Deck 5: Measuring the Economys Output
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/183
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 5: Measuring the Economys Output
1
Gross domestic product (GDP) measures and reports output:
A) as an index number.
B) in percentage terms.
C) in dollar amounts.
D) in quantities of physical units (for example, kilos, litres, and bushels).
A) as an index number.
B) in percentage terms.
C) in dollar amounts.
D) in quantities of physical units (for example, kilos, litres, and bushels).
in dollar amounts.
2
Assume a manufacturer of stereo speakers purchases $40 worth of components for each speaker. The completed speaker sells for $70. The value added by the manufacturer for each speaker is:
A) $110.
B) $30.
C) $40.
D) $70.
A) $110.
B) $30.
C) $40.
D) $70.
$30.
3
Which of the following is a final good or service?
A) diesel fuel bought for a delivery truck
B) fertilizer purchased by a farm supplier
C) a haircut
D) Chevrolet windows purchased by a General Motors assembly plant
A) diesel fuel bought for a delivery truck
B) fertilizer purchased by a farm supplier
C) a haircut
D) Chevrolet windows purchased by a General Motors assembly plant
a haircut
4
GDP includes:
A) neither intermediate nor final goods.
B) both intermediate and final goods.
C) intermediate, but not final, goods.
D) final, but not intermediate, goods.
A) neither intermediate nor final goods.
B) both intermediate and final goods.
C) intermediate, but not final, goods.
D) final, but not intermediate, goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The GDP is the:
A) monetary value of all final goods and services produced within a nation in a particular year.
B) national income minus all non-income charges against output.
C) monetary value of all economic resources used in producing a year's output.
D) monetary value of all goods and services, final and intermediate, produced in a specific year.
A) monetary value of all final goods and services produced within a nation in a particular year.
B) national income minus all non-income charges against output.
C) monetary value of all economic resources used in producing a year's output.
D) monetary value of all goods and services, final and intermediate, produced in a specific year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
"Value added" refers to:
A) any increase in GDP which has been adjusted for adverse environmental effects.
B) the excess of gross investment over net investment.
C) the difference between the value of a firm's output and the value of the inputs it has purchased from others.
D) the portion of any increase in GDP which is caused by inflation as opposed to an increase in real output.
A) any increase in GDP which has been adjusted for adverse environmental effects.
B) the excess of gross investment over net investment.
C) the difference between the value of a firm's output and the value of the inputs it has purchased from others.
D) the portion of any increase in GDP which is caused by inflation as opposed to an increase in real output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
National income accountants can avoid multiple counting by:
A) including transfers in their calculations.
B) counting both intermediate and final goods.
C) only counting final goods.
D) only counting intermediate goods.
A) including transfers in their calculations.
B) counting both intermediate and final goods.
C) only counting final goods.
D) only counting intermediate goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
If all the final goods and intermediate goods and services were included in GDP:
A) the GDP would then have to be deflated for changes in the price level.
B) nominal GDP would exceed real GDP.
C) the GDP would be overstated.
D) the GDP would be understated.
A) the GDP would then have to be deflated for changes in the price level.
B) nominal GDP would exceed real GDP.
C) the GDP would be overstated.
D) the GDP would be understated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The term "final goods and services" refers to:
A) goods and services which are unsold and therefore added to inventories.
B) goods and services whose value has been adjusted for changes in the price level.
C) goods and services purchased by ultimate users, as opposed to resale or further processing.
D) the excess of Canadians exports over Canadians imports.
A) goods and services which are unsold and therefore added to inventories.
B) goods and services whose value has been adjusted for changes in the price level.
C) goods and services purchased by ultimate users, as opposed to resale or further processing.
D) the excess of Canadians exports over Canadians imports.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which is included in GDP?
A) used autos purchased by consumers
B) transfer payments
C) telephone service for a home
D) bread for a restaurant
A) used autos purchased by consumers
B) transfer payments
C) telephone service for a home
D) bread for a restaurant

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
By summing the dollar value of all market transactions in the economy we would:
A) be determining the market value of all resources used in the production process.
