Deck 11: Solutions: Properties and Behavior
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/150
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 11: Solutions: Properties and Behavior
1
The interaction energy of LiF is -1.14 10-18 J. What is the distance between the Li+ and F- ions?
A)203 nm
B)203 pm
C)0.203 pm
D)494 pm
E)302 pm
A)203 nm
B)203 pm
C)0.203 pm
D)494 pm
E)302 pm
203 pm
2
Which of the following will require the greatest energy input to separate the ions?
A)MgI2
B)MgF2
C)MgCl2
D)MgBr2
E)NaCl
A)MgI2
B)MgF2
C)MgCl2
D)MgBr2
E)NaCl
MgF2
3
Which of the following will have the largest cation-anion attraction?
A)NaF
B)NaCl
C)NaBr
D)NaI
E)CsCl
A)NaF
B)NaCl
C)NaBr
D)NaI
E)CsCl
NaF
4
Predict the relationship between the lattice energies (U) of KBr and CaO.
A)UCaO > 4 UKBr because the ionic charges are +2 and -2 and the distance between the ions is smaller.
B)UCaO < 4 UKBr because the ionic charges are +2 and -2 and the distance between the ions is larger..
C)UCaO > 2 UKBr because the ionic charges are +2 and -2 and the distance between the ions is smaller.
D)UCaO < 4 UKBr because the ionic charges are +2 and -2 and the distance between the ions is larger.
E)UCaO and UKBr are about the same because the larger ionic charge is compensated by the larger distance between the ions.
A)UCaO > 4 UKBr because the ionic charges are +2 and -2 and the distance between the ions is smaller.
B)UCaO < 4 UKBr because the ionic charges are +2 and -2 and the distance between the ions is larger..
C)UCaO > 2 UKBr because the ionic charges are +2 and -2 and the distance between the ions is smaller.
D)UCaO < 4 UKBr because the ionic charges are +2 and -2 and the distance between the ions is larger.
E)UCaO and UKBr are about the same because the larger ionic charge is compensated by the larger distance between the ions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Predict which of the following ionic compounds has the highest melting point.
A)NaF
B)KCl
C)RbCl
D)BeF2
E)NaCl
A)NaF
B)KCl
C)RbCl
D)BeF2
E)NaCl

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Coulomb's law states that the interaction energy between ions depends ________
A)only on the ionic charges.
B)only on the distance between the ions.
C)directly on both the ionic charges and the distance between the ions.
D)on the temperature.
E)directly on the ionic charges and inversely on the distance between the ions.
A)only on the ionic charges.
B)only on the distance between the ions.
C)directly on both the ionic charges and the distance between the ions.
D)on the temperature.
E)directly on the ionic charges and inversely on the distance between the ions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Predict the relationship between the lattice energies (U) of KNO3 and NaBr.
A)UKNO3 > UNaBr
B)UKNO3 <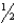 UNaBr
UNaBr
C)UKNO3 > 2 UNaBr
D)UKNO3 < UNaBr
E)UKNO3 and UNaBr are about the same.
A)UKNO3 > UNaBr
B)UKNO3 <
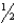 UNaBr
UNaBrC)UKNO3 > 2 UNaBr
D)UKNO3 < UNaBr
E)UKNO3 and UNaBr are about the same.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Rank the following compounds in order of increasing attraction between their ions: KBr, SrBr2, and CsBr.
A)CsBr < KBr < SrBr2
B)SrBr2 < CsBr < KBr
C)KBr < SrBr2 < CsBr
D)CsBr < SrBr2 < KBr
E)SrBr2 < KBr < CsBr
A)CsBr < KBr < SrBr2
B)SrBr2 < CsBr < KBr
C)KBr < SrBr2 < CsBr
D)CsBr < SrBr2 < KBr
E)SrBr2 < KBr < CsBr

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which arrangement below orders the cations from smallest to largest hydration energy? Smallest to largest means least negative hydration energy to most negative hydration energy.
A)Cs+ < K+< Ca2+ < Al3+
B)K+ < Cs+ < Ca2+ < Al3+
C)Al3+ < Ca2+< K+< Cs+
D)Al3+< Ca2+< Cs+< K+
E)K+< Cs+< Al3+< Ca2+
A)Cs+ < K+< Ca2+ < Al3+
B)K+ < Cs+ < Ca2+ < Al3+
C)Al3+ < Ca2+< K+< Cs+
D)Al3+< Ca2+< Cs+< K+
E)K+< Cs+< Al3+< Ca2+

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following must be true if the dissolution of an ionic solid in water is exothermic?
A)The process requires energy.
B)The solubility will increase with increasing temperature.
C)The hydration energy exceeds the lattice energy.
D)The ions must have charges greater in magnitude than 1.
E)The change in enthalpy for this process is positive.
A)The process requires energy.
B)The solubility will increase with increasing temperature.
C)The hydration energy exceeds the lattice energy.
D)The ions must have charges greater in magnitude than 1.
E)The change in enthalpy for this process is positive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following requires the smallest energy to separate the ions?
A)CaF2
B)KF
C)NaF
D)MgF2
E)LiCl
A)CaF2
B)KF
C)NaF
D)MgF2
E)LiCl

