Deck 8: Chemical Bonds: What Makes a Gas a Greenhouse Gas
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/156
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 8: Chemical Bonds: What Makes a Gas a Greenhouse Gas
1
Which statement A-D about chemical bonds is not correct?
A)The attraction of the negatively charged electrons to the positively charged nuclei causes the electrostatic potential energy to decrease as two atoms come together.
B)The repulsion of the negatively charged electrons with each other and the positively charged nuclei with each other causes the electrostatic potential energy to increase when the two atoms are very close together.
C)As two atoms come together, the electrostatic potential energy goes through a minimum.The distance between the atoms at which this minimum occurs is called the bond length.
D)The bond energy is the energy released when two atoms infinitely far apart come together at a distance that minimizes the electrostatic potential energy.
E)Statements A-D are all correct.
A)The attraction of the negatively charged electrons to the positively charged nuclei causes the electrostatic potential energy to decrease as two atoms come together.
B)The repulsion of the negatively charged electrons with each other and the positively charged nuclei with each other causes the electrostatic potential energy to increase when the two atoms are very close together.
C)As two atoms come together, the electrostatic potential energy goes through a minimum.The distance between the atoms at which this minimum occurs is called the bond length.
D)The bond energy is the energy released when two atoms infinitely far apart come together at a distance that minimizes the electrostatic potential energy.
E)Statements A-D are all correct.
Statements A-D are all correct.
2
Which of the following is the correct Lewis symbol for S?
A)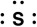
B)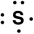
C)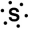
D)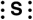
E)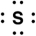
A)
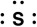
B)
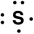
C)
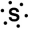
D)
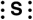
E)
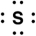
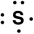
3
An Si-Si linkage would be classified as what type of bonding interaction?
A)polar covalent
B)metallic
C)ionic
D)nonpolar covalent
E)homogeneous
A)polar covalent
B)metallic
C)ionic
D)nonpolar covalent
E)homogeneous
nonpolar covalent
4
Which of the following elements contains the fewest number of valence electrons?
A)N
B)Se
C)Si
D)Al
E)Br
A)N
B)Se
C)Si
D)Al
E)Br

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A covalent bond results when ________
A)electrons are transferred from one atom to another atom.
B)atoms pool their electrons to form a "sea" of electrons.
C)atoms have outer electrons with the same principal quantum number.
D)electrons are shared between a pair of atoms.
E)an atom has 8 valence electrons.
A)electrons are transferred from one atom to another atom.
B)atoms pool their electrons to form a "sea" of electrons.
C)atoms have outer electrons with the same principal quantum number.
D)electrons are shared between a pair of atoms.
E)an atom has 8 valence electrons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which statement A-D about chemical bonds is not correct?
A)Atoms combine to form molecules because the energy of the molecule is lower than the energy of the free atoms.
B)The electrostatic potential energy explains why atoms bond together.
C)The electrostatic potential energy is directly proportional to the charges on two particles.
D)The electrostatic potential energy is inversely proportional to the distance between two charged particles.
E)Statements A-D are all correct.
A)Atoms combine to form molecules because the energy of the molecule is lower than the energy of the free atoms.
B)The electrostatic potential energy explains why atoms bond together.
C)The electrostatic potential energy is directly proportional to the charges on two particles.
D)The electrostatic potential energy is inversely proportional to the distance between two charged particles.
E)Statements A-D are all correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which type of bonding involves the sharing of valence electrons by two atoms?
A)covalent
B)ionic
C)polar ionic
D)intramolecular
E)metallic
A)covalent
B)ionic
C)polar ionic
D)intramolecular
E)metallic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which statement provides the best description of an ionic bond?
A)A high electron density between two positively charged atomic nuclei serves to attract the nuclei to each other.
B)The negative charge on one atom is attracted to the positive charge on a second atom.
C)Two or more electrons are attracted to each other, thereby holding the atoms together.
D)Two atomic nuclei are attracted to each other by the strong nuclear force.
E)Two atomic nuclei are attracted to each other by the Coulomb force.
A)A high electron density between two positively charged atomic nuclei serves to attract the nuclei to each other.
B)The negative charge on one atom is attracted to the positive charge on a second atom.
C)Two or more electrons are attracted to each other, thereby holding the atoms together.
D)Two atomic nuclei are attracted to each other by the strong nuclear force.
E)Two atomic nuclei are attracted to each other by the Coulomb force.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The following Lewis symbol corresponds to which element? 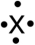
A)Be
B)B
C)C
D)N
E)O
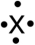
A)Be
B)B
C)C
D)N
E)O

