Deck 6: Properties of Gases: The Air We Breathe
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/164
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 6: Properties of Gases: The Air We Breathe
1
The atmospheric pressure in the eye of a hurricane is found to be 26.6 in of mercury. The pressure in the eye of this hurricane is ________
A)760 mm Hg.
B)1.00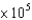 Pa.
Pa.
C)0.889 atm.
D)0.987 bar.
E)0.785 atm.
A)760 mm Hg.
B)1.00
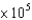 Pa.
Pa.C)0.889 atm.
D)0.987 bar.
E)0.785 atm.
0.889 atm.
2
A gas, initially at 2.50 atm and 3.00 L, expands to a volume of 10.00 L. What is the new pressure of the gas?
A)0.75 atm
B)1.33 atm
C)2.10 atm
D)8.33 atm
E)12.0 atm
A)0.75 atm
B)1.33 atm
C)2.10 atm
D)8.33 atm
E)12.0 atm
0.75 atm
3
A barometer measures a pressure of 745 mm Hg. What is this pressure in atm?
A)0.980 atm
B)1.02 atm
C)1.03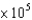 atm
atm
D)1.00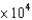 atm
atm
E)0.556 atm
A)0.980 atm
B)1.02 atm
C)1.03
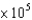 atm
atmD)1.00
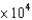 atm
atmE)0.556 atm
0.980 atm
4
A can of Diet Coke in a refrigerator has a pressure of 52 mmHg. What is the pressure in millibar? Recall 1.013 bar = 1 atm.
A)6.9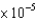 mbar
mbar
B)4.0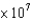 mbar
mbar
C)57 mbar
D)40 mbar
E)69 mbar
A)6.9
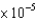 mbar
mbarB)4.0
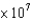 mbar
mbarC)57 mbar
D)40 mbar
E)69 mbar

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The SI unit of force is the Newton (N), and the unit of pressure is the Pascal (Pa). In SI base units, 1 N = 1 kg m s-2, and 1 Pa ________
A)1 kg m-1 s-2.
B)1 kg m2s-2.
C)1 kg m-1 s-1.
D)1 kg m-2 s-2.
E)1 kg s-2.
A)1 kg m-1 s-2.
B)1 kg m2s-2.
C)1 kg m-1 s-1.
D)1 kg m-2 s-2.
E)1 kg s-2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
What height of water (in meters) is necessary to measure a pressure of 760 mm Hg? The density of mercury is 13.79 g/cm3, and the density of water is 1.00 g/cm3.
A)0.760 m
B)1.05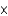 104 m
104 m
C)0.105 m
D)10.5 m
E)55.1 mm
A)0.760 m
B)1.05
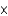 104 m
104 mC)0.105 m
D)10.5 m
E)55.1 mm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which statement about the properties of a gas is not correct?
A)Unlike a solid or a liquid, gases expand to occupy the entire volume of their container.
B)When the temperature is changed, the volume of gas changes much more than the volume of a solid or liquid.
C)Different gases are completely miscible with each other.
D)The density of a gas typically is much larger than the density of a solid or liquid.
E)When the pressure is changed, the volume of a gas changes much more than the volume of a solid or liquid.
A)Unlike a solid or a liquid, gases expand to occupy the entire volume of their container.
B)When the temperature is changed, the volume of gas changes much more than the volume of a solid or liquid.
C)Different gases are completely miscible with each other.
D)The density of a gas typically is much larger than the density of a solid or liquid.
E)When the pressure is changed, the volume of a gas changes much more than the volume of a solid or liquid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Gases can typically be mixed in any proportion, unless they chemically react. This property is called ________
A)density.
B)miscibility.
C)diffusion.
D)immiscibility.
E)effusion.
A)density.
B)miscibility.
C)diffusion.
D)immiscibility.
E)effusion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
If the pressure of a gas triples, by what factor does the volume change, assuming constant temperature?
A)1/3
B)3
C)1
D)9
E)1/9
A)1/3
B)3
C)1
D)9
E)1/9

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
What is the pressure in the gas bulb connected to the mercury manometer shown in the diagram if the ambient pressure is 750 torr? The heights labeled in the diagram are 15 mm and 21 mm. 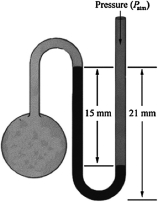
A)756 torr
B)771 torr
C)729 torr
D)765 torr
E)735 torr

