Deck 33: Control Systems in Plants
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/61
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 33: Control Systems in Plants
1
Bush beans grow as small bushes rather than as vines because their internodes are short and they branch close to the apical meristem. Which substance, if applied to a bush bean, might cause it to elongate its internodes and grow as a vine?
A) a cytokinin
B) a gibberellin
C) abscisic acid (ABA)
D) ethylene
A) a cytokinin
B) a gibberellin
C) abscisic acid (ABA)
D) ethylene
B
2
Grass shoots bend toward the light because, on the shadowed side, a(n)
A) reduction in auxin levels promotes cell elongation.
B) reduction in auxin levels prevents cell elongation.
C) increase in auxin levels promotes cell elongation.
D) increase in auxin levels prevents cell elongation.
A) reduction in auxin levels promotes cell elongation.
B) reduction in auxin levels prevents cell elongation.
C) increase in auxin levels promotes cell elongation.
D) increase in auxin levels prevents cell elongation.
C
3
Plants grow toward light through the action of
A) hormones.
B) nerves.
C) phytochrome.
D) chloroplasts.
A) hormones.
B) nerves.
C) phytochrome.
D) chloroplasts.
A
4
The event that triggers fruit formation is the growth of a pollen tube through the carpel of a flower. Identify a reasonable hypothesis about the basis of this effect.
A) Pollen tubes grow in response to a cytokinin produced by the carpel.
B) Pollen tubes grow in response to abscisic acid.
C) The growing pollen tube produces ethylene.
D) The growing pollen tube produces auxins and/or gibberellins.
A) Pollen tubes grow in response to a cytokinin produced by the carpel.
B) Pollen tubes grow in response to abscisic acid.
C) The growing pollen tube produces ethylene.
D) The growing pollen tube produces auxins and/or gibberellins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The most reliable way to stimulate branching in a plant is to
A) apply auxin to the roots.
B) remove the terminal bud.
C) give short-day light treatments.
D) add extra fertilizer.
A) apply auxin to the roots.
B) remove the terminal bud.
C) give short-day light treatments.
D) add extra fertilizer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Under what conditions would you expect a plant to have the highest concentration of abscisic acid (ABA)?
A) wet tropical rain forest
B) cool environment after a heavy rain
C) houseplant growing in low light conditions
D) desert after a long drought
A) wet tropical rain forest
B) cool environment after a heavy rain
C) houseplant growing in low light conditions
D) desert after a long drought

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which class of hormones produced in the roots of plants promotes cell division and growth and retards the aging of flowers and leaves?
A) gibberellins
B) phytochromes
C) cytokinins
D) ethylene
A) gibberellins
B) phytochromes
C) cytokinins
D) ethylene

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
One experiment in phototropism involved cutting off the tips of grass seedlings before exposing them to light from one side. The decapitated seedlings did not bend toward the light. A valid conclusion from this experiment would be that
A) plants cannot engage in photosynthesis without the tip of the plant.
B) light is perceived by the tip of grass plants.
C) a foil cover over the tip of the seedlings would cause them to bend.
D) hormones are produced in all parts of the plant.
A) plants cannot engage in photosynthesis without the tip of the plant.
B) light is perceived by the tip of grass plants.
C) a foil cover over the tip of the seedlings would cause them to bend.
D) hormones are produced in all parts of the plant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Fruit that forms on an unpollinated plant in response to a hormone will lack
A) flavor.
B) seeds.
C) rind.
D) naturally occurring hormones.
A) flavor.
B) seeds.
C) rind.
D) naturally occurring hormones.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which substance induces "bolting," the rapid elongation of a plant stem?
A) a gibberellin
B) abscisic acid (ABA)
C) ethylene
D) phytochrome
A) a gibberellin
B) abscisic acid (ABA)
C) ethylene
D) phytochrome

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which statement about plant hormones is true?
A) Plant hormones are produced in very small concentrations.
B) Plant hormones mainly affect reproductive processes.
C) A hormone typically has a single, specific effect on all cells.
D) Plant hormones play a vital role in photosynthesis.
A) Plant hormones are produced in very small concentrations.
B) Plant hormones mainly affect reproductive processes.
C) A hormone typically has a single, specific effect on all cells.
D) Plant hormones play a vital role in photosynthesis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
When a nursery worker pinches off the terminal buds on a young plant to make it grow bushy, which plant hormone, when produced, is mainly responsible for growth of side branches?
A) an auxin
B) a gibberellin
C) a cytokinin
D) abscisic acid (ABA)
A) an auxin
B) a gibberellin
C) a cytokinin
D) abscisic acid (ABA)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which substance might induce seeds treated with it to break dormancy?
A) an auxin
B) a cytokinin
C) a gibberellin
D) ethylene
A) an auxin
B) a cytokinin
C) a gibberellin
D) ethylene

