Deck 12: Electing the President
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/93
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 12: Electing the President
1
Use the following information to answer Questions
Seven board members of a company must decide between two other board members (A and B) for a certain position. The voters are concerned with two issues and their ideal points are represented as ordered pairs: (1, 5), (3, 3), (5, 2), (6, 4), (6, 2), (4, 4), and (3, 2). Assume that A and B announce policy positions of (2, 2) and (5, 4), respectively.
Which candidate would be elected for the position based on the ideal points?
Seven board members of a company must decide between two other board members (A and B) for a certain position. The voters are concerned with two issues and their ideal points are represented as ordered pairs: (1, 5), (3, 3), (5, 2), (6, 4), (6, 2), (4, 4), and (3, 2). Assume that A and B announce policy positions of (2, 2) and (5, 4), respectively.
Which candidate would be elected for the position based on the ideal points?
B
2
Use the following information to answer Questions
Suppose that 17 voters have ideal points as given in the following table.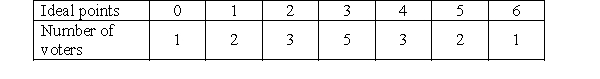 Candidate A announces a policy position of 1 and Candidate B announces a policy position of 5.
Candidate A announces a policy position of 1 and Candidate B announces a policy position of 5.
Suppose that a voter is added with ideal points of 3. Is there a 2/3-separation opportunity for a third Candidate C to enter the race?
Suppose that 17 voters have ideal points as given in the following table.
 Candidate A announces a policy position of 1 and Candidate B announces a policy position of 5.
Candidate A announces a policy position of 1 and Candidate B announces a policy position of 5.Suppose that a voter is added with ideal points of 3. Is there a 2/3-separation opportunity for a third Candidate C to enter the race?
Yes. There are 12 voters between 1 and 5 which is 2/3 of 18. For example, if Candidate C has a policy position of 2.5, then Candidate C would get 9 votes and win the election.
3
Describe the composition of the Electoral College.
Each state gets one electoral vote for each of its two senators and for each of its representatives in the House of Representatives. The District of Columbia is given three electoral votes.
4
Use the following information to answer Questions
Seven board members of a company must decide between two other board members (A and B) for a certain position. The voters are concerned with two issues and their ideal points are represented as ordered pairs: (1, 5), (3, 3), (5, 2), (6, 4), (6, 2), (4, 4), and (3, 2). Assume that A and B announce policy positions of (2, 2) and (5, 4), respectively.
Find the midpoint of the two policy positions.
Seven board members of a company must decide between two other board members (A and B) for a certain position. The voters are concerned with two issues and their ideal points are represented as ordered pairs: (1, 5), (3, 3), (5, 2), (6, 4), (6, 2), (4, 4), and (3, 2). Assume that A and B announce policy positions of (2, 2) and (5, 4), respectively.
Find the midpoint of the two policy positions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Use the following information to answer Questions
Suppose that the continuous distribution of voters' ideal points is the bent solid line below.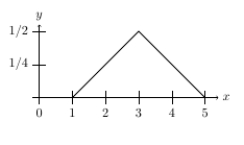
Assuming Candidate A and Candidate B's policy positions are 2.7 and 3.3, determine whether Candidate C can enter and win the election.
Suppose that the continuous distribution of voters' ideal points is the bent solid line below.

Assuming Candidate A and Candidate B's policy positions are 2.7 and 3.3, determine whether Candidate C can enter and win the election.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Use the following information to answer Questions
Seven board members of a company must decide between two other board members (A and B) for a certain position. The voters are concerned with two issues and their ideal points are represented as ordered pairs: (1, 5), (3, 3), (5, 2), (6, 4), (6, 2), (4, 4), and (3, 2). Assume that A and B announce policy positions of (2, 2) and (5, 4), respectively.
Find the number of board members who would vote for A based on ideal points.
Seven board members of a company must decide between two other board members (A and B) for a certain position. The voters are concerned with two issues and their ideal points are represented as ordered pairs: (1, 5), (3, 3), (5, 2), (6, 4), (6, 2), (4, 4), and (3, 2). Assume that A and B announce policy positions of (2, 2) and (5, 4), respectively.
Find the number of board members who would vote for A based on ideal points.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Use the following information to answer Questions
Suppose that the continuous distribution of voters' ideal points is the bent solid line below.
Assuming that Candidate A's policy position is 4 and Candidate B announces a policy position of 2.5, describe which voters vote for Candidate B.
Suppose that the continuous distribution of voters' ideal points is the bent solid line below.

Assuming that Candidate A's policy position is 4 and Candidate B announces a policy position of 2.5, describe which voters vote for Candidate B.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Use the following information to answer Questions
Suppose that the continuous distribution of voters' ideal points is the bent solid line below.
Explain why the bent solid line describes a continuous distribution.
Suppose that the continuous distribution of voters' ideal points is the bent solid line below.

Explain why the bent solid line describes a continuous distribution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Use the following information to answer Questions
Seven board members of a company must decide between two other board members (A and B) for a certain position. The voters are concerned with two issues and their ideal points are represented as ordered pairs: (1, 5), (3, 3), (5, 2), (6, 4), (6, 2), (4, 4), and (3, 2). Assume that A and B announce policy positions of (2, 2) and (5, 4), respectively.
Find the number of board members who would vote for B based on ideal points.
Seven board members of a company must decide between two other board members (A and B) for a certain position. The voters are concerned with two issues and their ideal points are represented as ordered pairs: (1, 5), (3, 3), (5, 2), (6, 4), (6, 2), (4, 4), and (3, 2). Assume that A and B announce policy positions of (2, 2) and (5, 4), respectively.
Find the number of board members who would vote for B based on ideal points.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Use the following information to answer Questions
Suppose that the continuous distribution of voters' ideal points is the bent solid line below.
Assuming that Candidate A's policy position is 4, if Candidate B announces a policy position between 1 and 2, then who will be the winner of the election?
Suppose that the continuous distribution of voters' ideal points is the bent solid line below.