A)756 torr
B)771 torr
C)729 torr
D)765 torr
E)735 torr

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The composition of Earth's atmosphere by volume is ________ nitrogen, ________ oxygen, 0.93% argon, 0.039% carbon dioxide, around 1% water vapor, and small amounts of other gases.
A)78%; 21%
B)68%; 31%
C)88%; 11%
D)49%; 49%
E)22%; 77%
A)78%; 21%
B)68%; 31%
C)88%; 11%
D)49%; 49%
E)22%; 77%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
What pressure will be measured (in Pa) if a gas is exerting a force of 10.00 N on a mercury barometer with an inner diameter of 10.00 mm?
Recall that the area of a circle is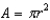 and that 1 N = 1 kg m/s2.
and that 1 N = 1 kg m/s2.
A)3.183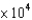 Pa
Pa
B)1.273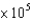 Pa
Pa
C)3.183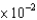 Pa
Pa
D)1.273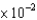 Pa
Pa
Recall that the area of a circle is
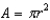 and that 1 N = 1 kg m/s2.
and that 1 N = 1 kg m/s2.A)3.183
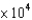 Pa
PaB)1.273
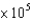 Pa
PaC)3.183
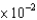 Pa
PaD)1.273
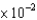 Pa
Pa
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following substances will require the highest column for measuring an atmospheric pressure of 0.950 atm? (Assume all the barometers have columns with the same diameter.)
A)Mercury (d = 13.59 g/cm3)
B)Ethanol (d = 0.79 g/cm3)
C)Ethylene glycol (d = 1.09 g/cm3)
D)Water (d = 1.00 g/cm3)
E)Carbon tetrachloride (d = 1.58 g/cm3)
A)Mercury (d = 13.59 g/cm3)
B)Ethanol (d = 0.79 g/cm3)
C)Ethylene glycol (d = 1.09 g/cm3)
D)Water (d = 1.00 g/cm3)
E)Carbon tetrachloride (d = 1.58 g/cm3)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A soft drink rises in a straw when you suck on the straw because ________
A)the vacuum pulls the liquid up the straw.
B)capillary forces attract the liquid to the walls of the straw.
C)the air pressure inside the straw is less than the air pressure outside the straw.
D)the air pressure inside the straw is greater than the air pressure outside the straw.
E)the liquid level inside the straw is pushed up by the liquid level outside the straw.
A)the vacuum pulls the liquid up the straw.
B)capillary forces attract the liquid to the walls of the straw.
C)the air pressure inside the straw is less than the air pressure outside the straw.
D)the air pressure inside the straw is greater than the air pressure outside the straw.
E)the liquid level inside the straw is pushed up by the liquid level outside the straw.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The cold inflation pressure of many car tires is 30 lb/in2, which is the gauge pressure. If 1 atm = 14.7 lb/in2, what is the gauge pressure of a car tire in torr?
A)2.04 torr
B)1.55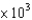 torr
torr
C)441 torr
D)0.580 torr
E)1.12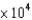 torr
torr
A)2.04 torr
B)1.55
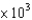 torr
torrC)441 torr
D)0.580 torr
E)1.12
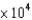 torr
torr
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The pressure of a gas is inversely proportional to ________
A)the volume of the gas.
B)the number of gas particles.
C)the temperature of the gas.
D)the molar mass of the gas.
E)the mass of the gas.
A)the volume of the gas.
B)the number of gas particles.
C)the temperature of the gas.
D)the molar mass of the gas.
E)the mass of the gas.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Two identical cement blocks are placed on a glass table in different positions, as shown in the diagram. Which statement about these blocks is correct? 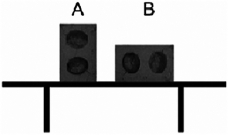
A)A exerts more pressure on the table.
B)B exerts more pressure on the table.
C)Both blocks exert the same pressure on the table.
D)A exerts more force on the table.
E)B exerts more force on the table.

A)A exerts more pressure on the table.
B)B exerts more pressure on the table.
C)Both blocks exert the same pressure on the table.
D)A exerts more force on the table.
E)B exerts more force on the table.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A 1.25 L bottle of soda exerts a force of ________ N and a pressure of ________ Pa when placed on a table. The round cylindrical bottle has a diameter of 10.0 cm and a height of 25.0 cm. Assume that the density of the soda is 1.0 g/mL, and that the mass of the plastic bottle is negligible. Remember, the acceleration due to gravity is 9.81 m/s2; 1 Newton = 1 kg m/s2, 1 Pascal = 1 kg/(m s2), 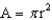 , and
, and 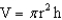 .
.
A)9.8 N; 1,200 Pa
B)12 N; 390 Pa
C)12 N; 16 Pa
D)12 N; 12 Pa
E)12 N; 1,600 Pa
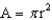 , and
, and 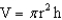 .
.A)9.8 N; 1,200 Pa
B)12 N; 390 Pa
C)12 N; 16 Pa
D)12 N; 12 Pa
E)12 N; 1,600 Pa

