Deck 9: Introduction to Estimation
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/85
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 9: Introduction to Estimation
1
The sample proportion 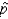 is a consistent estimator of the population proportion p because it is unbiased and the variance of
is a consistent estimator of the population proportion p because it is unbiased and the variance of 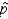 is p(1 - p) / n, which grows smaller as n grows larger.
is p(1 - p) / n, which grows smaller as n grows larger.
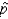 is a consistent estimator of the population proportion p because it is unbiased and the variance of
is a consistent estimator of the population proportion p because it is unbiased and the variance of 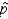 is p(1 - p) / n, which grows smaller as n grows larger.
is p(1 - p) / n, which grows smaller as n grows larger.True
2
An unbiased estimator is a sample statistic whose expected value equals the population parameter.
True
3
In determining the sample size needed to estimate the population proportion p, we let the sample proportion 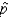 = 1 if we have no knowledge of even the approximate values of
= 1 if we have no knowledge of even the approximate values of 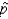 .
.
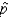 = 1 if we have no knowledge of even the approximate values of
= 1 if we have no knowledge of even the approximate values of 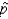 .
.False
4
The sample mean 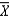 is a consistent estimator of the population mean .
is a consistent estimator of the population mean .
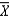 is a consistent estimator of the population mean .
is a consistent estimator of the population mean . 
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The confidence interval estimate of the population mean is constructed around the sample mean.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The sample variance (where you divide by n - 1) is an unbiased estimator of the population variance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
An interval estimate is a range of values within which the actual value of the population parameter, such as , may fall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Knowing that an estimator is unbiased only assures us that its expected value equals the parameter, but it does not tell us how close the estimator is to the parameter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
An unbiased estimator has an average value (across all samples) equal to the population parameter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The sample variance is a point estimate of the population variance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The sample variance s2 is an unbiased estimator of the population variance 2 when the denominator of s2 is n.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
An unbiased estimator is said to be consistent if the difference between the estimator and the parameter grows larger as the sample size grows larger.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A point estimate consists of a single sample statistic that is used to estimate the true population parameter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A specific confidence interval obtained from data will always correctly estimate the population parameter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
If there are two unbiased estimators of a parameter, the one whose variance is smaller is said to be relatively efficient.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The lower limit of the 90% confidence interval for the population proportion p, given that n = 400 and 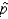 = 0.10, is 0.0247.
= 0.10, is 0.0247.
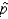 = 0.10, is 0.0247.
= 0.10, is 0.0247.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The sampling distribution of 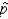 is approximately normal if the sample size is more than 30.
is approximately normal if the sample size is more than 30.
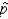 is approximately normal if the sample size is more than 30.
is approximately normal if the sample size is more than 30.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
An interval estimate is an estimate of the range for a sample statistic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
An unbiased estimator is said to be consistent if the difference between the estimator and the parameter grows smaller as the sample size grows larger.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
In testing a hypothesis about a population proportion p, the z test statistic measures how close the computed sample proportion 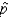 has come to the hypothesized population parameter.
has come to the hypothesized population parameter.
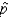 has come to the hypothesized population parameter.
has come to the hypothesized population parameter.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The use of the standard normal distribution for constructing confidence interval estimate for the population proportion p requires:
A) nand n(1 -) both greater than 5.
B) np and n(1 - p) both greater than 5.
C) n(1 +) and n(1 -) both greater than 5.
D) sample size greater than 5.
A) nand n(1 -) both greater than 5.
B) np and n(1 - p) both greater than 5.
C) n(1 +) and n(1 -) both greater than 5.
D) sample size greater than 5.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
If there are two unbiased estimators of a population parameter available, the one that has the smallest variance is said to be:
A) a biased estimator.
B) relatively efficient.
C) consistent.
D) relatively unbiased.
A) a biased estimator.
B) relatively efficient.
C) consistent.
D) relatively unbiased.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The problem with relying on a point estimate of a population parameter is that:
A) it is virtually certain to be wrong.
B) it doesn't have the capacity to reflect the effects of larger sample sizes.
C) it doesn't tell us how close or far the point estimate might be from the parameter.
