Deck 17: Thermodynamics: Spontaneous and Nonspontaneous Reactions and Processes
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/186
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 17: Thermodynamics: Spontaneous and Nonspontaneous Reactions and Processes
1
What is the entropy change to the surroundings when 1 mol of ice melts in someone's hand if the hand temperature is 32 C? Assume a final temperature for the water of 0 C. The heat of fusion of ice is 6.01 kJ/mol.
A)(-188 J/K)
B)(-22.0 J/K)
C)(-19.7 J/K)
D)(+19.7 J/K)
E)(+188 J/K)
A)(-188 J/K)
B)(-22.0 J/K)
C)(-19.7 J/K)
D)(+19.7 J/K)
E)(+188 J/K)
(-19.7 J/K)
2
For a chemical reaction that is not spontaneous, it is found that Ssys < 0. Which of the following could not be true?
A)( Ssurr < 0 and its magnitude is less than Ssys.)
B)( Ssurr > 0 and its magnitude is less than Ssys.)
C)( Ssurr < 0 and its magnitude is greater than Ssys.)
D)( Ssurr > 0 and its magnitude is greater than Ssys.)
E)( Suniv < 0)
A)( Ssurr < 0 and its magnitude is less than Ssys.)
B)( Ssurr > 0 and its magnitude is less than Ssys.)
C)( Ssurr < 0 and its magnitude is greater than Ssys.)
D)( Ssurr > 0 and its magnitude is greater than Ssys.)
E)( Suniv < 0)
( Ssurr > 0 and its magnitude is greater than Ssys.)
3
Ssys can be directly related to the heat, q. Which of statements A-D is not true regarding this relationship?
A)( Ssys can always be determined from the heat transferred during the actual process.)
B)For a reversible spontaneous endothermic process, both q and Ssys will be positive.
C)The more heat that is transferred, the larger the magnitude of the entropy change.
D)The higher the temperature at which heat is transferred, the lower the entropy change.
E)All of the above are true.
A)( Ssys can always be determined from the heat transferred during the actual process.)
B)For a reversible spontaneous endothermic process, both q and Ssys will be positive.
C)The more heat that is transferred, the larger the magnitude of the entropy change.
D)The higher the temperature at which heat is transferred, the lower the entropy change.
E)All of the above are true.
( Ssys can always be determined from the heat transferred during the actual process.)
4
Which of the following processes is/are reversible in the thermodynamic sense?
I. Iron in the open air rusts.
II. NaCl is dissolved in water and then recovered by the evaporation of the water.
III. The ice in a mixture of ice and water at 0 C and 1 atm melts.
A)I only
B)II only
C)III only
D)II and III only
E)I, II, and III are all reversible.
I. Iron in the open air rusts.
II. NaCl is dissolved in water and then recovered by the evaporation of the water.
III. The ice in a mixture of ice and water at 0 C and 1 atm melts.
A)I only
B)II only
C)III only
D)II and III only
E)I, II, and III are all reversible.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The entropy change of the surroundings, Ssurr, is related to heat transfer, q, with respect to the system and temperature T by ________
A)(-q/Tsys = Ssurr.)
B)(+q/Tsys = Ssurr.)
C)(-q/Tsurr = Ssurr.)
D)q/Tsurr = Ssurr.
E)None of these, unless the system undergoes a reversible process.
A)(-q/Tsys = Ssurr.)
B)(+q/Tsys = Ssurr.)
C)(-q/Tsurr = Ssurr.)
D)q/Tsurr = Ssurr.
E)None of these, unless the system undergoes a reversible process.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
In a spontaneous process, which of the following always increases?
A)the entropy of the system
B)the entropy of the surroundings
C)the entropy of the universe
D)the entropy of the system and the universe
E)the entropy of the system, the surroundings, and the universe
A)the entropy of the system
B)the entropy of the surroundings
C)the entropy of the universe
D)the entropy of the system and the universe
E)the entropy of the system, the surroundings, and the universe

