Deck 14: Predation
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/81
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 14: Predation
1
The movement of predators into areas of high prey density is a type of numerical response referred to as a(n)________ response.
aggregative
2
________ mimicry occurs when many unpalatable or venomous species share a similar color pattern.
Müllerian
3
A species that consumes only animal tissue is called a(n)________.
carnivore
4
________ mimicry occurs when a nontoxic species closely resembles a toxic species,both of which are avoided by predators.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The increase in a predator's reproduction in response to an increase in the consumption of prey is known as the predator's ________ response.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The per capita rate at which predators consume prey is assumed to increase ________ with the number of prey.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The costs of foraging can be measured in terms of the time and ________ expended in the act of foraging.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
________ prey on autotrophs and do not kill the individuals they feed on.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A species that consumes both plant and animal tissue is called a(n)________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
________ is the consumption of one living organism by another.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The recognition of a particular species as potential prey by a predator is called a(n)________ image.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The relationship between the per capita rate of consumption and the number of prey is known as the predator's ________ response.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A(n)________ is an organism that lives on or within another without killing the host.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Most predators are also ________ to other predatory species.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The cycle of change in the size of predator and prey populations in response of one to the other is known as ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
________ is a deliberate form of hunting with a quick attack.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The trade-off between conflicting demands faced by a predator is described by the ________ foraging theory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
________ defenses are not permanently present but,rather,are brought about by the presence or action of predators.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Animals that are boldly colored or patterned to warn potential predators possess warning coloration or ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The concept of ________ energy is the basis for models of optimal foraging.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the following is a positive numerical response of a predator in response to an increase in prey density?
A)decrease in predator mortality rate
B)increase in predator survival rate
C)immigration of predators to an area of high prey density
D)decrease in predator reproduction rate
A)decrease in predator mortality rate
B)increase in predator survival rate
C)immigration of predators to an area of high prey density
D)decrease in predator reproduction rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
A parasitoid
A)is a true predator.
B)actively pursues its prey.
C)attacks the host indirectly by laying its eggs in or on the prey's body.
D)preys only on animals.
A)is a true predator.
B)actively pursues its prey.
C)attacks the host indirectly by laying its eggs in or on the prey's body.
D)preys only on animals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
When predators come together in areas of high prey density,it is referred to as
A)predator satiation.
B)predator preference.
C)a functional response.
D)an aggregative response.
A)predator satiation.
B)predator preference.
C)a functional response.
D)an aggregative response.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
An organism that feeds on plant or algal tissues is referred to as a(n)
A)herbivore.
B)omnivore.
C)carnivore.
D)decomposer.
A)herbivore.
B)omnivore.
C)carnivore.
D)decomposer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
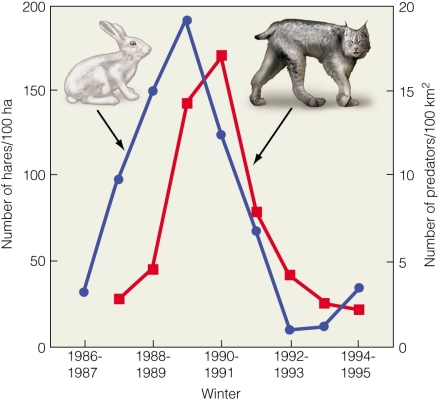 This figure shows that
This figure shows thatA)lynx populations numerically respond to hare populations.
B)lynx become better able to capture prey over time.
C)lynx become worse at capturing prey over time.
D)hares will go extinct over time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following is functionally a true predator?
A)parasite
B)planktivore
C)grazer
D)parasitoid
A)parasite
B)planktivore
C)grazer
D)parasitoid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
In the basic Lotka-Volterra equations that describe predator-prey interactions,the growth rate of the prey population (dNprey/dt)is zero when the density of predators (Nprey)is equal to
A)r/N.
B)N/r.
C)r/c.
D)c/r.
A)r/N.
B)N/r.
C)r/c.
D)c/r.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
In the Lotka-Volterra model of predator-prey interactions,population growth is regulated through
A)reproduction for both predator and prey.
B)reproduction for the predator and mortality for the prey.
C)reproduction for the prey and mortality for the predator.
D)mortality for both predator and prey.
A)reproduction for both predator and prey.
B)reproduction for the predator and mortality for the prey.
C)reproduction for the prey and mortality for the predator.
D)mortality for both predator and prey.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The maximum number of prey consumed per predator per unit time is limited by
A)Nprey.
B)Npredator.
C)Ts.
D)T/Th.
A)Nprey.
B)Npredator.
C)Ts.
D)T/Th.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
In a simple experiment involving only predator and prey with no refuge,
A)prey will always survive.
B)predators will typically drive their prey to extinction.
C)both populations will oscillate.
D)prey populations will oscillate.
A)prey will always survive.
B)predators will typically drive their prey to extinction.
C)both populations will oscillate.
D)prey populations will oscillate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
When a predator drives down a prey population to a low abundance,it will often
A)switch prey species.
B)consume prey to extinction.
C)go extinct.
D)decrease handling time of prey.
A)switch prey species.
B)consume prey to extinction.
C)go extinct.
D)decrease handling time of prey.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
In a graph that plots prey population (Nprey)on the x-axis against the number of predator offspring produced per unit of time on the y-axis,the slope represents the
A)efficiency of predation (c).
B)efficiency with which food is converted into predator population growth or reproduction (b).
C)predator population growth rate (r).
D)the rate of increase in prey availability.
A)efficiency of predation (c).
B)efficiency with which food is converted into predator population growth or reproduction (b).
C)predator population growth rate (r).
D)the rate of increase in prey availability.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Huffaker's experiment involving oranges showed
A)predators will always consume prey to extinction.
B)prey will always outlast predators.
C)with enough complexity,predator and prey populations will oscillate.
D)both species use oranges for refuge.
A)predators will always consume prey to extinction.
B)prey will always outlast predators.
C)with enough complexity,predator and prey populations will oscillate.
D)both species use oranges for refuge.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A plant may be able to compensate for the loss of leaves by increasing the rate of ________ in the remaining leaves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
European kestrels feed on Microtus voles,with the "kill" rate,defined as the number of prey taken during the breeding season,as linearly proportional to the density of Microtus.This type of functional response is referred to as
A)Type I.
B)Type II.
C)Type III.
D)Type IV.
A)Type I.
B)Type II.
C)Type III.
D)Type IV.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The sigmoidal relationship between prey density and per capita predation rate in a Type III functional response can be explained by all of the following factors,except
A)prey access to refuge.
B)predator preference.
C)recognition of prey by predator.
D)predator density.
A)prey access to refuge.
B)predator preference.
C)recognition of prey by predator.
D)predator density.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
A true predator is a species that
A)feeds upon any part of any organism,not necessarily killing it.
B)feeds only on animals.
C)kills its prey more or less immediately upon capture.
D)feeds on dead or living prey.
A)feeds upon any part of any organism,not necessarily killing it.
B)feeds only on animals.
C)kills its prey more or less immediately upon capture.
D)feeds on dead or living prey.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Many plants use ________ defenses,such as hairy leaves,thorns,or spines,to deter herbivory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The net outcome of predator-prey interactions in the basic Lotka-Volterra models is that
A)the predator drives its prey to extinction and then goes extinct itself.
B)the prey population declines and this causes the predator population to also decline.
C)predator and prey populations eventually converge on equilibrium population sizes that are maintained into infinity.
D)predator and prey populations oscillate,with each predictably increasing and decreasing in response to the other.
A)the predator drives its prey to extinction and then goes extinct itself.
B)the prey population declines and this causes the predator population to also decline.
C)predator and prey populations eventually converge on equilibrium population sizes that are maintained into infinity.
D)predator and prey populations oscillate,with each predictably increasing and decreasing in response to the other.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
With a highly abundant prey population size,which component of the functional response is most reduced?
A)handling time
B)prey population
C)search time
D)killing time
A)handling time
B)prey population
C)search time
D)killing time

