Deck 5: Adaptation and Natural Selection
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/76
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 5: Adaptation and Natural Selection
1
The alternate forms of a gene are called ________.
alleles
2
The outward appearance of an organism for a given characteristic is called its ________.
phenotype
3
The sum of genetic information (alleles)across all individuals in the population is referred to as the ________.
gene pool
4
________ are heritable changes in a gene or chromosome.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
________ is the mating of individuals in the population that are more closely related than expected by random chance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A(n)________ is any heritable behavioral,morphological,or physiological trait of an organism that has evolved over a period of time by the process of natural selection.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A(n)________ individual has the same alleles at the same locus on homologous chromosomes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
When genetic variation occurs among subpopulations of the same species,it is known as genetic ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
________ mating occurs when individuals choose mates nonrandomly with respect to some phenotypic trait.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
________ is the differential success of individuals in a population in response to environmental conditions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
All of the DNA in a cell is collectively called the ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Reversible phenotypic changes in an individual organism in response to changing environmental conditions are referred to as ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Phenotypic characteristics that have a continuous distribution are considered to be ________ traits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The phenotypic trait that selection acts upon directly is referred to as the ________ of selection.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A(n)________ is a population that has adapted to its unique local environmental conditions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The type of natural selection in which the mean value of a trait is shifted toward one extreme is called ________ selection.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The sum of genetic information (alleles)across all individuals in a population at any one time is called the ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
An organism's structure and ________ reflect adaptations to its particular environment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
If the physical expression of a heterozygous individual is intermediate between those of the homozygotes,the alleles are ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A(n)________ is a measurable,gradual change over a geographic region in the average value of a trait.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the following characteristics is an example of a qualitative trait?
A)flower color
B)arm length
C)body weight
D)root length
A)flower color
B)arm length
C)body weight
D)root length

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Researchers Rosemary and Peter Grant have discovered that beak size frequency of Galápagos Island medium ground finch populations varies with all the following,except
A)rainfall.
B)seed hardness.
C)seed size.
D)seed color.
A)rainfall.
B)seed hardness.
C)seed size.
D)seed color.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
If birds with larger beaks are favored by the environment,it is likely that ________ selection will occur.
A)directional
B)disruptive
C)stabilizing
D)standardizing
A)directional
B)disruptive
C)stabilizing
D)standardizing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
An allele that completely masks the effect of another allele is considered
A)codominant.
B)dominant.
C)ineffective.
D)recessive.
A)codominant.
B)dominant.
C)ineffective.
D)recessive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The process by which one species gives rise to multiple species that exploit different features of the environment is called ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The mechanism of evolution proposed by Charles Darwin in The Origin of Species is
A)acclimatization.
B)natural selection.
C)acquired inheritance.
D)adaptation.
A)acclimatization.
B)natural selection.
C)acquired inheritance.
D)adaptation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
If a population has an allele frequency of 1.0,you would say that
A)the allele frequency is ideal.
B)genetic variation of that allele is low.
C)genetic variation of that allele is high.
D)that allele is under selection.
A)the allele frequency is ideal.
B)genetic variation of that allele is low.
C)genetic variation of that allele is high.
D)that allele is under selection.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Identical twin raccoons are raised in different environments and yet behave very differently.This is an example of
A)heterozygous alleles.
B)the norm of reaction.
C)genetic differentiation.
D)acclimation.
A)heterozygous alleles.
B)the norm of reaction.
C)genetic differentiation.
D)acclimation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
A gene is
A)a stretch of DNA coding for a polypeptide chain (sequence of amino acids).
B)a microscopic,threadlike body within a cell.
C)any heritable behavioral,morphological,or physiological trait of an organism.
D)all of the DNA in a cell.
A)a stretch of DNA coding for a polypeptide chain (sequence of amino acids).
B)a microscopic,threadlike body within a cell.
C)any heritable behavioral,morphological,or physiological trait of an organism.
D)all of the DNA in a cell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Traits that have a continuous distribution are known as
A)quantitative traits.
B)qualitative traits.
C)phenotypic traits.
D)genotypic traits.
A)quantitative traits.
B)qualitative traits.
C)phenotypic traits.
D)genotypic traits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The color of a flower is controlled by two alternative alleles at a single locus,R (red)and r (white).If an individual has the Rr alleles,it is considered to be
A)homozygous dominant with a red color.
B)heterozygous with a red color.
C)heterozygous with a white color.
D)homozygous recessive with a white color.
A)homozygous dominant with a red color.
B)heterozygous with a red color.
C)heterozygous with a white color.
D)homozygous recessive with a white color.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The expression of different phenotypic traits for a given genotype under different environmental conditions is referred to as
A)acclimation.
B)phenotypic plasticity.
C)developmental plasticity.
D)habituation.
A)acclimation.
B)phenotypic plasticity.
C)developmental plasticity.
D)habituation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
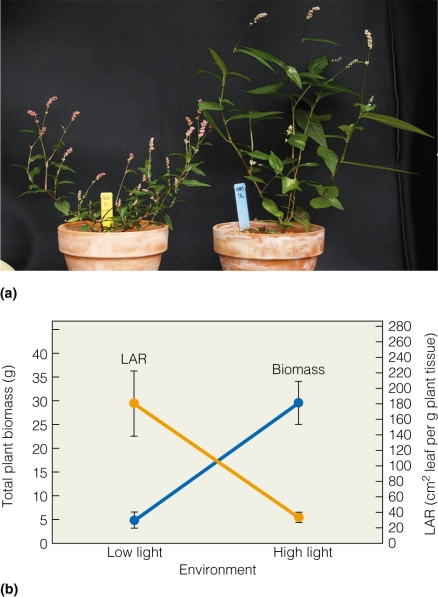 Plants grown under a medium light condition would exhibit how much biomass?
Plants grown under a medium light condition would exhibit how much biomass?A)5g
B)20g
C)30g
D)45g