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
If the auxin that is produced by an apical meristem is transported in equal amounts down all sides of a twig, the twig will probably
A) elongate evenly.
B) branch near its tip.
C) flower.
D) bend away from the apical meristem.
A) elongate evenly.
B) branch near its tip.
C) flower.
D) bend away from the apical meristem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which example of an evolutionary adaptation decreases herbivory?
A) Plants of the milkweed family produce a toxin that Monarch butterflies can store in their bodies.
B) Corn plants attacked by herbivores release an airborne chemical that turns on defensive genes in nearby corn plants.
C) Caterpillars that feed on plants tend to be green.
D) Damaged, partially eaten leaves can seal off the damaged area by hardening cell walls.
A) Plants of the milkweed family produce a toxin that Monarch butterflies can store in their bodies.
B) Corn plants attacked by herbivores release an airborne chemical that turns on defensive genes in nearby corn plants.
C) Caterpillars that feed on plants tend to be green.
D) Damaged, partially eaten leaves can seal off the damaged area by hardening cell walls.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Plant hormones
A) must be produced in large quantities to be effective.
B) act on all cells they encounter.
C) are chemical signals that influence growth and development.
D) are rare and produced only in response to stress.
A) must be produced in large quantities to be effective.
B) act on all cells they encounter.
C) are chemical signals that influence growth and development.
D) are rare and produced only in response to stress.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Shoot branching is controlled mainly by the interaction of
A) auxins and gibberellins.
B) auxins and cytokinins.
C) gibberellins and cytokinins.
D) cytokinins and abscisic acid.
A) auxins and gibberellins.
B) auxins and cytokinins.
C) gibberellins and cytokinins.
D) cytokinins and abscisic acid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
About how many gibberellins have been identified in plants?
A) one
B) five
C) over one hundred
D) thousands
A) one
B) five
C) over one hundred
D) thousands

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
What is one main effect of auxins on plant growth?
A) They reduce growth by inducing leaves to fall.
B) They increase growth by promoting cell elongation.
C) They increase growth by increasing the rate of photosynthesis.
D) Auxins have no effect on plant growth.
A) They reduce growth by inducing leaves to fall.
B) They increase growth by promoting cell elongation.
C) They increase growth by increasing the rate of photosynthesis.
D) Auxins have no effect on plant growth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which type of plant hormone generally acts as a growth inhibitor?
A) auxins
B) gibberellins
C) cytokinins
D) abscisic acid (ABA)
A) auxins
B) gibberellins
C) cytokinins
D) abscisic acid (ABA)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
What term refers to seasonal changes in the relative lengths of night and day?
A) photoperiod
B) circadian rhythm
C) gravitropism
D) phototropism
A) photoperiod
B) circadian rhythm
C) gravitropism
D) phototropism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
In many grocery stores, fresh fruits are sold in plastic bags dotted with holes so that they will not overripen. The main function of the holes is to
A) permit the fruit to drain after being washed.
B) facilitate diffusion of ethylene away from the fruit.
C) prevent buildup of CO2.
D) facilitate diffusion of O2 to the fruit.
A) permit the fruit to drain after being washed.
B) facilitate diffusion of ethylene away from the fruit.
C) prevent buildup of CO2.
D) facilitate diffusion of O2 to the fruit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
What dense storage granules in plant cells are thought to contribute to gravitropism?
A) starch
B) glucose
C) proteins
D) chlorophyll
A) starch
B) glucose
C) proteins
D) chlorophyll

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
There is concern over the use of 2,4-D, a synthetic plant hormone, as a weed killer because the by-product dioxin
A) can cause irreversible mutations in crop plants.
B) causes fruit to drop prematurely from plants.
C) can cause birth defects and leukemia in mammals.
D) weakens the shells of the eggs of predatory birds, resulting in the death of their offspring.
A) can cause irreversible mutations in crop plants.
B) causes fruit to drop prematurely from plants.
C) can cause birth defects and leukemia in mammals.
D) weakens the shells of the eggs of predatory birds, resulting in the death of their offspring.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which growth response causes the shoots of a plant grown in the dark to grow upward?
A) phototropism
B) thigmotropism
C) gravitropism
A) phototropism
B) thigmotropism
C) gravitropism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Synthetic auxins are used commercially
A) to promote seed germination.
B) to promote flowering in ornamental crops.
C) to promote side branching to produce bushier crops.
D) as a broadleaf weed killer.
A) to promote seed germination.
B) to promote flowering in ornamental crops.
C) to promote side branching to produce bushier crops.
D) as a broadleaf weed killer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Where might you put a green, unripe fruit to ripen it?
A) a dark but well-ventilated area
B) a sealed plastic bag with an overripe banana
C) a microwave, on low power, for 5 minutes
D) under a bright light for 24 hours
A) a dark but well-ventilated area
B) a sealed plastic bag with an overripe banana
C) a microwave, on low power, for 5 minutes
D) under a bright light for 24 hours

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
What initiates flowering in long-day plants?
A) nights shorter than a critical length
B) nights longer than a critical length
C) days longer than the nights that are in between them
D) days shorter than a critical length
A) nights shorter than a critical length
B) nights longer than a critical length
C) days longer than the nights that are in between them
D) days shorter than a critical length

