Deck 15: Parasitism and Infectious Diseases
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/61
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 15: Parasitism and Infectious Diseases
1
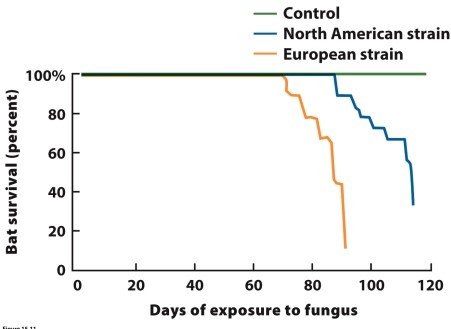
(Figure 15.11) The graph shows survival rates for North American populations of the little brown bat (Myotis lucifugus) after exposure to either a North American or European strain of white-nose fungus (Geomyces destructans). What did researchers conclude about the two strains?
Exposure to either strain of white-nose fungus caused high rates of bat death. However, bats did not die as quickly when exposed to the North American strain, which may suggest that bats in North America are evolving some resistance to the North American strain of the fungus.
Parasite and host dynamics are determined by the parasite's ability to infect the host.
Parasite and host dynamics are determined by the parasite's ability to infect the host.
2
Endoparasitic roundworms and flatworms that live in the tissues of plants and animals are called
A) protozoans.
B) prions.
C) helminths.
D) hemiparasites.
A) protozoans.
B) prions.
C) helminths.
D) hemiparasites.
C
3
What types of endoparasites replicate by altering their host's proteins and do not contain any nucleic acids?
A) viruses
B) hemiparasites
C) helminths
D) prions
A) viruses
B) hemiparasites
C) helminths
D) prions
D
4
When a new disease is discovered, it is called an _____ disease.
A) emerging invasive
B) increasing infectious
C) emerging infectious
D) increasing virulent
A) emerging invasive
B) increasing infectious
C) emerging infectious
D) increasing virulent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Why does the parasitic flatworm (Leucochloridium paradoxum) of the amber snail (Succinea putris) alter the behaviour of the snail so that it moves to the top of a plant stem?
A) The flatworm needs the snail to move off the ground to avoid predation.
B) The flatworm needs the snail to be eaten by a bird to complete its life cycle.
C) The conditions at the top of plant stems are better for flatworms.
D) There is more food for the snail at the top of plant stems than on the ground.
A) The flatworm needs the snail to move off the ground to avoid predation.
B) The flatworm needs the snail to be eaten by a bird to complete its life cycle.
C) The conditions at the top of plant stems are better for flatworms.
D) There is more food for the snail at the top of plant stems than on the ground.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following statements is NOT true about the endoparasite life cycle?
A) It has low exposure to its natural enemies.
B) It has low exposure to the host's immune system.
C) It finds it easy to feed on the host.
D) It hags low exposure to the external environment.
A) It has low exposure to its natural enemies.
B) It has low exposure to the host's immune system.
C) It finds it easy to feed on the host.
D) It hags low exposure to the external environment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The ability of a host to prevent infection by parasites is called
A) tolerance.
B) avoidance.
C) resistance.
D) reluctance.
A) tolerance.
B) avoidance.
C) resistance.
D) reluctance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Because of its relationship with its host, the ectoparasite has
A) low exposure to the host's immune system.
B) low exposure to its natural enemies.
C) low exposure to the external environment.
D) difficulty moving between hosts.
A) low exposure to the host's immune system.
B) low exposure to its natural enemies.
C) low exposure to the external environment.
D) difficulty moving between hosts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following in NOT an example of an ectoparasite?
A) a tick
B) a tapeworm
C) a flea
D) a mite
A) a tick
B) a tapeworm
C) a flea
D) a mite

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The number of parasites of a given species that an individual host can harbour is its
A) infection rate.
B) infection load.
C) parasite rate.
D) parasite load.
A) infection rate.
B) infection load.
C) parasite rate.
D) parasite load.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Endoparasites (such as tapeworms) seem to lead an ideal life in the interior of the host, protected from natural enemies and the external environment while having a continual supply of nutrients. What are challenges that endoparasites face?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Parasites generally have _____ reproductive rates than their hosts and often _____ them.
A) lower; do not kill
B) higher; do not kill
C) higher; kill
D) lower; kill
A) lower; do not kill
B) higher; do not kill
C) higher; kill
D) lower; kill

