Deck 6: Decision Making Under Uncertainty
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/106
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 6: Decision Making Under Uncertainty
1
When the lines for two alternatives cross on a strategy region chart,this shows:
A)A change in which decision alternative is optimal
B)The point at which a decision was made
C)The point where the rate of change in expected value is zero
D)Resolution of the uncertainty about the input variable
E)None of these options
A)A change in which decision alternative is optimal
B)The point at which a decision was made
C)The point where the rate of change in expected value is zero
D)Resolution of the uncertainty about the input variable
E)None of these options
A
2
In decision trees,time:
A)is constant
B)proceeds from bottom to top
C)proceeds from top to bottom
D)proceeds from right to left
E)proceeds from left to right
A)is constant
B)proceeds from bottom to top
C)proceeds from top to bottom
D)proceeds from right to left
E)proceeds from left to right
E
3
The solution procedure that was introduced in the book for decision trees is called the:
A)folding diagram
B)single-stage method
C)risk profile method
D)precision tree method
E)folding back on the tree
A)folding diagram
B)single-stage method
C)risk profile method
D)precision tree method
E)folding back on the tree
E
4
The sensitivity of the expected value to changes in the input variables can be inferred from a spider chart by observing:
A)The height of the line above the horizontal axis for each variable
B)The length of the line for each variable
C)The slope of the line for each variable
D)The color of the line for each variable
E)None of these options
A)The height of the line above the horizontal axis for each variable
B)The length of the line for each variable
C)The slope of the line for each variable
D)The color of the line for each variable
E)None of these options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A payoff table lists the monetary values (profit or loss)for each possible _____and each possible _____.
A)mean and standard deviation
B)decision and utility
C)decision and outcome
D)risk profile and outcome
E)None of these options
A)mean and standard deviation
B)decision and utility
C)decision and outcome
D)risk profile and outcome
E)None of these options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
In decision trees,probabilities are listed on probability branches.These probabilities may be _____ events that have already been observed.
A)marginal due to
B)conditional on
C)averaged with
D)increased by
E)the same as
A)marginal due to
B)conditional on
C)averaged with
D)increased by
E)the same as

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
If all monetary values in a decision problem are costs,then it is customary to list them as __________ values in a cost table.
A)positive
B)negative
C)either positive or negative
D)All of these options
A)positive
B)negative
C)either positive or negative
D)All of these options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Bayes' Rule is useful for?
A)Value of Sample Information
B)Value of Perfect Information
C)Sensitivity Analysis
D)All of these options
E)None of these options
A)Value of Sample Information
B)Value of Perfect Information
C)Sensitivity Analysis
D)All of these options
E)None of these options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
There are three types of nodes that are used with the decision trees.They are the:
A)mean nodes,variance nodes,and the standard deviation nodes
B)probability nodes,risk nodes,and the expected value nodes
C)supply nodes,demand nodes,and the expected value nodes
D)decision nodes,probability nodes,and end nodes.
E)horizontal nodes,vertical nodes,and the diagonal nodes
A)mean nodes,variance nodes,and the standard deviation nodes
B)probability nodes,risk nodes,and the expected value nodes
C)supply nodes,demand nodes,and the expected value nodes
D)decision nodes,probability nodes,and end nodes.
E)horizontal nodes,vertical nodes,and the diagonal nodes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following can be obtained with a tornado chart?
A)The absolute change in expected value resulting from the change in each input variable
B)The percent change in expected value resulting from the change in each input variable
C)A ranking of the relative sensitivity of expected value to each input variable
D)None of these options
E)All of these options
A)The absolute change in expected value resulting from the change in each input variable
B)The percent change in expected value resulting from the change in each input variable
C)A ranking of the relative sensitivity of expected value to each input variable
D)None of these options
E)All of these options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
All problems related to decision making under uncertainty have three common elements:
A)the mean,median,and mode
B)the set of decisions,the cost of each decision and the profit that can be made from each decision
C)the set of possible outcomes,the set of decision variables and the constraints
D)the set of decisions,the set of possible outcomes,and a value model that prescribes results
E)None of these options
A)the mean,median,and mode
B)the set of decisions,the cost of each decision and the profit that can be made from each decision
C)the set of possible outcomes,the set of decision variables and the constraints
D)the set of decisions,the set of possible outcomes,and a value model that prescribes results
E)None of these options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of these sensitivity analysis charts is most useful in determining whether the optimal decision changes over the range of the input variable?