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which experiment might be performed by a biologist who is interested in determining which plant organs (stems, buds, leaves, etc.) are responsible for sensing photoperiod?
A) Remove the apical meristems from different parts of the plant.
B) Measure auxin levels in different parts of the plant before and after exposure to light.
C) Cover different plant organs with a foil covering to prevent light exposure.
D) Expose the plants to different wavelengths of light.
A) Remove the apical meristems from different parts of the plant.
B) Measure auxin levels in different parts of the plant before and after exposure to light.
C) Cover different plant organs with a foil covering to prevent light exposure.
D) Expose the plants to different wavelengths of light.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
What stimulates germination of desert plant seeds after a hard rain?
A) production of auxins
B) removal of abscisic acid
C) cooler temperatures
D) activation of cytokinins
A) production of auxins
B) removal of abscisic acid
C) cooler temperatures
D) activation of cytokinins

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which hormone prevents a seed released in the fall from germinating immediately?
A) auxins
B) abscisic acid (ABA)
C) gibberellins
D) ethylene
A) auxins
B) abscisic acid (ABA)
C) gibberellins
D) ethylene

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The plant growth response to touch is known as
A) gravitropism.
B) geotropism.
C) thigmotropism.
A) gravitropism.
B) geotropism.
C) thigmotropism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
What is one adaptive advantage for deciduous plants that lose their leaves during the winter?
A) It prevents water loss from leaves when soil water is unavailable due to freezing.
B) Production of new leaves each spring uses less energy than supporting old leaves all winter.
C) If leaves are damaged by frost, the tree will die.
D) A layer of leaves on the ground helps keep plant roots warm.
A) It prevents water loss from leaves when soil water is unavailable due to freezing.
B) Production of new leaves each spring uses less energy than supporting old leaves all winter.
C) If leaves are damaged by frost, the tree will die.
D) A layer of leaves on the ground helps keep plant roots warm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which list correctly orders the events leading to leaf fall in deciduous trees?
A) formation of abscission layer, increase in ethylene levels, decrease in auxin levels
B) shortening days, increase in ethylene production, formation of abscission layer
C) shortening days, formation of abscission layer, decrease in ethylene levels
D) decrease in ethylene levels, shortening days, formation of abscission layer
A) formation of abscission layer, increase in ethylene levels, decrease in auxin levels
B) shortening days, increase in ethylene production, formation of abscission layer
C) shortening days, formation of abscission layer, decrease in ethylene levels
D) decrease in ethylene levels, shortening days, formation of abscission layer

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which statement concerning biological clocks is false?
A) Innate circadian rhythms are generally about 24 hours in length.
B) Circadian rhythms occur with or without external stimuli.
C) Biological clocks are strongly influenced by external temperatures.
D) Movement of plants long distances very quickly induces a kind of plant "jet lag."
A) Innate circadian rhythms are generally about 24 hours in length.
B) Circadian rhythms occur with or without external stimuli.
C) Biological clocks are strongly influenced by external temperatures.
D) Movement of plants long distances very quickly induces a kind of plant "jet lag."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which plant response is affected by photoperiod?
A) gravitropism
B) apical dominance
C) onset of dormancy
D) cell division
A) gravitropism
B) apical dominance
C) onset of dormancy
D) cell division

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which process underlies the thigmotropic behavior of a green bean tendril?
A) rotation of the tendril in response to photoperiod
B) rotation of the tendril in response to a biological clock
C) extra proliferation of cells on the shaded side of the tendril
D) slower growth on the side where an object is touching the tendril
A) rotation of the tendril in response to photoperiod
B) rotation of the tendril in response to a biological clock
C) extra proliferation of cells on the shaded side of the tendril
D) slower growth on the side where an object is touching the tendril