Assuming that Candidate A's policy position is 4, if Candidate B announces a policy position between 1 and 2, then who will be the winner of the election?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Explain the justification for the Electoral College.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Find the range of values that make up the extended median if the voters' ideal points are 2, 3, 4, 4, 6, 8, 8, 8, 9, 10.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Use the following information to answer Questions.
Consider the following distribution of 33 voters at eight different positions over the interval [0,1].![Use the following information to answer Questions. Consider the following distribution of 33 voters at eight different positions over the interval [0,1]. What is the equilibrium position in a two-candidate election?](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1043/11eaaa0e_a323_d554_9885_6137bda8b656_TB1043_00_TB1043_00_TB1043_00_TB1043_00.jpg)
What is the equilibrium position in a two-candidate election?
Consider the following distribution of 33 voters at eight different positions over the interval [0,1].
![Use the following information to answer Questions. Consider the following distribution of 33 voters at eight different positions over the interval [0,1]. What is the equilibrium position in a two-candidate election?](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1043/11eaaa0e_a323_d554_9885_6137bda8b656_TB1043_00_TB1043_00_TB1043_00_TB1043_00.jpg)
What is the equilibrium position in a two-candidate election?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Use the following information to answer Questions.
Consider the following distribution of 33 voters at eight different positions over the interval [0,1].![Use the following information to answer Questions. Consider the following distribution of 33 voters at eight different positions over the interval [0,1]. For two candidates A and B with distinct policy positions 0.3 and 0.75, respectively, find the number of votes for the candidate B based on voter's ideal positions.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1043/11eaaa0e_a323_d554_9885_6137bda8b656_TB1043_00_TB1043_00_TB1043_00_TB1043_00.jpg)
For two candidates A and B with distinct policy positions 0.3 and 0.75, respectively, find the number of votes for the candidate B based on voter's ideal positions.
Consider the following distribution of 33 voters at eight different positions over the interval [0,1].
![Use the following information to answer Questions. Consider the following distribution of 33 voters at eight different positions over the interval [0,1]. For two candidates A and B with distinct policy positions 0.3 and 0.75, respectively, find the number of votes for the candidate B based on voter's ideal positions.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1043/11eaaa0e_a323_d554_9885_6137bda8b656_TB1043_00_TB1043_00_TB1043_00_TB1043_00.jpg)
For two candidates A and B with distinct policy positions 0.3 and 0.75, respectively, find the number of votes for the candidate B based on voter's ideal positions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Use the following information to answer Questions
Suppose that 17 voters have ideal points as given in the following table. Candidate A announces a policy position of 1 and Candidate B announces a policy position of 5.
Candidate A announces a policy position of 1 and Candidate B announces a policy position of 5.
Is there a 2/3-separation opportunity for a third Candidate C to enter the race?
Suppose that 17 voters have ideal points as given in the following table.
 Candidate A announces a policy position of 1 and Candidate B announces a policy position of 5.
Candidate A announces a policy position of 1 and Candidate B announces a policy position of 5.Is there a 2/3-separation opportunity for a third Candidate C to enter the race?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Use the following information to answer Questions
Seven board members of a company must decide between two other board members (A and B) for a certain position. The voters are concerned with two issues and their ideal points are represented as ordered pairs: (1, 5), (3, 3), (5, 2), (6, 4), (6, 2), (4, 4), and (3, 2). Assume that A and B announce policy positions of (2, 2) and (5, 4), respectively.
Find the equation of the line which divides the two-dimensional space separating voters preferring A over B from those preferring B over A.
Seven board members of a company must decide between two other board members (A and B) for a certain position. The voters are concerned with two issues and their ideal points are represented as ordered pairs: (1, 5), (3, 3), (5, 2), (6, 4), (6, 2), (4, 4), and (3, 2). Assume that A and B announce policy positions of (2, 2) and (5, 4), respectively.
Find the equation of the line which divides the two-dimensional space separating voters preferring A over B from those preferring B over A.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Give an example of a voter distribution over the interval [0,1] that is skewed to the left.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Use the following information to answer Questions.
Consider the following distribution of 33 voters at eight different positions over the interval [0,1].![Use the following information to answer Questions. Consider the following distribution of 33 voters at eight different positions over the interval [0,1]. For two candidates A and B with distinct policy positions 0.3 and 0.75, respectively, find the number of votes for the candidate A based on voter's ideal positions.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1043/11eaaa0e_a323_d554_9885_6137bda8b656_TB1043_00_TB1043_00_TB1043_00_TB1043_00.jpg)
For two candidates A and B with distinct policy positions 0.3 and 0.75, respectively, find the number of votes for the candidate A based on voter's ideal positions.
Consider the following distribution of 33 voters at eight different positions over the interval [0,1].
![Use the following information to answer Questions. Consider the following distribution of 33 voters at eight different positions over the interval [0,1]. For two candidates A and B with distinct policy positions 0.3 and 0.75, respectively, find the number of votes for the candidate A based on voter's ideal positions.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1043/11eaaa0e_a323_d554_9885_6137bda8b656_TB1043_00_TB1043_00_TB1043_00_TB1043_00.jpg)
For two candidates A and B with distinct policy positions 0.3 and 0.75, respectively, find the number of votes for the candidate A based on voter's ideal positions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Use the following information to answer Questions
Suppose that the continuous distribution of voters' ideal points is the bent solid line below.
Assuming Candidate A and Candidate B's policy positions are 2 and 4, determine whether Candidate C can enter and win the election.
Suppose that the continuous distribution of voters' ideal points is the bent solid line below.

Assuming Candidate A and Candidate B's policy positions are 2 and 4, determine whether Candidate C can enter and win the election.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Use the following information to answer Questions.
Consider the following distribution of 33 voters at eight different positions over the interval [0,1].![Use the following information to answer Questions. Consider the following distribution of 33 voters at eight different positions over the interval [0,1]. What is the median of the distribution?](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1043/11eaaa0e_a323_d554_9885_6137bda8b656_TB1043_00_TB1043_00_TB1043_00_TB1043_00.jpg)
What is the median of the distribution?
Consider the following distribution of 33 voters at eight different positions over the interval [0,1].
![Use the following information to answer Questions. Consider the following distribution of 33 voters at eight different positions over the interval [0,1]. What is the median of the distribution?](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1043/11eaaa0e_a323_d554_9885_6137bda8b656_TB1043_00_TB1043_00_TB1043_00_TB1043_00.jpg)
What is the median of the distribution?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
What is 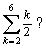
A) 2
B) 3
C) 10
D) 20
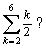
A) 2
B) 3
C) 10
D) 20