A)Strategy region chart
B)Tornado chart
C)Spider chart
D)All of these options
E)None of these options
A)Strategy region chart
B)Tornado chart
C)Spider chart
D)All of these options
E)None of these options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
In a single-stage decision tree problem,all ___________ are made first and then all ___________ is (are)resolved.
A)decisions; uncertainty
B)calculations; probabilities
C)EMV calculations; posterior probabilities
D)likelihoods; posterior probabilities
E)prior probabilities; joint probabilities
A)decisions; uncertainty
B)calculations; probabilities
C)EMV calculations; posterior probabilities
D)likelihoods; posterior probabilities
E)prior probabilities; joint probabilities

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following is true with regard to a good decision?
A)It ensures that good outcomes will be obtained
B)It accounts for unlucky outcomes
C)It should be independent of the sequencing of uncertainties and decisions
D)It should incorporate all information about uncertainties and alternatives
E)All of these options
A)It ensures that good outcomes will be obtained
B)It accounts for unlucky outcomes
C)It should be independent of the sequencing of uncertainties and decisions
D)It should incorporate all information about uncertainties and alternatives
E)All of these options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The preferred criterion in decision making is.
A)maximin
B)maximax
C)EMV
D)None of these options
A)maximin
B)maximax
C)EMV
D)None of these options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following statements are true?
A)Sensitivity analysis is a process of seeing how optimal decision and EMV vary when one or more inputs vary.
B)Multistage decision problem is one where decisions and observations of uncertain outcomes alternate.
C)Contingency plan is a strategy in a multistage decision problem that specifies which decision to make for each possible outcome.
D)All of the above
E)None of the above
A)Sensitivity analysis is a process of seeing how optimal decision and EMV vary when one or more inputs vary.
B)Multistage decision problem is one where decisions and observations of uncertain outcomes alternate.
C)Contingency plan is a strategy in a multistage decision problem that specifies which decision to make for each possible outcome.
D)All of the above
E)None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The expected value of sample information (EVSI)is equal to:
A)EMV with posterior information - EMV with prior information
B)EMV with free perfect information - EMV free information
C)EMV with perfect information - EMV without information
D)EMV with free information - EMV without information
E)None of these options
A)EMV with posterior information - EMV with prior information
B)EMV with free perfect information - EMV free information
C)EMV with perfect information - EMV without information
D)EMV with free information - EMV without information
E)None of these options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Expected monetary value (EMV)is:
A)the average or expected value of the decision if you knew what would happen ahead of time
B)the weighted average of possible monetary values,weighted by their probabilities
C)the average or expected value of the information if it was completely accurate
D)the amount that you would lose by not picking the best alternative
E)a decision criterion that places an equal amount on all states of nature
A)the average or expected value of the decision if you knew what would happen ahead of time
B)the weighted average of possible monetary values,weighted by their probabilities
C)the average or expected value of the information if it was completely accurate
D)the amount that you would lose by not picking the best alternative
E)a decision criterion that places an equal amount on all states of nature

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
A risk profile lists:
A)all possible monetary values and their corresponding probabilities
B)all possible outcomes and their corresponding utility
C)all options and their possible outcomes
D)the nodes and branches for each possible outcome
E)None of these options
A)all possible monetary values and their corresponding probabilities
B)all possible outcomes and their corresponding utility
C)all options and their possible outcomes
D)the nodes and branches for each possible outcome
E)None of these options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
In the nomenclature of Bayes' Rule,which of the following are probabilities that are conditioned on information that is obtained?
