Deck 13: Introduction to Optimization Modeling
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/91
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 13: Introduction to Optimization Modeling
1
The optimal solution to any linear programming model is:
A)the maximum objective function line
B)the minimum objective function line
C)the corner point of a polygon
D)the maximum or minimum of a parabola
A)the maximum objective function line
B)the minimum objective function line
C)the corner point of a polygon
D)the maximum or minimum of a parabola
C
2
If a manufacturing process takes 3 hours per unit of x and 5 hours per unit of y and a maximum of 100 hours of manufacturing process time are available,then an algebraic formulation of this constraint is:
A)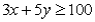
B)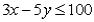
C)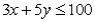
D)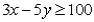
A)
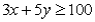
B)
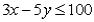
C)
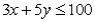
D)
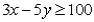
C
3
Suppose a company sells two different products,x and y,for net profits of $5 per unit and $10 per unit,respectively.The slope of the line representing the objective function is:
A)0.5
B)-0.5
C)2
D)-2
A)0.5
B)-0.5
C)2
D)-2
B
4
In using Excel to solve linear programming problems,the changing cells represent the:
A)value of the objective function
B)constraints
C)decision variables
D)total cost of the model
A)value of the objective function
B)constraints
C)decision variables
D)total cost of the model

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A linear programming problem with only decision variable(s)can be solved by a graphical solution method.
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The solution of a linear programming problem using Microsoft Excel typically involves the following three stages:
A)formulating the problem,invoking Solver,and sensitivity analysis
B)formulating the problem,graphing the problem,and sensitivity analysis
C)the changing cells,the target cells,and the constraints
D)the inputs,the changing cells,and the outputs
A)formulating the problem,invoking Solver,and sensitivity analysis
B)formulating the problem,graphing the problem,and sensitivity analysis
C)the changing cells,the target cells,and the constraints
D)the inputs,the changing cells,and the outputs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The most important solution method for linear programming problems is known as the:
A)spreadsheet method
B)solution mix method
C)complex method
D)simplex method
A)spreadsheet method
B)solution mix method
C)complex method
D)simplex method

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The equation of the line representing the constraint 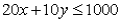 is:
is:
A)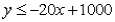
B)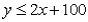
C)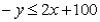
D)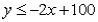
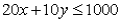 is:
is:A)
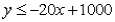
B)
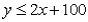
C)
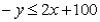
D)
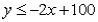

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The prototype linear programming problem is to select an optimal mix of products to produce to maximize profit.This type of problem is referred to as the:
A)product mix problem
B)production problem
C)product/process problem
D)product scheduling problem
A)product mix problem
B)production problem
C)product/process problem
D)product scheduling problem

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Every linear programming problem involves optimizing a:
A)linear regression model subject to several linear constraints
B)linear function subject to several linear constraints
C)linear function subject to several non-linear constraints
D)non-linear function subject to several linear constraints
A)linear regression model subject to several linear constraints
B)linear function subject to several linear constraints
C)linear function subject to several non-linear constraints
D)non-linear function subject to several linear constraints

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Suppose a firm must at least meet minimum expected demands of 60 for product x and 80 of product y.An algebraic formulation of these constraints is:
A)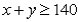
B)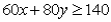
C)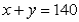
D)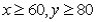
A)
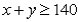
B)
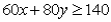
C)
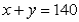
D)
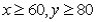

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
In an optimization model,there can only be one:
A)decision variable
B)constraint
C)objective function
D)shadow price
A)decision variable
B)constraint
C)objective function
D)shadow price

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
In most cases in solving linear programming problems,we want the decision variables to be:
A)equal to zero
B)nonnegative
C)nonpositive
D)All of these options
A)equal to zero
B)nonnegative
C)nonpositive
D)All of these options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Linear programming is a subset of a larger class of models called:
A)mathematical programming models
B)mathematical optimality models
C)linear regression models
D)linear simplex model
A)mathematical programming models
B)mathematical optimality models
C)linear regression models
D)linear simplex model

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
In using Excel to solve linear programming problems,the target cell represents the:
A)value of the objective function
B)constraints
C)decision variables
D)total cost of the model
A)value of the objective function
B)constraints
C)decision variables
D)total cost of the model

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
All optimization problems have:
A)an objective function and decision variables
B)an objective function and constraints
C)decision variables and constraints
D)an objective function,decision variables and constraints
A)an objective function and decision variables
B)an objective function and constraints
C)decision variables and constraints
D)an objective function,decision variables and constraints

