Deck 17: Electrochemistry-The Quest for Clean Energy
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/174
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 17: Electrochemistry-The Quest for Clean Energy
1
Which one of the following items does NOT characterize a reducing agent?
A)A reducing agent loses electrons.
B)A reducing agent causes another species to be reduced.
C)The oxidation number of a reducing agent increases.
D)A good reducing agent is a metal in a high oxidation state,such as Mn7+.
E)An example of a good reducing agent is an alkali metal,such as Na.
A)A reducing agent loses electrons.
B)A reducing agent causes another species to be reduced.
C)The oxidation number of a reducing agent increases.
D)A good reducing agent is a metal in a high oxidation state,such as Mn7+.
E)An example of a good reducing agent is an alkali metal,such as Na.
A good reducing agent is a metal in a high oxidation state,such as Mn7+.
2
You are to determine the amount of vitamin C (ascorbic acid)in orange juice by redox titration.The ascorbate,C6H7O6-,in the juice reacts with triiodide,I3- to form dehydroascorbate,C6H5O6-,and iodide,I-.How many electrons are transferred in the reaction? The reaction describing the titration is given below. C6H7O6-(aq)+ I3-(aq) C6H5O6-(aq)+ 2 H+(aq)+ 3 I-(aq)
A)1
B)2
C)4
D)0
E)It is impossible to tell.
A)1
B)2
C)4
D)0
E)It is impossible to tell.
2
3
Glancing at a periodic table,where do you expect to find elements that are good reducing agents?
A)in groups 16 and 17
B)on the left
C)in the middle
D)at the bottom
E)in group 17
A)in groups 16 and 17
B)on the left
C)in the middle
D)at the bottom
E)in group 17
on the left
4
Consider the reaction,Au(s)+ Cl2(g) AuCl4-(aq). Which statement,A-D,is NOT correct? If more than one is NOT correct,respond E.
A)Au loses three electrons in the oxidation half-reaction.
B)Each chlorine atom gains two electrons in the reduction half-reaction.
C)Au is the oxidizing agent.
D)There is no way to balance this equation as written.
E)More than one statement is NOT correct.
A)Au loses three electrons in the oxidation half-reaction.
B)Each chlorine atom gains two electrons in the reduction half-reaction.
C)Au is the oxidizing agent.
D)There is no way to balance this equation as written.
E)More than one statement is NOT correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 174 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The following reaction occurs in acidic solution.Identify the correct half-reaction that applies to the oxidizing agent.(Note: The equation is not balanced.) Cr2O72-(aq)+ C2H5OH(aq) C2H4O(aq)+ Cr3+(aq)
A)C2H5OH C2H4O + 2 H+ + 2 e-
B)Cr2O72- + 3 e- Cr3+ + 7 H2O
C)C2H5OH + 2 e-+ 2 H+ C2H4O + H2O
D)14 H+ + Cr2O72- 2 Cr3+ + 7 H2O + 8 e-
E)14 H+ + Cr2O72- + 6 e- 2 Cr3+ + 7 H2O
A)C2H5OH C2H4O + 2 H+ + 2 e-
B)Cr2O72- + 3 e- Cr3+ + 7 H2O
C)C2H5OH + 2 e-+ 2 H+ C2H4O + H2O
D)14 H+ + Cr2O72- 2 Cr3+ + 7 H2O + 8 e-
E)14 H+ + Cr2O72- + 6 e- 2 Cr3+ + 7 H2O

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 174 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The following reaction occurs in basic solution.Identify the reducing agent.(Note: The equation is not balanced.) Zn(s)+ NO3-(aq) Zn(OH)42-(aq)+ NH3(aq)
A)Zn(s)
B)NO3-(aq)
C)OH-(aq)
D)H2O( )
)
E)NH3(aq)
A)Zn(s)
B)NO3-(aq)
C)OH-(aq)
D)H2O(
 )
)E)NH3(aq)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 174 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Reduction is the ________
A)gain of electrons.
B)loss of electrons.
C)gain of protons.
D)loss of protons.
E)loss of mass.
A)gain of electrons.
B)loss of electrons.
C)gain of protons.
D)loss of protons.
E)loss of mass.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 174 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The following reaction occurs in basic solution.Identify the correct oxidation half-reaction.(Note: The equation is not balanced.) Zn(s)+ NO3-(aq) Zn(OH)42-(aq)+ NH3(aq)
A)Zn Zn(OH)42- + 2 e-
B)Zn + 2 H2O Zn(OH)42- + 2 e-
C)Zn + 4 OH- Zn(OH)42- + 2 e-
D)NO3- + 8 e- NH3
E)NO3- + 6 H2O + 8 e- NH3 + 9 OH-
A)Zn Zn(OH)42- + 2 e-
B)Zn + 2 H2O Zn(OH)42- + 2 e-
C)Zn + 4 OH- Zn(OH)42- + 2 e-
D)NO3- + 8 e- NH3
E)NO3- + 6 H2O + 8 e- NH3 + 9 OH-

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 174 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The following reaction occurs in basic solution.Identify the correct reduction half-reaction.(Note: The equation is not balanced.) Zn(s)+ NO3-(aq) Zn(OH)42-(aq)+ NH3(aq)
A)Zn Zn(OH)42- + 2 e-
B)Zn + 2 H2O Zn(OH)42- + 2 e-
C)Zn + 4 OH- Zn(OH)42- + 2 e-
D)NO3- + 8 e- NH3
E)NO3- + 6 H2O + 8 e- NH3 + 9 OH-
A)Zn Zn(OH)42- + 2 e-
B)Zn + 2 H2O Zn(OH)42- + 2 e-
C)Zn + 4 OH- Zn(OH)42- + 2 e-
D)NO3- + 8 e- NH3
E)NO3- + 6 H2O + 8 e- NH3 + 9 OH-

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 174 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The following reaction occurs in basic solution.Identify the oxidizing agent.(Note: The equation is not balanced.) Zn(s)+ NO3-(aq) Zn(OH)42-(aq)+ NH3(aq)
A)H2O( )
)
B)NO3-(aq)
C)OH-(aq)
D)Zn(s)
E)NH3(aq)
A)H2O(
 )
)B)NO3-(aq)
C)OH-(aq)
D)Zn(s)
E)NH3(aq)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 174 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Glancing at a periodic table,where do you expect to find elements that are good oxidizing agents?
A)at the bottom left
B)in the top left
C)in the transition metals
D)at the bottom
E)on the right (except for the last group)
A)at the bottom left
B)in the top left
C)in the transition metals
D)at the bottom
E)on the right (except for the last group)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 174 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
What is the oxidation number of chromium in the ionic compound ammonium dichromate,(NH4)2Cr2O7?
A)+3
B)+4
C)+5
D)+6
E)+7
A)+3
B)+4
C)+5
D)+6
E)+7