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Explain the median of a continuous voter distribution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Describe the spoiler problem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Use the following distribution of 33 voters at eight different positions over the interval [0, 1] to answer Questions ![<strong>Use the following distribution of 33 voters at eight different positions over the interval [0, 1] to answer Questions What is the median of the distribution?</strong> A) 0.5 B) 0.55 C) 0.56 D) 0.6](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1043/11eaaa0e_a326_465b_9885_bf0431b2b1dd_TB1043_00_TB1043_00_TB1043_00.jpg)
What is the median of the distribution?
A) 0.5
B) 0.55
C) 0.56
D) 0.6
![<strong>Use the following distribution of 33 voters at eight different positions over the interval [0, 1] to answer Questions What is the median of the distribution?</strong> A) 0.5 B) 0.55 C) 0.56 D) 0.6](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1043/11eaaa0e_a326_465b_9885_bf0431b2b1dd_TB1043_00_TB1043_00_TB1043_00.jpg)
What is the median of the distribution?
A) 0.5
B) 0.55
C) 0.56
D) 0.6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Describe the 1/3-separation obstacle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Describe the National Popular Vote law.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Explain the median-voter theorem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Use the following distribution of 33 voters at eight different positions over the interval [0, 1] to answer Questions ![<strong>Use the following distribution of 33 voters at eight different positions over the interval [0, 1] to answer Questions For two candidates A and B with distinct policy positions 0.3 and 0.8, respectively, find the number of votes for the candidate A based on voter's ideal positions.</strong> A) 16 B) 17 C) 23 D) 25](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1043/11eaaa0e_a326_465b_9885_bf0431b2b1dd_TB1043_00_TB1043_00_TB1043_00.jpg)
For two candidates A and B with distinct policy positions 0.3 and 0.8, respectively, find the number of votes for the candidate A based on voter's ideal positions.
A) 16
B) 17
C) 23
D) 25
![<strong>Use the following distribution of 33 voters at eight different positions over the interval [0, 1] to answer Questions For two candidates A and B with distinct policy positions 0.3 and 0.8, respectively, find the number of votes for the candidate A based on voter's ideal positions.</strong> A) 16 B) 17 C) 23 D) 25](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1043/11eaaa0e_a326_465b_9885_bf0431b2b1dd_TB1043_00_TB1043_00_TB1043_00.jpg)
For two candidates A and B with distinct policy positions 0.3 and 0.8, respectively, find the number of votes for the candidate A based on voter's ideal positions.
A) 16
B) 17
C) 23
D) 25

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Use the following distribution of 32 voters at eight different positions over the interval [0, 1] to answer Questions ![<strong>Use the following distribution of 32 voters at eight different positions over the interval [0, 1] to answer Questions For two candidates A and B with distinct policy positions 0.2 and 0.7, respectively, find the number of votes for the candidate A based on voter's ideal positions.</strong> A) 11 B) 16 C) 19 D) 23](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1043/11eaaa0e_a326_6d6c_9885_21b9436bd932_TB1043_00_TB1043_00.jpg)
For two candidates A and B with distinct policy positions 0.2 and 0.7, respectively, find the number of votes for the candidate A based on voter's ideal positions.
A) 11
B) 16
C) 19
D) 23
![<strong>Use the following distribution of 32 voters at eight different positions over the interval [0, 1] to answer Questions For two candidates A and B with distinct policy positions 0.2 and 0.7, respectively, find the number of votes for the candidate A based on voter's ideal positions.</strong> A) 11 B) 16 C) 19 D) 23](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1043/11eaaa0e_a326_6d6c_9885_21b9436bd932_TB1043_00_TB1043_00.jpg)
For two candidates A and B with distinct policy positions 0.2 and 0.7, respectively, find the number of votes for the candidate A based on voter's ideal positions.
A) 11
B) 16
C) 19
D) 23

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Describe the 2/3-separation opportunity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Give an example of a set of five data that is bimodal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Use the following distribution of 31 voters at seven different positions over the interval [0, 1] to answer Questions ![<strong>Use the following distribution of 31 voters at seven different positions over the interval [0, 1] to answer Questions What is the median of the distribution?</strong> A) 0.3 B) 0.35 C) 0.4 D) 0.47](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1043/11eaaa0e_a326_1f4a_9885_47e1552df8cc_TB1043_00_TB1043_00_TB1043_00.jpg)
What is the median of the distribution?
A) 0.3
B) 0.35
C) 0.4
D) 0.47
![<strong>Use the following distribution of 31 voters at seven different positions over the interval [0, 1] to answer Questions What is the median of the distribution?</strong> A) 0.3 B) 0.35 C) 0.4 D) 0.47](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1043/11eaaa0e_a326_1f4a_9885_47e1552df8cc_TB1043_00_TB1043_00_TB1043_00.jpg)
What is the median of the distribution?
A) 0.3
B) 0.35
C) 0.4
D) 0.47

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Suppose voters are distributed so that they are only located at certain positions along the left-right continuum. What is this type of distribution called?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Use the following distribution of 31 voters at seven different positions over the interval [0, 1] to answer Questions ![<strong>Use the following distribution of 31 voters at seven different positions over the interval [0, 1] to answer Questions For two candidates A and B with distinct policy positions 0.3 and 0.75, respectively, find the number of votes for the candidate A based on voter's ideal positions.</strong> A) 5 B) 10 C) 16 D) 21](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1043/11eaaa0e_a326_1f4a_9885_47e1552df8cc_TB1043_00_TB1043_00_TB1043_00.jpg)
For two candidates A and B with distinct policy positions 0.3 and 0.75, respectively, find the number of votes for the candidate A based on voter's ideal positions.
A) 5
B) 10
C) 16
D) 21
![<strong>Use the following distribution of 31 voters at seven different positions over the interval [0, 1] to answer Questions For two candidates A and B with distinct policy positions 0.3 and 0.75, respectively, find the number of votes for the candidate A based on voter's ideal positions.</strong> A) 5 B) 10 C) 16 D) 21](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1043/11eaaa0e_a326_1f4a_9885_47e1552df8cc_TB1043_00_TB1043_00_TB1043_00.jpg)
For two candidates A and B with distinct policy positions 0.3 and 0.75, respectively, find the number of votes for the candidate A based on voter's ideal positions.
A) 5
B) 10
C) 16
D) 21

