Deck 14: Allergy and Allergic Diseases
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/26
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 14: Allergy and Allergic Diseases
1
In the late 1990s, compounds that functioned as leukotriene receptor antagonists were approved for the treatment of asthma. The first such drug, zafirlukast, inhibits the actions of a major receptor for leukotrienes, known as CYSLTR1 (cysteinyl leukotriene receptor 1). One would predict that patients on this drug would show:
A) Enhanced mucus production
B) Enhanced vascular permeability
C) Increased accumulation of leukocytes in the lung
D) Reduced mast cell activation
E) Reduced bronchoconstriction
A) Enhanced mucus production
B) Enhanced vascular permeability
C) Increased accumulation of leukocytes in the lung
D) Reduced mast cell activation
E) Reduced bronchoconstriction
Reduced bronchoconstriction
2
Fatal anaphylaxis can be induced in mice by sensitizing the mice to penicillin V (Pen V). To elicit this response, Pen V is conjugated to a protein, such as chicken ovalbumin (OVA), and mice are immunized with this conjugate by intraperitoneal (IP) injection in a TH2-inducing adjuvant. Fourteen days later, mice are injected intravenously (IV) with Pen V conjugated to a different protein, bovine serum albumin (BSA), and examined 20 minutes later. In addition, a second set of mice received anti-IL-4 antibody injections on days 0, 2, and 4 of the sensitization phase of the response. The results in Table Q16)A were observed; (data are shown as the ratio of dead mice to total mice for each condition):as above. Twenty-four days later, serum from these mice was isolated and injected into a set of naive (unimmunized) recipient mice. Recipient mice were then sensitized by a single IP injection of Pen V-OVA in adjuvant, as above, and then 24 hours later, were given an IV injection of Pen V-BSA or BSA alone. In addition, one group of mice received serum that was depleted of specific antibodies prior to transfer into recipients. These mice develop a slightly milder disease, characterized by severe shock rather than death. Data are shown in Table Q16)B as the ratio of mice exhibiting severe shock to total mice for each condition/ 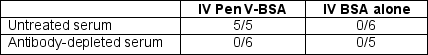 Table Q16)B
Table Q16)B
Which antibodies were depleted from the serum in the final experiment shown above:
A) Antibodies specific to BSA
B) Antibodies specific to OVA
C) All IgG antibodies
D) Antibodies to IL-4
E) All IgE antibodies
 Table Q16)B
Table Q16)BWhich antibodies were depleted from the serum in the final experiment shown above:
A) Antibodies specific to BSA
B) Antibodies specific to OVA
C) All IgG antibodies
D) Antibodies to IL-4
E) All IgE antibodies
All IgE antibodies
3
Once an individual becomes sensitized to an allergen, such as an inhaled antigen, the allergic response can become self-amplifying upon each re-exposure to the allergen. Thus, even in the absence of CD4 TH2 cell activation, increases in IgE secretion by mucosal-resident plasma cells can be induced by:
A) IL-4 secretion and CD40-ligand expression by mast cells and basophils
B) Inflammatory macrophages recruited to the site of allergen stimulation
C) Eosinophils that are stimulated by the production of IL-4 in the mucosal tissue
D) Dendritic cells that have received TLR stimulation
E) The activation of the complement cascade following allergen encounter
A) IL-4 secretion and CD40-ligand expression by mast cells and basophils
B) Inflammatory macrophages recruited to the site of allergen stimulation
C) Eosinophils that are stimulated by the production of IL-4 in the mucosal tissue
D) Dendritic cells that have received TLR stimulation
E) The activation of the complement cascade following allergen encounter
IL-4 secretion and CD40-ligand expression by mast cells and basophils
4
Allergic responses to inhaled antigens occur when an individual is first sensitized to the antigen (i.e., the allergen), inducing an immune response, and then has a subsequent exposure to the same antigen. The sensitization phase is characterized by:
A) Induction of IgA antibodies against the allergen
B) Activation of tissue-resident ILC3 cells following stimulation by the allergen
C) Induction of a CD4 T cell type II immune response
D) Production of high concentrations of IL-12 and IL-23 by tissue-resident dendritic cells
E) Recruitment of large numbers of neutrophils to the site of allergen entry
A) Induction of IgA antibodies against the allergen
B) Activation of tissue-resident ILC3 cells following stimulation by the allergen
C) Induction of a CD4 T cell type II immune response
D) Production of high concentrations of IL-12 and IL-23 by tissue-resident dendritic cells
E) Recruitment of large numbers of neutrophils to the site of allergen entry