B) obtain a sum substantially larger than the GDP.
C) be determining value added for the economy.
D) be measuring GDP.
A) be determining the market value of all resources used in the production process.
B) obtain a sum substantially larger than the GDP.
C) be determining value added for the economy.
D) be measuring GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
GDP is the total market value of:
A) all expenditures on natural resources, labor, and capital goods in an economy in a given year.
B) all expenditures on consumption, investment, and net exports in an economy in a given year.
C) all intermediate goods and services produced in an economy in a given year.
D) all final goods and services produced in an economy in a given year.
A) all expenditures on natural resources, labor, and capital goods in an economy in a given year.
B) all expenditures on consumption, investment, and net exports in an economy in a given year.
C) all intermediate goods and services produced in an economy in a given year.
D) all final goods and services produced in an economy in a given year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
GDP may be defined as:
A) the monetary value of all goods and services (final, intermediate, and non-market) produced in a given year.
B) total resource income less taxes, saving, and spending on exports.
C) the economic value of all economic resources used in the production of a year's output.
D) the market value of all final goods and services produced within country in a specific year.
A) the monetary value of all goods and services (final, intermediate, and non-market) produced in a given year.
B) total resource income less taxes, saving, and spending on exports.
C) the economic value of all economic resources used in the production of a year's output.
D) the market value of all final goods and services produced within country in a specific year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following is an intermediate good?
A) the purchase of gasoline for a ski trip to B.C
B) the purchase of a pizza by a college or university student
C) the purchase of baseball bats by a professional baseball team
D) the purchase of jogging shoes by a professor
A) the purchase of gasoline for a ski trip to B.C
B) the purchase of a pizza by a college or university student
C) the purchase of baseball bats by a professional baseball team
D) the purchase of jogging shoes by a professor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A nation's gross domestic product (GDP):
A) is the dollar value of the total output produced within the borders of the nation.
B) is the dollar value of the total output produced by its citizens, regardless of where they are living.
C) can be found by summing C + In + S + Xn.
D) is always some amount less than its C + Ig + G + Xn.
A) is the dollar value of the total output produced within the borders of the nation.
B) is the dollar value of the total output produced by its citizens, regardless of where they are living.
C) can be found by summing C + In + S + Xn.
D) is always some amount less than its C + Ig + G + Xn.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
An example of an intermediate good or service would be:
A) bricks bought by a homeowner for constructing a patio.
B) sacks of groceries bought by a dentist for his family.
C) a car bought by a household for commuting to work.
D) a desk bought by an accountant for her office.
A) bricks bought by a homeowner for constructing a patio.
B) sacks of groceries bought by a dentist for his family.
C) a car bought by a household for commuting to work.
D) a desk bought by an accountant for her office.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
An example of a final good in national income accounts would be new:
A) lawn mowers purchased by Cut-rite Mowers.
B) flowers purchased by homeowner Lenny Davis.
C) chemicals purchased by Green Grass Lawn Care.
D) trees purchased by Wendy Lee's Garden Center.
A) lawn mowers purchased by Cut-rite Mowers.
B) flowers purchased by homeowner Lenny Davis.
C) chemicals purchased by Green Grass Lawn Care.
D) trees purchased by Wendy Lee's Garden Center.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Subtracting the purchase of intermediate products from the value of the sales of final products determines the amount of:
A) net investment for a business.
B) profit and cost.
C) value added from the economic activity.
D) surplus or deficit from the economic activity.
A) net investment for a business.
B) profit and cost.
C) value added from the economic activity.
D) surplus or deficit from the economic activity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
A business buys $5,000 worth of resources to produce a product. The business makes 100 units of the product and each of them sells for $65. The value added by the business to these products is:
A) $5,000.
B) $6,500.
C) $1,000.
D) $1,500.
A) $5,000.
B) $6,500.
C) $1,000.