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Use the following distribution of 32 voters at eight different positions over the interval [0, 1] to answer Questions ![<strong>Use the following distribution of 32 voters at eight different positions over the interval [0, 1] to answer Questions What is the equilibrium position in a two-candidate election?</strong> A) 0.3 B) 0.4 C) 0.5 D) 0.6](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1043/11eaaa0e_a326_6d6c_9885_21b9436bd932_TB1043_00_TB1043_00.jpg)
What is the equilibrium position in a two-candidate election?
A) 0.3
B) 0.4
C) 0.5
D) 0.6
![<strong>Use the following distribution of 32 voters at eight different positions over the interval [0, 1] to answer Questions What is the equilibrium position in a two-candidate election?</strong> A) 0.3 B) 0.4 C) 0.5 D) 0.6](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1043/11eaaa0e_a326_6d6c_9885_21b9436bd932_TB1043_00_TB1043_00.jpg)
What is the equilibrium position in a two-candidate election?
A) 0.3
B) 0.4
C) 0.5
D) 0.6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Give an example of five data that is unimodal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Use the following distribution of 31 voters at seven different positions over the interval [0, 1] to answer Questions ![<strong>Use the following distribution of 31 voters at seven different positions over the interval [0, 1] to answer Questions What is the equilibrium position in a two-candidate election?</strong> A) 0.3 B) 0.35 C) 0.4 D) 0.47](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1043/11eaaa0e_a326_1f4a_9885_47e1552df8cc_TB1043_00_TB1043_00_TB1043_00.jpg)
What is the equilibrium position in a two-candidate election?
A) 0.3
B) 0.35
C) 0.4
D) 0.47
![<strong>Use the following distribution of 31 voters at seven different positions over the interval [0, 1] to answer Questions What is the equilibrium position in a two-candidate election?</strong> A) 0.3 B) 0.35 C) 0.4 D) 0.47](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1043/11eaaa0e_a326_1f4a_9885_47e1552df8cc_TB1043_00_TB1043_00_TB1043_00.jpg)
What is the equilibrium position in a two-candidate election?
A) 0.3
B) 0.35
C) 0.4
D) 0.47

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Use the following distribution of 33 voters at eight different positions over the interval [0, 1] to answer Questions ![<strong>Use the following distribution of 33 voters at eight different positions over the interval [0, 1] to answer Questions What is the equilibrium position in a two-candidate election?</strong> A) 0.5 B) 0.55 C) 0.56 D) 0.6](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1043/11eaaa0e_a326_465b_9885_bf0431b2b1dd_TB1043_00_TB1043_00_TB1043_00.jpg)
What is the equilibrium position in a two-candidate election?
A) 0.5
B) 0.55
C) 0.56
D) 0.6
![<strong>Use the following distribution of 33 voters at eight different positions over the interval [0, 1] to answer Questions What is the equilibrium position in a two-candidate election?</strong> A) 0.5 B) 0.55 C) 0.56 D) 0.6](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1043/11eaaa0e_a326_465b_9885_bf0431b2b1dd_TB1043_00_TB1043_00_TB1043_00.jpg)
What is the equilibrium position in a two-candidate election?
A) 0.5
B) 0.55
C) 0.56
D) 0.6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Explain the extended median of a discrete distribution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Define an equilibrium position.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Use the following information to answer Questions
Seven board members of a company must decide between two other board members (A and B) for a certain position. The voters are concerned with two issues and their ideal points are represented as ordered pairs: (1, 4), (2, 3), (5, 2), (6, 3), (6, 1), (4, 4), and (3, 3). Assume that A and B announce policy positions of (1, 1) and (6, 4), respectively.
What is the equation of the line which divides the two-dimensional space separating voters preferring A over B from those preferring B over A?
A) QUOTE
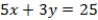
B)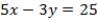
C)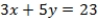
D) QUOTE
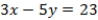
Seven board members of a company must decide between two other board members (A and B) for a certain position. The voters are concerned with two issues and their ideal points are represented as ordered pairs: (1, 4), (2, 3), (5, 2), (6, 3), (6, 1), (4, 4), and (3, 3). Assume that A and B announce policy positions of (1, 1) and (6, 4), respectively.
What is the equation of the line which divides the two-dimensional space separating voters preferring A over B from those preferring B over A?
A) QUOTE

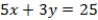
B)
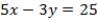
C)
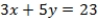
D) QUOTE

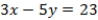

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Use the following information to answer Questions
Seven board members of a company must decide between two other board members (A and B) for a certain position. The voters are concerned with two issues and their ideal points are represented as ordered pairs: (1, 4), (2, 3), (5, 2), (6, 3), (6, 1), (4, 4), and (3, 3). Assume that A and B announce policy positions of (1, 1) and (6, 4), respectively.
What is the midpoint of the two policy positions?
A) (7/2, 5/2)
B) (3, 4)
C) (7/2, 3)
D) (5/2, 3/2)
Seven board members of a company must decide between two other board members (A and B) for a certain position. The voters are concerned with two issues and their ideal points are represented as ordered pairs: (1, 4), (2, 3), (5, 2), (6, 3), (6, 1), (4, 4), and (3, 3). Assume that A and B announce policy positions of (1, 1) and (6, 4), respectively.
What is the midpoint of the two policy positions?
A) (7/2, 5/2)
B) (3, 4)
C) (7/2, 3)
D) (5/2, 3/2)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Use the following information to answer Questions
Seven board members of a company must decide between two other board members (A and B) for a certain position. The voters are concerned with two issues and their ideal points are represented as ordered pairs: (1, 4), (2, 3), (5, 2), (6, 3), (6, 1), (4, 4), and (3, 3). Assume that A and B announce policy positions of (1, 1) and (6, 4), respectively.
How many board members would vote for B based on ideal points?
A) 2
B) 3
C) 4
D) 5
Seven board members of a company must decide between two other board members (A and B) for a certain position. The voters are concerned with two issues and their ideal points are represented as ordered pairs: (1, 4), (2, 3), (5, 2), (6, 3), (6, 1), (4, 4), and (3, 3). Assume that A and B announce policy positions of (1, 1) and (6, 4), respectively.
How many board members would vote for B based on ideal points?
A) 2
B) 3
C) 4
D) 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
A distribution of voters is symmetric and unimodal, and the first two candidates have chosen different positions, A and B, that are equidistant from the median. A is below the median and B is above the median, and two thirds of the voters lie between A and B. To win the election, a third candidate should take a position C that lies:
A) below A.
B) between A and B.
C) above B.
D) nowhere; C cannot win.
A) below A.
B) between A and B.
C) above B.
D) nowhere; C cannot win.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Use the following information to answer Questions
Five board members of a company must decide between two other board members (A and B) for a certain position. The voters are concerned with two issues and their ideal points are represented as ordered pairs: (1, 5), (3, 4), (5, 2), (6, 4), and (6, 2). Assume that A and B announce policy positions of (1, 2) and (5, 4), respectively.
What is the midpoint of the two policy positions?
A) (2, 2)
B) (2, 3)
C) (3, 3)
D) (3, 4)
Five board members of a company must decide between two other board members (A and B) for a certain position. The voters are concerned with two issues and their ideal points are represented as ordered pairs: (1, 5), (3, 4), (5, 2), (6, 4), and (6, 2). Assume that A and B announce policy positions of (1, 2) and (5, 4), respectively.
What is the midpoint of the two policy positions?
A) (2, 2)
B) (2, 3)
C) (3, 3)
D) (3, 4)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Use the following information to answer Questions
Five board members of a company must decide between two other board members (A and B) for a certain position. The voters are concerned with two issues and their ideal points are represented as ordered pairs: (1, 5), (3, 4), (5, 2), (6, 4), and (6, 2). Assume that A and B announce policy positions of (1, 2) and (5, 4), respectively.
Which candidate would win the election?
A) A
B) B
Five board members of a company must decide between two other board members (A and B) for a certain position. The voters are concerned with two issues and their ideal points are represented as ordered pairs: (1, 5), (3, 4), (5, 2), (6, 4), and (6, 2). Assume that A and B announce policy positions of (1, 2) and (5, 4), respectively.
Which candidate would win the election?
A) A
B) B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A candidate selects a point on the horizontal axis of a voter distribution where no position can guarantee a better outcome, no matter what position another candidate adopts. This position is the:
A) median.
B) mean.
C) mode.
D) maximin position.
A) median.
B) mean.
C) mode.
D) maximin position.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Use the following information to answer Questions
Five board members of a company must decide between two other board members (A and B) for a certain position. The voters are concerned with two issues and their ideal points are represented as ordered pairs: (1, 5), (3, 4), (5, 2), (6, 4), and (6, 2). Assume that A and B announce policy positions of (1, 2) and (5, 4), respectively.
How many board members would vote for B based on ideal points?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
Five board members of a company must decide between two other board members (A and B) for a certain position. The voters are concerned with two issues and their ideal points are represented as ordered pairs: (1, 5), (3, 4), (5, 2), (6, 4), and (6, 2). Assume that A and B announce policy positions of (1, 2) and (5, 4), respectively.
How many board members would vote for B based on ideal points?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The point on the horizontal axis of a voter distribution where half of the voters have attitudes that lie to the left and half of the voters have attitudes that lie to the right is the:
A) median.
B) mean.
C) mode.
D) maximin position.
A) median.
B) mean.
C) mode.
D) maximin position.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Use the following information to answer Questions
Five board members of a company must decide between two other board members (A and B) for a certain position. The voters are concerned with two issues and their ideal points are represented as ordered pairs: (1, 5), (3, 4), (5, 2), (6, 4), and (6, 2). Assume that A and B announce policy positions of (1, 2) and (5, 4), respectively.
What is the equation of the line which divides the two-dimensional space separating voters preferring A over B from those preferring B over A?
A)
B) QUOTE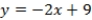
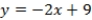
C)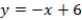
D)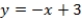
Five board members of a company must decide between two other board members (A and B) for a certain position. The voters are concerned with two issues and their ideal points are represented as ordered pairs: (1, 5), (3, 4), (5, 2), (6, 4), and (6, 2). Assume that A and B announce policy positions of (1, 2) and (5, 4), respectively.
What is the equation of the line which divides the two-dimensional space separating voters preferring A over B from those preferring B over A?
A)

