Deck 10: Molecular Biology of the Gene
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/85
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 10: Molecular Biology of the Gene
1
Multiple origins of replication on the DNA molecules of eukaryotic cells serve to
A) remove errors in DNA replication.
B) create multiple copies of the DNA molecule at the same time.
C) shorten the time necessary for DNA replication.
D) assure the correct orientation of the two strands in the newly growing double helix.
A) remove errors in DNA replication.
B) create multiple copies of the DNA molecule at the same time.
C) shorten the time necessary for DNA replication.
D) assure the correct orientation of the two strands in the newly growing double helix.
C
2
Which of the following enzymes catalyzes the elongation of a new DNA strand?
A) RNA polymerase
B) DNA ligase
C) reverse transcriptase
D) DNA polymerase
A) RNA polymerase
B) DNA ligase
C) reverse transcriptase
D) DNA polymerase
D
3
When a T2 bacteriophage infects an Escherichia coli cell, which part of the phage enters the bacterial cytoplasm?
A) the whole phage
B) only the RNA
C) only the DNA
D) the protein "head" and its enclosed nucleic acid
A) the whole phage
B) only the RNA
C) only the DNA
D) the protein "head" and its enclosed nucleic acid
C
4
The transfer of genetic information from DNA to RNA is called
A) translation.
B) transcription.
C) initiation.
D) elongation.
A) translation.
B) transcription.
C) initiation.
D) elongation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
DNA replication
A) occurs through the addition of nucleotides to the end of the parental DNA molecule.
B) results in the formation of four new DNA strands.
C) uses each strand of a DNA molecule as a template for the creation of a new strand.
D) begins when two DNA molecules join together to exchange segments.
A) occurs through the addition of nucleotides to the end of the parental DNA molecule.
B) results in the formation of four new DNA strands.
C) uses each strand of a DNA molecule as a template for the creation of a new strand.
D) begins when two DNA molecules join together to exchange segments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
If one strand of DNA is CGGTAC, then the complementary strand would be
A) GCCTAG.
B) GCCAUC.
C) TAACGT.
D) GCCATG.
A) GCCTAG.
B) GCCAUC.
C) TAACGT.
D) GCCATG.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The way that genetic material of a bacteriophage enters a bacterium is most like the way that
A) a drug is injected with a hypodermic needle.
B) a person swallows a pill.
C) skin lotion is rubbed onto the hands.
D) water soaks into a sponge.
A) a drug is injected with a hypodermic needle.
B) a person swallows a pill.
C) skin lotion is rubbed onto the hands.
D) water soaks into a sponge.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A phage is a virus that infects
A) bacteria.
B) plants.
C) animals.
D) humans.
A) bacteria.
B) plants.
C) animals.
D) humans.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following statements regarding RNA is false?
A) RNA contains the sugar dextrose.
B) RNA contains the nitrogenous base uracil.
C) One RNA molecule can include four different nucleotides in its structure.
D) RNA molecules have a sugar-phosphate backbone.
A) RNA contains the sugar dextrose.
B) RNA contains the nitrogenous base uracil.
C) One RNA molecule can include four different nucleotides in its structure.
D) RNA molecules have a sugar-phosphate backbone.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
When one DNA molecule is copied to make two new DNA molecules, the resulting DNA molecules contain
A) none of the parent DNA.
B) 50% of the parent DNA.
C) 75% of the parent DNA.
D) 100% of the parent DNA
A) none of the parent DNA.
B) 50% of the parent DNA.
C) 75% of the parent DNA.
D) 100% of the parent DNA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following statements regarding the structure of DNA is false?
A) The DNA molecule has a uniform diameter.
B) In a DNA molecule, adenine bonds to thymine and guanine to cytosine.
C) Watson and Crick received a Nobel Prize for their description of the structure of DNA.
D) The sequence of nucleotides along the length of a single DNA strand is restricted by the base-pairing rules.
A) The DNA molecule has a uniform diameter.
B) In a DNA molecule, adenine bonds to thymine and guanine to cytosine.
C) Watson and Crick received a Nobel Prize for their description of the structure of DNA.
D) The sequence of nucleotides along the length of a single DNA strand is restricted by the base-pairing rules.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following people conducted the experiments that demonstrated that DNA is the genetic material of bacteriophages?
A) Watson and Crick
B) Hershey and Chase
C) Franklin
A) Watson and Crick
B) Hershey and Chase
C) Franklin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following options best depicts the flow of information when a gene directs the synthesis of a cellular component?
A) RNA → DNA → RNA → protein
B) DNA → RNA → protein
C) protein → RNA → DNA
D) DNA → tRNA → mRNA → protein
A) RNA → DNA → RNA → protein
B) DNA → RNA → protein
C) protein → RNA → DNA
D) DNA → tRNA → mRNA → protein

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following statements regarding DNA is false?
A) DNA contains the sugar deoxyribose.
B) DNA contains the nitrogenous base uracil.
C) One DNA molecule can include four different nucleotides in its structure.
D) DNA molecules have a sugar-phosphate backbone.
A) DNA contains the sugar deoxyribose.
B) DNA contains the nitrogenous base uracil.
C) One DNA molecule can include four different nucleotides in its structure.
D) DNA molecules have a sugar-phosphate backbone.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The shape of a DNA molecule is most like
A) a set of railroad tracks.
B) a wooden ladder.
C) a twisted rope ladder.
D) beads on a string.
A) a set of railroad tracks.
B) a wooden ladder.
C) a twisted rope ladder.
D) beads on a string.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Why does a DNA strand grow only in the 5ʹ to 3ʹ direction?
A) because DNA polymerases can only add nucleotides to the 3ʹ end of the growing molecule
B) because DNA polymerases can only add nucleotides to the 5ʹ end of the growing molecule
C) because the DNA molecule only unwinds in the 5ʹ to 3ʹ direction
D) because DNA polymerase requires the addition of a starter nucleotide at the 5ʹ end
A) because DNA polymerases can only add nucleotides to the 3ʹ end of the growing molecule
B) because DNA polymerases can only add nucleotides to the 5ʹ end of the growing molecule
C) because the DNA molecule only unwinds in the 5ʹ to 3ʹ direction
D) because DNA polymerase requires the addition of a starter nucleotide at the 5ʹ end

