Deck 14: Decision Analysis
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/125
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 14: Decision Analysis
1
The expected value of perfect information (EVPI) is equivalent to the minimum expected opportunity loss (EOL).
True
2
Exhibit 14.5
The following questions are based on the information below.
An investor is considering 4 investments, A, B, C, D. The payoff from each investment is a function of the economic climate over the next 2 years. The economy can expand or decline. The following decision tree has been developed for the problem. The investor has estimated the probability of a declining economy at 40% and an expanding economy at 60%.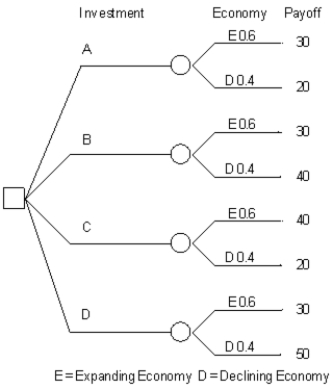
A(n) ____ is a course of action intended to solve a problem.
A) decision
B) criteria
C) state of nature
D) alternative
The following questions are based on the information below.
An investor is considering 4 investments, A, B, C, D. The payoff from each investment is a function of the economic climate over the next 2 years. The economy can expand or decline. The following decision tree has been developed for the problem. The investor has estimated the probability of a declining economy at 40% and an expanding economy at 60%.

A(n) ____ is a course of action intended to solve a problem.
A) decision
B) criteria
C) state of nature
D) alternative
alternative
3
Exhibit 14.8
The following questions use the information below.
A company needs to buy a new insurance policy. They have three policies to choose from, A, B and C. The policies differ with respect to price, coverage and ease of billing. The company has developed the following AHP tables for price and summary. The other tables are not shown due to space limitations.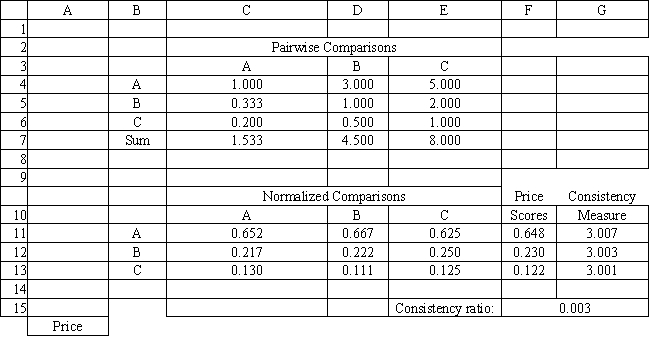
The expected monetary value criterion (EMV) is the decision-making approach used
A) in decision-making under risk
B) in decision-making under uncertainty
C) in decision-making under certainty
D) all of the above
The following questions use the information below.
A company needs to buy a new insurance policy. They have three policies to choose from, A, B and C. The policies differ with respect to price, coverage and ease of billing. The company has developed the following AHP tables for price and summary. The other tables are not shown due to space limitations.


The expected monetary value criterion (EMV) is the decision-making approach used
A) in decision-making under risk
B) in decision-making under uncertainty
C) in decision-making under certainty
D) all of the above
in decision-making under risk
4
The criteria in a decision problem represent various factors that are important to the decision maker.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Exhibit 14.5
The following questions are based on the information below.
An investor is considering 4 investments, A, B, C, D. The payoff from each investment is a function of the economic climate over the next 2 years. The economy can expand or decline. The following decision tree has been developed for the problem. The investor has estimated the probability of a declining economy at 40% and an expanding economy at 60%.
Suppose that the payoffs for an alternative with three states of nature are: 10, 20, and 30. The probabilities of these states of nature are 0.2, 0.3, and 0.5, respectively. The expected payoff for the alternative is equal to
A) 23
B) 30
C) 60
D) 20
The following questions are based on the information below.
An investor is considering 4 investments, A, B, C, D. The payoff from each investment is a function of the economic climate over the next 2 years. The economy can expand or decline. The following decision tree has been developed for the problem. The investor has estimated the probability of a declining economy at 40% and an expanding economy at 60%.

Suppose that the payoffs for an alternative with three states of nature are: 10, 20, and 30. The probabilities of these states of nature are 0.2, 0.3, and 0.5, respectively. The expected payoff for the alternative is equal to
A) 23
B) 30
C) 60
D) 20

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A payoff matrix depicts ____ versus ____ with payoffs for each intersection cell.
A) decision criteria; states of nature.
B) decision alternatives; potential outcomes.
C) decision alternatives; states of nature.
D) decision criteria; potential outcomes.
A) decision criteria; states of nature.
B) decision alternatives; potential outcomes.
C) decision alternatives; states of nature.
D) decision criteria; potential outcomes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following is a goal of decision analysis?
A) Help individuals make good decisions.
B) Ensure decisions lead to good outcomes.
C) Avoiding decisions leading to bad outcomes.
D) Reduce the role of luck in a decision.
A) Help individuals make good decisions.
B) Ensure decisions lead to good outcomes.
C) Avoiding decisions leading to bad outcomes.
D) Reduce the role of luck in a decision.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Exhibit 14.3
The following questions are based on the information below.
An investor is considering 4 investments, A, B, C and leaving his money in the bank. The payoff from each investment is a function of the economic climate over the next 2 years. The economy can expand or decline. The following payoff matrix has been developed for the decision problem. The investor has estimated the probability of a declining economy at 70% and an expanding economy at 30%.
Refer to Exhibit 14.3. What decision should be made according to the expected monetary value decision rule?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) Bank
The following questions are based on the information below.
An investor is considering 4 investments, A, B, C and leaving his money in the bank. The payoff from each investment is a function of the economic climate over the next 2 years. The economy can expand or decline. The following payoff matrix has been developed for the decision problem. The investor has estimated the probability of a declining economy at 70% and an expanding economy at 30%.

Refer to Exhibit 14.3. What decision should be made according to the expected monetary value decision rule?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) Bank

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A payoff matrix is a table that summarizes the final outcome (or regret) for each decision alternative under each possible condition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The expected monetary value decision rule selects the decision alternative with the largest expected regret.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The decision rules that assume that probabilities of occurrence can be assigned to the states of nature in a decision problem are called probabilistic methods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A company is planning a plant expansion. They can build a large or small plant. The payoffs for the plant depend on the level of consumer demand for the company's products. The company believes that there is an 69% chance that demand for their products will be high and a 31% chance that it will be low. The company can pay a market research firm to survey consumer attitudes towards the company's products. There is a 63% chance that the customers will like the products and a 37% chance that they won't. The payoff matrix and costs of the two plants are listed below. The company believes that if the survey is favorable there is a 92% chance that demand will be high for the products. If the survey is unfavorable there is only a 30% chance that the demand will be high. The following decision tree has been built for this problem. The company has computed that the expected monetary value of the best decision without sample information is 154.35 million. What is the EVSI for this problem (in $ million)? 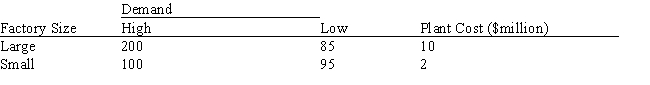
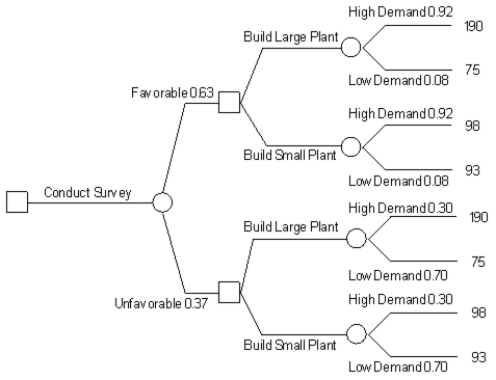
A) 0.07
B) 26.38
C) 109.5
D) 180.8
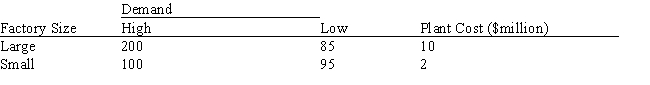

A) 0.07
B) 26.38
C) 109.5
D) 180.8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
An analyst can apply a process known as rolling back to a decision tree to determine the decision with the largest EMV.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
One of the primary advantages in decision making is that we usually know which state of nature will occur.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Exhibit 14.5
The following questions are based on the information below.
An investor is considering 4 investments, A, B, C, D. The payoff from each investment is a function of the economic climate over the next 2 years. The economy can expand or decline. The following decision tree has been developed for the problem. The investor has estimated the probability of a declining economy at 40% and an expanding economy at 60%.
Refer to Exhibit 14.5. What is the correct decision for this investor based on an expected monetary value criterion?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
The following questions are based on the information below.
An investor is considering 4 investments, A, B, C, D. The payoff from each investment is a function of the economic climate over the next 2 years. The economy can expand or decline. The following decision tree has been developed for the problem. The investor has estimated the probability of a declining economy at 40% and an expanding economy at 60%.

Refer to Exhibit 14.5. What is the correct decision for this investor based on an expected monetary value criterion?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The scores in a scoring model range from
A) 0 to 1
B) −1 to +1
C) 0 to 5
D) 0 to 10
A) 0 to 1
B) −1 to +1
C) 0 to 5
D) 0 to 10

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Exhibit 14.5
The following questions are based on the information below.
An investor is considering 4 investments, A, B, C, D. The payoff from each investment is a function of the economic climate over the next 2 years. The economy can expand or decline. The following decision tree has been developed for the problem. The investor has estimated the probability of a declining economy at 40% and an expanding economy at 60%.
The ____ in a decision problem represent factors that are important to the decision maker.
A) payoffs
B) states of nature
C) criteria
D) alternatives
The following questions are based on the information below.
An investor is considering 4 investments, A, B, C, D. The payoff from each investment is a function of the economic climate over the next 2 years. The economy can expand or decline. The following decision tree has been developed for the problem. The investor has estimated the probability of a declining economy at 40% and an expanding economy at 60%.

The ____ in a decision problem represent factors that are important to the decision maker.
A) payoffs
B) states of nature
C) criteria
D) alternatives

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Exhibit 14.4
The following questions are based on the information below.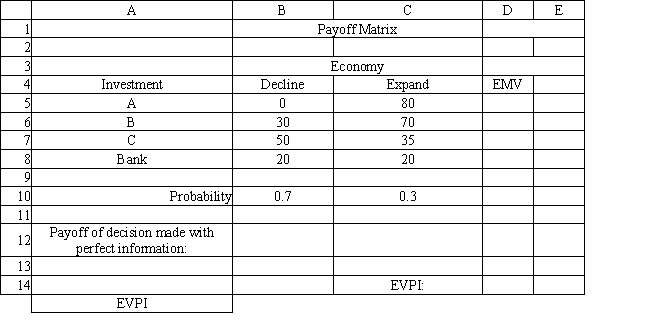
Refer to Exhibit 14.4. What is the expected value of perfect information for the investor?
A) 13.5
B) 20
C) 45.5
D) 59
The following questions are based on the information below.