D) $1,500.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Suppose the total market value of all final goods and services produced in a particular country in 2000 is $600 billion and the total market value of final goods and services sold is $525 billion. We can conclude that:
A) GDP in 2000 is $525 billion.
B) NDI in 2000 is $525 billion.
C) GDP in 2000 is $600 billion.
D) inventories in 2000 fell by $75 billion.
A) GDP in 2000 is $525 billion.
B) NDI in 2000 is $525 billion.
C) GDP in 2000 is $600 billion.
D) inventories in 2000 fell by $75 billion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Tom Atoe grows tomatoes for home consumption. This activity is:
A) excluded from GDP in order to avoid double counting.
B) excluded from GDP because an intermediate good is involved.
C) productive but is excluded from GDP because no market transaction occurs.
D) included in GDP because it reflects production.
A) excluded from GDP in order to avoid double counting.
B) excluded from GDP because an intermediate good is involved.
C) productive but is excluded from GDP because no market transaction occurs.
D) included in GDP because it reflects production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following is not an economic investment?
A) the purchase of a drill press by the Ajax Manufacturing Company
B) the purchase of 100 shares of Bell Canada by a retired business executive
C) construction of a suburban housing project
D) the piling up of inventories on a grocer's shelf
A) the purchase of a drill press by the Ajax Manufacturing Company
B) the purchase of 100 shares of Bell Canada by a retired business executive
C) construction of a suburban housing project
D) the piling up of inventories on a grocer's shelf

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A nation's gross domestic product (GDP) by the expenditure approach:
A) can be found by summing C + Ig + G + Xn.
B) is the dollar value of the total output produced by its citizens, regardless of where they are living.
C) can be found by summing C + S + G + Xn.
D) is always some amount less than its NDI.
A) can be found by summing C + Ig + G + Xn.
B) is the dollar value of the total output produced by its citizens, regardless of where they are living.
C) can be found by summing C + S + G + Xn.
D) is always some amount less than its NDI.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Value added is the value of a firm's output minus:
A) the value of intermediate goods purchased from other firms.
B) the compensation it pays to employees.
C) the value of its capital goods.
D) its depreciation.
A) the value of intermediate goods purchased from other firms.
B) the compensation it pays to employees.
C) the value of its capital goods.
D) its depreciation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Subtracting the purchase of intermediate products from the value of the sales of final products determines the amount of:
A) net investment for a business.
B) profit and cost.
C) value added from the economic activity.
D) surplus or deficit from the economic activity.
A) net investment for a business.
B) profit and cost.
C) value added from the economic activity.
D) surplus or deficit from the economic activity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Transfer payments are:
A) excluded when calculating GDP because they only reflect inflation.
B) excluded when calculating GDP because they do not reflect current production.
C) included when calculating GDP because they are a category of investment spending.
D) included when calculating GDP because they increase the spending of recipients.
A) excluded when calculating GDP because they only reflect inflation.
B) excluded when calculating GDP because they do not reflect current production.
C) included when calculating GDP because they are a category of investment spending.
D) included when calculating GDP because they increase the spending of recipients.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The largest component of total expenditures in Canada is:
A) net exports.
B) government purchases.
C) consumption.
D) gross investment.
A) net exports.
B) government purchases.
C) consumption.
D) gross investment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
In calculating GDP, governmental transfer payments, such as welfare payments, are:
A) not counted.
B) counted as investment spending.
C) counted as government spending.
D) counted as consumption spending.
A) not counted.
B) counted as investment spending.
C) counted as government spending.
D) counted as consumption spending.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The value added by firms A-E from the production of the product described below is: 
A) $3,000.
B) $3,800.
C) $6,500.
D) $10,300.

A) $3,000.
B) $3,800.
C) $6,500.
D) $10,300.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
As defined in national income accounting, investment includes:
A) business expenditures on machinery and equipment.
B) all consumption.
C) imports, but not exports.
D) all nonfood items.
