Deck 7: Sampling and Sampling Distributions
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/92
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 7: Sampling and Sampling Distributions
1
A sampling error is the result of:
A)measurement error
B)nonresponse bias
C)nontruthful responses
D)bad luck
A)measurement error
B)nonresponse bias
C)nontruthful responses
D)bad luck
D
2
The mean of the sampling distribution of 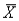 always equals
always equals
A)the population mean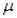
B)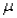 / n
/ n
C)the population standard deviation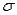
D)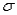 / n
/ n
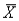 always equals
always equalsA)the population mean
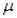
B)
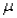 / n
/ nC)the population standard deviation
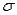
D)
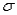 / n
/ nA
3
A judgmental sample is a sample in which the
A)sampling units are chosen using a random number table
B)quality of sampling units judged
C)sampling units are chosen according to the sampler's judgment
D)sampling units are all biased and vocal about it
A)sampling units are chosen using a random number table
B)quality of sampling units judged
C)sampling units are chosen according to the sampler's judgment
D)sampling units are all biased and vocal about it
C
4
Which of the following is not a consideration when determining appropriate sample size?
A)The cost of sampling
B)The timely collection of the data
C)Interviewer fatigue
D)The likelihood of nonsampling error
A)The cost of sampling
B)The timely collection of the data
C)Interviewer fatigue
D)The likelihood of nonsampling error

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The probability of being chosen in a simple random sample of size n from a population of size N is:
A)1/N
B)N - 1/n
C)N/n
D)n/N
A)1/N
B)N - 1/n
C)N/n
D)n/N

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The opportunity for nonsampling error is increased by:
A)larger sample sizes
B)smaller sample sizes
C)affluent samples
D)educated samples
A)larger sample sizes
B)smaller sample sizes
C)affluent samples
D)educated samples

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
In sampling,a population is:
A)the set of all humans
B)the set of all members about which a study intends to make inferences
C)any group of test subjects
D)a random group of individuals,households,cities or countries
A)the set of all humans
B)the set of all members about which a study intends to make inferences
C)any group of test subjects
D)a random group of individuals,households,cities or countries

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following statements correctly describe estimation?
A)It is the process of inferring the values of known population parameters from those of unknown sample statistics.
B)It is the process of inferring the values of unknown sample statistics from those of known population parameters.
C)It is the process of inferring the values of known sample statistics from those of unknown population parameters.
D)It is the process of inferring the values of unknown population parameters from those of known sample statistics.
A)It is the process of inferring the values of known population parameters from those of unknown sample statistics.
B)It is the process of inferring the values of unknown sample statistics from those of known population parameters.
C)It is the process of inferring the values of known sample statistics from those of unknown population parameters.
D)It is the process of inferring the values of unknown population parameters from those of known sample statistics.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The standard deviation of 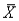 is usually called the
is usually called the
A)standard error of the mean
B)standard error of the sample
C)standard error of the population
D)randomized standard error
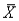 is usually called the
is usually called theA)standard error of the mean
B)standard error of the sample
C)standard error of the population
D)randomized standard error

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The defining property of a simple random sample is that:
A)every sample has the same chance of being chosen
B)the easiest method to access samples are chosen
C)the fewest samples are chosen
D)every fourth subject is chosen as a sample
A)every sample has the same chance of being chosen
B)the easiest method to access samples are chosen
C)the fewest samples are chosen
D)every fourth subject is chosen as a sample

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The key to using stratified sampling is:
A)identifying the strata
B)selecting the appropriate strata
C)defining the strata
D)randomizing the strata
A)identifying the strata
B)selecting the appropriate strata
C)defining the strata
D)randomizing the strata

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Potential sample members,called sampling units,are:
A)people
B)companies
C)households
D)All of these options
A)people
B)companies
C)households
D)All of these options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
When a portion of the sample does not respond to the survey,_____ results.
A)measurement error
B)nonresponse bias
C)sampling error
D)systematic failure
E)nonlinear error
A)measurement error
B)nonresponse bias
C)sampling error
D)systematic failure
E)nonlinear error

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The sampling method in which a population is divided into blocks and then selected by choosing a random mechanism is called a
A)random sampling
B)systematic sampling
C)stratified sampling
D)cluster sampling
A)random sampling
B)systematic sampling
C)stratified sampling
D)cluster sampling

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The accuracy of the point estimate is measured by its:
A)standard deviation
B)standard error
C)sampling error
D)nonsampling error
A)standard deviation
B)standard error
C)sampling error
D)nonsampling error