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The copying mechanism of DNA is most like
A) taking a picture of yourself and of your reflection in a mirror.
B) mixing flour, sugar, and water to make bread dough.
C) looking at your reflection in a pool of water.
D) carving a figure out of wood.
A) taking a picture of yourself and of your reflection in a mirror.
B) mixing flour, sugar, and water to make bread dough.
C) looking at your reflection in a pool of water.
D) carving a figure out of wood.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The monomers of DNA and RNA are
A) monosaccharides.
B) nucleotides.
C) fatty acids.
D) nucleic acids.
A) monosaccharides.
B) nucleotides.
C) fatty acids.
D) nucleic acids.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
How would the shape of a DNA molecule change if adenine paired with guanine and cytosine paired with thymine?
A) The DNA molecule would be longer.
B) The DNA molecule would be shorter.
C) The DNA molecule would be circular.
D) The DNA molecule would have irregular widths along its length.
A) The DNA molecule would be longer.
B) The DNA molecule would be shorter.
C) The DNA molecule would be circular.
D) The DNA molecule would have irregular widths along its length.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following statements regarding a DNA double helix is true?
A) The amount of adenine is equal to the amount of uracil, and the amount of guanine is equal to the amount of cytosine.
B) The amount of adenine is equal to the amount of guanine, and the amount of thymine is equal to the amount of cytosine.
C) The amount of adenine is equal to the amount of cytosine, and the amount of guanine is equal to the amount of thymine.
D) The amount of adenine is equal to the amount of thymine, and the amount of guanine is equal to the amount of cytosine.
A) The amount of adenine is equal to the amount of uracil, and the amount of guanine is equal to the amount of cytosine.
B) The amount of adenine is equal to the amount of guanine, and the amount of thymine is equal to the amount of cytosine.
C) The amount of adenine is equal to the amount of cytosine, and the amount of guanine is equal to the amount of thymine.
D) The amount of adenine is equal to the amount of thymine, and the amount of guanine is equal to the amount of cytosine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The directions for each amino acid in a polypeptide are indicated by a codon that consists of ________ nucleotides in an RNA molecule.
A) five
B) four
C) three
D) two
A) five
B) four
C) three
D) two

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following is a function of a tRNA molecule?
A) recognizing the appropriate anticodons in mRNA
B) transferring nucleotides to rRNA
C) helping to translate codons into nucleic acids
D) joining to only one specific type of amino acid
A) recognizing the appropriate anticodons in mRNA
B) transferring nucleotides to rRNA
C) helping to translate codons into nucleic acids
D) joining to only one specific type of amino acid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Consider the following sentence: "The dog did not eat." Which of the following variations of this sentence is most like a frameshift mutation?
A) The did dog not eat.
B) The dod idn ote at.
C) The did not eat.
D) The dog did dog did not eat.
A) The did dog not eat.
B) The dod idn ote at.
C) The did not eat.
D) The dog did dog did not eat.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following options most accurately lists the sequence of events in translation?
A) codon recognition → translocation → peptide bond formation → termination
B) peptide bond formation → codon recognition → translocation → termination
C) codon recognition → peptide bond formation → translocation → termination
D) codon recognition → peptide bond formation → termination → translocation
A) codon recognition → translocation → peptide bond formation → termination
B) peptide bond formation → codon recognition → translocation → termination
C) codon recognition → peptide bond formation → translocation → termination
D) codon recognition → peptide bond formation → termination → translocation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Where do transcription and translation occur in prokaryotic cells?
A) in the plasma membrane
B) in the nucleus
C) in the cytoplasm
D) in mitochondria
A) in the plasma membrane
B) in the nucleus
C) in the cytoplasm
D) in mitochondria