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
According to the second law of thermodynamics, the change in the entropy of the universe ( Suniv) during a spontaneous reaction is ________
A)zero.
B)negative.
C)positive.
D)less than the change in entropy of the system ( Ssys).
E)greater than the change in entropy of the system ( Ssys).
A)zero.
B)negative.
C)positive.
D)less than the change in entropy of the system ( Ssys).
E)greater than the change in entropy of the system ( Ssys).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Heat transfer from the system to the surroundings has a large effect on Ssurr ________
A)when the temperature of the surroundings is low.
B)when the temperature of the surroundings is high.
C)when the temperature of the system is low.
D)when the temperature of the system is high.
E)at any temperature, because the amount of heat transferred is independent of temperature.
A)when the temperature of the surroundings is low.
B)when the temperature of the surroundings is high.
C)when the temperature of the system is low.
D)when the temperature of the system is high.
E)at any temperature, because the amount of heat transferred is independent of temperature.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The entropy change in a system ( Ssys) during a spontaneous process must be ________
A)greater than zero.
B)less than zero.
C)equal to zero.
D)greater than or equal to zero.
E)greater than, less than, or equal to zero.
A)greater than zero.
B)less than zero.
C)equal to zero.
D)greater than or equal to zero.
E)greater than, less than, or equal to zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following processes is/are spontaneous?
I. Iron in the open air rusts.
II. Liquid water in a freezer turns to ice.
III. A spark ignites a mixture of propane and air.
A)I only
B)I and II only
C)I and III only
D)II and III only
E)I, II, and III are all spontaneous.
I. Iron in the open air rusts.
II. Liquid water in a freezer turns to ice.
III. A spark ignites a mixture of propane and air.
A)I only
B)I and II only
C)I and III only
D)II and III only
E)I, II, and III are all spontaneous.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
If 1 mol of ice melts at its melting point of 273 K, the entropy change for the ice is 22.0 J/K. If the ice melts in someone's hand at 34 C, what is the change in the entropy of the universe? Assume a final temperature for the water of 0 C. The enthalpy of fusion for ice is 6.01 kJ/mol.
A)(+19.6 J/K)
B)(-19.6 J/K)
C)(+2.4 J/K)
D)(-2.4 J/K)
E)(+41.5 J/K)
A)(+19.6 J/K)
B)(-19.6 J/K)
C)(+2.4 J/K)
D)(-2.4 J/K)
E)(+41.5 J/K)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Care must be taken when dissolving solid pellets of sodium hydroxide (NaOH) in water, because the temperature of the water can rise dramatically. Taking NaOH as the system, what can you deduce about the signs of the entropy change of the system ( Ssys) and surroundings ( Ssurr) from this?
A)( Ssys < 0 and Ssurr < 0)
B)( Ssys < 0 and Ssurr > 0)
C)( Ssys > 0 and Ssurr < 0)
D)( Ssys > 0 and Ssurr > 0)
E)Nothing can be deduced from this limited information.
A)( Ssys < 0 and Ssurr < 0)
B)( Ssys < 0 and Ssurr > 0)
C)( Ssys > 0 and Ssurr < 0)
D)( Ssys > 0 and Ssurr > 0)
E)Nothing can be deduced from this limited information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
During a spontaneous chemical reaction, it is found that Ssys < 0. This means ________
A)( Ssurr < 0 and its magnitude is < Ssys.)
B)( Ssurr < 0 and its magnitude is < Ssys.).
C)( Ssurr > 0 and its magnitude is > Ssys.
D)( Ssurr > 0 and its magnitude is > Ssys.)
E)an error has been made, because Ssys > 0 by necessity for a spontaneous process.
A)( Ssurr < 0 and its magnitude is < Ssys.)
B)( Ssurr < 0 and its magnitude is < Ssys.).
C)( Ssurr > 0 and its magnitude is > Ssys.
D)( Ssurr > 0 and its magnitude is > Ssys.)
E)an error has been made, because Ssys > 0 by necessity for a spontaneous process.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
During a spontaneous chemical reaction, it is found that Ssys > 0. Which of the following could not be true?
A)( Ssurr < 0 and its magnitude is < Ssys.)
B)( Ssurr > 0 and its magnitude is < Ssys.)
C)( Ssurr < 0 and its magnitude is > Ssys.)
D)( Ssurr > 0 and its magnitude is > Ssys.)
E)( univ > 0)
A)( Ssurr < 0 and its magnitude is < Ssys.)
B)( Ssurr > 0 and its magnitude is < Ssys.)
C)( Ssurr < 0 and its magnitude is > Ssys.)
D)( Ssurr > 0 and its magnitude is > Ssys.)
E)( univ > 0)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
For a chemical reaction that is not spontaneous, it is found that Ssys > 0. Which of the following could be true?
A)( Ssurr < 0 and its magnitude is less than Ssys.)
B)( Ssurr > 0 and its magnitude is less than Ssys.)
C)( Ssurr < 0 and its magnitude is greater than Ssys.)
D)( Ssurr > 0 and its magnitude is greater than Ssys.)
E)( Suniv > 0)
A)( Ssurr < 0 and its magnitude is less than Ssys.)
B)( Ssurr > 0 and its magnitude is less than Ssys.)
C)( Ssurr < 0 and its magnitude is greater than Ssys.)
D)( Ssurr > 0 and its magnitude is greater than Ssys.)
E)( Suniv > 0)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which, if any, of statements A-D is not true of entropy?
A)It is a measure of the distribution of energy in a system at a specific temperature.
B)It is a measure of the number of accessible microstates in a pure substance.
C)It is a property of the universe that increases during a spontaneous process.
D)It is a property of a system that may increase or decrease during a spontaneous process.
E)All of the above are true statements.
A)It is a measure of the distribution of energy in a system at a specific temperature.
B)It is a measure of the number of accessible microstates in a pure substance.
C)It is a property of the universe that increases during a spontaneous process.
D)It is a property of a system that may increase or decrease during a spontaneous process.
E)All of the above are true statements.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
In a spontaneous process, the entropy of the universe ________
A)always increases.
B)always decreases.
C)does not change.
D)may decrease if the entropy of the system decreases sufficiently.
E)may decrease if the entropy of the system increases sufficiently.
A)always increases.
B)always decreases.
C)does not change.
D)may decrease if the entropy of the system decreases sufficiently.
E)may decrease if the entropy of the system increases sufficiently.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The entropy change in the surroundings ( Ssurr) during a spontaneous process must be ________
A)greater than zero.
B)less than zero.
C)equal to zero.
D)greater than or equal to zero.
E)greater than, less than, or equal to zero.
A)greater than zero.
B)less than zero.
C)equal to zero.
D)greater than or equal to zero.
E)greater than, less than, or equal to zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
An ice cube at 0 C melts in a swimming pool at 25 C. What is the change in the entropy of the universe as a result? The ice cube was 2.00 inches on a side. Assume ice has a density of 0.917 g/cm3 and that the enthalpy of fusion of water is 6.01 kJ/mol.
A)( +3.1 J/K)
B)(-3.1 J/K)
C)0.0 J/K
D)(+12.3 J/K)
E)(-12.3 J/K)
A)( +3.1 J/K)
B)(-3.1 J/K)
C)0.0 J/K
D)(+12.3 J/K)
E)(-12.3 J/K)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The enthalpy of fusion for benzene (C6H6) is 127.40 kJ/kg, and its melting point is 5.5 C. What is the entropy change when 1 mole of benzene melts at 5.5 C?
A)9.95 kJ/K
B)35.7 J/K
C)1,809 J/K
D)1.81 J/K
E)127.40 kJ/K
A)9.95 kJ/K
B)35.7 J/K
C)1,809 J/K
D)1.81 J/K
E)127.40 kJ/K

