Deck 7: Pages of Earths Past: Sedimentary Rocks
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/60
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 7: Pages of Earths Past: Sedimentary Rocks
1
The sedimentary rocks breccia and conglomerate most commonly form in a ________ environment.
A) beach
B) lake
C) mountain stream
D) deep-ocean basin
A) beach
B) lake
C) mountain stream
D) deep-ocean basin
C
2
Chemical sedimentary rocks are classified primarily on the basis of
A) grain size.
B) degree of sorting.
C) angularity.
D) mineral composition.
A) grain size.
B) degree of sorting.
C) angularity.
D) mineral composition.
D
3
When limestone becomes chemically altered so that half of the calcium atoms are replaced by magnesium,the resultant rock is termed
A) agate.
B) dolostone.
C) jasper.
D) travertine.
A) agate.
B) dolostone.
C) jasper.
D) travertine.
B
4
Which of the following is true regarding biochemical chert?
A) It is massive (lacking layers).
B) It is made of cryptocrystalline quartz.
C) It is made of aragonite shell fragments.
D) It is composed of the minerals calcite and dolomite.
A) It is massive (lacking layers).
B) It is made of cryptocrystalline quartz.
C) It is made of aragonite shell fragments.
D) It is composed of the minerals calcite and dolomite.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Biochemical limestones are dominated by carbonate mud and fragments of
A) siliceous shells of planktonic diatoms and foraminifera.
B) skeletons of marine invertebrates made of calcite and aragonite.
C) the phosphatic bones of fish.
D) the organic breakdown products of wood and leaves from trees.
A) siliceous shells of planktonic diatoms and foraminifera.
B) skeletons of marine invertebrates made of calcite and aragonite.
C) the phosphatic bones of fish.
D) the organic breakdown products of wood and leaves from trees.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Grains become rounded primarily during
A) weathering at the outcrop.
B) lithification.
C) transportation.
D) deposition.
A) weathering at the outcrop.
B) lithification.
C) transportation.
D) deposition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
What is the difference in the formation of chalk versus chert?
A) They have different grain sizes.
B) They are made of different source materials.
C) Chalk is terrestrial; chert is marine.
D) Chalk is biochemical; chert is chemical.
A) They have different grain sizes.
B) They are made of different source materials.
C) Chalk is terrestrial; chert is marine.
D) Chalk is biochemical; chert is chemical.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The breakdown of exposed rock into small fragments and dissolved ions is termed
A) deposition.
B) erosion.
C) weathering.
D) lithification.
A) deposition.
B) erosion.
C) weathering.
D) lithification.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The removal of detritus from weathered rock at an outcrop is termed
A) deposition.
B) erosion.
C) weathering.
D) lithification.
A) deposition.
B) erosion.
C) weathering.
D) lithification.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The primary difference between breccia and conglomerate is that conglomerate
A) is finer-grained than breccia.
B) is coarser-grained than breccia.
C) possesses more angular grains than breccia.
D) possesses more rounded grains than breccia.
A) is finer-grained than breccia.
B) is coarser-grained than breccia.
C) possesses more angular grains than breccia.
D) possesses more rounded grains than breccia.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Chemically precipitated limestone that forms in caves or around hot springs is termed
A) agate.
B) dolostone.
C) jasper.
D) travertine.
A) agate.
B) dolostone.
C) jasper.
D) travertine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Compaction and cementation of grains occurs during
A) erosion.
B) lithification.
C) transport.
D) weathering.
A) erosion.
B) lithification.
C) transport.
D) weathering.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following are most likely to preserve conditions of ancient environments on the Earth?
A) intrusive igneous rocks
B) extrusive igneous rocks
C) metamorphic rocks
D) sedimentary rocks
A) intrusive igneous rocks
B) extrusive igneous rocks
C) metamorphic rocks
D) sedimentary rocks

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Precipitation of gypsum due to evaporation of seawater produces which kind of sedimentary rock?
A) biochemical
B) chemical
C) clastic
D) organic
A) biochemical
B) chemical
C) clastic
D) organic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The image below shows an outcrop of coarse-grained sedimentary rock.Note the rock hammer for scale.What is the name of this rock type?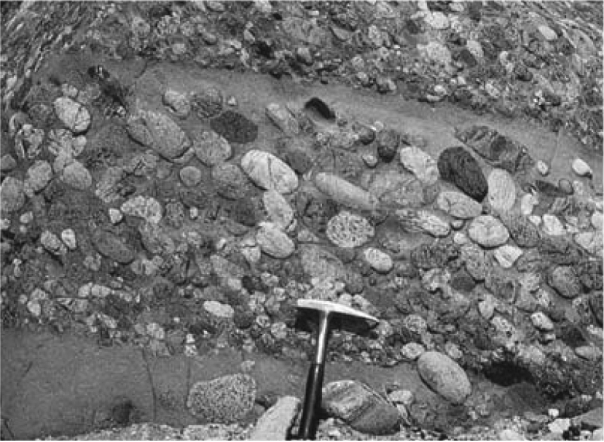 
A) sandstone
B) shale
C) breccia
D) conglomerate