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 174 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Proteins containing a certain functional group (identified as RSH)can be titrated with triiodide ion to produce another functional group (identified as RSSR).The reaction equation is given below.What is oxidized and what is reduced in this reaction? 2 RSH(aq)+ I3-(aq) 3 I-(aq)+ RSSR(aq)+ 2 H+(aq)
A)RSH is oxidized,I3- is reduced.
B)RSH is reduced,I is oxidized.
C)Both RSH and I are oxidized.
D)Both RSH and I are reduced.
E)This reaction is not oxidation-reduction.
A)RSH is oxidized,I3- is reduced.
B)RSH is reduced,I is oxidized.
C)Both RSH and I are oxidized.
D)Both RSH and I are reduced.
E)This reaction is not oxidation-reduction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 174 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Oxidation is the ________
A)gain of electrons.
B)loss of electrons.
C)gain of protons.
D)loss of protons.
E)loss of mass.
A)gain of electrons.
B)loss of electrons.
C)gain of protons.
D)loss of protons.
E)loss of mass.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 174 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Oxidation refers to ________
A)an increase in oxidation number.
B)a decrease in oxidation number.
C)a gain in the number of protons.
D)an increase in the atomic number.
E)an increase in mass.
A)an increase in oxidation number.
B)a decrease in oxidation number.
C)a gain in the number of protons.
D)an increase in the atomic number.
E)an increase in mass.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 174 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Consider the reaction,Sn + Au3+ Sn2+ + Au.Which of the following is NOT correct? If more than one is NOT correct,respond E.
A)The oxidation half-reaction is Sn Sn2+ + 2 e-.
B)The reduction half-reaction is Au3+ + 3 e- Au.
C)Au3+ is the oxidizing agent.
D)The equation is balanced as written.
E)More than one statement is NOT correct.
A)The oxidation half-reaction is Sn Sn2+ + 2 e-.
B)The reduction half-reaction is Au3+ + 3 e- Au.
C)Au3+ is the oxidizing agent.
D)The equation is balanced as written.
E)More than one statement is NOT correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 174 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
In the smelting of iron from iron oxide according to the equation Fe2O3(s)+ 3 CO(g) 2 Fe(s)+ 3 CO2(g),what is the change in oxidation number for iron?
A)"+3"
B)"+2"
C)"0"
D)"-2"
E)"-3"
A)"+3"
B)"+2"
C)"0"
D)"-2"
E)"-3"

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 174 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Reduction refers to ________
A)loss of mass.
B)an increase in oxidation number.
C)a decrease in oxidation number.
D)a decrease in the atomic number.
E)a gain in the number of protons.
A)loss of mass.
B)an increase in oxidation number.
C)a decrease in oxidation number.
D)a decrease in the atomic number.
E)a gain in the number of protons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 174 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
When hydrogen reacts with a metal to form a hydride (e.g.,CaH2),what are the oxidation numbers of the calcium (in this case)and hydrogen,respectively,in the product?
A)"-2 and +1"
B)"+1 and -2"
C)"+2 and -1
D)"0 and 0"
E)"+2 and -2"
A)"-2 and +1"
B)"+1 and -2"
C)"+2 and -1
D)"0 and 0"
E)"+2 and -2"

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 174 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The following reaction occurs in acidic solution.Identify the correct half-reaction that applies to the reducing agent.(Note: The equation is not balanced.) Cr2O72-(aq)+ C2H5OH(aq) C2H4O(aq)+ Cr3+(aq)
A)C2H5OH C2H4O + 2 H+ + 2 e-
B)Cr2O72- + 3 e- Cr3+ + 7 H2O
C)C2H5OH + 2 e-+ 2 H+ C2H4O + H2O
D)14 H+ + Cr2O72- 2 Cr3+ + 7 H2O + 8 e-
E)14 H+ + Cr2O72- + 6 e- 2 Cr3+ + 7 H2O
A)C2H5OH C2H4O + 2 H+ + 2 e-
B)Cr2O72- + 3 e- Cr3+ + 7 H2O
C)C2H5OH + 2 e-+ 2 H+ C2H4O + H2O
D)14 H+ + Cr2O72- 2 Cr3+ + 7 H2O + 8 e-
E)14 H+ + Cr2O72- + 6 e- 2 Cr3+ + 7 H2O

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 174 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
A voltaic cell is constructed based on the oxidation of zinc metal and the reduction of silver (I)ions.Solutions of 1.00 M silver nitrate and zinc nitrate also were used.The anode is on the left; the cathode,on the right.Where does oxidation occur? 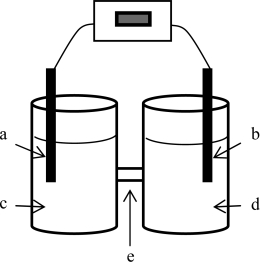
A)a
B)b
C)c
D)d
E)e

A)a
B)b
C)c
D)d
E)e

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 174 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Balance the chemical equation for the following redox reaction under basic aqueous conditions with the smallest whole-number coefficients possible using the half-reaction method.What is the coefficient of ClO-? ClO-(aq)+ Pb(OH)42-(aq) Cl-(aq)+ PbO2(s)
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)5
E)10
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)5
E)10

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 174 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Based on the cell diagram,Fe(s)| Fe2+(aq)|| O2(g)| H+(aq),H2O(  )| Pt(s),which of the following statements is NOT correct?
)| Pt(s),which of the following statements is NOT correct?
A)Fe is oxidized at the anode.
B)O2 is reduced at the cathode.
C)H+ is oxidized at the anode.
D)Four moles of electrons are transferred in the balanced redox reaction.
E)The reaction occurs under acidic conditions.
 )| Pt(s),which of the following statements is NOT correct?
)| Pt(s),which of the following statements is NOT correct?A)Fe is oxidized at the anode.
B)O2 is reduced at the cathode.
C)H+ is oxidized at the anode.
D)Four moles of electrons are transferred in the balanced redox reaction.
E)The reaction occurs under acidic conditions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 174 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Balance the chemical equation for the following redox reaction under basic aqueous conditions with the smallest whole-number coefficients possible using the half-reaction method.How many moles of electrons are transferred in the balanced reaction? ClO3-(aq)+ N2H4(g) Cl-(aq)+ NO(g)
A)6
B)8
C)16
D)24
E)48
A)6
B)8
C)16
D)24
E)48

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 174 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A voltaic cell is constructed based on the oxidation of zinc metal and the reduction of silver (I)ions.Solutions of 1.00 M silver nitrate and zinc nitrate also were used.The anode is on the left; the cathode,on the right.Where does reduction occur? 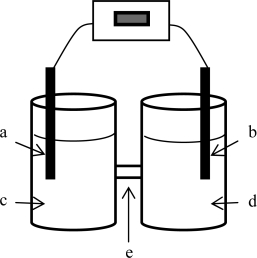
A)a
B)b
C)c
D)d
E)e

