Deck 21: Dry Regions: the Geology of Deserts
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/60
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 21: Dry Regions: the Geology of Deserts
1
The Sahara is a desert primarily because it is located ________.
A) in the subtropics
B) within the rain shadow of a mountain range
C) near the center of a large continent
D) next to a cold ocean current
A) in the subtropics
B) within the rain shadow of a mountain range
C) near the center of a large continent
D) next to a cold ocean current
A
2
The figure below illustrates the formation of a ________. 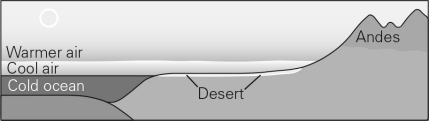
A) coastal desert
B) subtropical desert
C) rain-shadow desert
D) continental-interior desert

A) coastal desert
B) subtropical desert
C) rain-shadow desert
D) continental-interior desert
A
3
A desert may form along a coastline because a ________.
A) warm current warms and dries the air
B) warm current forces hot air inland
C) cold current cools and dries the air
D) cold current forces hot air inland
A) warm current warms and dries the air
B) warm current forces hot air inland
C) cold current cools and dries the air
D) cold current forces hot air inland
C
4
Fine-grained sediment,such as dust and silt,can stay in the air and be transported by wind in ________.
A) suspension
B) saltation
C) deflation
D) surface creep
A) suspension
B) saltation
C) deflation
D) surface creep

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
During heavy rainstorms,rates of physical weathering and erosion are ________.
A) greater in humid climates than in deserts because dry desert soils soak up all the available moisture
B) greater in deserts than in humid climates because soil tends to be more easily eroded in deserts than in humid regions
C) greater in humid climates than in deserts because vegetation tends to break up the soil
D) about equally fast in both deserts and humid climates
A) greater in humid climates than in deserts because dry desert soils soak up all the available moisture
B) greater in deserts than in humid climates because soil tends to be more easily eroded in deserts than in humid regions
C) greater in humid climates than in deserts because vegetation tends to break up the soil
D) about equally fast in both deserts and humid climates

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The definition of a desert depends on a region's ________.
A) latitude
B) elevation
C) aridity
D) temperature
A) latitude
B) elevation
C) aridity
D) temperature

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Desert climate associated with a rain shadow is found ________.
A) on the windward side of mountain ranges
B) on the leeward side of mountain ranges
C) in the middle of flat plains
D) along continental coastlines
A) on the windward side of mountain ranges
B) on the leeward side of mountain ranges
C) in the middle of flat plains
D) along continental coastlines

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The deserts found in the western United States are primarily the result of being located ________.
A) in the subtropics
B) within the rain shadow of one or more mountain ranges
C) near the center of a large continent
D) next to a cold ocean current
A) in the subtropics
B) within the rain shadow of one or more mountain ranges
C) near the center of a large continent
D) next to a cold ocean current

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Very hot air just above the ground creates a wavering pool of light on the ground known as a(n)________.
A) sabkha
B) wadi
C) arroyo
D) mirage
A) sabkha
B) wadi
C) arroyo
D) mirage

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Compared with humid climates,the rates of chemical weathering in deserts are ________.
A) much faster
B) much slower
C) very similar
D) too variable to compare
A) much faster
B) much slower
C) very similar
D) too variable to compare

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The most expansive hot deserts on the Earth occur in the ________.
A) tropics,at or near the equator
B) subtropics,between 20° and 30° north or south of the equator
C) temperate zone,between 30° and 50° north or south of the equator
D) latitudes higher than 50° north or south of the equator
A) tropics,at or near the equator
B) subtropics,between 20° and 30° north or south of the equator
C) temperate zone,between 30° and 50° north or south of the equator
D) latitudes higher than 50° north or south of the equator

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Coastal region deserts are most likely near ocean currents that are ________.
A) warm
B) cold
C) flowing east
D) flowing west
A) warm
B) cold
C) flowing east
D) flowing west