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Indicate the ion that does not have 8 valence electrons.
A)O-
B)Na+
C)Al3+
D)P3-
E)Ar
A)O-
B)Na+
C)Al3+
D)P3-
E)Ar

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
What type of bonding is present in NaCl?
A)polar covalent
B)metallic
C)ionic
D)nonpolar covalent
E)amorphous
A)polar covalent
B)metallic
C)ionic
D)nonpolar covalent
E)amorphous

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
How many valence electrons does S2- have?
A)8
B)6
C)16
D)4
E)14
A)8
B)6
C)16
D)4
E)14

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
How many valence electrons does F have?
A)5
B)7
C)8
D)9
E)19
A)5
B)7
C)8
D)9
E)19

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which statement provides the best description of a covalent bond?
A)A high electron density between two positively charged atomic nuclei serves to attract the nuclei to each other.
B)The negative charge on one atom is attracted to the positive charge on a second atom.
C)Two or more electrons are attracted to each other, thereby holding the atoms together.
D)Two atomic nuclei are attracted to each other by the strong nuclear force.
E)Two atomic nuclei are attracted to each other by the Coulomb force.
A)A high electron density between two positively charged atomic nuclei serves to attract the nuclei to each other.
B)The negative charge on one atom is attracted to the positive charge on a second atom.
C)Two or more electrons are attracted to each other, thereby holding the atoms together.
D)Two atomic nuclei are attracted to each other by the strong nuclear force.
E)Two atomic nuclei are attracted to each other by the Coulomb force.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following is most likely a polar covalent bond?
A)Na - Cl
B)H - H
C)C - N
D)K - F
E)Ca - O
A)Na - Cl
B)H - H
C)C - N
D)K - F
E)Ca - O

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Based on electronegativities, which one of the following would have ionic bonds?
A)O2
B)MgO
C)H2O
D)CF4
E)SiO2
A)O2
B)MgO
C)H2O
D)CF4
E)SiO2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following is an example of a nonpolar covalent bond?
A)C - S
B)C - N
C)C - F
D)C - C
E)C - O
A)C - S
B)C - N
C)C - F
D)C - C
E)C - O

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following elements has 6 valence electrons?
A)C
B)S
C)N
D)Br
E)Be
A)C
B)S
C)N
D)Br
E)Be

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following elements contains the largest number of valence electrons?
A)P
B)Sr
C)C
D)B
E)F
A)P
B)Sr
C)C
D)B
E)F

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
How many valence electrons does aluminum have?
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)11
E)13
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)11
E)13

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which diatomic molecule has the least number of valence electrons?
A)O2
B)N2
C)NO
D)Cl2
E)F2
A)O2
B)N2
C)NO
D)Cl2
E)F2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
How many valence electrons are there in a correctly drawn Lewis structure for formamide, HCONH2?
A)12
B)14
C)16
D)18
E)20
A)12
B)14
C)16
D)18
E)20

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following has 13 valence electrons?
A)SH-
B)IO
C)NO
D)ICl
E)Cl2
A)SH-
B)IO
C)NO
D)ICl
E)Cl2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following molecular ions has 3 valence electrons?
A)H2+
B)He2+
C)C2+
D)B2+
E)O2-
A)H2+
B)He2+
C)C2+
D)B2+
E)O2-

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Describe the position of electrons around one N atom in the Lewis structure of N2.
A)3 shared electron pairs, 1 lone pair
B)2 shared electron pairs, 2 lone pairs
C)1 shared electron pair, 3 lone pairs
D)3 shared electron pairs
E)2 shared electron pairs, 1 lone pair
A)3 shared electron pairs, 1 lone pair
B)2 shared electron pairs, 2 lone pairs
C)1 shared electron pair, 3 lone pairs
D)3 shared electron pairs
E)2 shared electron pairs, 1 lone pair

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Triple bonds________
A)involve sharing of 3 total electrons between atoms.
B)involve sharing of 6 total electrons between atoms.
C)always occur between 2 metal atoms.
D)occur only between atoms with 3 valence electrons.
E)typically occur between hydrogen and another atom.
A)involve sharing of 3 total electrons between atoms.
B)involve sharing of 6 total electrons between atoms.
C)always occur between 2 metal atoms.
D)occur only between atoms with 3 valence electrons.
E)typically occur between hydrogen and another atom.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the following molecules does not contain a triple bond?
A)N2
B)HCN
C)C2H2
D)SO2
E)CO
A)N2
B)HCN
C)C2H2
D)SO2
E)CO