D) All of these choices are true.
A) it is virtually certain to be wrong.
B) it doesn't have the capacity to reflect the effects of larger sample sizes.
C) it doesn't tell us how close or far the point estimate might be from the parameter.
D) All of these choices are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Under what condition(s) does the test statistic for p have an approximate normal distribution?
A) When np > 5.
B) When np and np(1 - p) are both > 5.
C) When n > 30.
D) When np and n(1 - p) are both > 5.
A) When np > 5.
B) When np and np(1 - p) are both > 5.
C) When n > 30.
D) When np and n(1 - p) are both > 5.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Assuming that all necessary conditions are met, what needs to be changed in the formula 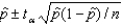 so that we can use it to construct a (1 - ) confidence interval estimate for the population proportion p?
so that we can use it to construct a (1 - ) confidence interval estimate for the population proportion p?
A) should be replaced by p.
B) t should be replaced by z .
C) t should be replaced by t / 2.
D) t should be replaced by z / 2.
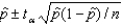 so that we can use it to construct a (1 - ) confidence interval estimate for the population proportion p?
so that we can use it to construct a (1 - ) confidence interval estimate for the population proportion p?A) should be replaced by p.
B) t should be replaced by z .
C) t should be replaced by t / 2.
D) t should be replaced by z / 2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following would be an appropriate null hypothesis?
A) The population proportion is equal to 0.60.
B) The sample proportion is equal to 0.60.
C) The population proportion is not equal to 0.60.
D) All of these choices are true.
A) The population proportion is equal to 0.60.
B) The sample proportion is equal to 0.60.
C) The population proportion is not equal to 0.60.
D) All of these choices are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the following statements is true?
A) The sample mean is relatively more efficient than the sample median.
B) The version of the sample variance where you divide by n is biased.
C) The sample mean is consistent.
D) All of these choices are true.
A) The sample mean is relatively more efficient than the sample median.
B) The version of the sample variance where you divide by n is biased.
C) The sample mean is consistent.
D) All of these choices are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
An unbiased estimator of a population parameter is defined as:
A) an estimator whose expected value is equal to the parameter.
B) an estimator whose variance is equal to one.
C) an estimator whose expected value is equal to zero.
D) an estimator whose variance goes to zero as the sample size goes to infinity.
A) an estimator whose expected value is equal to the parameter.
B) an estimator whose variance is equal to one.
C) an estimator whose expected value is equal to zero.
D) an estimator whose variance goes to zero as the sample size goes to infinity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
An estimator is said to be consistent if:
A) the difference between the estimator and the population parameter grows smaller as the sample size grows larger.
B) it is an unbiased estimator.
C) the variance of the estimator is zero.
D) the difference between the estimator and the population parameter stays the same as the sample size grows larger.
A) the difference between the estimator and the population parameter grows smaller as the sample size grows larger.
B) it is an unbiased estimator.
C) the variance of the estimator is zero.
D) the difference between the estimator and the population parameter stays the same as the sample size grows larger.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
A point estimator is defined as:
A) a range of values that estimates an unknown population parameter.
B) a single value that estimates an unknown population parameter.
C) a range of values that estimates an unknown sample statistic.
D) a single value that estimates an unknown sample statistic.
A) a range of values that estimates an unknown population parameter.
B) a single value that estimates an unknown population parameter.
C) a range of values that estimates an unknown sample statistic.
D) a single value that estimates an unknown sample statistic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
After calculating the sample size needed to estimate a population proportion to within 0.04, your statistics professor told you the maximum allowable error must be reduced to just .01. If the original calculation led to a sample size of 800, the sample size will now have to be:
A) 800
B) 3,200
C) 6,400
D) 12,800
A) 800
B) 3,200
C) 6,400
D) 12,800

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The width of a confidence interval estimate for a proportion will be:
A) narrower for 90% confidence than for 95% confidence.
B) wider for a sample size of 100 than for a sample size of 50.
C) narrower for 99% confidence than for 95% confidence.
D) narrower when the sample proportion if 0.50 than when the sample proportion is 0.20.