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Most hot deserts ________.
A) retain their high temperatures throughout the night because there is no vegetation to absorb heat from the sediment at the surface
B) cool off greatly at night because of sparse vegetation,dry air,and little cloud cover
C) cool off by no more than 8°C on most nights
D) gain additional heat at night because the desert air rises
A) retain their high temperatures throughout the night because there is no vegetation to absorb heat from the sediment at the surface
B) cool off greatly at night because of sparse vegetation,dry air,and little cloud cover
C) cool off by no more than 8°C on most nights
D) gain additional heat at night because the desert air rises

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The measured rainfall shown in the figure below is characteristic of a ________. 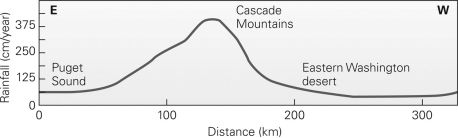
A) coastal desert
B) subtropical desert
C) rain-shadow desert
D) continental-interior desert

A) coastal desert
B) subtropical desert
C) rain-shadow desert
D) continental-interior desert

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Deserts represent ________ of the Earth's land surface.
A) less than 5%
B) about 10%
C) about 25%
D) more than 50%
A) less than 5%
B) about 10%
C) about 25%
D) more than 50%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The Atacama Desert in Chile is a desert primarily because it is located ________.
A) in the subtropics
B) near the South Pole
C) near the center of a large continent
D) next to a cold ocean current
A) in the subtropics
B) near the South Pole
C) near the center of a large continent
D) next to a cold ocean current

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The Gobi in Mongolia is a desert primarily because it is located ________.
A) in the subtropics
B) in a polar region
C) near the center of a large continent
D) next to a cold ocean current
A) in the subtropics
B) in a polar region
C) near the center of a large continent
D) next to a cold ocean current

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
According to the textbook,the highest recorded temperature on the Earth was in a ________.
A) tropical rainforest in Brazil
B) low-latitude,high-elevation desert in Mexico
C) high-latitude,high-elevation desert in Mongolia
D) low-latitude,low-elevation desert in Libya
A) tropical rainforest in Brazil
B) low-latitude,high-elevation desert in Mexico
C) high-latitude,high-elevation desert in Mongolia
D) low-latitude,low-elevation desert in Libya

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
To qualify as a desert,a region must ________.
A) be hot,with a mean annual temperature greater than 25°C (77°F)
B) be arid,with less than 15% of the ground surface vegetated
C) have a mean annual temperature greater than 25°C and less than 5 cm annual rainfall
D) have no rainfall three out of four seasons
A) be hot,with a mean annual temperature greater than 25°C (77°F)
B) be arid,with less than 15% of the ground surface vegetated
C) have a mean annual temperature greater than 25°C and less than 5 cm annual rainfall
D) have no rainfall three out of four seasons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
At 30° north latitude,at the northern edge of tropical (Hadley)cell convection in the northern hemisphere,________.
A) cool,dry air sinks,becoming drier as it heats up
B) warm,moist air rises,increasing in relative humidity as it rises
C) warm,dry air rises,becoming cooler
D) cool moist air sinks,providing abundant rainfall
A) cool,dry air sinks,becoming drier as it heats up
B) warm,moist air rises,increasing in relative humidity as it rises
C) warm,dry air rises,becoming cooler
D) cool moist air sinks,providing abundant rainfall

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Evaporite deposits in coastal,subtropical regions derived from the evaporation of seawater stranded above high tide are termed ________.
A) mirages
B) caliches
C) sabkhas
D) yardangs
A) mirages
B) caliches
C) sabkhas
D) yardangs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Badlands are characterized by ________.
A) thick caliche crusts
B) closely spaced parallel drainages
C) sabkhas
D) perennial streams
A) thick caliche crusts
B) closely spaced parallel drainages
C) sabkhas
D) perennial streams

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Native Americans produced petroglyphs by etching into ________.
A) rocks that had been subjected to case hardening
B) rocks that had been coated with desert varnish
C) dark basalts
D) obsidian
A) rocks that had been subjected to case hardening
B) rocks that had been coated with desert varnish
C) dark basalts
D) obsidian