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The term nonnegativity refers to the condition where:
A)the objective function cannot be less that zero
B)the decision variables cannot be less than zero
C)the right hand side of the constraints cannot be greater then zero
D)the reduced cost cannot be less than zero
A)the objective function cannot be less that zero
B)the decision variables cannot be less than zero
C)the right hand side of the constraints cannot be greater then zero
D)the reduced cost cannot be less than zero

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Suppose a liquor store sells beer for a net profit of $1 per unit and wine for a net profit of $2 per unit.Let x equal the amount of beer sold and y equal the amount of wine sold.An algebraic formulation of the profit function is:
A)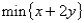
B)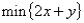
C)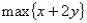
D)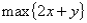
A)
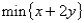
B)
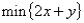
C)
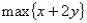
D)
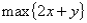

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The feasible region in all linear programming problems is bounded by:
A)corner points
B)hyperplanes
C)an objective line
D)all of these options
A)corner points
B)hyperplanes
C)an objective line
D)all of these options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
When using the graphical solution method to solve linear programming problems,the set of points that satisfy all constraints is called the:
A)optimal region
B)feasible region
C)constrained region
D)logical region
A)optimal region
B)feasible region
C)constrained region
D)logical region

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The equation of the line representing the constraint 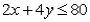 passes through the points:
passes through the points:
A)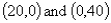
B)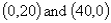
C)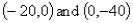
D)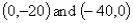
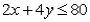 passes through the points:
passes through the points:A)
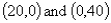
B)
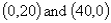
C)
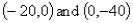
D)
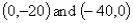

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Related to sensitivity analysis in linear programming,when the profit increases with a unit increase in a resource,this change in profit is referred to as the:
A)add-in price
B)sensitivity price
C)shadow price
D)additional profit
A)add-in price
B)sensitivity price
C)shadow price
D)additional profit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
One of the things that you can do with linear programming and a spreadsheet model is to develop a user interface to make it easier for someone who is not an expert in using linear programming.The output can be a report that explains the optimal policy in non-technical terms.The type of system being described is called a (n):
A)expert system
B)decision support system
C)linear programming support system
D)production planning system
A)expert system
B)decision support system
C)linear programming support system
D)production planning system

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Consider the following linear programming problem: Maximize 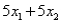 Subject to
Subject to 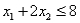
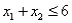
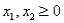 The above linear programming problem:
The above linear programming problem:
A)has only one optimal solution
B)has more than one optimal solution
C)exhibits infeasibility
D)exhibits unboundedness
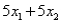 Subject to
Subject to 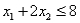
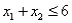
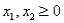 The above linear programming problem:
The above linear programming problem:A)has only one optimal solution
B)has more than one optimal solution
C)exhibits infeasibility
D)exhibits unboundedness

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
There are generally two steps in solving an optimization problem,model development and optimization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
When there is a problem with Solver being able to find a solution,many times it is an indication of a (n):
A)older version of Excel
B)nonlinear programming problem
C)problem that cannot be solved using linear programming
D)mistake in the formulation of the problem
A)older version of Excel
B)nonlinear programming problem
C)problem that cannot be solved using linear programming
D)mistake in the formulation of the problem

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
In some cases,a linear programming problem can be formulated such that the objective can become infinitely large (for a maximization problem)or infinitely small (for a minimization problem).This type of problem is said to be:
A)infeasible
B)inconsistent
C)unbounded
D)redundant
A)infeasible
B)inconsistent
C)unbounded
D)redundant

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
In general,the complete solution of a linear programming problem involves three stages: formulating the model,invoking Solver to find the optimal solution,and performing sensitivity analysis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Consider the following linear programming problem: Maximize 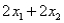 Subject to
Subject to 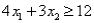
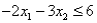
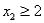
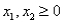 The above linear programming problem:
The above linear programming problem:
A)has only one optimal solution
B)has more than one optimal solution
C)exhibits infeasibility
D)exhibits unboundedness
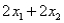 Subject to
Subject to 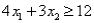
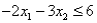
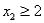
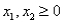 The above linear programming problem:
The above linear programming problem:A)has only one optimal solution
B)has more than one optimal solution
C)exhibits infeasibility
D)exhibits unboundedness

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
There are two primary ways to formulate a linear programming problem,the traditional algebraic way and in spreadsheets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The additivity property of linear programming implies that the contribution of any decision variable to the objective is of/on the levels of the other decision variables.
A)dependent
B)independent
C)conditional
D)the sum
A)dependent
B)independent
C)conditional
D)the sum

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The divisibility property of linear programming means that a solution can have both:
A)integer and noninteger levels of an activity
B)linear and nonlinear relationships
C)positive and negative values
D)revenue and cost information in the model
A)integer and noninteger levels of an activity
B)linear and nonlinear relationships
C)positive and negative values
D)revenue and cost information in the model