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
We would expect that a 15-nucleotide sequence that includes a stop codon at the end (as part of the 15-nucleotide sequence) will direct the production of a polypeptide that consists of
A) two amino acids.
B) three amino acids.
C) four amino acids.
D) five amino acids.
A) two amino acids.
B) three amino acids.
C) four amino acids.
D) five amino acids.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the following statements about eukaryotic RNA is true?
A) Introns are not transcribed from DNA to RNA.
B) Exons are spliced together.
C) A small cap of extra nucleotides is added to both ends of the RNA.
D) The modified RNA molecule is transported into the nucleus.
A) Introns are not transcribed from DNA to RNA.
B) Exons are spliced together.
C) A small cap of extra nucleotides is added to both ends of the RNA.
D) The modified RNA molecule is transported into the nucleus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the following statements is false?
A) Translation consists of initiation, elongation, and termination.
B) During polypeptide initiation, an mRNA molecule, the first amino acid attached to its tRNA, and the two subunits of a ribosome are brought together.
C) The start codon can be different depending on what kind of protein is to be translated.
D) During the first step of initiation, an mRNA molecule binds to a small ribosomal subunit.
A) Translation consists of initiation, elongation, and termination.
B) During polypeptide initiation, an mRNA molecule, the first amino acid attached to its tRNA, and the two subunits of a ribosome are brought together.
C) The start codon can be different depending on what kind of protein is to be translated.
D) During the first step of initiation, an mRNA molecule binds to a small ribosomal subunit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following takes place during translation?
A) the conversion of genetic information from the language of nucleic acids to the language of proteins
B) the conversion of genetic information from DNA nucleotides into RNA nucleotides
C) the conversion of genetic information from the language of proteins to the language of enzymes
A) the conversion of genetic information from the language of nucleic acids to the language of proteins
B) the conversion of genetic information from DNA nucleotides into RNA nucleotides
C) the conversion of genetic information from the language of proteins to the language of enzymes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
________ marks the end of a gene and causes transcription to stop.
A) A stop codon
B) RNA ligase
C) A terminator
D) Methionine
A) A stop codon
B) RNA ligase
C) A terminator
D) Methionine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Experiments have demonstrated that the "words" of the genetic code (the units that specify amino acids) are
A) single nucleotides.
B) two-nucleotide sequences.
C) three-nucleotide sequences.
D) nucleotide sequences of various lengths.
A) single nucleotides.
B) two-nucleotide sequences.
C) three-nucleotide sequences.
D) nucleotide sequences of various lengths.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Considering only the steps that take place during translation, which of the following is not needed in order for translation to occur?
A) DNA template
B) ribosomes
C) tRNA
D) sources of energy, including ATP
A) DNA template
B) ribosomes
C) tRNA
D) sources of energy, including ATP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Consider the following sentence: "The dog did not eat." Which of the following variations of this sentence is most like a base substitution mutation?
A) The dog did not et.
B) The dog dog did not eat.
C) The did dog not eat.
D) The doe did not eat.
A) The dog did not et.
B) The dog dog did not eat.
C) The did dog not eat.
D) The doe did not eat.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which of the following statements about ribosomes is false?
A) A ribosome consists of two subunits.
B) Ribosomal subunits are made of proteins and ribosomal RNA.
C) The ribosomes of prokaryotes and eukaryotes are the exactly the same in structure and function.
D) Each ribosome has two binding sites for tRNA molecules.
A) A ribosome consists of two subunits.
B) Ribosomal subunits are made of proteins and ribosomal RNA.
C) The ribosomes of prokaryotes and eukaryotes are the exactly the same in structure and function.
D) Each ribosome has two binding sites for tRNA molecules.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Any change in the nucleotide sequence of DNA is called a
A) mutation.
B) frameshift.
C) base substitution.
A) mutation.
B) frameshift.
C) base substitution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following occurs when RNA polymerase attaches to the promoter DNA?
A) elongation of the growing RNA molecule
B) termination of the RNA molecule
C) initiation of a new RNA molecule
D) initiation of a new polypeptide chain
A) elongation of the growing RNA molecule
B) termination of the RNA molecule
C) initiation of a new RNA molecule
D) initiation of a new polypeptide chain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The "one gene-one enzyme" hypothesis states that
A) the synthesis of each gene is catalyzed by one specific enzyme.
B) the synthesis of each enzyme is catalyzed by one specific gene.
C) the function of an individual gene is to dictate the production of a specific polypeptide.
D) the function of each polypeptide is to regulate the synthesis of each corresponding gene.
A) the synthesis of each gene is catalyzed by one specific enzyme.
B) the synthesis of each enzyme is catalyzed by one specific gene.
C) the function of an individual gene is to dictate the production of a specific polypeptide.
D) the function of each polypeptide is to regulate the synthesis of each corresponding gene.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
In the genetic code
A) some codons specify more than one amino acid.
B) some codons consist of two nucleotides.
C) some amino acids are not specified by any codons.
D) many amino acids are specified by more than one codon.
A) some codons specify more than one amino acid.
B) some codons consist of two nucleotides.
C) some amino acids are not specified by any codons.
D) many amino acids are specified by more than one codon.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of the following enzymes catalyzes the production of a strand of RNA from DNA?
A) RNA polymerase
B) DNA ligase
C) DNA polymerase
D) reverse transcriptase
A) RNA polymerase
B) DNA ligase
C) DNA polymerase
D) reverse transcriptase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following statements regarding the flow of genetic information is false?
A) Polypeptides form proteins that determine the appearance and function of the cell and organism.
B) Eukaryotic mRNA is processed in several ways before export out of the nucleus.
C) Transcription occurs in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells.
D) Ribosomes function as factories that coordinate the functioning of mRNA and tRNA.
A) Polypeptides form proteins that determine the appearance and function of the cell and organism.
B) Eukaryotic mRNA is processed in several ways before export out of the nucleus.
C) Transcription occurs in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells.
D) Ribosomes function as factories that coordinate the functioning of mRNA and tRNA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which of the following statements regarding viral diseases is false?
A) RNA viruses tend to have an unusually high rate of mutation because their RNA genomes cannot be corrected by proofreading.
B) New viral diseases often emerge when a virus infects a new host species.
C) Very few new human diseases have originated in other animals because the genetic differences are too great.
D) AIDS was around for decades before becoming a widespread epidemic.
A) RNA viruses tend to have an unusually high rate of mutation because their RNA genomes cannot be corrected by proofreading.
B) New viral diseases often emerge when a virus infects a new host species.
C) Very few new human diseases have originated in other animals because the genetic differences are too great.
D) AIDS was around for decades before becoming a widespread epidemic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
A friend accidentally sends an email to you that contains a computer virus from his computer. Without knowing it, you infect your computer with the virus when you open the email. This process of spreading the computer virus via email is most like which of the following processes?
A) binary fission
B) conjugation
C) transduction
D) transformation
A) binary fission
B) conjugation
C) transduction
D) transformation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Transduction
A) is the direct transfer of DNA from one bacterium to another.
B) occurs when a bacterium acquires DNA from the surrounding environment.
C) occurs when a phage transfers bacterial DNA from one bacterium to another.
D) requires DNA polymerase.
A) is the direct transfer of DNA from one bacterium to another.
B) occurs when a bacterium acquires DNA from the surrounding environment.
C) occurs when a phage transfers bacterial DNA from one bacterium to another.
D) requires DNA polymerase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
In the 1920s, Frederick Griffith conducted an experiment in which he mixed the dead cells of a bacterial strain that can cause pneumonia with live cells of a bacterial strain that cannot. When he cultured the live cells, some of the daughter colonies proved able to cause pneumonia. Which of the following processes of bacterial DNA transfer does this experiment demonstrate?
A) transduction
B) conjugation
C) transformation
A) transduction
B) conjugation