Refer to Exhibit 14.4. What is the expected value of perfect information for the investor?
A) 13.5
B) 20
C) 45.5
D) 59

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Exhibit 14.8
The following questions use the information below.
A company needs to buy a new insurance policy. They have three policies to choose from, A, B and C. The policies differ with respect to price, coverage and ease of billing. The company has developed the following AHP tables for price and summary. The other tables are not shown due to space limitations.

Refer to Exhibit 14.8. What formula should go in cell G15 of the Price worksheet to compute the Consistency Ratio?
A) =AVERAGE(G11:G13)-3)/(2*0.58)
B) =AVERAGE(G11:G13)-3)
C) =AVERAGE(G11:G13))/(2*0.58)
D) =AVERAGE(G11:G13)-3)/0.58
The following questions use the information below.
A company needs to buy a new insurance policy. They have three policies to choose from, A, B and C. The policies differ with respect to price, coverage and ease of billing. The company has developed the following AHP tables for price and summary. The other tables are not shown due to space limitations.


Refer to Exhibit 14.8. What formula should go in cell G15 of the Price worksheet to compute the Consistency Ratio?
A) =AVERAGE(G11:G13)-3)/(2*0.58)
B) =AVERAGE(G11:G13)-3)
C) =AVERAGE(G11:G13))/(2*0.58)
D) =AVERAGE(G11:G13)-3)/0.58

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Under maximin rule a decision maker hedges against the worst possible outcome of a decision.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Exhibit 14.2
The following questions are based on the information below.
An investor is considering 4 investments, A, B, C and leaving his money in the bank. The payoff from each investment is a function of the economic climate over the next 2 years. The economy can expand or decline. The following payoff matrix has been developed for the decision problem.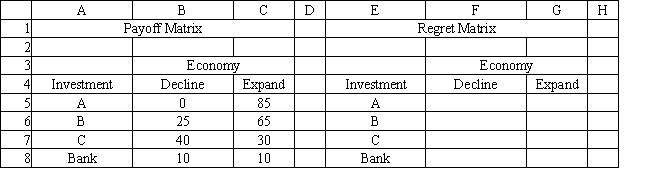
Sensitivity analysis is most useful in
A) decision-making under risk
B) decision-making under uncertainty
C) decision-making under certainty
D) all of the above
The following questions are based on the information below.
An investor is considering 4 investments, A, B, C and leaving his money in the bank. The payoff from each investment is a function of the economic climate over the next 2 years. The economy can expand or decline. The following payoff matrix has been developed for the decision problem.

Sensitivity analysis is most useful in
A) decision-making under risk
B) decision-making under uncertainty
C) decision-making under certainty
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Exhibit 14.5
The following questions are based on the information below.
An investor is considering 4 investments, A, B, C, D. The payoff from each investment is a function of the economic climate over the next 2 years. The economy can expand or decline. The following decision tree has been developed for the problem. The investor has estimated the probability of a declining economy at 40% and an expanding economy at 60%.
The scores in a scoring model can be thought of as subjective assessments of
A) usefulness.
B) worthiness.
C) utility.
D) payoff.
The following questions are based on the information below.
An investor is considering 4 investments, A, B, C, D. The payoff from each investment is a function of the economic climate over the next 2 years. The economy can expand or decline. The following decision tree has been developed for the problem. The investor has estimated the probability of a declining economy at 40% and an expanding economy at 60%.

The scores in a scoring model can be thought of as subjective assessments of
A) usefulness.
B) worthiness.
C) utility.
D) payoff.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Exhibit 14.8
The following questions use the information below.
A company needs to buy a new insurance policy. They have three policies to choose from, A, B and C. The policies differ with respect to price, coverage and ease of billing. The company has developed the following AHP tables for price and summary. The other tables are not shown due to space limitations.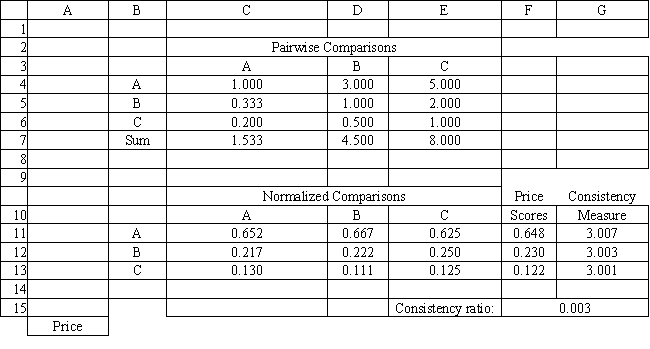
The decision rule which determines the maximum payoff for each alternative and then selects the alternative associated with the largest payoff is the
A) maximax decision rule.
B) maximin decision rule.
C) minimax regret decision rule.
D) minimin decision rule.
The following questions use the information below.
A company needs to buy a new insurance policy. They have three policies to choose from, A, B and C. The policies differ with respect to price, coverage and ease of billing. The company has developed the following AHP tables for price and summary. The other tables are not shown due to space limitations.


The decision rule which determines the maximum payoff for each alternative and then selects the alternative associated with the largest payoff is the
A) maximax decision rule.
B) maximin decision rule.
C) minimax regret decision rule.
D) minimin decision rule.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Exhibit 14.1
The following questions are based on the information below.
An investor is considering 4 investments, A, B, C and leaving his money in the bank. The payoff from each investment is a function of the economic climate over the next 2 years. The economy can expand or decline. The following payoff matrix has been developed for the decision problem.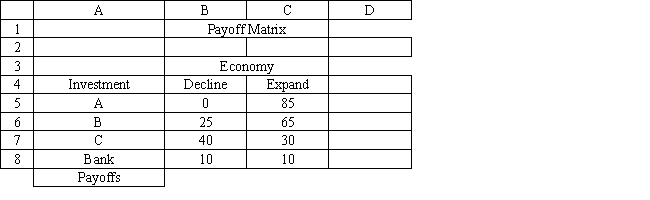
Refer to Exhibit 14.1. What decision should be made according to the minimax regret decision rule?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) Bank
The following questions are based on the information below.
An investor is considering 4 investments, A, B, C and leaving his money in the bank. The payoff from each investment is a function of the economic climate over the next 2 years. The economy can expand or decline. The following payoff matrix has been developed for the decision problem.

Refer to Exhibit 14.1. What decision should be made according to the minimax regret decision rule?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) Bank

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Exhibit 14.2
The following questions are based on the information below.
An investor is considering 4 investments, A, B, C and leaving his money in the bank. The payoff from each investment is a function of the economic climate over the next 2 years. The economy can expand or decline. The following payoff matrix has been developed for the decision problem.
Refer to Exhibit 14.2. What formula should go in cell F5 of the Regret Matrix above to compute the regret value?
A) =B$5-MAX(B$5:B$8)
B) =MAX(B$5:B$8)-MAX(B5)
C) =MAX(B$5:B$8)-MIN(B$5:B$8)
D) =MAX(B$5:B$8)-B5
The following questions are based on the information below.
An investor is considering 4 investments, A, B, C and leaving his money in the bank. The payoff from each investment is a function of the economic climate over the next 2 years. The economy can expand or decline. The following payoff matrix has been developed for the decision problem.

Refer to Exhibit 14.2. What formula should go in cell F5 of the Regret Matrix above to compute the regret value?
A) =B$5-MAX(B$5:B$8)
B) =MAX(B$5:B$8)-MAX(B5)
C) =MAX(B$5:B$8)-MIN(B$5:B$8)
D) =MAX(B$5:B$8)-B5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Exhibit 14.2
The following questions are based on the information below.
An investor is considering 4 investments, A, B, C and leaving his money in the bank. The payoff from each investment is a function of the economic climate over the next 2 years. The economy can expand or decline. The following payoff matrix has been developed for the decision problem.
A course of action intended to solve a problem is called a(n)
A) alternative.
B) option.
C) decision.
D) criteria.
The following questions are based on the information below.
An investor is considering 4 investments, A, B, C and leaving his money in the bank. The payoff from each investment is a function of the economic climate over the next 2 years. The economy can expand or decline. The following payoff matrix has been developed for the decision problem.

A course of action intended to solve a problem is called a(n)
A) alternative.
B) option.
C) decision.
D) criteria.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Exhibit 14.5
The following questions are based on the information below.
An investor is considering 4 investments, A, B, C, D. The payoff from each investment is a function of the economic climate over the next 2 years. The economy can expand or decline. The following decision tree has been developed for the problem. The investor has estimated the probability of a declining economy at 40% and an expanding economy at 60%.
An alternative
A) is a course of action intended to solve a problem
B) is always feasible
C) is never feasible
D) is realistic
The following questions are based on the information below.
An investor is considering 4 investments, A, B, C, D. The payoff from each investment is a function of the economic climate over the next 2 years. The economy can expand or decline. The following decision tree has been developed for the problem. The investor has estimated the probability of a declining economy at 40% and an expanding economy at 60%.

An alternative
A) is a course of action intended to solve a problem
B) is always feasible
C) is never feasible
D) is realistic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Exhibit 14.1
The following questions are based on the information below.
An investor is considering 4 investments, A, B, C and leaving his money in the bank. The payoff from each investment is a function of the economic climate over the next 2 years. The economy can expand or decline. The following payoff matrix has been developed for the decision problem.
Refer to Exhibit 14.1. What formula should go in cell D5 to implement the maximax decision rule?
A) =MAX(MAX(B5:C5))
B) =MIN(B5:C5)
C) =AVERAGE(B5:C5)
D) =MAX(B5:C5)
The following questions are based on the information below.
An investor is considering 4 investments, A, B, C and leaving his money in the bank. The payoff from each investment is a function of the economic climate over the next 2 years. The economy can expand or decline. The following payoff matrix has been developed for the decision problem.

