flower
A) is the sexual reproductive organ.
B) is composed of whorls of modified leaves.
C) serves to attract animal pollinators.
D) may contain male and female reproductive parts.
E) All of the choices characterize flowers.
A) is the sexual reproductive organ.
B) is composed of whorls of modified leaves.
C) serves to attract animal pollinators.
D) may contain male and female reproductive parts.
E) All of the choices characterize flowers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following stages occurs immediately after the development of the zygote?
A) The development of the proembryo.
B) The development of globular stage.
C) The torpedo stage embryo forms.
D) The heart stage when the cotyledon develops.
A) The development of the proembryo.
B) The development of globular stage.
C) The torpedo stage embryo forms.
D) The heart stage when the cotyledon develops.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A moth-pollinated flower is likely to have
A) lightly colored flowers, no landing area, and strong sweet perfume.
B) white flowers with short tubes, a wide landing area, and no odor.
C) blue or yellow flowers, a wide landing area, and not very much odor.
D) blue or yellow flowers, a wide landing area, and no odor.
E) red flowers that open in daytime, a wide landing area, and an odor resembling dead meat.
A) lightly colored flowers, no landing area, and strong sweet perfume.
B) white flowers with short tubes, a wide landing area, and no odor.
C) blue or yellow flowers, a wide landing area, and not very much odor.
D) blue or yellow flowers, a wide landing area, and no odor.
E) red flowers that open in daytime, a wide landing area, and an odor resembling dead meat.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Pollen grains are formed in _________ and ova are formed in ____________.
A) pistil; stamens
B) sepals; calyx
C) receptacles; peduncles
D) petals; corolla
E) stamens; carpels
A) pistil; stamens
B) sepals; calyx
C) receptacles; peduncles
D) petals; corolla
E) stamens; carpels

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
If you have picked a bouquet of anther-less flowers, you have picked
A) male gametophytes retained within the body of sporophytes.
B) female gametophytes retained within the body of sporophytes.
C) sporophytes retained within the body of microgametophytes.
D) sporophytes retained within the body of megagametophytes.
E) microgametophytes retained within the body of megagametophytes.
A) male gametophytes retained within the body of sporophytes.
B) female gametophytes retained within the body of sporophytes.
C) sporophytes retained within the body of microgametophytes.
D) sporophytes retained within the body of megagametophytes.
E) microgametophytes retained within the body of megagametophytes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of these typically occur in both angiosperms and gymnosperms?
A) Seeds develop within a cone.
B) Seeds develop within a flower.
C) Seeds are surrounded by a fruit at maturity.
D) Pollen is carried by the wind for pollination.
E) Pollen is carried by animal pollinators.
A) Seeds develop within a cone.
B) Seeds develop within a flower.
C) Seeds are surrounded by a fruit at maturity.
D) Pollen is carried by the wind for pollination.
E) Pollen is carried by animal pollinators.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following methods is used by plants when they are undergoing asexual reproduction?
A) Production of stolons.
B) Development of rhizomes.
C) Growth of suckers from the root base of specific types of trees.
D) All of the answer choices are methods of asexual reproduction in plants.
A) Production of stolons.
B) Development of rhizomes.
C) Growth of suckers from the root base of specific types of trees.
D) All of the answer choices are methods of asexual reproduction in plants.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Identify the labeled parts of the flower: 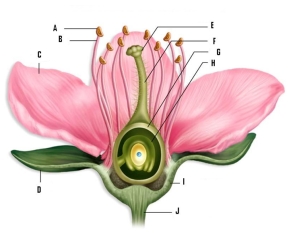
A) ________ F. ________
B) ________ G. ________
C) ________ H. ________
D) ________ I. ________
E) ________ J. ________