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Mimosa plants spread their leaflets during the day and fold them at night. You decide to design an experiment to test whether Mimosa's leaf movements are controlled by a biological clock. Which experiment would be the best test of your hypothesis?
A) Growing the plant indoors and turning the lights on in the middle of the night. If a biological clock is controlling leaf movement, the leaves will open.
B) Putting the plant under a bright light in the middle of the day. If the leaves close, a biological clock mechanism is ruled out.
C) Subjecting the plant to a flash of red light in the middle of the night. If the leaves open at the usual time the next morning, a biological clock mechanism is ruled out.
D) Putting the plant in a dark closet at nightfall. Check on the plant at noon the next day, while the plant is still in the closet. If the leaves are open, a biological clock is indicated.
A) Growing the plant indoors and turning the lights on in the middle of the night. If a biological clock is controlling leaf movement, the leaves will open.
B) Putting the plant under a bright light in the middle of the day. If the leaves close, a biological clock mechanism is ruled out.
C) Subjecting the plant to a flash of red light in the middle of the night. If the leaves open at the usual time the next morning, a biological clock mechanism is ruled out.
D) Putting the plant in a dark closet at nightfall. Check on the plant at noon the next day, while the plant is still in the closet. If the leaves are open, a biological clock is indicated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
In leaf abscission, the abscission layer forms where the
A) leaf stalk joins the stem.
B) axillary bud joins the stem.
C) root joins the stem.
D) leaf stalk joins the leaf.
A) leaf stalk joins the stem.
B) axillary bud joins the stem.
C) root joins the stem.
D) leaf stalk joins the leaf.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
A plant will only flower if the night length is longer than 14 hours. This plant is a
A) long-day plant.
B) short-night plant.
C) short-day plant.
D) day-neutral plant.
A) long-day plant.
B) short-night plant.
C) short-day plant.
D) day-neutral plant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Citrus fruit has always been distributed from areas where the fruit is grown to other parts of the country, often by train. In the early 1900s train cars were heated with coal, and it was believed that this heat helped ripen the fruit. Imagine the surprise of growers and suppliers when fruit that arrived in new boxcars heated by steam arrived unripe. Why did the fruit no longer ripen?
A) The length of time needed to ripen the fruit was met by slow-moving older trains; newer steam-powered locomotives arrived before the fruit ripened.
B) Ethylene, a by-product of coal burning, ripened the fruit in the cars with the coal stove but was absent from the steam-powered trains.
C) The light from the coal-burning stoves caused the fruits to experience short nights, so without this light, they no longer ripened.
D) The steam prevented the buildup of abscisic acid, which is needed to ripen fruit.
A) The length of time needed to ripen the fruit was met by slow-moving older trains; newer steam-powered locomotives arrived before the fruit ripened.
B) Ethylene, a by-product of coal burning, ripened the fruit in the cars with the coal stove but was absent from the steam-powered trains.
C) The light from the coal-burning stoves caused the fruits to experience short nights, so without this light, they no longer ripened.
D) The steam prevented the buildup of abscisic acid, which is needed to ripen fruit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
After reading the paragraphs below, answer the questions that follow.
Ethylene triggers the ripening of fruit for many plant species but does not seem to play an important role for the ripening of grapes. Scientists hypothesized that the trigger for the ripening of grape fruits is abscisic acid (ABA). They sprayed unripe Cabernet Sauvignon grapes with different concentrations of ABA and tracked several fruit characteristics over time: percent of fruits that are purple, concentration of anthocyanin (a purple pigment) per fruit, weight of each fruit, and total soluble solids per fruit as measured by °Brix. °Brix measurements indicate the amount of sugar in the fruit, and determine how much alcohol a wine will have. Higher values of each measurement indicate a greater degree of ripening. The scientists' results are shown in these four graphs.
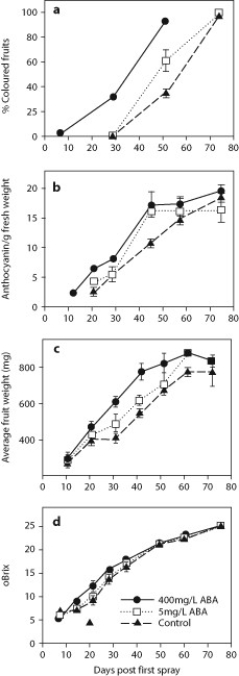 Source: Wheeler, S., Loveys, B., Ford, C., & Davies, C. (2009). The relationship between the expression of abscisic acid biosynthesis genes, accumulation of abscisic acid and the promotion of Vitis vinifera L. berry ripening by abscisic acid. Australian Journal of Grape and Wine Research, 15(3), 195-204.
Source: Wheeler, S., Loveys, B., Ford, C., & Davies, C. (2009). The relationship between the expression of abscisic acid biosynthesis genes, accumulation of abscisic acid and the promotion of Vitis vinifera L. berry ripening by abscisic acid. Australian Journal of Grape and Wine Research, 15(3), 195-204.
The visual indicator for grape ripening is the color of the fruit. Does adding ABA appear to speed up the ripening of grape fruit?
A) Yes, because fruits that were treated with ABA have more anthocyanin (purple pigment) earlier than the control.
B) Yes, because there were always more colored fruits in both ABA treatments compared to the control.
C) No, because fruits in all the treatments were colored by the end of the experiment.
D) No, because fruits in all the treatments have similar amounts of anthocyanin (purple pigment) by the end of the experiment.
Ethylene triggers the ripening of fruit for many plant species but does not seem to play an important role for the ripening of grapes. Scientists hypothesized that the trigger for the ripening of grape fruits is abscisic acid (ABA). They sprayed unripe Cabernet Sauvignon grapes with different concentrations of ABA and tracked several fruit characteristics over time: percent of fruits that are purple, concentration of anthocyanin (a purple pigment) per fruit, weight of each fruit, and total soluble solids per fruit as measured by °Brix. °Brix measurements indicate the amount of sugar in the fruit, and determine how much alcohol a wine will have. Higher values of each measurement indicate a greater degree of ripening. The scientists' results are shown in these four graphs.
 Source: Wheeler, S., Loveys, B., Ford, C., & Davies, C. (2009). The relationship between the expression of abscisic acid biosynthesis genes, accumulation of abscisic acid and the promotion of Vitis vinifera L. berry ripening by abscisic acid. Australian Journal of Grape and Wine Research, 15(3), 195-204.
Source: Wheeler, S., Loveys, B., Ford, C., & Davies, C. (2009). The relationship between the expression of abscisic acid biosynthesis genes, accumulation of abscisic acid and the promotion of Vitis vinifera L. berry ripening by abscisic acid. Australian Journal of Grape and Wine Research, 15(3), 195-204.The visual indicator for grape ripening is the color of the fruit. Does adding ABA appear to speed up the ripening of grape fruit?
A) Yes, because fruits that were treated with ABA have more anthocyanin (purple pigment) earlier than the control.
B) Yes, because there were always more colored fruits in both ABA treatments compared to the control.
C) No, because fruits in all the treatments were colored by the end of the experiment.
D) No, because fruits in all the treatments have similar amounts of anthocyanin (purple pigment) by the end of the experiment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
A plant's first line of defense against infection is
A) cell elongation.
B) its epidermis.
C) phytochrome.
D) salicylic acid.
A) cell elongation.
B) its epidermis.
C) phytochrome.
D) salicylic acid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
After reading the paragraphs below, answer the questions that follow.
A student taking a plant physiology class is interested in investigating what will happen if the apical bud is removed from a growing plant and supplementary hormones are introduced.
He set up his experiment with two groups of plants of the same species. In groups A and B, the apical buds were removed and the cut apical ends were wrapped with hormone-impregnated cotton. The plants were observed over a 5-week period for growth and development. In group A, many axillary buds and leaves appeared along the sides of the stem, and the plants had minimal root growth. In group B, minimal growth occurred in the shoot and roots, and no axillary buds formed.
What hormone was in the cotton used to wrap the apical ends of the group B plants?
A) cytokinin
B) giberellin
C) abscisic acid
D) auxin
A student taking a plant physiology class is interested in investigating what will happen if the apical bud is removed from a growing plant and supplementary hormones are introduced.
He set up his experiment with two groups of plants of the same species. In groups A and B, the apical buds were removed and the cut apical ends were wrapped with hormone-impregnated cotton. The plants were observed over a 5-week period for growth and development. In group A, many axillary buds and leaves appeared along the sides of the stem, and the plants had minimal root growth. In group B, minimal growth occurred in the shoot and roots, and no axillary buds formed.
What hormone was in the cotton used to wrap the apical ends of the group B plants?
A) cytokinin
B) giberellin
C) abscisic acid
D) auxin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Use the figure below to answer the questions that follow.
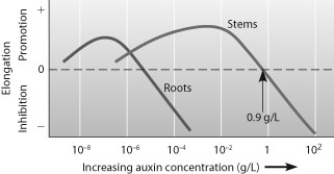
If you cut off the top of a carrot and place it in water to see if you can get it to grow new roots, you should add
A) more than 10−2 g/L of auxin.
B) approximately 10−8 g/L of auxin.
C) at least 10−4 g/L of auxin.
D) equal amounts of auxin and cytokinin.