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following will have the largest lattice energy?
A)NaF
B)NaCl
C)NaBr
D)NaI
E)CsCl
A)NaF
B)NaCl
C)NaBr
D)NaI
E)CsCl

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Arrange the three ionic compounds sodium chloride, magnesium chloride, and aluminum chloride in order of increasing melting point.
A)NaCl < MgCl2 < AlCl3
B)MgCl2 < NaCl < AlCl3
C)AlCl3 < MgCl2 < NaCl
D)AlCl3 < NaCl < MgCl2
E)NaCl < AlCl3 < MgCl2
A)NaCl < MgCl2 < AlCl3
B)MgCl2 < NaCl < AlCl3
C)AlCl3 < MgCl2 < NaCl
D)AlCl3 < NaCl < MgCl2
E)NaCl < AlCl3 < MgCl2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Ion interaction energies are determined by Coulomb's law: 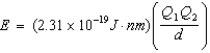 Which of the following compounds has an interaction energy = -3.83 10-18 J?
Which of the following compounds has an interaction energy = -3.83 10-18 J?
A)NaCl (d = 294 pm)
B)MgS (d = 241 pm)
C)LiF (d = 189 pm)
D)CaO (d = 235 pm)
E)AlN (d = 185 pm)
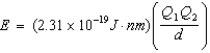 Which of the following compounds has an interaction energy = -3.83 10-18 J?
Which of the following compounds has an interaction energy = -3.83 10-18 J?A)NaCl (d = 294 pm)
B)MgS (d = 241 pm)
C)LiF (d = 189 pm)
D)CaO (d = 235 pm)
E)AlN (d = 185 pm)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following ranks the compounds from lowest to highest lattice energy?
A)LiF < CaCl2 < CaS < KBr
B)KBr < LiF < CaCl2 < CaS
C)CaCl2 < CaS < LiF < KBr
D)CaS < CaCl2 < LiF < KBr
E)KBr < LiF < CaS < CaCl2
A)LiF < CaCl2 < CaS < KBr
B)KBr < LiF < CaCl2 < CaS
C)CaCl2 < CaS < LiF < KBr
D)CaS < CaCl2 < LiF < KBr
E)KBr < LiF < CaS < CaCl2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following must be true if the dissolution of an ionic solid in water is endothermic?
A)The change in enthalpy for this process is negative.
B)The process releases energy.
C)The hydration energy exceeds the lattice energy.
D)The ions have charges greater than 1 unit.
E)The solubility will increase with increasing temperature.
A)The change in enthalpy for this process is negative.
B)The process releases energy.
C)The hydration energy exceeds the lattice energy.
D)The ions have charges greater than 1 unit.
E)The solubility will increase with increasing temperature.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Coulomb's law states that the energy of attraction between ions depends ________
A)only on the charge of the cation.
B)only on the charge of the anion.
C)directly on the distance between the ions.
D)on the charges of both ions.
E)on the temperature.
A)only on the charge of the cation.
B)only on the charge of the anion.
C)directly on the distance between the ions.
D)on the charges of both ions.
E)on the temperature.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which statement A-D about ionic solids is not correct?
A)The enthalpy of hydration includes two terms: one for ion-dipole interactions and one for dipole-dipole interactions.
B)The melting point of an ionic solid increases as the lattice energy increases.
C)The enthalpy of solution consists of two terms: the lattice energy and the enthalpy of hydration.
D)The lattice energy depends directly on the product of ionic charges, inversely on the distance between the ions, and on the structure of the solid.
E)Statements A-D are all correct.
A)The enthalpy of hydration includes two terms: one for ion-dipole interactions and one for dipole-dipole interactions.
B)The melting point of an ionic solid increases as the lattice energy increases.
C)The enthalpy of solution consists of two terms: the lattice energy and the enthalpy of hydration.
D)The lattice energy depends directly on the product of ionic charges, inversely on the distance between the ions, and on the structure of the solid.
E)Statements A-D are all correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which arrangement below orders the cations from smallest to largest hydration energy? Smallest to largest means least negative hydration energy to most negative hydration energy.
A)Fe3+ < Mg2+ < Rb+ < Na+
B)Na+ < Rb+ < Mg2+< Fe3+
C)Fe3+< Mg2+< Na+ < Rb+
D)Rb+ < Na+ < Mg2+ < Fe3+
E)Na+ < Rb+ < Fe3+ < Mg2+
A)Fe3+ < Mg2+ < Rb+ < Na+
B)Na+ < Rb+ < Mg2+< Fe3+
C)Fe3+< Mg2+< Na+ < Rb+
D)Rb+ < Na+ < Mg2+ < Fe3+
E)Na+ < Rb+ < Fe3+ < Mg2+