A) ________ F. ________
B) ________ G. ________
C) ________ H. ________
D) ________ I. ________
E) ________ J. ________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The name monocot and eudicot are derived from the differences in the number of
A) roots.
B) cotyledons.
C) seeds.
D) None of the choices are correct.
A) roots.
B) cotyledons.
C) seeds.
D) None of the choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
What is the correct sequence for the development of a eudicot embryo?
A) Globular stage
B) Heart stage
C) Proembryo stage
D) Mature embryo
E) Zygote forms
F) Torpedo stage rev: 11_13_2013_QC_40197
A) e - c - a - b - f - d
B) e - b - c - a - f - d
C) d - e - a - b - f - c
D) d - a - e - b - f - c
A) Globular stage
B) Heart stage
C) Proembryo stage
D) Mature embryo
E) Zygote forms
F) Torpedo stage rev: 11_13_2013_QC_40197
A) e - c - a - b - f - d
B) e - b - c - a - f - d
C) d - e - a - b - f - c
D) d - a - e - b - f - c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The anther and filament are parts of the
A) pistil.
B) sepal.
C) receptacle.
D) petal.
E) stamen.
A) pistil.
B) sepal.
C) receptacle.
D) petal.
E) stamen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the following statements is NOT true about the germinated pollen grain?
A) The generative cell produces two sperm.
B) The pollen tube forms in the style.
C) The tube cell produces the pollen tube.
D) There are two sperm nuclei that move down the pollen tube to the micropyle.
E) Fertilization occurs when the pollen grain germinates.
A) The generative cell produces two sperm.
B) The pollen tube forms in the style.
C) The tube cell produces the pollen tube.
D) There are two sperm nuclei that move down the pollen tube to the micropyle.
E) Fertilization occurs when the pollen grain germinates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following mechanisms is NOT as likely to disperse seeds at a great distance from the parent plant?
A) Coconuts are carried by ocean currents.
B) Squirrels bury seeds and nuts for future use.
C) Seeds are dispersed as projectiles from the parent plant.
D) Hooks and spines attach the seed to animal fur or human clothing.
E) Seeds eaten with fruit by animals are dropped with the animals' feces.
A) Coconuts are carried by ocean currents.
B) Squirrels bury seeds and nuts for future use.
C) Seeds are dispersed as projectiles from the parent plant.
D) Hooks and spines attach the seed to animal fur or human clothing.
E) Seeds eaten with fruit by animals are dropped with the animals' feces.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The function of fruit is to
A) attract pollinators.
B) protect and help disperse seeds.
C) supply nutrients to the embryo.
D) protect flower buds.
A) attract pollinators.
B) protect and help disperse seeds.
C) supply nutrients to the embryo.
D) protect flower buds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A megasporocyte is found in the
A) anther.
B) stigma.
C) ovule.
D) filament.
E) style.
A) anther.
B) stigma.
C) ovule.
D) filament.
E) style.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
All of the following statements are true about seed germination EXCEPT
A) all seeds require a period of dormancy before germinating.
B) in the temperate region, seeds often require a period of cold weather before dormancy is broken.
C) fleshy fruits contain inhibitors of germination.
D) some seeds require fire or bacterial action before germination can occur.
A) all seeds require a period of dormancy before germinating.
B) in the temperate region, seeds often require a period of cold weather before dormancy is broken.
C) fleshy fruits contain inhibitors of germination.
D) some seeds require fire or bacterial action before germination can occur.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Why and when is asexual reproduction advantageous in plants?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
In a 1977 article in Science, a botanist reported the strange case of the Tambalacoque tree (Calvaria major) of the Mauritius Islands in the Indian Ocean. All of the trees appear to be hundreds of years old and date, as seedlings, to a time before the extinction of the dodo bird. The seeds of Calvaria are very hard and apparently needed to pass through the digestive tract of the dodo bird before they would germinate. Therefore, when there were no more dodo birds, no more young Calvaria trees germinated. Luckily, foresters can artificially scarify the seeds and germinate new trees now that they know this. The relationship between the dodo bird and the Tambalacoque tree is an example of
A) micropropagation.
B) spontaneous dispersal.
C) coevolution.
D) genetic engineering.
E) vegetative propagation.
A) micropropagation.
B) spontaneous dispersal.
C) coevolution.
D) genetic engineering.
E) vegetative propagation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
As the embryo matures,
A) the suspensor transfers nutrients from the endosperm to the embryo.
B) the embryonic cells near the suspensor become the shoot.
C) the innermost cells become the protective, dermal tissue.
D) it becomes a ball of cells and assumes a torpedo shape.
A) the suspensor transfers nutrients from the endosperm to the embryo.
B) the embryonic cells near the suspensor become the shoot.
C) the innermost cells become the protective, dermal tissue.
D) it becomes a ball of cells and assumes a torpedo shape.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
How are dry fruits different than fleshy fruits? How might these differences affect the way that their seeds are dispersed?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
In mammals, an egg fertilized by one sperm divides repeatedly (1-2-4-8-16-32-64, etc.). At the 64-cell stage, only three cells go on to become the embryo while 61 grow to become the fetal side of the placenta. In plants, fertilization likewise results in the development of an embryo and nourishing endosperm. However, how does this process differ from the mammal embryo and placenta?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Bee pollinated flowers
A) are red.
B) are predominately blue or yellow.
C) have little odor.
D) All of the choices apply.
A) are red.
B) are predominately blue or yellow.
C) have little odor.
D) All of the choices apply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Identify the labeled structures of this seed.
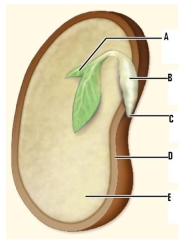
A. ________
B. ________
C. ________
D. ________
E. ________