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Consider the following linear programming problem: Maximize 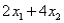 Subject to
Subject to 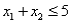
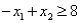
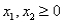 The above linear programming problem:
The above linear programming problem:
A)has only one optimal solution
B)has more than one optimal solution
C)exhibits infeasibility
D)exhibits unboundedness
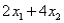 Subject to
Subject to 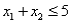
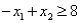
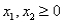 The above linear programming problem:
The above linear programming problem:A)has only one optimal solution
B)has more than one optimal solution
C)exhibits infeasibility
D)exhibits unboundedness

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
All optimization problems include decision variables,an objective function,and constraints.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Consider the following linear programming problem: Minimize 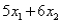 Subject to
Subject to 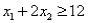
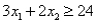
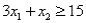
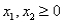 The above linear programming problem:
The above linear programming problem:
A)has only one optimal solution
B)has more than one optimal solution
C)exhibits infeasibility
D)exhibits unboundedness
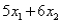 Subject to
Subject to 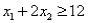
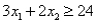
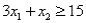
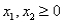 The above linear programming problem:
The above linear programming problem:A)has only one optimal solution
B)has more than one optimal solution
C)exhibits infeasibility
D)exhibits unboundedness

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
There is often more than one objective in linear programming problems

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
In linear programming we can use the shadow price to calculate increases or decreases in:
A)binding constraints
B)nonbinding constraints
C)values of the decision variables
D)the value of the objective function
A)binding constraints
B)nonbinding constraints
C)values of the decision variables
D)the value of the objective function

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
All linear programming problems should have a unique solution,if they can be solved.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
In linear programming,sensitivity analysis involves examining how sensitive the optimal solution is to changes in:
A)profit of variables in model
B)cost of variables in model
C)resources available
D)All of these options
A)profit of variables in model
B)cost of variables in model
C)resources available
D)All of these options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Linear programming models have three important properties.They are:
A)optimality,additivity and sensitivity
B)optimality,linearity and divisibility
C)divisibility,linearity and nonnegativity
D)proportionality,additivity and divisibility
A)optimality,additivity and sensitivity
B)optimality,linearity and divisibility
C)divisibility,linearity and nonnegativity
D)proportionality,additivity and divisibility