A)Prior probabilities
B)Posterior probabilities
C)Marginal probabilities
D)Objective probabilities
E)Subjective probabilities
A)Prior probabilities
B)Posterior probabilities
C)Marginal probabilities
D)Objective probabilities
E)Subjective probabilities

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Decision trees are composed of nodes (circles,squares,and triangles)and branches (lines).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
One class of "ready-made" utility functions is called exponential utility.Exponential utility has an adjustable parameter called risk tolerance.The risk tolerance parameter measures:
A)how much money the decision maker has to spend
B)the decision maker's attitude toward risk
C)how much risk there is in a given decision
D)the probability of an unfavorable outcome
E)None of these options
A)how much money the decision maker has to spend
B)the decision maker's attitude toward risk
C)how much risk there is in a given decision
D)the probability of an unfavorable outcome
E)None of these options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
With regard to decision making,most individuals are __________________.
A)risk averse
B)risk seekers
C)risk maximizers
D)EMV maximizers
E)None of these options
A)risk averse
B)risk seekers
C)risk maximizers
D)EMV maximizers
E)None of these options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The expected value of perfect information (EVPI)is equal to:
A)EMV with posterior information - EMV with prior information
B)EMV with free perfect information - EMV with information
C)EMV with free perfect information - EMV with no information
D)EMV with perfect information - EMV with less than perfect information
A)EMV with posterior information - EMV with prior information
B)EMV with free perfect information - EMV with information
C)EMV with free perfect information - EMV with no information
D)EMV with perfect information - EMV with less than perfect information

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Utility functions are mathematical functions that transform monetary values - payoffs and costs - into ________________.
A)expected values
B)utility values
C)EMV values
D)anchor values
E)None of the above
A)expected values
B)utility values
C)EMV values
D)anchor values
E)None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
In a single-stage decision problem,a single decision is made first,and then all uncertainty is resolved.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
In making decisions,we choose the decision with the largest expected monetary value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
In decision trees,a decision node (a square)is a time when the result of an uncertain event becomes known.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Mathematically,the utility function for risk adverse individuals is said to be _____________ and/or _______________.
A)decreasing ,linear
B)decreasing ,convex
C)increasing ,linear
D)increasing ,concave
E)increasing ,decreasing
A)decreasing ,linear
B)decreasing ,convex
C)increasing ,linear
D)increasing ,concave
E)increasing ,decreasing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
A risk profile lists all possible monetary values and their corresponding probabilities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
When you use the expected monetary value (EMV)criterion,you are not using all of the information that is shown in the risk profiles of alternatives,since you are only comparing the means.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
For each possible decision and each possible outcome,the payoff table lists the monetary value earned by an organization,where a positive value represents a profit and a negative value represents a loss.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
In decision trees,a probability node (a circle)is a time when the decision maker makes a decision.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
In decision trees,an end node (a triangle)indicates that the problem is completed; that is,all decisions have been made,all uncertainty has been resolved,and all payoffs/costs have been incurred.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Tornado charts and spider charts can be used to determine which input variables have the most impact on the expected value in a decision problem

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
If 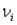 is the monetary value corresponding to outcome i and
is the monetary value corresponding to outcome i and 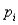 is its probability,then the expected monetary value is defined as: EMV =
is its probability,then the expected monetary value is defined as: EMV = 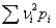 .
.
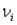 is the monetary value corresponding to outcome i and
is the monetary value corresponding to outcome i and 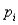 is its probability,then the expected monetary value is defined as: EMV =
is its probability,then the expected monetary value is defined as: EMV = 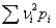 .