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A sample chosen in such a way that every possible subset of same size has an equal chance of being selected is called a(n)
A)interval estimation
B)point estimation
C)simple random sample.
D)statistic
A)interval estimation
B)point estimation
C)simple random sample.
D)statistic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Selecting a random sample from each identifiable subgroup within a population is called:
A)random sampling
B)systematic sampling
C)stratified sampling
D)cluster sampling
E)None of these options
A)random sampling
B)systematic sampling
C)stratified sampling
D)cluster sampling
E)None of these options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A sample in which the sampling units are chosen from the population by means of a random mechanism is a
A)probability sample
B)judgmental sample
C)stratified sample
D)systematic sample
A)probability sample
B)judgmental sample
C)stratified sample
D)systematic sample

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Identifiable subpopulations within a population are called:
A)clusters
B)samples
C)blocks
D)strata
E)None of these options
A)clusters
B)samples
C)blocks
D)strata
E)None of these options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The sampling mean 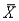 is the _____ estimate for the population mean
is the _____ estimate for the population mean 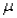 .
.
A)random
B)point
C)simple
D)interval
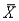 is the _____ estimate for the population mean
is the _____ estimate for the population mean 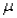 .
.A)random
B)point
C)simple
D)interval

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
With proportional sample sizes:
A)The proportion of a stratum in the sample is independent of the proportion of that stratum in the population
B)The proportion of a stratum in the sample is the same as the proportion of that stratum in the population
C)The proportion of a stratum in the sample is greater than the proportion of that stratum in the population
D)The proportion of a stratum in the sample is less than the proportion of that stratum in the population
A)The proportion of a stratum in the sample is independent of the proportion of that stratum in the population
B)The proportion of a stratum in the sample is the same as the proportion of that stratum in the population
C)The proportion of a stratum in the sample is greater than the proportion of that stratum in the population
D)The proportion of a stratum in the sample is less than the proportion of that stratum in the population

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
An unbiased estimator is a:
A)sample statistic used to approximate a population parameter
B)sample statistic,which has an expected value equal to the value of the population parameter
C)sample statistic whose value is usually less than the population parameter
D)standard error of the mean
A)sample statistic used to approximate a population parameter
B)sample statistic,which has an expected value equal to the value of the population parameter
C)sample statistic whose value is usually less than the population parameter
D)standard error of the mean

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The two basic sources for error when using random sampling are:
A)sampling and selection
B)identification and selection
C)sampling and nonsampling
D)bias and randomness
E)linear and nonlinear
A)sampling and selection
B)identification and selection
C)sampling and nonsampling
D)bias and randomness
E)linear and nonlinear

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The finite population correction factor, 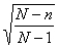 ,should generally be used when:
,should generally be used when:
A)N is any finite size
B)n is less than 5% of the population size N
C)n is greater than 5% of the population size N
D)n is any finite size
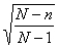 ,should generally be used when:
,should generally be used when:A)N is any finite size
B)n is less than 5% of the population size N
C)n is greater than 5% of the population size N
D)n is any finite size

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The Central Limit Theorem (CLT)is generally valid for:
A)n > 5
B)n > 10
C)n > 20
D)n > 30
E)any size n
A)n > 5
B)n > 10
C)n > 20
D)n > 30
E)any size n

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
If systematic sampling is chosen as the sampling technique,it is probably because:
A)Systematic sampling has better statistical properties than simple random sampling
B)Systematic sampling is more convenient
C)Systematic sampling always results in more representative sampling than simple random sampling
D)None of these options
A)Systematic sampling has better statistical properties than simple random sampling
B)Systematic sampling is more convenient
C)Systematic sampling always results in more representative sampling than simple random sampling
D)None of these options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
There is approximately _____ % chance that any particular 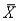 will be within two standard deviations of the population mean (
will be within two standard deviations of the population mean ( 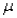 ).
).
A)90
B)95
C)99
D)99.7
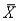 will be within two standard deviations of the population mean (
will be within two standard deviations of the population mean ( 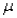 ).
).A)90
B)95
C)99
D)99.7

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the following are reasons for why simple random sampling is used infrequently in real applications?
A)Samples can be spread over a large geographic region
B)Simple random sampling requires that all sampling units be identified prior to sampling
C)Simple random sampling can result in underrepresentation or overrepresentation of certain segments of the population
D)All of these options
A)Samples can be spread over a large geographic region
B)Simple random sampling requires that all sampling units be identified prior to sampling
C)Simple random sampling can result in underrepresentation or overrepresentation of certain segments of the population
D)All of these options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Sampling error is evident when:
A)a question is poorly worded
B)the sample is too small
C)the sample is not random
D)the sample mean differs from the population mean
A)a question is poorly worded
B)the sample is too small
C)the sample is not random
D)the sample mean differs from the population mean

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The approximate standard error of the sample mean is calculated as:
A)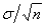
B)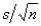
C)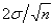
D)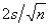
A)
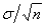
B)
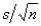
C)
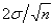
D)
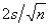