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
How many valence electrons are there in PO43-?
A)10
B)14
C)23
D)29
E)32
A)10
B)14
C)23
D)29
E)32

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
How many total shared electrons are there in the Lewis structure of CS2?
A)2
B)6
C)4
D)8
E)10
A)2
B)6
C)4
D)8
E)10

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following has the most valence electrons?
A)HF
B)NS
C)CN-
D)ArF
E)Ar+
A)HF
B)NS
C)CN-
D)ArF
E)Ar+

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
How many covalent bonds are there in CN-?
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)0
E)4
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)0
E)4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
How many lone pairs are there in ClO-?
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4
E)6
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4
E)6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
How many valence electrons are there in BrO-?
A)7
B)6
C)13
D)14
E)18
A)7
B)6
C)13
D)14
E)18

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which of the following species contains a double bond?
A)NO-
B)F2
C)CH
D)OH-
E)Br2
A)NO-
B)F2
C)CH
D)OH-
E)Br2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of the following ions does not have a complete valence-shell octet?
A)Al3+
B)I-
C)Ca2+
D)Pb2+
E)S2-
A)Al3+
B)I-
C)Ca2+
D)Pb2+
E)S2-

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Indicate which of the following molecules has four shared electrons.
A)O2
B)CO
C)HI
D)N2
E)Cl2
A)O2
B)CO
C)HI
D)N2
E)Cl2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The following Lewis symbol corresponds to which ion? 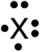
A)F-
B)O-
C)C2-
D)B3+
E)N2-
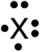
A)F-
B)O-
C)C2-
D)B3+
E)N2-

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
How many shared electron pairs are there in the Lewis structure of CN-?
A)3
B)6
C)4
D)2
E)10
A)3
B)6
C)4
D)2
E)10

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
How many valence electrons are there in SF4?
A)13
B)28
C)21
D)34
E)40
A)13
B)28
C)21
D)34
E)40

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Indicate which of the following molecules has only a single bond.
A)O2
B)CO
C)CN-
D)N2
E)Cl2
A)O2
B)CO
C)CN-
D)N2
E)Cl2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which of the following properties is typically used to identify whether a bond is polar, nonpolar, or ionic?
A)electronegativity
B)ionization energy
C)atomic radius
D)electron affinity
E)atomic mass
A)electronegativity
B)ionization energy
C)atomic radius
D)electron affinity
E)atomic mass

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which statements correctly describe a polar covalent bond?
I. Electrons are shared but not equally by the two atoms.
II. One atom has a small negative charge, and the other atom has a small positive charge.
III. The bond dipole is zero.
IV. One or more electrons are transferred from one atom to a second atom.
A)I and II only
B)II and III only
C)III and IV only
D)I and III only
E)I and IV only
I. Electrons are shared but not equally by the two atoms.
II. One atom has a small negative charge, and the other atom has a small positive charge.
III. The bond dipole is zero.
IV. One or more electrons are transferred from one atom to a second atom.
A)I and II only
B)II and III only
C)III and IV only
D)I and III only
E)I and IV only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Carbon dioxide is a greenhouse gas. Which of the following is the correct Lewis structure for carbon dioxide?
A)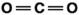
B)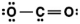
C)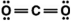
D)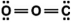
A)
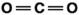
B)
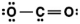
C)
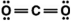
D)
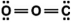

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
How many lone-pair electrons are on the central oxygen atom in the Lewis structure for dinitrogen pentoxide (N2O5)? A skeleton of the molecule is provided below. 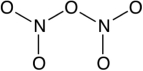
A)0
B)2
C)4
D)1
E)3