C) transformation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
A protein coat that enclosed a viral genome is known as a(n)
A) capsule.
B) envelope.
C) capsid.
D) prophage.
A) capsule.
B) envelope.
C) capsid.
D) prophage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
When a bacterial cell with a chromosome-borne F factor conjugates with another bacterium, how is the transmitted donor DNA incorporated into the recipient's genome?
A) It is substituted for the equivalent portion of the recipient's chromosome by the process of crossing over.
B) It circularizes and becomes one of the recipient cell's plasmids.
C) Any genes on the donor DNA of which the recipient does not have are added to the recipient chromosome; the remainder of the donor DNA is degraded.
D) The donor and recipient DNA are both chopped into segments by restriction enzymes, and a new, composite chromosome is assembled from the fragments.
A) It is substituted for the equivalent portion of the recipient's chromosome by the process of crossing over.
B) It circularizes and becomes one of the recipient cell's plasmids.
C) Any genes on the donor DNA of which the recipient does not have are added to the recipient chromosome; the remainder of the donor DNA is degraded.
D) The donor and recipient DNA are both chopped into segments by restriction enzymes, and a new, composite chromosome is assembled from the fragments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Which of the following statements characterizes the lytic cycle of a viral infection?
A) The cycle typically ends when the host bacterium divides.
B) The cycle typically leads to the lysis of the host cell.
C) The virus reproduces outside of the host cell.
D) The viral genes typically remain inactive once they are inside the host cell.
A) The cycle typically ends when the host bacterium divides.
B) The cycle typically leads to the lysis of the host cell.
C) The virus reproduces outside of the host cell.
D) The viral genes typically remain inactive once they are inside the host cell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Conjugation
A) is the direct transfer of DNA from one bacterium to another.
B) occurs when a bacterium acquires DNA from the surrounding environment.
C) is the result of cell division.
D) occurs when a phage transfers bacterial DNA from one bacterium to another.
A) is the direct transfer of DNA from one bacterium to another.
B) occurs when a bacterium acquires DNA from the surrounding environment.
C) is the result of cell division.
D) occurs when a phage transfers bacterial DNA from one bacterium to another.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Which of the following statements about herpesviruses is false?
A) Herpesviruses reproduce inside the host cell's mitochondria.
B) Herpesviruses acquire their envelopes from the host cell nuclear membrane.
C) Herpesviruses may remain dormant for long periods of time while inside the host cell nucleus.
D) Herpesviruses may cause cold sores or genital sores to appear during times of physical or emotional stress.
A) Herpesviruses reproduce inside the host cell's mitochondria.
B) Herpesviruses acquire their envelopes from the host cell nuclear membrane.
C) Herpesviruses may remain dormant for long periods of time while inside the host cell nucleus.
D) Herpesviruses may cause cold sores or genital sores to appear during times of physical or emotional stress.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which of the following statements is false?
A) Some prophage genes can cause the transformation of a nonpathogenic bacterium into a form that causes human disease.
B) Sometimes an environmental signal can trigger a switchover from the lysogenic to the lytic cycle.
C) The lysogenic cycle always occurs inside of host cells.
D) The lysogenic cycle typically results in the rapid lysis of all infected cells.
A) Some prophage genes can cause the transformation of a nonpathogenic bacterium into a form that causes human disease.
B) Sometimes an environmental signal can trigger a switchover from the lysogenic to the lytic cycle.
C) The lysogenic cycle always occurs inside of host cells.
D) The lysogenic cycle typically results in the rapid lysis of all infected cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Viral DNA incorporated into host cell DNA is known as a(n)
A) capsid.
B) prophage.
C) envelope.
D) phage.
A) capsid.
B) prophage.
C) envelope.
D) phage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The envelope of a mumps virus
A) helps the virus enter the cell.
B) is coded by host genes.
C) helps the virus insert its DNA into the host cell genome.
D) accounts for viral resistance to antibiotics.
A) helps the virus enter the cell.
B) is coded by host genes.
C) helps the virus insert its DNA into the host cell genome.
D) accounts for viral resistance to antibiotics.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
HIV does the greatest damage to
A) the adrenal glands.
B) pancreatic cells.
C) nervous tissue.
D) white blood cells.
A) the adrenal glands.
B) pancreatic cells.
C) nervous tissue.
D) white blood cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Conjugation, transformation, and transduction are all ways that bacteria
A) reduce their DNA content.
B) increase the amount of RNA in the cytoplasm.
C) increase their genetic diversity.
D) alter their oxygen requirements.
A) reduce their DNA content.
B) increase the amount of RNA in the cytoplasm.
C) increase their genetic diversity.
D) alter their oxygen requirements.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The 2009 H1N1 flu virus
A) was an avian flu virus.
B) was spread by mosquitoes.
C) evolved through the genetic reshuffling of viruses that infect humans, birds, and pigs.
D) killed over 50 million people worldwide.
A) was an avian flu virus.
B) was spread by mosquitoes.
C) evolved through the genetic reshuffling of viruses that infect humans, birds, and pigs.
D) killed over 50 million people worldwide.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
In many bacteria, genes that confer resistance to antibiotics are carried on
A) F factors.
B) R plasmids.
C) introns.
D) exons.
A) F factors.
B) R plasmids.
C) introns.
D) exons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which of the following statements about treatment or prevention of a prion infection is true?
A) Antibiotic therapies such as penicillin are very effective cures.
B) High doses of anti-inflammatory drugs such as ibuprofen reduce the symptoms of prion infections.
C) Preventative vaccines have recently been shown to be effective in preventing prion infections.
D) There is no known treatment or cure for prion infections.
A) Antibiotic therapies such as penicillin are very effective cures.
B) High doses of anti-inflammatory drugs such as ibuprofen reduce the symptoms of prion infections.
C) Preventative vaccines have recently been shown to be effective in preventing prion infections.
D) There is no known treatment or cure for prion infections.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which of the following statements about plant viruses is false?
A) Once in a plant, a virus can spread from cell to cell through plasmodesmata.
B) The genetic material in most plant viruses is RNA.
C) Preventing infections and breeding resistant plants can control viral infection in plants.
D) There are many successful ways to rid infected plants of a virus.
A) Once in a plant, a virus can spread from cell to cell through plasmodesmata.
B) The genetic material in most plant viruses is RNA.
C) Preventing infections and breeding resistant plants can control viral infection in plants.
D) There are many successful ways to rid infected plants of a virus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
A physical or chemical agent that changes the nucleotide sequence of DNA is called a(n)
A) terminator.
B) prion.
C) mutagen.
D) anticodon.
A) terminator.
B) prion.
C) mutagen.
D) anticodon.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Which of the following enzymes does HIV use to synthesize DNA on an RNA template?
A) DNA ligase
B) RNA polymerase
C) reverse transcriptase
D) DNA polymerase
A) DNA ligase
B) RNA polymerase
C) reverse transcriptase
D) DNA polymerase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
After reading the paragraphs below, answer the questions that follow.
Exposure to the HIV virus doesn't necessarily mean that a person will develop AIDS. Some people have genetic resistance to infection by HIV. Dr. Stephen O'Brien from the U.S. National Cancer Institute has recently identified a mutant form of a gene, called CCR5, that can protect against HIV infection. The mutation probably originated in Europe and became more prevalent among survivors of the bubonic plague. The mutated gene prevents the plague bacteria from attaching to cell membranes and, therefore, from entering and infecting body cells.
Although the HIV virus is very different from the bacteria that causes the plague, both diseases affect the exact same cells and use the same method of infection. The presence of the mutated gene in descendants of plague survivors helps prevent them from contracting AIDS. Pharmaceutical companies are using this information as the basis for a new approach to AIDS prevention. This could be very important in areas of the world where the mutation is scarce or absent, such as Africa.
The most likely method by which the mutated CCR5 gene prevents AIDS is by
A) covering the cell membrane.
B) rupturing the nuclear membrane.
C) attacking and destroying the HIV virus particles.
D) coding for a protective protein in the cell membrane.
