Deck 5: Normal, binomial, poisson, and Exponential Distributions
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/118
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 5: Normal, binomial, poisson, and Exponential Distributions
1
Given that Z is a standard normal random variable,P(-1.0 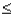 Z
Z 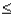 1.5)is
1.5)is
A)0.7745
B)0.8413
C)0.0919
D)0.9332
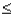 Z
Z 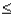 1.5)is
1.5)isA)0.7745
B)0.8413
C)0.0919
D)0.9332
A
2
The higher the value of the density function f(x),
A)the less likely the value x
B)the more likely the value x
C)the less likely the distribution is normal
D)None of the above
A)the less likely the value x
B)the more likely the value x
C)the less likely the distribution is normal
D)None of the above
B
3
A continuous probability distribution is characterized by:
A)a list of possible values
B)counts
C)an array of individual values
D)a continuum of possible values
A)a list of possible values
B)counts
C)an array of individual values
D)a continuum of possible values
D
4
Which of the following equations shows the process of standardizing?
A)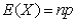
B)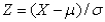
C)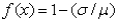
D)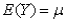
A)
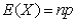
B)
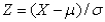
C)
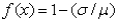
D)
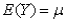

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The standard normal distribution has a mean and a standard deviation respectively equal to
A)0 and 0
B)1 and 1
C)1 and 0
D)0 and 1
A)0 and 0
B)1 and 1
C)1 and 0
D)0 and 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A Poisson distribution is:
A)relevant when we sample from a population with only two types of members.
B)relevant when we perform a series of independent,identical experiments with only two possible outcomes.
C)usually relevant when we are interested in the number of events that occur over a given interval of time
D)the cornerstone of statistical theory
E)All of the above
A)relevant when we sample from a population with only two types of members.
B)relevant when we perform a series of independent,identical experiments with only two possible outcomes.
C)usually relevant when we are interested in the number of events that occur over a given interval of time
D)the cornerstone of statistical theory
E)All of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
One reason for standardizing random variables is to measure variables with:
A)different means and standard deviations on a non-standard scale
B)different means and standard deviations on a single scale
C)dissimilar means and standard deviations in like terms
D)similar means and standard deviations on two scales
A)different means and standard deviations on a non-standard scale
B)different means and standard deviations on a single scale
C)dissimilar means and standard deviations in like terms
D)similar means and standard deviations on two scales

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
We assume that the outcomes of successive trials in a binomial experiment are:
A)probabilistically independent
B)probabilistically dependent
C)identical from trial to trial
D)random number between 0 and 1
A)probabilistically independent
B)probabilistically dependent
C)identical from trial to trial
D)random number between 0 and 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
If the value of the standard normal random variable Z is positive,then the original score is where in relationship to the mean?
A)equal to the mean
B)to the left of the mean
C)to the right of the mean
D)None of the above
A)equal to the mean
B)to the left of the mean
C)to the right of the mean
D)None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The normal distribution is:
A)a discrete distribution with two parameters
B)a binomial distribution with only one parameter
C)a density function of a discrete random variable
D)a continuous distribution with two parameters
A)a discrete distribution with two parameters
B)a binomial distribution with only one parameter
C)a density function of a discrete random variable
D)a continuous distribution with two parameters

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following might not be appropriately modeled with a normal distribution?
A)The daily low temperature in Anchorage,Alaska
B)The returns on a stock
C)The daily change in inventory at a computer manufacturer
D)The salaries of employees at a large company
A)The daily low temperature in Anchorage,Alaska
B)The returns on a stock
C)The daily change in inventory at a computer manufacturer
D)The salaries of employees at a large company

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Sampling done without replacement means that
A)only certain members of the population can be sampled
B)each member of the population can be sampled repeatedly
C)each member of the population can be sampled only once
D)each member of the population can be sampled twice
A)only certain members of the population can be sampled
B)each member of the population can be sampled repeatedly
C)each member of the population can be sampled only once
D)each member of the population can be sampled twice

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The mean  of a probability distribution is a:
of a probability distribution is a:
A)measure of variability of the distribution
B)measure of central location
C)measure of relative likelihood
D)measure of skewness of the distribution
 of a probability distribution is a:
of a probability distribution is a:A)measure of variability of the distribution
B)measure of central location
C)measure of relative likelihood
D)measure of skewness of the distribution

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which probability distribution applies to the number of events occurring within a specified period of time or space
A)Binomial distribution
B)Poisson distribution
C)Any discrete probability distribution
D)Any continuous probability distribution
A)Binomial distribution
B)Poisson distribution
C)Any discrete probability distribution
D)Any continuous probability distribution

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The Poisson random variable is a:
A)discrete random variable with infinitely many possible values
B)discrete random variable with finite number of possible values
C)continuous random variable with infinitely many possible values
D)continuous random variable with finite number of possible values
A)discrete random variable with infinitely many possible values
B)discrete random variable with finite number of possible values
C)continuous random variable with infinitely many possible values
D)continuous random variable with finite number of possible values