B) QUOTE
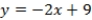
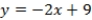
C)
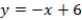
D)
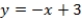

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Use the following information to answer Questions
Five board members of a company must decide between two other board members (A and B) for a certain position. The voters are concerned with two issues and their ideal points are represented as ordered pairs: (1, 5), (3, 4), (5, 2), (6, 4), and (6, 2). Assume that A and B announce policy positions of (1, 2) and (5, 4), respectively.
What is the equation of the line passing through candidates' policy positions?
A) 7?? = 5??+2
B) 3?? = −5??+7
C) 5?? = 3??+2
D) 5?? = −7??+12
Five board members of a company must decide between two other board members (A and B) for a certain position. The voters are concerned with two issues and their ideal points are represented as ordered pairs: (1, 5), (3, 4), (5, 2), (6, 4), and (6, 2). Assume that A and B announce policy positions of (1, 2) and (5, 4), respectively.
What is the equation of the line passing through candidates' policy positions?
A) 7?? = 5??+2
B) 3?? = −5??+7
C) 5?? = 3??+2
D) 5?? = −7??+12

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
What is the smallest value of the extended median if the voters' ideal points are 2, 2, 4, 4, 6, 8, 8, 8, 10, 10?
A) 2
B) 4
C) 6
D) 8
A) 2
B) 4
C) 6
D) 8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
What is 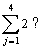
A) 4
B) 8
C) 10
D) 12
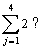
A) 4
B) 8
C) 10
D) 12

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
What is the largest value of the extended median if the voters' ideal points are 2, 2, 4, 4, 6, 8, 8, 8, 10, 10?
A) 4
B) 6
C) 8
D) 10
A) 4
B) 6
C) 8
D) 10

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Use the following information to answer Questions
Seven board members of a company must decide between two other board members (A and B) for a certain position. The voters are concerned with two issues and their ideal points are represented as ordered pairs: (1, 4), (2, 3), (5, 2), (6, 3), (6, 1), (4, 4), and (3, 3). Assume that A and B announce policy positions of (1, 1) and (6, 4), respectively.
Which candidate would win the election based on ideal points?
A) A
B) B
Seven board members of a company must decide between two other board members (A and B) for a certain position. The voters are concerned with two issues and their ideal points are represented as ordered pairs: (1, 4), (2, 3), (5, 2), (6, 3), (6, 1), (4, 4), and (3, 3). Assume that A and B announce policy positions of (1, 1) and (6, 4), respectively.
Which candidate would win the election based on ideal points?
A) A
B) B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Use the following information to answer Questions
Seven board members of a company must decide between two other board members (A and B) for a certain position. The voters are concerned with two issues and their ideal points are represented as ordered pairs: (1, 4), (2, 3), (5, 2), (6, 3), (6, 1), (4, 4), and (3, 3). Assume that A and B announce policy positions of (1, 1) and (6, 4), respectively.
What is the equation of the line passing through candidates' policy positions?
A) QUOTE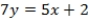
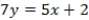
B) QUOTE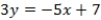
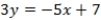
C) QUOTE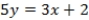
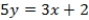
D) QUOTE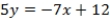
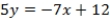
Seven board members of a company must decide between two other board members (A and B) for a certain position. The voters are concerned with two issues and their ideal points are represented as ordered pairs: (1, 4), (2, 3), (5, 2), (6, 3), (6, 1), (4, 4), and (3, 3). Assume that A and B announce policy positions of (1, 1) and (6, 4), respectively.
What is the equation of the line passing through candidates' policy positions?
A) QUOTE
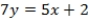
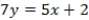
B) QUOTE
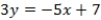
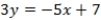
C) QUOTE
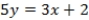
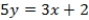
D) QUOTE
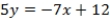
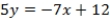

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
A distribution of voters is symmetric and unimodal, and the first two candidates have chosen different positions, A and B, that are equidistant from the median. A is below the median and B is above the median. No more than one third of the voters lie between A and B. To win the election, a third candidate should take a position C that lies:
A) below A.
B) between A and B.
C) above B.
D) nowhere; C cannot win.
A) below A.
B) between A and B.
C) above B.
D) nowhere; C cannot win.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
A peak of a voter distribution is a:
A) median.
B) mean.
C) mode.
D) maximin position.
A) median.
B) mean.
C) mode.
D) maximin position.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which statement is correct for the bent solid line given below? 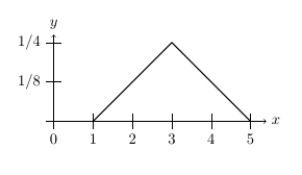
A) It describes a continuous distribution because the bent line is continuous.
B) It does not describe a continuous distribution because the area beneath the bent line is not 1.
C) It describes a continuous distribution because the area beneath the bent line is 1.
D) None of the above.