If you cut off the top of a carrot and place it in water to see if you can get it to grow new roots, you should add
A) more than 10−2 g/L of auxin.
B) approximately 10−8 g/L of auxin.
C) at least 10−4 g/L of auxin.
D) equal amounts of auxin and cytokinin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Under which condition would plant cells treated with auxin be able to enlarge?
A) lack of light for growing
B) blocked proton pumps
C) long, dry growing season
D) presence of ethylene
A) lack of light for growing
B) blocked proton pumps
C) long, dry growing season
D) presence of ethylene

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Use the figure below to answer the questions that follow.
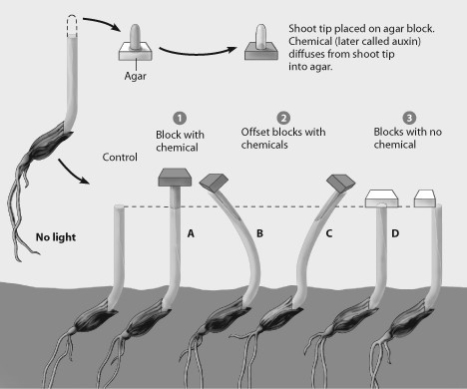
Which plant in Went's experiment shows auxin stimulating elongation in the left side of the plant only?
A) plant A
B) plant B
C) plant C
D) plant D