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Ion interaction energies are determined by Coulomb's law: 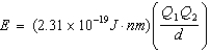 Determine the energy of potassium chloride if the radius of the potassium ion is 133 pm and that of the chloride ion is 181 pm.
Determine the energy of potassium chloride if the radius of the potassium ion is 133 pm and that of the chloride ion is 181 pm.
A)(-7.36 10-19 J)
B)(-7.36 10-22 J)
C)7.36 10-19 J
D)1.74 10-18 J
E)(-7.36 10-25 J)
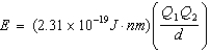 Determine the energy of potassium chloride if the radius of the potassium ion is 133 pm and that of the chloride ion is 181 pm.
Determine the energy of potassium chloride if the radius of the potassium ion is 133 pm and that of the chloride ion is 181 pm.A)(-7.36 10-19 J)
B)(-7.36 10-22 J)
C)7.36 10-19 J
D)1.74 10-18 J
E)(-7.36 10-25 J)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the following requires the smallest energy to separate the ions?
A)CaF2
B)KF
C)NaF
D)MgF2
E)LiF
A)CaF2
B)KF
C)NaF
D)MgF2
E)LiF

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following ionic compounds would you predict to have the lowest solubility in water?
A)MgF2
B)MgCl2
C)CaBr2
D)SrI2
E)BaI2
A)MgF2
B)MgCl2
C)CaBr2
D)SrI2
E)BaI2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Why would you expect or predict sodium fluoride to have the lowest solubility in water compared to the other sodium halide salts?
A)Fluoride has the largest (most negative) enthalpy of hydration of all the halide ions.
B)Fluoride has the smallest (least negative) enthalpy of hydration of all the halide ions.
C)Sodium fluoride has the largest (most negative) lattice energy of all the sodium halides.
D)Sodium fluoride has the smallest molar mass of all the sodium halides.
E)Fluoride is the most basic of all the halide ions and forms HF in aqueous solution.
A)Fluoride has the largest (most negative) enthalpy of hydration of all the halide ions.
B)Fluoride has the smallest (least negative) enthalpy of hydration of all the halide ions.
C)Sodium fluoride has the largest (most negative) lattice energy of all the sodium halides.
D)Sodium fluoride has the smallest molar mass of all the sodium halides.
E)Fluoride is the most basic of all the halide ions and forms HF in aqueous solution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
In the following Born-Haber cycle for the formation of sodium chloride from its elements, which step (A-E) corresponds to the ionization energy of one of the reactants? 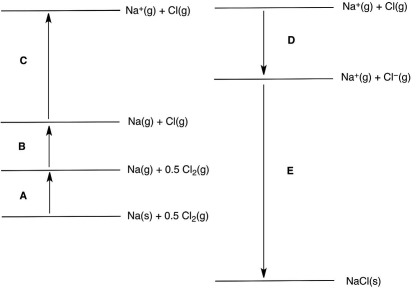
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E

A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
In the following Born-Haber cycle for the formation of sodium chloride from its elements, which step (A-E) corresponds to the electron affinity of one of the intermediate species? 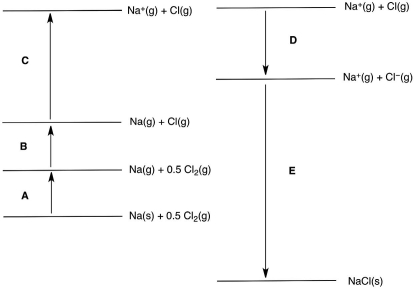
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E

A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following will have the smallest lattice energy?
A)LiCl
B)K2O
C)MgBr2
D)Al2S3
E)CsI
A)LiCl
B)K2O
C)MgBr2
D)Al2S3
E)CsI

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the following is not typically needed to calculate the lattice energy of an ionic compound?
A)enthalpy of vaporization
B)bond enthalpy
C)enthalpy of solution
D)electron affinity
E)ionization energy
A)enthalpy of vaporization
B)bond enthalpy
C)enthalpy of solution
D)electron affinity
E)ionization energy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the following ionic compounds would you predict to have the highest solubility in water?
A)MgF2
B)MgCl2
C)CaBr2
D)SrI2
E)BaI2
A)MgF2
B)MgCl2
C)CaBr2
D)SrI2
E)BaI2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which one of the ionic compounds below would you expect to have the smallest (least negative) lattice energy?
A)MgF2
B)MgCl2
C)MgBr2
D)MgI2
E)CaI2
A)MgF2
B)MgCl2
C)MgBr2
D)MgI2
E)CaI2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Calculate the lattice energy of magnesium chloride from the following data: First ionization energy of Mg: 738 kJ/mol
Second ionization energy of Mg: 1,451 kJ/mol
Electron affinity of Cl: -349 kJ/mol
Energy to vaporize Mg: 147.1 kJ/mol
Cl2 bond energy: 243 kJ/mol
Energy change for the reaction: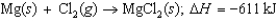
A)1,246 kJ/mol
B)(-779 kJ/mol)
C)(-2,492 kJ/mol)
D)2,492 kJ/mol
E)(-1,246 kJ/mol)
Second ionization energy of Mg: 1,451 kJ/mol
Electron affinity of Cl: -349 kJ/mol
Energy to vaporize Mg: 147.1 kJ/mol
Cl2 bond energy: 243 kJ/mol
Energy change for the reaction:
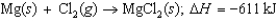
A)1,246 kJ/mol
B)(-779 kJ/mol)
C)(-2,492 kJ/mol)
D)2,492 kJ/mol
E)(-1,246 kJ/mol)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which one of the ionic compounds below would you expect to have the smallest (least negative) lattice energy?
A)MgO
B)CaO
C)SrO
D)BaO
E)BeO
A)MgO
B)CaO
C)SrO
D)BaO
E)BeO