A) It describes a continuous distribution because the bent line is continuous.
B) It does not describe a continuous distribution because the area beneath the bent line is not 1.
C) It describes a continuous distribution because the area beneath the bent line is 1.
D) None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Which statement is correct for the curve given below? 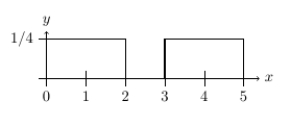
A) It describes a continuous distribution because the area beneath the curve is 1.
B) It does not describe a continuous distribution because the area beneath the curve is not 1.
C) It does not describe a continuous distribution because the curve is not continuous.
D) None of the above.

A) It describes a continuous distribution because the area beneath the curve is 1.
B) It does not describe a continuous distribution because the area beneath the curve is not 1.
C) It does not describe a continuous distribution because the curve is not continuous.
D) None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Use the following to answer Questions
A distribution of voters is uniform over [0, 1]. Candidates A and B have already entered the election and have chosen positions at 1/4 and 3/4, respectively.
If C enters at 1, what fraction of the vote does the winner receive?
A) 1/3
B) 1/2
C) 11/24
D) 7/12
A distribution of voters is uniform over [0, 1]. Candidates A and B have already entered the election and have chosen positions at 1/4 and 3/4, respectively.
If C enters at 1, what fraction of the vote does the winner receive?
A) 1/3
B) 1/2
C) 11/24
D) 7/12

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Consider the following distribution of 34 voters at eight different positions over the interval [0, 1]. ![<strong>Consider the following distribution of 34 voters at eight different positions over the interval [0, 1]. This distribution of voters is best described as:</strong> A) skewed left. B) skewed right. C) symmetric. D) bimodal.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1043/11eaaa0e_a32b_ebc7_9885_1b3a9f364d1f_TB1043_00.jpg) This distribution of voters is best described as:
This distribution of voters is best described as:
A) skewed left.
B) skewed right.
C) symmetric.
D) bimodal.
![<strong>Consider the following distribution of 34 voters at eight different positions over the interval [0, 1]. This distribution of voters is best described as:</strong> A) skewed left. B) skewed right. C) symmetric. D) bimodal.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1043/11eaaa0e_a32b_ebc7_9885_1b3a9f364d1f_TB1043_00.jpg) This distribution of voters is best described as:
This distribution of voters is best described as:A) skewed left.
B) skewed right.
C) symmetric.
D) bimodal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Use the following information to answer Questions
Consider the following distribution of 34 voters at eight different positions over the interval [0, 1].![<strong>Use the following information to answer Questions Consider the following distribution of 34 voters at eight different positions over the interval [0, 1]. Candidate A announces a policy position of 0.3 and Candidate B announces a policy position of 0.8. Is there a 2/3-separation opportunity for a third Candidate C to enter the race?</strong> A) Yes B) No](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1043/11eaaa0e_a32c_8809_9885_5db2396760f1_TB1043_00_TB1043_00_TB1043_00_TB1043_00.jpg)
Candidate A announces a policy position of 0.3 and Candidate B announces a policy position of 0.8. Is there a 2/3-separation opportunity for a third Candidate C to enter the race?
A) Yes
B) No
Consider the following distribution of 34 voters at eight different positions over the interval [0, 1].
![<strong>Use the following information to answer Questions Consider the following distribution of 34 voters at eight different positions over the interval [0, 1]. Candidate A announces a policy position of 0.3 and Candidate B announces a policy position of 0.8. Is there a 2/3-separation opportunity for a third Candidate C to enter the race?</strong> A) Yes B) No](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1043/11eaaa0e_a32c_8809_9885_5db2396760f1_TB1043_00_TB1043_00_TB1043_00_TB1043_00.jpg)
Candidate A announces a policy position of 0.3 and Candidate B announces a policy position of 0.8. Is there a 2/3-separation opportunity for a third Candidate C to enter the race?
A) Yes
B) No

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Use the following information to answer Questions
Consider the following distribution of 35 voters at eight different positions over the interval [0, 1].![<strong>Use the following information to answer Questions Consider the following distribution of 35 voters at eight different positions over the interval [0, 1]. What is the median position of the voters?</strong> A) 0.45 B) 0.5 C) 0.55 D) 0.6](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1043/11eaaa0e_a32b_2875_9885_1f2191f5ac13_TB1043_00_TB1043_00_TB1043_00.jpg)
What is the median position of the voters?
A) 0.45
B) 0.5
C) 0.55
D) 0.6
Consider the following distribution of 35 voters at eight different positions over the interval [0, 1].
![<strong>Use the following information to answer Questions Consider the following distribution of 35 voters at eight different positions over the interval [0, 1]. What is the median position of the voters?</strong> A) 0.45 B) 0.5 C) 0.55 D) 0.6](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1043/11eaaa0e_a32b_2875_9885_1f2191f5ac13_TB1043_00_TB1043_00_TB1043_00.jpg)
What is the median position of the voters?
A) 0.45
B) 0.5
C) 0.55
D) 0.6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Use the following to answer Questions
Suppose that the continuous distribution of voters' ideal points is the bent solid line below.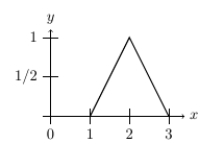
Assume that Candidate A and Candidate B's policy positions are 1.5 and 2.5. If Candidate C enters at 1, what fraction of the vote does the winner receive?
A) 9/32
B) 7/16
C) 1/2
D) 9/16
Suppose that the continuous distribution of voters' ideal points is the bent solid line below.