.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
In general,the expected monetary values (EMV)represent possible payoffs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The expected monetary value (EMV)criterion is sometimes referred to as "playing the averages" and for that reason should only be used for recurring decisions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
In a multistage decision problem,decisions and outcomes alternate.That is,a decision maker makes a decision,then some uncertainty is resolved,then the decision maker makes a second decision,then some further uncertainty is resolved,and so on.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
If x is a monetary value (a payoff if positive,a cost if negative),U(x)the utility of this value,and R > 0 is an adjustable parameter called the risk tolerance,then the function U(x)= 1 - 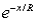 is called
is called
A)Poisson utility
B)exponential utility
C)binomial utility
D)normal utility
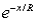 is called
is calledA)Poisson utility
B)exponential utility
C)binomial utility
D)normal utility

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
(A)Construct a decision tree to help the landowner make her decision.Make sure to label all decision and chance nodes and include appropriate costs,payoffs and probabilities.
(B)What should the landowner do? Why?
(C)Suppose the landowner is uncertain about the reliability of her geologist friend's estimate of the probability that oil will be found on her land.If she thinks the probability could be anywhere between 40% and 80%,would that change her decision?
(D)Suppose that,in addition to the uncertainty about the probability of finding oil,the landowner is also uncertain about the cost of the exploratory well (could vary +/- 25%)and the future profits (could vary +/- 50%).To which of these variables is the expected value most sensitive?
(E)What does the risk profile show about the relative risk levels for the landowner's two options?
(F)Suppose the landowner suspects that she may be a somewhat risk-averse decision maker,because the she doesn't feel there is as much of a difference between the two options as their expected values would indicate.She consults with a decision analysis expert who asks her to decide between two hypothetical alternatives: 1)a gamble with equal probabilities of winning an amount $X and losing an amount -$X/2,and 2)doing nothing,with a payoff of $0.The point at which she cannot decide between 1)and 2)is when X=$1,500,000.What is her risk tolerance if she uses an exponential utility function to model her preferences?
(G)Apply the risk tolerance given in your answer to the previous question to the landowner's decision tree in (A).What is the optimal decision in this case? What is the resulting certainty equivalent?
(H)If the landowner could hire an expert geologist prepare a report to help her make her decision,what is the most that information could be worth? Assume the geologist's information is perfectly reliable.
(B)What should the landowner do? Why?
(C)Suppose the landowner is uncertain about the reliability of her geologist friend's estimate of the probability that oil will be found on her land.If she thinks the probability could be anywhere between 40% and 80%,would that change her decision?
(D)Suppose that,in addition to the uncertainty about the probability of finding oil,the landowner is also uncertain about the cost of the exploratory well (could vary +/- 25%)and the future profits (could vary +/- 50%).To which of these variables is the expected value most sensitive?
(E)What does the risk profile show about the relative risk levels for the landowner's two options?
(F)Suppose the landowner suspects that she may be a somewhat risk-averse decision maker,because the she doesn't feel there is as much of a difference between the two options as their expected values would indicate.She consults with a decision analysis expert who asks her to decide between two hypothetical alternatives: 1)a gamble with equal probabilities of winning an amount $X and losing an amount -$X/2,and 2)doing nothing,with a payoff of $0.The point at which she cannot decide between 1)and 2)is when X=$1,500,000.What is her risk tolerance if she uses an exponential utility function to model her preferences?
(G)Apply the risk tolerance given in your answer to the previous question to the landowner's decision tree in (A).What is the optimal decision in this case? What is the resulting certainty equivalent?
(H)If the landowner could hire an expert geologist prepare a report to help her make her decision,what is the most that information could be worth? Assume the geologist's information is perfectly reliable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
A strategy region chart is useful for seeing whether the decision changes over the range of the input variable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Utility function is a function that encodes a person's or company's feelings toward risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The slope of the lines for the input variables on a tornado chart indicates their relative impact on the expected value

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
(A)Construct a decision tree to help the power company decide what to do.Make sure to label all decision and chance nodes and include appropriate costs,payoffs and probabilities.
(B)Where should the power company build the plant? What is the expected cost?