A)a
B)b
C)c
D)d
E)e

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 174 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which statement about a cathode in a voltaic cell is NOT correct?
A)Oxidation occurs at the cathode.
B)Reduction occurs at the cathode.
C)Usually the cathode is a metal strip.
D)In the external circuit,electrons flow toward the cathode.
E)Chemical species can have their oxidation number decreased at the cathode.
A)Oxidation occurs at the cathode.
B)Reduction occurs at the cathode.
C)Usually the cathode is a metal strip.
D)In the external circuit,electrons flow toward the cathode.
E)Chemical species can have their oxidation number decreased at the cathode.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 174 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A voltaic cell is constructed based on the reaction of Ag(CN)2-(aq)with Cr(s)producing Ag(s)and Cr3+(s).Identify the correct cell diagram.
A)Ag(CN)2-(aq)| Cr(s)|| Ag(s)| Cr3+(aq)
B)Ag(s)| Cr3+(aq)|| Ag(CN)2-(aq)| Cr(s)
C)Cr(s)| Cr3+(aq)|| Ag(s)| Ag(CN)2-(aq)
D)Ag(CN)2-(aq)| Ag(s)|| Cr(s)| Cr3+(aq)
E)Cr(s)| Cr3+(aq)|| Ag(CN)2-(aq)| Ag(s)
A)Ag(CN)2-(aq)| Cr(s)|| Ag(s)| Cr3+(aq)
B)Ag(s)| Cr3+(aq)|| Ag(CN)2-(aq)| Cr(s)
C)Cr(s)| Cr3+(aq)|| Ag(s)| Ag(CN)2-(aq)
D)Ag(CN)2-(aq)| Ag(s)|| Cr(s)| Cr3+(aq)
E)Cr(s)| Cr3+(aq)|| Ag(CN)2-(aq)| Ag(s)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 174 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Balance the chemical equation for the following redox reaction under acidic aqueous conditions with the smallest whole-number coefficients possible using the half-reaction method.What is the coefficient of C2H5OH? Cr2O72-(aq)+ C2H5OH(aq) Cr3+(aq)+ CO2(g)
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4
E)5
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4
E)5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 174 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which statement regarding voltaic cells is NOT correct?
A)Reduction occurs at the cathode.
B)Anions move through the barrier or bridge toward the electrode where oxidation is occurring.
C)The electrode where reduction is occurring is represented by a positive sign.
D)Electrons flow in the external circuit from the cathode to the anode.
E)Electrons flow in the external circuit toward the electrode represented by a positive sign.
A)Reduction occurs at the cathode.
B)Anions move through the barrier or bridge toward the electrode where oxidation is occurring.
C)The electrode where reduction is occurring is represented by a positive sign.
D)Electrons flow in the external circuit from the cathode to the anode.
E)Electrons flow in the external circuit toward the electrode represented by a positive sign.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 174 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Balance the chemical equation for the following redox reaction under acidic aqueous conditions with the smallest whole-number coefficients possible using the half-reaction method.What is the coefficient of Cl-? Cl2(g)+ S2O32-(aq) Cl-(aq)+ SO42-(aq)
A)2
B)4
C)5
D)8
E)10
A)2
B)4
C)5
D)8
E)10

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 174 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A voltaic cell is constructed based on the reaction of Zn(s)with Pb2+(aq)producing Zn2+(aq)and Pb(s).Identify the correct cell diagram.
A)Zn2+(aq)| Pb2+(aq)|| Zn(s)| Pb(s)
B)Zn(s)| Zn2+(aq)|| Pb2+(aq)| Pb(s)
C)Zn(s)| Pb2+(aq)|| Zn2+(aq)| Pb(s)
D)Pb2+(aq)| Pb(s)|| Zn(s)| Zn2+(aq)
E)Pb(s)| Pb2+(aq)|| Zn2+(aq)| Zn(s)
A)Zn2+(aq)| Pb2+(aq)|| Zn(s)| Pb(s)
B)Zn(s)| Zn2+(aq)|| Pb2+(aq)| Pb(s)
C)Zn(s)| Pb2+(aq)|| Zn2+(aq)| Pb(s)
D)Pb2+(aq)| Pb(s)|| Zn(s)| Zn2+(aq)
E)Pb(s)| Pb2+(aq)|| Zn2+(aq)| Zn(s)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 174 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A voltaic cell is constructed based on the oxidation of zinc metal and the reduction of silver (I)ions.Solutions of 1.00 M silver nitrate and zinc nitrate also were used.The anode is on the left; the cathode,on the right.Locate the zinc nitrate solution on the diagram. 
A)a
B)b
C)c
D)d
E)e

A)a
B)b
C)c
D)d
E)e

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 174 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Balance the chemical equation for the following redox reaction under acidic aqueous conditions with the smallest whole-number coefficients possible using the half-reaction method.How many moles of electrons are transferred in the balanced reaction? Te(s)+ ClO3-(aq) H6TeO6(aq)+ Cl2(g)
A)5
B)6
C)10
D)15
E)30
A)5
B)6
C)10
D)15
E)30

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 174 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A voltaic cell is constructed based on the oxidation of zinc metal and the reduction of silver (I)ions.Solutions of 1.00 M silver nitrate and zinc nitrate also were used.The anode is on the left; the cathode,on the right.Locate the silver electrode on the diagram. 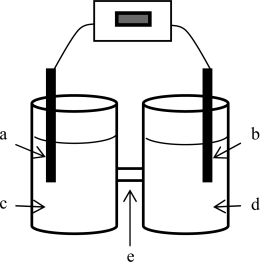
A)a
B)b
C)c
D)d
E)e

A)a
B)b
C)c
D)d
E)e

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 174 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of the following statements regarding reduction potentials is NOT correct?
A)Higher reduction potentials are associated with stronger reducing agents.
B)As reduction potential increases,the ease of reduction increases.
C)A substance with a higher reduction potential will oxidize a substance with a lower reduction potential.
D)Metals such as sodium and potassium are strong reducing agents.
E)The reduction potential of a substance depends on conditions such as concentration and pH.
A)Higher reduction potentials are associated with stronger reducing agents.
B)As reduction potential increases,the ease of reduction increases.
C)A substance with a higher reduction potential will oxidize a substance with a lower reduction potential.
D)Metals such as sodium and potassium are strong reducing agents.
E)The reduction potential of a substance depends on conditions such as concentration and pH.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 174 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
A voltaic cell is constructed based on the reaction of Br -(aq)with Cl2(g)producing Cl -(g)and Br2(  ),with platinum serving as inert electrodes.Identify the correct cell diagram.
),with platinum serving as inert electrodes.Identify the correct cell diagram.
A)Br2( )| Br-(aq)|| Cl2(g)| Cl-(aq)
)| Br-(aq)|| Cl2(g)| Cl-(aq)
B)Pt(s)| Cl2(g)| Cl-(aq)|| Br2( )| Br -(aq)| Pt(s)
)| Br -(aq)| Pt(s)
C)Pt(s)| Br--(aq)| Cl2(g)|| Br2( )| Cl-(aq)| Pt(s)
)| Cl-(aq)| Pt(s)
D)Pt(s)| Br -(aq)| Br2( )|| Cl2(g)| Cl-(aq)| Pt(s)
)|| Cl2(g)| Cl-(aq)| Pt(s)
E)Pt(s)| Br2( )| Br -(aq)|| Cl2(g)| Cl-(aq)| Pt(s)
)| Br -(aq)|| Cl2(g)| Cl-(aq)| Pt(s)
 ),with platinum serving as inert electrodes.Identify the correct cell diagram.
),with platinum serving as inert electrodes.Identify the correct cell diagram.A)Br2(
 )| Br-(aq)|| Cl2(g)| Cl-(aq)
)| Br-(aq)|| Cl2(g)| Cl-(aq)B)Pt(s)| Cl2(g)| Cl-(aq)|| Br2(
 )| Br -(aq)| Pt(s)
)| Br -(aq)| Pt(s)C)Pt(s)| Br--(aq)| Cl2(g)|| Br2(
 )| Cl-(aq)| Pt(s)
)| Cl-(aq)| Pt(s)D)Pt(s)| Br -(aq)| Br2(
 )|| Cl2(g)| Cl-(aq)| Pt(s)
)|| Cl2(g)| Cl-(aq)| Pt(s)E)Pt(s)| Br2(
 )| Br -(aq)|| Cl2(g)| Cl-(aq)| Pt(s)
)| Br -(aq)|| Cl2(g)| Cl-(aq)| Pt(s)
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 174 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Balance the chemical equation for the following redox reaction under basic aqueous conditions with the smallest whole-number coefficients possible using the half-reaction method.On which side does OH- appear,and what is its coefficient? ClO3-(aq)+ N2H4(g) Cl-(aq)+ NO(g)
A)right,2
B)left,4
C)left,1
D)right,3
E)OH- is not required to balance the equation
A)right,2
B)left,4
C)left,1
D)right,3
E)OH- is not required to balance the equation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 174 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which statement about a voltaic cell is NOT correct?
A)Usually the cathode is a metal strip.
B)Reduction occurs at the cathode.
C)Electrons are produced at the cathode.
D)In the external circuit,electrons flow toward the cathode.
E)Chemical species can have their oxidation number decreased at the cathode.
A)Usually the cathode is a metal strip.
B)Reduction occurs at the cathode.
C)Electrons are produced at the cathode.
D)In the external circuit,electrons flow toward the cathode.
E)Chemical species can have their oxidation number decreased at the cathode.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 174 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Balance the chemical equation for the following redox reaction under acidic aqueous conditions with the smallest whole-number coefficients possible using the half-reaction method.On which side does H2O(l)appear,and what is its coefficient? Te(s)+ ClO3-(aq) H6TeO6(aq)+ Cl2(g)
A)left,6
B)right,6
C)left,12
D)right,12
E)left,30
A)left,6
B)right,6
C)left,12
D)right,12
E)left,30