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which of the following represents acclimation?
A)Deeper beaks evolve in a population.
B)Marine lionfish are able to tolerate freshwater in estuaries.
C)Tropical trees grow taller than temperate ones to compete for light.
D)Poisonous animals are brightly colored to ward off predators.
A)Deeper beaks evolve in a population.
B)Marine lionfish are able to tolerate freshwater in estuaries.
C)Tropical trees grow taller than temperate ones to compete for light.
D)Poisonous animals are brightly colored to ward off predators.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The gene pool refers to all of the genetic information within a
A)cell.
B)individual.
C)population.
D)species.
A)cell.
B)individual.
C)population.
D)species.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The alternate forms of a gene are called
A)chromosomes.
B)loci.
C)alleles.
D)genomes.
A)chromosomes.
B)loci.
C)alleles.
D)genomes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The specific traits of a particular organism enabling it to survive,grow,and reproduce within a given environment are called
A)mutations.
B)genes.
C)adaptations.
D)phenotypes.
A)mutations.
B)genes.
C)adaptations.
D)phenotypes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A population of a species that is distinguishable from other populations by one or more characteristics is referred to as a(n)________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The tongue length of an animal is controlled by two alternative alleles at a single locus,L (long)and l (short).If an individual has parents that are both homozygous dominant,it will be
A)homozygous dominant with a long tongue.
B)heterozygous with a long tongue.
C)heterozygous with a short tongue.
D)homozygous recessive with a long tongue.
A)homozygous dominant with a long tongue.
B)heterozygous with a long tongue.
C)heterozygous with a short tongue.
D)homozygous recessive with a long tongue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The fitness of an individual is measured by
A)the proportion of heterozygous alleles within its genome.
B)its body size.
C)its efficiency in obtaining energy.
D)the proportionate contribution it makes to future generations.
A)the proportion of heterozygous alleles within its genome.
B)its body size.
C)its efficiency in obtaining energy.
D)the proportionate contribution it makes to future generations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The Galápagos Islands are inhabited by 13 species of Darwin's finches that evolved from a single species.This is an example of
A)clinal variation.
B)adaptive radiation.
C)directional selection.
D)genetic drift.
A)clinal variation.
B)adaptive radiation.
C)directional selection.
D)genetic drift.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
A gradual change in phenotype across an environmental gradient,such as white-tailed deer changing gradually in size from large in the north to small in the south,is referred to as
A)migration.
B)a subspecies.
C)a cline.
D)an ecotype.
A)migration.
B)a subspecies.
C)a cline.
D)an ecotype.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
In a population with a q allele frequency of 0.6,what would the frequency of allele p be?
A)0)6
B)0)5
C)0)36
D)0)4
A)0)6
B)0)5
C)0)36
D)0)4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
In tiger salamanders one phenotype is cannibalistic while another is not.Both are stable strategies.Which form of selection is best represented by this scenario?
A)stabilizing
B)directional
C)disruptive
D)proportional
A)stabilizing
B)directional
C)disruptive
D)proportional

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Peter and Rosemary Grant are known for their work on
A)Tenebrionid beetles.
B)marine iguanas.
C)Galápagos tortoises.
D)Darwin's finches.
A)Tenebrionid beetles.
B)marine iguanas.
C)Galápagos tortoises.
D)Darwin's finches.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
A transgenic organism is one that
A)changes gene frequency over time.
B)provides gene information to another organism.
C)changes gender over time.
D)has received genetic information from another organism.
A)changes gene frequency over time.
B)provides gene information to another organism.
C)changes gender over time.
D)has received genetic information from another organism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Several years of heavy precipitation occur on the Galápagos Islands.What do you predict would happen to the beaks of Darwin's medium ground finches?
A)Populations would crash.
B)Disruptive selection on seed size would occur.
C)Midparent beak size would decrease.
D)Offspring beak depth would increase.
A)Populations would crash.
B)Disruptive selection on seed size would occur.
C)Midparent beak size would decrease.
D)Offspring beak depth would increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Bt corn is
A)adapted to resist Bt pesticides.
B)grown only on no till farms.
C)a variety that possesses genes from a bacterium.
D)a drought tolerant form of corn.
A)adapted to resist Bt pesticides.
B)grown only on no till farms.
C)a variety that possesses genes from a bacterium.
D)a drought tolerant form of corn.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The simplest response an individual organism can make to a change in environmental conditions is to
A)remain still.
B)move to a more suitable location.
C)produce offspring that are better suited to the new conditions.
D)reduce foraging activity.
A)remain still.
B)move to a more suitable location.
C)produce offspring that are better suited to the new conditions.
D)reduce foraging activity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Under which of the following conditions would genetic drift exert the greatest influence?
A)a population with a large range
B)a very small population
C)a very large population
D)a population that has access to sufficient resources
A)a population with a large range
B)a very small population
C)a very large population
D)a population that has access to sufficient resources

