Deck 12: Time Series Analysis and Forecasting
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/104
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 12: Time Series Analysis and Forecasting
1
Extrapolation methods attempt to:
A)use non-quantitative methods to predict future values
B)search for patterns in the data and then use those to predict future values
C)find variables that are correlated with the data being predicted
D)predict the next period's value by using the latest period's value
A)use non-quantitative methods to predict future values
B)search for patterns in the data and then use those to predict future values
C)find variables that are correlated with the data being predicted
D)predict the next period's value by using the latest period's value
B
2
Models such as moving average,exponential smoothing,and linear trend use only:
A)future values of Y to forecast previous values of Y
B)previous values of Y to forecast future values of Y
C)multiple explanatory variables (not just values of Y)to forecast future values of Y
D)ratio-to-moving-average methods
A)future values of Y to forecast previous values of Y
B)previous values of Y to forecast future values of Y
C)multiple explanatory variables (not just values of Y)to forecast future values of Y
D)ratio-to-moving-average methods
B
3
The random walk model is written as: 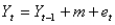 .In this model,
.In this model, 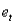 represents the:
represents the:
A)average of the Y's
B)average of the X's
C)forecasted value
D)random series with mean 0 and some constant standard deviation
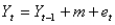 .In this model,
.In this model, 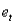 represents the:
represents the:A)average of the Y's
B)average of the X's
C)forecasted value
D)random series with mean 0 and some constant standard deviation
D
4
The linear trend 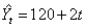 was estimated using a time series with 20 time periods.The forecasted value for time period 21 is
was estimated using a time series with 20 time periods.The forecasted value for time period 21 is
A)120
B)122
C)160
D)162
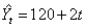 was estimated using a time series with 20 time periods.The forecasted value for time period 21 is
was estimated using a time series with 20 time periods.The forecasted value for time period 21 isA)120
B)122
C)160
D)162

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Related to the runs test,if you use a Z-statistic and you get a Z value greater than 2.0,this means that there is evidence of in the series
A)randomness
B)nonrandomness
C)nonnormality
D)heteroscedasticity
A)randomness
B)nonrandomness
C)nonnormality
D)heteroscedasticity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
In a random series,successive observations are probabilistically independent of one another.If this property is violated,the observations are said to be:
A)autocorrelated
B)intercorrelated
C)causal
D)seasonal
A)autocorrelated
B)intercorrelated
C)causal
D)seasonal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The components of a time series include:
A)base series
B)trend
C)seasonal component
D)cyclic component
E)all of these options
A)base series
B)trend
C)seasonal component
D)cyclic component
E)all of these options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A linear trend means that the time series variable changes by a:
A)constant amount each time period
B)constant percentage each time period
C)positive amount each time period
D)negative amount each time period
A)constant amount each time period
B)constant percentage each time period
C)positive amount each time period
D)negative amount each time period

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The idea behind the runs test is that a random number series should have a number of runs that is:
A)large
B)small
C)not large or small
D)constant
A)large
B)small
C)not large or small
D)constant

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following is not one of the summary measures for forecast errors that is commonly used?
A)MAE (mean absolute error)
B)MFE (mean forecast error)
C)RMSE (root mean square error)
D)MAPE (mean absolute percentage error)
A)MAE (mean absolute error)
B)MFE (mean forecast error)
C)RMSE (root mean square error)
D)MAPE (mean absolute percentage error)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Econometric models can also be called:
A)judgmental models
B)time series models
C)causal models
D)environmetric models
A)judgmental models
B)time series models
C)causal models
D)environmetric models

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The most common form of autocorrelation is positive autocorrelation,in which:
A)large observations tend to follow both large and small observations
B)small observations tend to follow both large and small observations
C)large observations tend to follow large observations and small observations tend to follow small observations
D)large observations tend to follow small observations and small observations tend to follow large observations
A)large observations tend to follow both large and small observations
B)small observations tend to follow both large and small observations
C)large observations tend to follow large observations and small observations tend to follow small observations
D)large observations tend to follow small observations and small observations tend to follow large observations

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following is not one of the techniques that can be used to identify whether a time series is truly random?
A)A graph (plot the data)
B)The runs test
C)A control chart
D)The autocorrelations (or a correlogram)
A)A graph (plot the data)
B)The runs test
C)A control chart
D)The autocorrelations (or a correlogram)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Examples of non-random patterns that may be evident on a time series graph include:
A)trends
B)increasing variance over time
C)a meandering pattern
D)too many zigzags
E)all of these options
A)trends
B)increasing variance over time
C)a meandering pattern
D)too many zigzags
E)all of these options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The runs test uses a series of 0's and 1's.The 0's and 1's represent whether each observation is:
A)above or below the predicted value of Y
B)above or below the mean value of Y
C)is above or below the mean value of the previous two observations
D)is positive or negative
A)above or below the predicted value of Y
B)above or below the mean value of Y
C)is above or below the mean value of the previous two observations
D)is positive or negative