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
When a molecule of ethylenediamine replaces two molecules of NH3 in Co(NH3) 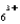 , the entropy of the system ________
, the entropy of the system ________
A)increases.
B)decreases.
C)remains the same.
D)cannot be determined.
E)is irrelevant.
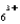 , the entropy of the system ________
, the entropy of the system ________A)increases.
B)decreases.
C)remains the same.
D)cannot be determined.
E)is irrelevant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Consider a closed container containing a 1 M solution of HCl, above which is air that contains water vapor at its equilibrium vapor pressure. Assume the pressure of the air and water vapor is 1 bar and the temperature of the system is 298 K. Which of the following is/are in its their thermodynamic standard state?
I. the liquid water
II. the HCl solution
III. the water vapor
A)I only
B)II only
C)III only
D)I and II only
E)I, II, and III are all in their standard states.
I. the liquid water
II. the HCl solution
III. the water vapor
A)I only
B)II only
C)III only
D)I and II only
E)I, II, and III are all in their standard states.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Indicate which one of the following reactions most certainly results in a negative Ssys.
A)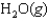
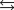
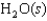
B)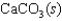
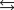
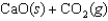
C)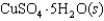
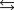
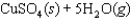
D)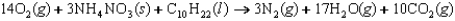
E)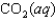
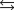
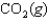
A)
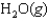
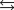
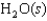
B)
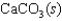
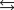
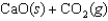
C)
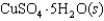
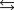
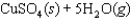
D)
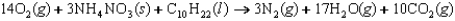
E)
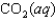
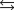
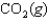

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Perfect crystals of carbon monoxide (CO) are difficult to prepare because the very small dipole moment allows a few molecules to align in a pattern such as CO OC CO instead of CO CO CO. If such disordered crystals were cooled to 0 K, what would be the value of their absolute entropy?
A)(> 0)
B)(= 0)
C)(< 0)
D)(> 0, = 0, or < 0, depending on how carefully it was cooled)
E)(> 0 or = 0, depending on how carefully it was cooled)
A)(> 0)
B)(= 0)
C)(< 0)
D)(> 0, = 0, or < 0, depending on how carefully it was cooled)
E)(> 0 or = 0, depending on how carefully it was cooled)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Before class, students were distributed throughout a classroom. When the bell rang, all the students sat down at three tables in the center of the room. The entropy of the class ________
A)increased.
B)decreased.
C)remained the same.
D)cannot be determined.
E)is irrelevant.
A)increased.
B)decreased.
C)remained the same.
D)cannot be determined.
E)is irrelevant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Indicate which one of the following reactions most certainly does not result in a decrease in entropy.
A)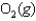
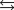
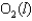
B)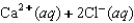 )
) 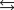
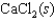
C)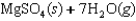
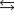
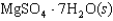
D)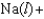
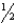
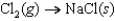
E)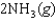
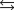
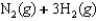
A)
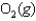
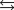
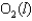
B)
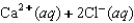 )
) 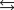
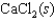
C)
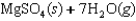
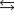
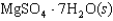
D)
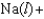
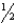
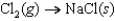
E)
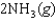
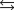
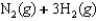

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Indicate which one of the following reactions results in a positive Ssys.
A)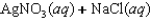
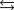
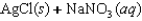
B)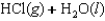
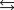
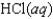
C)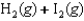
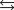
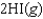
D)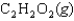
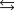
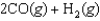
E)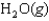
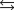
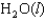
A)
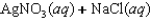
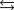
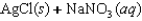
B)
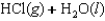
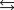
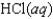
C)
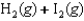
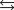
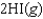
D)
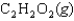
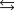
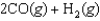
E)
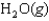
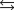
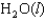

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The enthalpy of vaporization for toluene (C7H8) is 380.00 kJ/kg, and its boiling point is 110.6 C. What is the entropy change when 0.75 mole of toluene vaporizes at 110.6 C?
A)743 J/K
B)139 J/K
C)68.5 J/K
D)36.3 J/K
E)253 kJ/K
A)743 J/K
B)139 J/K
C)68.5 J/K
D)36.3 J/K
E)253 kJ/K

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The following figures represent distributions of two types of gas molecules between two containers connected by an open tube. In which figure is the entropy of the system maximized?
A)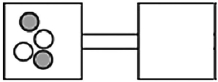
B)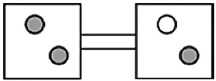
C)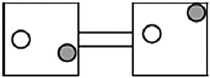
D)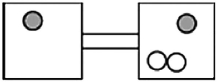
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Indicate which one of the following reactions results in a negative Ssys.
A)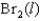
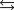
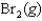
B)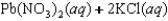
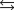
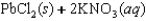
C)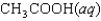
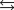
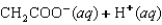
D)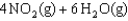
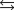
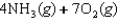
E)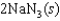
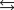
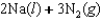
A)
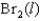
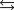
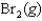
B)
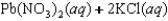
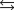
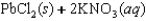
C)
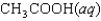
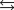
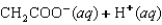
D)
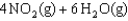
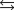
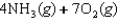
E)
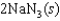
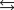