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The prevention of inflammatory immune responses to inhaled antigens in healthy individuals has mechanisms in common with those that prevent inflammatory immune responses to commensal microbes in the gut. One important component of immune regulation shared by these two situations is:
A) The presence of tissue-resident dendritic cells that produce IL-23 when activated
B) The presence of tissue-resident mast cells that bind IgE through the high affinity IgE receptor
C) The high levels of constitutive IL-10 present in the mucosal surfaces of both the airway and the gastrointestinal tract
D) The induction of increased numbers of IFN- -producing T cells and ILCs in the airway and gastrointestinal epithelium
E) The important role for CD4 regulatory T cells in suppressing inflammatory immune responses in these tissues
A) The presence of tissue-resident dendritic cells that produce IL-23 when activated
B) The presence of tissue-resident mast cells that bind IgE through the high affinity IgE receptor
C) The high levels of constitutive IL-10 present in the mucosal surfaces of both the airway and the gastrointestinal tract
D) The induction of increased numbers of IFN- -producing T cells and ILCs in the airway and gastrointestinal epithelium
E) The important role for CD4 regulatory T cells in suppressing inflammatory immune responses in these tissues

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Genome-wide association studies of large cohorts of individuals (>5000 allergic versus >10,000 controls) with IgE-mediated allergies revealed a set of genes significantly correlated with atopy. Further studies of the top ten candidate genes indicated that each gene showed allelic variations that were likely associated with differences in gene expression. One of these ten genes encodes STAT6, the transcription factor activated downstream of the IL-4 receptor. What would you predict for the allelic variant of STAT6 found more frequently in allergic individuals compared to the allele found more frequently in non-allergic controls?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Individuals with peanut allergies can exhibit a variety of symptoms following exposure to the peanut allergen. These symptoms can include a runny nose, skin reactions such as hives, itching in the mouth and throat, digestive problems such as cramps, diarrhea or vomiting, and shortness of breath or wheezing. This variety of symptoms is a result of:
A) Systemic production of inflammatory mediators causing responses in many tissues
B) The presence of mast cells with pre-bound IgE in all mucosal tissues
C) The simultaneous exposure of skin, oral mucosa, throat, and gastrointestinal tract to an ingested allergen
D) The high concentrations of histamine present in pre-stored mast cell granules
E) The presence of high concentrations of monomeric IgE in the circulation
A) Systemic production of inflammatory mediators causing responses in many tissues
B) The presence of mast cells with pre-bound IgE in all mucosal tissues
C) The simultaneous exposure of skin, oral mucosa, throat, and gastrointestinal tract to an ingested allergen
D) The high concentrations of histamine present in pre-stored mast cell granules
E) The presence of high concentrations of monomeric IgE in the circulation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A relatively new form of therapy for IgE-mediated allergic diseases is the periodic injection of patients with anti-IgE antibody. This antibody binds to the Fc portion of IgE antibodies, and prevents the IgE antibodies from binding to both high affinity and low affinity IgE receptors on inflammatory cells. IgE bound to the high affinity IgE receptor on mast cells and basophils stimulates degranulation of these cells and their production of inflammatory mediators, following antigen encounter. In contrast, the low affinity IgE receptor is expressed on dendritic cells, and functions to trap allergen-IgE complexes for uptake, degradation, and presentation to T cells. Given these functions, individuals treated with this anti-IgE therapy would be expected to show:
A) Reduced symptoms upon allergen encounter and no progressive worsening of disease
B) Reduced symptoms upon allergen encounter, but rebound to severe disease if therapy is discontinued
C) Beneficial effects for allergic asthma, but no effect on food or skin allergies
D) No reduction in mucus production in the airways or GI tract
E) A normal response to helminthic parasite infections
A) Reduced symptoms upon allergen encounter and no progressive worsening of disease
B) Reduced symptoms upon allergen encounter, but rebound to severe disease if therapy is discontinued
C) Beneficial effects for allergic asthma, but no effect on food or skin allergies
D) No reduction in mucus production in the airways or GI tract
E) A normal response to helminthic parasite infections