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The binomial probability distribution is used with
A)a discrete random variable
B)a continuous random variable
C)either a discrete or a continuous random variable,depending on the variance
D)either a discrete or a continuous random variable,depending on the sample size
A)a discrete random variable
B)a continuous random variable
C)either a discrete or a continuous random variable,depending on the variance
D)either a discrete or a continuous random variable,depending on the sample size

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The variance of a binomial distribution for which n = 100 and p = 0.20 is:
A)100
B)80
C)20
D)16
A)100
B)80
C)20
D)16

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Tossing a coin is an example of a (n)
A)binomial distribution
B)normal distribution
C)exponential distribution
D)Poisson distribution
A)binomial distribution
B)normal distribution
C)exponential distribution
D)Poisson distribution

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The standard deviation 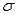 of a probability distribution is a:
of a probability distribution is a:
A)measure of variability of the distribution
B)measure of central location
C)measure of relative likelihood
D)measure of skewness of the distribution
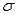 of a probability distribution is a:
of a probability distribution is a:A)measure of variability of the distribution
B)measure of central location
C)measure of relative likelihood
D)measure of skewness of the distribution

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
If we plot a continuous probability distribution f(x),the total probability under the curve is
A)-1
B)0
C)1
D)100
A)-1
B)0
C)1
D)100

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The number of loan defaults per month at a bank is Poisson distributed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Using the standard normal distribution,the Z-score representing the 5th percentile is 1.645.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The total area under the normal distribution curve is equal to one.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Given that Z is a standard normal variable,the value z for which P(Z 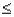 z)= 0.2580 is
z)= 0.2580 is
A)0.70
B)0.758
C)-0.65
D)0.242
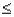 z)= 0.2580 is
z)= 0.2580 isA)0.70
B)0.758
C)-0.65
D)0.242

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
If the random variable X is exponentially distributed with parameter 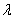 = 3,then P(X
= 3,then P(X 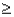 2),up to 4 decimal places ,is
2),up to 4 decimal places ,is
A)0.3333
B)0.5000
C)0.6667
D)0.0025
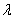 = 3,then P(X
= 3,then P(X 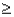 2),up to 4 decimal places ,is
2),up to 4 decimal places ,isA)0.3333
B)0.5000
C)0.6667
D)0.0025

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
If the random variable X is exponentially distributed with parameter 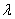 = 1.5,then P(2
= 1.5,then P(2 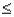 X
X  4),up to 4 decimal places,is
4),up to 4 decimal places,is
A)0.6667
B)0.0473
C)0.5000
D)0.2500
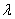 = 1.5,then P(2
= 1.5,then P(2 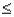 X
X  4),up to 4 decimal places,is
4),up to 4 decimal places,isA)0.6667
B)0.0473
C)0.5000
D)0.2500

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
For a given probability of success p that is not too close to 0 or 1,the binomial distribution tends to take on more of a symmetric bell shape as the number of trials n increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The variance of a binomial distribution is given by the formula 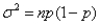 ,where n is the number of trials,and p is the probability of success in any trial.
,where n is the number of trials,and p is the probability of success in any trial.
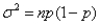 ,where n is the number of trials,and p is the probability of success in any trial.
,where n is the number of trials,and p is the probability of success in any trial.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
If the random variable X is normally distributed with mean 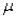 and standard deviation
and standard deviation 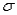 ,then the random variable Z defined by
,then the random variable Z defined by 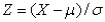 is also normally distributed with mean 0 and standard deviation 1.
is also normally distributed with mean 0 and standard deviation 1.
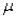 and standard deviation
and standard deviation 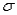 ,then the random variable Z defined by
,then the random variable Z defined by 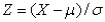 is also normally distributed with mean 0 and standard deviation 1.
is also normally distributed with mean 0 and standard deviation 1.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
If the mean of an exponential distribution is 2,then the value of the parameter 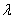 is
is
A)4
B)2
C)1
D)0.5
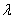 is
isA)4
B)2
C)1
D)0.5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Much of the study of probabilistic inventory models,queuing models,and reliability models relies heavily on the Poisson and Exponential distributions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Poisson distribution is appropriate to determine the probability of a given number of defective items in a shipment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Given that the random variable X is normally distributed with a mean of 80 and a standard deviation of 10,P(85 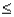 X
X 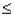 90)is
90)is
A)0.5328
B)0.3413
C)0.1915
D)0.1498
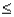 X
X 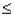 90)is
90)isA)0.5328
B)0.3413
C)0.1915
D)0.1498