A) business expenditures on machinery and equipment.
B) all consumption.
C) imports, but not exports.
D) all nonfood items.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
By summing the values added at each stage in the production of some good we obtain:
A) the price of that good.
B) the total income generated by that good's production.
C) the total cost (including profits) of that product.
D) all of the above.
A) the price of that good.
B) the total income generated by that good's production.
C) the total cost (including profits) of that product.
D) all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
In calculating GDP by the expenditure approach, we sum up:
A) consumption, investment, government purchases, exports, and imports.
B) investment, government purchases, consumption, and net exports.
C) consumption, investment, wages, and rents.
D) consumption, investment, government purchases, and imports.
A) consumption, investment, government purchases, exports, and imports.
B) investment, government purchases, consumption, and net exports.
C) consumption, investment, wages, and rents.
D) consumption, investment, government purchases, and imports.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of the following do national income accountants consider to be "investment"?
A) the purchase of an automobile for private, non-business use
B) the purchase of a new house
C) the purchase of corporate bonds
D) the purchase of gold coins
A) the purchase of an automobile for private, non-business use
B) the purchase of a new house
C) the purchase of corporate bonds
D) the purchase of gold coins

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Economists define investment to include:
A) any increase in business inventories.
B) the addition of cash to a savings account.
C) the purchase of common or preferred stock.
D) the purchase of any durable good, for example, an automobile or a refrigerator.
A) any increase in business inventories.
B) the addition of cash to a savings account.
C) the purchase of common or preferred stock.
D) the purchase of any durable good, for example, an automobile or a refrigerator.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Setup Corporation buys $100,000 of sand, rock, and cement to produce ready-mix concrete. It sells 10,000 cubic yards of concrete at $30 a cubic yard. The value added by Setup Corporation is:
A) $200,000.
B) $100,000.
C) $300,000.
D) zero dollars.
A) $200,000.
B) $100,000.
C) $300,000.
D) zero dollars.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
A distinguishing characteristic of public transfer payments is that:
A) they are used to subsidize the major transportation carriers to reduce transportation costs.
B) they are counted as part of government purchases in the calculation of the gross domestic product.
C) there is a tax on the amount of the subsidy above a certain income level.
D) the recipients make no contribution to current production in return for them.
A) they are used to subsidize the major transportation carriers to reduce transportation costs.
B) they are counted as part of government purchases in the calculation of the gross domestic product.
C) there is a tax on the amount of the subsidy above a certain income level.
D) the recipients make no contribution to current production in return for them.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Suppose Smith pays $100 to Jones.
A) We can say with certainty that the GDP has increased by $100.
B) We can say with certainty that the GDP has increased, but we cannot determine the amount.
C) We can say with certainty that the nominal GDP has increased, but we can't say whether real GDP has increased or decreased.
D) We need more information to determine whether GDP has changed.
A) We can say with certainty that the GDP has increased by $100.
B) We can say with certainty that the GDP has increased, but we cannot determine the amount.
C) We can say with certainty that the nominal GDP has increased, but we can't say whether real GDP has increased or decreased.
D) We need more information to determine whether GDP has changed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
In calculating GDP by the income approach, we should sum up:
A) wages, consumption, investment and rent.
B) wages, rent, interest and profit income.
C) wages, interest, investment, and exports.
D) wages, profit income, investment, and consumption.
A) wages, consumption, investment and rent.
B) wages, rent, interest and profit income.
C) wages, interest, investment, and exports.
D) wages, profit income, investment, and consumption.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
A business buys $7,000 worth of resources to produce a product. The business makes 150 units of the product and each of them sells for $90. The value added by the business to these products is:
A) $13,500.
B) $6,500.
C) $7,000.
D) $6,850.
A) $13,500.
B) $6,500.
C) $7,000.
D) $6,850.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
GDP excludes expenditures by:
A) businesses on pollution control equipment.
B) business for travel and entertainment.
C) government on military hardware.
D) consumers on used automobiles.