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Desert varnish consists of ________.
A) pesticide and other pollutant residues
B) thick coatings of iron and magnesium oxides
C) dust deposits affected by microorganisms
D) carbonate cements with iron impurities (e.g.,siderite)
A) pesticide and other pollutant residues
B) thick coatings of iron and magnesium oxides
C) dust deposits affected by microorganisms
D) carbonate cements with iron impurities (e.g.,siderite)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A mushroom-shaped landform consisting of a column of less-resistant rock supporting a broader extent of wind-resistant rock is termed a ________.
A) blowout
B) ventifact
C) wadi
D) yardang
A) blowout
B) ventifact
C) wadi
D) yardang

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The saltation of sand involves ________.
A) spherical grains rolling along the surface of dunes
B) grains traveling short distances (approximately 1 m)in the air
C) grains traveling long distances (approximately 1-100 km)in the air by strong winds
D) the mixing of mineral sand and salt to form a weakly cemented soil
A) spherical grains rolling along the surface of dunes
B) grains traveling short distances (approximately 1 m)in the air
C) grains traveling long distances (approximately 1-100 km)in the air by strong winds
D) the mixing of mineral sand and salt to form a weakly cemented soil

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
When fine-grained sediment is blown away as shown in the figure below,the coarser sediment left behind is known as ________. 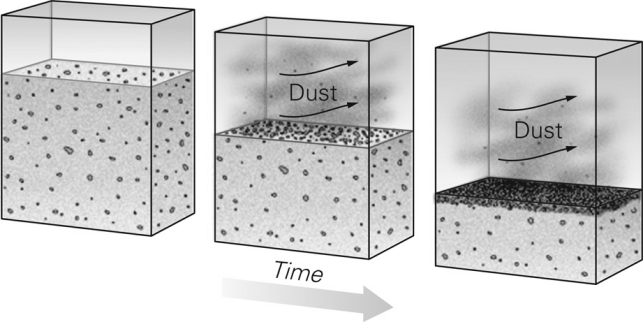
A) a sabkha
B) ventifacts
C) a lag deposit
D) talus

A) a sabkha
B) ventifacts
C) a lag deposit
D) talus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Calcrete (caliche)forms in a desert climate through the dissolution and the re-precipitation of ________ during and after rainstorms.
A) manganese oxide
B) quartz
C) calcite
D) iron oxide
A) manganese oxide
B) quartz
C) calcite
D) iron oxide

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
In the figure below,the sand grains are being transported by ________. 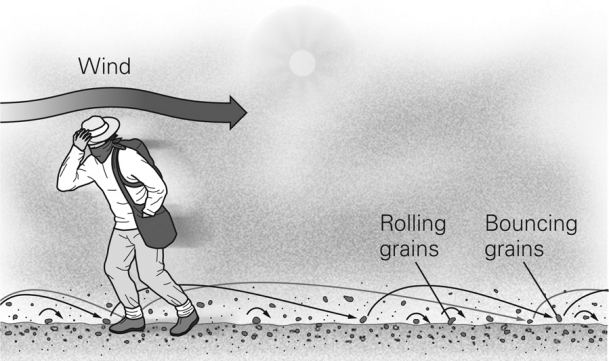
A) suspension
B) saltation
C) surface creep
D) deflation

A) suspension
B) saltation
C) surface creep
D) deflation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
An apron-shaped pile of alluvium that forms at the mouth of a canyon is known as a(n)________.
A) playa
B) sabkha
C) alluvial fan
D) inselberg
A) playa
B) sabkha
C) alluvial fan
D) inselberg

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Talus aprons represent accumulations of ________.
A) angular debris at the base of a hill
B) lag deposits
C) coarse sediment in a deflation basin
D) loess at the edge of a desert
A) angular debris at the base of a hill
B) lag deposits
C) coarse sediment in a deflation basin
D) loess at the edge of a desert