Refer to Exhibit 14.1. What formula should go in cell D5 to implement the maximax decision rule?
A) =MAX(MAX(B5:C5))
B) =MIN(B5:C5)
C) =AVERAGE(B5:C5)
D) =MAX(B5:C5)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Exhibit 14.7
The following questions use the information below.
A decision maker is faced with two alternatives. The decision maker has determined that she is indifferent between the two alternatives when p = 0.45.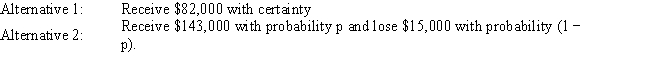
The category of decision rules that contains the maximax decision rule is the
A) optimistic category.
B) non-probabilistic category.
C) probabilistic category.
D) optimality category.
The following questions use the information below.
A decision maker is faced with two alternatives. The decision maker has determined that she is indifferent between the two alternatives when p = 0.45.
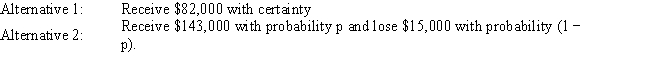
The category of decision rules that contains the maximax decision rule is the
A) optimistic category.
B) non-probabilistic category.
C) probabilistic category.
D) optimality category.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Exhibit 14.8
The following questions use the information below.
A company needs to buy a new insurance policy. They have three policies to choose from, A, B and C. The policies differ with respect to price, coverage and ease of billing. The company has developed the following AHP tables for price and summary. The other tables are not shown due to space limitations.

Refer to Exhibit 14.8. What formula should go in cell G11 and get copied to G12:G13 of the Price worksheet to compute the Consistency Measure?
A) =MMULT(C4:E4,$F$11:$F$13)
B) =SUMPRODUCT(C4:E4,$F$11:$F$13)/F11
C) =MMULT(C4:E4,$F$11:$F$13)/F11
D) =MMULT(C7:E7,$F$11:$F$13)/F11
The following questions use the information below.
A company needs to buy a new insurance policy. They have three policies to choose from, A, B and C. The policies differ with respect to price, coverage and ease of billing. The company has developed the following AHP tables for price and summary. The other tables are not shown due to space limitations.


Refer to Exhibit 14.8. What formula should go in cell G11 and get copied to G12:G13 of the Price worksheet to compute the Consistency Measure?
A) =MMULT(C4:E4,$F$11:$F$13)
B) =SUMPRODUCT(C4:E4,$F$11:$F$13)/F11
C) =MMULT(C4:E4,$F$11:$F$13)/F11
D) =MMULT(C7:E7,$F$11:$F$13)/F11

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Exhibit 14.8
The following questions use the information below.
A company needs to buy a new insurance policy. They have three policies to choose from, A, B and C. The policies differ with respect to price, coverage and ease of billing. The company has developed the following AHP tables for price and summary. The other tables are not shown due to space limitations.

Based on the radar chart of raw scores provided below, why is this decision complex? 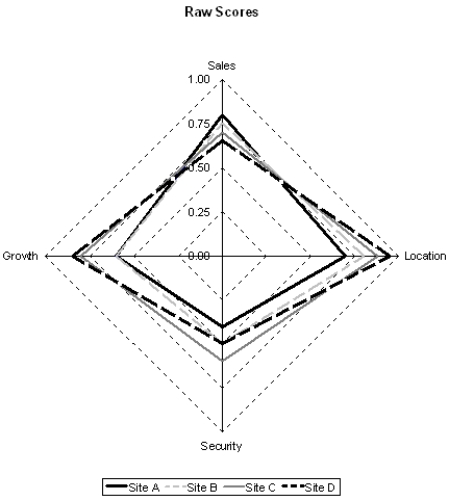
A) The chart is hard to read.
B) No site wins on all four criteria.
C) No site achieves a perfect score of 1.0 on a criteria.
D) No sites have sufficient security.
The following questions use the information below.
A company needs to buy a new insurance policy. They have three policies to choose from, A, B and C. The policies differ with respect to price, coverage and ease of billing. The company has developed the following AHP tables for price and summary. The other tables are not shown due to space limitations.


Based on the radar chart of raw scores provided below, why is this decision complex?

A) The chart is hard to read.
B) No site wins on all four criteria.
C) No site achieves a perfect score of 1.0 on a criteria.
D) No sites have sufficient security.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Exhibit 14.2
The following questions are based on the information below.
An investor is considering 4 investments, A, B, C and leaving his money in the bank. The payoff from each investment is a function of the economic climate over the next 2 years. The economy can expand or decline. The following payoff matrix has been developed for the decision problem.
The amount of opportunity lost in making a decision is called
A) loss.
B) frustration.
C) negative profit.
D) regret.
The following questions are based on the information below.
An investor is considering 4 investments, A, B, C and leaving his money in the bank. The payoff from each investment is a function of the economic climate over the next 2 years. The economy can expand or decline. The following payoff matrix has been developed for the decision problem.

The amount of opportunity lost in making a decision is called
A) loss.
B) frustration.
C) negative profit.
D) regret.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Exhibit 14.7
The following questions use the information below.
A decision maker is faced with two alternatives. The decision maker has determined that she is indifferent between the two alternatives when p = 0.45.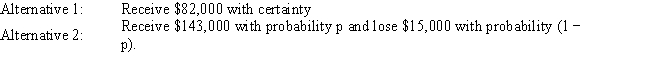
Refer to Exhibit 14.7. What is the decision maker's certainty equivalent for this problem?
A) −$15,000
B) $84,000
C) $56,100
D) $82,000
The following questions use the information below.
A decision maker is faced with two alternatives. The decision maker has determined that she is indifferent between the two alternatives when p = 0.45.
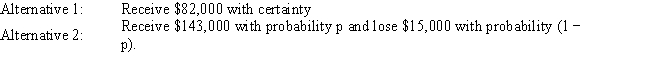
Refer to Exhibit 14.7. What is the decision maker's certainty equivalent for this problem?
A) −$15,000
B) $84,000
C) $56,100
D) $82,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Exhibit 14.7
The following questions use the information below.
A decision maker is faced with two alternatives. The decision maker has determined that she is indifferent between the two alternatives when p = 0.45.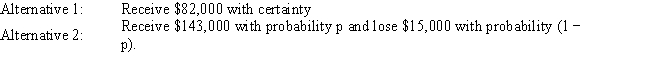
The maximin approach to decision-making
A) maximizes the minimum return
B) maximizes the maximum return
C) maximizes the minimum regret
D) minimizes the minimum regret
The following questions use the information below.
A decision maker is faced with two alternatives. The decision maker has determined that she is indifferent between the two alternatives when p = 0.45.
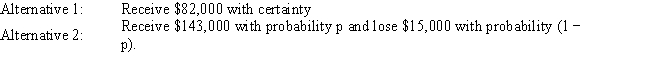
The maximin approach to decision-making
A) maximizes the minimum return
B) maximizes the maximum return
C) maximizes the minimum regret
D) minimizes the minimum regret

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Exhibit 14.7
The following questions use the information below.
A decision maker is faced with two alternatives. The decision maker has determined that she is indifferent between the two alternatives when p = 0.45.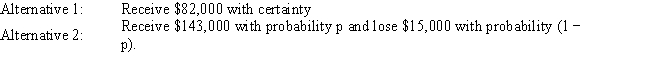
A state of nature
A) is observed
B) is under control of a decision maker
C) is known with certainty
D) is estimated using a decision model of choice
The following questions use the information below.
A decision maker is faced with two alternatives. The decision maker has determined that she is indifferent between the two alternatives when p = 0.45.
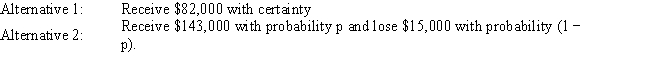
A state of nature
A) is observed
B) is under control of a decision maker
C) is known with certainty
D) is estimated using a decision model of choice

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Exhibit 14.5
The following questions are based on the information below.
An investor is considering 4 investments, A, B, C, D. The payoff from each investment is a function of the economic climate over the next 2 years. The economy can expand or decline. The following decision tree has been developed for the problem. The investor has estimated the probability of a declining economy at 40% and an expanding economy at 60%.
In decision-making, luck
A) often plays a role in determining whether good or bad outcomes occur
B) can be quantified
C) cannot be quantified
D) can be ignored
The following questions are based on the information below.
An investor is considering 4 investments, A, B, C, D. The payoff from each investment is a function of the economic climate over the next 2 years. The economy can expand or decline. The following decision tree has been developed for the problem. The investor has estimated the probability of a declining economy at 40% and an expanding economy at 60%.

In decision-making, luck
A) often plays a role in determining whether good or bad outcomes occur
B) can be quantified
C) cannot be quantified
D) can be ignored

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Exhibit 14.3
The following questions are based on the information below.
An investor is considering 4 investments, A, B, C and leaving his money in the bank. The payoff from each investment is a function of the economic climate over the next 2 years. The economy can expand or decline. The following payoff matrix has been developed for the decision problem. The investor has estimated the probability of a declining economy at 70% and an expanding economy at 30%.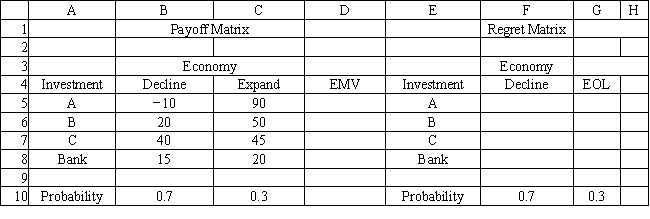
Refer to Exhibit 14.3. What decision should be made according to the expected regret decision rule?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) Bank
The following questions are based on the information below.
An investor is considering 4 investments, A, B, C and leaving his money in the bank. The payoff from each investment is a function of the economic climate over the next 2 years. The economy can expand or decline. The following payoff matrix has been developed for the decision problem. The investor has estimated the probability of a declining economy at 70% and an expanding economy at 30%.

Refer to Exhibit 14.3. What decision should be made according to the expected regret decision rule?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) Bank

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Exhibit 14.5
The following questions are based on the information below.
An investor is considering 4 investments, A, B, C, D. The payoff from each investment is a function of the economic climate over the next 2 years. The economy can expand or decline. The following decision tree has been developed for the problem. The investor has estimated the probability of a declining economy at 40% and an expanding economy at 60%.
In decision analysis, good decisions
A) always result in good outcomes
B) always result in bad outcomes
C) guarantee good outcomes
D) may be reached when the model accounts for unforeseeable circumstances
The following questions are based on the information below.
An investor is considering 4 investments, A, B, C, D. The payoff from each investment is a function of the economic climate over the next 2 years. The economy can expand or decline. The following decision tree has been developed for the problem. The investor has estimated the probability of a declining economy at 40% and an expanding economy at 60%.