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following summary measures for forecast errors does not depend on the units of the forecast variable?
A)MAE (mean absolute error)
B)MFE (mean forecast error)
C)RMSE (root mean square error)
D)MAPE (mean absolute percentage error)
A)MAE (mean absolute error)
B)MFE (mean forecast error)
C)RMSE (root mean square error)
D)MAPE (mean absolute percentage error)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Forecasting models can be divided into three groups.They are:
A)time series,optimization,and simulation methods
B)judgmental,extrapolation,and econometric methods
C)judgmental,random,and linear methods
D)linear,non-linear,and extrapolation methods
A)time series,optimization,and simulation methods
B)judgmental,extrapolation,and econometric methods
C)judgmental,random,and linear methods
D)linear,non-linear,and extrapolation methods

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The forecast error is the difference between
A)this period's value and the next period's value
B)the average value and the expected value of the response variable
C)the explanatory variable value and the response variable value
D)the actual value and the forecast
A)this period's value and the next period's value
B)the average value and the expected value of the response variable
C)the explanatory variable value and the response variable value
D)the actual value and the forecast

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
In contrast to linear trend,exponential trend is appropriate when the time series changes by a:
A)constant amount each time period
B)constant percentage each time period
C)positive amount each time period
D)negative amount each time period
A)constant amount each time period
B)constant percentage each time period
C)positive amount each time period
D)negative amount each time period

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Related to the runs test,if T is reasonably large (T > 20 is suggested),then the statistic can be used to perform this test.
A)F
B)t
C)Z
D)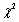
A)F
B)t
C)Z
D)
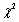

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
When using Holt's model,choosing values of the smoothing constant 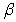 that are near 1 will result in forecast models which
that are near 1 will result in forecast models which
A)react very quickly to changes in the level
B)react very quickly to changes in the trend
C)react very quickly to changes in the level and the trend
D)react very slowly to changes in the level and the trend
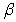 that are near 1 will result in forecast models which
that are near 1 will result in forecast models whichA)react very quickly to changes in the level
B)react very quickly to changes in the trend
C)react very quickly to changes in the level and the trend
D)react very slowly to changes in the level and the trend

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
A trend component of a time series is a long-term,relatively smooth pattern or direction exhibited by a series,and its duration is more than one year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Winters' model differs from Holt's model and simple exponential smoothing in that it includes an index for:
A)seasonality
B)trend
C)residuals
D)cyclical fluctuations
A)seasonality
B)trend
C)residuals
D)cyclical fluctuations

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Perhaps the simplest and one of the most frequently used extrapolation methods is the:
A)moving average
B)linear trend
C)exponential trend
D)causal model
A)moving average
B)linear trend
C)exponential trend
D)causal model

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
When using exponential smoothing,if you want the forecast to react quickly to movements in the series,you should choose:
A)values of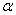 near 1
near 1
B)values of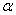 near 0
near 0
C)values of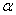 midway between 0 and 1
midway between 0 and 1
D)it depends on the data set
A)values of
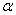 near 1
near 1B)values of
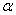 near 0
near 0C)values of
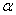 midway between 0 and 1
midway between 0 and 1D)it depends on the data set

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
When using exponential smoothing,a smoothing constant 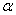 must be used.The value for
must be used.The value for 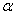 :
:
A)ranges between 0 and 1
B)ranges between -1 and +1
C)equals the largest observed value in the series
D)represents the strength of the association between the forecasted and observed values
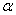 must be used.The value for
must be used.The value for 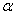 :
:A)ranges between 0 and 1
B)ranges between -1 and +1
C)equals the largest observed value in the series
D)represents the strength of the association between the forecasted and observed values

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A time series can consist of four different components: trend,seasonal,cyclical,and random (or noise).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
In a random walk model the
A)series itself is random
B)series itself is not random but its differences are random
C)series itself and its differences are random
D)series itself and its differences are not random
A)series itself is random
B)series itself is not random but its differences are random
C)series itself and its differences are random
D)series itself and its differences are not random

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following is not a method for dealing with seasonality in data
A)Winter's exponential smoothing model
B)deseasonalizing the data,using any forecasting model,then reseasonalizing the data
C)multiple regression with lags for the seasons
D)multiple regression with dummy variables for the seasons
A)Winter's exponential smoothing model
B)deseasonalizing the data,using any forecasting model,then reseasonalizing the data
C)multiple regression with lags for the seasons
D)multiple regression with dummy variables for the seasons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The moving average method can also be referred to as a (n)_____ method.
A)causal
B)smoothing
C)exponential
D)econometric
A)causal
B)smoothing
C)exponential
D)econometric