A)0
B)2
C)4
D)1
E)3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The measure of an atom's ability to attract electrons in a chemical bond is called ________
A)hybridization.
B)ionization energy.
C)electron affinity.
D)electronegativity.
E)ionic radius.
A)hybridization.
B)ionization energy.
C)electron affinity.
D)electronegativity.
E)ionic radius.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Acetonitrile (CH3CN) is an important industrial chemical. Among other things, it is used to make plastic moldings, which have multiple uses, from car parts to Lego bricks. Which one of the following statements about acetonitrile is not correct?
A)Acetonitrile has 16 valence electrons.
B)Acetonitrile has one triple bond.
C)Acetonitrile has one pair of nonbonding electrons.
D)All atoms satisfy the octet rule in acetonitrile.
E)One carbon atom and the nitrogen atom have nonzero formal charges.
A)Acetonitrile has 16 valence electrons.
B)Acetonitrile has one triple bond.
C)Acetonitrile has one pair of nonbonding electrons.
D)All atoms satisfy the octet rule in acetonitrile.
E)One carbon atom and the nitrogen atom have nonzero formal charges.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Identify the molecule or ion that contains a polar covalent bond.
A)O2
B)N2
C)CN-
D)H2
E)I2
A)O2
B)N2
C)CN-
D)H2
E)I2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Identify the molecule below that contains a double bond.
A)HCN
B)O3
C)C2H2
D)S2
E)N2
A)HCN
B)O3
C)C2H2
D)S2
E)N2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Which of the following are listed in order of decreasing electronegativity?
A)F S
S  Na
Na  H
H
B)F N
N  P
P  O
O
C)N P
P  Si
Si  S
S
D)F Cl
Cl  Br
Br  C
C
E)Te Se
Se  S
S  O
O
A)F
 S
S  Na
Na  H
HB)F
 N
N  P
P  O
OC)N
 P
P  Si
Si  S
SD)F
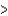 Cl
Cl 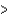 Br
Br 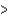 C
CE)Te
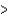 Se
Se  S
S  O
O
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Indicate the element with the smallest electronegativity.
A)Cl
B)F
C)Be
D)K
E)C
A)Cl
B)F
C)Be
D)K
E)C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Indicate the element with the largest electronegativity.
A)K
B)Cs
C)Mg
D)B
E)Li
A)K
B)Cs
C)Mg
D)B
E)Li

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which statement A-D regarding electronegativity is not correct?
A)Electronegativity is a measure of an atom's ability to attract electrons in a molecule.
B)If the electronegativity difference is sufficiently large, then an ionic bond is formed.
C)All bonds are polar except those between the same atoms (e.g., CO vs.O2).
D)Pauling assigned electronegativity values to atoms based on their ionization energies and electron affinities.
E)Statements A-D are all correct.
A)Electronegativity is a measure of an atom's ability to attract electrons in a molecule.
B)If the electronegativity difference is sufficiently large, then an ionic bond is formed.
C)All bonds are polar except those between the same atoms (e.g., CO vs.O2).
D)Pauling assigned electronegativity values to atoms based on their ionization energies and electron affinities.
E)Statements A-D are all correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Electronegativity increases from left to right across a period because of ________
A)increased shielding of valence electrons by the core electrons.
B)an increase in the number of protons in the nucleus.
C)a decrease in the effective nuclear charge (Zeff).
D)an increase in the shielding of core electrons by the valence electrons.
E)a decrease in the ionization potential.
A)increased shielding of valence electrons by the core electrons.
B)an increase in the number of protons in the nucleus.
C)a decrease in the effective nuclear charge (Zeff).
D)an increase in the shielding of core electrons by the valence electrons.
E)a decrease in the ionization potential.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Indicate which one of the following does not contain a polar covalent bond.
A)I2
B)CO
C)HF
D)NO
E)CN-
A)I2
B)CO
C)HF
D)NO
E)CN-