In decision analysis, good decisions
A) always result in good outcomes
B) always result in bad outcomes
C) guarantee good outcomes
D) may be reached when the model accounts for unforeseeable circumstances

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Exhibit 14.2
The following questions are based on the information below.
An investor is considering 4 investments, A, B, C and leaving his money in the bank. The payoff from each investment is a function of the economic climate over the next 2 years. The economy can expand or decline. The following payoff matrix has been developed for the decision problem.
How are states of nature assigned probabilities?
A) Use historical data.
B) Use best judgement.
C) Use interview results.
D) All of these.
The following questions are based on the information below.
An investor is considering 4 investments, A, B, C and leaving his money in the bank. The payoff from each investment is a function of the economic climate over the next 2 years. The economy can expand or decline. The following payoff matrix has been developed for the decision problem.

How are states of nature assigned probabilities?
A) Use historical data.
B) Use best judgement.
C) Use interview results.
D) All of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Exhibit 14.8
The following questions use the information below.
A company needs to buy a new insurance policy. They have three policies to choose from, A, B and C. The policies differ with respect to price, coverage and ease of billing. The company has developed the following AHP tables for price and summary. The other tables are not shown due to space limitations.

Which decision rule optimistically assumes that nature will always be "on our side" regardless of what decision we make?
A) maximax decision rule.
B) maximin decision rule.
C) minimax regret decision rule.
D) minimin decision rule.
The following questions use the information below.
A company needs to buy a new insurance policy. They have three policies to choose from, A, B and C. The policies differ with respect to price, coverage and ease of billing. The company has developed the following AHP tables for price and summary. The other tables are not shown due to space limitations.


Which decision rule optimistically assumes that nature will always be "on our side" regardless of what decision we make?
A) maximax decision rule.
B) maximin decision rule.
C) minimax regret decision rule.
D) minimin decision rule.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Exhibit 14.8
The following questions use the information below.
A company needs to buy a new insurance policy. They have three policies to choose from, A, B and C. The policies differ with respect to price, coverage and ease of billing. The company has developed the following AHP tables for price and summary. The other tables are not shown due to space limitations.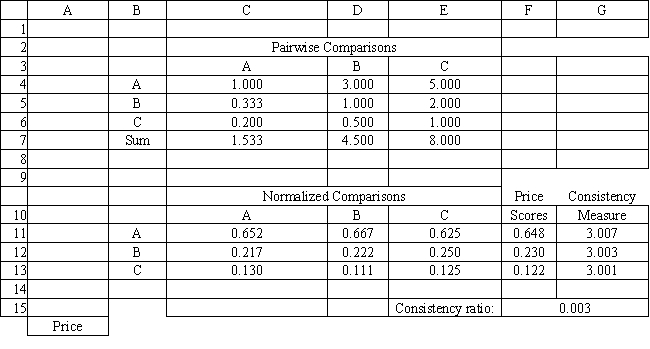
Expected regret is also called
A) EMV.
B) EOL.
C) EPA.
D) EOQ.
The following questions use the information below.
A company needs to buy a new insurance policy. They have three policies to choose from, A, B and C. The policies differ with respect to price, coverage and ease of billing. The company has developed the following AHP tables for price and summary. The other tables are not shown due to space limitations.


Expected regret is also called
A) EMV.
B) EOL.
C) EPA.
D) EOQ.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Exhibit 14.8
The following questions use the information below.
A company needs to buy a new insurance policy. They have three policies to choose from, A, B and C. The policies differ with respect to price, coverage and ease of billing. The company has developed the following AHP tables for price and summary. The other tables are not shown due to space limitations.

Decision Analysis techniques provide modeling techniques to help decision makers make decisions. Which of the following is not typically a benefit of decision analysis?
A) Incorporating uncertainty via probabilities.
B) Incorporating risk via utility theory functions.
C) Incorporating uncertainty via exponential distributions.
D) Structuring decision strategies via decision trees.
The following questions use the information below.
A company needs to buy a new insurance policy. They have three policies to choose from, A, B and C. The policies differ with respect to price, coverage and ease of billing. The company has developed the following AHP tables for price and summary. The other tables are not shown due to space limitations.


Decision Analysis techniques provide modeling techniques to help decision makers make decisions. Which of the following is not typically a benefit of decision analysis?
A) Incorporating uncertainty via probabilities.
B) Incorporating risk via utility theory functions.
C) Incorporating uncertainty via exponential distributions.
D) Structuring decision strategies via decision trees.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Exhibit 14.7
The following questions use the information below.
A decision maker is faced with two alternatives. The decision maker has determined that she is indifferent between the two alternatives when p = 0.45.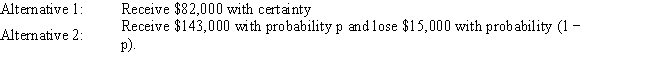
Refer to Exhibit 14.7. What is the decision maker's risk premium for this problem?
A) −$20,000
B) −$25,900
C) $70,000
D) $80,000
The following questions use the information below.
A decision maker is faced with two alternatives. The decision maker has determined that she is indifferent between the two alternatives when p = 0.45.
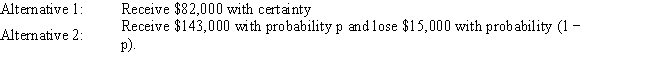
Refer to Exhibit 14.7. What is the decision maker's risk premium for this problem?
A) −$20,000
B) −$25,900
C) $70,000
D) $80,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Exhibit 14.1
The following questions are based on the information below.
An investor is considering 4 investments, A, B, C and leaving his money in the bank. The payoff from each investment is a function of the economic climate over the next 2 years. The economy can expand or decline. The following payoff matrix has been developed for the decision problem.
In a graphical representation of decision trees the event nodes are represented by
A) squares
B) circles
C) solid dots
D) ovals
The following questions are based on the information below.
An investor is considering 4 investments, A, B, C and leaving his money in the bank. The payoff from each investment is a function of the economic climate over the next 2 years. The economy can expand or decline. The following payoff matrix has been developed for the decision problem.

In a graphical representation of decision trees the event nodes are represented by
A) squares
B) circles
C) solid dots
D) ovals

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Exhibit 14.7
The following questions use the information below.
A decision maker is faced with two alternatives. The decision maker has determined that she is indifferent between the two alternatives when p = 0.45.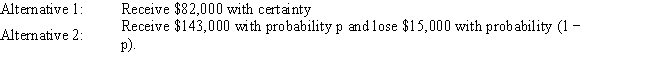
A fast food restaurant is considering opening a new store at one of four locations. They have developed the following multi-criteria scoring model for this problem. What location should they choose based on this information?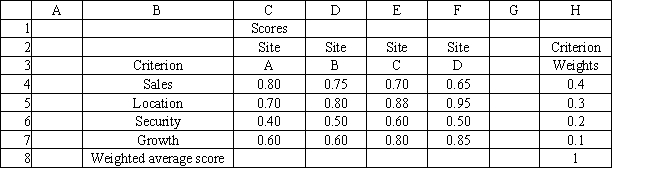
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
The following questions use the information below.
A decision maker is faced with two alternatives. The decision maker has determined that she is indifferent between the two alternatives when p = 0.45.
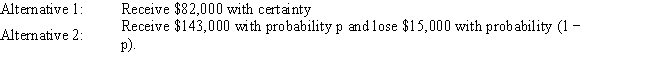
A fast food restaurant is considering opening a new store at one of four locations. They have developed the following multi-criteria scoring model for this problem. What location should they choose based on this information?

A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Exhibit 14.8
The following questions use the information below.
A company needs to buy a new insurance policy. They have three policies to choose from, A, B and C. The policies differ with respect to price, coverage and ease of billing. The company has developed the following AHP tables for price and summary. The other tables are not shown due to space limitations.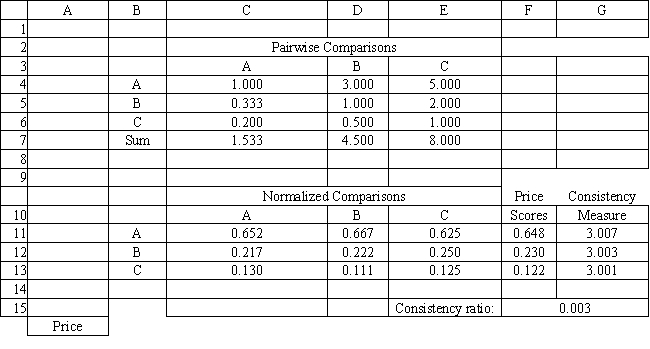
Refer to Exhibit 14.8. The Consistency Ratio indicates consistency in the pairwise comparison matrix if the ratio is
A) ≤ 0.05
B) ≤ 0.10
C) ≤ 0.20
D) ≤ 0.30
The following questions use the information below.
A company needs to buy a new insurance policy. They have three policies to choose from, A, B and C. The policies differ with respect to price, coverage and ease of billing. The company has developed the following AHP tables for price and summary. The other tables are not shown due to space limitations.


Refer to Exhibit 14.8. The Consistency Ratio indicates consistency in the pairwise comparison matrix if the ratio is
A) ≤ 0.05
B) ≤ 0.10
C) ≤ 0.20
D) ≤ 0.30

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Exhibit 14.7
The following questions use the information below.
A decision maker is faced with two alternatives. The decision maker has determined that she is indifferent between the two alternatives when p = 0.45.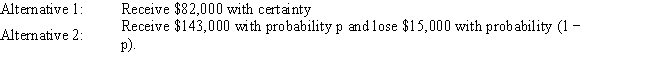
The total worth, value or desirability of a decision alternative is called its
A) usefulness.
B) worthiness.
C) utility.
D) risk.
The following questions use the information below.
A decision maker is faced with two alternatives. The decision maker has determined that she is indifferent between the two alternatives when p = 0.45.
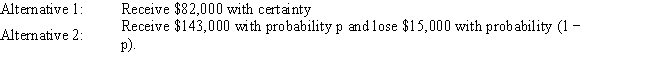
The total worth, value or desirability of a decision alternative is called its
A) usefulness.
B) worthiness.
C) utility.
D) risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Exhibit 14.8
The following questions use the information below.
A company needs to buy a new insurance policy. They have three policies to choose from, A, B and C. The policies differ with respect to price, coverage and ease of billing. The company has developed the following AHP tables for price and summary. The other tables are not shown due to space limitations.

The ____ correspond to future events that are not under the control of the decision maker.
A) payoffs
B) states of nature
C) criteria
D) alternatives
The following questions use the information below.
A company needs to buy a new insurance policy. They have three policies to choose from, A, B and C. The policies differ with respect to price, coverage and ease of billing. The company has developed the following AHP tables for price and summary. The other tables are not shown due to space limitations.