A) businesses on pollution control equipment.
B) business for travel and entertainment.
C) government on military hardware.
D) consumers on used automobiles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
From an economist's perspective, which is not considered to be an investment?
A) construction of a new factory
B) purchase of shares of company stock
C) the building of an apartment complex
D) additions to inventories at steel plants
A) construction of a new factory
B) purchase of shares of company stock
C) the building of an apartment complex
D) additions to inventories at steel plants

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Net investment refers to:
A) the amount of machinery and equipment used up in producing GDP in a specific year.
B) the difference between the market value and book value of outstanding capital stock.
C) gross domestic investment less net exports.
D) gross investment less consumption of fixed capital.
A) the amount of machinery and equipment used up in producing GDP in a specific year.
B) the difference between the market value and book value of outstanding capital stock.
C) gross domestic investment less net exports.
D) gross investment less consumption of fixed capital.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
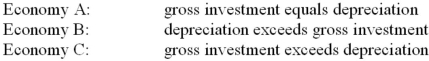
Refer to the above information. Negative net investment is occurring in:
A) economy A only.
B) economy B only.
C) economy C only.
D) economies A and B only.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
If the economy adds to its inventory of goods during 2012:
A) gross investment will exceed net investment by the amount of the inventory increase.
B) this amount should be ignored in calculating 2012's GDP.
C) this amount should be subtracted in calculating 2012's GDP.
D) this amount should be included in calculating 2012's GDP.
A) gross investment will exceed net investment by the amount of the inventory increase.
B) this amount should be ignored in calculating 2012's GDP.
C) this amount should be subtracted in calculating 2012's GDP.
D) this amount should be included in calculating 2012's GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Gross investment refers to:
A) private investment minus public investment.
B) net investment plus replacement investment.
C) net investment after it has been "inflated" for changes in the price level.
D) net investment plus net exports.
A) private investment minus public investment.
B) net investment plus replacement investment.
C) net investment after it has been "inflated" for changes in the price level.
D) net investment plus net exports.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
In an economy experiencing a declining production capacity:
A) the nation's stock of capital goods is expanding.
B) net exports are necessarily zero.
C) Net Investment exceeds GDP.
D) depreciation exceeds gross investment.
A) the nation's stock of capital goods is expanding.
B) net exports are necessarily zero.
C) Net Investment exceeds GDP.
D) depreciation exceeds gross investment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
In November 2012, General Motors produced an automobile that was delivered to a local dealership in December 2012. The auto was sold to Sharon Smith for personal use in February of 2013. Following national income accounting practices, this auto would be counted as:
A) consumption in 2012 and consumption in 2012.
B) consumption in 2012 and investment in 2013.
C) disinvestment in 2012 and consumption in 2013.
D) investment in 2012 and disinvestment in 2013.
A) consumption in 2012 and consumption in 2012.
B) consumption in 2012 and investment in 2013.
C) disinvestment in 2012 and consumption in 2013.
D) investment in 2012 and disinvestment in 2013.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
In 1933 net investment was minus $208 million. This meant that:
A) gross investment exceeded depreciation by $208 million.
B) the economy was expanding in that year.
C) the production of 1933's GDP used up more capital goods than were produced in that year.
D) the economy produced no capital goods at all in 1933.
A) gross investment exceeded depreciation by $208 million.
B) the economy was expanding in that year.
C) the production of 1933's GDP used up more capital goods than were produced in that year.
D) the economy produced no capital goods at all in 1933.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
An economy is enlarging its stock of capital goods:
A) when net investment exceeds gross investment.
B) when gross investment exceeds replacement investment.
C) whenever gross investment is positive.
D) when replacement investment exceeds gross investment.
A) when net investment exceeds gross investment.
B) when gross investment exceeds replacement investment.
C) whenever gross investment is positive.
D) when replacement investment exceeds gross investment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which would be considered an investment according to economists?