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
In individuals with a peanut allergy, mild allergic responses are those that involve a single site, typically a skin reaction such as hives. More severe allergic reactions generally involve multiple tissue sites, such as the skin, oral mucosa, airway mucosa and gastrointestinal tract. Given two groups of allergic patients, one with only skin responses, and the other with 3-4 different tissue sites involved, one would expect that:
A) Patients with the severe allergic responses would have higher concentrations of allergen-specific IgE.
B) Patients with mild allergic responses would have fewer mast cells in the majority of their mucosal tissues.
C) Patients with severe allergic responses would also have allergies to several other substances, such as bee venom or pollen.
D) Patients with severe allergic responses would have reduced expression of antioxidant enzymes, such as glutathione-S-transferases.
E) Patients with mild allergic responses would have higher numbers of CD4+ Treg cells.
A) Patients with the severe allergic responses would have higher concentrations of allergen-specific IgE.
B) Patients with mild allergic responses would have fewer mast cells in the majority of their mucosal tissues.
C) Patients with severe allergic responses would also have allergies to several other substances, such as bee venom or pollen.
D) Patients with severe allergic responses would have reduced expression of antioxidant enzymes, such as glutathione-S-transferases.
E) Patients with mild allergic responses would have higher numbers of CD4+ Treg cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The 'hygiene hypothesis' has been proposed as an explanation for the rapid increase in allergies and asthma incidence in Western countries over the last half century. One line of evidence supporting this hypothesis is:
A) Individuals living in Western countries have fewer CD4 Treg cells in their mucosal tissues.
B) Individuals of African descent have much higher incidence of atopic disease when living in Western countries.
C) Individuals that are infected with RSV as infants are protected from developing allergies and asthma later in life.
D) Individuals that are infected with Hepatitis A virus are more likely to develop allergies and asthma.
E) Persistent exposure with helminthic parasites predisposes individuals to developing atopic diseases due to increased Type II immune responses.
A) Individuals living in Western countries have fewer CD4 Treg cells in their mucosal tissues.
B) Individuals of African descent have much higher incidence of atopic disease when living in Western countries.
C) Individuals that are infected with RSV as infants are protected from developing allergies and asthma later in life.
D) Individuals that are infected with Hepatitis A virus are more likely to develop allergies and asthma.
E) Persistent exposure with helminthic parasites predisposes individuals to developing atopic diseases due to increased Type II immune responses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
NRF2 is a transcription factor that is required to induce anti-oxidant genes, such as glutathione-S-transferase genes, in response to reactive oxygen and reactive nitrogen species released by inflammatory cells in the airways following phagocytosis of inhaled particles. Mice deficient in Nrf2 were tested for their allergic airway response to inhaled allergens in comparison to wild-type controls. Compared to wild type mice, the Nrf2-/- mice would be expected to show:
A) Reduced recruitment of eosinophils to the airway mucosa
B) Enhanced production of IL-17 and IL-22 required to repair damaged epithelium
C) Increased levels of IL-4 and IL-13 in the airway
D) Increased numbers of CD4 Treg cells in the airway epithelium
E) Reduced levels of allergen-specific IgE
A) Reduced recruitment of eosinophils to the airway mucosa
B) Enhanced production of IL-17 and IL-22 required to repair damaged epithelium
C) Increased levels of IL-4 and IL-13 in the airway
D) Increased numbers of CD4 Treg cells in the airway epithelium
E) Reduced levels of allergen-specific IgE