The ____ correspond to future events that are not under the control of the decision maker.
A) payoffs
B) states of nature
C) criteria
D) alternatives

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Exhibit 14.7
The following questions use the information below.
A decision maker is faced with two alternatives. The decision maker has determined that she is indifferent between the two alternatives when p = 0.45.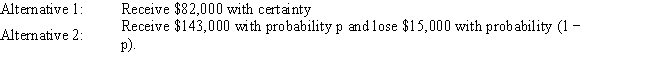
What is the formula for the exponential utility function U(x)?
A) −e−x/R
B) 1 + e−x/R
C) 1 − ex/R
D) 1 − e−x/R
The following questions use the information below.
A decision maker is faced with two alternatives. The decision maker has determined that she is indifferent between the two alternatives when p = 0.45.
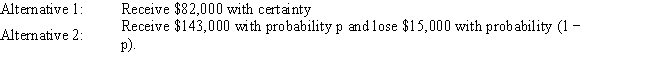
What is the formula for the exponential utility function U(x)?
A) −e−x/R
B) 1 + e−x/R
C) 1 − ex/R
D) 1 − e−x/R

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Exhibit 14.5
The following questions are based on the information below.
An investor is considering 4 investments, A, B, C, D. The payoff from each investment is a function of the economic climate over the next 2 years. The economy can expand or decline. The following decision tree has been developed for the problem. The investor has estimated the probability of a declining economy at 40% and an expanding economy at 60%.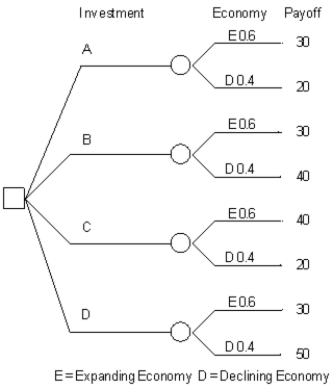
Refer to Exhibit 14.5. What is the expected monetary value for the investor's problem?
A) 32
B) 36
C) 38
D) 42
The following questions are based on the information below.
An investor is considering 4 investments, A, B, C, D. The payoff from each investment is a function of the economic climate over the next 2 years. The economy can expand or decline. The following decision tree has been developed for the problem. The investor has estimated the probability of a declining economy at 40% and an expanding economy at 60%.

Refer to Exhibit 14.5. What is the expected monetary value for the investor's problem?
A) 32
B) 36
C) 38
D) 42

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Exhibit 14.8
The following questions use the information below.
A company needs to buy a new insurance policy. They have three policies to choose from, A, B and C. The policies differ with respect to price, coverage and ease of billing. The company has developed the following AHP tables for price and summary. The other tables are not shown due to space limitations.

A circular node in a decision tree is called a(n) ____ node.
A) chance
B) random
C) decision
D) event
The following questions use the information below.
A company needs to buy a new insurance policy. They have three policies to choose from, A, B and C. The policies differ with respect to price, coverage and ease of billing. The company has developed the following AHP tables for price and summary. The other tables are not shown due to space limitations.


A circular node in a decision tree is called a(n) ____ node.
A) chance
B) random
C) decision
D) event

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Exhibit 14.3
The following questions are based on the information below.
An investor is considering 4 investments, A, B, C and leaving his money in the bank. The payoff from each investment is a function of the economic climate over the next 2 years. The economy can expand or decline. The following payoff matrix has been developed for the decision problem. The investor has estimated the probability of a declining economy at 70% and an expanding economy at 30%.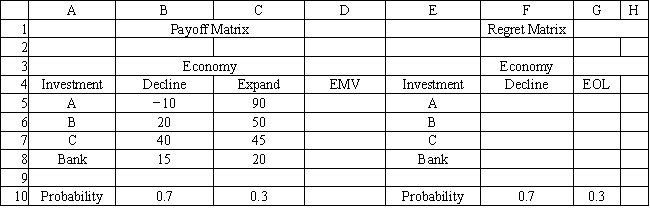
Refer to Exhibit 14.3. What formula should go in cell F5 and copied to F6:F8 of the spreadsheet if the expected regret decision rule is to be used?
A) =B$5-MAX(B$5:B$8)
B) =MAX(B$5:B$8)-MAX(B5)
C) =MAX(B$5:B$8)-MIN(B$5:B$8)
D) =MAX(B$5:B$8)-B5
The following questions are based on the information below.
An investor is considering 4 investments, A, B, C and leaving his money in the bank. The payoff from each investment is a function of the economic climate over the next 2 years. The economy can expand or decline. The following payoff matrix has been developed for the decision problem. The investor has estimated the probability of a declining economy at 70% and an expanding economy at 30%.

Refer to Exhibit 14.3. What formula should go in cell F5 and copied to F6:F8 of the spreadsheet if the expected regret decision rule is to be used?
A) =B$5-MAX(B$5:B$8)
B) =MAX(B$5:B$8)-MAX(B5)
C) =MAX(B$5:B$8)-MIN(B$5:B$8)
D) =MAX(B$5:B$8)-B5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Exhibit 14.1
The following questions are based on the information below.
An investor is considering 4 investments, A, B, C and leaving his money in the bank. The payoff from each investment is a function of the economic climate over the next 2 years. The economy can expand or decline. The following payoff matrix has been developed for the decision problem.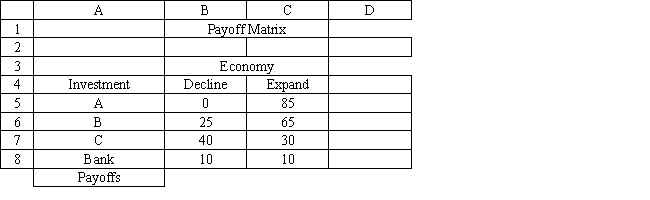
Refer to Exhibit 14.1. What decision should be made according to the maximin decision rule?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) Bank
The following questions are based on the information below.
An investor is considering 4 investments, A, B, C and leaving his money in the bank. The payoff from each investment is a function of the economic climate over the next 2 years. The economy can expand or decline. The following payoff matrix has been developed for the decision problem.

Refer to Exhibit 14.1. What decision should be made according to the maximin decision rule?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) Bank

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Exhibit 14.8
The following questions use the information below.
A company needs to buy a new insurance policy. They have three policies to choose from, A, B and C. The policies differ with respect to price, coverage and ease of billing. The company has developed the following AHP tables for price and summary. The other tables are not shown due to space limitations.

A "risk averse" decision maker assigns the ____ relative utility to any payoff but has a(n) ____ marginal utility for increased payoffs.
A) largest; increasing
B) largest; diminishing
C) smallest; diminishing
D) smallest; increasing
The following questions use the information below.
A company needs to buy a new insurance policy. They have three policies to choose from, A, B and C. The policies differ with respect to price, coverage and ease of billing. The company has developed the following AHP tables for price and summary. The other tables are not shown due to space limitations.


A "risk averse" decision maker assigns the ____ relative utility to any payoff but has a(n) ____ marginal utility for increased payoffs.
A) largest; increasing
B) largest; diminishing
C) smallest; diminishing
D) smallest; increasing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Exhibit 14.4
The following questions are based on the information below.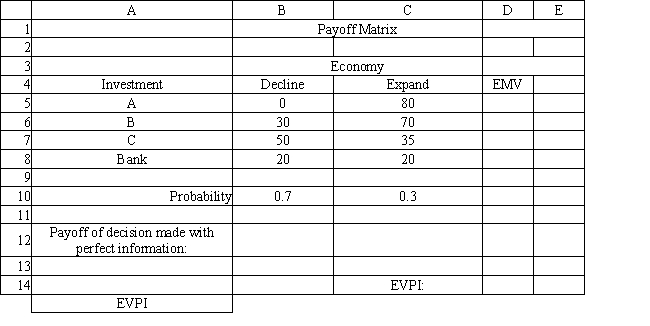
Refer to Exhibit 14.4. What is the expected value with perfect information for the investor?
A) 13.5
B) 45.5
C) 59
D) 80
The following questions are based on the information below.

Refer to Exhibit 14.4. What is the expected value with perfect information for the investor?
A) 13.5
B) 45.5
C) 59
D) 80

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Exhibit 14.8
The following questions use the information below.
A company needs to buy a new insurance policy. They have three policies to choose from, A, B and C. The policies differ with respect to price, coverage and ease of billing. The company has developed the following AHP tables for price and summary. The other tables are not shown due to space limitations.

Every nonprobabilistic method has a weakness for decision making. Which of the following is incorrect regarding a method and its weakness?
A) The maximax method ignores potentially large losses.
B) The maximin method ignores potentially large payoffs.
C) The minimax regret method can lead to inconsistent decisions.
D) All of these are correct.
The following questions use the information below.
A company needs to buy a new insurance policy. They have three policies to choose from, A, B and C. The policies differ with respect to price, coverage and ease of billing. The company has developed the following AHP tables for price and summary. The other tables are not shown due to space limitations.


Every nonprobabilistic method has a weakness for decision making. Which of the following is incorrect regarding a method and its weakness?
A) The maximax method ignores potentially large losses.
B) The maximin method ignores potentially large payoffs.
C) The minimax regret method can lead to inconsistent decisions.
D) All of these are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Exhibit 14.7
The following questions use the information below.
A decision maker is faced with two alternatives. The decision maker has determined that she is indifferent between the two alternatives when p = 0.45.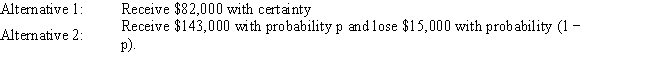
Which are characteristics of decision-making under uncertainty?
A) the probability of possible future events is unknown
B) decision-makers must rely on probabilities in evaluating outcomes
C) all process parameters have known values
D) some process parameters have known values
The following questions use the information below.
A decision maker is faced with two alternatives. The decision maker has determined that she is indifferent between the two alternatives when p = 0.45.
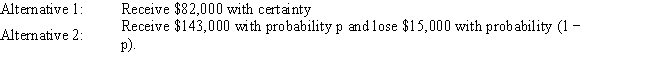
Which are characteristics of decision-making under uncertainty?
A) the probability of possible future events is unknown
B) decision-makers must rely on probabilities in evaluating outcomes
C) all process parameters have known values
D) some process parameters have known values

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Exhibit 14.1
The following questions are based on the information below.
An investor is considering 4 investments, A, B, C and leaving his money in the bank. The payoff from each investment is a function of the economic climate over the next 2 years. The economy can expand or decline. The following payoff matrix has been developed for the decision problem.
Although modeling provides valuable insight to decision makers, decision making remains a difficult task. Which of the following is not a primary cause for this difficulty discussed in the Decision Analysis chapter?
A) Uncertainty regarding the future.
B) Models provide decisions for the decision maker.
C) Conflicting values.
D) Conflicting objectives.
The following questions are based on the information below.
An investor is considering 4 investments, A, B, C and leaving his money in the bank. The payoff from each investment is a function of the economic climate over the next 2 years. The economy can expand or decline. The following payoff matrix has been developed for the decision problem.