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
What pressure (in Pa) will be exerted on the bottom of a 63.5 kg hiker's foot when she stands on a rusty nail? Assume the diameter of the tip of the nail is 1.00 mm. The acceleration due to gravity is 9.81 m/s2. Recall that the area of a circle is: A = r2 and that 1 Pa = 1 kg m-1 s-2.
A)1.98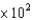 Pa
Pa
B)7.93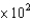 Pa
Pa
C)1.98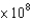 Pa
Pa
D)7.93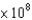 Pa
Pa
E)7.93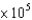 Pa
Pa
A)1.98
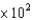 Pa
PaB)7.93
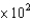 Pa
PaC)1.98
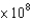 Pa
PaD)7.93
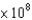 Pa
PaE)7.93
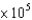 Pa
Pa
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A balloon is filled with 3.00 L of helium at a pressure of 765 torr. What is the volume of the balloon at an altitude where the pressure in the balloon is 530 torr?
A)0.231 L
B)4.33 L
C)2.08 L
D)1.00 L
E)3.00 L
A)0.231 L
B)4.33 L
C)2.08 L
D)1.00 L
E)3.00 L

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the gases shown here will exert the lowest pressure, assuming that each container has the same volume and temperature?
A)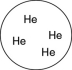
B)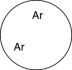
C)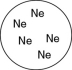
D)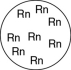
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The temperature of a gas is directly proportional to ________
A)the number of moles of the gas.
B)the identity of the gas.
C)the volume of the gas.
D)the density of the gas.
E)the mass of the gas.
A)the number of moles of the gas.
B)the identity of the gas.
C)the volume of the gas.
D)the density of the gas.
E)the mass of the gas.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following graphs shows the correct relationship between the temperature and volume of an ideal gas at a given pressure? Note the origin corresponds to V = 0 and T = 0.
A)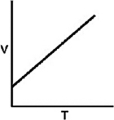
B)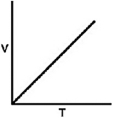
C)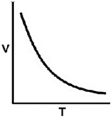
D)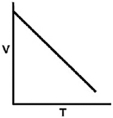
A)

B)
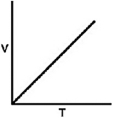
C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A sample of gas at 4.0 atm and 25.0 mL is heated from 25 C to 40 C. If the pressure remains constant, what is the final volume of the gas?
A)26.2 mL
B)40.0 mL
C)23.8 mL
D)105 mL
E)25.0 mL
A)26.2 mL
B)40.0 mL
C)23.8 mL
D)105 mL
E)25.0 mL

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Four containers, each with the same volume and at the same temperature, are shown in the following diagrams. Which container is at the highest pressure?
A)
B)
C)
D)
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
A 1.50 mol sample of He occupies a volume of 2.50 L at a pressure of 14.7 atm. What will be the pressure of a 1.50 mol sample of H2 gas under the same conditions?
A)7.33 atm
B)14.7 atm
C)29.4 atm
D)1.00 atm
E)24.5 atm
A)7.33 atm
B)14.7 atm
C)29.4 atm
D)1.00 atm
E)24.5 atm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which statement A-D regarding an ideal gas is not correct?
A)The volume occupied by an individual molecule is negligible.
B)No interactions occur between molecules other than hard sphere collisions.
C)Molecules move in random directions and collide with each other.
D)The volume occupied by 1 mol of molecules at STP is 22.4 L.
E)Statements A-D all are correct.
A)The volume occupied by an individual molecule is negligible.
B)No interactions occur between molecules other than hard sphere collisions.
C)Molecules move in random directions and collide with each other.
D)The volume occupied by 1 mol of molecules at STP is 22.4 L.
E)Statements A-D all are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The volume of a 15.0 g sample of N2 gas at a pressure of 2.7 atm is 6.24 L. What is the temperature of the sample?
A)14 C
B)190 C
C)3.8 C
D)110 C
E)76 C
A)14 C
B)190 C
C)3.8 C
D)110 C
E)76 C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
A sample of gas at 30 C changes volume from 20.0 mL to 25.0 mL. If the pressure remained constant, what is the final temperature of the gas?
A)31 C
B)-31 C
C)24 C
D)106 C
E)74 C
A)31 C
B)-31 C
C)24 C
D)106 C
E)74 C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following graphs shows the correct relationship between the pressure and volume of an ideal gas at a given temperature? Note the origin corresponds to P = 0 and V = 0.
A)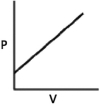
B)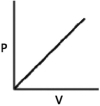
C)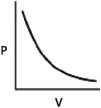
D)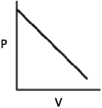
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following is unimportant when using the ideal gas law?
A)the chemical identity of the gas sample
B)the temperature of the gas sample
C)the pressure of the gas sample
D)the volume of the container holding the gas sample
E)the amount of gas
A)the chemical identity of the gas sample
B)the temperature of the gas sample
C)the pressure of the gas sample
D)the volume of the container holding the gas sample
E)the amount of gas