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following will have the greatest standard molar entropy (S )?
A)NH3(g)
B)He(g)
C)C(s, graphite)
D)H2O(l )
E)CaCO3(s)
A)NH3(g)
B)He(g)
C)C(s, graphite)
D)H2O(l )
E)CaCO3(s)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
At 0 K, the entropy of a perfect crystal is ________
A)(> 0.)
B)(= 0.)
C)(< 0.)
D)(> 0, = 0, or < 0, depending on the chemical structure of the crystal.)
E)(> 0 or = 0, depending on the chemical structure of the crystal.)
A)(> 0.)
B)(= 0.)
C)(< 0.)
D)(> 0, = 0, or < 0, depending on the chemical structure of the crystal.)
E)(> 0 or = 0, depending on the chemical structure of the crystal.)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of the processes A-D will lead to a positive change in the entropy of the system?
A)Sodium chloride crystals form as salt water evaporates.
B)Helium gas escapes from the hole in a balloon.
C)Stalactites form in a cave.
D)Water freezes in a freezer.
E)All of these lead to a positive change in entropy of the system, because they are all spontaneous.
A)Sodium chloride crystals form as salt water evaporates.
B)Helium gas escapes from the hole in a balloon.
C)Stalactites form in a cave.
D)Water freezes in a freezer.
E)All of these lead to a positive change in entropy of the system, because they are all spontaneous.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which of the following processes will lead to a decrease in the entropy of the system?
A)Salt crystals dissolve in water.
B)Air escapes from a hole in a balloon.
C)Iron and oxygen react to form rust.
D)Ice melts in your hand.
E)None of these leads to a negative change in the entropy of the system, because they are all spontaneous.
A)Salt crystals dissolve in water.
B)Air escapes from a hole in a balloon.
C)Iron and oxygen react to form rust.
D)Ice melts in your hand.
E)None of these leads to a negative change in the entropy of the system, because they are all spontaneous.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Before class, students were seated at three tables. When the school alarm went off suddenly, all the students distributed throughout the room to collect their belongings. The entropy of the class ________
A)increased.
B)decreased.
C)remained the same.
D)cannot be determined.
E)is irrelevant.
A)increased.
B)decreased.
C)remained the same.
D)cannot be determined.
E)is irrelevant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following graphs best depicts the entropy of a pure substance as the temperature is raised from its solid form through its liquid and gaseous forms?
A)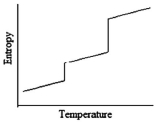
B)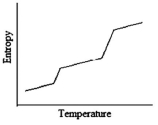
C)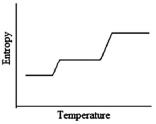
D)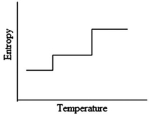
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The gas above the liquid in a sealed bottle of soda is primarily carbon dioxide. Carbon dioxide is also dissolved in the soda. When the distribution of carbon dioxide between the gas and liquid is at equilibrium, molecules of carbon dioxide in the gas phase can still dissolve in the liquid phase if they strike the surface and are captured. Similarly, molecules of carbon dioxide can escape from the liquid phase. What is the entropy change of the universe, Suni v, for the dissolution of carbon dioxide under these conditions?
A)( Suniv < 0, because the dissolved carbon dioxide has fewer accessible states.)
B)( Suniv > 0, because the dissolved carbon dioxide has fewer accessible states.)
C)( Suniv = 0, because this is an equilibrium situation.)
D)( Suniv < 0, because the gas dissolves spontaneously.)
E)( Suniv > 0, because the gas dissolves spontaneously.)
A)( Suniv < 0, because the dissolved carbon dioxide has fewer accessible states.)
B)( Suniv > 0, because the dissolved carbon dioxide has fewer accessible states.)
C)( Suniv = 0, because this is an equilibrium situation.)
D)( Suniv < 0, because the gas dissolves spontaneously.)
E)( Suniv > 0, because the gas dissolves spontaneously.)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The following figures represent distributions of gas molecules between two containers connected by an open tube. In which figure is the entropy of the system maximized?
A)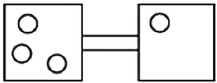
B)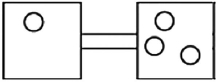
C)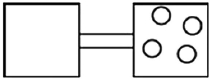
D)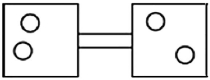
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of the following must be true for a spontaneous exothermic process?
A)only that Ssys < 0
B)only that Ssys > 0
C)both Ssys < 0 and the magnitude of Ssys < the magnitude of Ssurr
D)both Ssys < 0 and the magnitude of Ssys > the magnitude of Ssurr
E)either Ssys > 0 or Ssys < 0 and the magnitude of Ssys < the magnitude of Ssurr
A)only that Ssys < 0
B)only that Ssys > 0
C)both Ssys < 0 and the magnitude of Ssys < the magnitude of Ssurr
D)both Ssys < 0 and the magnitude of Ssys > the magnitude of Ssurr
E)either Ssys > 0 or Ssys < 0 and the magnitude of Ssys < the magnitude of Ssurr

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Indicate which of the following has the largest standard molar entropy (S ).
A)CH4(g)
B)CH3CH2OH(l )
C)CO2(s)
D)Na(s)
E)NH3(l )
A)CH4(g)
B)CH3CH2OH(l )
C)CO2(s)
D)Na(s)
E)NH3(l )

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The standard molar entropy of magnesium fluoride (MgF2) is 57.2 J/(mol . K). What is the entropy of 4.75 g of MgF2?
A)(+4.36 J/K)
B)(-4.36 J/K)
C)(+272 J/K)
D)(-272 J/K)
E)0 J/K
A)(+4.36 J/K)
B)(-4.36 J/K)
C)(+272 J/K)
D)(-272 J/K)
E)0 J/K

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
In an experiment, 1.00 atm of N2(g) in a 10.0 L container at 25 C was reacted under standard state conditions with a stoichiometric quantity of H2(g) to form ammonia: 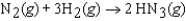 .
.
What is the entropy change for the reaction?
A)(-198.7 J/K)
B)(-81.5 J/K)
C)(-27.2 J/K)
D)(+81.5 J/K)
E)(+198.7 J/K)
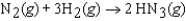 .
. What is the entropy change for the reaction?

A)(-198.7 J/K)
B)(-81.5 J/K)
C)(-27.2 J/K)
D)(+81.5 J/K)
E)(+198.7 J/K)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
NO gas is converted to NO2 gas according to the following reaction: 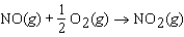
What is the standard entropy change when 0.5 mol of NO gas reacts with 0.5 mol of O2 gas?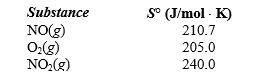
A)(-36.6 J/K)
B)(-175.7 J/K)
C)(-83.4 J/K)
D)(+83.4 J/K)
E)(+36.6 J/K)
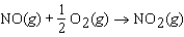
What is the standard entropy change when 0.5 mol of NO gas reacts with 0.5 mol of O2 gas?
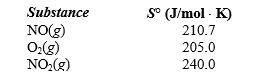
A)(-36.6 J/K)
B)(-175.7 J/K)
C)(-83.4 J/K)
D)(+83.4 J/K)
E)(+36.6 J/K)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The entropy of a NaCl crystal is ________
A)an intensive property and a state function.
B)an intensive property and a path function.
C)an extensive property and a state function.
D)an extensive property and a path function.
E)not appropriately described in terms of an intensive property, an extensive property, a state function, or a path function.
A)an intensive property and a state function.
B)an intensive property and a path function.
C)an extensive property and a state function.
D)an extensive property and a path function.
E)not appropriately described in terms of an intensive property, an extensive property, a state function, or a path function.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Indicate which of the following has the highest entropy at 298 K.
A)0.5 g of HCN
B)1 mol of HCN
C)2 kg of HCN
D)2 mol of HCN
E)All of the above have the same entropy at 298 K.
A)0.5 g of HCN
B)1 mol of HCN
C)2 kg of HCN
D)2 mol of HCN
E)All of the above have the same entropy at 298 K.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Indicate which of the following has the smallest standard molar entropy (S ).
A)NH3(g)
B)H2O(l)
C)Mg(s)
D)Hg(l )
E)Ar(g)
A)NH3(g)
B)H2O(l)
C)Mg(s)
D)Hg(l )
E)Ar(g)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The symbol 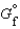 (CH4, g) refers to which of the following reactions?
(CH4, g) refers to which of the following reactions?
A)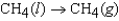
B)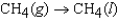
C)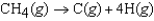
D)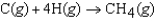
E)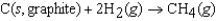
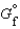 (CH4, g) refers to which of the following reactions?
(CH4, g) refers to which of the following reactions?A)
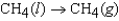
B)
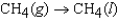
C)
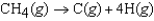
D)
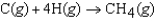
E)
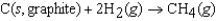