Although modeling provides valuable insight to decision makers, decision making remains a difficult task. Which of the following is not a primary cause for this difficulty discussed in the Decision Analysis chapter?
A) Uncertainty regarding the future.
B) Models provide decisions for the decision maker.
C) Conflicting values.
D) Conflicting objectives.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Exhibit 14.3
The following questions are based on the information below.
An investor is considering 4 investments, A, B, C and leaving his money in the bank. The payoff from each investment is a function of the economic climate over the next 2 years. The economy can expand or decline. The following payoff matrix has been developed for the decision problem. The investor has estimated the probability of a declining economy at 70% and an expanding economy at 30%.
The decision rule which determines the minimum payoff for each alternative and then selects the alternative associated with the largest minimum payoff is the
A) maximax decision rule.
B) maximin decision rule.
C) minimax regret decision rule.
D) minimin decision rule.
The following questions are based on the information below.
An investor is considering 4 investments, A, B, C and leaving his money in the bank. The payoff from each investment is a function of the economic climate over the next 2 years. The economy can expand or decline. The following payoff matrix has been developed for the decision problem. The investor has estimated the probability of a declining economy at 70% and an expanding economy at 30%.

The decision rule which determines the minimum payoff for each alternative and then selects the alternative associated with the largest minimum payoff is the
A) maximax decision rule.
B) maximin decision rule.
C) minimax regret decision rule.
D) minimin decision rule.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Exhibit 14.8
The following questions use the information below.
A company needs to buy a new insurance policy. They have three policies to choose from, A, B and C. The policies differ with respect to price, coverage and ease of billing. The company has developed the following AHP tables for price and summary. The other tables are not shown due to space limitations.

Refer to Exhibit 14.8. What formula should go in cell F11 and get copied to F12:F13 of the Price worksheet to compute the Price Score?
A) =AVERAGE(C4:C6)
B) =AVERAGE(C11:E11)
C) =AVERAGE(G11:G13)
D) =AVERAGE(C7:E7)
The following questions use the information below.
A company needs to buy a new insurance policy. They have three policies to choose from, A, B and C. The policies differ with respect to price, coverage and ease of billing. The company has developed the following AHP tables for price and summary. The other tables are not shown due to space limitations.


Refer to Exhibit 14.8. What formula should go in cell F11 and get copied to F12:F13 of the Price worksheet to compute the Price Score?
A) =AVERAGE(C4:C6)
B) =AVERAGE(C11:E11)
C) =AVERAGE(G11:G13)
D) =AVERAGE(C7:E7)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Exhibit 14.5
The following questions are based on the information below.
An investor is considering 4 investments, A, B, C, D. The payoff from each investment is a function of the economic climate over the next 2 years. The economy can expand or decline. The following decision tree has been developed for the problem. The investor has estimated the probability of a declining economy at 40% and an expanding economy at 60%.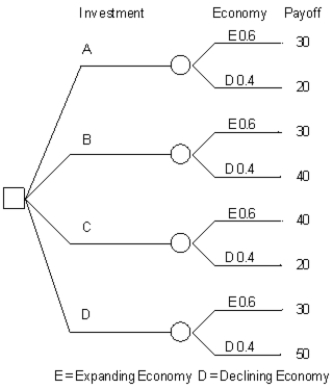
A square node in a decision tree is called a(n) ____ node.
A) chance
B) random
C) decision
D) event
The following questions are based on the information below.
An investor is considering 4 investments, A, B, C, D. The payoff from each investment is a function of the economic climate over the next 2 years. The economy can expand or decline. The following decision tree has been developed for the problem. The investor has estimated the probability of a declining economy at 40% and an expanding economy at 60%.

A square node in a decision tree is called a(n) ____ node.
A) chance
B) random
C) decision
D) event

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Exhibit 14.8
The following questions use the information below.
A company needs to buy a new insurance policy. They have three policies to choose from, A, B and C. The policies differ with respect to price, coverage and ease of billing. The company has developed the following AHP tables for price and summary. The other tables are not shown due to space limitations.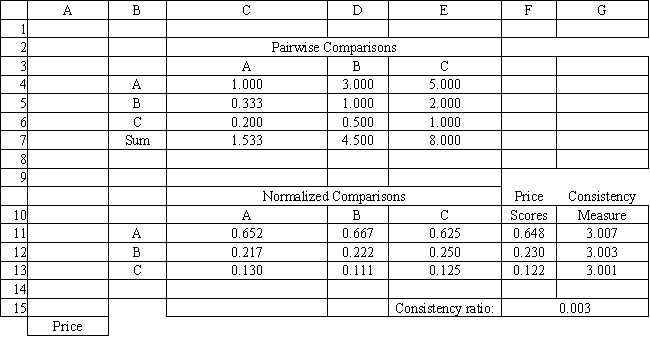
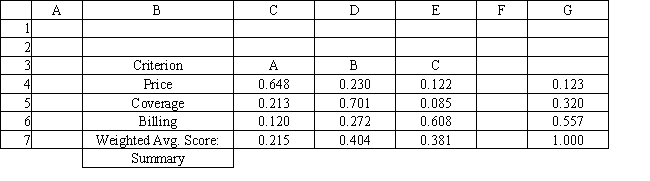
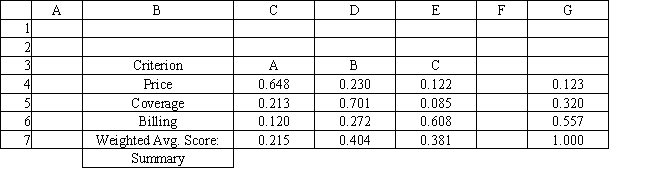
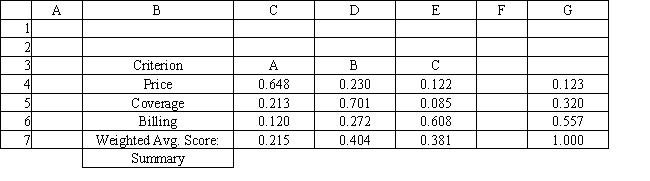
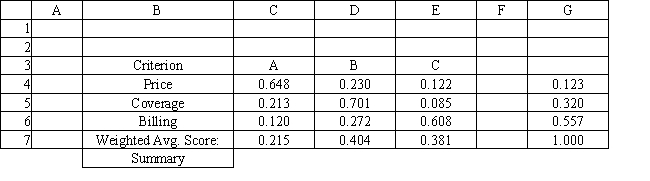
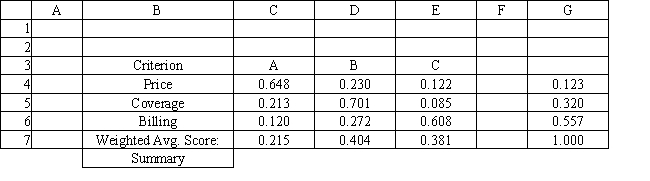
Refer to Exhibit 14.8. What formula should go in cell C7 and get copied to D7:E7 of the Summary worksheet to compute the Weighted Average Score?
A) =SUMPRODUCT(C4:E4,$G$4:$G$6)
B) =SUMPRODUCT(C4:C6,$C$5:$C$7)
C) =SUMPRODUCT($G$4,$G$6)
D) =SUMPRODUCT(C4:C6,$G$4:$G$6)
The following questions use the information below.
A company needs to buy a new insurance policy. They have three policies to choose from, A, B and C. The policies differ with respect to price, coverage and ease of billing. The company has developed the following AHP tables for price and summary. The other tables are not shown due to space limitations.


Refer to Exhibit 14.8. What formula should go in cell C7 and get copied to D7:E7 of the Summary worksheet to compute the Weighted Average Score?
A) =SUMPRODUCT(C4:E4,$G$4:$G$6)
B) =SUMPRODUCT(C4:C6,$C$5:$C$7)
C) =SUMPRODUCT($G$4,$G$6)
D) =SUMPRODUCT(C4:C6,$G$4:$G$6)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Exhibit 14.4
The following questions are based on the information below.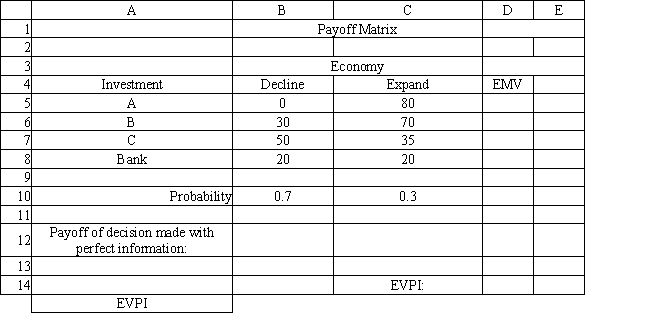
Refer to Exhibit 14.4. What formula should go in cell D14 of the spreadsheet to compute the EVPI?
A) MAX(D5:D8)-D12
B) D12-MIN(D5:D8)
C) SUMPRODUCT(B12:C12,B10:C10)-MAX(D5:D8)
D) D12-MAX(D5:D8)
The following questions are based on the information below.

Refer to Exhibit 14.4. What formula should go in cell D14 of the spreadsheet to compute the EVPI?
A) MAX(D5:D8)-D12
B) D12-MIN(D5:D8)
C) SUMPRODUCT(B12:C12,B10:C10)-MAX(D5:D8)
D) D12-MAX(D5:D8)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Exhibit 14.5
The following questions are based on the information below.
An investor is considering 4 investments, A, B, C, D. The payoff from each investment is a function of the economic climate over the next 2 years. The economy can expand or decline. The following decision tree has been developed for the problem. The investor has estimated the probability of a declining economy at 40% and an expanding economy at 60%.
Refer to Exhibit 14.5. How high can P(E) go before the investor's decision, based on expected monetary value criteria, changes?
A) 0.65
B) 0.70
C) 0.75
D) 0.80
The following questions are based on the information below.
An investor is considering 4 investments, A, B, C, D. The payoff from each investment is a function of the economic climate over the next 2 years. The economy can expand or decline. The following decision tree has been developed for the problem. The investor has estimated the probability of a declining economy at 40% and an expanding economy at 60%.

Refer to Exhibit 14.5. How high can P(E) go before the investor's decision, based on expected monetary value criteria, changes?
A) 0.65
B) 0.70
C) 0.75
D) 0.80

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Exhibit 14.8
The following questions use the information below.
A company needs to buy a new insurance policy. They have three policies to choose from, A, B and C. The policies differ with respect to price, coverage and ease of billing. The company has developed the following AHP tables for price and summary. The other tables are not shown due to space limitations.