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Suppose that a simple exponential smoothing model is used (with a = 0.30)to forecast monthly sandwich sales at a local sandwich shop.After June's demand is observed at 1520 sandwiches,the forecasted demand for July is 1600 sandwiches.At the beginning of July,what would be the forecasted demand for August?
A)1520
B)1544
C)1550
D)1600
A)1520
B)1544
C)1550
D)1600

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A time series is any variable that is measured over time in sequential order.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The time series component that reflects a long-term,relatively smooth pattern or direction exhibited by a time series over a long time period,is called seasonal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Holt's model differs from simple exponential smoothing in that it includes a term for:
A)seasonality
B)trend
C)residuals
D)cyclical fluctuations
A)seasonality
B)trend
C)residuals
D)cyclical fluctuations

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The following are the values of a time series for the first four time periods: 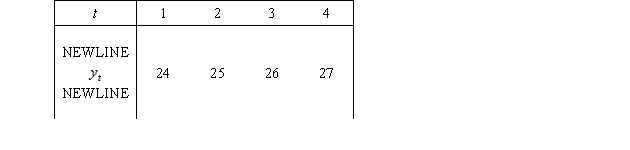 Using a four-period moving average,the forecasted value for time period 5 is:
Using a four-period moving average,the forecasted value for time period 5 is:
A)24.5
B)25.5
C)26.5
D)27.5
 Using a four-period moving average,the forecasted value for time period 5 is:
Using a four-period moving average,the forecasted value for time period 5 is:A)24.5
B)25.5
C)26.5
D)27.5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
If the observations of a time series increase or decrease regularly through time,we say that the time series has a random (or noise)component.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Suppose that a simple exponential smoothing model is used (with 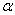 = 0.40)to forecast monthly sandwich sales at a local sandwich shop.The forecasted demand for September was 1560 and the actual demand was 1480 sandwiches.Given this information,what would be the forecast number of sandwiches for October?
= 0.40)to forecast monthly sandwich sales at a local sandwich shop.The forecasted demand for September was 1560 and the actual demand was 1480 sandwiches.Given this information,what would be the forecast number of sandwiches for October?
A)1480
B)1528
C)1560
D)1592
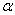 = 0.40)to forecast monthly sandwich sales at a local sandwich shop.The forecasted demand for September was 1560 and the actual demand was 1480 sandwiches.Given this information,what would be the forecast number of sandwiches for October?
= 0.40)to forecast monthly sandwich sales at a local sandwich shop.The forecasted demand for September was 1560 and the actual demand was 1480 sandwiches.Given this information,what would be the forecast number of sandwiches for October?A)1480
B)1528
C)1560
D)1592

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
When using the moving average method,you must select _____which represent(s)the number of terms in the moving average.
A)a smoothing constant
B)the explanatory variables
C)an alpha value
D)a span
A)a smoothing constant
B)the explanatory variables
C)an alpha value
D)a span

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
There are a variety of deseasonalizing methods,but they are typically variations of:
A)ratio-to-seasonality methods
B)ratio-to-exponential-smoothing methods
C)ratio-to-moving-average methods
D)linear trend
A)ratio-to-seasonality methods
B)ratio-to-exponential-smoothing methods
C)ratio-to-moving-average methods
D)linear trend

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
A regression approach can also be used to deal with seasonality by using_____variables for the seasons.
A)smoothing
B)response
C)residual
D)dummy
A)smoothing
B)response
C)residual
D)dummy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Forecasting software packages typically report several summary measures of the forecasting error.The most important of these are MAE (mean absolute error),RMSE (root mean square error),and MAPE (mean absolute percentage error).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
In a random walk model,there are significantly more runs than expected,and the autocorrelations are not significant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
An exponential trend is appropriate when the time series changes by a constant percentage each period.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The most common form of autocorrelation is positive autocorrelation,where large observations tend to follow large observations and small observations tend to follow small observations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The cyclic component of a time series is more likely to exhibit business cycles that record periods of economic recession and inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The trend line 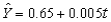 was calculated from quarterly data for 2000 - 2004,where t = 1 for the first quarter of 2000.The trend value for the second quarter of the year 2005 is 0.75.
was calculated from quarterly data for 2000 - 2004,where t = 1 for the first quarter of 2000.The trend value for the second quarter of the year 2005 is 0.75.
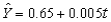 was calculated from quarterly data for 2000 - 2004,where t = 1 for the first quarter of 2000.The trend value for the second quarter of the year 2005 is 0.75.
was calculated from quarterly data for 2000 - 2004,where t = 1 for the first quarter of 2000.The trend value for the second quarter of the year 2005 is 0.75.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
If a time series exhibits an exponential trend,then a plot of its logarithm should be approximately linear.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
If a random series has too few runs,then it is zigzagging too often.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The null hypothesis in a runs test is 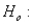 the data series is random
the data series is random
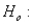 the data series is random
the data series is random
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
An autocorrelation is a type of correlation used to measure whether the values of a time series are related to their own past values.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
A meandering pattern is an example of a random time series.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The time series component that reflects a wavelike pattern describing a long-term trend that is generally apparent over a number of years is called cyclical.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
A shortcoming of the RMSE (root mean square error)is that it is not in the same units as the forecast variable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Extrapolation forecasting methods are quantitative methods that use past data of a time series variable - and nothing else,except possible time itself - to forecast values of the variable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
As is the case with residuals from regression,the forecast errors for nonregression methods will always average to zero