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which of the relationships between the free-energy change of a system and associated entropy changes is true?
A)( Gsys = +T Ssystem)
B)( Gsys = -T Ssystem)
C)( Gsys = +T Suniverse)
D)( Gsys = -T Ssurroundings)
E)( Gsys = -T Suniverse)
A)( Gsys = +T Ssystem)
B)( Gsys = -T Ssystem)
C)( Gsys = +T Suniverse)
D)( Gsys = -T Ssurroundings)
E)( Gsys = -T Suniverse)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The standard molar entropy of silver chloride (AgCl) is 96.2 J/(mol . K). What is the entropy of 1.78 g of AgCl?
A)(-1.19 J/K)
B)(+1.19 J/K)
C)(+96.2 J/K)
D)(-96.2 J/K)
E)0 J/K
A)(-1.19 J/K)
B)(+1.19 J/K)
C)(+96.2 J/K)
D)(-96.2 J/K)
E)0 J/K

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
What is the entropy change if 4.500 g of CaCO3(s) is placed in a container and allowed to decompose to CaO(s) and CO2(g) according to the following reaction? 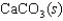

A)(+7.2 J/K)
B)(-160.5 J/K)
C)(+35.7 J/K)
D)(+160.5 J/K)
E)(+3.57 J/K)
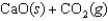

A)(+7.2 J/K)
B)(-160.5 J/K)
C)(+35.7 J/K)
D)(+160.5 J/K)
E)(+3.57 J/K)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Determine the standard entropy of N2(g) given the following information: 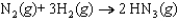
 = -198.3 J/K
= -198.3 J/K 
A)(-260.2 J/K)
B)(+260.2 J/K)
C)(+93.9 J/K)
D)(+191.5 J/K)
E)(-191.5 J/K)
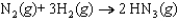
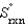 = -198.3 J/K
= -198.3 J/K 
A)(-260.2 J/K)
B)(+260.2 J/K)
C)(+93.9 J/K)
D)(+191.5 J/K)
E)(-191.5 J/K)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Determine  for
for 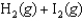
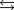
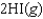 given the following information:
given the following information: 
A)(-41.10 J/K)
B)(-165.29 J/K)
C)(+398.75 J/K)
D)(+165.29 J/K)
E)(+41.10 J/K)
 for
for 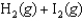
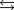
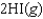 given the following information:
given the following information: 
A)(-41.10 J/K)
B)(-165.29 J/K)
C)(+398.75 J/K)
D)(+165.29 J/K)
E)(+41.10 J/K)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
What is the difference between G and G ?
A)( G refers to the formation of a compound from its elements; G can be defined for any reaction.)
B)( G refers to the formation of a pure compound; G can be defined for an impure compound.)
C)( G refers to a reaction that goes to completion; G is defined for a reaction that goes to any extent.)
D)( G refers to the conversion of reactants in their standard state to products in their standard state; G is defined for a reaction under any conditions.)
E)( G refers to reactions of one mole quantities of reactants; G is defined for any quantity of reactants.)
A)( G refers to the formation of a compound from its elements; G can be defined for any reaction.)
B)( G refers to the formation of a pure compound; G can be defined for an impure compound.)
C)( G refers to a reaction that goes to completion; G is defined for a reaction that goes to any extent.)
D)( G refers to the conversion of reactants in their standard state to products in their standard state; G is defined for a reaction under any conditions.)
E)( G refers to reactions of one mole quantities of reactants; G is defined for any quantity of reactants.)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Determine the entropy change for the reaction 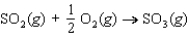 given the following information:
given the following information: 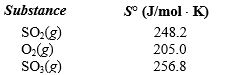
A)(-196.4 J/K)
B)(+196.4 J/K)
C)(-93.9 J/K)
D)(+93.9 J/K)
E)(+401.4 J/K)
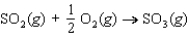 given the following information:
given the following information: 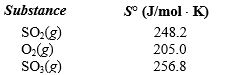
A)(-196.4 J/K)
B)(+196.4 J/K)
C)(-93.9 J/K)
D)(+93.9 J/K)
E)(+401.4 J/K)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The symbol  (CH3OH, l) refers to which of the following reactions?
(CH3OH, l) refers to which of the following reactions?
A)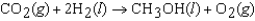
B)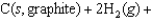
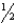
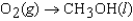
C)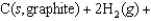
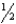
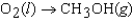
D)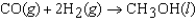
E)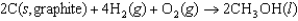
 (CH3OH, l) refers to which of the following reactions?
(CH3OH, l) refers to which of the following reactions?A)
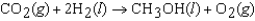
B)
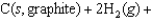
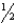
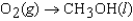
C)
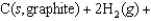
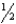
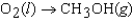
D)
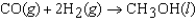
E)
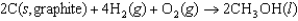

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which of the following is in the correct order of standard state entropy?
I. diamond < graphite
II. liquid water < solid water
III. NH3 < H2
A)I only
B)II only
C)III only
D)I and II only
E)I and III only
I. diamond < graphite
II. liquid water < solid water
III. NH3 < H2
A)I only
B)II only
C)III only
D)I and II only
E)I and III only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The standard molar entropy of lead(II) bromide (PbBr2) is 161 J/(mol . K). What is the entropy of 2.45 g of PbBr2?
A)(+1.07 J/K)
B)(-1.07 J/K)
C)(+161 J/K)
D)(-161 J/K)
E)0 J/K
A)(+1.07 J/K)
B)(-1.07 J/K)
C)(+161 J/K)
D)(-161 J/K)
E)0 J/K