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which one of the ionic compounds below would you expect to have the largest (most negative) lattice energy?
A)MgF2
B)MgCl2
C)MgBr2
D)MgI2
E)CaI2
A)MgF2
B)MgCl2
C)MgBr2
D)MgI2
E)CaI2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which one of the ionic compounds below would you expect to have the largest (most negative) lattice energy?
A)MgO
B)CaO
C)SrO
D)BaO
E)BeO
A)MgO
B)CaO
C)SrO
D)BaO
E)BeO

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which of the following compounds has the largest melting point?
A)NaF
B)KCl
C)RbCl
D)BeF2
E)NaCl
A)NaF
B)KCl
C)RbCl
D)BeF2
E)NaCl

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which listing of ionic compounds is in order of increasing melting point?
A)NaF < MgF2 < AlF3
B)MgF2 < NaF < AlF3
C)AlF3 < MgF2 < NaF
D)AlF3 < NaF < MgF2
E)NaF < AlF3 < MgF2
A)NaF < MgF2 < AlF3
B)MgF2 < NaF < AlF3
C)AlF3 < MgF2 < NaF
D)AlF3 < NaF < MgF2
E)NaF < AlF3 < MgF2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following will require the greatest energy input to separate the ions?
A)MgI2
B)MgF2
C)MgCl2
D)MgBr2
E)NaCl
A)MgI2
B)MgF2
C)MgCl2
D)MgBr2
E)NaCl

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the following compounds has the lowest melting point?
A)NaF
B)KCl
C)RbCl
D)BeF2
E)NaCl
A)NaF
B)KCl
C)RbCl
D)BeF2
E)NaCl

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
In the following Born-Haber cycle for the formation of sodium chloride from its elements, which step (A-E) corresponds to a molar heat of sublimation for one of the reactants? 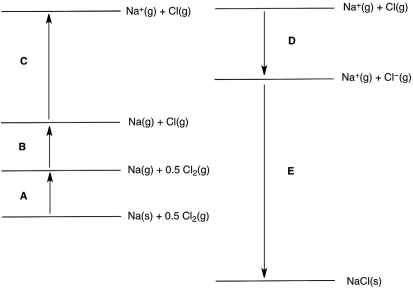
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E

A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
In the following Born-Haber cycle for the formation of sodium chloride from its elements, which step (A-E) corresponds to the lattice energy for NaCl? 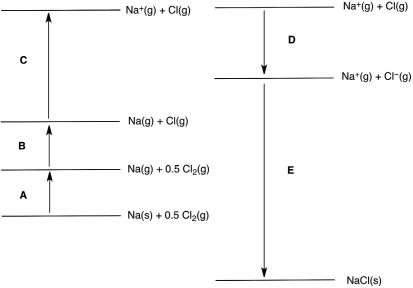
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E

A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Calculate the lattice energy of sodium fluoride from the following data: Ionization energy of Na: 496 kJ/mol
Electron affinity of F: -328 kJ/mol
Energy to vaporize Na: 108 kJ/mol
F2 bond energy: 160 kJ/mol
Energy change for the reaction: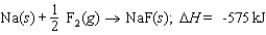
A)931 kJ/mol
B)(-931 kJ/mol)
C)(-1,011 kJ/mol)
D)1,011 kJ/mol
E)(-851 kJ/mol)
Electron affinity of F: -328 kJ/mol
Energy to vaporize Na: 108 kJ/mol
F2 bond energy: 160 kJ/mol
Energy change for the reaction:
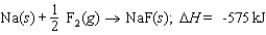
A)931 kJ/mol
B)(-931 kJ/mol)
C)(-1,011 kJ/mol)
D)1,011 kJ/mol
E)(-851 kJ/mol)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which of the solutions shown here will have the lowest vapor pressure? White circles indicate solvent molecules; black circles indicate molecules of a nonvolatile solute.
A)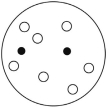
B)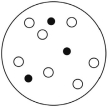
C)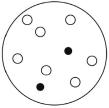
D)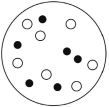
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which graph best describes how the vapor pressure of a solution varies according to Raoult's law as a nonvolatile solute is added to a liquid? The vapor pressure of the solution is plotted on the y-axis, and the mole fraction of solute is plotted on the x-axis. The origin (0, 0) is not necessarily located where the axes cross. 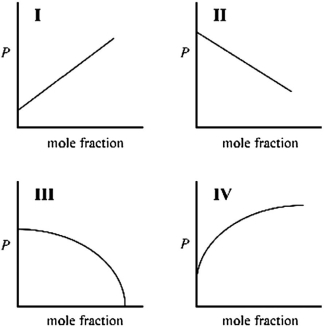
A)I
B)II
C)III
D)IV