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The temperature of a 10.0 g sample of Ne gas at a pressure of 1.6 atm is 17 C. What is the volume of the sample?
A)7.37 L
B)9.38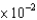 L
L
C)76.8 L
D)18.9 L
E)3.45 L
A)7.37 L
B)9.38
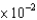 L
LC)76.8 L
D)18.9 L
E)3.45 L

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A balloon vendor at a street fair is using a tank of helium to inflate the balloons. The tank has a volume of 75 L and a pressure of 95 atm at 22°C. The valve is not closed completely and some helium leaks out. After some time, the pressure drops to 85 atm. How many moles of helium have been lost?
A)0.90 mol
B)1.2 mol
C)73 mol
D)263 mol
E)31 mol
A)0.90 mol
B)1.2 mol
C)73 mol
D)263 mol
E)31 mol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
If the pressure of a system is halved in a given volume, by what factor will the temperature change?
A)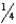
B)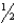
C)1
D)2
E)4
A)
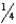
B)
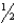
C)1
D)2
E)4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
A 25.0 L balloon is filled with 2.75 mol of helium. If the helium leaks out at the rate of 0.105 mol/hr, what is the volume of the balloon after 12.0 hr? Assume the pressure and temperature don't change.
A)11.5 L
B)13.5 L
C)23.7 L
D)1.26 L
E)17.4 L
A)11.5 L
B)13.5 L
C)23.7 L
D)1.26 L
E)17.4 L

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
A sample of Ar gas at 35 C occupies a volume of 1.50 L at a pressure of 3.2 atm. How many moles of the gas are present in the sample?
A)3.32 moles
B)0.599 moles
C)5.26 moles
D)1.67 moles
E)0.190 moles
A)3.32 moles
B)0.599 moles
C)5.26 moles
D)1.67 moles
E)0.190 moles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the following graphs shows the correct relationship between the pressure and temperature of an ideal gas in a given volume? Note the origin corresponds to P = 0 atm and T = 0 K.
A)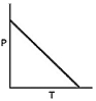
B)
C)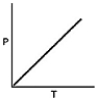
D)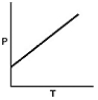
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
An unknown gas held in a 25.0 mL flask at 45°F exerts a pressure of 25 mtorr. Using this information with the ideal gas law, it is possible to determine ________
A)the mass of the gas in the container.
B)the identity of the gas in the container.
C)the number of molecules of the gas in the container.
D)the molecular geometry of the gas in the container.
E)nothing more about the gas.
A)the mass of the gas in the container.
B)the identity of the gas in the container.
C)the number of molecules of the gas in the container.
D)the molecular geometry of the gas in the container.
E)nothing more about the gas.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
A hot air balloon, under the conditions shown below, experiences an increase in pressure. What will the new volume of the balloon be? 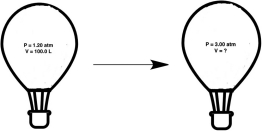
A)3.6 10-2 L
B)12 L
C)28 L
D)40 L
E)250 L

A)3.6 10-2 L
B)12 L
C)28 L
D)40 L
E)250 L

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
What is the volume of a gas that exerts a pressure of 457 mm Hg if it exerted a pressure of 2.50 atm when its volume was 25.0 mL?
A)9.62 mL
B)1.80 L
C)0.104 L
D)6.01 mL
E)25.0 L
A)9.62 mL
B)1.80 L
C)0.104 L
D)6.01 mL
E)25.0 L