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Most of the erosion in desert environments is caused by ________.
A) wind
B) surface water
C) ground water
D) salt wedging
A) wind
B) surface water
C) ground water
D) salt wedging

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A salt-encrusted muddy tidal flat is known as a ________.
A) wadi
B) pediment
C) sabkha
D) bajada
A) wadi
B) pediment
C) sabkha
D) bajada

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The process of lowering the land surface by wind erosion is known as ________.
A) saltation
B) deflation
C) desertification
D) escarpment
A) saltation
B) deflation
C) desertification
D) escarpment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
A(n)________ consists of sand and gravel deposited by ephemeral distributary channels that occur where a gully or a canyon discharges from its mouth.
A) alluvial fan
B) ventifact
C) wadi
D) yardang
A) alluvial fan
B) ventifact
C) wadi
D) yardang

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Over time,alluvial fans may merge to form a ________.
A) wadi
B) talus apron
C) playa
D) bajada
A) wadi
B) talus apron
C) playa
D) bajada

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
As shown in the figure below,wind erosion can create a faceted rock known as a ________. 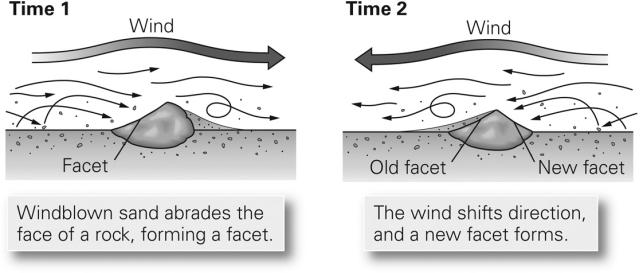
A) ventifact
B) lag deposit
C) yardang
D) wadi

A) ventifact
B) lag deposit
C) yardang
D) wadi

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Fine-grained,wind-blown sediments are eventually deposited as ________.
A) loess
B) ventifacts
C) dunes
D) desert pavement
A) loess
B) ventifacts
C) dunes
D) desert pavement

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
A rock that has been significantly reshaped on multiple surfaces by windborne particles and sometimes has a sharp edge is a(n)________.
A) inselberg
B) ventifact
C) wadi
D) yardang
A) inselberg
B) ventifact
C) wadi
D) yardang

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
What is an ephemeral stream?
A) A stream that flows perennially through the desert supporting lush vegetation.
B) A stream that flows perennially through the desert but supports little to no vegetation because of its high mineral content.
C) A desert stream that contains water only immediately following a rain event.
D) A steep-walled canyon that was formed by wind erosion.
A) A stream that flows perennially through the desert supporting lush vegetation.
B) A stream that flows perennially through the desert but supports little to no vegetation because of its high mineral content.
C) A desert stream that contains water only immediately following a rain event.
D) A steep-walled canyon that was formed by wind erosion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Why is the Great Salt Lake in Utah so salty?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Conversion of productive land to desert is known as ________.
A) deflation
B) saltation
C) degradation
D) desertification
A) deflation
B) saltation
C) degradation
D) desertification

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The Dust Bowl event in 1933 resulted from which natural event?
A) overpopulation
B) long-term drought
C) global climate change
D) change in the course of rivers
A) overpopulation
B) long-term drought
C) global climate change
D) change in the course of rivers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which statement about desert life is correct?
A) Mammals,unlike reptiles and birds,very rarely inhabit deserts.
B) Animal life in the desert is limited to herbivores only.
C) Animals that live in the desert must be able to retain water and survive extreme temperatures.
D) Animals that live in the desert are only active at night when it is cooler.
A) Mammals,unlike reptiles and birds,very rarely inhabit deserts.
B) Animal life in the desert is limited to herbivores only.
C) Animals that live in the desert must be able to retain water and survive extreme temperatures.
D) Animals that live in the desert are only active at night when it is cooler.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
What is a desert? Explain how a desert could be formed at one of the poles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
What is desert varnish? How does it form? Why doesn't one find desert varnish in humid climates?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Areas with relatively scarce sand and constantly shifting winds will develop ________ dunes.
A) star
B) barchans
C) parabolic
D) longitudinal
A) star
B) barchans
C) parabolic
D) longitudinal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Illustrate how a rain-shadow desert might form.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Which of the following hazards could lead to desertification?
A) climate change
B) earthquakes
C) landslides
D) flooding
A) climate change
B) earthquakes
C) landslides
D) flooding