A)I
B)II
C)III
D)IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
In the diagram below, one beaker contains pure water and the other contains an equal volume of seawater. Seawater has various salts dissolved in it. The beakers are sitting in a totally enclosed chamber, and the outside temperature and pressure are held constant. Identify the statements below about this situation that are not correct. 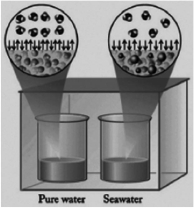
I. Water will be transferred from the pure water beaker to the seawater beaker.
II. Water will be transferred from the seawater beaker to the pure water beaker.
III.The vapor pressure of the pure water is higher than the vapor pressure of the seawater.
IV. Pure water evaporates at a faster rate than seawater.
V. Water in the gas phase condenses into both beakers at the same rate.
A)II only
B)II and V
C)II, IV, and V
D)II, III, and IV
E)I, III, and IV

I. Water will be transferred from the pure water beaker to the seawater beaker.
II. Water will be transferred from the seawater beaker to the pure water beaker.
III.The vapor pressure of the pure water is higher than the vapor pressure of the seawater.
IV. Pure water evaporates at a faster rate than seawater.
V. Water in the gas phase condenses into both beakers at the same rate.
A)II only
B)II and V
C)II, IV, and V
D)II, III, and IV
E)I, III, and IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which statement about the vapor pressure of a liquid is not correct?
A)Temperature, solute concentration, and solvent identity all play roles in determining the vapor pressure above a solution.
B)The mole fraction of the solvent is used to calculate the vapor pressure above a solution.
C)The vapor pressure of a solution is not related to the vapor pressure of the pure solvent.
D)In ideal solutions that obey Raoult's law, solute and solvent molecules both experience similar intermolecular forces.
E)Vapor pressure of a solution is a colligative property, which means pressure depends on the concentration of a solute, not its identity.
A)Temperature, solute concentration, and solvent identity all play roles in determining the vapor pressure above a solution.
B)The mole fraction of the solvent is used to calculate the vapor pressure above a solution.
C)The vapor pressure of a solution is not related to the vapor pressure of the pure solvent.
D)In ideal solutions that obey Raoult's law, solute and solvent molecules both experience similar intermolecular forces.
E)Vapor pressure of a solution is a colligative property, which means pressure depends on the concentration of a solute, not its identity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Indicate which aqueous solution has the highest vapor pressure.
A)0.1 M KCl
B)0.2 M Na2CO3
C)0.2 M NaCl
D)0.1 M MgCl2
E)0.2 M MgCl2
A)0.1 M KCl
B)0.2 M Na2CO3
C)0.2 M NaCl
D)0.1 M MgCl2
E)0.2 M MgCl2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
A solution is prepared by adding 1.50 mol glucose, which is not volatile, to 3.50 mol diethyl ether. What is the vapor pressure of this solution at 25 C given that the vapor pressure of pure diethyl ether is 23.8 torr?
A)7.00 torr
B)16.7 torr
C)10.2 torr
D)7.14 torr
E)34.0 torr
A)7.00 torr
B)16.7 torr
C)10.2 torr
D)7.14 torr
E)34.0 torr

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Which of the solutions shown here will have the highest vapor pressure? White circles indicate solvent molecules; black circles indicate molecules of a nonvolatile solute.
A)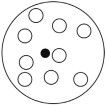
B)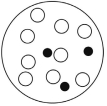
C)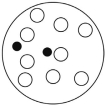
D)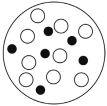
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Indicate which aqueous solution has the lowest vapor pressure.
A)0.25 M LiBr
B)0.2 M K3PO4
C)0.3 M Cs2CO3
D)0.1 M CaI2
E)0.4 M AgNO3
A)0.25 M LiBr
B)0.2 M K3PO4
C)0.3 M Cs2CO3
D)0.1 M CaI2
E)0.4 M AgNO3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Which statement about the vapor pressure of a liquid is not correct?
A)The vapor pressure increases with increasing temperature because more molecules have sufficient energy to overcome the attractive forces that hold them in the liquid.
B)The vapor pressure decreases with increasing strength of intermolecular interactions.
C)The pressure at which the rate of molecules evaporating equals the rate of molecules condensing is called the vapor pressure.
D)Adding a nonvolatile solute to a liquid increases the vapor pressure.
E)The enthalpy of vaporization determines how sensitive the vapor pressure of a substance is to a change in temperature.
A)The vapor pressure increases with increasing temperature because more molecules have sufficient energy to overcome the attractive forces that hold them in the liquid.
B)The vapor pressure decreases with increasing strength of intermolecular interactions.
C)The pressure at which the rate of molecules evaporating equals the rate of molecules condensing is called the vapor pressure.
D)Adding a nonvolatile solute to a liquid increases the vapor pressure.
E)The enthalpy of vaporization determines how sensitive the vapor pressure of a substance is to a change in temperature.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which statement below regarding vapor pressure is not correct?
A)Vapor pressure is an intensive property.
B)The substance with the stronger intermolecular forces has the lower vapor pressure.
C)Vapor pressure increases with increasing temperature.
D)Pure water has a higher vapor pressure at a given temperature than seawater.
E)A nonvolatile solute increases the vapor pressure of the solvent.
A)Vapor pressure is an intensive property.
B)The substance with the stronger intermolecular forces has the lower vapor pressure.
C)Vapor pressure increases with increasing temperature.
D)Pure water has a higher vapor pressure at a given temperature than seawater.
E)A nonvolatile solute increases the vapor pressure of the solvent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which of the following is needed to calculate the lattice energy of an ionic compound?
A)enthalpy of solution
B)enthalpy of combustion
C)specific heat
D)ionization energy
E)enthalpy of solvation
A)enthalpy of solution
B)enthalpy of combustion
C)specific heat
D)ionization energy
E)enthalpy of solvation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Indicate which aqueous solution has the lowest vapor pressure.
A)0.1 M KCl
B)0.1 M Na2CO3
C)0.2 M NaCl
D)0.1 M MgCl2
E)0.2 M MgCl2
A)0.1 M KCl
B)0.1 M Na2CO3
C)0.2 M NaCl
D)0.1 M MgCl2
E)0.2 M MgCl2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which graph best describes how the vapor pressure of a substance varies with temperature according to the Clausius-Clapeyron equation? ln(P) is plotted on the y-axis, and 1/T is plotted on the x-axis. The origin (0, 0) is not necessarily located where the axes cross. 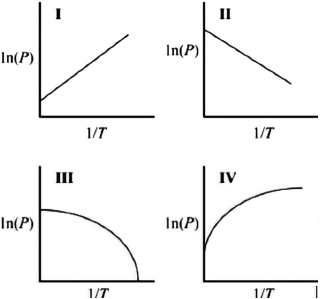
A)I
B)II
C)III
D)IV