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following statements are correct?
A)An interval estimate describes a range of values that is likely not to include the actual population parameter
B)An interval estimate is an estimate of the range for a sample statistic.
C)An interval estimate is an estimate of the range of possible values for a population parameter.
D)None of these options
A)An interval estimate describes a range of values that is likely not to include the actual population parameter
B)An interval estimate is an estimate of the range for a sample statistic.
C)An interval estimate is an estimate of the range of possible values for a population parameter.
D)None of these options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Measurement error occurs when:
A)a portion of the sample does not respond to the survey
B)the sample responses are not clear
C)the responses to question do not reflect what the investigator had in mind
D)the investigator does not correctly tally all responses
A)a portion of the sample does not respond to the survey
B)the sample responses are not clear
C)the responses to question do not reflect what the investigator had in mind
D)the investigator does not correctly tally all responses

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Non-truthful response is a particular problem when:
A)sensitive questions are asked.
B)surveys are anonymous.
C)interviewers are not trained.
D)the sample is from an unusual population.
A)sensitive questions are asked.
B)surveys are anonymous.
C)interviewers are not trained.
D)the sample is from an unusual population.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The reason the Central Limit Theorem (CLT)is such an important result in statistics is because:
A)The CLT allows us to assume that the population distribution is approximately normal,provided n is reasonably large
B)The CLT allows us to estimate the population mean without knowing the exact form of the population distribution,provided n is reasonably large
C)The CLT allows us to construct confidence intervals for the population mean without knowing the exact form of the population distribution,provided n is reasonably large
D)All of these options
A)The CLT allows us to assume that the population distribution is approximately normal,provided n is reasonably large
B)The CLT allows us to estimate the population mean without knowing the exact form of the population distribution,provided n is reasonably large
C)The CLT allows us to construct confidence intervals for the population mean without knowing the exact form of the population distribution,provided n is reasonably large
D)All of these options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The theorem that states that the sampling distribution of the sample mean  is approximately normal when the sample size n is reasonably large is known as the:
is approximately normal when the sample size n is reasonably large is known as the:
A)central limit theorem
B)central tendency theorem
C)simple random sample theorem
D)point estimate theorem
 is approximately normal when the sample size n is reasonably large is known as the:
is approximately normal when the sample size n is reasonably large is known as the:A)central limit theorem
B)central tendency theorem
C)simple random sample theorem
D)point estimate theorem

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The averaging effect means that as you average more and more observations from a given distribution,the variance of the average
A)increases
B)decreases
C)is unaffected
D)could either increase,decrease or stay the same
A)increases
B)decreases
C)is unaffected
D)could either increase,decrease or stay the same

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
A list of all members of the population is called a:
A)sampling unit
B)probability sample
C)frame
D)relevant population
A)sampling unit
B)probability sample
C)frame
D)relevant population

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The opportunity for sampling error is decreased by:
A)larger sample sizes
B)smaller sample sizes
C)affluent samples
D)educated samples
A)larger sample sizes
B)smaller sample sizes
C)affluent samples
D)educated samples

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The approximate 95% confidence interval for a population mean is:
A)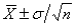
B)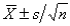
C)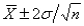
D)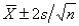
A)
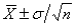
B)
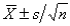
C)
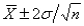
D)
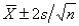