A) sandstone
B) shale
C) breccia
D) conglomerate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
If water is the transport mechanism of sediment,the grain size of sedimentary deposits most closely indicates the
A) geographic extent of the weathering source rock at outcrop.
B) average velocity of the water from the time of erosion until deposition.
C) velocity of the water at the moment the sediment settled to the bottom.
D) climate conditions at the time of deposition.
A) geographic extent of the weathering source rock at outcrop.
B) average velocity of the water from the time of erosion until deposition.
C) velocity of the water at the moment the sediment settled to the bottom.
D) climate conditions at the time of deposition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The majority of the rocks that form at the surface of the Earth are
A) intrusive igneous rocks.
B) foliated metamorphic rocks.
C) sedimentary rocks.
D) non-foliated metamorphic rocks.
A) intrusive igneous rocks.
B) foliated metamorphic rocks.
C) sedimentary rocks.
D) non-foliated metamorphic rocks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A shale differs from a mudstone in that it
A) breaks into platy sheets.
B) is compositionally richer in quartz.
C) has smaller grains.
D) has larger grains.
A) breaks into platy sheets.
B) is compositionally richer in quartz.
C) has smaller grains.
D) has larger grains.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Sedimentary rocks are most likely to form
A) near the Earth's surface.
B) in high-temperature conditions.
C) in high-pressure conditions.
D) in the upper mantle.
A) near the Earth's surface.
B) in high-temperature conditions.
C) in high-pressure conditions.
D) in the upper mantle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Lithified detritus (breakdown products of preexisting rocks)forms which kind of sedimentary rock?
A) biochemical
B) chemical
C) clastic
D) organic
A) biochemical
B) chemical
C) clastic
D) organic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the following is NOT true? Sediments deposited in a beach environment are typically
A) well sorted.
B) medium-grained.
C) composed of angular grains.
D) composed of mostly quartz.
A) well sorted.
B) medium-grained.
C) composed of angular grains.
D) composed of mostly quartz.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Topset,foreset,and bottomset beds are indicative of ________ environments.
A) alluvial fan
B) lake bottom
C) delta
D) deep-marine
A) alluvial fan
B) lake bottom
C) delta
D) deep-marine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Cemented shells of marine organisms form which kind of sedimentary rock?
A) biochemical
B) chemical
C) clastic
D) organic
A) biochemical
B) chemical
C) clastic
D) organic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
If a geologist found preserved mud cracks,he or she could conclude that the environment in which they formed
A) was once covered in wet mud.
B) was once covered by a glacier.
C) has been subjected to a major climate change event.
D) was the site of a mass extinction event.
A) was once covered in wet mud.
B) was once covered by a glacier.
C) has been subjected to a major climate change event.
D) was the site of a mass extinction event.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Stratification refers to
A) the development of layering within sedimentary rocks.
B) the act of deposition of sediment that will ultimately form sedimentary rock.
C) physical and chemical alterations,including compaction and cementation,that occur as sediment is transformed into rock.
D) the process of breaking down a source rock into smaller pieces called grains.
A) the development of layering within sedimentary rocks.
B) the act of deposition of sediment that will ultimately form sedimentary rock.
C) physical and chemical alterations,including compaction and cementation,that occur as sediment is transformed into rock.
D) the process of breaking down a source rock into smaller pieces called grains.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
It is unusual for ________ to carry grains larger than sand.
A) ice in glaciers
B) water in rivers
C) wind
D) water at a seaside beach
A) ice in glaciers
B) water in rivers
C) wind
D) water at a seaside beach

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Geologists call individual layers of sedimentary rocks ________,whereas several of them together are called ________.
A) beds; strata
B) strata; beds
C) laminations; graded beds
D) graded beds; laminations
A) beds; strata
B) strata; beds
C) laminations; graded beds
D) graded beds; laminations

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
When graded beds are observed in a rock outcrop,this tells geologists that a
A) turbidity current deposited these beds,depositing finer material first.
B) turbidity current deposited these beds,depositing coarser material first.
C) slurry deposited these beds with little sorting.
D) glacier deposited these beds,depositing coarser material first.
A) turbidity current deposited these beds,depositing finer material first.
B) turbidity current deposited these beds,depositing coarser material first.
C) slurry deposited these beds with little sorting.
D) glacier deposited these beds,depositing coarser material first.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
What type of sediment is typically found in lake bottoms?
A) gravel
B) sand
C) silt
D) clay/mud
A) gravel
B) sand
C) silt
D) clay/mud