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Geographic isolates of a particular species that differ from other populations by one or more characteristics are considered to be
A)clines.
B)subspecies.
C)evolutionary "dead ends."
D)ecotypes.
A)clines.
B)subspecies.
C)evolutionary "dead ends."
D)ecotypes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
According to the Hardy-Weinberg principle,which of the following must be true for gene frequencies in a population to remain the same?
A)Mating is random.
B)Mutations occur consistently.
C)The population is small.
D)Natural selection occurs.
A)Mating is random.
B)Mutations occur consistently.
C)The population is small.
D)Natural selection occurs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The effect of positive assortative mating is to
A)increase the number of homozygotes in the population.
B)increase the number of heterozygotes in the population.
C)reduce the number of individuals with diseases in the population.
D)increase the fertility of individuals in the population.
A)increase the number of homozygotes in the population.
B)increase the number of heterozygotes in the population.
C)reduce the number of individuals with diseases in the population.
D)increase the fertility of individuals in the population.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
What is the primary original source of genetic variation in a population?
A)mutation
B)genetic drift
C)blending inheritance
D)cloning
A)mutation
B)genetic drift
C)blending inheritance
D)cloning

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
In the Hardy-Weinberg equation P + H + Q = 1,what does "Q" represent?
A)total number of individuals in the population
B)frequency of heterozygotes
C)frequency of dominant homozygotes
D)frequency of recessive homozygotes
A)total number of individuals in the population
B)frequency of heterozygotes
C)frequency of dominant homozygotes
D)frequency of recessive homozygotes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
What is the allele frequency of q in a population with genotypic frequencies of P = 0.3,H = 0.4,and Q = 0.3?
A)0)3
B)0)5
C)0)6
D)0)9
A)0)3
B)0)5
C)0)6
D)0)9

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Squirrels tend to have larger body sizes at higher latitudes.This could be an example of
A)acclimation.
B)positive assortative mating.
C)a cline.
D)the Hardy-Weinberg principle.
A)acclimation.
B)positive assortative mating.
C)a cline.
D)the Hardy-Weinberg principle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Individual beak size of individual finches of the Galápagos Islands
A)may change during a bird's lifetime.
B)will always match the beak size useful for seed foraging.
C)has nothing to do with overall population characteristics.
D)will greatly influence individual survival.
A)may change during a bird's lifetime.
B)will always match the beak size useful for seed foraging.
C)has nothing to do with overall population characteristics.
D)will greatly influence individual survival.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Measurements of bill length in a population of seed-eating birds reveals two distinct groups: small-billed individuals feeding on soft-shelled seeds and large-billed individuals feeding on hard-shelled seeds.This bimodal distribution most likely resulted from
A)stabilizing selection.
B)natural selection.
C)directional selection.
D)disruptive selection.
A)stabilizing selection.
B)natural selection.
C)directional selection.
D)disruptive selection.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The movement of genes between populations is referred to as
A)mutation.
B)migration.
C)genetic drift.
D)gene flow.
A)mutation.
B)migration.
C)genetic drift.
D)gene flow.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Charles Darwin advocated a theory of evolution that involved individuals acquiring useful characteristics during their lifetimes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Gene flow is restricted between subspecies because of some extrinsic barrier,such as rivers or mountain ridges.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Genes are arranged in threadlike bodies called chromosomes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
An individual evolves during its lifetime.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Inbreeding is usually beneficial to a population because it increases genetic diversity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The expression of most phenotypic traits is affected to varying degrees by the environment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Most traits are influenced by only one locus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Changes due to developmental plasticity are reversible.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The position occupied by a gene on the chromosome is called the locus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Variation within and among species would increase dramatically if the environment were homogeneous.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The selective agent is the environmental cause of fitness differences among organisms with different phenotypes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Disruptive selection favors individuals possessing traits near the mean value of a population.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The characteristics maximize the fitness of an individual under one set of environmental conditions generally limit its fitness under a different set of conditions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
A trait cannot be subject to natural selection unless it is heritable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Ecotypes are variants within a species that are adapted to local environmental conditions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Most mutations are beneficial.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