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Malaria in humans and animals is caused by
A) a prion.
B) a protozoan.
C) a fungus.
D) a virus.
A) a prion.
B) a protozoan.
C) a fungus.
D) a virus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of an emerging infectious disease?
A) high fatality rate
B) recent discovery
C) increased occurrence
D) recent jump to a new host
A) high fatality rate
B) recent discovery
C) increased occurrence
D) recent jump to a new host

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Crop rust is a _____ disease.
A) protozoan
B) prion
C) viral
D) fungal
A) protozoan
B) prion
C) viral
D) fungal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Infection tolerance is the ability of a host to
A) minimize harm that an infection can cause.
B) prevent infection by parasites.
C) prevent a parasite from reproducing.
D) recover from an existing infection.
A) minimize harm that an infection can cause.
B) prevent infection by parasites.
C) prevent a parasite from reproducing.
D) recover from an existing infection.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Dutch elm disease is caused by
A) a protozoan.
B) a virus.
C) a fungus.
D) bacteria.
A) a protozoan.
B) a virus.
C) a fungus.
D) bacteria.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Dutch elm disease is caused by
A) a fungus.
B) a virus.
C) a prion.
D) a protozoan.
A) a fungus.
B) a virus.
C) a prion.
D) a protozoan.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The World Health Organization estimates that _____ of human deaths are caused by infectious diseases.
A) 30 percent
B) 45 percent
C) 25 percent
D) 15 percent
A) 30 percent
B) 45 percent
C) 25 percent
D) 15 percent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A parasite moving between individuals other than parents and their offspring uses _____ transmission.
A) horizontal
B) vertical
C) diagonal
D) vector
A) horizontal
B) vertical
C) diagonal
D) vector

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
In S-I-R models, if R0 > 1,
A) the infection fails to take hold in the host population.
B) the population becomes resistant to the infection.
C) the infection becomes an epidemic.
D) the population is immune to the infection.
A) the infection fails to take hold in the host population.
B) the population becomes resistant to the infection.
C) the infection becomes an epidemic.
D) the population is immune to the infection.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following is NOT an example of horizontal transmission through a vector?
A) transmission of the flu virus between adult humans
B) transmission of West Nile virus between bird conspecifics via a mosquito
C) transmission of HIV to a human infant from its mother via breast milk
D) transmission of liver fluke to a sheep via a helminth
A) transmission of the flu virus between adult humans
B) transmission of West Nile virus between bird conspecifics via a mosquito
C) transmission of HIV to a human infant from its mother via breast milk
D) transmission of liver fluke to a sheep via a helminth

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
In S-I-R models of infectious disease transmission, I represents _____ individuals.
A) immune
B) immigrated
C) infected
D) infectious
A) immune
B) immigrated
C) infected
D) infectious

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
In the disease malaria, the Anopheles mosquito is the
A) vector.
B) reservoir species.
C) host.
D) parasite.
A) vector.
B) reservoir species.
C) host.
D) parasite.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
In S-I-R models, the variable g represents
A) the rate of recovery.
B) the rate of infection.
C) the proportion of infected individuals.
D) the rate of transmission.
A) the rate of recovery.
B) the rate of infection.
C) the proportion of infected individuals.
D) the rate of transmission.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Diseases such as HIV and African sleeping sickness can avoid the host's immune system by
A) having little negative effect on the host.
B) making themselves undetectable.
C) living in a reservoir species.
D) resembling red blood cells.
A) having little negative effect on the host.
B) making themselves undetectable.
C) living in a reservoir species.
D) resembling red blood cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
How do reservoir populations allow parasites to persist in nature?
A) Reservoir species transmit the parasite more frequently than host species, so the parasite infects a larger number of individuals.
B) Reservoir species are necessary for reproduction of the parasite.
C) Reservoir species do not die of the parasite and can be a continuous source of the parasite.
D) Without the reservoir species, the parasite could not disperse from one host to another.
A) Reservoir species transmit the parasite more frequently than host species, so the parasite infects a larger number of individuals.
B) Reservoir species are necessary for reproduction of the parasite.
C) Reservoir species do not die of the parasite and can be a continuous source of the parasite.
D) Without the reservoir species, the parasite could not disperse from one host to another.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The prion that causes bovine spongiform encephalopathy is _____ transmitted _____.
A) horizontally; via a mosquito vector
B) vertically; from parent to offspring
C) horizontally; via a helminth
D) horizontally; directly via ingestion of infected cow tissue
A) horizontally; via a mosquito vector
B) vertically; from parent to offspring
C) horizontally; via a helminth
D) horizontally; directly via ingestion of infected cow tissue