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 174 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
A voltaic cell is constructed based on the oxidation of zinc metal and the reduction of silver (I)ions.Solutions of 1.00 M silver nitrate and zinc nitrate also were used.The anode is on the left; the cathode,on the right.Locate the silver nitrate solution on the diagram. 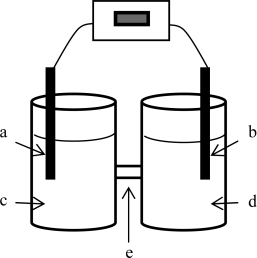
A)a
B)b
C)c
D)d
E)e

A)a
B)b
C)c
D)d
E)e

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 174 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which one of the following items does NOT characterize an oxidizing agent?
A)An oxidizing agent has a high reduction potential.
B)An oxidizing agent causes another species to be oxidized.
C)An oxidizing agent gains electrons in a redox reaction.
D)A good oxidizing agent is a metal in a high oxidation state,such as Mn(VII).
E)An example of a good oxidizing agent is an alkali metal,such as Na.
A)An oxidizing agent has a high reduction potential.
B)An oxidizing agent causes another species to be oxidized.
C)An oxidizing agent gains electrons in a redox reaction.
D)A good oxidizing agent is a metal in a high oxidation state,such as Mn(VII).
E)An example of a good oxidizing agent is an alkali metal,such as Na.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 174 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Silver tarnish (Ag2S)can be removed by immersing silverware in a hot solution of baking soda (NaHCO3)in a pan lined with aluminum foil; however,foul-smelling hydrogen sulfide gas (H2S)is produced.Which one of the following reactions does not represent part or all of what is happening? 
A)Al Al3+ + 3 e-
B)Ag+ + e- Ag
C)2 HCO3-+S2- H2S + 2 CO32-
D)3 Ag2S + 2 Al +3 H2O 6 Ag + Al2O3 +3 H2S
E)2 HCO3-+Ag2S H2S + 2 CO32- + 2 Ag

A)Al Al3+ + 3 e-
B)Ag+ + e- Ag
C)2 HCO3-+S2- H2S + 2 CO32-
D)3 Ag2S + 2 Al +3 H2O 6 Ag + Al2O3 +3 H2S
E)2 HCO3-+Ag2S H2S + 2 CO32- + 2 Ag

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 174 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Identify the strongest reducing agent in the following half-reactions.The standard reduction potentials are listed.
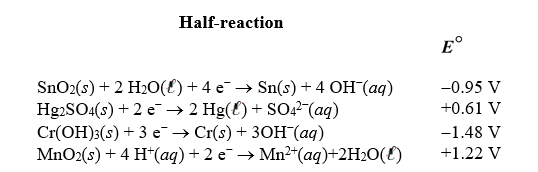
A)Cr
B)MnO2
C)Hg2SO4
D)Sn
E)Hg
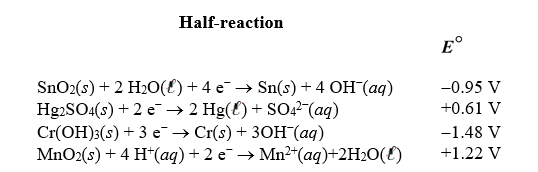
A)Cr
B)MnO2
C)Hg2SO4
D)Sn
E)Hg

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 174 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Based on the information in the table of standard reduction potentials below,what is the standard cell potential for an electrochemical cell that has iron (Fe)and magnesium (Mg)electrodes immersed in 1M Fe3+ and Mg2+ solutions? Also,identify the cathode. 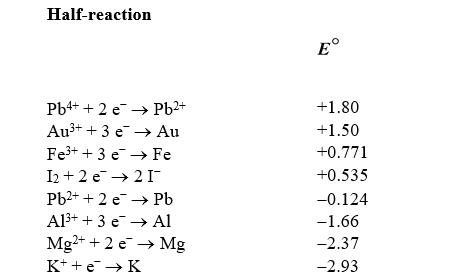
A)"+1.60 V with Fe as the cathode"
B)"+3.14 V with Mg as the cathode"
C)"-3.14 V with Fe as the cathode"
D)"-3.14 V with Mg as the cathode"
E)"+3.14 V with Fe as the cathode"
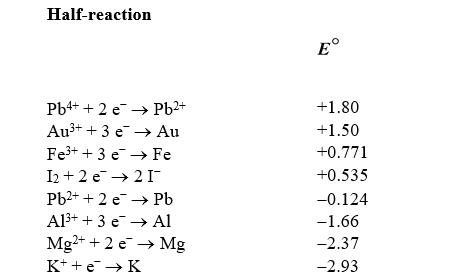
A)"+1.60 V with Fe as the cathode"
B)"+3.14 V with Mg as the cathode"
C)"-3.14 V with Fe as the cathode"
D)"-3.14 V with Mg as the cathode"
E)"+3.14 V with Fe as the cathode"

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 174 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Using the following data,determine the standard cell potential 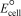 for the electrochemical cell constructed using the following reaction: Zn(s)+ Pb2+(aq) Zn2+(aq)+ Pb(s). Half-reaction Standard reduction potential
for the electrochemical cell constructed using the following reaction: Zn(s)+ Pb2+(aq) Zn2+(aq)+ Pb(s). Half-reaction Standard reduction potential
Zn2+(aq)+ 2 e- Zn(s) -0.763
Pb2+(aq)+ 2 e- Pb(s) -0.126
A)"+0.637 V
B)"-0.637 V"
C)"+1.274 V"
D)"-0.889 V"
E)"+0.889 V"
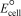 for the electrochemical cell constructed using the following reaction: Zn(s)+ Pb2+(aq) Zn2+(aq)+ Pb(s). Half-reaction Standard reduction potential
for the electrochemical cell constructed using the following reaction: Zn(s)+ Pb2+(aq) Zn2+(aq)+ Pb(s). Half-reaction Standard reduction potentialZn2+(aq)+ 2 e- Zn(s) -0.763
Pb2+(aq)+ 2 e- Pb(s) -0.126
A)"+0.637 V
B)"-0.637 V"
C)"+1.274 V"
D)"-0.889 V"
E)"+0.889 V"