A) narrower for 90% confidence than for 95% confidence.
B) wider for a sample size of 100 than for a sample size of 50.
C) narrower for 99% confidence than for 95% confidence.
D) narrower when the sample proportion if 0.50 than when the sample proportion is 0.20.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
In selecting the sample size to estimate the population proportion p, if we have no knowledge of even the approximate values of the sample proportion 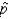 , we:
, we:
A) take another sample and estimate.
B) take two more samples and find the average of their.
C) let= 0.50.
D) let= 0.95.
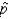 , we:
, we:A) take another sample and estimate.
B) take two more samples and find the average of their.
C) let= 0.50.
D) let= 0.95.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which of the following statements is correct?
A) The sample mean is an unbiased estimator of the population mean.
B) The sample proportion is an unbiased estimator of the population proportion.
C) The difference between two sample means is an unbiased estimator of the difference between two population means.
D) All of these choices are true.
A) The sample mean is an unbiased estimator of the population mean.
B) The sample proportion is an unbiased estimator of the population proportion.
C) The difference between two sample means is an unbiased estimator of the difference between two population means.
D) All of these choices are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of the following is not a characteristic for a good estimator?
A) Being unbiased
B) Being consistent
C) Having relative efficiency
D) All of these choices are true.
A) Being unbiased
B) Being consistent
C) Having relative efficiency
D) All of these choices are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
If we have some idea about the value of sample proportion 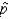 , we use that value in determining the sample size needed to estimate the population proportion p.
, we use that value in determining the sample size needed to estimate the population proportion p.
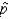 , we use that value in determining the sample size needed to estimate the population proportion p.
, we use that value in determining the sample size needed to estimate the population proportion p.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
When determining the sample size needed for a proportion for a given level of confidence and sampling error, the closer to 0.50 that p is estimated to be:
A) the smaller the sample size required.
B) the larger the sample size required.
C) the sample size is not affected.
D) the effect cannot be determined from the information given.
A) the smaller the sample size required.
B) the larger the sample size required.
C) the sample size is not affected.
D) the effect cannot be determined from the information given.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The librarian at the New York City Public Library has asked her assistant for an interval estimate of the mean number of books checked out each day. The assistant took a sample and found the mean to be 880 books. She provides the librarian with an interval estimate of between 790 and 970 books checked out per day. An efficient, unbiased point estimate of the number of books checked out each day at the New York City Public Library is:
A) 790
B) 880
C) 90
D) None of these choices.
A) 790
B) 880
C) 90
D) None of these choices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The 95% confidence interval would indicate that, for this shipment, the proportion of defective fuses is between 0 and 0.28.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following would be an appropriate alternative hypothesis?
A) The population proportion is less than 0.65.
B) The sample proportion is less than 0.65.
C) The population proportion is equal to 0.65.
D) The sample proportion is equal to 0.65.
A) The population proportion is less than 0.65.
B) The sample proportion is less than 0.65.
C) The population proportion is equal to 0.65.
D) The sample proportion is equal to 0.65.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
When a population is small, it is necessary to include the ____________________ factor in our hypothesis tests and confidence interval estimators for p.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
A survey claims that 9 out of 10 doctors recommend aspirin for their patients with headaches. To test this claim against the alternative that the actual proportion of doctors who recommend aspirin is less than 0.90, a random sample of 100 doctors' results in 83 who indicate that they recommend aspirin. The value of the test statistic in this problem is approximately equal to:
A) -1.67
B) -2.33
C) -1.86
D) -0.14
A) -1.67
B) -2.33
C) -1.86
D) -0.14

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
It is intuitively reasonable to expect that a larger sample will produce more ____________________ results.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The sampling error for a confidence interval is also defined as the ____________________ of ____________________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
____________________ estimators reflect the effects of larger sample sizes, but ____________________ estimators do not.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The formula 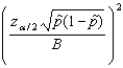 is used to find the sample size needed to estimate a population proportion. In this formula, B represents the ____________________ on the error of estimation.
is used to find the sample size needed to estimate a population proportion. In this formula, B represents the ____________________ on the error of estimation.