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Thick accumulations of sediments and fossils in the deep ocean tend to be ___________-sized because of the low amount of energy in the environment.
A) cobble
B) gravel
C) sand
D) clay
A) cobble
B) gravel
C) sand
D) clay

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Consult the figure below.Here,distinct internal laminations are inclined at an angle to the boundary of the main sedimentary layers.These are termed 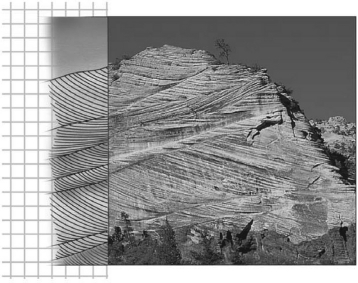
A) graded beds.
B) cross beds.
C) horizontal beds.
D) tilted beds.

A) graded beds.
B) cross beds.
C) horizontal beds.
D) tilted beds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which environment would most likely produce sedimentary deposits characterized by poorly to moderately sorted,angular to subangular grains that consist of feldspar,quartz,and lithics (rock fragments)?
A) river
B) glacier
C) beach
D) alluvial fan
A) river
B) glacier
C) beach
D) alluvial fan

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Two major sources of energy,coal and oil shale,are considered ________ sedimentary rocks.
A) clastic
B) biochemical
C) organic
D) chemical
A) clastic
B) biochemical
C) organic
D) chemical

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Large layers of cross-bedded sand can be indicative of a ____________ environment.
A) river
B) desert
C) shallow-marine
D) deep-marine
A) river
B) desert
C) shallow-marine
D) deep-marine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which environment would most likely produce sedimentary deposits characterized by very well-sorted,very well-rounded grains that are nearly pure quartz?
A) river
B) glacier
C) beach
D) alluvial fan
A) river
B) glacier
C) beach
D) alluvial fan

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Symmetric ripples form when
A) wind blows in a consistent direction and deposits sediment in an arid climate.
B) water flows in a consistent direction and deposits sediment in layers.
C) water deposits sediment in layers,but the direction of flow periodically changes.
D) a mountain stream reaches a flat basin and sediment is deposited in a fan-shaped pattern.
A) wind blows in a consistent direction and deposits sediment in an arid climate.
B) water flows in a consistent direction and deposits sediment in layers.
C) water deposits sediment in layers,but the direction of flow periodically changes.
D) a mountain stream reaches a flat basin and sediment is deposited in a fan-shaped pattern.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Limestone is most likely formed in which of the following environments?
A) shallow-marine clastic
B) shallow-marine carbonate
C) marine delta
D) deep-marine
A) shallow-marine clastic
B) shallow-marine carbonate
C) marine delta
D) deep-marine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which transport medium carries the largest particles?
A) ice in glaciers
B) water in rivers
C) wind
D) water in lakes
A) ice in glaciers
B) water in rivers
C) wind
D) water in lakes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The image below shows a series of graded beds.How many graded beds are shown?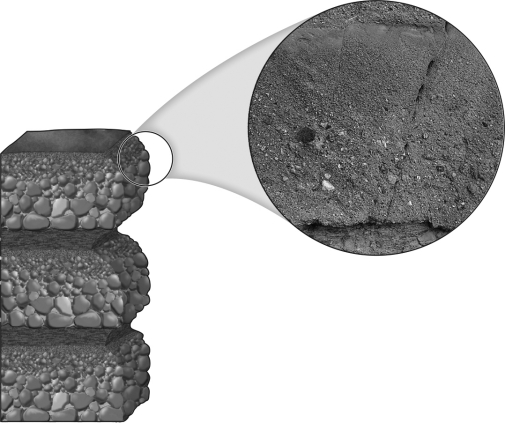 
A) 1
B) 3
C) 6
D) 9

A) 1
B) 3
C) 6
D) 9

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The image below shows ancient dunes exposed in Zion National Park in Utah.Using the interpreted portion of the image at the left,what was the dominant wind direction that formed these sedimentary structures? 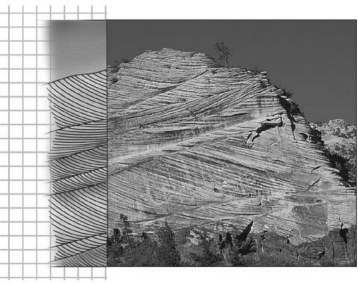
A) toward the right
B) toward the left
C) toward both the left and right
D) vertical,both up and down

A) toward the right
B) toward the left
C) toward both the left and right
D) vertical,both up and down