Which plant in Went's experiment shows auxin stimulating elongation in the left side of the plant only?
A) plant A
B) plant B
C) plant C
D) plant D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Application of herbicides made from plant hormones may have unintended consequences because
A) different types of plants could respond differently to the same herbicide.
B) soil erosion may increase when herbicides are used instead of tillage.
C) plants may concentrate the herbicides in their fruits so that they can be released from the plant.
D) plants create new mutations to avoid herbicides.
A) different types of plants could respond differently to the same herbicide.
B) soil erosion may increase when herbicides are used instead of tillage.
C) plants may concentrate the herbicides in their fruits so that they can be released from the plant.
D) plants create new mutations to avoid herbicides.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
In plant research labs, plants are often grown in light-proof chambers where the hours of light and dark are carefully controlled. A new researcher goes into a chamber and accidentally turns on the light during the "dark" period. How should the researcher respond to get the plants back to their controlled schedule quickly?
A) If the plants are short-day plants, the researcher should do nothing.
B) The researcher should quickly produce a flash of far-red light and close the door.
C) The researcher does not need to respond if the plants are not yet flowering.
D) If the light is only red light and not far-red light, there will be no impact.
A) If the plants are short-day plants, the researcher should do nothing.
B) The researcher should quickly produce a flash of far-red light and close the door.
C) The researcher does not need to respond if the plants are not yet flowering.
D) If the light is only red light and not far-red light, there will be no impact.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Christmas cactus is a short-day plant that usually blooms in the winter. Which strategy might induce it to bloom for the 4th of July?
A) putting it in a cool, well-lighted place from time to time during June
B) leaving it in a dark closet all night and part of each morning during June
C) putting it in a dark closet for a short time every afternoon during June
D) exposing it to light several times during each night in June
A) putting it in a cool, well-lighted place from time to time during June
B) leaving it in a dark closet all night and part of each morning during June
C) putting it in a dark closet for a short time every afternoon during June
D) exposing it to light several times during each night in June

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Use the figure below to answer the questions that follow.

In the figure, the shoot emerged through the soil toward the light rather than growing down in the direction of the roots due to
A) thigmotropism.
B) phototropism.
C) gravitropism.
D) circadian rhythm.

In the figure, the shoot emerged through the soil toward the light rather than growing down in the direction of the roots due to
A) thigmotropism.
B) phototropism.
C) gravitropism.
D) circadian rhythm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Fall is coming, with the prospect of frost, so you decide to pick the last tomatoes on the vine even though they are still green. If you wanted to ripen these tomatoes, which method would be most effective?
A) Put the green tomatoes in a paper bag, and keep the top of the bag open.
B) Put the green tomatoes in a dark closet, but with a flash of light about every 4 hours.
C) Put the green tomatoes in a plastic bag with an overripe apple.
D) Store each green tomato in a separate plastic bag and put them in the dark.
A) Put the green tomatoes in a paper bag, and keep the top of the bag open.
B) Put the green tomatoes in a dark closet, but with a flash of light about every 4 hours.
C) Put the green tomatoes in a plastic bag with an overripe apple.
D) Store each green tomato in a separate plastic bag and put them in the dark.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
How does phytochrome control flowering?
A) by disrupting the plant's photoperiod
B) by detecting differences in temperature in the spring
C) by sensing sunrise and sunset
D) by inducing differentiation of cells in the apical meristem
A) by disrupting the plant's photoperiod
B) by detecting differences in temperature in the spring
C) by sensing sunrise and sunset
D) by inducing differentiation of cells in the apical meristem