The minimum EOL in a decision problem will always
A) exceed the EVPI.
B) be less than the EVPI.
C) equal the EVPI.
D) equal the EMV.
The following questions use the information below.
A company needs to buy a new insurance policy. They have three policies to choose from, A, B and C. The policies differ with respect to price, coverage and ease of billing. The company has developed the following AHP tables for price and summary. The other tables are not shown due to space limitations.


The minimum EOL in a decision problem will always
A) exceed the EVPI.
B) be less than the EVPI.
C) equal the EVPI.
D) equal the EMV.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Exhibit 14.5
The following questions are based on the information below.
An investor is considering 4 investments, A, B, C, D. The payoff from each investment is a function of the economic climate over the next 2 years. The economy can expand or decline. The following decision tree has been developed for the problem. The investor has estimated the probability of a declining economy at 40% and an expanding economy at 60%.
Which decision rule pessimistically assumes that nature will always be "against us" regardless of what decision we make?
A) maximax decision rule.
B) maximin decision rule.
C) minimax regret decision rule.
D) minimin decision rule.
The following questions are based on the information below.
An investor is considering 4 investments, A, B, C, D. The payoff from each investment is a function of the economic climate over the next 2 years. The economy can expand or decline. The following decision tree has been developed for the problem. The investor has estimated the probability of a declining economy at 40% and an expanding economy at 60%.

Which decision rule pessimistically assumes that nature will always be "against us" regardless of what decision we make?
A) maximax decision rule.
B) maximin decision rule.
C) minimax regret decision rule.
D) minimin decision rule.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Exhibit 14.6
The following questions use the information below.
A company is planning a plant expansion. They can build a large or small plant. The payoffs for the plant depend on the level of consumer demand for the company's products. The company believes that there is an 69% chance that demand for their products will be high and a 31% chance that it will be low. The company can pay a market research firm to survey consumer attitudes towards the company's products. There is a 63% chance that the customers will like the products and a 37% chance that they won't. The payoff matrix and costs of the two plants are listed below. The company believes that if the survey is favorable there is a 92% chance that demand will be high for the products. If the survey is unfavorable there is only a 30% chance that the demand will be high. The following decision tree has been built for this problem. The company has computed that the expected monetary value of the best decision without sample information is 154.35 million. The company has developed the following conditional probability table for their decision problem.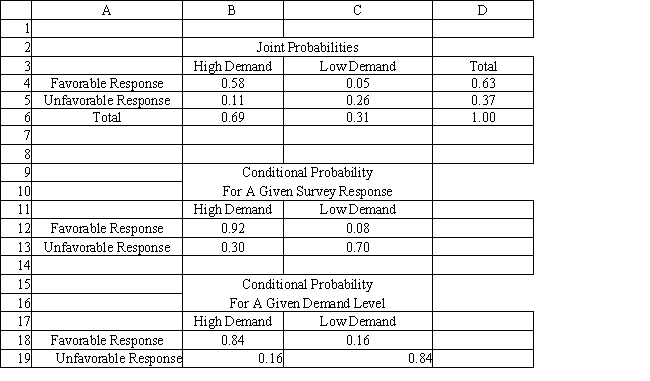
Refer to Exhibit 14.6. What is P(F∩H), where F = favorable response and H = high demand?
A) .58
B) .63
C) .84
D) .92
The following questions use the information below.
A company is planning a plant expansion. They can build a large or small plant. The payoffs for the plant depend on the level of consumer demand for the company's products. The company believes that there is an 69% chance that demand for their products will be high and a 31% chance that it will be low. The company can pay a market research firm to survey consumer attitudes towards the company's products. There is a 63% chance that the customers will like the products and a 37% chance that they won't. The payoff matrix and costs of the two plants are listed below. The company believes that if the survey is favorable there is a 92% chance that demand will be high for the products. If the survey is unfavorable there is only a 30% chance that the demand will be high. The following decision tree has been built for this problem. The company has computed that the expected monetary value of the best decision without sample information is 154.35 million. The company has developed the following conditional probability table for their decision problem.

Refer to Exhibit 14.6. What is P(F∩H), where F = favorable response and H = high demand?
A) .58
B) .63
C) .84
D) .92

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Exhibit 14.5
The following questions are based on the information below.
An investor is considering 4 investments, A, B, C, D. The payoff from each investment is a function of the economic climate over the next 2 years. The economy can expand or decline. The following decision tree has been developed for the problem. The investor has estimated the probability of a declining economy at 40% and an expanding economy at 60%.
Based on the radar chart of the weighted scores provided below, which of the following interpretations is incorrect? 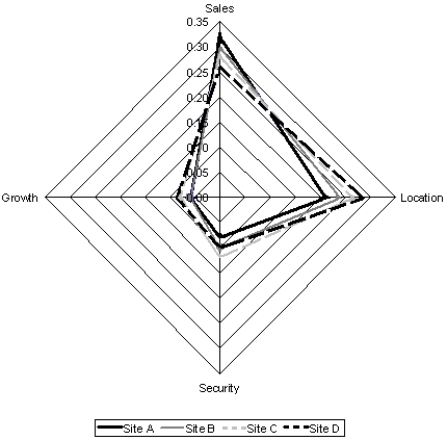
A) Site A wins on the Sales criteria but is last on the Location criteria.
B) Site C wins on the Security criteria and scores high on the remaining three criteria.
C) Site B scores lowest on each of the four criteria.
D) No site dominates on each of the four criteria.
The following questions are based on the information below.
An investor is considering 4 investments, A, B, C, D. The payoff from each investment is a function of the economic climate over the next 2 years. The economy can expand or decline. The following decision tree has been developed for the problem. The investor has estimated the probability of a declining economy at 40% and an expanding economy at 60%.

Based on the radar chart of the weighted scores provided below, which of the following interpretations is incorrect?

A) Site A wins on the Sales criteria but is last on the Location criteria.
B) Site C wins on the Security criteria and scores high on the remaining three criteria.
C) Site B scores lowest on each of the four criteria.
D) No site dominates on each of the four criteria.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Exhibit 14.2
The following questions are based on the information below.
An investor is considering 4 investments, A, B, C and leaving his money in the bank. The payoff from each investment is a function of the economic climate over the next 2 years. The economy can expand or decline. The following payoff matrix has been developed for the decision problem.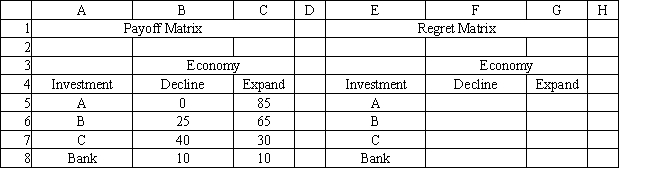
Suppose that EVPI=0. This means that
A) the decision problem involves no risk
B) the decision problem is certain
C) the payoff under risk iz zero
D) the decision problem is incorrectly formulated
The following questions are based on the information below.
An investor is considering 4 investments, A, B, C and leaving his money in the bank. The payoff from each investment is a function of the economic climate over the next 2 years. The economy can expand or decline. The following payoff matrix has been developed for the decision problem.

Suppose that EVPI=0. This means that
A) the decision problem involves no risk
B) the decision problem is certain
C) the payoff under risk iz zero
D) the decision problem is incorrectly formulated

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Exhibit 14.5
The following questions are based on the information below.
An investor is considering 4 investments, A, B, C, D. The payoff from each investment is a function of the economic climate over the next 2 years. The economy can expand or decline. The following decision tree has been developed for the problem. The investor has estimated the probability of a declining economy at 40% and an expanding economy at 60%.
Decision models are applicable when
A) there are multiple alternatives
B) there are multiple states of nature
C) there is only one alternative
D) there is only one state of nature
The following questions are based on the information below.
An investor is considering 4 investments, A, B, C, D. The payoff from each investment is a function of the economic climate over the next 2 years. The economy can expand or decline. The following decision tree has been developed for the problem. The investor has estimated the probability of a declining economy at 40% and an expanding economy at 60%.

Decision models are applicable when
A) there are multiple alternatives
B) there are multiple states of nature
C) there is only one alternative
D) there is only one state of nature

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Exhibit 14.6
The following questions use the information below.
A company is planning a plant expansion. They can build a large or small plant. The payoffs for the plant depend on the level of consumer demand for the company's products. The company believes that there is an 69% chance that demand for their products will be high and a 31% chance that it will be low. The company can pay a market research firm to survey consumer attitudes towards the company's products. There is a 63% chance that the customers will like the products and a 37% chance that they won't. The payoff matrix and costs of the two plants are listed below. The company believes that if the survey is favorable there is a 92% chance that demand will be high for the products. If the survey is unfavorable there is only a 30% chance that the demand will be high. The following decision tree has been built for this problem. The company has computed that the expected monetary value of the best decision without sample information is 154.35 million. The company has developed the following conditional probability table for their decision problem.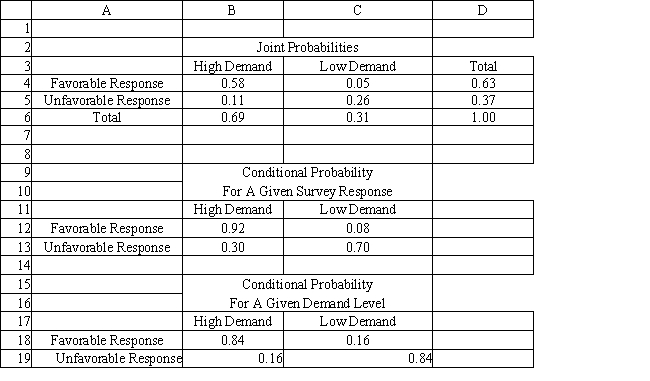
Refer to Exhibit 14.6. What formula should go in cell C13 of the probability table?
A) =C5/$D4
B) =C5/C$6
C) =C5/$D5
D) =C4/$D4
The following questions use the information below.
A company is planning a plant expansion. They can build a large or small plant. The payoffs for the plant depend on the level of consumer demand for the company's products. The company believes that there is an 69% chance that demand for their products will be high and a 31% chance that it will be low. The company can pay a market research firm to survey consumer attitudes towards the company's products. There is a 63% chance that the customers will like the products and a 37% chance that they won't. The payoff matrix and costs of the two plants are listed below. The company believes that if the survey is favorable there is a 92% chance that demand will be high for the products. If the survey is unfavorable there is only a 30% chance that the demand will be high. The following decision tree has been built for this problem. The company has computed that the expected monetary value of the best decision without sample information is 154.35 million. The company has developed the following conditional probability table for their decision problem.