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Pulling a block of clay apart,resulting in the middle portion thinning and sinking,is an adequate analogy for
A) passive margins and subsidence.
B) foreland basins and diagenesis.
C) rift basins and subsidence.
D) intercontinental basins and diagenesis.
A) passive margins and subsidence.
B) foreland basins and diagenesis.
C) rift basins and subsidence.
D) intercontinental basins and diagenesis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Diagenesis refers to
A) the development of layering within sedimentary rocks.
B) the act of deposition of sediment that will determine the characteristics of and,ultimately,form a sedimentary rock.
C) physical and chemical alterations,including compaction and cementation,that occur as sediment is transformed into rock.
D) the natural process of separating sediment by grain size.
A) the development of layering within sedimentary rocks.
B) the act of deposition of sediment that will determine the characteristics of and,ultimately,form a sedimentary rock.
C) physical and chemical alterations,including compaction and cementation,that occur as sediment is transformed into rock.
D) the natural process of separating sediment by grain size.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
As compared with metamorphism,diagenesis
A) means exactly the same thing.
B) takes place at lower temperatures and pressures.
C) takes place at higher temperatures and pressures.
D) takes place at greater depths that are well within the mantle.
A) means exactly the same thing.
B) takes place at lower temperatures and pressures.
C) takes place at higher temperatures and pressures.
D) takes place at greater depths that are well within the mantle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Because the velocity of sediment settling (deposition)is positively related to grain size for waterborne sediments,fluvial deposits are more likely than glacial deposits to
A) be well sorted.
B) include coarse grains,such as cobbles.
C) include fine grains,such as clay.
D) have angular grains.
A) be well sorted.
B) include coarse grains,such as cobbles.
C) include fine grains,such as clay.
D) have angular grains.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
How are a marine transgression and regression different? What happens to the shoreline in each?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
What are the steps involved in the formation of a clastic sedimentary rock?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
In which of the following three basin types might you be able to find oil forming and why? Rift basin,passive-margin basin,and foreland basin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which of the following is true about regressions?
A) They are typically well preserved in the sedimentary record.
B) They occur when the climate warms and continental ice sheets melt.
C) They occur when the land is uplifted by tectonic processes.
D) Coastal environments will migrate landward.
A) They are typically well preserved in the sedimentary record.
B) They occur when the climate warms and continental ice sheets melt.
C) They occur when the land is uplifted by tectonic processes.
D) Coastal environments will migrate landward.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Sea level rises locally,and marine sediments are deposited on top of terrestrial sediments during events termed
A) transgressions.
B) regressions.
C) turbidity currents.
D) cross bedding.
A) transgressions.
B) regressions.
C) turbidity currents.
D) cross bedding.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Notice the turbidity current in the image below.Briefly describe and sketch the deposit that will result. 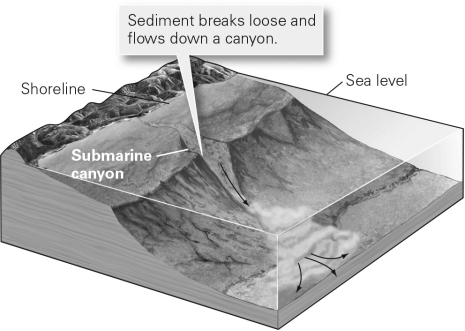


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The image below of Death Valley,CA,shows a road that curves around a(n) 
A) delta.
B) alluvial fan.
C) turbidite.
D) glacial till.

A) delta.
B) alluvial fan.
C) turbidite.
D) glacial till.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Describe the difference between lithification and diagenesis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Basins that form on the continental side of mountain ranges are called _________ basins.
A) rift
B) passive-margin
C) foreland
D) intracontinental
A) rift
B) passive-margin
C) foreland
D) intracontinental

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Limestone can be either a biochemical or a chemical sedimentary rock.Explain how both types of limestone are formed.Make sure to describe the environments in which they were formed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
A well-sorted sandstone with asymmetric ripples was most likely deposited as sand by a
A) river (far from source).
B) glacier.
C) river (near source).
D) alluvial fan.
A) river (far from source).
B) glacier.
C) river (near source).
D) alluvial fan.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which of the three types of rock would you expect to be most abundant at the Earth's surface? Why? How does this relate to how these rocks form?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Illustrate a rock formation that is bedded.How might this sequence have formed?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Death Valley is currently sinking partly due to the weight of continuously accumulating sediment shed from the mountains that border the valley.What phenomenon is this an example of and what depositional environment is created by the sediment deposition?
A) regression and deltas
B) subsidence and deltas
C) regression and alluvial fans
D) subsidence and alluvial fans
A) regression and deltas
B) subsidence and deltas
C) regression and alluvial fans
D) subsidence and alluvial fans

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
What attributes would a clastic sedimentary rock have if it had traveled far from its source and was carried in a current with uniform energy?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
What is an alluvial fan? How is it different from a marine delta?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