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Within minutes after encounter with an allergen, individuals with allergic rhinitis show symptoms of nasal itching, nasal congestion, sneezing, and a runny nose. These symptoms generally subside within 30 minutes, but reappear several hours later. Analysis of the nasal epithelium in such an individual 6 hours after allergen encounter would show:
A) Infiltration of eosinophils, basophils, neutrophils, T cells, and macrophages
B) High concentrations of IL-22 important in repair of the damaged epithelium
C) An influx of commensal microbes due to breaches in the epithelial barrier
D) The absence of allergen-specific IgE on mast cells in the tissue
E) Very low levels of histamine and other inflammatory mediators
A) Infiltration of eosinophils, basophils, neutrophils, T cells, and macrophages
B) High concentrations of IL-22 important in repair of the damaged epithelium
C) An influx of commensal microbes due to breaches in the epithelial barrier
D) The absence of allergen-specific IgE on mast cells in the tissue
E) Very low levels of histamine and other inflammatory mediators

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Studies using mouse models of allergic asthma have provided information about the cell types and soluble mediators that contribute to this disease. One common experimental model uses airway exposure to protease allergens, such as papain from papaya or the house dust mite allergen. Interestingly, papain is able to induce allergic lung inflammation even in RAG-deficient mice. In this system, the type 2 cytokines, IL-5, IL-9, and IL-13, are likely coming from:
A) Airway epithelial cells
B) ILC2 cells
C) Eosinophils
D) TH2 cells
E) Macrophages
A) Airway epithelial cells
B) ILC2 cells
C) Eosinophils
D) TH2 cells
E) Macrophages

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Allergen-induced airway remodeling in mice is used as a model for human allergic asthma. This disease is induced by first sensitizing mice to the protein antigen, chicken ovalbumin (OVA) by intraperitoneal immunization with OVA in a TH2-inducing adjuvant. Three weeks later, mice are challenged by inhalation of aerosolized OVA (or saline alone, as a control) daily for the following three weeks. At the end of the entire six week period, the lungs of the mice are examined for leukocyte numbers in the bronchial alveolar lavage fluid (BALF) and for tissue remodeling as assessed by measuring fibrotic areas in the lung tissue. To determine the cell type most likely responsible for the tissue damage in this disease, IL-5 receptor-deficient mice (IL5R-/-) are compared to wild-type, as shown in Figure Q13). 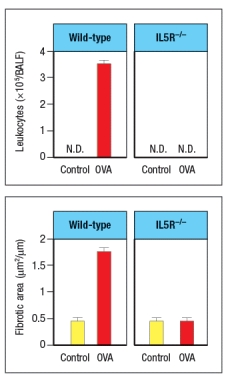 airway remodeling disease model is:
airway remodeling disease model is:
A) Neutrophils
B) Macrophages
C) Mast cells
D) TH2 cells
E) Eosinophils
 airway remodeling disease model is:
airway remodeling disease model is:A) Neutrophils
B) Macrophages
C) Mast cells
D) TH2 cells
E) Eosinophils