A)I
B)II
C)III
D)IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which intermolecular interactions are likely to result in the lowest vapor pressure of a substance?
A)dispersion interactions
B)dipole-dipole interactions
C)hydrogen bonds
D)ion-dipole interactions
E)ion-ion interactions
A)dispersion interactions
B)dipole-dipole interactions
C)hydrogen bonds
D)ion-dipole interactions
E)ion-ion interactions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
A solution contains 6.50 mol water, 0.300 mol sucrose, and 0.200 mol glucose. The solutes are nonvolatile. What is the vapor pressure of the solution at 35 C given that the vapor pressure of water is 42.2 torr?
A)35.0 torr
B)36.0 torr
C)37.0 torr
D)39.2 torr
E)39.0 torr
A)35.0 torr
B)36.0 torr
C)37.0 torr
D)39.2 torr
E)39.0 torr

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which statement about how the vapor pressure (P) of a liquid depends on temperature is correct?
A)The larger the enthalpy of vaporization, the smaller the change in vapor pressure for a given change in temperature.
B)A graph of P versus 1/T is linear with a slope Hvap /R.
C)The smaller the intermolecular interactions, the greater the change in vapor pressure for a given change in temperature.
D)A graph of ln(P) versus T is linear with a slope Hvap /R.
E)A graph of ln(P) versus 1/T is linear with a slope Hvap /R.
A)The larger the enthalpy of vaporization, the smaller the change in vapor pressure for a given change in temperature.
B)A graph of P versus 1/T is linear with a slope Hvap /R.
C)The smaller the intermolecular interactions, the greater the change in vapor pressure for a given change in temperature.
D)A graph of ln(P) versus T is linear with a slope Hvap /R.
E)A graph of ln(P) versus 1/T is linear with a slope Hvap /R.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which intermolecular interactions are likely to result in the highest vapor pressure of a substance?
A)dispersion interactions
B)dipole-dipole interactions
C)hydrogen bonds
D)ion-dipole interactions
E)ion-ion interactions
A)dispersion interactions
B)dipole-dipole interactions
C)hydrogen bonds
D)ion-dipole interactions
E)ion-ion interactions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
A solution is prepared by adding 0.250 mol napthalene, which is not volatile, to 2.25 mol diethyl ether. What is the vapor pressure of this solution at 25 C given that the vapor pressure of pure diethyl ether is 532 torr?
A)53.2 torr
B)59.1 torr
C)473 torr
D)479 torr
E)591 torr
A)53.2 torr
B)59.1 torr
C)473 torr
D)479 torr
E)591 torr

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
What is the vapor pressure of an aqueous solution that has a solute mol fraction of = 0.100 ? The vapor pressure of water is 25.756 mm Hg at 25 C.
A)23.2 mm Hg
B)2.58 mm Hg
C)25.8 mm Hg
D)0.900 mm Hg
E)22.3 mm Hg
A)23.2 mm Hg
B)2.58 mm Hg
C)25.8 mm Hg
D)0.900 mm Hg
E)22.3 mm Hg