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following strategies do schistosomes use to circumvent the host's immune system?
A) They produce chemical factors that suppress their host's immune system.
B) They produce surface proteins that mimic the host's own proteins.
C) They continually produce novel surface proteins to confuse their host's immune system.
D) They coat themselves with their host's proteins.
A) They produce chemical factors that suppress their host's immune system.
B) They produce surface proteins that mimic the host's own proteins.
C) They continually produce novel surface proteins to confuse their host's immune system.
D) They coat themselves with their host's proteins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The bacterium that causes chlamydia in humans can be transmitted from mother to fetus by _____ transmission or between any two individuals by _____ transmission.
A) horizontal; horizontal
B) vertical; vertical
C) horizontal; vertical
D) vertical; horizontal
A) horizontal; horizontal
B) vertical; vertical
C) horizontal; vertical
D) vertical; horizontal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which characterizes the rate of infection between susceptible and infected individuals in an S-I-R model?
A) g × I × S
B) g ÷ (I × S)
C) I + (S ÷ g)
D) S + (I × g)
A) g × I × S
B) g ÷ (I × S)
C) I + (S ÷ g)
D) S + (I × g)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
What does the S-I-R model characterize for infectious diseases?
A) immunity rates
B) treatments
C) fatality rates
D) transmission
A) immunity rates
B) treatments
C) fatality rates
D) transmission

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Vertical transmission of parasites is
A) intraspecific transmission through a vector.
B) interspecific transmission through a vector.
C) direct transmission from parent to offspring.
D) direct interspecific transmission.
A) intraspecific transmission through a vector.
B) interspecific transmission through a vector.
C) direct transmission from parent to offspring.
D) direct interspecific transmission.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Describe two ways a parasite can decrease the likelihood that it will run out of potential hosts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
In S-I-R models, which of the following does NOT determine the proportion of S, I, and R individuals in a population?
A) recovery of infected individuals
B) rates of transmission of the disease
C) acquisition of immunity
D) birth of new susceptible individuals
A) recovery of infected individuals
B) rates of transmission of the disease
C) acquisition of immunity
D) birth of new susceptible individuals

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
In S-I-R models, if the ratio of new infections to recoveries is less than 1,
A) the infection becomes an epidemic.
B) all individuals in the population become resistant to the infection.
C) the infection fails to take hold in the host population.
D) all infected individuals in the population recover.
A) the infection becomes an epidemic.
B) all individuals in the population become resistant to the infection.
C) the infection fails to take hold in the host population.
D) all infected individuals in the population recover.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
In S-I-R models, which of the following represents the probability of contact between susceptible and infected individuals?
A) S × I
B) S ÷ I
C) I ÷ S
D) S + I
A) S × I
B) S ÷ I
C) I ÷ S
D) S + I

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Unlike predators, most parasites do not kill their hosts. Why is this beneficial?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
In S-I-R models of infectious disease transmission, R represents _____ individuals.
A) resistant
B) recovered
C) relocated
D) resilient
A) resistant
B) recovered
C) relocated
D) resilient