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
What is the standard entropy change when 10.0 g of methane reacts with 10.0 g of oxygen? 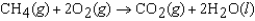

A)(-121 J/K)
B)(-37.9 J/K)
C)(-242.6 J/K)
D)(-154.4 J/K)
E)(-16.8 J/K)
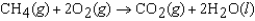

A)(-121 J/K)
B)(-37.9 J/K)
C)(-242.6 J/K)
D)(-154.4 J/K)
E)(-16.8 J/K)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Determine 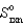 for
for 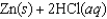
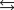
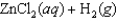 given the following information:
given the following information: 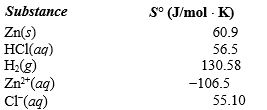
A)(-39.6 J/K)
B)0 J/K
C)(+39.6 J/K)
D)(-38.2 J/K)
E)(+38.2 J/K)
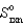 for
for 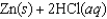
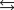
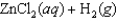 given the following information:
given the following information: 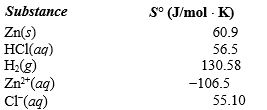
A)(-39.6 J/K)
B)0 J/K
C)(+39.6 J/K)
D)(-38.2 J/K)
E)(+38.2 J/K)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
If 3.500 g of Ni are reacted with excess oxygen to form nickel oxide (NiO) under standard state conditions, what is the entropy change for the reaction? 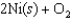
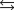
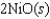
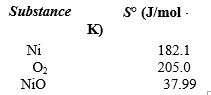
A)(-49.3 J/K)
B)(-24.7 J/K)
C)(-14.7 J/K)
D)(+49.3 J/K)
E)(-10.4 J/K)
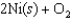
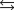
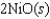
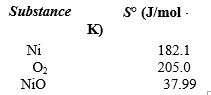
A)(-49.3 J/K)
B)(-24.7 J/K)
C)(-14.7 J/K)
D)(+49.3 J/K)
E)(-10.4 J/K)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Given the following data relevant to the combustion of ethanol, determine the free energy of formation for liquid ethanol, C2H5OH. 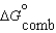 (C2H5OH, l) -930.7 kJ/mol
(C2H5OH, l) -930.7 kJ/mol 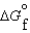 (CO2, g) -394.4 kJ/mol
(CO2, g) -394.4 kJ/mol 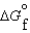 (H2O, g) -105.6 kJ/mol
(H2O, g) -105.6 kJ/mol
A)(-1,640.3 kJ/mol)
B)(-244.2 kJ/mol)
C)(-174.9 kJ/mol)
D)(+174.9 kJ/mol)
E)(+244.2 kJ/mol)
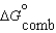 (C2H5OH, l) -930.7 kJ/mol
(C2H5OH, l) -930.7 kJ/mol 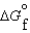 (CO2, g) -394.4 kJ/mol
(CO2, g) -394.4 kJ/mol 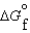 (H2O, g) -105.6 kJ/mol
(H2O, g) -105.6 kJ/molA)(-1,640.3 kJ/mol)
B)(-244.2 kJ/mol)
C)(-174.9 kJ/mol)
D)(+174.9 kJ/mol)
E)(+244.2 kJ/mol)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Hydrogen reacts with nitrogen to form ammonia (NH3) according to the reaction



The value of H is -92.38 kJ/mol, and that of S is -198.2 J/(mol . K). Determine G at 25 C.
A)(-5.897 104 kJ/mol)
B)(-297.8 kJ/mol)
C)(-33.32 kJ/mol)
D)(-16.66 kJ/mol)
E)(+49.5 kJ/mol)



The value of H is -92.38 kJ/mol, and that of S is -198.2 J/(mol . K). Determine G at 25 C.
A)(-5.897 104 kJ/mol)
B)(-297.8 kJ/mol)
C)(-33.32 kJ/mol)
D)(-16.66 kJ/mol)
E)(+49.5 kJ/mol)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
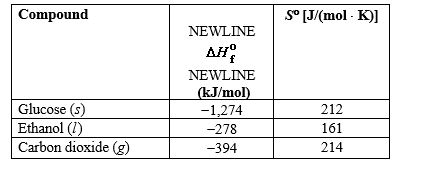
Alcohols for use as biofuels can be produced from glucose that is obtained from starch and cellulose in plants. Use the information in the table below to determine the free-energy change and whether or not this reaction is spontaneous at 78 C, which is the boiling point of an ethanol-water azeotrope. 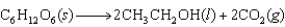
A)(-6 kJ, spontaneous)
B)(+76 kJ, not spontaneous)
C)(-76 kJ, spontaneous)
D)(-258 kJ, not spontaneous)
E)(-258 kJ, spontaneous)
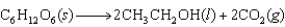