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
According to the Red Queen hypothesis,
A)the population density of a predator depends on the population density of its prey.
B)natural selection should favor the most efficient foragers.
C)prey must continually evolve means of avoiding capture to avoid extinction.
D)most predators consume a varied diet in order to meet their nutritional requirements.
A)the population density of a predator depends on the population density of its prey.
B)natural selection should favor the most efficient foragers.
C)prey must continually evolve means of avoiding capture to avoid extinction.
D)most predators consume a varied diet in order to meet their nutritional requirements.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Coevolution between predator and prey suggests
A)as prey decrease in number,predators will switch prey.
B)as predators become smarter at catching prey,prey will become smarter at escaping predation.
C)as predators feed on prey,prey will become more palatable over time.
D)as predators drive down prey populations,they become worse at catching prey.
A)as prey decrease in number,predators will switch prey.
B)as predators become smarter at catching prey,prey will become smarter at escaping predation.
C)as predators feed on prey,prey will become more palatable over time.
D)as predators drive down prey populations,they become worse at catching prey.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The profitability of a prey item
A)increases as its handling time (Th)increases.
B)decreases as its search time (Ts)decreases.
C)increases as its energy content (E)decreases.
D)increases as its E/Th increases.
A)increases as its handling time (Th)increases.
B)decreases as its search time (Ts)decreases.
C)increases as its energy content (E)decreases.
D)increases as its E/Th increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which of the following is considered a nonlethal effect of predation?
A)reduced activity of prey
B)prey consumption
C)reduced competition
D)increased predator mortality
A)reduced activity of prey
B)prey consumption
C)reduced competition
D)increased predator mortality

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Which of the following is an example of cryptic coloration?
A)a brown bird that nests on the ground
B)a deer with a large,white tail
C)skunks with black and white stripes
D)snakes with black,yellow,and red bands
A)a brown bird that nests on the ground
B)a deer with a large,white tail
C)skunks with black and white stripes
D)snakes with black,yellow,and red bands