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Question: Anthropologists studying a tribe on an island in the South Pacific ask you to help them with an intriguing health problem: the chiefs of the tribe keep dying at a much more rapid rate than other members of the population. You travel to the island to observe the tribe, and you find that each time an animal is killed during a hunt, the body of the animal is shared communally among all of the members of the tribe. However, one part of the animal, its brain, is reserved exclusively for the tribal chief. The chief consumes the brain raw because it is believed that this allows him to assimilate the animal's knowledge of the island. What would you suggest is causing the death of the tribal chiefs, how is it killing them, and what is the mechanism of transmission?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The amphibian pathogen the chytrid fungus does not fit the S-I-R model because
A) the host does not recover from the fungal infection.
B) the host has no resistance to the fungus.
C) the fungus kills the host.
D) the fungus infects many species of amphibians.
A) the host does not recover from the fungal infection.
B) the host has no resistance to the fungus.
C) the fungus kills the host.
D) the fungus infects many species of amphibians.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Mice infected with Toxoplasma gondii are often attracted to bobcat urine. This is an example of
A) a host adaptation.
B) coevolution.
C) a parasite adaptation.
D) a reservoir species adaptation.
A) a host adaptation.
B) coevolution.
C) a parasite adaptation.
D) a reservoir species adaptation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
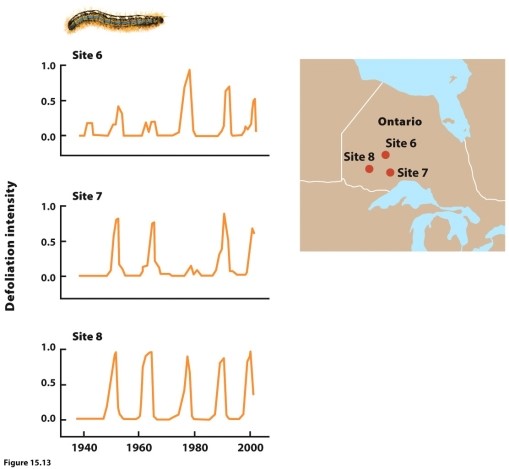
(Figure 15.13) The figure shows population fluctuations in forest tent caterpillars over a 60-year period. The caterpillars were susceptible to a viral infection throughout this time. What causes the 10- to 15-year population fluctuation in the caterpillars?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which of the following characterizes the rate of recovery of infected individuals in an S-I-R model?
A) I ÷ b
B) I × b
C) I + b
D) I − b
A) I ÷ b
B) I × b
C) I + b
D) I − b

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Reduction in virulence of myxomatosis in rabbits in Australia in the second outbreak was a result of
A) a parasite adaptation.
B) coevolution.
C) horizontal transmission.
D) a host adaptation.
A) a parasite adaptation.
B) coevolution.
C) horizontal transmission.
D) a host adaptation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Vaccinations slow or stop the spread of diseases by
A) reducing the virulence of the disease.
B) increasing the rate of recovery.
C) reducing the size of the susceptible population.
D) increasing the number of reservoirs.
A) reducing the virulence of the disease.
B) increasing the rate of recovery.
C) reducing the size of the susceptible population.
D) increasing the number of reservoirs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
When parasites require a series of hosts to complete their life cycle, they often evolve adaptations that
A) help them reproduce more quickly.
B) help them get transmitted from one host to the next.
C) protect them from multiple hosts' immune systems.
D) allow them to reproduce in any of their hosts.
A) help them reproduce more quickly.
B) help them get transmitted from one host to the next.
C) protect them from multiple hosts' immune systems.
D) allow them to reproduce in any of their hosts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Chimpanzees infected with intestinal worms sometimes eat Aspilia leaves. This is an example of
A) coevolution.
B) a reservoir species adaptation.
C) a parasite adaptation.
D) a host adaptation.
A) coevolution.
B) a reservoir species adaptation.
C) a parasite adaptation.
D) a host adaptation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Which of the following diseases has the highest R0 value?
A) HIV
B) malaria
C) measles
D) chicken pox
A) HIV
B) malaria
C) measles
D) chicken pox

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The parasitic worm Acanthocephalus dirus has evolved an adaptation that causes its isopod host, Caecidotea intermedius, to
A) spend more time out in the open.
B) be attracted to larger fish.
C) spend more time in refuges.
D) be scared of larger fish.
A) spend more time out in the open.
B) be attracted to larger fish.
C) spend more time in refuges.
D) be scared of larger fish.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Two populations with sample sizes of 25 and 27 are compared with a t-test. What is the value for the degrees of freedom?
A) 52
B) 54
C) 50
D) 26
A) 52
B) 54
C) 50
D) 26