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
After reading the paragraphs below, answer the questions that follow.
Ethylene triggers the ripening of fruit for many plant species but does not seem to play an important role for the ripening of grapes. Scientists hypothesized that the trigger for the ripening of grape fruits is abscisic acid (ABA). They sprayed unripe Cabernet Sauvignon grapes with different concentrations of ABA and tracked several fruit characteristics over time: percent of fruits that are purple, concentration of anthocyanin (a purple pigment) per fruit, weight of each fruit, and total soluble solids per fruit as measured by °Brix. °Brix measurements indicate the amount of sugar in the fruit, and determine how much alcohol a wine will have. Higher values of each measurement indicate a greater degree of ripening. The scientists' results are shown in these four graphs.
 Source: Wheeler, S., Loveys, B., Ford, C., & Davies, C. (2009). The relationship between the expression of abscisic acid biosynthesis genes, accumulation of abscisic acid and the promotion of Vitis vinifera L. berry ripening by abscisic acid. Australian Journal of Grape and Wine Research, 15(3), 195-204.
Source: Wheeler, S., Loveys, B., Ford, C., & Davies, C. (2009). The relationship between the expression of abscisic acid biosynthesis genes, accumulation of abscisic acid and the promotion of Vitis vinifera L. berry ripening by abscisic acid. Australian Journal of Grape and Wine Research, 15(3), 195-204.
What is the difference between fruits sprayed with the low (5 mg/L) concentration of ABA and the high (400 mg/L) concentration of ABA?
A) The high concentration results in the earlier occurrence of colored fruit and maximum fruit size.
B) The high concentration induces an earlier occurrence of the maximum amount of anthocyanin (purple pigment).
C) The high concentration has smaller fruit until the end of the experiment.
D) The high concentration produces fruit with less sugar at the end of the experiment.
Ethylene triggers the ripening of fruit for many plant species but does not seem to play an important role for the ripening of grapes. Scientists hypothesized that the trigger for the ripening of grape fruits is abscisic acid (ABA). They sprayed unripe Cabernet Sauvignon grapes with different concentrations of ABA and tracked several fruit characteristics over time: percent of fruits that are purple, concentration of anthocyanin (a purple pigment) per fruit, weight of each fruit, and total soluble solids per fruit as measured by °Brix. °Brix measurements indicate the amount of sugar in the fruit, and determine how much alcohol a wine will have. Higher values of each measurement indicate a greater degree of ripening. The scientists' results are shown in these four graphs.
 Source: Wheeler, S., Loveys, B., Ford, C., & Davies, C. (2009). The relationship between the expression of abscisic acid biosynthesis genes, accumulation of abscisic acid and the promotion of Vitis vinifera L. berry ripening by abscisic acid. Australian Journal of Grape and Wine Research, 15(3), 195-204.
Source: Wheeler, S., Loveys, B., Ford, C., & Davies, C. (2009). The relationship between the expression of abscisic acid biosynthesis genes, accumulation of abscisic acid and the promotion of Vitis vinifera L. berry ripening by abscisic acid. Australian Journal of Grape and Wine Research, 15(3), 195-204.What is the difference between fruits sprayed with the low (5 mg/L) concentration of ABA and the high (400 mg/L) concentration of ABA?
A) The high concentration results in the earlier occurrence of colored fruit and maximum fruit size.
B) The high concentration induces an earlier occurrence of the maximum amount of anthocyanin (purple pigment).
C) The high concentration has smaller fruit until the end of the experiment.
D) The high concentration produces fruit with less sugar at the end of the experiment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
A student wanted to plant an avocado seed to try to grow an avocado plant, but she could not tell which end of the seed was the bottom and which was the top. She asked her friends what she should do. Which friend's suggestion will have the highest success of growing the avocado plant?
A) One friend said it doesn't matter in which direction the seed is planted as long as there is a strong light on the soil, since the shoots will seek the light and turn the seed right side up.
B) One friend said to put the seed in in any direction, because as the seed is watered, it will be able to detect the direction the water is coming from and point the shoots that way.
C) One friend suggested a compromise: Put the seed sideways, since gravity will ensure that the shoots grow up and the roots grow down.
D) One friend said just to put the seed in one direction or the other, because it will only sprout if it is in the right direction, and there's a fifty-fifty chance that it will be in the right orientation.
A) One friend said it doesn't matter in which direction the seed is planted as long as there is a strong light on the soil, since the shoots will seek the light and turn the seed right side up.
B) One friend said to put the seed in in any direction, because as the seed is watered, it will be able to detect the direction the water is coming from and point the shoots that way.
C) One friend suggested a compromise: Put the seed sideways, since gravity will ensure that the shoots grow up and the roots grow down.
D) One friend said just to put the seed in one direction or the other, because it will only sprout if it is in the right direction, and there's a fifty-fifty chance that it will be in the right orientation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
After reading the paragraphs below, answer the questions that follow.
A student taking a plant physiology class is interested in investigating what will happen if the apical bud is removed from a growing plant and supplementary hormones are introduced.
He set up his experiment with two groups of plants of the same species. In groups A and B, the apical buds were removed and the cut apical ends were wrapped with hormone-impregnated cotton. The plants were observed over a 5-week period for growth and development. In group A, many axillary buds and leaves appeared along the sides of the stem, and the plants had minimal root growth. In group B, minimal growth occurred in the shoot and roots, and no axillary buds formed.
What hormone was in the cotton used to wrap the apical ends of the group A plants?
A) cytokinin
B) giberellin
C) ethylene
D) auxin
A student taking a plant physiology class is interested in investigating what will happen if the apical bud is removed from a growing plant and supplementary hormones are introduced.
He set up his experiment with two groups of plants of the same species. In groups A and B, the apical buds were removed and the cut apical ends were wrapped with hormone-impregnated cotton. The plants were observed over a 5-week period for growth and development. In group A, many axillary buds and leaves appeared along the sides of the stem, and the plants had minimal root growth. In group B, minimal growth occurred in the shoot and roots, and no axillary buds formed.
What hormone was in the cotton used to wrap the apical ends of the group A plants?
A) cytokinin
B) giberellin
C) ethylene
D) auxin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Iris is a long-day plant that normally flowers in the spring. Which regimen would be the most effective in making an iris bloom in late fall?
A) interrupting the plant's nights at 2:00 am with a flash of far-red light
B) interrupting the plant's nights at 2:00 am with a flash of red light followed by a flash of far-red light
C) interrupting the plant's nights at 2:00 am with a red flash, then a far-red flash, then a red flash
D) interrupting the plant's days at 2:00 pm by putting it in the dark
A) interrupting the plant's nights at 2:00 am with a flash of far-red light
B) interrupting the plant's nights at 2:00 am with a flash of red light followed by a flash of far-red light
C) interrupting the plant's nights at 2:00 am with a red flash, then a far-red flash, then a red flash
D) interrupting the plant's days at 2:00 pm by putting it in the dark

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Use the figure below to answer the questions that follow.

Which statement is supported by this figure?
A) The greater the concentration of auxin, the more promotion of root elongation occurs.
B) Auxin concentrations below 10−8 g/L promote both root and stem elongation.
C) Auxin concentrations around 10−4 g/L promote stem elongation but inhibit root elongation.
D) Auxin concentrations above 0.9 g/L are best for promoting stem elongation.