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Label the image below with the name of the type of sand dune shown. 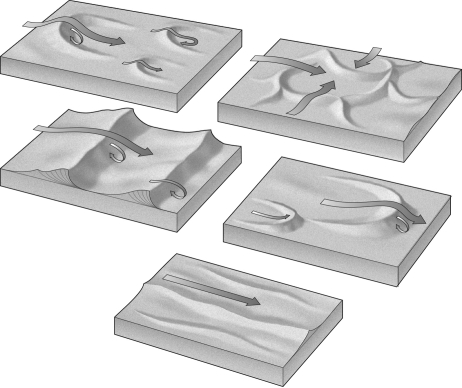


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which of the following human activities will lead to desertification?
A) addition of fertilizer to soil
B) diversion of water from an area
C) over-irrigating an area
D) building a city in an area
A) addition of fertilizer to soil
B) diversion of water from an area
C) over-irrigating an area
D) building a city in an area

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which of the following is NOT an adaptation of plants that helps them survive in deserts?
A) a thick waxy outer coating and needlelike leaves
B) shallow,expansive root systems that can uptake infiltrated water over a broad area
C) succulence (tissues that retain moisture for a long period of time)
D) thin-skinned seeds that can quickly germinate when it rains
A) a thick waxy outer coating and needlelike leaves
B) shallow,expansive root systems that can uptake infiltrated water over a broad area
C) succulence (tissues that retain moisture for a long period of time)
D) thin-skinned seeds that can quickly germinate when it rains

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
What is the dominant erosional force in deserts: wind or water? Why?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Imagine you are a farmer moving into the Great Plains area after the Dust Bowl of 1933.What can you do to make the land fertile enough for farming again? What can be done to prevent a similar disaster from happening again?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
After extensive erosion of a hill in a desert environment,the small remnant surrounded by alluvium-filled basins is known as a(n)________.
A) inselberg
B) hogback
C) questa
D) mesa
A) inselberg
B) hogback
C) questa
D) mesa

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Vegetation in the desert consists of ________.
A) cacti only
B) extensive grasslands with water-seeking deep roots
C) scattered succulents,such as cacti,with adaptations to obtain and retain as much water as they can
D) forests of tall,broad-leafed trees
A) cacti only
B) extensive grasslands with water-seeking deep roots
C) scattered succulents,such as cacti,with adaptations to obtain and retain as much water as they can
D) forests of tall,broad-leafed trees

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Contrast a lag deposit and desert pavement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Examine the images of the Aral Sea below.What happened and why? 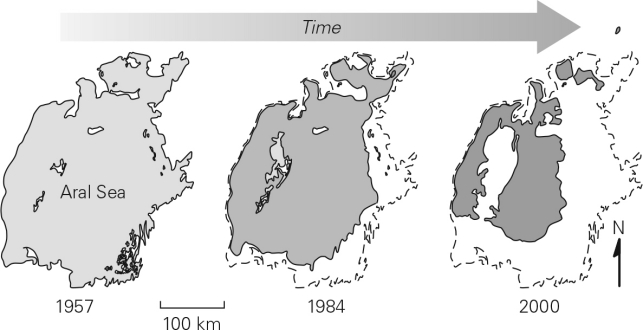


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Deserts are defined as regions with minimal precipitation and vegetation that covers no more than 15% of the land surface.How are any plants able to survive in the desert? Describe two different adaptations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The geometry of sand dunes is NOT strongly influenced by the ________.
A) strength of the wind
B) consistency of wind direction
C) abundance of sand
D) timing of the monsoon season
A) strength of the wind
B) consistency of wind direction
C) abundance of sand
D) timing of the monsoon season

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