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
In an experiment, 7.5 mol of a gas are held in a 3.5 L container at 39 C. What pressure does the gas exert if it is assumed to be ideal?
A)5.5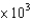 atm
atm
B)2.9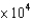 atm
atm
C)6.9 atm
D)55 atm
E)96 atm
A)5.5
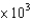 atm
atmB)2.9
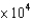 atm
atmC)6.9 atm
D)55 atm
E)96 atm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Considering that PV = nRT, which one of these samples contains the largest number of particles? STP= 0 C and 1 atm.
A)2.0 L of H2 at STP
B)2.0 L of N2 at STP
C)2.0 L of H2 at 25 C and 760 torr
D)2.0 L of N2 at 0 C and 900 torr
E)2.0 L of He at STP
A)2.0 L of H2 at STP
B)2.0 L of N2 at STP
C)2.0 L of H2 at 25 C and 760 torr
D)2.0 L of N2 at 0 C and 900 torr
E)2.0 L of He at STP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which of the following reactions will result in a reduced total pressure?
A)CH4(g)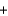 2O2(g)
2O2(g)  CO2(g)
CO2(g) 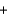 2H2O(g)
2H2O(g)
B)2N2O(g) 2N2(g)
2N2(g) 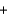 O2(g)
O2(g)
C)2HI(g) H2(g)
H2(g)  I2(g)
I2(g)
D)2H2(g) O2(g)
O2(g)  2H2O(l )
2H2O(l )
A)CH4(g)
 2O2(g)
2O2(g)  CO2(g)
CO2(g)  2H2O(g)
2H2O(g)B)2N2O(g)
 2N2(g)
2N2(g)  O2(g)
O2(g)C)2HI(g)
 H2(g)
H2(g) 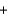 I2(g)
I2(g)D)2H2(g)
 O2(g)
O2(g)  2H2O(l )
2H2O(l )
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The pressure gauge on a 100-L cylinder used to fill balloons with helium shows a pressure of 1,470 psi at a temperature of 22oC. How many kilograms of helium does the cylinder contain?
A)6.04 kg
B)1.65 kg
C)0.779 kg
D)4.30 kg
E)0.464 kg
A)6.04 kg
B)1.65 kg
C)0.779 kg
D)4.30 kg
E)0.464 kg

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
How many moles of propane are contained in a 5.00 L tank at 450 torr and 25 C?
A)0.12 mol
B)92 mol
C)1.4 mol
D)1,100 mol
E)41 mol
A)0.12 mol
B)92 mol
C)1.4 mol
D)1,100 mol
E)41 mol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
What volume is occupied by 1.00 mol of an ideal gas at 1.00 atm and 0.00 C?
A)22.4 L
B)22.7 L
C)22.1 L
D)15.0 L
E)27.2 L
A)22.4 L
B)22.7 L
C)22.1 L
D)15.0 L
E)27.2 L

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Which one of these samples contains the smallest number of molecules?
A)1.0 L of H2 at STP (0 C and 1 atm)
B)1.0 L of N2 at STP
C)1.0 L of H2 at 20 C and 760 torr
D)1.0 L of N2 at 0 C and 800 torr
E)1.0 L of He at STP
A)1.0 L of H2 at STP (0 C and 1 atm)
B)1.0 L of N2 at STP
C)1.0 L of H2 at 20 C and 760 torr
D)1.0 L of N2 at 0 C and 800 torr
E)1.0 L of He at STP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Calcium carbonate (100.1 g/mol) decomposes according to the following reaction equation: CaCO3(s)  CaO(s)
CaO(s) 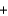 CO2(g)
CO2(g)
What pressure of CO2 gas will form in a 25.0 mL jar containing 5.00 g CaCO3 at 300 K if 0.00500% of the solid decomposes?
A)0.246 atm
B)2.46 atm
C)1.00 atm
D)2.46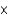 103 atm
103 atm
E)2.46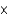 10-3 atm
10-3 atm
 CaO(s)
CaO(s) 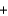 CO2(g)
CO2(g)What pressure of CO2 gas will form in a 25.0 mL jar containing 5.00 g CaCO3 at 300 K if 0.00500% of the solid decomposes?
A)0.246 atm
B)2.46 atm
C)1.00 atm
D)2.46
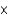 103 atm
103 atmE)2.46
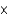 10-3 atm
10-3 atm
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Which of the following reactions will result in a negligible change in pressure?
A)Na(s)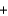 Cl2(g)
Cl2(g)  NaCl(s)
NaCl(s)
B)CO(g) H2O(l )
H2O(l )  CO2(g)
CO2(g)  H2(g)
H2(g)
C)CH4(g) H2O(l )
H2O(l )  CO(g)
CO(g)  3H2(g)
3H2(g)
D)BrNO2(g) NO(g)
NO(g)  NO2(g)
NO2(g) 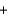 BrNO(g)
BrNO(g)
E)2Na(s)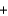 2H2O(g) 2NaOH(s)
2H2O(g) 2NaOH(s) 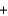 H2(g)
H2(g)
A)Na(s)
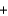 Cl2(g)
Cl2(g)  NaCl(s)
NaCl(s)B)CO(g)
 H2O(l )
H2O(l )  CO2(g)
CO2(g)  H2(g)
H2(g)C)CH4(g)
 H2O(l )
H2O(l )  CO(g)
CO(g)  3H2(g)
3H2(g)D)BrNO2(g)
 NO(g)
NO(g)  NO2(g)
NO2(g) 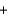 BrNO(g)
BrNO(g)E)2Na(s)
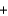 2H2O(g) 2NaOH(s)
2H2O(g) 2NaOH(s) 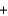 H2(g)
H2(g)
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The pressure gauge on a cylinder used to fill balloons with He shows a pressure of 1,275 psi at a temperature of 25 C. Assuming the cylinder has a volume of 10 L, how many grams of He does the cylinder contain?
A)520 g
B)142 g
C)6.70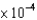 g
g
D)37.0 g
E)4.00 g
A)520 g
B)142 g
C)6.70
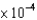 g
gD)37.0 g
E)4.00 g