A)(-6 kJ, spontaneous)
B)(+76 kJ, not spontaneous)
C)(-76 kJ, spontaneous)
D)(-258 kJ, not spontaneous)
E)(-258 kJ, spontaneous)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Consider substances that exist as liquids under standard state conditions. What must be the relationship between the enthalpy and free energy of formation for the liquid and the gaseous form of such a substance? (Read < as more negative and > as less negative.)
A)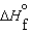 (l ) <
(l ) < 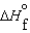 (g) and
(g) and 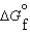 (l ) <
(l ) < 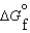 (g)
(g)
B)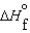 (l ) <
(l ) <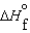 (g) and
(g) and 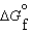 (l ) >
(l ) > 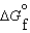 (g)
(g)
C)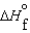 (l ) >
(l ) > 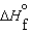 (g) and
(g) and 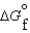 (l ) >
(l ) > 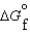 (g)
(g)
D)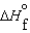 (l ) >
(l ) > 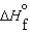 (g) and
(g) and 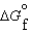 (l ) <
(l ) < 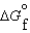 (g)
(g)
E)No strict relationship between these values applies.
A)
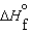 (l ) <
(l ) < 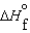 (g) and
(g) and 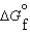 (l ) <
(l ) < 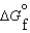 (g)
(g)B)
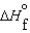 (l ) <
(l ) <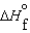 (g) and
(g) and 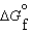 (l ) >
(l ) > 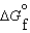 (g)
(g)C)
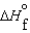 (l ) >
(l ) > 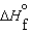 (g) and
(g) and 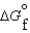 (l ) >
(l ) > 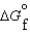 (g)
(g)D)
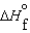 (l ) >
(l ) > 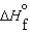 (g) and
(g) and 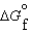 (l ) <
(l ) < 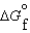 (g)
(g)E)No strict relationship between these values applies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Which of the following is/are true for a reversible process at equilibrium?
I. Suniv = 0
II. Ssys = 0
III. Gsys = 0
A)I only
B)II only
C)III only
D)I and III only
E)I, II, and III are all true.
I. Suniv = 0
II. Ssys = 0
III. Gsys = 0
A)I only
B)II only
C)III only
D)I and III only
E)I, II, and III are all true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Determine 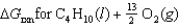
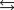
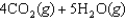 given the following information:
given the following information: 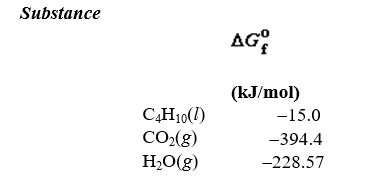
A)(-2,705 kJ)
B)(-608.0 kJ)
C)(-1,791 kJ)
D)(-3,457 kJ)
E)(+608.0 kJ)
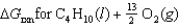
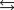
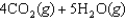 given the following information:
given the following information: 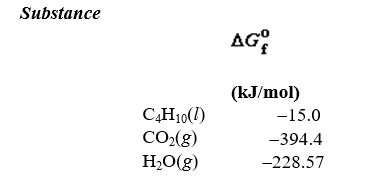
A)(-2,705 kJ)
B)(-608.0 kJ)
C)(-1,791 kJ)
D)(-3,457 kJ)
E)(+608.0 kJ)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The symbol 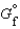 (MgSO4, s) refers to which of the following reactions?
(MgSO4, s) refers to which of the following reactions?
A)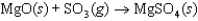
B)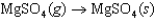
C)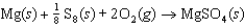
D)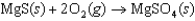
E)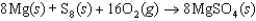
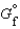 (MgSO4, s) refers to which of the following reactions?
(MgSO4, s) refers to which of the following reactions?A)
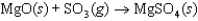
B)
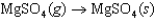
C)
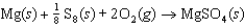
D)
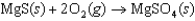
E)
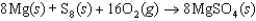

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Hydrochloric acid (HCl) reacts with sodium hydroxide (NaOH) to form sodium chloride (NaCl) and water. If H -56.13 kJ/mol and S = 79.11 J/mol . K, what is the temperature of the reaction if G = -80.89 kJ/mol?
A)154 C
B)313 C
C)0.313 C
D)40.0 C
E)75 C
A)154 C
B)313 C
C)0.313 C
D)40.0 C
E)75 C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Processes are always spontaneous when ________ (H and S refer to the system).
A)( H > 0 and S < 0)
B)( H < 0 and S < 0)
C)( H > 0 and S > 0)
D)( H < 0 and S > 0)
E)None of these is true, because temperature must always be taken into account.
A)( H > 0 and S < 0)
B)( H < 0 and S < 0)
C)( H > 0 and S > 0)
D)( H < 0 and S > 0)
E)None of these is true, because temperature must always be taken into account.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Hydrochloric acid (HCl) reacts with sodium hydroxide (NaOH) to form sodium chloride (NaCl) and water. If H = -56.13 kJ/mol and S = 79.11 J/mol . K, what is G for this reaction at 20 C?
A)(-79.31 kJ/mol)
B)(-77.73 kJ/mol)
C)(-2.324 104 kJ/mol)
D)79.31 kJ/mol
E)(-1,638 kJ/mol)
A)(-79.31 kJ/mol)
B)(-77.73 kJ/mol)
C)(-2.324 104 kJ/mol)
D)79.31 kJ/mol
E)(-1,638 kJ/mol)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Determine the value of G for the reaction at 298 K.
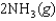
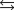
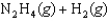 Given
Given 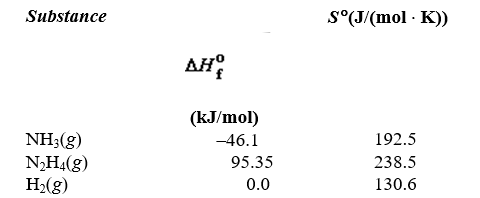
A)(-88.8 kJ)
B)(+88.8 kJ)
C)(+192 kJ)
D)(-192 kJ)
E)(-3.38 kJ)
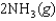
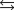
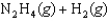 Given
Given 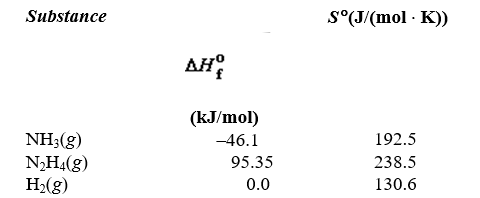
A)(-88.8 kJ)
B)(+88.8 kJ)
C)(+192 kJ)
D)(-192 kJ)
E)(-3.38 kJ)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Determine the value of G for the reaction at 298 K. 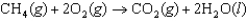 Given
Given 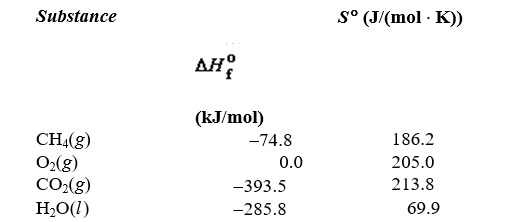
A)(-962 kJ)
B)(+573 kJ)
C)(-573 kJ)
D)(-817 kJ)
E)(+817 kJ)
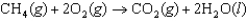 Given
Given 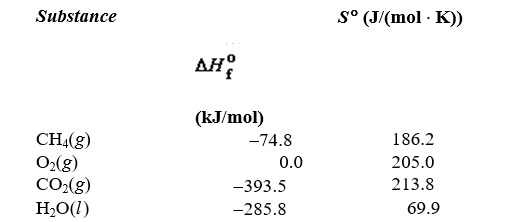
A)(-962 kJ)
B)(+573 kJ)
C)(-573 kJ)
D)(-817 kJ)
E)(+817 kJ)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Determine the value of G for the reaction 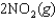
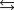
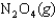 given
given 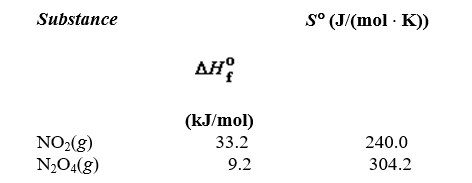
A)(-4.8 kJ)
B)(+4.8 kJ)
C)(+52.3 kJ)
D)(-52.3 kJ)
E)(-43 kJ)
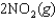
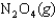 given
given 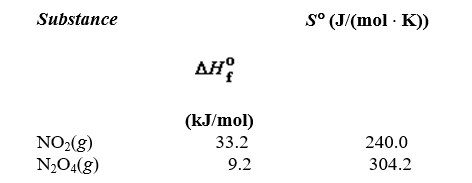
A)(-4.8 kJ)
B)(+4.8 kJ)
C)(+52.3 kJ)
D)(-52.3 kJ)
E)(-43 kJ)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
What is the maximum amount of work that can be done by the reaction 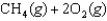
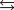
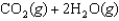
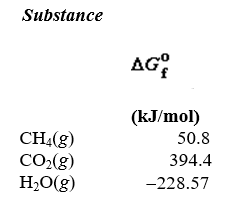
A)(-50.8 kJ/mol)
B)(-751 kJ/mol)
C)(+113 kJ/mol)
D)(-115 kJ/mol)
E)(-807 kJ/mol)
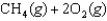
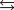
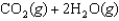