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Determine the energy change for the reaction 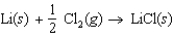 from the following data: Lattice energy of LiCl = -861 kJ/mol
from the following data: Lattice energy of LiCl = -861 kJ/mol
Energy to vaporize Li = 159 kJ/mol
Ionization energy of Li = 520 kJ/mol
Cl2 bond energy: 240 kJ/mol
Electron affinity of Cl: -349 kJ/mol
A)(-411 kJ/mol)
B)(-528 kJ/mol)
C)311 kJ/mol
D)(-861 kJ/mol)
E)(-291 kJ/mol)
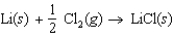 from the following data: Lattice energy of LiCl = -861 kJ/mol
from the following data: Lattice energy of LiCl = -861 kJ/molEnergy to vaporize Li = 159 kJ/mol
Ionization energy of Li = 520 kJ/mol
Cl2 bond energy: 240 kJ/mol
Electron affinity of Cl: -349 kJ/mol
A)(-411 kJ/mol)
B)(-528 kJ/mol)
C)311 kJ/mol
D)(-861 kJ/mol)
E)(-291 kJ/mol)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
At 25 C, the vapor pressure of pure water is 25.756 mm Hg. What is the vapor pressure of water in a 0.500 m solution of sodium chloride?
A)25.52 mm Hg
B)0.2301 mm Hg
C)0.4602 mm Hg
D)25.35 mm Hg
E)12.88 mm Hg
A)25.52 mm Hg
B)0.2301 mm Hg
C)0.4602 mm Hg
D)25.35 mm Hg
E)12.88 mm Hg

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
How many moles of solute are there in a 0.155 m glucose solution prepared with 50.0 kg of water?
A)15.5 mol
B)15.0 mol
C)0.155 mol
D)31.0 mol
E)7.75 mol
A)15.5 mol
B)15.0 mol
C)0.155 mol
D)31.0 mol
E)7.75 mol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
What is the molality of a solution produced by dissolving 14.40 g of LiCl (42.39 g/mol) in water to make 0.104 L of solution with a density of 1.102 g/mL?
A)0.340 m
B)3.39 m
C)3.27 m
D)3.74 m
E)2.96 m
A)0.340 m
B)3.39 m
C)3.27 m
D)3.74 m
E)2.96 m

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
A medical company separates methanol (CH3OH)) and ethanol (CH3CH2OH) by distillation. In one run, the starting solution was 25% methanol and 75% ethanol by mass at 25 C. In the liquid, the mole ratio of methanol to ethanol was ________, and in the vapor it was ________. The vapor pressures for methanol and ethanol at this temperature are 92 torr and 45 torr, respectively.
A)0.48; 2.0
B)2.0; 0.48
C)0.33; 2.0
D)0.48; 0.33
E)2.3; 0.55
A)0.48; 2.0
B)2.0; 0.48
C)0.33; 2.0
D)0.48; 0.33
E)2.3; 0.55

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The molality of a solution is defined as ________
A)moles of solute per liter of solution.
B)grams of solute per liter of solution.
C)moles of solute per kilogram of solution.
D)moles of solute per kilogram of solvent.
E)grams of solute per kilogram of solvent.
A)moles of solute per liter of solution.
B)grams of solute per liter of solution.
C)moles of solute per kilogram of solution.
D)moles of solute per kilogram of solvent.
E)grams of solute per kilogram of solvent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The concentration unit of molality is symbolized as ________
A)M.
B)m.
C)M..
D)mol.
E)mo.
A)M.
B)m.
C)M..
D)mol.
E)mo.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Indicate which aqueous solution has the fastest evaporation rate.
A)0.10 M CaCO3
B)0.20 M NaNO3
C)0.15 M KBr
D)0.30 M Li2SO4
E)0.10 M MgCl2
A)0.10 M CaCO3
B)0.20 M NaNO3
C)0.15 M KBr
D)0.30 M Li2SO4
E)0.10 M MgCl2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
What physical property is used to separate the hydrocarbon components in petroleum (crude oil)?
A)melting point
B)density
C)boiling point
D)molar mass
E)viscosity
A)melting point
B)density
C)boiling point
D)molar mass
E)viscosity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Which graph best describes how the vapor pressure of a solution varies according to Raoult's law as a nonvolatile solute is added to a liquid? The vapor pressure of the solution is plotted on the y-axis, and the mole fraction of solvent is plotted on the x-axis. The origin (0, 0) is not necessarily located where the axes cross. 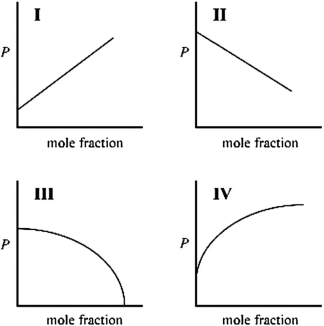
A)I
B)II
C)III
D)IV

A)I
B)II
C)III
D)IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The vapor pressure of an aqueous solution is found to be 24.9 mm Hg at 25 C. What is the mole fraction of solute in this solution? The vapor pressure of water is 25.756 mm Hg at 25 C.
A)0.967
B)0.0332
C)1.03
D)0.0344
E)0.976
A)0.967
B)0.0332
C)1.03
D)0.0344
E)0.976