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 174 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Based on the information in the table of standard reduction potentials below,calculate  for Mg2+ + 2 I - Mg + I2.
for Mg2+ + 2 I - Mg + I2. 
A)"+1.84 V"
B)"+3.44 V"
C)"-3.44 V"
D)"-2.91 V"
E)"+2.91 V"
 for Mg2+ + 2 I - Mg + I2.
for Mg2+ + 2 I - Mg + I2. 
A)"+1.84 V"
B)"+3.44 V"
C)"-3.44 V"
D)"-2.91 V"
E)"+2.91 V"

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 174 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The bromate ion,BrO3-,can form in drinking water if ozone disinfection is performed under basic conditions when bromide ions are present.If this redox reaction were performed in an electrochemical cell,what would the standard cell potential be? The relevant reduction reactions and standard reduction potentials are given below. 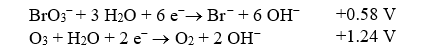
A)"-3.14 V"
B)"+3.14 V"
C)"+1.05 V"
D)"+1.82 V"
E)"+0.66 V"
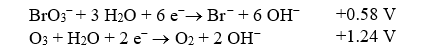
A)"-3.14 V"
B)"+3.14 V"
C)"+1.05 V"
D)"+1.82 V"
E)"+0.66 V"

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 174 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Using the following standard reduction potentials,calculate the cell potential for the voltaic cell that would have the largest 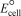 .
.

A)2.70 V
B)2.43 V
C)2.17 V
D)2.09 V
E)1.83 V
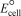 .
. 
A)2.70 V
B)2.43 V
C)2.17 V
D)2.09 V
E)1.83 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 174 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Use the table of standard reduction potentials below to identify which of the following statements is NOT correct.

A)Pb4+ will oxidize all of the species on the right side of the arrows in the other half-reactions.
B)K+ will reduce all of the species on the left side of the arrows in the other half-reactions.
C)I2 is a better reducing agent than Pb2+.
D)Al is easier to oxidize than Fe.
E)Mg is a better reducing agent than Pb.

A)Pb4+ will oxidize all of the species on the right side of the arrows in the other half-reactions.
B)K+ will reduce all of the species on the left side of the arrows in the other half-reactions.
C)I2 is a better reducing agent than Pb2+.
D)Al is easier to oxidize than Fe.
E)Mg is a better reducing agent than Pb.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 174 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Copper is oxidized by nitric acid.If this property were utilized in an electrochemical cell,what would the standard cell potential be? The relevant reduction reactions and standard reduction potentials are given below.
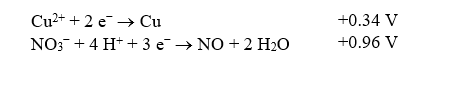
A)"-0.62 V"
B)"+0.62 V"
C)"-1.30 V"
D)"+1.30 V"
E)"+0.68 V"
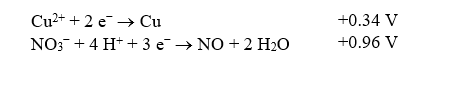
A)"-0.62 V"
B)"+0.62 V"
C)"-1.30 V"
D)"+1.30 V"
E)"+0.68 V"

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 174 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Using the following data,determine 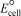 for the electrochemical cell constructed using the reaction of nitrous oxide and oxalic acid under acidic conditions.Unbalanced: N2O(g)+ H2C2O4(s) 2 CO2(g)+ N2(g)+ H2O(
for the electrochemical cell constructed using the reaction of nitrous oxide and oxalic acid under acidic conditions.Unbalanced: N2O(g)+ H2C2O4(s) 2 CO2(g)+ N2(g)+ H2O(  )
)
Half-reaction Standard reduction potential
2 CO2(g)+ 2 H+(aq)+ 2 e- H2C2O4(s)-0.49
N2O(g)+ 2 H+(aq)+ 2 e- N2(g)+ H2O( )+1.78
)+1.78
A)"+1.29 V"
B)"-1.29 V"
C)"+2.27 V"
D)"-2.27 V"
E)"+0.87 V"
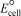 for the electrochemical cell constructed using the reaction of nitrous oxide and oxalic acid under acidic conditions.Unbalanced: N2O(g)+ H2C2O4(s) 2 CO2(g)+ N2(g)+ H2O(
for the electrochemical cell constructed using the reaction of nitrous oxide and oxalic acid under acidic conditions.Unbalanced: N2O(g)+ H2C2O4(s) 2 CO2(g)+ N2(g)+ H2O(  )
)Half-reaction Standard reduction potential
2 CO2(g)+ 2 H+(aq)+ 2 e- H2C2O4(s)-0.49
N2O(g)+ 2 H+(aq)+ 2 e- N2(g)+ H2O(
 )+1.78
)+1.78A)"+1.29 V"
B)"-1.29 V"
C)"+2.27 V"
D)"-2.27 V"
E)"+0.87 V"

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 174 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Based on the information in the table of standard reduction potentials below,calculate 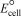 for Al(s)| Al3+(aq)|| Br2(aq),Br -(aq).
for Al(s)| Al3+(aq)|| Br2(aq),Br -(aq). 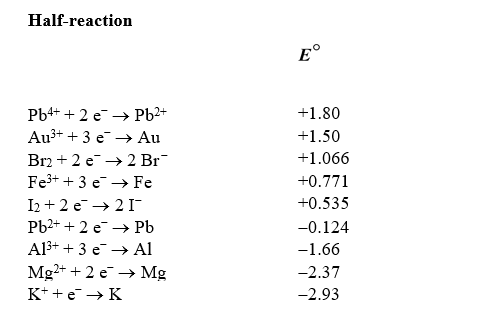
A)"+0.12 V"
B)"+2.73 V"
C)"-2.73 V"
D)"-0.59 V"
E)"+0.59 V"
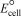 for Al(s)| Al3+(aq)|| Br2(aq),Br -(aq).
for Al(s)| Al3+(aq)|| Br2(aq),Br -(aq). 
A)"+0.12 V"
B)"+2.73 V"
C)"-2.73 V"
D)"-0.59 V"
E)"+0.59 V"

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 174 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Silver tarnish (Ag2S)can be removed by immersing silverware in a hot solution of baking soda (NaHCO3)in a pan lined with aluminum foil; however,foul-smelling hydrogen sulfide gas (H2S)is produced.Which of the following statements is correct? 
A)Aluminum ions react with S2-,form aluminum sulfide,and gaseous carbon dioxide is released.
B)Silver ions in the presence of the baking soda (NaHCO3)oxidize sulfide to elemental sulfur that attacks the aluminum foil,which produces aluminum sulfide.
C)The aluminum acts as a reducing agent for the silver(I)in silver sulfide; then bicarbonate ion protonates the sulfide ion that is released.
D)Aluminum is plated onto the silver surface,making it shiny again,and then the reaction of bicarbonate with aluminum oxide releases CO2.
E)Silver in Ag2S reduces the aluminum,becomes metallic silver in the process,and releases hydrogen sulfide,H2S.