A)(-50.8 kJ/mol)
B)(-751 kJ/mol)
C)(+113 kJ/mol)
D)(-115 kJ/mol)
E)(-807 kJ/mol)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The reaction 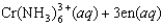
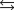
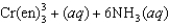 where en represents ethylenediamine, has a small value for the enthalpy change, Hrxn, yet the free-energy change is large because ________
where en represents ethylenediamine, has a small value for the enthalpy change, Hrxn, yet the free-energy change is large because ________
A)the reaction rate is fast.
B)the entropy change is large and positive.
C)the enthalpy change is large enough to matter.
D)the entropy change is large and negative.
E)ethylenediamine has amino groups that are stronger bases than ammonia.
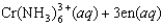
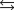
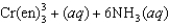 where en represents ethylenediamine, has a small value for the enthalpy change, Hrxn, yet the free-energy change is large because ________
where en represents ethylenediamine, has a small value for the enthalpy change, Hrxn, yet the free-energy change is large because ________A)the reaction rate is fast.
B)the entropy change is large and positive.
C)the enthalpy change is large enough to matter.
D)the entropy change is large and negative.
E)ethylenediamine has amino groups that are stronger bases than ammonia.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
A reaction is at equilibrium at a given temperature and constant pressure when ________
A)( Srxn = 0.)
B)(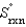 = 0.)
= 0.)
C)( Grxn = 0.)
D)( = 0.)
= 0.)
E)( Hrxn = 0.)
A)( Srxn = 0.)
B)(
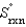 = 0.)
= 0.)C)( Grxn = 0.)
D)(
 = 0.)
= 0.)E)( Hrxn = 0.)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The symbol 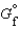 (NH4NO3, s) refers to which of the following reactions?
(NH4NO3, s) refers to which of the following reactions?
A)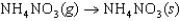
B)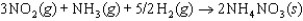
C)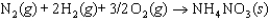
D)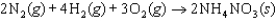
E)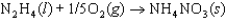
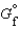 (NH4NO3, s) refers to which of the following reactions?
(NH4NO3, s) refers to which of the following reactions?A)
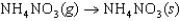
B)
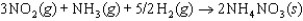
C)
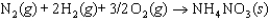
D)
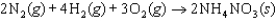
E)
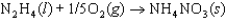

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Given the following data, determine the molar free energy of combustion for propane gas, C3H8.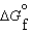 (C3H8, g) -23.5 kJ/mol
(C3H8, g) -23.5 kJ/mol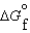 (CO2, g) -394.4 kJ/mol
(CO2, g) -394.4 kJ/mol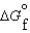 (H2O, g) -5.6 kJ/mol
(H2O, g) -5.6 kJ/mol
A)(-1,629.1 kJ/mol)
B)(-1,582.1 kJ/mol)
C)(-476.5 kJ/mol)
D)(+476.5 kJ/mol)
E)(+1,582.1 kJ/mol)
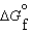 (C3H8, g) -23.5 kJ/mol
(C3H8, g) -23.5 kJ/mol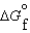 (CO2, g) -394.4 kJ/mol
(CO2, g) -394.4 kJ/mol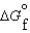 (H2O, g) -5.6 kJ/mol
(H2O, g) -5.6 kJ/molA)(-1,629.1 kJ/mol)
B)(-1,582.1 kJ/mol)
C)(-476.5 kJ/mol)
D)(+476.5 kJ/mol)
E)(+1,582.1 kJ/mol)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
The equilibrium vapor pressure for benzene is 94.4 mm Hg. When liquid benzene is in equilibrium with its vapor, we must have ________
A)( G = 0 and G = 0.)
B)( G = 0 and G > 0.).
C)( G = 0 and G < 0.)
D)( G = 0 and G = 0.) .
E)( G < 0 and G = 0.)
A)( G = 0 and G = 0.)
B)( G = 0 and G > 0.).
C)( G = 0 and G < 0.)
D)( G = 0 and G = 0.) .
E)( G < 0 and G = 0.)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
At constant T and P, any reaction will be spontaneous if ________
A)( Gsys > 0.)
B)( Gsys < 0.)
C)( Ssys > 0.)
D)( Ssys < 0.)
E)( Hsys < 0.)
A)( Gsys > 0.)
B)( Gsys < 0.)
C)( Ssys > 0.)
D)( Ssys < 0.)
E)( Hsys < 0.)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