Assume that Candidate A and Candidate B's policy positions are 1.5 and 2.5. If Candidate C enters at 1, what fraction of the vote does the winner receive?
A) 9/32
B) 7/16
C) 1/2
D) 9/16

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Use the following to answer Questions
Suppose that the continuous distribution of voters' ideal points is the bent solid line below.
Assuming that Candidate A's policy position is 1.5 and Candidate B announces a policy position of 2.3, which voters would vote for Candidate B?
A) Voters with ideal points between 1.5 and 2.3
B) Voters with ideal points between 1.5 and 3
C) Voters with ideal points between 2 and 2.3
D) Voters with ideal points between 1.9 and 3
Suppose that the continuous distribution of voters' ideal points is the bent solid line below.

Assuming that Candidate A's policy position is 1.5 and Candidate B announces a policy position of 2.3, which voters would vote for Candidate B?
A) Voters with ideal points between 1.5 and 2.3
B) Voters with ideal points between 1.5 and 3
C) Voters with ideal points between 2 and 2.3
D) Voters with ideal points between 1.9 and 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Use the following information to answer Questions
Consider the following distribution of 34 voters at eight different positions over the interval [0, 1].![<strong>Use the following information to answer Questions Consider the following distribution of 34 voters at eight different positions over the interval [0, 1]. Candidate A announces a policy position of 0.3 and Candidate B announces a policy position of 0.8. Is there a 2/3-separation opportunity for a third Candidate C to enter the race?</strong> A) Yes B) No](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1043/11eaaa0e_a32c_12d8_9885_a755fa8cec2b_TB1043_00_TB1043_00_TB1043_00.jpg)
Candidate A announces a policy position of 0.3 and Candidate B announces a policy position of 0.8. Is there a 2/3-separation opportunity for a third Candidate C to enter the race?
A) Yes
B) No
Consider the following distribution of 34 voters at eight different positions over the interval [0, 1].
![<strong>Use the following information to answer Questions Consider the following distribution of 34 voters at eight different positions over the interval [0, 1]. Candidate A announces a policy position of 0.3 and Candidate B announces a policy position of 0.8. Is there a 2/3-separation opportunity for a third Candidate C to enter the race?</strong> A) Yes B) No](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1043/11eaaa0e_a32c_12d8_9885_a755fa8cec2b_TB1043_00_TB1043_00_TB1043_00.jpg)
Candidate A announces a policy position of 0.3 and Candidate B announces a policy position of 0.8. Is there a 2/3-separation opportunity for a third Candidate C to enter the race?
A) Yes
B) No

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Use the following to answer Questions
A distribution of voters is uniform over [0, 1]. Candidates A and B have already entered the election and have chosen positions at 1/4 and 3/4, respectively.
If C enters at 1/3, what fraction of the vote does the winner receive?
A) 2/3
B) 3/4
C) 11/24
D) 7/12
A distribution of voters is uniform over [0, 1]. Candidates A and B have already entered the election and have chosen positions at 1/4 and 3/4, respectively.
If C enters at 1/3, what fraction of the vote does the winner receive?
A) 2/3
B) 3/4
C) 11/24
D) 7/12

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Use the following to answer Questions
A distribution of voters is uniform over [0, 1]. Candidates A and B have already entered the election and have chosen positions at 1/4 and 3/4, respectively.
If C enters at 1, who receives a plurality?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) None of the candidates
A distribution of voters is uniform over [0, 1]. Candidates A and B have already entered the election and have chosen positions at 1/4 and 3/4, respectively.
If C enters at 1, who receives a plurality?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) None of the candidates

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Use the following to answer Questions
Suppose that the continuous distribution of voters' ideal points is the bent solid line below.
Assume that Candidate A and Candidate B's policy positions are 1.5 and 2.5. If Candidate C enters at 2, what fraction of the vote does the winner receive?
A) 9/32
B) 7/16
C) 1/2
D) 9/16
Suppose that the continuous distribution of voters' ideal points is the bent solid line below.

Assume that Candidate A and Candidate B's policy positions are 1.5 and 2.5. If Candidate C enters at 2, what fraction of the vote does the winner receive?
A) 9/32
B) 7/16
C) 1/2
D) 9/16

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Consider the following distribution of 35 voters at eight different positions over the interval [0, 1]. ![<strong>Consider the following distribution of 35 voters at eight different positions over the interval [0, 1]. This distribution of voters is best described as:</strong> A) skewed left. B) skewed right. C) symmetric. D) bimodal.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1043/11eaaa0e_a32b_9da6_9885_2f7b1ffe0c25_TB1043_00.jpg) This distribution of voters is best described as:
This distribution of voters is best described as:
A) skewed left.
B) skewed right.
C) symmetric.
D) bimodal.
![<strong>Consider the following distribution of 35 voters at eight different positions over the interval [0, 1]. This distribution of voters is best described as:</strong> A) skewed left. B) skewed right. C) symmetric. D) bimodal.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1043/11eaaa0e_a32b_9da6_9885_2f7b1ffe0c25_TB1043_00.jpg) This distribution of voters is best described as:
This distribution of voters is best described as:A) skewed left.
B) skewed right.
C) symmetric.
D) bimodal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Use the following information to answer Questions
Consider the following distribution of 35 voters at eight different positions over the interval [0, 1].![<strong>Use the following information to answer Questions Consider the following distribution of 35 voters at eight different positions over the interval [0, 1]. This distribution of voters is best described as:</strong> A) skewed left. B) skewed right. C) symmetric. D) bimodal.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1043/11eaaa0e_a32b_2875_9885_1f2191f5ac13_TB1043_00_TB1043_00_TB1043_00.jpg)
This distribution of voters is best described as:
A) skewed left.
B) skewed right.
C) symmetric.
D) bimodal.
Consider the following distribution of 35 voters at eight different positions over the interval [0, 1].
![<strong>Use the following information to answer Questions Consider the following distribution of 35 voters at eight different positions over the interval [0, 1]. This distribution of voters is best described as:</strong> A) skewed left. B) skewed right. C) symmetric. D) bimodal.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1043/11eaaa0e_a32b_2875_9885_1f2191f5ac13_TB1043_00_TB1043_00_TB1043_00.jpg)
This distribution of voters is best described as:
A) skewed left.
B) skewed right.
C) symmetric.
D) bimodal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Use the following to answer Questions
Suppose that the continuous distribution of voters' ideal points is the bent solid line below.
Assume that Candidate A and Candidate B's policy positions are 1.5 and 2.5. If Candidate C enters at 2, who would win the election?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) A and B tie.
Suppose that the continuous distribution of voters' ideal points is the bent solid line below.