A. ________
B. ________
C. ________
D. ________
E. ________

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Seeds contain all of the following EXCEPT
A) an embryo sporophyte.
B) sufficient water for germination.
C) stored food.
D) a seed coat
A) an embryo sporophyte.
B) sufficient water for germination.
C) stored food.
D) a seed coat

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Double fertilization in an angiosperm produces
A) a diploid zygote and a haploid polar nucleus.
B) a diploid zygote and a diploid endosperm.
C) a diploid embryo and a triploid zygote.
D) a triploid embryo and a diploid endosperm.
E) a diploid zygote and a triploid endosperm.
A) a diploid zygote and a haploid polar nucleus.
B) a diploid zygote and a diploid endosperm.
C) a diploid embryo and a triploid zygote.
D) a triploid embryo and a diploid endosperm.
E) a diploid zygote and a triploid endosperm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The function of endosperm is to
A) form the seedling.
B) develop into the fruit.
C) provide water to the embryo.
D) provide nutrients to the embryo.
E) provide a protective coating for the embryo.
A) form the seedling.
B) develop into the fruit.
C) provide water to the embryo.
D) provide nutrients to the embryo.
E) provide a protective coating for the embryo.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following is NOT a simple fruit?
A) peach
B) pea
C) rice
D) pineapple
A) peach
B) pea
C) rice
D) pineapple

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the following statements about fruits is NOT true?
A) A blackberry is an example of a simple fruit.
B) A fleshy fruit has a fleshy pericarp, as in a peach.
C) Most fruits are simple fruits, derived from a single ovary.
D) A dry fruit may split at maturity to release its seeds, as a pea or bean pod.
E) A multiple fruit, such as a pineapple, forms from many individual flowers on a stem.
A) A blackberry is an example of a simple fruit.
B) A fleshy fruit has a fleshy pericarp, as in a peach.
C) Most fruits are simple fruits, derived from a single ovary.
D) A dry fruit may split at maturity to release its seeds, as a pea or bean pod.
E) A multiple fruit, such as a pineapple, forms from many individual flowers on a stem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Ovules are contained within the
A) ovary.
B) stigma.
C) anther.
D) filament.
E) style.
A) ovary.
B) stigma.
C) anther.
D) filament.
E) style.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Monocots protect their first true leaves by __________, whereas eudicots protect their first leaves by __________.
A) bending the coleorhiza as the shoot grows through the soil; a surrounding sheath called the coleoptile.
B) providing a protective layer called sepals; surrounding them with endosperm.
C) bending their shoot as it grows through the soil; surrounding them with a protective sheath called the coleorhiza.
D) surrounding them with a sheath called a coleoptile; bending the shoot as it grows through the soil.
A) bending the coleorhiza as the shoot grows through the soil; a surrounding sheath called the coleoptile.
B) providing a protective layer called sepals; surrounding them with endosperm.
C) bending their shoot as it grows through the soil; surrounding them with a protective sheath called the coleorhiza.
D) surrounding them with a sheath called a coleoptile; bending the shoot as it grows through the soil.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The transfer of pollen from an anther to the stigma of a carpel is
A) germination.
B) pollination.
C) fertilization.
D) coevolution.
A) germination.
B) pollination.
C) fertilization.
D) coevolution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which method of asexual reproduction would be most likely to occur in a wild population of plants? This method enables the parent plant to produce multiple offspring that start to grow away from the parent plant.
A) Growth of stolons.
B) Growth of rhizomes.
C) Production of suckers from the parent plant.
D) The root develops slips which can produce new offspring.
A) Growth of stolons.
B) Growth of rhizomes.
C) Production of suckers from the parent plant.
D) The root develops slips which can produce new offspring.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which of the following fruits is a compound fleshy fruit?
A) tomato
B) peach
C) blackberry
D) pineapple
E) All of these are compound fleshy fruits.
A) tomato
B) peach
C) blackberry
D) pineapple
E) All of these are compound fleshy fruits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
List the stages, in the correct order, of the development of a eudicot embryo.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Explain the 8 key components of the flowering plants life cycle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Which of the following structures is found in the eudicot seed but not in the monocot seed?
A) radicle
B) cotyledon
C) plumule
D) pericarp
A) radicle
B) cotyledon
C) plumule
D) pericarp