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
According to an S-I-R model, if a pathogen can kill its host
A) the pathogen should decrease in abundance until hosts begin to die.
B) the pathogen should increase in abundance until the hosts begin to die.
C) the disease will not become an epidemic.
D) the individuals in the population will either die or become resistant.
A) the pathogen should decrease in abundance until hosts begin to die.
B) the pathogen should increase in abundance until the hosts begin to die.
C) the disease will not become an epidemic.
D) the individuals in the population will either die or become resistant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which of the following is NOT an assumption of the S-I-R model?
A) There are no births of new susceptible individuals.
B) Individuals retain any resistance they develop.
C) The epidemic continues until all individuals are resistant or there are too few susceptible individuals to sustain the spread of the disease.
D) All infected individuals die.
A) There are no births of new susceptible individuals.
B) Individuals retain any resistance they develop.
C) The epidemic continues until all individuals are resistant or there are too few susceptible individuals to sustain the spread of the disease.
D) All infected individuals die.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
In S-I-R models, which of the following models the ratio of new infections to recoveries?
A) S × (b ÷ g)
B) g × (S ÷ b)
C) S × (g ÷ b)
D) S ÷ (g × b)
A) S × (b ÷ g)
B) g × (S ÷ b)
C) S × (g ÷ b)
D) S ÷ (g × b)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The growth rates of two plant species are 5.3 millimetres per year for plant A and 4.6 millimetres per year for plant B. The t-statistic is calculated as 1.12, and the critical t for an alpha of 0.05 with 18 degrees of freedom is 1.734. What is concluded about the growth rates of the species?
A) Species A has a significantly faster growth rate than species B.
B) Species B has a significantly faster growth rate than species A.
C) Species A and species B have similar growth rates.
D) There is not enough information to make any determination about the growth rates of species A and species B.
A) Species A has a significantly faster growth rate than species B.
B) Species B has a significantly faster growth rate than species A.
C) Species A and species B have similar growth rates.
D) There is not enough information to make any determination about the growth rates of species A and species B.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which species is a reservoir for Borrelia burgdorferi, the bacterium that causes Lyme disease?
A) deer
B) mouse
C) dog
D) human
A) deer
B) mouse
C) dog
D) human

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
While you are conducting a study of the optimal growing conditions for commercially grown sunflowers, all of the sunflower plants in the field you are studying die. You discover that an emerging fungal pathogen kills sunflowers by destroying their roots. The fungus uses honeybees, which pollinate your flowers, as a vector to transmit fungal spores among sunflower plants. The next year the farm reseeds, hoping that the fungus has died over the winter. Early in the growing season some plants begin dying again, but then the honeybee population develops colony collapse disorder and all of the honeybees die. To compensate for the loss in pollinators, the farmers introduce large numbers of bumblebees. The number of new sunflower plants that become infected during the remainder of the growing season drops to near zero. Using the variables in the susceptible-infected-resistant (S-I-R) model equation: R0 = (S × I × g) ÷ (I × b), explain what has happened to alter the disease dynamics in the second year of your study and how this has occurred.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Organisms that produce antibacterial or antifungal chemicals have developed this ability as the result of
A) coevolution.
B) a parasite adaptation.
C) a host adaptation.
D) a prey adaptation.
A) coevolution.
B) a parasite adaptation.
C) a host adaptation.
D) a prey adaptation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Researchers set up an experiment in which they treat plants with a new fertilizer and compare plant height after 2 months to a control (untreated) group of plants. Using the data that follow, perform a t-test (α = 0.05) to determine whether the fertilizer affected plant height in this experiment. Use this formula:
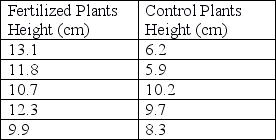
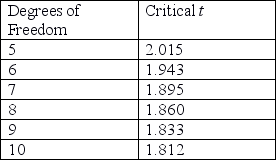
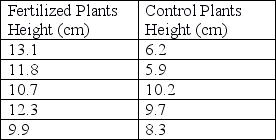
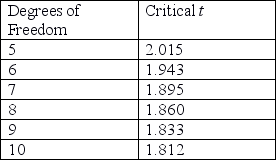

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
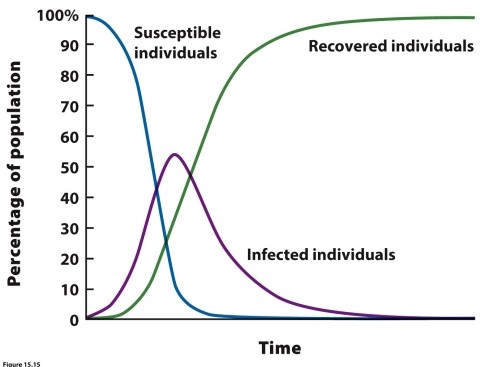
(Figure 15.15) In the figure showing dynamics of an infected population over time, what the curves A, B, and C represent?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Describe the 2-year cycle of Lyme disease, including all hosts and how the parasite is transmitted between hosts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