A)Aluminum ions react with S2-,form aluminum sulfide,and gaseous carbon dioxide is released.
B)Silver ions in the presence of the baking soda (NaHCO3)oxidize sulfide to elemental sulfur that attacks the aluminum foil,which produces aluminum sulfide.
C)The aluminum acts as a reducing agent for the silver(I)in silver sulfide; then bicarbonate ion protonates the sulfide ion that is released.
D)Aluminum is plated onto the silver surface,making it shiny again,and then the reaction of bicarbonate with aluminum oxide releases CO2.
E)Silver in Ag2S reduces the aluminum,becomes metallic silver in the process,and releases hydrogen sulfide,H2S.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 174 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Using the following standard reduction potentials,calculate the 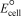 for the reaction of tin with chromium(III)hydroxide producing tin(IV)oxide and chromium under basic conditions.
for the reaction of tin with chromium(III)hydroxide producing tin(IV)oxide and chromium under basic conditions. 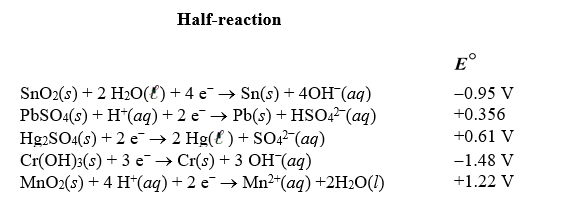
A)"+3.07 V"
B)"-2.43 V"
C)"+2.43 V"
D)"+0.53 V"
E)"-0.53V"
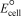 for the reaction of tin with chromium(III)hydroxide producing tin(IV)oxide and chromium under basic conditions.
for the reaction of tin with chromium(III)hydroxide producing tin(IV)oxide and chromium under basic conditions. 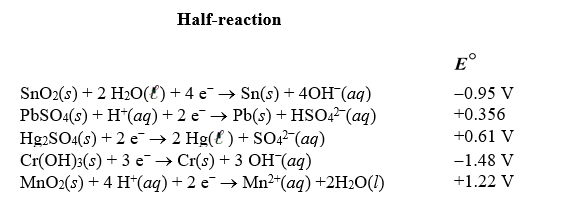
A)"+3.07 V"
B)"-2.43 V"
C)"+2.43 V"
D)"+0.53 V"
E)"-0.53V"

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 174 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Where do you expect to find elements that have high reduction potentials on the periodic table?
A)on the right (except for the last group)
B)in the middle left
C)in the top left
D)at the bottom
E)in the transition metals
A)on the right (except for the last group)
B)in the middle left
C)in the top left
D)at the bottom
E)in the transition metals

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 174 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Use the table of standard reduction potentials below to identify the metal or metal ion that is the strongest reducing agent.

A)Pb4+
B)Pb2+
C)K+
D)K
E)Al

A)Pb4+
B)Pb2+
C)K+
D)K
E)Al

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 174 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Using the following data,determine the standard cell potential  for the electrochemical cell constructed based on the following unbalanced reaction expression: Al(s)+ Cr3+(aq) Al3+(g)+ Cr2+(aq).
for the electrochemical cell constructed based on the following unbalanced reaction expression: Al(s)+ Cr3+(aq) Al3+(g)+ Cr2+(aq).
Half-reaction Standard reduction potential
Al3+(aq)+ 3 e- Al(s)-1.66
Cr3+(aq)+ e- Cr2+(aq)-0.41
A)"-1.25 V
B)"+1.25 V"
C)"+2.07 V"
D)"-0.43 V"
E)"+0.43 V"
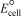 for the electrochemical cell constructed based on the following unbalanced reaction expression: Al(s)+ Cr3+(aq) Al3+(g)+ Cr2+(aq).
for the electrochemical cell constructed based on the following unbalanced reaction expression: Al(s)+ Cr3+(aq) Al3+(g)+ Cr2+(aq).Half-reaction Standard reduction potential
Al3+(aq)+ 3 e- Al(s)-1.66
Cr3+(aq)+ e- Cr2+(aq)-0.41
A)"-1.25 V
B)"+1.25 V"
C)"+2.07 V"
D)"-0.43 V"
E)"+0.43 V"

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 174 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
What is the standard cell potential for a voltaic cell using the Pb2+/Pb and Mg2+/Mg half-reactions? Which metal is the cathode?
A)"-2.25 V,Pb is the cathode"
B)"+2.25 V,Mg is the cathode"
C)"-2.25 V,Mg is the cathode"
D)"+2.25 V,Pb is the cathode"
E)"-2.49 V,Mg is the cathode"
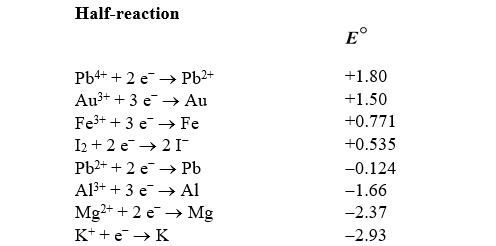
A)"-2.25 V,Pb is the cathode"
B)"+2.25 V,Mg is the cathode"
C)"-2.25 V,Mg is the cathode"
D)"+2.25 V,Pb is the cathode"
E)"-2.49 V,Mg is the cathode"

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 174 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Use the table of standard reduction potentials below to identify the metal or metal ion that is the strongest oxidizing agent.
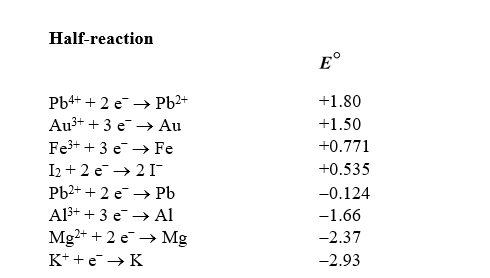
A)Pb4+
B)Pb2+
C)K+
D)K
E)Al
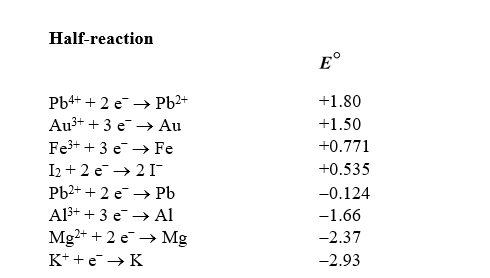
A)Pb4+
B)Pb2+
C)K+
D)K
E)Al

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 174 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Using the following data,determine 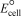 for the electrochemical cell constructed using the reaction of zinc and chromate ions under basic conditions.Unbalanced: Zn(s)+ 2 CrO42-(aq) Zn(OH)2(s)+ Cr(OH)3(s)
for the electrochemical cell constructed using the reaction of zinc and chromate ions under basic conditions.Unbalanced: Zn(s)+ 2 CrO42-(aq) Zn(OH)2(s)+ Cr(OH)3(s)
Half-reaction Standard reduction potential
Zn(OH)2(s)+ 2 e- Zn(s)+ 2 OH-(aq) -1.25
CrO42-(aq)+ 4 H2O( )+ 3 e- Cr(OH)3(s)+ 5 OH-(aq)-0.13
)+ 3 e- Cr(OH)3(s)+ 5 OH-(aq)-0.13
A)"-3.49 V"
B)"+3.49 V"
C)"+1.12 V"
D)"-1.12 V"
E)"+1.38 V"
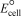 for the electrochemical cell constructed using the reaction of zinc and chromate ions under basic conditions.Unbalanced: Zn(s)+ 2 CrO42-(aq) Zn(OH)2(s)+ Cr(OH)3(s)
for the electrochemical cell constructed using the reaction of zinc and chromate ions under basic conditions.Unbalanced: Zn(s)+ 2 CrO42-(aq) Zn(OH)2(s)+ Cr(OH)3(s)Half-reaction Standard reduction potential
Zn(OH)2(s)+ 2 e- Zn(s)+ 2 OH-(aq) -1.25
CrO42-(aq)+ 4 H2O(
 )+ 3 e- Cr(OH)3(s)+ 5 OH-(aq)-0.13
)+ 3 e- Cr(OH)3(s)+ 5 OH-(aq)-0.13A)"-3.49 V"
B)"+3.49 V"
C)"+1.12 V"
D)"-1.12 V"
E)"+1.38 V"