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
In going down a column in the periodic table, the electronegativity ________
A)decreases because the valence electrons are further from the nucleus.
B)increases because the nuclear charge increases.
C)decreases because the atomic number increases.
D)increases because the ionization potential increases.
E)increases because the electron repulsion increases.
A)decreases because the valence electrons are further from the nucleus.
B)increases because the nuclear charge increases.
C)decreases because the atomic number increases.
D)increases because the ionization potential increases.
E)increases because the electron repulsion increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which group of elements is listed in order of increasing electronegativity?
A)F Cl
Cl  Ge
Ge  Sn
Sn
B)Rb Ca
Ca  Sc
Sc  Cs
Cs
C)Zr V
V  Nb
Nb  Ta
Ta
D)Sn P
P 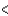 Cl
Cl  F
F
E)Cl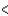 Br
Br 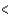 I
I 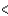 F
F
A)F
 Cl
Cl  Ge
Ge  Sn
SnB)Rb
 Ca
Ca  Sc
Sc  Cs
CsC)Zr
 V
V  Nb
Nb  Ta
TaD)Sn
 P
P  Cl
Cl  F
FE)Cl
 Br
Br  I
I  F
F
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Trends in electronegativity are primarily a result of ________
A)the number of core electrons in an element.
B)an element's atomic number.
C)the effective nuclear charge (Zeff) that an outer electron experiences.
D)the number of valence electrons of an element.
E)the atomic mass.
A)the number of core electrons in an element.
B)an element's atomic number.
C)the effective nuclear charge (Zeff) that an outer electron experiences.
D)the number of valence electrons of an element.
E)the atomic mass.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
What types of bonds form between the chlorine and oxygen atoms of the chlorite ion (ClO2-) to minimize the formal charge?
A)single
B)between single and double
C)double
D)triple
E)ionic
A)single
B)between single and double
C)double
D)triple
E)ionic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Indicate which molecule contains the largest number of nonbonding electrons.
A)H2
B)CO
C)N2
D)NO
E)O2
A)H2
B)CO
C)N2
D)NO
E)O2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
How many lone-pair electrons are on each of the nitrogen atoms in the Lewis structure for dinitrogen tetroxide (N2O4)?
A)0
B)2
C)4
D)1
E)3
A)0
B)2
C)4
D)1
E)3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
In addition to CO2, which of the gases in the atmosphere listed below can contribute to the greenhouse effect?
A)CH4
B)N2
C)O2
D)Ar
E)None of these gases can contribute to the greenhouse effect.
A)CH4
B)N2
C)O2
D)Ar
E)None of these gases can contribute to the greenhouse effect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Which of these statements about greenhouse gases and the greenhouse effect is not correct?
I. Greenhouse gases prevent infrared radiation from escaping through the atmosphere.
II. To absorb infrared radiation, a molecule must have a vibration that produces a change in
The dipole moment of the molecule.
III. Argon is the third most abundant species in the atmosphere (after nitrogen and oxygen),
And therefore is a significant greenhouse gas.
IV. The average amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere increases when fossil fuels are
Burned, but not when ethanol (CH3CH2OH) produced from plants is burned.
A)I only
B)II only
C)III only
D)IV only
E)III and IV only
I. Greenhouse gases prevent infrared radiation from escaping through the atmosphere.
II. To absorb infrared radiation, a molecule must have a vibration that produces a change in
The dipole moment of the molecule.
III. Argon is the third most abundant species in the atmosphere (after nitrogen and oxygen),
And therefore is a significant greenhouse gas.
IV. The average amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere increases when fossil fuels are
Burned, but not when ethanol (CH3CH2OH) produced from plants is burned.
A)I only
B)II only
C)III only
D)IV only
E)III and IV only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
In which bond does the Cl atom have the highest electron density?
A)H-Cl
B)O-Cl
C)S-Cl
D)N-Cl
E)Br-Cl
A)H-Cl
B)O-Cl
C)S-Cl
D)N-Cl
E)Br-Cl

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
In general, resonance ________ electrons and ________ molecules.
A)delocalizes; stabilizes
B)destabilizes; destabilizes
C)localizes; stabilizes
D)delocalizes; destabilizes
E)localizes; destabilizes
A)delocalizes; stabilizes
B)destabilizes; destabilizes
C)localizes; stabilizes
D)delocalizes; destabilizes
E)localizes; destabilizes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Resonance structures indicate that ________
A)there is more than one allotropic form of a compound.
B)more than one ionic form of a compound exists.
C)the electronic structure is an average or superposition of the diagrams.
D)more than one isotopic form of an element exists in the molecule.
E)the molecule jumps back and forth between two or more different electronic structures.
A)there is more than one allotropic form of a compound.
B)more than one ionic form of a compound exists.
C)the electronic structure is an average or superposition of the diagrams.
D)more than one isotopic form of an element exists in the molecule.
E)the molecule jumps back and forth between two or more different electronic structures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
How many total bonding pairs of electrons exist in a single resonance structure for NO3-?
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4
E)8
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4
E)8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Which of the following gases in the atmosphere does not contribute to the greenhouse effect?
A)CO2
B)CO
C)H2O
D)CH4
E)Ar
A)CO2
B)CO
C)H2O
D)CH4
E)Ar

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Which of the following bonds is most polar?
A)B-H
B)N-H
C)P-H
D)Al-H
E)C-H
A)B-H
B)N-H
C)P-H
D)Al-H
E)C-H