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Common allergens that trigger atopic responses in humans share several features. For example, nearly all allergens are proteases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Genetic studies have identified more than 40 genes that show allelic variations associated with the development of allergic asthma and atopic dermatitis, as well as the predisposition to develop allergies to particular antigens. Among these genes are several that implicate CD4 T cell responses in the development of these allergic diseases. Name two genes (or gene clusters) associated with atopic diseases that indicate a central role for CD4 T cells in these diseases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Genetic variations in proteins involved in immune and inflammatory responses have been shown to be associated with the development of atopic dermatitis and other allergic diseases. However, several genes associated with these conditions do not affect the immune system directly. For example, among this latter group are genes that:
A) Regulate the recruitment of inflammatory cells to the airways or other mucosa
B) Function in cytokine receptor signaling pathways
C) Encode proteins expressed in airway epithelial cells
D) Regulate barrier function by airway and skin epithelial cells
E) Are common to atopic diseases and to autoimmune diseases
A) Regulate the recruitment of inflammatory cells to the airways or other mucosa
B) Function in cytokine receptor signaling pathways
C) Encode proteins expressed in airway epithelial cells
D) Regulate barrier function by airway and skin epithelial cells
E) Are common to atopic diseases and to autoimmune diseases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Red blood cells are common targets of drug-induced anemia, a disorder that occurs when some drugs bind to the surface of red blood cells and trigger the development of IgG antibodies that bind to the drug-coated red blood cell and promote red blood cell destruction. Since the drug binding to the red blood cell surface does not actually harm the red blood cell, the anemia resulting in this disorder is caused by:
A) Activation of the complement cascade leading to red blood cell lysis
B) Trapping of red blood cells on large endothelial vessels
C) Phagocytosis by Fc -receptor expressing macrophages in the spleen
D) Stimulation of CD4 T cells recognizing modified red blood cell surface proteins formed by the binding of the drug
E) Stimulation of CD8 cytotoxic T cells that recognize drug-self protein conjugates and are triggered to kill the red blood cells
A) Activation of the complement cascade leading to red blood cell lysis
B) Trapping of red blood cells on large endothelial vessels
C) Phagocytosis by Fc -receptor expressing macrophages in the spleen
D) Stimulation of CD4 T cells recognizing modified red blood cell surface proteins formed by the binding of the drug
E) Stimulation of CD8 cytotoxic T cells that recognize drug-self protein conjugates and are triggered to kill the red blood cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Individuals with allergic responses to inhaled antigens show an immediate (within minutes) response to encounter with the allergen, resulting in bronchial smooth muscle constriction and edema that makes breathing difficult. Which over-the-counter medication that might be taken to prevent or reduce this response, and how does it act?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
In mice, an allergic response in the airways can be induced by systemic immunization with a protein antigen (chicken ovalbumin) in an adjuvant that promotes Type II immune responses, followed by several exposures to aerosolized ovalbumin administered via the airways. Mice that have a genetic deficiency in expression of the receptor c-kit are resistant to this disease because:
A) They are unable to generate an IgE antibody response to ovalbumin.
B) They lack expression of the high affinity IgE receptor.
C) Their inflammatory cells do not respond to chemokine receptor stimulation.
D) They lack mast cells.
E) They lack B cells.
A) They are unable to generate an IgE antibody response to ovalbumin.
B) They lack expression of the high affinity IgE receptor.
C) Their inflammatory cells do not respond to chemokine receptor stimulation.
D) They lack mast cells.