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
An equation for the random walk model is given by the equation: 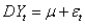 ,where
,where 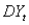 is the change in the time series from time t to time t - 1,
is the change in the time series from time t to time t - 1, 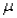 is a constant,and
is a constant,and 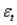 is a random variable (noise)with mean 0 and some standard deviation
is a random variable (noise)with mean 0 and some standard deviation 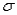 .
.
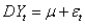 ,where
,where 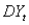 is the change in the time series from time t to time t - 1,
is the change in the time series from time t to time t - 1, 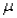 is a constant,and
is a constant,and 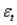 is a random variable (noise)with mean 0 and some standard deviation
is a random variable (noise)with mean 0 and some standard deviation 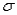 .
.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Econometric forecasting models,also called causal models,use regression to forecast a time series variable by using other explanatory time series variables.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The runs test is a formal test of the null hypothesis of randomness.If there are too many or too few runs in the series,then we conclude that the series is not random.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
You will always get more accurate forecasts by using more complex forecasting methods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The seasonal component of a time series is harder to predict than the cyclic component; the reason is that cyclic variation is much more regular.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
We compute the five-period moving averages for all time periods except the first two.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
In an additive seasonal model,we add an appropriate seasonal index to a "base" forecast.These indexes,one for each season,typically average to 0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
If we use a value close to 1 for the smoothing constant 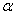 in a simple exponential smoothing model,then we expect the model to respond very slowly to changes in the level.
in a simple exponential smoothing model,then we expect the model to respond very slowly to changes in the level.
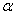 in a simple exponential smoothing model,then we expect the model to respond very slowly to changes in the level.
in a simple exponential smoothing model,then we expect the model to respond very slowly to changes in the level.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
A moving average is the average of the observations in the past few periods,where the number of terms in the average is the span.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The moving average method is perhaps the simplest and one of the most frequently-used extrapolation methods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The smoothing constants in exponential smoothing models are effectively a way to assign different weights to past levels,trends and cycles in the data.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Seasonal variations will not be present in a deseasonalized time series.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Every form of exponential smoothing model has at least one smoothing constant,which is always between 0 and 1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
If we use a value close to 1 for the level smoothing constant 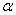 and a value close to 0 for the trend smoothing constant
and a value close to 0 for the trend smoothing constant 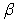 in Holt's exponential smoothing model,then we expect the model to respond very quickly to changes in the level,but very slowly to changes in the trend.
in Holt's exponential smoothing model,then we expect the model to respond very quickly to changes in the level,but very slowly to changes in the trend.
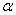 and a value close to 0 for the trend smoothing constant
and a value close to 0 for the trend smoothing constant 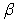 in Holt's exponential smoothing model,then we expect the model to respond very quickly to changes in the level,but very slowly to changes in the trend.
in Holt's exponential smoothing model,then we expect the model to respond very quickly to changes in the level,but very slowly to changes in the trend.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Correlogram is a bar chart of autocorrelation at different lags.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
To deseasonalize an observation (assuming a multiplicative model of seasonality),multiply it by the appropriate seasonal index.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Simple exponential smoothing is appropriate for a series without a pronounced trend or seasonality.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The seasonal component of a time series is more likely to exhibit the relatively steady growth of a variable,such as the population of Egypt from 35 million in 1960 to 75 million in 2005.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Holt's method is an exponential smoothing method,which is appropriate for a series with seasonality and possibly a trend.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The smoothing constant used in simple exponential smoothing is analogous to the span in moving averages.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
To calculate the five-period moving average for a time series,we average the values in the two preceding periods,and the values in the three following time periods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Winter's method is an exponential smoothing method,which is appropriate for a series with trend but no seasonality.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
The purpose of using the moving average is to take away the short-term seasonal and random variation,leaving behind a combined trend and cyclical movement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
In exponential smoothing models,the forecast is based on the level at time t,Lt,which is not observable and can only be estimated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
If the span of a moving average is large - say,12 months - then few observations go into each average,and extreme values have relatively large effect on the forecasts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