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
What is the temperature if 3.0 g of propane (C3H8) in a 400.0 mL container exerts a pressure of 5.5 atm?
A)(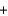 75.5 C)
75.5 C)
B) ( 75.5 C)
75.5 C)
C)121 C
D)175 C
E)264 C
A)(
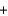 75.5 C)
75.5 C)B) (
 75.5 C)
75.5 C)C)121 C
D)175 C
E)264 C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which of the gas samples shown below in identical containers has the lowest density (g/L)?
A)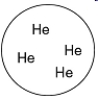
B)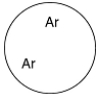
C)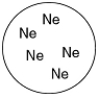
D)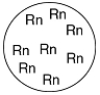
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Considering that PV = nRT, which one of these samples contains the smallest number of particles?
STP = 0 C and 1 atm.
A)2.0 L of H2 at STP
B)2.0 L of N2 at STP
C)2.0 L of H2 at 25 C and 760 torr
D)2.0 L of N2 at 0 C and 900 torr
E)2.0 L of He at STP
STP = 0 C and 1 atm.
A)2.0 L of H2 at STP
B)2.0 L of N2 at STP
C)2.0 L of H2 at 25 C and 760 torr
D)2.0 L of N2 at 0 C and 900 torr
E)2.0 L of He at STP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
What is the pressure of a 0.17 mol sample of carbon monoxide gas contained in a 750mL flask at 50 C?
A)0.930 atm
B)6.01 atm
C)1.08 atm
D)0.166 atm
E)6.01 atm
atm
A)0.930 atm
B)6.01 atm
C)1.08 atm
D)0.166 atm
E)6.01
 atm
atm
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Automobile air bags inflate during a crash or sudden stop by the rapid generation of nitrogen gas from sodium azide. 2NaN3(s)  2Na(s)
2Na(s) 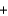 3N2(g)
3N2(g)
How many moles of sodium azide are needed to produce sufficient nitrogen to fill a 50.0 L air bag to a pressure of 1.25 atm at 25°C?
A)2.56 mol
B)3.83 mol
C)5.31 mol
D)1.70 mol
E)4.92 mol
 2Na(s)
2Na(s)  3N2(g)
3N2(g)How many moles of sodium azide are needed to produce sufficient nitrogen to fill a 50.0 L air bag to a pressure of 1.25 atm at 25°C?
A)2.56 mol
B)3.83 mol
C)5.31 mol
D)1.70 mol
E)4.92 mol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
In an experiment, 25.0 mL of a gas with a pressure of 1.00 atm is contained in a balloon at 25.0°C. The balloon is then cooled to 5.0 C, and the pressure is found to be 0.750 atm. What is the volume of the gas under the new conditions?
A)17.5 mL
B)20.1 mL
C)25.0 mL
D)31.1 mL
E)35.7 mL
A)17.5 mL
B)20.1 mL
C)25.0 mL
D)31.1 mL
E)35.7 mL

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
A 22.4-L sealed chamber at 273 K is filled with air at a pressure of 1.00 atm. A solid state chemical reaction in the chamber adds 1.25 mol hydrogen gas. The temperature of the chamber must be decreased to ________ to maintain the pressure at 1.00 atm.
A)121 K
B)218 K
C)12.2 K
D)182 K
E)211 K
A)121 K
B)218 K
C)12.2 K
D)182 K
E)211 K

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
In the presence of a catalyst, potassium chlorate decomposes and provides a very simple way to generate oxygen via the following decomposition reaction: 2KClO3(s)  3O2(g)
3O2(g)  2KCl(s)
2KCl(s)
How many grams of potassium chlorate are needed to produce 38.2 L of oxygen gas at a pressure of 2.00 atm at a temperature of 310 K?
A)10.7 g
B)245 g
C)157 g
D)423 g
E)61.7 g
 3O2(g)
3O2(g)  2KCl(s)
2KCl(s)How many grams of potassium chlorate are needed to produce 38.2 L of oxygen gas at a pressure of 2.00 atm at a temperature of 310 K?
A)10.7 g
B)245 g
C)157 g
D)423 g
E)61.7 g