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which of the following caused massive declines in U.S.commercial fish populations?
A)recreational anglers
B)freak weather events in the 1980s
C)huge factory trawlers
D)foreign commercial fisherman
A)recreational anglers
B)freak weather events in the 1980s
C)huge factory trawlers
D)foreign commercial fisherman

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
 All three of these species are harmful.This is an example of
All three of these species are harmful.This is an example ofA)Müllerian mimicry.
B)Batesian mimicry.
C)optimal foraging theory.
D)functional response.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The ideal number of fish to catch to provide the most yield while sustaining fisheries is
A)at K/2.
B)at K.
C)dN/dt.
D)rN(1 - N/K).
A)at K/2.
B)at K.
C)dN/dt.
D)rN(1 - N/K).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
If you are stranded on a desert island,which prey should you avoid consuming?
A)fast mobile prey
B)large prey
C)cryptic prey
D)brightly colored prey
A)fast mobile prey
B)large prey
C)cryptic prey
D)brightly colored prey

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which of the following is an example of Müllerian mimicry?
A)walking sticks that resemble twigs
B)stinkbugs that produce a noxious odor
C)flounders whose colors resemble the sea floor
D)wasps with black and yellow bands
A)walking sticks that resemble twigs
B)stinkbugs that produce a noxious odor
C)flounders whose colors resemble the sea floor
D)wasps with black and yellow bands

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which of the following is an induced defense?
A)bright coloration of poison dart frogs
B)high-pitched alarm calls by a squirrel
C)background color matching by a chameleon
D)walking sticks resembling twigs
A)bright coloration of poison dart frogs
B)high-pitched alarm calls by a squirrel
C)background color matching by a chameleon
D)walking sticks resembling twigs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which of the following is not a class of plant secondary compounds?
A)terpenoids
B)phenolics
C)nitrogen-based compounds
D)alkanes
A)terpenoids
B)phenolics
C)nitrogen-based compounds
D)alkanes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Scavengers are heterotrophs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
When prey produce so many offspring in a short period of time that predators can attack only a fraction of them,it is referred to as
A)a numerical response.
B)a functional response.
C)predator satiation.
D)cryptic reproduction.
A)a numerical response.
B)a functional response.
C)predator satiation.
D)cryptic reproduction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
In the Lotka-Volterra models of predator-prey interactions,prey density does not influence predator mortality.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
According to the optimal foraging theory,a predator will select prey 1 (P1)over prey 2 (P2)when
A)E1 < E2.
B)Th1 < Th2.
C)E1/Th1 < E2/Th2.
D)Nprey1 > N prey2.
A)E1 < E2.
B)Th1 < Th2.
C)E1/Th1 < E2/Th2.
D)Nprey1 > N prey2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Quantitative inhibitors
A)are produced in small quantities by a plant.
B)are toxic to herbivores.
C)reduce digestibility of plant material.
D)include cyanide and alkaloids.
A)are produced in small quantities by a plant.
B)are toxic to herbivores.
C)reduce digestibility of plant material.
D)include cyanide and alkaloids.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Grazers and browsers are true predators.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which of the following hunting methods has the lowest frequency of success but requires the least amount of energy?
A)satiation
B)ambush
C)stalking
D)pursuit
A)satiation
B)ambush
C)stalking
D)pursuit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Which animal does not employ protective armor for predator defense?
A)armadillo
B)beetle
C)scorpion
D)porcupine
A)armadillo
B)beetle
C)scorpion
D)porcupine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The risk of predation can sometimes have a significant impact on the foraging choices made by animals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Cryptic coloration is a strategy employed only by prey.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The response of a predator's consumption rate to prey density is a key factor as to whether a predator can regulate a prey population.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
One explanation for the shape of the Type II functional response is that predators develop a search image for prey after they have encountered them.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
It is difficult to quantify the consequences of a specific behavioral choice on the probability of survivorship and reproduction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Most grasses tolerate grazing and actually benefit from it.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
In the Lotka-Volterra equations that represent predator-prey interactions,predators are a source of density-independent mortality for prey.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
A Type III functional response is the most commonly reported for predators.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Most predator populations grow slowly in comparison to those of their prey.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Some animals acquire their toxic chemical compounds from plants that they consume.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
A Type I functional response leads to regulation of the prey population by the predator.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Some plants are able to attract beneficial insects that act as predators on the herbivores of that plant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
As prey species evolve more effective means to avoid being caught,predators evolve more effective means to capture them.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The Lotka-Volterra model of predator-prey interactions assumes a mutual regulation of predator and prey populations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Acoustic mimicry by some nonvenomous snakes that rattle their tails like rattlesnakes is a form of Müllerian mimicry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Quantitative inhibitors in plants are toxic secondary compounds,often causing herbivores to avoid their consumption.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
If defoliation of trees is complete,the leaves that regrow are often larger than the original leaves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
The amount of time an organism spends foraging must be balanced against other time constraints,such as defense,avoiding predators,searching for mates,or caring for young.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Herbivory does not affect a plant's ability to survive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Pursuit hunting requires minimal search time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