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
To absorb infrared radiation, a molecule must have ________
A)a vibrational motion that causes a change in dipole moment.
B)a double or triple bond.
C)no center of symmetry, so one side is different from the other.
D)atoms other than carbon and hydrogen.
E)at least one carbon and one hydrogen atom.
A)a vibrational motion that causes a change in dipole moment.
B)a double or triple bond.
C)no center of symmetry, so one side is different from the other.
D)atoms other than carbon and hydrogen.
E)at least one carbon and one hydrogen atom.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Which of the following molecules cannot absorb infrared radiation?
A)HCl
B)CH4
C)N2
D)C6H6
E)CO
A)HCl
B)CH4
C)N2
D)C6H6
E)CO

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Not all the vibrations of carbon dioxide can absorb infrared radiation because ________
A)the molecule is not polar.
B)the molecule possesses a permanent dipole moment.
C)only some of the vibrations produce a transient dipole moment.
D)there are no hydrogen atoms in carbon dioxide.
E)the molecule is linear.
A)the molecule is not polar.
B)the molecule possesses a permanent dipole moment.
C)only some of the vibrations produce a transient dipole moment.
D)there are no hydrogen atoms in carbon dioxide.
E)the molecule is linear.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
When sulfur-containing fuels are burned, sulfur trioxide (SO3) is formed in the atmosphere and contributes to acid rain (sulfur trioxide plus water produces sulfuric acid). How many resonance structures are there for SO3 when each atom satisfies the octet rule?
A)0
B)1
C)2
D)3
E)4
A)0
B)1
C)2
D)3
E)4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
How many total equivalent Lewis structures are needed to describe the carbonate anion, CO32-?
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4
E)5
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4
E)5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Sodium nitrite (NaNO2) is often used in meat curing because it prevents bacterial growth. How many major resonance contributing Lewis structures can be drawn for the nitrite anion (NO2-) ?
A)0
B)1
C)2
D)3
E)4
A)0
B)1
C)2
D)3
E)4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Which sequence does not have the elements arranged correctly in order of increasing electronegativity?
A)I Br
Br  Cl
Cl
B)B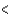 N
N 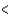 O
O
C)H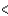 C
C 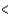 N
N
D)H Li
Li  S
S
E)Al S
S  Cl
Cl
A)I
 Br
Br  Cl
ClB)B
 N
N  O
OC)H
 C
C  N
ND)H
 Li
Li  S
SE)Al
 S
S  Cl
Cl
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Which of these statements correctly describes why methane and carbon dioxide are considered to be significant greenhouse gases?
I. Both have permanent dipole moments that change with vibration of the molecule.
II. Neither has a permanent dipole moment, but a dipole moment is produced when the
Molecule vibrates.
III. The concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere increases when fossil fuels are
Mined and burned.
A)I only
B)II only
C)III only
D)I and III only
E)II and III only
I. Both have permanent dipole moments that change with vibration of the molecule.
II. Neither has a permanent dipole moment, but a dipole moment is produced when the
Molecule vibrates.
III. The concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere increases when fossil fuels are
Mined and burned.
A)I only
B)II only
C)III only
D)I and III only
E)II and III only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Which of these statements correctly describes the electronic charge distribution in a molecule?
I. The charge density around each atom is the same as it is in the free atom.
II. The electronic charge is distributed equally around each atom in the molecule.
III. Electrons are attracted preferentially to atoms with high electronegativity.
IV. Electronic charge density is enhanced in the space between atoms to form a bond.
V. Electrons are always shared between atoms and never transferred from one atom to another.
A)I only
B)II and III only
C)III and IV only
D)II only
E)V only
I. The charge density around each atom is the same as it is in the free atom.
II. The electronic charge is distributed equally around each atom in the molecule.
III. Electrons are attracted preferentially to atoms with high electronegativity.
IV. Electronic charge density is enhanced in the space between atoms to form a bond.
V. Electrons are always shared between atoms and never transferred from one atom to another.
A)I only
B)II and III only
C)III and IV only
D)II only
E)V only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
In which bond does the H atom have the highest electron density?
A)H-Cl
B)H-Li
C)H-N
D)H-O
E)H-C
A)H-Cl
B)H-Li
C)H-N
D)H-O
E)H-C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Which of the following bonds is least polar?
A)H-O
B)H-N
C)H-B
D)H-C
E)H-F
A)H-O
B)H-N
C)H-B
D)H-C
E)H-F

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Which of the following bonds is primarily ionic? 
A)Li-C
B)Li-H
C)Li-O
D)Li-Li
E)C-O

A)Li-C
B)Li-H
C)Li-O
D)Li-Li
E)C-O

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