Which statement is supported by this figure?
A) The greater the concentration of auxin, the more promotion of root elongation occurs.
B) Auxin concentrations below 10−8 g/L promote both root and stem elongation.
C) Auxin concentrations around 10−4 g/L promote stem elongation but inhibit root elongation.
D) Auxin concentrations above 0.9 g/L are best for promoting stem elongation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
What is one way that plants use animals as a defense against herbivores?
A) production of an amino acid that harms herbivores
B) attraction of wasps that kill herbivorous caterpillars
C) release of microbe-killing chemicals in response to infection
D) coevolution between plants and predators
A) production of an amino acid that harms herbivores
B) attraction of wasps that kill herbivorous caterpillars
C) release of microbe-killing chemicals in response to infection
D) coevolution between plants and predators

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Use the figure below to answer the questions that follow.

In addition to demonstrating that auxin stimulates elongation, this diagram also shows that
A) application of additional auxin causes greater bending.
B) the application of auxin causes growth.
C) removing shoot tips also removes auxin receptors.
D) the lower parts of the shoot are able to detect light.

In addition to demonstrating that auxin stimulates elongation, this diagram also shows that
A) application of additional auxin causes greater bending.
B) the application of auxin causes growth.
C) removing shoot tips also removes auxin receptors.
D) the lower parts of the shoot are able to detect light.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
After reading the paragraphs below, answer the questions that follow.
Ethylene triggers the ripening of fruit for many plant species but does not seem to play an important role for the ripening of grapes. Scientists hypothesized that the trigger for the ripening of grape fruits is abscisic acid (ABA). They sprayed unripe Cabernet Sauvignon grapes with different concentrations of ABA and tracked several fruit characteristics over time: percent of fruits that are purple, concentration of anthocyanin (a purple pigment) per fruit, weight of each fruit, and total soluble solids per fruit as measured by °Brix. °Brix measurements indicate the amount of sugar in the fruit, and determine how much alcohol a wine will have. Higher values of each measurement indicate a greater degree of ripening. The scientists' results are shown in these four graphs.
 Source: Wheeler, S., Loveys, B., Ford, C., & Davies, C. (2009). The relationship between the expression of abscisic acid biosynthesis genes, accumulation of abscisic acid and the promotion of Vitis vinifera L. berry ripening by abscisic acid. Australian Journal of Grape and Wine Research, 15(3), 195-204.
Source: Wheeler, S., Loveys, B., Ford, C., & Davies, C. (2009). The relationship between the expression of abscisic acid biosynthesis genes, accumulation of abscisic acid and the promotion of Vitis vinifera L. berry ripening by abscisic acid. Australian Journal of Grape and Wine Research, 15(3), 195-204.
Should the wine industry recommend the use of ABA to speed up ripening of grapes for wine making?
A) No, because any early increases in fruit sugars as a result of ABA addition decreases as ripening progresses.
B) No, because there is no difference in the trajectory of ripening when ABA is added compared to when it is not.
C) Yes, because colored, full-sized fruit can be produced earlier when ABA is added.
D) Yes, because more fruit sugars will be present earlier in fruits sprayed with ABA compared to fruits that are not.
Ethylene triggers the ripening of fruit for many plant species but does not seem to play an important role for the ripening of grapes. Scientists hypothesized that the trigger for the ripening of grape fruits is abscisic acid (ABA). They sprayed unripe Cabernet Sauvignon grapes with different concentrations of ABA and tracked several fruit characteristics over time: percent of fruits that are purple, concentration of anthocyanin (a purple pigment) per fruit, weight of each fruit, and total soluble solids per fruit as measured by °Brix. °Brix measurements indicate the amount of sugar in the fruit, and determine how much alcohol a wine will have. Higher values of each measurement indicate a greater degree of ripening. The scientists' results are shown in these four graphs.
 Source: Wheeler, S., Loveys, B., Ford, C., & Davies, C. (2009). The relationship between the expression of abscisic acid biosynthesis genes, accumulation of abscisic acid and the promotion of Vitis vinifera L. berry ripening by abscisic acid. Australian Journal of Grape and Wine Research, 15(3), 195-204.
Source: Wheeler, S., Loveys, B., Ford, C., & Davies, C. (2009). The relationship between the expression of abscisic acid biosynthesis genes, accumulation of abscisic acid and the promotion of Vitis vinifera L. berry ripening by abscisic acid. Australian Journal of Grape and Wine Research, 15(3), 195-204.Should the wine industry recommend the use of ABA to speed up ripening of grapes for wine making?
A) No, because any early increases in fruit sugars as a result of ABA addition decreases as ripening progresses.
B) No, because there is no difference in the trajectory of ripening when ABA is added compared to when it is not.
C) Yes, because colored, full-sized fruit can be produced earlier when ABA is added.
D) Yes, because more fruit sugars will be present earlier in fruits sprayed with ABA compared to fruits that are not.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