E) They lack B cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Celiac disease occurs when an individual makes an aberrant immune response to a protein in gluten, such as -gliadin. Evidence suggests that very few proteins are able to elicit the immune response that causes celiac disease. A key piece of this evidence is that:
A) All patients with celiac disease make IgA antibodies to transglutaminase.
B) Gliadin-derived peptides stimulate epithelial cells to produce IL-15.
C) Innate immune responses to gluten induce up-regulation of MIC-A on epithelial cells.
D) More than 95% of patients express the MHC class II DQ2 allele.
E) Monozygotic twins show an 80% concordance for developing celiac disease.
A) All patients with celiac disease make IgA antibodies to transglutaminase.
B) Gliadin-derived peptides stimulate epithelial cells to produce IL-15.
C) Innate immune responses to gluten induce up-regulation of MIC-A on epithelial cells.
D) More than 95% of patients express the MHC class II DQ2 allele.
E) Monozygotic twins show an 80% concordance for developing celiac disease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
T-bet and GATA-3 are transcription factors known to regulate the development of polarized subsets of CD4 T cells. To investigate the effects of altering the cytokines produced by CD4 effector T cells during chronic airway inflammation, transgenic mice were generated that constitutively express either T-bet or GATA-3 in all T cells. These strains of mice are referred to as T-bet-tg or GATA-3-tg, respectively. Wild-type, T-bet-tg and GATA-3-tg mice were then sensitized by intraperitoneal injection of chicken ovalbumin protein (OVA) in a TH2-inducing adjuvant. Three weeks later, mice were challenged daily by intranasal administration of OVA protein in saline for 8 weeks. Control mice were immunized and challenged with saline alone. One day following the final intranasal challenge with OVA or saline, the mice were euthanized, and their lungs were examined by histological analysis for the percentages of mucus-positive cells and for thickening of airway walls as a measure of airway remodeling. These data were quantified, and are shown in Figure Q25)A. Note that the airway remodeling is scored on a relative scale in arbitrary units (AU). 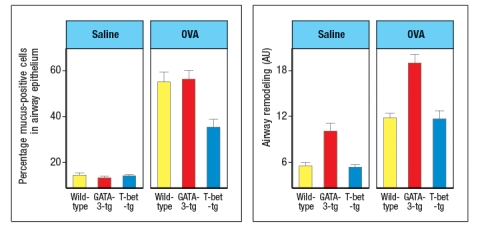
a) What is the effect of GATA-3-expressing T cells on the numbers of mucus-producing cells compared to its effect on airway remodeling?
b) What is the effect of enforcing T-bet expression in T cells on the numbers of mucus-producing cells compared to its effect on airway remodeling?
One day after the final challenge with intranasal OVA or saline, mice were also examined for the numbers of eosinophils in their lungs. Lung homogenates were also tested for cytokine levels by ELISA. These data are shown in Figure .
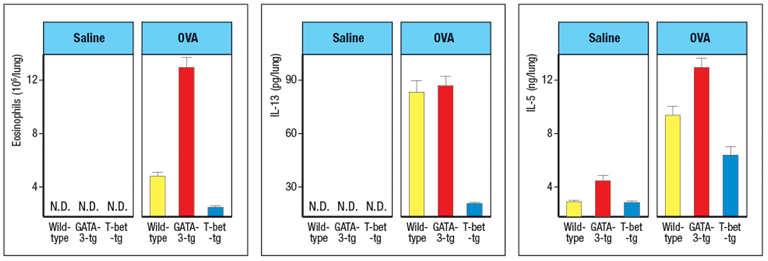
c) What is the effect of enforced expression of GATA-3 or T-bet in T cells on the numbers of eosinophils in the lung? Based on the cytokine data, which cytokine is likely contributing to this effect?
In a final experiment, mice are euthanized one day after the final saline or OVA administration, and lymphocytes are isolated from the lungs. The isolated lymphocytes are stimulated through their T-cell receptors to induce cytokine production from effector T cells. During this 5-hour in vitro stimulation to elicit cytokine production, the cells are also incubated with a protein secretion inhibitor. After the 5-hour incubation, the cells are stained with antibodies to CD3 and CD4, then the cells are fixed and permeabilized, and stained with antibodies to IFN- For IL-4. The percentages of CD4 T cells expressing each cytokine are shown in Figure .
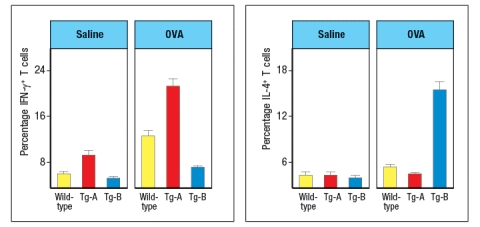
d) Based on these data, deduce whether Tg-A is the GATA-3-tg line or the T-bet-tg line, and similarly, deduce the identity of Tg-B. Explain your reasoning.
IL-12 is an important cytokine that induces T-bet up-regulation in CD4 T cells. If one discovered that polymorphisms in the IL-12 locus were linked to increased susceptibility to allergies and asthma based on GWAS (genome-wide association studies) data derived from human population cohorts, what difference would be expected when comparing the allele in healthy controls versus the allele found more frequently in asthma patients?