A) the buying of shares of Janus mutual funds
B) the purchase of a new machinery by Ford
C) the purchase of stock of MacDonald's
D) the selling of IBM corporate bonds
A) the buying of shares of Janus mutual funds
B) the purchase of a new machinery by Ford
C) the purchase of stock of MacDonald's
D) the selling of IBM corporate bonds

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
If in some year gross investment was $120 billion and net investment was $65 billion, then in that year the country's capital stock:
A) may have either increased or decreased.
B) increased by $65 billion.
C) increased by $55 billion.
D) decreased by $55 billion.
A) may have either increased or decreased.
B) increased by $65 billion.
C) increased by $55 billion.
D) decreased by $55 billion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A nation's stock of capital goods will decline when:
A) gross investment exceeds net investment.
B) net investment is positive, but less than gross investment.
C) depreciation exceeds gross investment.
D) gross investment exceeds depreciation.
A) gross investment exceeds net investment.
B) net investment is positive, but less than gross investment.
C) depreciation exceeds gross investment.
D) gross investment exceeds depreciation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
In calculating GDP, national income accountants:
A) treat inventory changes as an adjustment to personal consumption expenditures.
B) ignore inventories because they do not represent final goods.
C) subtract increases in inventories and add decreases in inventories.
D) add increases in inventories and subtract decreases in inventories.
A) treat inventory changes as an adjustment to personal consumption expenditures.
B) ignore inventories because they do not represent final goods.
C) subtract increases in inventories and add decreases in inventories.
D) add increases in inventories and subtract decreases in inventories.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
In 2011 Trailblazer Bicycle Company produced a mountain bike which was delivered to a retail outlet in November of 1998. The bicycle was sold to
A) consumption in 2011 and as disinvestment in 2012.
B) disinvestment in 2011 and as consumption in 2012.
C) disinvestment in 2011 and as investment in 2012.
D) investment in 2011 and as disinvestment in 2012.
E)Z. Ryder in March of 2012. This bicycle is counted as:
A) consumption in 2011 and as disinvestment in 2012.
B) disinvestment in 2011 and as consumption in 2012.
C) disinvestment in 2011 and as investment in 2012.
D) investment in 2011 and as disinvestment in 2012.
E)Z. Ryder in March of 2012. This bicycle is counted as:

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The ZZZ Corporation issued $25 million in new common stock in 2012. It used $18 million of the proceeds to replace obsolete equipment in its factory and $7 million to repay bank loans. As a result, investment:
A) of $7 million has occurred.
B) of $25 million has occurred.
C) of $18 million has occurred.
D) has not occurred.
A) of $7 million has occurred.
B) of $25 million has occurred.
C) of $18 million has occurred.
D) has not occurred.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
If depreciation exceeds gross investment:
A) the economy's stock of capital may be either growing or shrinking.
B) the economy's stock of capital is shrinking.
C) the economy's stock of capital is growing.
D) net investment is zero.
A) the economy's stock of capital may be either growing or shrinking.
B) the economy's stock of capital is shrinking.
C) the economy's stock of capital is growing.
D) net investment is zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
When an economy's production capacity is expanding:
A) nominal GDP, but not necessarily real GDP, is rising.
B) net exports is always a positive amount.
C) disposable income exceeds personal income.
D) gross investment exceeds depreciation.
A) nominal GDP, but not necessarily real GDP, is rising.
B) net exports is always a positive amount.
C) disposable income exceeds personal income.
D) gross investment exceeds depreciation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Money spent on the purchase of a new house is included in the GDP as a part of:
A) the consumption of private fixed capital.
B) personal consumption expenditures.
C) personal saving.
D) investment.
A) the consumption of private fixed capital.
B) personal consumption expenditures.
C) personal saving.
D) investment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which would be considered an investment according to economists?