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The set of all values of the changing cells that satisfy all constraints,not including the nonnegativity constraints,is called the feasible region.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
If the objective function has the equation 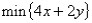 ,then the slope of the objective function line is 2:
,then the slope of the objective function line is 2:
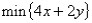 ,then the slope of the objective function line is 2:
,then the slope of the objective function line is 2:
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
If a constraint has the equation 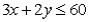 ,then the constraint line passes through the points (0,20)and (30,0):
,then the constraint line passes through the points (0,20)and (30,0):
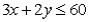 ,then the constraint line passes through the points (0,20)and (30,0):
,then the constraint line passes through the points (0,20)and (30,0):
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
If a constraint has the equation 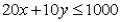 ,then the slope of the constraint line is function line is -2:
,then the slope of the constraint line is function line is -2:
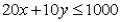 ,then the slope of the constraint line is function line is -2:
,then the slope of the constraint line is function line is -2:
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The optimal solution to any linear programming model is a corner point of a polygon.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
When formulating a linear programming spreadsheet model,we specify the constraints in a Solver dialog box,since Excel does not show the constraints directly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Reduced costs indicate how much the objective coefficient of a decision variable that is currently 0 or at its upper bound must change before that the value of that variable changes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Linear programming problems can always be formulated algebraically,but not always on spreadsheet.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Proportionality,additivity,and divisibility are three important properties that LP models possess,which distinguish them from general mathematical programming models:.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
It is instructive to look at a graphical solution procedure for LP models with three or more decision variables.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The feasible region in a graphical solution of a linear programming problem will appear as some type of polygon,with lines forming all sides.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
It is often useful to perform sensitivity analysis to see how,or if,the optimal solution to a linear programming problem changes as we change one or more model inputs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
If the objective function has the equation 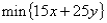 ,then the y-intercept of the objective function line is 40:
,then the y-intercept of the objective function line is 40:
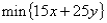 ,then the y-intercept of the objective function line is 40:
,then the y-intercept of the objective function line is 40:
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Suppose the allowable increase and decrease for an objective coefficient of a decision variable that has a current value of $50 are $25 (increase)and $10 (decrease).If the coefficient were to change from $50 to $60,the optimal value of the objective function would not change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
When formulating a linear programming spreadsheet model,there is a set of designated cells that play the role of the decision variables.These are called the objective cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Shadow prices are associated with nonbinding constraints,and show the change in the optimal objective function value when the right side of the constraint equation changes by one unit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
In determining the optimal solution to a linear programming problem graphically,if the objective is to maximize the objective,we pull the objective function line down until it contacts the feasible region.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
When formulating a linear programming spreadsheet model,there is one target (objective)cell that contains the value of the objective function.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Suppose the allowable increase and decrease for shadow price for a constraint are $25 (increase)and $10 (decrease).If the right hand side of that constraint were to increase by $10 the optimal value of the objective function would change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Nonbinding constraints will always have slack,which is the difference between the two sides of the inequality in the constraint equation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The proportionality property of LP models means that if the level of any activity is multiplied by a constant factor,then the contribution of this activity to the objective function,or to any of the constraints in which the activity is involved,is multiplied by the same factor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
(A)What is the objective function in this problem?
(B)What are the constraints in this problem? Write an algebraic expression for each.
(C)Find an optimal solution to the problem using the formulation given in (A)and (B).What is the call plan,and what is the total cost?
(D)Implement the model in (C)in Excel Solver and obtain an answer report.Which constraints are binding on the optimal solution?
(E)Obtain a sensitivity report for the model in (D).If the professor could cut the cost of evening calls from $4 to $3,what would the new calling plan be?
(F)Again using the sensitivity report obtained for (E),suppose the professor could get by with just 100 calls for single females.What would the call costs be in that case? Explain your answer.
(B)What are the constraints in this problem? Write an algebraic expression for each.
(C)Find an optimal solution to the problem using the formulation given in (A)and (B).What is the call plan,and what is the total cost?
(D)Implement the model in (C)in Excel Solver and obtain an answer report.Which constraints are binding on the optimal solution?
(E)Obtain a sensitivity report for the model in (D).If the professor could cut the cost of evening calls from $4 to $3,what would the new calling plan be?
(F)Again using the sensitivity report obtained for (E),suppose the professor could get by with just 100 calls for single females.What would the call costs be in that case? Explain your answer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Find an optimal solution to the problem,assuming that the company will not produce any units in either month that it cannot sell in that month.What is the production plan,and what is the total revenue?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
If a solution to an LP problem satisfies all of the constraints,then is must be feasible.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
What is the objective function in this problem?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
When the proportionality property of LP models is violated,then we generally must use non-linear optimization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Unboundedness refers to the situation in which the LP model has been formulated in such a way that the objective function is unbounded - that is,it can be made as large (for maximization problems)or as small (for minimization problems)as we like.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
What are the constraints in this problem?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
What is the optimal shipping plan? What are the total costs in that case?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
What is the objective function in this problem?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Infeasibility refers to the situation in which there are no feasible solutions to the LP model

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
If an LP model does have an unbounded solution,then we must have made a mistake - either we made an input error or we omitted one or more constraints.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The divisibility property of LP models simply means that we allow only integer levels of the activities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
What are the decision variables in this problem?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The additivity property of LP models implies that the sum of the contributions from the various activities to a particular constraint equals the total contribution to that constraint.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
(A)Formulate a linear programming model that will enable the farmer to determine the number of acres that should be planted cotton and/or corn in order to maximize his profit.
(B)Find an optimal solution to the model in (A)and determine the maximum profit.
(C)Implement the model in (A)in Excel Solver and obtain an answer report.Which constraints are binding on the optimal solution?
(D)Obtain a sensitivity report for the model in (A).How much should the farmer be willing to pay for an additional worker?
(E)Suppose the farmer hires 10 additional workers.Can you use the sensitivity analysis obtained for (D)to determine his expected profit? Would his planting plan change? Explain your answer.
(F)Suppose the farmer now wants to hire 20 additional workers,instead of just 10.Can you use the sensitivity analysis obtained for (D)to determine his expected profit? Explain your answer.
(B)Find an optimal solution to the model in (A)and determine the maximum profit.
(C)Implement the model in (A)in Excel Solver and obtain an answer report.Which constraints are binding on the optimal solution?
(D)Obtain a sensitivity report for the model in (A).How much should the farmer be willing to pay for an additional worker?
(E)Suppose the farmer hires 10 additional workers.Can you use the sensitivity analysis obtained for (D)to determine his expected profit? Would his planting plan change? Explain your answer.
(F)Suppose the farmer now wants to hire 20 additional workers,instead of just 10.Can you use the sensitivity analysis obtained for (D)to determine his expected profit? Explain your answer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
What are the constraints in this problem?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
It helps to ensure that Solver can find a solution to a linear programming problem if the model is well-scaled; that is,all of the numbers are of roughly the same magnitude.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
What are the decision variables in this problem?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
What are the decision variables in this problem?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