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which of the gas samples shown below in identical containers has the highest density (g/L)?
A)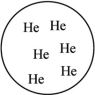
B)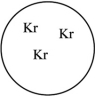
C)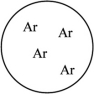
D)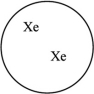
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Which of the following reactions will result in an increased total pressure?
A)ClNO2(g)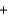 NO(g)
NO(g)  NO2(g)
NO2(g)  ClNO(g)
ClNO(g)
B)CO(g)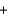 Cl2(g)
Cl2(g)  COCl2(g)
COCl2(g)
C)N2O4(g) 2NO2(g)
2NO2(g)
D)2H2(g)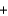 O2(g)
O2(g)  2H2O(l )
2H2O(l )
E)CO2(g)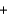 CF4(g)
CF4(g)  2COF2(g)
2COF2(g)
A)ClNO2(g)
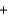 NO(g)
NO(g)  NO2(g)
NO2(g)  ClNO(g)
ClNO(g)B)CO(g)
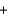 Cl2(g)
Cl2(g)  COCl2(g)
COCl2(g)C)N2O4(g)
 2NO2(g)
2NO2(g)D)2H2(g)
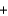 O2(g)
O2(g)  2H2O(l )
2H2O(l )E)CO2(g)
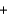 CF4(g)
CF4(g)  2COF2(g)
2COF2(g)
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Indicate the gas with the lowest density at STP.
A)CH4
B)F2
C)N2O
D)Cl2
E)N2
A)CH4
B)F2
C)N2O
D)Cl2
E)N2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Which of the following graphs shows how the density of an ideal gas changes with pressure?
A)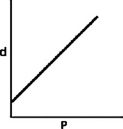
B)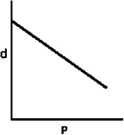
C)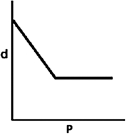
D)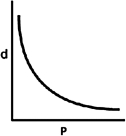
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
What is the temperature of CO2 gas (density = 2.62 g/L) at a pressure of 3.0 atm?
A)253 C
B)195 C
C)341 C
D)614 C
E)468 C
A)253 C
B)195 C
C)341 C
D)614 C
E)468 C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
When a certain acid and a certain base are mixed together, a reaction occurs that produces a gas as one of the products. The gas has a density of 2.62 g/L at 1.47 atm and 27 C. What are the molar mass and identity of the gas?
A)H2, 2 g/mol
B)CO, 28 g/mol
C)O2, 32 g/mol
D)CO2, 44 g/mol
E)SO2, 64 g/mol
A)H2, 2 g/mol
B)CO, 28 g/mol
C)O2, 32 g/mol
D)CO2, 44 g/mol
E)SO2, 64 g/mol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Nitrous oxide (N2O, also known as laughing gas) has been used as an anesthetic. What is the density of N2O at 750 torr and 30 C?
A)1.2 g/L
B)1.1 g/L
C)1.9 g/L
D)1.7 g/L
E)1.5 g/L
A)1.2 g/L
B)1.1 g/L
C)1.9 g/L
D)1.7 g/L
E)1.5 g/L

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
What is the molar mass of a gas that has a density of 2.62 g/L at 2.00 atm and 25.0 C?
A)32.0 g/mol
B)16.0 g/mol
C)64.0 g/mol
D)28.0 g/mol
E)2.69 g/mol
A)32.0 g/mol
B)16.0 g/mol
C)64.0 g/mol
D)28.0 g/mol
E)2.69 g/mol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
What is the density of propane gas (CH3CH2CH3, 44.1 g/mol) at 25 C and 650 mm Hg?
A)1.54 g/L
B)3.55 g/mL
C)18.3 g/L
D)2.05 g/L
E)1.17 g/L
A)1.54 g/L
B)3.55 g/mL
C)18.3 g/L
D)2.05 g/L
E)1.17 g/L