Refer to Exhibit 14.6. What formula should go in cell C13 of the probability table?
A) =C5/$D4
B) =C5/C$6
C) =C5/$D5
D) =C4/$D4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Exhibit 14.5
The following questions are based on the information below.
An investor is considering 4 investments, A, B, C, D. The payoff from each investment is a function of the economic climate over the next 2 years. The economy can expand or decline. The following decision tree has been developed for the problem. The investor has estimated the probability of a declining economy at 40% and an expanding economy at 60%.
The decision with the smallest expected opportunity loss (EOL) will also have the
A) smallest EMV.
B) largest EMV.
C) smallest regret.
D) largest regret.
The following questions are based on the information below.
An investor is considering 4 investments, A, B, C, D. The payoff from each investment is a function of the economic climate over the next 2 years. The economy can expand or decline. The following decision tree has been developed for the problem. The investor has estimated the probability of a declining economy at 40% and an expanding economy at 60%.

The decision with the smallest expected opportunity loss (EOL) will also have the
A) smallest EMV.
B) largest EMV.
C) smallest regret.
D) largest regret.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Exhibit 14.5
The following questions are based on the information below.
An investor is considering 4 investments, A, B, C, D. The payoff from each investment is a function of the economic climate over the next 2 years. The economy can expand or decline. The following decision tree has been developed for the problem. The investor has estimated the probability of a declining economy at 40% and an expanding economy at 60%.
The decision rule which selects the alternative associated with the smallest maximum opportunity loss is the
A) maximax decision rule.
B) maximin decision rule.
C) minimax regret decision rule.
D) minimin decision rule.
The following questions are based on the information below.
An investor is considering 4 investments, A, B, C, D. The payoff from each investment is a function of the economic climate over the next 2 years. The economy can expand or decline. The following decision tree has been developed for the problem. The investor has estimated the probability of a declining economy at 40% and an expanding economy at 60%.

The decision rule which selects the alternative associated with the smallest maximum opportunity loss is the
A) maximax decision rule.
B) maximin decision rule.
C) minimax regret decision rule.
D) minimin decision rule.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Exhibit 14.5
The following questions are based on the information below.
An investor is considering 4 investments, A, B, C, D. The payoff from each investment is a function of the economic climate over the next 2 years. The economy can expand or decline. The following decision tree has been developed for the problem. The investor has estimated the probability of a declining economy at 40% and an expanding economy at 60%.
Business decision models can be categorized as
A) decision-making under uncertainty
B) decision-making under risk
C) decision making under certainty
D) (a) and (b) only
The following questions are based on the information below.
An investor is considering 4 investments, A, B, C, D. The payoff from each investment is a function of the economic climate over the next 2 years. The economy can expand or decline. The following decision tree has been developed for the problem. The investor has estimated the probability of a declining economy at 40% and an expanding economy at 60%.

Business decision models can be categorized as
A) decision-making under uncertainty
B) decision-making under risk
C) decision making under certainty
D) (a) and (b) only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Exhibit 14.2
The following questions are based on the information below.
An investor is considering 4 investments, A, B, C and leaving his money in the bank. The payoff from each investment is a function of the economic climate over the next 2 years. The economy can expand or decline. The following payoff matrix has been developed for the decision problem.
Refer to Exhibit 14.2. What formula should go in cell H5 and copied to H6:H8 of the Regret Table above to implement the minimax regret decision rule?
A) =MAX(MAX(F5:G5))
B) =MIN(F5:G5)
C) =AVERAGE(F5:G5)
D) =MAX(F5:G5)
The following questions are based on the information below.
An investor is considering 4 investments, A, B, C and leaving his money in the bank. The payoff from each investment is a function of the economic climate over the next 2 years. The economy can expand or decline. The following payoff matrix has been developed for the decision problem.

Refer to Exhibit 14.2. What formula should go in cell H5 and copied to H6:H8 of the Regret Table above to implement the minimax regret decision rule?
A) =MAX(MAX(F5:G5))
B) =MIN(F5:G5)
C) =AVERAGE(F5:G5)
D) =MAX(F5:G5)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Exhibit 14.6
The following questions use the information below.
A company is planning a plant expansion. They can build a large or small plant. The payoffs for the plant depend on the level of consumer demand for the company's products. The company believes that there is an 69% chance that demand for their products will be high and a 31% chance that it will be low. The company can pay a market research firm to survey consumer attitudes towards the company's products. There is a 63% chance that the customers will like the products and a 37% chance that they won't. The payoff matrix and costs of the two plants are listed below. The company believes that if the survey is favorable there is a 92% chance that demand will be high for the products. If the survey is unfavorable there is only a 30% chance that the demand will be high. The following decision tree has been built for this problem. The company has computed that the expected monetary value of the best decision without sample information is 154.35 million. The company has developed the following conditional probability table for their decision problem.
Which of the following summarizes the final outcome for each decision alternative?
A) payoff matrix
B) outcome matrix
C) yield matrix
D) performance matrix
The following questions use the information below.
A company is planning a plant expansion. They can build a large or small plant. The payoffs for the plant depend on the level of consumer demand for the company's products. The company believes that there is an 69% chance that demand for their products will be high and a 31% chance that it will be low. The company can pay a market research firm to survey consumer attitudes towards the company's products. There is a 63% chance that the customers will like the products and a 37% chance that they won't. The payoff matrix and costs of the two plants are listed below. The company believes that if the survey is favorable there is a 92% chance that demand will be high for the products. If the survey is unfavorable there is only a 30% chance that the demand will be high. The following decision tree has been built for this problem. The company has computed that the expected monetary value of the best decision without sample information is 154.35 million. The company has developed the following conditional probability table for their decision problem.

Which of the following summarizes the final outcome for each decision alternative?
A) payoff matrix
B) outcome matrix
C) yield matrix
D) performance matrix

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Exhibit 14.5
The following questions are based on the information below.
An investor is considering 4 investments, A, B, C, D. The payoff from each investment is a function of the economic climate over the next 2 years. The economy can expand or decline. The following decision tree has been developed for the problem. The investor has estimated the probability of a declining economy at 40% and an expanding economy at 60%.
What is the formula for the weighted average score for alternative j when using a multi-criteria scoring model?
A)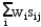
B)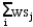
C)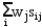
D)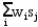
The following questions are based on the information below.
An investor is considering 4 investments, A, B, C, D. The payoff from each investment is a function of the economic climate over the next 2 years. The economy can expand or decline. The following decision tree has been developed for the problem. The investor has estimated the probability of a declining economy at 40% and an expanding economy at 60%.

What is the formula for the weighted average score for alternative j when using a multi-criteria scoring model?
A)
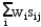
B)
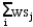
C)
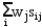
D)
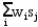

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Exhibit 14.1
The following questions are based on the information below.
An investor is considering 4 investments, A, B, C and leaving his money in the bank. The payoff from each investment is a function of the economic climate over the next 2 years. The economy can expand or decline. The following payoff matrix has been developed for the decision problem.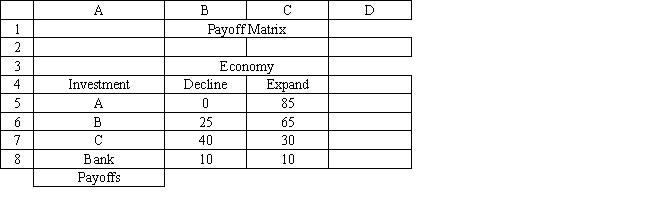
Refer to Exhibit 14.1. What decision should be made according to the maximax decision rule?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) Bank
The following questions are based on the information below.
An investor is considering 4 investments, A, B, C and leaving his money in the bank. The payoff from each investment is a function of the economic climate over the next 2 years. The economy can expand or decline. The following payoff matrix has been developed for the decision problem.

Refer to Exhibit 14.1. What decision should be made according to the maximax decision rule?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) Bank

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Exhibit 14.8
The following questions use the information below.
A company needs to buy a new insurance policy. They have three policies to choose from, A, B and C. The policies differ with respect to price, coverage and ease of billing. The company has developed the following AHP tables for price and summary. The other tables are not shown due to space limitations.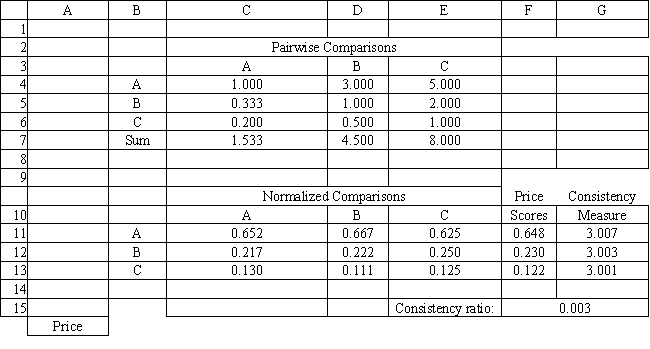
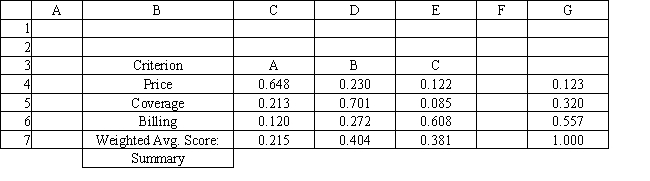
Refer to Exhibit 14.8. Which policy should the company choose based on the Summary worksheet?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) None of these
The following questions use the information below.
A company needs to buy a new insurance policy. They have three policies to choose from, A, B and C. The policies differ with respect to price, coverage and ease of billing. The company has developed the following AHP tables for price and summary. The other tables are not shown due to space limitations.


Refer to Exhibit 14.8. Which policy should the company choose based on the Summary worksheet?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) None of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Exhibit 14.8
The following questions use the information below.
A company needs to buy a new insurance policy. They have three policies to choose from, A, B and C. The policies differ with respect to price, coverage and ease of billing. The company has developed the following AHP tables for price and summary. The other tables are not shown due to space limitations.

In a graphical representation of decision trees the decision nodes are represented by
A) squares
B) circles
C) solid dots
D) ovals
The following questions use the information below.
A company needs to buy a new insurance policy. They have three policies to choose from, A, B and C. The policies differ with respect to price, coverage and ease of billing. The company has developed the following AHP tables for price and summary. The other tables are not shown due to space limitations.


In a graphical representation of decision trees the decision nodes are represented by
A) squares
B) circles
C) solid dots
D) ovals

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