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Many plants are totipotent, which means
A) they are capable of providing their own nutrition, requiring no external nutritional sources.
B) the cell has the genetic capability of becoming an entire plant.
C) they are incapable of dividing to produce daughter cells.
D) they are metabolically inactive, existing in a state of dormancy.
A) they are capable of providing their own nutrition, requiring no external nutritional sources.
B) the cell has the genetic capability of becoming an entire plant.
C) they are incapable of dividing to produce daughter cells.
D) they are metabolically inactive, existing in a state of dormancy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
All of the following statements about cell suspension cultures are true EXCEPT
A) digitalis, digitoxin, and quinine are produced by cell suspension culture.
B) large numbers of plants are grown and collected from the natural environment to produce chemicals in the laboratory.
C) chemicals are produced and extracted in high concentrations, sometimes from genetically modified cells.
D) cell suspension cultures produce the same chemicals the entire plant produces.
A) digitalis, digitoxin, and quinine are produced by cell suspension culture.
B) large numbers of plants are grown and collected from the natural environment to produce chemicals in the laboratory.
C) chemicals are produced and extracted in high concentrations, sometimes from genetically modified cells.
D) cell suspension cultures produce the same chemicals the entire plant produces.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
During which stage of eudicot development does the embryo continue to enlarge and elongate and the cotyledons are obvious?
A) Zygote stage
B) Proembryo stage
C) Globular stage
D) Heart stage
E) Torpedo stage
A) Zygote stage
B) Proembryo stage
C) Globular stage
D) Heart stage
E) Torpedo stage

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Which of the following floral structures are present during the diploid stage of a flowering plants life cycle?
A) Anther
B) Ovule
C) Sporophyte
D) Pollen grain
E) Everything but for the pollen grain.
A) Anther
B) Ovule
C) Sporophyte
D) Pollen grain
E) Everything but for the pollen grain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Explain how the sexual life cycle of flowering plants is adapted to the terrestrial environment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Plants that reproduce asexually by growth of a new plant from stems or roots show vegetative propagation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Single plant cells can be stimulated to become a callus and then further stimulated to become a new entire plant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which of the following events is not associated with the development of the female gametophyte?
A) A single parenchyma cell will enlarge to become a megaspore mother cell.
B) The megaspore undergoes meiosis producing four haploid megaspores.
C) The nucleus of the megaspore divides mitotically to produce eight nuclei.
D) The female gametophyte will contain three antipodal cells.
E) All of these are associated with the development of the female gametophyte.
A) A single parenchyma cell will enlarge to become a megaspore mother cell.
B) The megaspore undergoes meiosis producing four haploid megaspores.
C) The nucleus of the megaspore divides mitotically to produce eight nuclei.
D) The female gametophyte will contain three antipodal cells.
E) All of these are associated with the development of the female gametophyte.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