Exposure to the HIV virus doesn't necessarily mean that a person will develop AIDS. Some people have genetic resistance to infection by HIV. Dr. Stephen O'Brien from the U.S. National Cancer Institute has recently identified a mutant form of a gene, called CCR5, that can protect against HIV infection. The mutation probably originated in Europe and became more prevalent among survivors of the bubonic plague. The mutated gene prevents the plague bacteria from attaching to cell membranes and, therefore, from entering and infecting body cells.
Although the HIV virus is very different from the bacteria that causes the plague, both diseases affect the exact same cells and use the same method of infection. The presence of the mutated gene in descendants of plague survivors helps prevent them from contracting AIDS. Pharmaceutical companies are using this information as the basis for a new approach to AIDS prevention. This could be very important in areas of the world where the mutation is scarce or absent, such as Africa.
The most likely method by which the mutated CCR5 gene prevents AIDS is by
A) covering the cell membrane.
B) rupturing the nuclear membrane.
C) attacking and destroying the HIV virus particles.
D) coding for a protective protein in the cell membrane.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
After reading the paragraphs below, answer the questions that follow.
Diabetes mellitus is a metabolic disease that is characterized by the buildup of glucose in the blood, or hyperglycemia. Diabetes results either from the pancreas not being able to produce the hormone insulin (type 1 diabetes) or if the body's cells become resistant to insulin (type 2 diabetes). Insulin is a protein that binds to receptors on cell surfaces to allow glucose to enter the cell.
In order to manage the disease, type 1 diabetics require frequent insulin injections. Until the 1970s, insulin was obtained from processing the pancreases of large mammals such as cows and pigs; it was then purified for medicinal use. This all changed in the 1970s with the advent of recombinant DNA technology, which allows scientists to insert genes from other species into bacterial plasmids and have bacteria produce proteins from these other species' genes. In 1978, the gene that codes for human insulin was added to a bacterial plasmid and bacteria were used to produce human insulin. These bacteria acted as mini-factories that produced human insulin for type 1 diabetes patients. Today, the production of human insulin from bacteria is commonplace and is a multibillion dollar market for pharmaceutical companies.
In order for bacterial cells to be able to produce the human insulin protein, which of the following is not required?
A) Bacteria and humans have to use the same genetic code.
B) Bacterial RNA polymerases have to recognize human promoters.
C) Bacterial ribosomes have to recognize human start and stop codons.
D) Bacteria have to have a gene for a bacterial form of insulin.
Diabetes mellitus is a metabolic disease that is characterized by the buildup of glucose in the blood, or hyperglycemia. Diabetes results either from the pancreas not being able to produce the hormone insulin (type 1 diabetes) or if the body's cells become resistant to insulin (type 2 diabetes). Insulin is a protein that binds to receptors on cell surfaces to allow glucose to enter the cell.
In order to manage the disease, type 1 diabetics require frequent insulin injections. Until the 1970s, insulin was obtained from processing the pancreases of large mammals such as cows and pigs; it was then purified for medicinal use. This all changed in the 1970s with the advent of recombinant DNA technology, which allows scientists to insert genes from other species into bacterial plasmids and have bacteria produce proteins from these other species' genes. In 1978, the gene that codes for human insulin was added to a bacterial plasmid and bacteria were used to produce human insulin. These bacteria acted as mini-factories that produced human insulin for type 1 diabetes patients. Today, the production of human insulin from bacteria is commonplace and is a multibillion dollar market for pharmaceutical companies.
In order for bacterial cells to be able to produce the human insulin protein, which of the following is not required?
A) Bacteria and humans have to use the same genetic code.
B) Bacterial RNA polymerases have to recognize human promoters.
C) Bacterial ribosomes have to recognize human start and stop codons.
D) Bacteria have to have a gene for a bacterial form of insulin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Conjugation between a bacterium that lacks an F factor (F−) and a bacterium that has an F factor on its chromosome (F+) could produce which of the following results?
A) The F− bacterium ends up carrying one or more plasmids from the F+ bacterium; the F+ bacterium is unchanged.
B) The F+ bacterium ends up with a recombinant chromosome that carries some genes from the F− bacterium, and the F− bacterium ends up with an unaltered chromosome.
C) The F+ bacterium ends up with a recombinant chromosome that carries some genes from the F− bacterium, and the F− bacterium ends up with a chromosome that lacks those genes.
D) The F− bacterium ends up with a recombinant chromosome that carries some genes from the F+ bacterium, and the F+ bacterium ends up with an unaltered chromosome.
A) The F− bacterium ends up carrying one or more plasmids from the F+ bacterium; the F+ bacterium is unchanged.
B) The F+ bacterium ends up with a recombinant chromosome that carries some genes from the F− bacterium, and the F− bacterium ends up with an unaltered chromosome.
C) The F+ bacterium ends up with a recombinant chromosome that carries some genes from the F− bacterium, and the F− bacterium ends up with a chromosome that lacks those genes.
D) The F− bacterium ends up with a recombinant chromosome that carries some genes from the F+ bacterium, and the F+ bacterium ends up with an unaltered chromosome.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
After reading the paragraphs below, answer the questions that follow.
Diabetes mellitus is a metabolic disease that is characterized by the buildup of glucose in the blood, or hyperglycemia. Diabetes results either from the pancreas not being able to produce the hormone insulin (type 1 diabetes) or if the body's cells become resistant to insulin (type 2 diabetes). Insulin is a protein that binds to receptors on cell surfaces to allow glucose to enter the cell.
In order to manage the disease, type 1 diabetics require frequent insulin injections. Until the 1970s, insulin was obtained from processing the pancreases of large mammals such as cows and pigs; it was then purified for medicinal use. This all changed in the 1970s with the advent of recombinant DNA technology, which allows scientists to insert genes from other species into bacterial plasmids and have bacteria produce proteins from these other species' genes. In 1978, the gene that codes for human insulin was added to a bacterial plasmid and bacteria were used to produce human insulin. These bacteria acted as mini-factories that produced human insulin for type 1 diabetes patients. Today, the production of human insulin from bacteria is commonplace and is a multibillion dollar market for pharmaceutical companies.
Suppose that the human insulin protein that was produced by the bacteria was much shorter than it should be. Upon further investigation, it was found that the DNA of the human insulin gene had a mutation while in the bacterial cells. What type of mutation could not result in these observations?
A) nucleotide insertion
B) silent mutation
C) nucleotide deletion
D) nonsense mutation
Diabetes mellitus is a metabolic disease that is characterized by the buildup of glucose in the blood, or hyperglycemia. Diabetes results either from the pancreas not being able to produce the hormone insulin (type 1 diabetes) or if the body's cells become resistant to insulin (type 2 diabetes). Insulin is a protein that binds to receptors on cell surfaces to allow glucose to enter the cell.
In order to manage the disease, type 1 diabetics require frequent insulin injections. Until the 1970s, insulin was obtained from processing the pancreases of large mammals such as cows and pigs; it was then purified for medicinal use. This all changed in the 1970s with the advent of recombinant DNA technology, which allows scientists to insert genes from other species into bacterial plasmids and have bacteria produce proteins from these other species' genes. In 1978, the gene that codes for human insulin was added to a bacterial plasmid and bacteria were used to produce human insulin. These bacteria acted as mini-factories that produced human insulin for type 1 diabetes patients. Today, the production of human insulin from bacteria is commonplace and is a multibillion dollar market for pharmaceutical companies.
Suppose that the human insulin protein that was produced by the bacteria was much shorter than it should be. Upon further investigation, it was found that the DNA of the human insulin gene had a mutation while in the bacterial cells. What type of mutation could not result in these observations?
A) nucleotide insertion
B) silent mutation
C) nucleotide deletion
D) nonsense mutation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Use the figure below to answer the questions that follow.
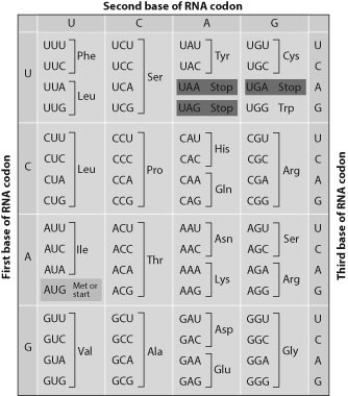
Examine the following two DNA sequences. Sequence 1: ATGCGATGCTAGCAT
Sequence 2: ATGCGATGATAGCAT
If both of these sequences code for proteins, how might the function of protein 2 differ from the function of protein 1? Use the genetic code shown for assistance.
A) Protein 1 and protein 2 will function exactly the same.
B) Protein 1 will be shorter than protein 2, so they will not function the same.
C) Protein 2 will be shorter than protein 1, so they will not function the same.
D) Protein 2 has a different sequence, so it will function differently from protein 1.