Assume that Candidate A and Candidate B's policy positions are 1.5 and 2.5. If Candidate C enters at 2, who would win the election?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) A and B tie.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Use the following information to answer Questions
Consider the following distribution of 34 voters at eight different positions over the interval [0, 1].![<strong>Use the following information to answer Questions Consider the following distribution of 34 voters at eight different positions over the interval [0, 1]. This distribution of voters is best described as:</strong> A) skewed left. B) skewed right. C) symmetric. D) bimodal.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1043/11eaaa0e_a32c_8809_9885_5db2396760f1_TB1043_00_TB1043_00_TB1043_00_TB1043_00.jpg)
This distribution of voters is best described as:
A) skewed left.
B) skewed right.
C) symmetric.
D) bimodal.
Consider the following distribution of 34 voters at eight different positions over the interval [0, 1].
![<strong>Use the following information to answer Questions Consider the following distribution of 34 voters at eight different positions over the interval [0, 1]. This distribution of voters is best described as:</strong> A) skewed left. B) skewed right. C) symmetric. D) bimodal.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1043/11eaaa0e_a32c_8809_9885_5db2396760f1_TB1043_00_TB1043_00_TB1043_00_TB1043_00.jpg)
This distribution of voters is best described as:
A) skewed left.
B) skewed right.
C) symmetric.
D) bimodal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Use the following to answer Questions
A distribution of voters is uniform over [0, 1]. Candidates A and B have already entered the election and have chosen positions at 1/4 and 3/4, respectively.
If C enters at 1/3, who receives a plurality?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
A distribution of voters is uniform over [0, 1]. Candidates A and B have already entered the election and have chosen positions at 1/4 and 3/4, respectively.
If C enters at 1/3, who receives a plurality?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Use the following information to answer Questions
Consider the following distribution of 35 voters at eight different positions over the interval [0, 1].![<strong>Use the following information to answer Questions Consider the following distribution of 35 voters at eight different positions over the interval [0, 1]. Candidate A announces a policy position of 0.3 and Candidate B announces a policy position of 0.7. Is there a 2/3-separation opportunity for a third Candidate C to enter the race?</strong> A) Yes B) No](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1043/11eaaa0e_a32b_2875_9885_1f2191f5ac13_TB1043_00_TB1043_00_TB1043_00.jpg)
Candidate A announces a policy position of 0.3 and Candidate B announces a policy position of 0.7. Is there a 2/3-separation opportunity for a third Candidate C to enter the race?
A) Yes
B) No
Consider the following distribution of 35 voters at eight different positions over the interval [0, 1].
![<strong>Use the following information to answer Questions Consider the following distribution of 35 voters at eight different positions over the interval [0, 1]. Candidate A announces a policy position of 0.3 and Candidate B announces a policy position of 0.7. Is there a 2/3-separation opportunity for a third Candidate C to enter the race?</strong> A) Yes B) No](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1043/11eaaa0e_a32b_2875_9885_1f2191f5ac13_TB1043_00_TB1043_00_TB1043_00.jpg)
Candidate A announces a policy position of 0.3 and Candidate B announces a policy position of 0.7. Is there a 2/3-separation opportunity for a third Candidate C to enter the race?
A) Yes
B) No

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Use the following information to answer Questions
Consider the following distribution of 34 voters at eight different positions over the interval [0, 1].![<strong>Use the following information to answer Questions Consider the following distribution of 34 voters at eight different positions over the interval [0, 1]. This distribution of voters is best described as:</strong> A) skewed left. B) skewed right. C) symmetric. D) bimodal.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1043/11eaaa0e_a32c_12d8_9885_a755fa8cec2b_TB1043_00_TB1043_00_TB1043_00.jpg)
This distribution of voters is best described as:
A) skewed left.
B) skewed right.
C) symmetric.
D) bimodal.
Consider the following distribution of 34 voters at eight different positions over the interval [0, 1].
![<strong>Use the following information to answer Questions Consider the following distribution of 34 voters at eight different positions over the interval [0, 1]. This distribution of voters is best described as:</strong> A) skewed left. B) skewed right. C) symmetric. D) bimodal.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1043/11eaaa0e_a32c_12d8_9885_a755fa8cec2b_TB1043_00_TB1043_00_TB1043_00.jpg)
This distribution of voters is best described as:
A) skewed left.
B) skewed right.
C) symmetric.
D) bimodal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Use the following to answer Questions
A distribution of voters is uniform over [0, 1]. Candidates A and B have already entered the election and have chosen positions at 1/4 and 3/4, respectively.
If C enters at 1/2, who wins the election?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) A and B tie.
A distribution of voters is uniform over [0, 1]. Candidates A and B have already entered the election and have chosen positions at 1/4 and 3/4, respectively.
If C enters at 1/2, who wins the election?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) A and B tie.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Use the following to answer Questions
Suppose that the continuous distribution of voters' ideal points is the bent solid line below.
Assuming that Candidate A's policy position is 2.5, if Candidate B announces a policy position between 1 and 1.5, then who will be the winner of the election?
A) A
B) B
C) A and B tie.
D) No conclusion can be made.
Suppose that the continuous distribution of voters' ideal points is the bent solid line below.

Assuming that Candidate A's policy position is 2.5, if Candidate B announces a policy position between 1 and 1.5, then who will be the winner of the election?
A) A
B) B
C) A and B tie.
D) No conclusion can be made.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Use the following information to answer Questions
Consider the following distribution of 34 voters at eight different positions over the interval [0, 1].![<strong>Use the following information to answer Questions Consider the following distribution of 34 voters at eight different positions over the interval [0, 1]. Assume that Candidate A and Candidate B's policy positions are 0.3 and 0.8. If Candidate C enters at 0.55, what fraction of the vote does the winner receive?</strong> A) 6/17 B) 7/17 C) 19/34 D) 12/17](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1043/11eaaa0e_a32c_12d8_9885_a755fa8cec2b_TB1043_00_TB1043_00_TB1043_00.jpg)
Assume that Candidate A and Candidate B's policy positions are 0.3 and 0.8. If Candidate C enters at 0.55, what fraction of the vote does the winner receive?
A) 6/17
B) 7/17
C) 19/34
D) 12/17
Consider the following distribution of 34 voters at eight different positions over the interval [0, 1].
![<strong>Use the following information to answer Questions Consider the following distribution of 34 voters at eight different positions over the interval [0, 1]. Assume that Candidate A and Candidate B's policy positions are 0.3 and 0.8. If Candidate C enters at 0.55, what fraction of the vote does the winner receive?</strong> A) 6/17 B) 7/17 C) 19/34 D) 12/17](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1043/11eaaa0e_a32c_12d8_9885_a755fa8cec2b_TB1043_00_TB1043_00_TB1043_00.jpg)
Assume that Candidate A and Candidate B's policy positions are 0.3 and 0.8. If Candidate C enters at 0.55, what fraction of the vote does the winner receive?
A) 6/17
B) 7/17
C) 19/34
D) 12/17

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