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Which of the following is a colligative property?
I. osmotic pressure
II. molar mass
III. density
IV. freezing point depression
V. boiling point
A)I, II, IV, and V only
B)I and IV only
C)II and IV only
D)II, III, and V only
E)I, II, and V only
I. osmotic pressure
II. molar mass
III. density
IV. freezing point depression
V. boiling point
A)I, II, IV, and V only
B)I and IV only
C)II and IV only
D)II, III, and V only
E)I, II, and V only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
A colligative property does not depend on ________
A)the concentration of solute.
B)the type of solvent.
C)the volume of solution.
D)whether a solute is a strong or weak electrolyte.
E)the identity of the solute present.
A)the concentration of solute.
B)the type of solvent.
C)the volume of solution.
D)whether a solute is a strong or weak electrolyte.
E)the identity of the solute present.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Calculate the molality of a solution containing 0.755 mol glucose and 1.75 kg of water.
A)0.875 m
B)0.583 m
C)0.431 m
D)580 m
E)0.850 m
A)0.875 m
B)0.583 m
C)0.431 m
D)580 m
E)0.850 m

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Which statement regarding the fractional distillation of two substances is not correct?
A)The substance with the lower boiling point has a higher concentration in the vapor than in the liquid.
B)The boiling point of the mixture is not constant, changing as the distillation progresses.
C)The substance with the higher vapor pressure has a higher concentration in the vapor than in the liquid.
D)The mole ratio of the two substances in the vapor is not the same as it is in the liquid.
E)When the vapor at any stage of the distillation is condensed, the resulting distillate has the same composition as the original mixture of the two substances.
A)The substance with the lower boiling point has a higher concentration in the vapor than in the liquid.
B)The boiling point of the mixture is not constant, changing as the distillation progresses.
C)The substance with the higher vapor pressure has a higher concentration in the vapor than in the liquid.
D)The mole ratio of the two substances in the vapor is not the same as it is in the liquid.
E)When the vapor at any stage of the distillation is condensed, the resulting distillate has the same composition as the original mixture of the two substances.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
A solution is prepared by mixing 75 g of benzene (C6H6) with 25 g of toluene (C7H8). Use the following data to determine the vapor pressure of this solution at 20 C. 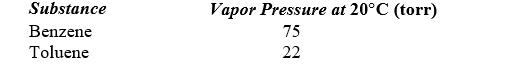
A)63 torr
B)49 torr
C)87 torr
D)35 torr
E)71 torr
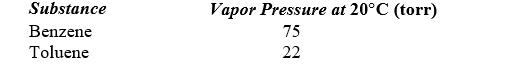
A)63 torr
B)49 torr
C)87 torr
D)35 torr
E)71 torr

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Isopropyl alcohol has a boiling point of 82.3 C. Solutions of isopropyl alcohol in water have normal boiling points less than 100 C. Is this observation consistent with the following equation? Explain. Tb = iKbm
A)No, boiling point elevation only pertains to ionic solutes.
B)No, boiling point elevation only pertains to nonvolatile solutes.
C)Yes, boiling point depression occurs for all solutions.
D)Yes, the boiling point depression constant for isopropyl alcohol is large.
E)No, isopropyl alcohol can hydrogen bond with water.
A)No, boiling point elevation only pertains to ionic solutes.
B)No, boiling point elevation only pertains to nonvolatile solutes.
C)Yes, boiling point depression occurs for all solutions.
D)Yes, the boiling point depression constant for isopropyl alcohol is large.
E)No, isopropyl alcohol can hydrogen bond with water.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Indicate which aqueous solution has the slowest evaporation rate.
A)0.1 M KCl
B)0.2 M Na2CO3
C)0.2 M NaCl
D)0.1 M MgCl2
E)0.1 M NaBr
A)0.1 M KCl
B)0.2 M Na2CO3
C)0.2 M NaCl
D)0.1 M MgCl2
E)0.1 M NaBr

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
A petroleum company separates benzene (78 g/mol) and n-octane (114 g/mol) by distillation. In one run, the starting solution was 15% benzene and 85% n-octane by mass at 25 C. In the liquid, the mole ratio of benzene to n-octane was ________, and in the vapor it was ________. The vapor pressures for benzene and n-octane at this temperature are 11 torr and 95 torr, respectively.
A)0.26; 0.12
B)0.18; 0.12
C)0.80; 0.20
D)0.26; 0.18
E)0.31; 0.23
A)0.26; 0.12
B)0.18; 0.12
C)0.80; 0.20
D)0.26; 0.18
E)0.31; 0.23

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Calculate the molality of a solution containing 0.355 mol sodium hydrogen carbonate (baking soda) and 245 g of water.
A)1.45 m
B)1.12 10-2 m
C)2.11 m
D)1.12 10-3 m
E)0.0211 m
A)1.45 m
B)1.12 10-2 m
C)2.11 m
D)1.12 10-3 m
E)0.0211 m

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
A solution is prepared by mixing 50 g of methanol (CH3OH) with 50 g of ethanol (CH3CH2OH). Use the following data to determine the vapor pressure of this solution at 20 C. 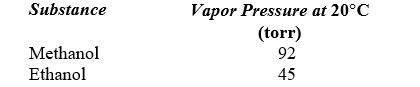
A)69 torr
B)57 torr
C)80 torr
D)73 torr
E)83 torr
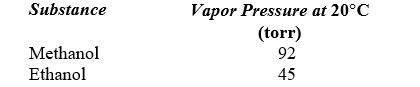
A)69 torr
B)57 torr
C)80 torr
D)73 torr
E)83 torr

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