(C)Suppose that a geologist (and his team)can be hired to analyze the fault structure at Chico Canyon.He will either predict whether an earthquake will occur or not.If the geologist is perfectly reliable,what is the most the company should be willing to pay for his services?
(D)Suppose that an actual (not perfectly reliable)geologist can be hired to analyze the earthquake risk.The geologist's past record indicates that he will predict an earthquake on 90% of the occasions for which an earthquake will occur and no earthquake on 85% of the occasions for which an earthquake will not occur.Given this information,what are the posterior probabilities that an earthquake will and will not occur,given the geologists predictions?
(E)Should the company hire the geologist if his fee is $1.5M?
(B)Where should the power company build the plant? What is the expected cost?
(C)Suppose that a geologist (and his team)can be hired to analyze the fault structure at Chico Canyon.He will either predict whether an earthquake will occur or not.If the geologist is perfectly reliable,what is the most the company should be willing to pay for his services?
(D)Suppose that an actual (not perfectly reliable)geologist can be hired to analyze the earthquake risk.The geologist's past record indicates that he will predict an earthquake on 90% of the occasions for which an earthquake will occur and no earthquake on 85% of the occasions for which an earthquake will not occur.Given this information,what are the posterior probabilities that an earthquake will and will not occur,given the geologists predictions?
(E)Should the company hire the geologist if his fee is $1.5M?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The expected value of perfect information (EVPI)is the most the decision maker would be willing to pay for the sample information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Tyson Manufacturing (a maker of industrial products)is interested in marketing a new product.The company must decide whether to manufacture this product essentially on its own or employ a subcontractor to manufacture it.Below are two tables that represent the information related to the estimated probability distribution of the cost of one unit of this product under each alternative.
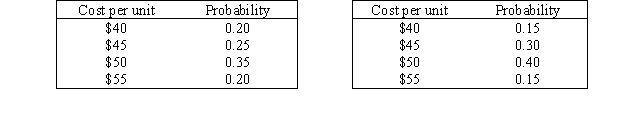 Assuming that Tyson seeks to minimize the expected unit cost of manufacturing of buying the new product,should the company make the new product or buy it from a subcontractor? Show your work.
Assuming that Tyson seeks to minimize the expected unit cost of manufacturing of buying the new product,should the company make the new product or buy it from a subcontractor? Show your work.
 Assuming that Tyson seeks to minimize the expected unit cost of manufacturing of buying the new product,should the company make the new product or buy it from a subcontractor? Show your work.
Assuming that Tyson seeks to minimize the expected unit cost of manufacturing of buying the new product,should the company make the new product or buy it from a subcontractor? Show your work.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Bayes' rule can be used for updating the probability of an uncertain outcome after observing the results of a test or study.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Prior probabilities are sometimes called likelihoods,the probabilities that are influenced by information about the outcome of an earlier uncertainty.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
A spider chart shows both the range (as a percentage)of the variability of the input variables as well as the resulting changes in the expected value

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Bayes' is useful in determining the value of perfect information (EVPI).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The expected value of sample information (EVSI)is the difference between the EMV we can obtain with sample information and the EMV we can obtain without information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
(A)Construct a decision tree to help her model her option decision making.Make sure to label all decision and chance nodes and include appropriate costs,payoffs and probabilities.
(B)What is the optimal decision making policy regarding the options in all possible scenarios over the next two years?
(C)What is the expected value of the stock options? Ignore the time value of money (assume no discounting of future payoffs)
(D)If her estimates of the increases/decreases or probabilities are inaccurate,could the options have a negative EMV?
(B)What is the optimal decision making policy regarding the options in all possible scenarios over the next two years?