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
When a certain acid and a certain base are mixed together, a reaction occurs that produces a gas as one of the products. The gas has a density of 1.83 g/L at 1.00 atm and 20 C. What are the molar mass and identity of the gas?
A)H2, 2 g/mol
B)CO, 28 g/mol
C)O2, 32 g/mol
D)CO2, 44 g/mol
E)SO2, 64 g/mol
A)H2, 2 g/mol
B)CO, 28 g/mol
C)O2, 32 g/mol
D)CO2, 44 g/mol
E)SO2, 64 g/mol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Potassium superoxide reacts violently with water to produce potassium hydroxide and oxygen according to the following balanced equation. What would the temperature be if 5.0 g of KO2 reacts to produce a pressure of 1.0 atm and 2.0 L of O2 gas?
4KO2(s)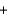 2H2O(l)
2H2O(l)  4KOH(s)
4KOH(s) 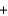 3O2(g)
3O2(g)
A)150 C
B)30 C
C) - 12 C
D)190 C
E)74 C
4KO2(s)
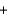 2H2O(l)
2H2O(l)  4KOH(s)
4KOH(s) 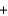 3O2(g)
3O2(g)A)150 C
B)30 C
C) - 12 C
D)190 C
E)74 C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The density of a pure gas at STP depends on its ________
A)molar mass.
B)concentration.
C)temperature.
D)volume.
E)pressure.
A)molar mass.
B)concentration.
C)temperature.
D)volume.
E)pressure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Indicate the gas with the greatest density at STP.
A)CH4
B)He
C)Ar
D)H2
E)O2
A)CH4
B)He
C)Ar
D)H2
E)O2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
What is the pressure of NO gas (density 1.34 g/L) at 25 C?
A)0.916 atm
B)1.09 atm
C)32.8 atm
D)9.16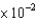 atm
atm
E)10.9 atm
A)0.916 atm
B)1.09 atm
C)32.8 atm
D)9.16
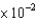 atm
atmE)10.9 atm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Which of the following samples of an ideal gas has the lowest density?
A)
B)
C)
D)
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Which one of the following gases could most easily be differentiated from propane (CH3CH2CH3) on the basis of density when compared at the same temperature and pressure?
A)CO2
B)N2O
C)NO2
D)F2
E)CH2 CH-CH3
CH-CH3
A)CO2
B)N2O
C)NO2
D)F2
E)CH2
 CH-CH3
CH-CH3
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Oxygen for astronauts in space can be produced chemically using a solid fuel oxygen generator. The reaction takes place at 600 C and is shown below. NaClO3(s) 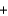 Fe(s)
Fe(s)  3O2(g)
3O2(g) 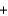 NaCl(s)
NaCl(s) 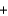 FeO(s)
FeO(s)
What volume of O2 gas will be produced when 855 g of NaClO3 reacts with excess iron at a pressure of 3 atm?
A)575 L
B)2.80 L
C)192 L
D)6.13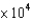 L
L
E)396 L
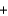 Fe(s)
Fe(s)  3O2(g)
3O2(g) 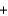 NaCl(s)
NaCl(s) 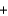 FeO(s)
FeO(s)What volume of O2 gas will be produced when 855 g of NaClO3 reacts with excess iron at a pressure of 3 atm?
A)575 L
B)2.80 L
C)192 L
D)6.13
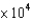 L
LE)396 L

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Poisonous carbon monoxide can be produced by furnaces in basements if the combustion and exhaust are not complete. Calculate the density of carbon monoxide in g/L at 292 K and 1.00 atm of pressure to determine whether it is more or less dense than air. If it is more dense, it will remain in the basement; if it is less dense it will rise to the upper levels of the house. The density of dry air is 1.20 g/L.
A)1.14 g/L
B)1.17 g/L
C)1.20 g/L
D)1.23 g/L
E)1.26 g/L
A)1.14 g/L
B)1.17 g/L
C)1.20 g/L
D)1.23 g/L
E)1.26 g/L

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Which of the following graphs shows how the density of an ideal gas changes with temperature?
A)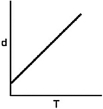
B)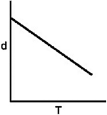
C)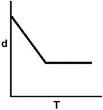
D)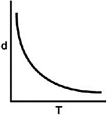
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Which of the following gases has nearly the same density as CO2 at room temperature and atmospheric pressure?
A)N2
B)O2
C)N2O
D)Ar
E)CO
A)N2
B)O2
C)N2O
D)Ar
E)CO

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
The density of a gaseous compound of nitrogen and oxygen is 4.11 g/L at STP. What is the most likely formula of this gas?
A)N2O4
B)N2O5
C)N2O
D)NO2
E)NO
A)N2O4
B)N2O5
C)N2O
D)NO2
E)NO

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
The density of an unknown gas is 1.72 g/L at 750.0 torr and 30.0 C. Which of the following could be the unknown gas?
A)CS2
B)NO
C)N2O
D)NH3
E)NO2
A)CS2
B)NO
C)N2O
D)NH3
E)NO2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