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 174 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Calculate 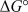 for an electrochemical cell reaction that occurs under acidic aqueous conditions based on the following two half-reactions for which the standard reduction potentials are given.Use the smallest whole-number coefficients possible when balancing the overall reaction.
for an electrochemical cell reaction that occurs under acidic aqueous conditions based on the following two half-reactions for which the standard reduction potentials are given.Use the smallest whole-number coefficients possible when balancing the overall reaction.
Cr2O72- + 14 H+ + 6 e- 2 Cr3+ + 7 H2O +1.33 V
CH3COOH + 4 H+ + 4 e- C2H5OH + H2O +0.058 V
A)"-1610 kJ"
B)"+1610 kJ"
C)"-1470 kJ"
D)"+2880 kJ"
E)"-2880 kJ"
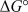 for an electrochemical cell reaction that occurs under acidic aqueous conditions based on the following two half-reactions for which the standard reduction potentials are given.Use the smallest whole-number coefficients possible when balancing the overall reaction.
for an electrochemical cell reaction that occurs under acidic aqueous conditions based on the following two half-reactions for which the standard reduction potentials are given.Use the smallest whole-number coefficients possible when balancing the overall reaction. Cr2O72- + 14 H+ + 6 e- 2 Cr3+ + 7 H2O +1.33 V
CH3COOH + 4 H+ + 4 e- C2H5OH + H2O +0.058 V
A)"-1610 kJ"
B)"+1610 kJ"
C)"-1470 kJ"
D)"+2880 kJ"
E)"-2880 kJ"

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 174 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
An electronic device requires two 1.50-V AA zinc-carbon batteries,which,connected in series,give 3.00 V.If the cell transfers two moles of electrons for each mole of reaction,how much electrical work can be performed by the batteries?
A)5.79 102 kJ
B)4.34 102 kJ
C)8.69 102 kJ
D)2.90 102 kJ
E)72.4 kJ
A)5.79 102 kJ
B)4.34 102 kJ
C)8.69 102 kJ
D)2.90 102 kJ
E)72.4 kJ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 174 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The Nernst equation can be used to calculate ________
A)standard cell potentials from standard reduction potentials.
B)the change in standard Gibbs free energy from standard cell potentials.
C)cell potentials from standard cell potentials when the conditions of concentration and temperature are not standard.
D)cell potentials given the temperature and reactant concentrations.
E)cell potentials from standard oxidation potentials.
A)standard cell potentials from standard reduction potentials.
B)the change in standard Gibbs free energy from standard cell potentials.
C)cell potentials from standard cell potentials when the conditions of concentration and temperature are not standard.
D)cell potentials given the temperature and reactant concentrations.
E)cell potentials from standard oxidation potentials.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 174 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
If the potential of a voltaic cell is +1.20 V,what is the free-energy change when one mole of electrons is transferred in the oxidation-reduction reaction?
A)"+116 kJ"
B)"-116 kJ"
C)"-1.20 kJ"
D)"-1.200 kJ"
E)"+602 kJ"
A)"+116 kJ"
B)"-116 kJ"
C)"-1.20 kJ"
D)"-1.200 kJ"
E)"+602 kJ"

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 174 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Which statement does NOT correctly describe a standard hydrogen electrode (SHE)?
A)The SHE is assigned a standard reduction potential of exactly 1 V.
B)2 H+(aq)+ 2 e- H2(g)
C)Pt | H2(g,1 atm)| H+(aq,1 M)||
D)|| H+(aq,1 M)| H2(g,1 atm)| Pt
E)The SHE consists of a platinum electrode immersed in an acid solution and a stream of hydrogen gas.
A)The SHE is assigned a standard reduction potential of exactly 1 V.
B)2 H+(aq)+ 2 e- H2(g)
C)Pt | H2(g,1 atm)| H+(aq,1 M)||
D)|| H+(aq,1 M)| H2(g,1 atm)| Pt
E)The SHE consists of a platinum electrode immersed in an acid solution and a stream of hydrogen gas.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 174 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Based on the information in the table of standard reduction potentials below,calculate G for the redox reaction of bromine with potassium. 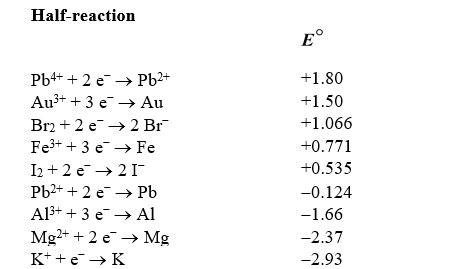
A)"+359 kJ"
B)"-359 kJ"
C)"-1340 kJ"
D)"+1340 kJ"
E)"-771 kJ"
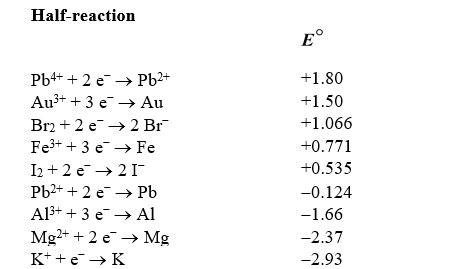
A)"+359 kJ"
B)"-359 kJ"
C)"-1340 kJ"
D)"+1340 kJ"
E)"-771 kJ"

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 174 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
In one episode of the 1960s television sitcom,Gilligan's Island,the famous "professor" constructed voltaic cells to use as substitutes for their radio's dead batteries.A single D-cell has an emf of 1.5 V.Which scraps of metal from their damaged boat,the Minnow,could best be used to create a 1.5 V voltaic cell? Assume that coconuts make great beakers and that seawater is a terrific electrolyte. 
A)silver anode and lead cathode
B)aluminum anode and lead cathode
C)iron anode and aluminum cathode
D)aluminum anode and silver cathode
E)lead cathode and silver anode

A)silver anode and lead cathode
B)aluminum anode and lead cathode
C)iron anode and aluminum cathode
D)aluminum anode and silver cathode
E)lead cathode and silver anode

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 174 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
An electronic device requires two 1.50-V AA zinc-carbon batteries,which,connected in series,give 3.00 V.If the cell transfers two moles of electrons for each mole of reaction,how much electrical work can be performed by the batteries?
A)5.79 102 kJ
B)4.34 102 kJ
C)8.69 102 kJ
D)2.90 102 kJ
E)72.4 kJ
A)5.79 102 kJ
B)4.34 102 kJ
C)8.69 102 kJ
D)2.90 102 kJ
E)72.4 kJ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 174 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Calculate 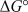 for an electrochemical cell reaction that occurs under basic aqueous conditions based on the following two half-reactions for which the standard reduction potentials are given.Use the smallest whole-number coefficients possible when balancing the overall reaction.
for an electrochemical cell reaction that occurs under basic aqueous conditions based on the following two half-reactions for which the standard reduction potentials are given.Use the smallest whole-number coefficients possible when balancing the overall reaction.
Cd(OH)2 + 2 e- Cd + 2 OH- -0.824 V
NiO(OH)+ H2O + e- Ni(OH)2 + OH- +1.32 V
A)"-669 kJ"
B)"+95.7 kJ"
C)"-95.7 kJ"
D)"-414 kJ"
E)"+414 kJ"
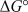 for an electrochemical cell reaction that occurs under basic aqueous conditions based on the following two half-reactions for which the standard reduction potentials are given.Use the smallest whole-number coefficients possible when balancing the overall reaction.
for an electrochemical cell reaction that occurs under basic aqueous conditions based on the following two half-reactions for which the standard reduction potentials are given.Use the smallest whole-number coefficients possible when balancing the overall reaction. Cd(OH)2 + 2 e- Cd + 2 OH- -0.824 V
NiO(OH)+ H2O + e- Ni(OH)2 + OH- +1.32 V
A)"-669 kJ"
B)"+95.7 kJ"
C)"-95.7 kJ"
D)"-414 kJ"
E)"+414 kJ"