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following statements are correct?
A)A point estimate is an estimate of the range of a population parameter
B)A point estimate is a single value estimate of the value of a population parameter
C)A point estimate is an unbiased estimator if its standard deviation is the same as the actual value of the population standard deviation
D)All of these options
A)A point estimate is an estimate of the range of a population parameter
B)A point estimate is a single value estimate of the value of a population parameter
C)A point estimate is an unbiased estimator if its standard deviation is the same as the actual value of the population standard deviation
D)All of these options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
If a simple random sample of size n is chosen from a population of size N,then each member of the population has probability N / n of being chosen in the sample.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The sampling distribution of any point estimate (such as the sample mean or proportion)is the distribution of the point estimates we would obtain from all possible samples of a given size drawn from the population.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Simple random sampling can result in under-representation or over-representation of certain segments of the population.This is one of several reasons that simple random samples are almost never used in real applications.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Stratified samples are typically not used in real applications because they provide less accurate estimates of population parameters for a given sampling cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
A point estimate is a single numeric value,a "best guess" of a population parameter,calculated from the sample data.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
In cluster sampling,the population is divided into subsets called clusters (such as cities or city blocks),and then a random sample of the clusters is selected.Once the clusters are selected,we typically sample all of the members in each selected cluster.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
An interval estimate is an interval calculated from the population data,where we strongly believe the true value of the population parameter lies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
In stratified sampling with proportional sample sizes,the proportion of each stratum selected differs from stratum to stratum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The primary advantage of cluster sampling is sampling convenience (and possibly less cost).The downside,however,is that the inferences drawn from a cluster sample can be less accurate,for a given sample size,than for other sampling plans.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Cluster sampling is often less convenient and more costly than other random sampling methods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Simple random samples are typically used in real applications.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
When we sample less than 5% of the population,the finite population correction factor; fpc = 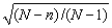 ,is used to modify the formula for the standard error of the sample mean.
,is used to modify the formula for the standard error of the sample mean.
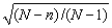 ,is used to modify the formula for the standard error of the sample mean.
,is used to modify the formula for the standard error of the sample mean.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
In systematic sampling,one of the first k members is selected randomly,and then every kth member after this one is selected.The value k is called the sampling interval and equals the ratio N / n,where N is the population size and n is the desired sample size.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
We can measure the accuracy of judgmental samples by applying some simple rules of probability.This way,judgmental samples are not likely to contain our built-in biases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
In stratified sampling,the population is divided into relatively homogeneous subsets called strata,and then random samples are taken from each stratum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The difference between the point estimate and the true value of the population parameter being estimated is called the estimation error.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
A simple random sample is one where each member of the population has a known chance (this may differ from one member to another)or probability of being chosen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
A sample of size 20 is selected at random from a population of size N.If the finite population correction factor is 0.9418,then N must be 169.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
A list of all members of the population from which we can choose a sample is called a frame,and the potential sample members are called sampling units.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
One obvious advantage of stratified sampling is that we obtain separate estimates within each stratum - which we would not obtain if we took a simple random sample from the entire population.A more important advantage is that we can increase the accuracy of the resulting population estimates by using appropriately defined strata.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Ideally,we prefer estimates that have large standard errors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
A probability sample is a sample in which the sampling units are chosen from the population by means of a random mechanism such as a random number table.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The Central Limit Theorem (CLT)says that as long as the sample size is reasonably large,there is about a 95% chance that the magnitude of the sampling error for the mean will be no more than two standard errors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
If the sample size is greater than 30,the Central Limit Theorem (CLT)will always apply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The standard error of sample mean 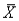 is large when the observations in the population are spread out (large
is large when the observations in the population are spread out (large 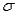 ),but that the standard error can be reduced by taking a smaller sample.
),but that the standard error can be reduced by taking a smaller sample.
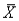 is large when the observations in the population are spread out (large
is large when the observations in the population are spread out (large 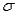 ),but that the standard error can be reduced by taking a smaller sample.
),but that the standard error can be reduced by taking a smaller sample.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Systematic sampling is generally similar to simple random sampling in its statistical properties.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
An estimator is said to be unbiased if the mean of its sampling distribution equals the value of the population parameter being estimated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The averaging effect says that as you average more and more observations from a given distribution,the variance of the average increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
It is customary to approximate the standard error of the sample mean 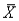 by substituting the sample standard deviation s for
by substituting the sample standard deviation s for 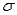 in the formula: SE(
in the formula: SE( 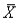 )=
)= 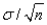 .
.
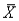 by substituting the sample standard deviation s for
by substituting the sample standard deviation s for 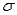 in the formula: SE(
in the formula: SE( 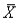 )=
)= 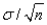 .
.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The size of a sample can be selected by first determining the desired standard error and then using the formula 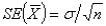 to calculate n.
to calculate n.
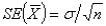 to calculate n.
to calculate n.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Consider the frame of 50 full-time employees of Computer Technologies,Inc (CTI).CTI's human resources manager has collected annual salary figures for all employees and she has calculated a mean of $47,723,a median of $41,082 and a standard deviation of $24,167.A simple random sample of 10 employees is presented below (salary is in $1,000's).Compute the mean,median,and standard deviation for the sample and compare these statistics with the measures for the entire company.



Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
The Central Limit Theorem (CLT)states that the sampling distribution of the mean is approximately normal,no matter what the distribution of the population,so long as the sample size is large enough.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The sampling distribution of the mean will have the same mean as the original population from which the samples were drawn.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Estimation is the process of inferring the value of an unknown population parameter using data from a random sample

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
A sales manager for a company that makes commercial ovens for restaurants is interested in estimating the average number of restaurants in all metropolitan areas across the entire country.He does not have access to the data for each metropolitan location,so he had decided to select a sample that will be representative of all such areas,and will use a sample size of 30.Do you believe that simple random sampling is the best approach to obtaining a representative subset of the metropolitan areas in the given frame? Explain.If not,recommend how the sales manager might proceed to select a better sample of size 30 from this data?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
The sampling distribution of the mean will have the same standard deviation as the original population from which the samples were drawn.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
An unbiased estimate is a point estimate such that the mean of its sampling distribution is equal to the true value of the population parameter being estimated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Voluntary response bias occurs when the responses to questions do not reflect what the investigator had in mind.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
The standard error of an estimate is the standard deviation of the sampling distribution of the estimate.It measures how much estimates from different samples vary.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
The randomized response technique is a way of getting at sensitive information to avoid estimation errors due to nontruthful responses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 92 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