(C)What is the expected value of the stock options? Ignore the time value of money (assume no discounting of future payoffs)
(D)If her estimates of the increases/decreases or probabilities are inaccurate,could the options have a negative EMV?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The expected value of perfect information (EVPI)is the difference between the EMV with perfect information and the EMV with no additional information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The certainty equivalent is the certain dollar amount a risk-averse decision maker would accept in order to avoid a gamble altogether.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Rational decision makers are never willing to violate the expected monetary value (EMV)maximization criterion when large amounts of money are at stake.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
For a risk averse decision maker,the certainty equivalent is less than the expected monetary value (EMV).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
(A)Construct a decision tree to help the company make its decision.Make sure to label all decision and chance nodes and include appropriate costs,payoffs and probabilities.
(B)What is the best lease option? Why?
(C)Suppose the company could hire an experienced mechanic to inspect the old grader to determine the repair cost before the company makes its final decision.If the mechanic is always correct in his assessments,what is the most the company would pay for the inspection?
(B)What is the best lease option? Why?
(C)Suppose the company could hire an experienced mechanic to inspect the old grader to determine the repair cost before the company makes its final decision.If the mechanic is always correct in his assessments,what is the most the company would pay for the inspection?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The expected value of perfect information (EVPI)is irrelevant concept since perfect information is almost never available at any price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
(A)Construct a decision tree to help the investor make his decision.Make sure to label all decision and chance nodes and include appropriate costs,payoffs and probabilities.
(B)What is the best choice for the investor? Why?
(C)Suppose that investor has an exponential utility function for final assets with a risk tolerance parameter equal to $60,000.Which investment opportunity will he prefer in this case? What is his certainty equivalent?
(B)What is the best choice for the investor? Why?
(C)Suppose that investor has an exponential utility function for final assets with a risk tolerance parameter equal to $60,000.Which investment opportunity will he prefer in this case? What is his certainty equivalent?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
What should the credit union do? What is their expected profit?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The station is most uncertain about the average monthly revenue associated with the rock format and an A1 audience.Construct a strategy region chart for this input variable with a possible range from $85,000 to $200,000.Does the optimal decision to select the country format change at any point in this range?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Formulate a payoff table that specifies WTC's payoff (in dollars)associated with each possible decision and each market condition in the future.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Construct a decision tree to identify the buyer's course of action that maximizes the expected profit earned by the chain from the purchase and subsequent sale of footballs in the coming year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
What are the expected payoffs for the three alternatives?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
As the average monthly revenue associated with the rock format and an A1 audience varies between $85,000 to about $140,000,what happens to the maximum expected revenue? Briefly explain why.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
What is the probability that a randomly selected individual from this population earns less than $50,000 per year?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
What course of action is optimal for WTC? What is the expected profit in that case?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
What format is optimal? What is the expected profit in that case?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Construct a decision tree to help the station identify its optimal format.Make sure to label all decision and chance nodes and include appropriate costs,payoffs and probabilities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Formulate a payoff table that specifies the contribution to profit (in dollars)from the sales of footballs by this chain for each possible purchase decision (in hundreds of pairs)and each outcome with respect to consumer demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
What else might one consider in choosing from among these alternatives?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Generate a risk profile for each possible decision in this problem.Would this have any impact on your decision?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Construct a decision tree to help the credit union decide whether or not to make the loan.Make sure to label all decision and chance nodes and include appropriate costs,payoffs and probabilities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Construct a decision tree to identify the course of action that maximizes WTC's expected profit.Make sure to label all decision and chance nodes and include appropriate costs,payoffs and probabilities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
What is the optimal strategy for order quantity,and what is the expected profit in that case?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
If a randomly selected individual is observed to earn at least $50,000 per year,what is the probability that this person is a man?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
As the average monthly revenue associated with the rock format and an A1 audience varies between about $142,500 and $200,000,what happens to the maximum expected revenue? Briefly explain why.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
If a randomly selected individual is observed to earn less than $50,000 per year,what is the probability that this person is a woman?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Generate a risk profile for each of WTC's possible decisions in this problem.Characterize the differences in risk for the different options.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 106 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