A) the purchase of newly-issued shares of stock in Microsoft
B) the construction of a new computer chip factory by Intel
C) the purchase of shares of stock by Fidelity, a mutual fund company
D) the sale of government bonds by the nation's central bank
A) the purchase of newly-issued shares of stock in Microsoft
B) the construction of a new computer chip factory by Intel
C) the purchase of shares of stock by Fidelity, a mutual fund company
D) the sale of government bonds by the nation's central bank

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
If depreciation (consumption of fixed capital) exceeds gross investment, it can be concluded that:
A) nominal GDP is rising but real GDP is declining.
B) net investment is negative.
C) the economy is importing more than it exports.
D) the economy is expanding.
A) nominal GDP is rising but real GDP is declining.
B) net investment is negative.
C) the economy is importing more than it exports.
D) the economy is expanding.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Refer to the information below. GDP is: All figures are in billions of dollars. 
A) $422.
B) $467.
C) $417.
D) $402.

A) $422.
B) $467.
C) $417.
D) $402.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
In national income accounting, G stands for:
A) government purchases.
B) gross investment.
C) government transfer payments.
D) gross saving.
A) government purchases.
B) gross investment.
C) government transfer payments.
D) gross saving.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
GDP by the expenditure approach is equal to:
A) C + Ig + G + Xn.
B) C + Ig + G - Xn.
C) C + In + G + Xn.
D) C + In + G - Xn.
A) C + Ig + G + Xn.
B) C + Ig + G - Xn.
C) C + In + G + Xn.
D) C + In + G - Xn.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Refer to the information below. Net investment: All figures are in billions. 
A) cannot be determined from the data given.
B) is $45.
C) is $53.
D) is $72.

A) cannot be determined from the data given.
B) is $45.
C) is $53.
D) is $72.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
In an economy, the value of inventories rose from $100 billion in 2012 to $150 billion in 2013. In calculating total investment for 2013, national income accountants would:
A) decrease it by $50 billion.
B) increase it by $50 billion.
C) decrease it by $100 billion.
D) increase it by $150 billion.
A) decrease it by $50 billion.
B) increase it by $50 billion.
C) decrease it by $100 billion.
D) increase it by $150 billion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66

Refer to the above information. Canadian imports:
A) cannot be calculated
B) are $26.
C) are $16.
D) are $11.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The smallest component of aggregate spending in Canada is:
A) net exports.
B) government purchases.
C) investment.
D) consumption.
A) net exports.
B) government purchases.
C) investment.
D) consumption.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Net exports are a negative number when:
A) a nation's imports of goods and services fall.
B) a nation's imports of goods and services rise.
C) a nation's exports of goods and services are greater than its imports.
D) a nation's imports of goods and services are greater than its exports.
A) a nation's imports of goods and services fall.
B) a nation's imports of goods and services rise.
C) a nation's exports of goods and services are greater than its imports.
D) a nation's imports of goods and services are greater than its exports.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The following are national income account data for a hypothetical economy in billions of dollars: gross investment ($320); imports ($35); exports ($22); personal consumption expenditures ($2,460); and, government purchases ($470). What is GDP in this economy?
A) $3,237 billion
B) $3,263 billion
C) $3,273 billion
D) $3,290 billion
A) $3,237 billion
B) $3,263 billion
C) $3,273 billion
D) $3,290 billion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The following are national income account data for a hypothetical economy in billions of dollars: government purchases ($1,050); personal consumption expenditures ($4,800); imports ($370); exports ($240); gross investment ($1,130). Personal consumption expenditures are approximately what percentage of this economy?
A) 60 percent
B) 65 percent
C) 70 percent
D) 75 percent
A) 60 percent
B) 65 percent
C) 70 percent
D) 75 percent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Net exports are negative when:
A) a nation's imports exceed its exports.
B) the economy's stock of capital goods is declining.
C) depreciation exceeds domestic investment.
D) a nation's exports exceed its imports.
A) a nation's imports exceed its exports.
B) the economy's stock of capital goods is declining.
C) depreciation exceeds domestic investment.
D) a nation's exports exceed its imports.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72

Refer to the above information. The gross domestic product is:
A) $328.