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 174 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
An electronic device requires four 1.50-V AA alkaline batteries,which,connected in series,give 6.00 V.If the cell transfers two moles of electrons for each mole of reaction,what is the Gibbs free-energy change for the redox reaction in each of the batteries?
A)"-1.45 102 kJ"
B)"+1.45 102 kJ"
C)"+5.79 102 kJ"
D)"-8.69 102 kJ"
E)"-2.90 102 kJ"
A)"-1.45 102 kJ"
B)"+1.45 102 kJ"
C)"+5.79 102 kJ"
D)"-8.69 102 kJ"
E)"-2.90 102 kJ"

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 174 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The spontaneous redox reaction in a voltaic cell has ________
A)a negative value of Ecell and a negative value of G.
B)a positive value of Ecell and a positive value of G.
C)a negative value of Ecell and a positive value of G.
D)a positive value of Ecell and a negative value of F G.
E)a positive value of Ecell and a value of zero for G.
A)a negative value of Ecell and a negative value of G.
B)a positive value of Ecell and a positive value of G.
C)a negative value of Ecell and a positive value of G.
D)a positive value of Ecell and a negative value of F G.
E)a positive value of Ecell and a value of zero for G.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 174 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Based on the information in the table of standard reduction potentials below,calculate G for 2Pb2+ Pb + Pb4+.

A)"+371 kJ"
B)"-371 kJ"
C)"-323 kJ"
D)"+323 kJ"
E)"-186 kJ"

A)"+371 kJ"
B)"-371 kJ"
C)"-323 kJ"
D)"+323 kJ"
E)"-186 kJ"

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 174 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The change in free energy for a reaction, G,depends on the stoichiometric coefficients used in writing the reaction,but cell potentials,E,do not depend on these coefficients.Which statement accounts for this difference?
A)These quantities ( G and E)are not related,so this difference is not an issue.
B)The free-energy change is defined for general reactions,and the electromotive force is defined for electrochemical reactions,so this difference is not an issue.
C)The difference is not relevant because the units differ: kJ/mol for G,and V for E.
D)The change in free energy depends on both the reaction and the amount of material reacting,while the cell potential depends only on the reaction.
E)The statement is false. G does not depend on the stoichiometric coefficients.
A)These quantities ( G and E)are not related,so this difference is not an issue.
B)The free-energy change is defined for general reactions,and the electromotive force is defined for electrochemical reactions,so this difference is not an issue.
C)The difference is not relevant because the units differ: kJ/mol for G,and V for E.
D)The change in free energy depends on both the reaction and the amount of material reacting,while the cell potential depends only on the reaction.
E)The statement is false. G does not depend on the stoichiometric coefficients.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 174 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
An electrochemical cell is constructed with a zinc metal anode in contact with a 0.052 M solution of zinc nitrate and a silver cathode in contact with a 0.0042 M solution of silver(I)nitrate.What is the value of Q to use in the Nernst equation for this cell?
A)2.9 103
B)12
C)8.1 10-2
D)3.4 10-4
E)1.00
A)2.9 103
B)12
C)8.1 10-2
D)3.4 10-4
E)1.00

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 174 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The magnitude of the charge on a mole of electrons is ________
A)"1 C."
B)"9.65 C."
C)"9.65 104 C."
D)"6.02 1023 C."
E)"9650 C."
A)"1 C."
B)"9.65 C."
C)"9.65 104 C."
D)"6.02 1023 C."
E)"9650 C."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 174 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
An electrochemical cell contains a standard hydrogen electrode and a cathode consisting of a metallic chromium electrode,Cr(s),in contact with a 1.00 M chromium solution,Cr3+(aq).The voltage produced by this cell was measured at 25°C.Which statements describe the results of this measurement,assuming the conditions are ideal? The cell voltage with the appropriate sign equals ________ I.the cell potential.
II)the electromotive force.
III)the standard cell potential.
IV)the standard reduction potential for Cr3+/Cr.
A)I only
B)I and II
C)I,II,and III
D)I,II,III,and IV
E)III only
II)the electromotive force.
III)the standard cell potential.
IV)the standard reduction potential for Cr3+/Cr.
A)I only
B)I and II
C)I,II,and III
D)I,II,III,and IV
E)III only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 174 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The standard hydrogen electrode is ________
A)used to calibrate voltmeters.
B)the reference point for all standard reduction potentials.
C)needed to activate electrochemical cells.
D)often overlooked in measuring standard reduction potentials.
E)used to produce a standard cell potential of exactly 1 V.
A)used to calibrate voltmeters.
B)the reference point for all standard reduction potentials.
C)needed to activate electrochemical cells.
D)often overlooked in measuring standard reduction potentials.
E)used to produce a standard cell potential of exactly 1 V.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 174 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Silver tarnish (Ag2S)can be removed by immersing silverware in a hot solution of baking soda (NaHCO3)in a pan lined with aluminum foil; however,foul-smelling hydrogen sulfide gas (H2S)is produced.What is 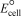 for the redox reaction that occurs?
for the redox reaction that occurs?

A)+3.512 V
B)+1.051 V
C)+2.461 V
D)+1.521 V
E)+0.940 V
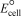 for the redox reaction that occurs?
for the redox reaction that occurs? 
A)+3.512 V
B)+1.051 V
C)+2.461 V
D)+1.521 V
E)+0.940 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 174 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Which of the following statements regarding chemical energy and electrical work is NOT correct?
A)The amount of work available from an electrochemical cell is independent of the amounts of reactants present.
B)The amount of charge transferred in an electrochemical cell is directly proportional to the electrical work the cell performs.
C)When the free energy of an electrochemical cell decreases,the cell potential is positive.
D)The amount of work done by an electrochemical cell depends on the amount of charge transferred.
E)As cell potential increases,the amount of work available increases.
A)The amount of work available from an electrochemical cell is independent of the amounts of reactants present.
B)The amount of charge transferred in an electrochemical cell is directly proportional to the electrical work the cell performs.
C)When the free energy of an electrochemical cell decreases,the cell potential is positive.
D)The amount of work done by an electrochemical cell depends on the amount of charge transferred.
E)As cell potential increases,the amount of work available increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 174 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
The work involved in moving exactly 1 mole of electrons through a potential difference of exactly 1 V is ________
A)1 J.
B)1 kJ.
C)96.5 J.
D)6.02 kJ.
E)96.5 kJ.
A)1 J.
B)1 kJ.
C)96.5 J.
D)6.02 kJ.
E)96.5 kJ.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 174 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