a) What is the effect of GATA-3-expressing T cells on the numbers of mucus-producing cells compared to its effect on airway remodeling?
b) What is the effect of enforcing T-bet expression in T cells on the numbers of mucus-producing cells compared to its effect on airway remodeling?
One day after the final challenge with intranasal OVA or saline, mice were also examined for the numbers of eosinophils in their lungs. Lung homogenates were also tested for cytokine levels by ELISA. These data are shown in Figure .

c) What is the effect of enforced expression of GATA-3 or T-bet in T cells on the numbers of eosinophils in the lung? Based on the cytokine data, which cytokine is likely contributing to this effect?
In a final experiment, mice are euthanized one day after the final saline or OVA administration, and lymphocytes are isolated from the lungs. The isolated lymphocytes are stimulated through their T-cell receptors to induce cytokine production from effector T cells. During this 5-hour in vitro stimulation to elicit cytokine production, the cells are also incubated with a protein secretion inhibitor. After the 5-hour incubation, the cells are stained with antibodies to CD3 and CD4, then the cells are fixed and permeabilized, and stained with antibodies to IFN- For IL-4. The percentages of CD4 T cells expressing each cytokine are shown in Figure .

d) Based on these data, deduce whether Tg-A is the GATA-3-tg line or the T-bet-tg line, and similarly, deduce the identity of Tg-B. Explain your reasoning.
IL-12 is an important cytokine that induces T-bet up-regulation in CD4 T cells. If one discovered that polymorphisms in the IL-12 locus were linked to increased susceptibility to allergies and asthma based on GWAS (genome-wide association studies) data derived from human population cohorts, what difference would be expected when comparing the allele in healthy controls versus the allele found more frequently in asthma patients?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
IL-33 is a cytokine known as an 'alarmin'. Following stimulation by pathogens or allergens, or in response to damage, epithelial cells in the skin, lungs, and gastrointestinal tract will release IL-33. This cytokine binds to its receptor, which is expressed on several cell types important in type 2 immune responses. When mice are injected with recombinant IL-33 once per day for 7 days (or saline as a control), specific cytokines are found elevated in multiple tissues and in their serum. An example of data from lung is shown in Figure Q26)A, with cytokine mRNA being measured by RT-PCR. Other cytokines, such as IL-2, IL-4, IL-6, IL-10, IL-12, TNF- , and IFN- were not altered by IL-33 injection. 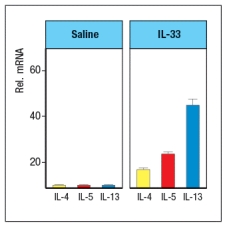
a) Name three cell types that are likely to express IL-33 receptors.
These experiments were repeated using Rag-deficient mice, in comparison to wild-type controls. When cytokines were analyzed after IL-33 treatment of Rag-deficient mice, similar amounts of the same cytokines were observed as seen in wild-type controls.
b) Do these data affect your answer to part (a) above? Why or why not?
When IL-33-deficient mice were compared to wild-type controls in a mouse model of chronic airway inflammation, disease symptoms were reduced in IL33-/- mice. In this model, chicken ovalbumin protein (OVA) is mixed with a TH2-inducing adjuvant, and used to sensitize mice by intraperitoneal injection. Four weeks later, mice are challenged intranasally with OVA or saline alone on days 28, 29, and 30. The number of cells in the bronchiolar lavage fluid is then assessed, as shown in Figure .
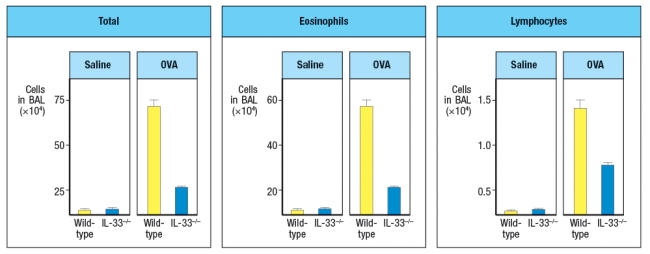
c) Given these data, as well as the cytokine data above, what are two important functions of IL-33?
Leukocytes are isolated from the lung epithelium of wild-type mice in which chronic airway inflammation has been induced to OVA. The cells are separated into two subsets: lymphocytes and non-lymphocytes. Then each population is stimulated in vitro with IL-33 in the presence or absence of OVA protein, and 48 hours later the cytokines in the supernatants are assessed by ELISA. The results are shown in Figure for one cytokine. Similar data were obtained for IL-9 and IL-13.
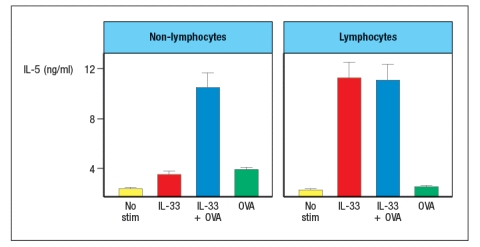
d) What are the likely cell types responding in each isolated population?