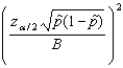 is used to find the sample size needed to estimate a population proportion. In this formula, B represents the ____________________ on the error of estimation.
is used to find the sample size needed to estimate a population proportion. In this formula, B represents the ____________________ on the error of estimation.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
An unbiased estimator is ____________________ if its variance gets smaller as n gets larger.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The sample ____________________ is relatively more efficient than the sample ____________________ when estimating the population mean.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The sample ____________________ is an unbiased estimator for the population mean.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Estimating or testing for p is used in situations when the data are ____________________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
To produce a confidence interval estimator for the total, we multiply the lower and upper confidence limits of the interval estimator of p by ____________________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A(n) ____________________ estimator of a population parameter is an estimator whose expected value is equal to that parameter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The version of the sample variance where you divide by ____________________ gives you an unbiased estimator of the population variance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The test statistic for p is approximately normal when np and n(1 - p) are both ____________________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The formula 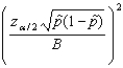 is used to find the ____________________ to estimate a population proportion.
is used to find the ____________________ to estimate a population proportion.
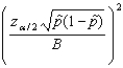 is used to find the ____________________ to estimate a population proportion.
is used to find the ____________________ to estimate a population proportion.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
If there are two unbiased estimators of the same parameter, the one whose variance is smaller is said to be relatively more ____________________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
____________________ estimators do not have the capacity to reflect the effects of larger sample sizes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
An interval estimator estimates the value of an unknown ____________________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The test statistic for p is approximately normal when ____________________ and ____________________ are both greater than 5.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
From a sample of 400 items, 14 are found to be defective. The point estimate of the population proportion defective will be:
A) 0.035
B) 0.05
C) 14
D) 28.57
A) 0.035
B) 0.05
C) 14
D) 28.57

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
If the population standard deviation is guesstimated, and it turned out to be larger than you assumed, then the sample size you calculated is ____________________ than it needs to be.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Draw a sampling distribution of an unbiased estimator for .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Socialist Party Voters: A pollster in Italy wants to challenge a claim that 5% of the registered voters in his country are Socialists; he thinks the percentage is lower than that. In a test of hypothesis, H0: p = 0.05 vs. H1: p < 0.05, his random sample of size 1,000 registered voters revealed that the number of Socialists was 40.
-{Compute the p-value and explain how to use it to test the hypotheses.
-{Compute the p-value and explain how to use it to test the hypotheses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Define unbiasedness.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Statisticians can control the ____________________ of a confidence interval by determining the sample size necessary to produce the desired results.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
When determining the required sample size for a confidence interval, you need to know the population ____________________, the confidence ____________________, and the ____________________ on the error of estimation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The error of estimation is the ____________________ between an estimator and the parameter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Is the sample mean a consistent estimator of the population mean? Explain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Explain briefly why interval estimators are preferred to point estimators.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Define relative efficiency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The bound on the error of estimation is the ____________________ amount of sampling error that we are willing to tolerate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Draw a sampling distribution of a biased estimator for .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Socialist Party Voters: A pollster in Italy wants to challenge a claim that 5% of the registered voters in his country are Socialists; he thinks the percentage is lower than that. In a test of hypothesis, H0: p = 0.05 vs. H1: p < 0.05, his random sample of size 1,000 registered voters revealed that the number of Socialists was 40.
-Test the hypotheses at the 5% significance level.
-Test the hypotheses at the 5% significance level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Draw the sampling distribution of two unbiased estimators for , one of which is relatively efficient.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
If the population standard deviation is guesstimated, and it turned out to be smaller than you assumed, then the sample size you calculated is ____________________ than it needs to be.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Define consistency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Draw sampling distributions of a consistent estimator for where one sample mean is larger than the other.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Because n is an integer and we want the bound on the error of estimation to be no more than a given amount, any non-integer value found for n must always be rounded ____________________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
As the bound on the error of estimation decreases, the sample size ____________________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
If the bound on the error of estimation decreases, the sample size ____________________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