Examine the following two DNA sequences. Sequence 1: ATGCGATGCTAGCAT
Sequence 2: ATGCGATGATAGCAT
If both of these sequences code for proteins, how might the function of protein 2 differ from the function of protein 1? Use the genetic code shown for assistance.
A) Protein 1 and protein 2 will function exactly the same.
B) Protein 1 will be shorter than protein 2, so they will not function the same.
C) Protein 2 will be shorter than protein 1, so they will not function the same.
D) Protein 2 has a different sequence, so it will function differently from protein 1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
What is the transcription product of the sequence GCTAGCGATGAC?
A) CGTUCGCUTCUG
B) CGAUCGCUACUG
C) CAGTAGCGATCG
D) CGUTCGCUTCUG
A) CGTUCGCUTCUG
B) CGAUCGCUACUG
C) CAGTAGCGATCG
D) CGUTCGCUTCUG

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
After reading the paragraphs below, answer the questions that follow.
Exposure to the HIV virus doesn't necessarily mean that a person will develop AIDS. Some people have genetic resistance to infection by HIV. Dr. Stephen O'Brien from the U.S. National Cancer Institute has recently identified a mutant form of a gene, called CCR5, that can protect against HIV infection. The mutation probably originated in Europe and became more prevalent among survivors of the bubonic plague. The mutated gene prevents the plague bacteria from attaching to cell membranes and, therefore, from entering and infecting body cells.
Although the HIV virus is very different from the bacteria that causes the plague, both diseases affect the exact same cells and use the same method of infection. The presence of the mutated gene in descendants of plague survivors helps prevent them from contracting AIDS. Pharmaceutical companies are using this information as the basis for a new approach to AIDS prevention. This could be very important in areas of the world where the mutation is scarce or absent, such as Africa.
Imagine that a pharmaceutical company was successful at producing a drug based on the CCR5 gene product that is effective at preventing the contraction of AIDS. However, shortly after the drug has been in use, patients and doctors report that the drug is not as effective as it once was. What is the most likely explanation for this result?
A) The people taking the drug have built up a tolerance to the drug.
B) Some HIV viruses have genetic variations in the RNA genome that provide resistance to the actions of the drug.
C) The HIV virus gained mutations in its DNA genome in order to become resistant to the actions of the drug.
D) The DNA of white blood cells of the people taking the drug has mutated to become resistant to the drug.
Exposure to the HIV virus doesn't necessarily mean that a person will develop AIDS. Some people have genetic resistance to infection by HIV. Dr. Stephen O'Brien from the U.S. National Cancer Institute has recently identified a mutant form of a gene, called CCR5, that can protect against HIV infection. The mutation probably originated in Europe and became more prevalent among survivors of the bubonic plague. The mutated gene prevents the plague bacteria from attaching to cell membranes and, therefore, from entering and infecting body cells.
Although the HIV virus is very different from the bacteria that causes the plague, both diseases affect the exact same cells and use the same method of infection. The presence of the mutated gene in descendants of plague survivors helps prevent them from contracting AIDS. Pharmaceutical companies are using this information as the basis for a new approach to AIDS prevention. This could be very important in areas of the world where the mutation is scarce or absent, such as Africa.
Imagine that a pharmaceutical company was successful at producing a drug based on the CCR5 gene product that is effective at preventing the contraction of AIDS. However, shortly after the drug has been in use, patients and doctors report that the drug is not as effective as it once was. What is the most likely explanation for this result?
A) The people taking the drug have built up a tolerance to the drug.
B) Some HIV viruses have genetic variations in the RNA genome that provide resistance to the actions of the drug.
C) The HIV virus gained mutations in its DNA genome in order to become resistant to the actions of the drug.
D) The DNA of white blood cells of the people taking the drug has mutated to become resistant to the drug.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
What nucleotide sequence would be found on the complementary DNA strand of the strand shown here? 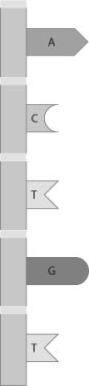
A) ACTGT
B) UGAGA
C) TGACA
D) TGUGU