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The Poisson probability distribution is one of the most commonly used continuous probability distributions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The binomial distribution is a discrete distribution that deals with a sequence of identical trials,each of which has only two possible outcomes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
If X is a normal random variable with a standard deviation of 10,then 3X has a standard deviation equal to
A)10
B)13
C)30
D)90
A)10
B)13
C)30
D)90

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
A binomial distribution with n number of trials,and probability of success p can be approximated well by a normal distribution with mean np and variance 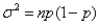 if np > 5 and n(1-p)> 5.
if np > 5 and n(1-p)> 5.
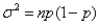 if np > 5 and n(1-p)> 5.
if np > 5 and n(1-p)> 5.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The Poisson and Exponential distributions are commonly used in which of the following applications
A)Inventory models
B)Financial models
C)Failure analysis models
D)All of these options
A)Inventory models
B)Financial models
C)Failure analysis models
D)All of these options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of the following distributions is appropriate to measure the length of time between arrivals at a grocery checkout counter?
A)Uniform
B)Normal
C)Exponential
D)Poisson
A)Uniform
B)Normal
C)Exponential
D)Poisson

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The binomial distribution is a continuous distribution that is not far behind the normal distribution in order of importance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
What is the probability that a randomly selected customer will spend less than $15?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
An exponential distribution with parameter 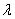 = 0.2 has mean and standard deviation both equal to 5.
= 0.2 has mean and standard deviation both equal to 5.
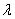 = 0.2 has mean and standard deviation both equal to 5.
= 0.2 has mean and standard deviation both equal to 5.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The binomial random variable represents the number of successes that occur in a specific period of time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Using the standard normal curve,the Z- score representing the 10th percentile is 1.28.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The binomial distribution deals with consecutive trials,each of which has two possible outcomes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The Poisson distribution is applied to events for which the probability of occurrence over a given span of time,space,or distance is very small.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Using the standard normal distribution,the Z- score representing the 99th percentile is 2.326.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
What is the probability that a randomly selected customer will spend $20 or more?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The Poisson distribution is characterized by a single parameter 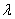 ,which must be positive.
,which must be positive.
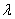 ,which must be positive.
,which must be positive.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
What is the probability that a randomly selected customer will spend between $20 and $35?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
What two dollar amounts,equidistant from the mean of $30,such that 98% of all customer purchases are between these values?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A random variable X is standardized when each value of X has the mean of X subtracted from it,and the difference is divided by the standard deviation of X.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The mean and standard deviation of a normally distributed random variable which has been "standardized" are zero and one,respectively.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
What is the probability that a randomly selected customer will spend $30 or more?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The variance of a binomial distribution for which n = 50 and p = 0.20 is 8.0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
What two dollar amounts,equidistant from the mean of $30,such that 90% of all customer purchases are between these values?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
A random variable X is normally distributed with a mean of 175 and a standard deviation of 50.Given that X = 150,its corresponding Z- score is -0.50.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
There is a 5% chance that GM will sell more than what number of cars during the next year?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Using the standard normal curve,the Z- score representing the 75th percentile is 0.674.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The Poisson random variable is a discrete random variable with infinitely many possible values.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
What number of cars,equidistant from the mean,such that 90% of car sales are between these values?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
What is the probability that GM will sell between 2.0 and 2.3 million cars during the next year?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
What is the probability that this company will sell between 2.0 and 2.15 million cars next year?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
What is the probability that none of the 20 new microwaves sold will require a warranty repair in the first 90 days?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
What is the probability that less than two of the 20 new microwaves sold will require a warranty repair in the first 90 days?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
How many chicken sandwiches must the restaurant stock to be 99% sure of not running out on a given day?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Calculate the mean,variance,and standard deviation for the entire year (assume 52 weeks in the year).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Let Y be the number of the 12 male adults who are less than 62 inches tall.Determine the mean and standard deviation of Y.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
What type of probability distribution will most likely be used to analyze warranty repair needs on new microwaves in this situation?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
What number of cars,equidistant from the mean,such that 98% of car sales are between these values?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Why is the independence assumption in Question 74 probably not realistic? Using a more realistic assumption,do you think the probability in Question 74 would increase or decrease?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
What is the probability that exactly two of the 20 new microwaves sold will require a warranty repair in the first 90 days?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Only 5% of the students taking the test scored higher than what value?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
What is the probability of getting a score higher than 85 on this exam?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
What is the probability that exactly half the male adults will be less than 62 inches tall?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
What percentage of students scored between 81 and 89 on this exam?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
If the restaurant stocks 600 hamburgers and 150 chicken sandwiches for a given day,what is the probability that it will run out of hamburgers or chicken sandwiches (or both)that day? Assume that the demands for hamburgers and chicken sandwiches are probabilistically independent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
What is the probability that this company will sell more than 2 million cars next year?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
How many hamburgers must the restaurant stock to be 99% sure of not running out on a given day?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
There is a 1% chance that this company will sell more than what number of cars during the next year?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