B) $402.
C) $382.
D) $336.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
In Year 1, inventories rose by $25 billion. In Year 2, inventories fell by $20 billion. In calculating total investment, national income accountants would have:
A) decreased it by $25 billion in Year 1 and increased it by $20 billion in Year 2.
B) decreased it by $25 billion in Year 1 and increased it by $5 billion in Year 2.
C) increased it by $25 billion in Year 1 and decreased it by $5 billion in Year 2.
D) increased it by $25 billion in Year 1 and decreased it by $20 billion in Year 2.
A) decreased it by $25 billion in Year 1 and increased it by $20 billion in Year 2.
B) decreased it by $25 billion in Year 1 and increased it by $5 billion in Year 2.
C) increased it by $25 billion in Year 1 and decreased it by $5 billion in Year 2.
D) increased it by $25 billion in Year 1 and decreased it by $20 billion in Year 2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The value of Canadian imports is:
A) added to exports when calculating GDP because imports reflect spending by Canadians.
B) subtracted from exports when calculating GDP because imports do not entail spending by Canadians.
C) subtracted from exports when calculating GDP because imports do not entail production in Canada.
D) added when calculating GDP because imports do not entail production in Canada.
A) added to exports when calculating GDP because imports reflect spending by Canadians.
B) subtracted from exports when calculating GDP because imports do not entail spending by Canadians.
C) subtracted from exports when calculating GDP because imports do not entail production in Canada.
D) added when calculating GDP because imports do not entail production in Canada.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The following are national income account data for a hypothetical economy in billions of dollars: government purchases ($940); personal consumption expenditures ($4,920); imports ($170); exports ($133); gross investment ($640). What is GDP in this economy?
A) $6,463 billion
B) $6,500 billion
C) $6,537 billion
D) $6,633 billion
A) $6,463 billion
B) $6,500 billion
C) $6,537 billion
D) $6,633 billion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
In an economy, the value of inventories fell from $75 billion in 2012 to $63 billion in 2013. In calculating total investment for 2013, national income accountants would:
A) decrease it by $75 billion.
B) increase it by $63 billion.
C) decrease it by $12 billion.
D) increase it by $138 billion.
A) decrease it by $75 billion.
B) increase it by $63 billion.
C) decrease it by $12 billion.
D) increase it by $138 billion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
A nation's capital stock was valued at $300 billion at the start of the year and $350 billion at the end. Consumption of private fixed capital in the year was $25 billion. Assuming stable prices, gross investment was:
A) $25 billion.
B) $50 billion.
C) $75 billion.
D) $90 billion.
A) $25 billion.
B) $50 billion.
C) $75 billion.
D) $90 billion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Gross domestic product (GDP) is equal to personal consumption expenditures:
A) plus gross investment, minus government spending, and plus net exports.
B) plus gross investment, plus government spending, and minus net exports.
C) minus gross investment, plus government spending, and plus net exports.
D) plus gross investment, plus government spending, and plus net exports.
A) plus gross investment, minus government spending, and plus net exports.
B) plus gross investment, plus government spending, and minus net exports.
C) minus gross investment, plus government spending, and plus net exports.
D) plus gross investment, plus government spending, and plus net exports.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Net exports are:
A) that portion of consumption and investment goods sent to other countries.
B) exports plus imports.
C) exports less imports.
D) imports less exports.
A) that portion of consumption and investment goods sent to other countries.
B) exports plus imports.
C) exports less imports.
D) imports less exports.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
In the treatment of Canadian exports and imports, national income accountants:
A) subtract exports, but add imports, in calculating GDP.
B) subtract both exports and imports in calculating GDP.
C) add both exports and imports in calculating GDP.
D) add exports, but subtract imports, in calculating GDP.
A) subtract exports, but add imports, in calculating GDP.
B) subtract both exports and imports in calculating GDP.
C) add both exports and imports in calculating GDP.
D) add exports, but subtract imports, in calculating GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 183 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