A) ACTGT
B) UGAGA
C) TGACA
D) TGUGU

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
If the left end of the daughter strand indicated by the arrow in the figure is being synthesized in one continuous piece, then 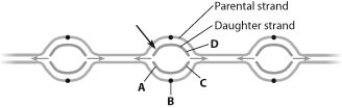
A) the DNA at point A is being synthesized in one continuous piece.
B) the DNA at point B is being synthesized in small pieces.
C) the DNA at point C is being synthesized in one continuous piece.
D) the DNA at point D is being synthesized in one continuous piece.

A) the DNA at point A is being synthesized in one continuous piece.
B) the DNA at point B is being synthesized in small pieces.
C) the DNA at point C is being synthesized in one continuous piece.
D) the DNA at point D is being synthesized in one continuous piece.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Normal genes have a promoter followed by a start codon. In a mutant gene, the "A" in the start codon has been deleted. Which of the following is not a possible outcome?
A) The normal protein will be produced.
B) A shorter protein will be produced.
C) A longer protein will be produced.
D) No protein will be produced.
A) The normal protein will be produced.
B) A shorter protein will be produced.
C) A longer protein will be produced.
D) No protein will be produced.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
If Hershey and Chase had used radioactive oxygen in their experiments instead of phosphorus and sulfur, what results would they have likely obtained?
A) They would have observed a radioactive signal in the pellet only.
B) They would have observed a radioactive signal in the liquid only.
C) They would have observed a radioactive signal in both the pellet and the liquid.
D) They would have not observed radioactivity anywhere.
A) They would have observed a radioactive signal in the pellet only.
B) They would have observed a radioactive signal in the liquid only.
C) They would have observed a radioactive signal in both the pellet and the liquid.
D) They would have not observed radioactivity anywhere.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
After reading the paragraphs below, answer the questions that follow.
Exposure to the HIV virus doesn't necessarily mean that a person will develop AIDS. Some people have genetic resistance to infection by HIV. Dr. Stephen O'Brien from the U.S. National Cancer Institute has recently identified a mutant form of a gene, called CCR5, that can protect against HIV infection. The mutation probably originated in Europe and became more prevalent among survivors of the bubonic plague. The mutated gene prevents the plague bacteria from attaching to cell membranes and, therefore, from entering and infecting body cells.
Although the HIV virus is very different from the bacteria that causes the plague, both diseases affect the exact same cells and use the same method of infection. The presence of the mutated gene in descendants of plague survivors helps prevent them from contracting AIDS. Pharmaceutical companies are using this information as the basis for a new approach to AIDS prevention. This could be very important in areas of the world where the mutation is scarce or absent, such as Africa.
Which of the following shows the steps of a viral infection in the proper order?
A) virus locates host cell → enters nucleus → alters host cell DNA → destroys cell membrane
B) virus locates host cell → alters host cell DNA → host cell produces copies of virus → copies enter host cell nucleus → nucleus leaves cell
C) virus locates host cell → penetrates cell membrane → enters nucleus → alters host cell DNA → host cell produces copies of virus
D) virus locates host cell → forms hydrogen bonds → changes DNA to RNA→ host cell produces copies of virus
Exposure to the HIV virus doesn't necessarily mean that a person will develop AIDS. Some people have genetic resistance to infection by HIV. Dr. Stephen O'Brien from the U.S. National Cancer Institute has recently identified a mutant form of a gene, called CCR5, that can protect against HIV infection. The mutation probably originated in Europe and became more prevalent among survivors of the bubonic plague. The mutated gene prevents the plague bacteria from attaching to cell membranes and, therefore, from entering and infecting body cells.
Although the HIV virus is very different from the bacteria that causes the plague, both diseases affect the exact same cells and use the same method of infection. The presence of the mutated gene in descendants of plague survivors helps prevent them from contracting AIDS. Pharmaceutical companies are using this information as the basis for a new approach to AIDS prevention. This could be very important in areas of the world where the mutation is scarce or absent, such as Africa.
Which of the following shows the steps of a viral infection in the proper order?
A) virus locates host cell → enters nucleus → alters host cell DNA → destroys cell membrane
B) virus locates host cell → alters host cell DNA → host cell produces copies of virus → copies enter host cell nucleus → nucleus leaves cell
C) virus locates host cell → penetrates cell membrane → enters nucleus → alters host cell DNA → host cell produces copies of virus
D) virus locates host cell → forms hydrogen bonds → changes DNA to RNA→ host cell produces copies of virus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
A eukaryotic cell has a nuclear envelope that allows tRNA molecules, but not mRNA molecules, to leave the nucleus. Which of the following processes will not be able to take place in this cell?
A) DNA replication
B) tRNAs binding to codons
C) RNA being made from DNA
D) tRNAs binding to amino acids
A) DNA replication
B) tRNAs binding to codons
C) RNA being made from DNA
D) tRNAs binding to amino acids

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Below are three statements. Which of the following choices properly matches the statements with the correct biological processes? I. This occurs in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells with DNA polymerase.
II) Transfer RNAs bind amino acids in the cytoplasm.
III) An RNA polymerase enzyme is required.
A) I: replication; II: translation; III: transcription
B) I: translation; II: translation; III: replication
C) I: transcription; II: translation; III: translation
D) I: replication; II: transcription; III: replication
II) Transfer RNAs bind amino acids in the cytoplasm.
III) An RNA polymerase enzyme is required.
A) I: replication; II: translation; III: transcription
B) I: translation; II: translation; III: replication
C) I: transcription; II: translation; III: translation
D) I: replication; II: transcription; III: replication