a) Name three cell types that are likely to express IL-33 receptors.
These experiments were repeated using Rag-deficient mice, in comparison to wild-type controls. When cytokines were analyzed after IL-33 treatment of Rag-deficient mice, similar amounts of the same cytokines were observed as seen in wild-type controls.
b) Do these data affect your answer to part (a) above? Why or why not?
When IL-33-deficient mice were compared to wild-type controls in a mouse model of chronic airway inflammation, disease symptoms were reduced in IL33-/- mice. In this model, chicken ovalbumin protein (OVA) is mixed with a TH2-inducing adjuvant, and used to sensitize mice by intraperitoneal injection. Four weeks later, mice are challenged intranasally with OVA or saline alone on days 28, 29, and 30. The number of cells in the bronchiolar lavage fluid is then assessed, as shown in Figure .

c) Given these data, as well as the cytokine data above, what are two important functions of IL-33?
Leukocytes are isolated from the lung epithelium of wild-type mice in which chronic airway inflammation has been induced to OVA. The cells are separated into two subsets: lymphocytes and non-lymphocytes. Then each population is stimulated in vitro with IL-33 in the presence or absence of OVA protein, and 48 hours later the cytokines in the supernatants are assessed by ELISA. The results are shown in Figure for one cytokine. Similar data were obtained for IL-9 and IL-13.

d) What are the likely cell types responding in each isolated population?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
On occasion, individuals on antibiotics such as Minomycin have an allergic response to the antibiotic. Symptoms often include an urticarial rash on the skin, and swelling (edema) of the legs and ankles. When this occurs, patients are advised to stop taking the antibiotic, and are treated with corticosteroids. During follow-up visits to their physician, patients are often given a skin test for hypersensitivity to the drug. This skin test involves intradermal injection of a small amount of Minomycin, and 15 minutes later the site of injection is examined for redness and swelling. In cases where this skin test is negative, the patient most likely generated:
A) IgE antibodies to the Minomycin
B) IgG antibodies to the Minomycin
C) CD4 TH2 cells specific to Minomycin-modified red blood cells
D) CD4 TH1 cells specific to Minomycin-modified self proteins
E) Activated macrophages that produce IL-1 and TNF-
A) IgE antibodies to the Minomycin
B) IgG antibodies to the Minomycin
C) CD4 TH2 cells specific to Minomycin-modified red blood cells
D) CD4 TH1 cells specific to Minomycin-modified self proteins
E) Activated macrophages that produce IL-1 and TNF-

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The response of most individuals to contact with poison ivy includes the development of redness, swelling, blistering (edema fluid accumulation between the dermis and the epidermis), and itching. If one intended to transfer this response from a sensitized to a naive individual, one would transfer:
A) Mast cells with their pre-bound IgE from the sensitized to the naive individual
B) Purified IgG antibody from the serum of the sensitized to the naive individual
C) T cells from the skin-draining lymph nodes of the sensitized to the naive individual
D) Dendritic cells from the skin of the sensitized to the naive individual
E) Fc -receptor positive phagocytes from the skin of the sensitized to the naive individual
A) Mast cells with their pre-bound IgE from the sensitized to the naive individual
B) Purified IgG antibody from the serum of the sensitized to the naive individual
C) T cells from the skin-draining lymph nodes of the sensitized to the naive individual
D) Dendritic cells from the skin of the sensitized to the naive individual
E) Fc -receptor positive phagocytes from the skin of the sensitized to the naive individual

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Hypersensitivity responses to divalent cations such as nickel are relatively common. Individuals sensitized to these metals will develop a skin rash within 15 minutes of putting on a bracelet or ring containing that metal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