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
A single base mutation occurs in a gene that codes for a protein due to an error in DNA replication. Which of the following outcomes is not possible?
A) The mutation results in changed protein function.
B) The mutation results in a longer or shorter protein or a protein of the same length.
C) The mutation results in a human disease such as sickle-cell disease.
D) The mutation results in mRNA being made from the protein.
A) The mutation results in changed protein function.
B) The mutation results in a longer or shorter protein or a protein of the same length.
C) The mutation results in a human disease such as sickle-cell disease.
D) The mutation results in mRNA being made from the protein.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
You are interested in designing an experiment to test the hypothesis that frogs use the same genetic code as humans. Which of the following experiments would not give you useful data to test this hypothesis?
A) Purify tRNAs from frog cells and human cells and compare their structures.
B) Insert a human gene into a frog cell and see if the correct protein is produced.
C) Insert a frog gene into a human cell and see if the correct protein is produced.
D) Compare nucleotide sequences of promoters from similar frog and human genes.
A) Purify tRNAs from frog cells and human cells and compare their structures.
B) Insert a human gene into a frog cell and see if the correct protein is produced.
C) Insert a frog gene into a human cell and see if the correct protein is produced.
D) Compare nucleotide sequences of promoters from similar frog and human genes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
After reading the paragraphs below, answer the questions that follow.
Diabetes mellitus is a metabolic disease that is characterized by the buildup of glucose in the blood, or hyperglycemia. Diabetes results either from the pancreas not being able to produce the hormone insulin (type 1 diabetes) or if the body's cells become resistant to insulin (type 2 diabetes). Insulin is a protein that binds to receptors on cell surfaces to allow glucose to enter the cell.
In order to manage the disease, type 1 diabetics require frequent insulin injections. Until the 1970s, insulin was obtained from processing the pancreases of large mammals such as cows and pigs; it was then purified for medicinal use. This all changed in the 1970s with the advent of recombinant DNA technology, which allows scientists to insert genes from other species into bacterial plasmids and have bacteria produce proteins from these other species' genes. In 1978, the gene that codes for human insulin was added to a bacterial plasmid and bacteria were used to produce human insulin. These bacteria acted as mini-factories that produced human insulin for type 1 diabetes patients. Today, the production of human insulin from bacteria is commonplace and is a multibillion dollar market for pharmaceutical companies.
In order to add the gene for human insulin to a bacterial plasmid, the DNA molecules have to be "cut" with enzymes called restriction endonucleases and then pasted back together with enzymes called DNA ligases. Imagine that during this process, the first five nucleotides of the human insulin gene were accidentally cut out before it was pasted into the bacterial plasmid. What is the most likely outcome if this plasmid was added to bacterial cells?
A) The human insulin protein would not be produced because transcription would not take place since the RNA polymerase would not recognize the promoter.
B) The human insulin protein would be produced as normal.
C) The human insulin protein would not be produced because the start codon is missing.
D) The human insulin protein would be shorter than normal because it will be missing one amino acid.
Diabetes mellitus is a metabolic disease that is characterized by the buildup of glucose in the blood, or hyperglycemia. Diabetes results either from the pancreas not being able to produce the hormone insulin (type 1 diabetes) or if the body's cells become resistant to insulin (type 2 diabetes). Insulin is a protein that binds to receptors on cell surfaces to allow glucose to enter the cell.
In order to manage the disease, type 1 diabetics require frequent insulin injections. Until the 1970s, insulin was obtained from processing the pancreases of large mammals such as cows and pigs; it was then purified for medicinal use. This all changed in the 1970s with the advent of recombinant DNA technology, which allows scientists to insert genes from other species into bacterial plasmids and have bacteria produce proteins from these other species' genes. In 1978, the gene that codes for human insulin was added to a bacterial plasmid and bacteria were used to produce human insulin. These bacteria acted as mini-factories that produced human insulin for type 1 diabetes patients. Today, the production of human insulin from bacteria is commonplace and is a multibillion dollar market for pharmaceutical companies.
In order to add the gene for human insulin to a bacterial plasmid, the DNA molecules have to be "cut" with enzymes called restriction endonucleases and then pasted back together with enzymes called DNA ligases. Imagine that during this process, the first five nucleotides of the human insulin gene were accidentally cut out before it was pasted into the bacterial plasmid. What is the most likely outcome if this plasmid was added to bacterial cells?
A) The human insulin protein would not be produced because transcription would not take place since the RNA polymerase would not recognize the promoter.
B) The human insulin protein would be produced as normal.
C) The human insulin protein would not be produced because the start codon is missing.
D) The human insulin protein would be shorter than normal because it will be missing one amino acid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Use the figure below to answer the questions that follow.

Using the genetic code shown, what protein sequence does the RNA sequence CUAGCUCGAUAUCUC code for?
A) Asp - Ala - Arg - Ile - Leu
B) Val - Arg - Ala - Phe - Stop
C) Leu - Gly - Tyr - Ala - Leu
D) Leu - Ala - Arg - Tyr - Leu

Using the genetic code shown, what protein sequence does the RNA sequence CUAGCUCGAUAUCUC code for?
A) Asp - Ala - Arg - Ile - Leu
B) Val - Arg - Ala - Phe - Stop
C) Leu - Gly - Tyr - Ala - Leu
D) Leu - Ala - Arg - Tyr - Leu

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
It is possible to synthesize proteins in vitro (in a test tube) without the use of living cells. If starting from a mature mRNA transcript, which of the following components would not be needed to do this?
A) adenine molecules
B) amino acids
C) tRNAs
D) ribosomes
A) adenine molecules
B) amino acids
C) tRNAs
D) ribosomes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Which of the following human activities has contributed to an increase in the number of bacteria having R plasmids?
A) nitrogen fixation by genetically engineered plants
B) improper use of restriction enzymes in research and medical facilities
C) increased carcinogen exposure from excessive fossil fuel burning
D) heavy use of antibiotics in medicine and in agriculture
A) nitrogen fixation by genetically engineered plants
B) improper use of restriction enzymes in research and medical facilities
C) increased carcinogen exposure from excessive fossil fuel burning
D) heavy use of antibiotics in medicine and in agriculture

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



